Conus Artery on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The coronary arteries are the arterial blood vessels of

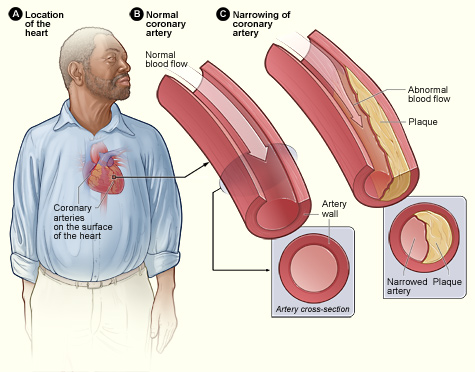 Narrowing of the arteries can be caused by a process known as atherosclerosis (most common), arteriosclerosis, or
Narrowing of the arteries can be caused by a process known as atherosclerosis (most common), arteriosclerosis, or 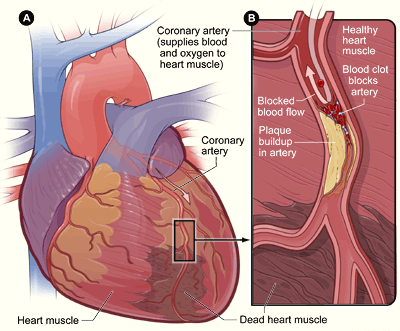 A
A
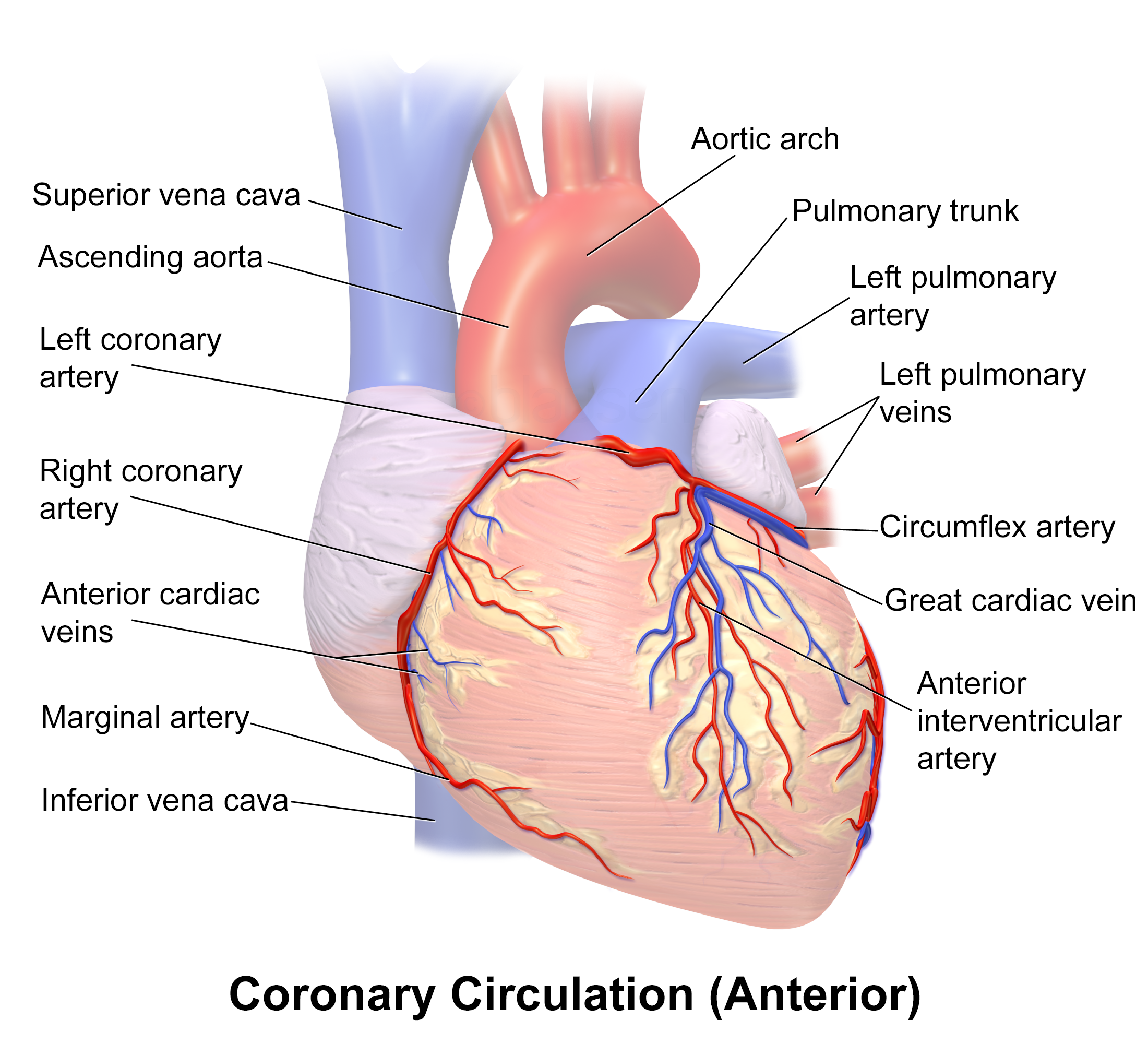

coronary circulation
Coronary circulation is the circulation of blood in the blood vessels that supply the heart muscle (myocardium).
Coronary arteries supply oxygenated blood to the heart muscle. Cardiac veins then drain away the blood after it has been deoxygenat ...
, which transport oxygenated blood
Blood is a body fluid in the circulatory system of humans and other vertebrates that delivers necessary substances such as nutrients and oxygen to the cells, and transports metabolic waste products away from those same cells. Blood in the ci ...
to the heart muscle
Cardiac muscle (also called heart muscle, myocardium, cardiomyocytes and cardiac myocytes) is one of three types of vertebrate muscle tissues, with the other two being skeletal muscle and smooth muscle. It is an involuntary, striated muscle tha ...
. The heart
The heart is a muscular organ in most animals. This organ pumps blood through the blood vessels of the circulatory system. The pumped blood carries oxygen and nutrients to the body, while carrying metabolic waste such as carbon dioxide t ...
requires a continuous supply of oxygen to function and survive, much like any other tissue or organ of the body.
The coronary arteries wrap around the entire heart. The two main branches are the left coronary artery
The left coronary artery (LCA) is a coronary artery that arises from the aorta above the left cusp of the aortic valve, and feeds blood to the left side of the heart muscle. It is also known as the left main coronary artery (LMCA) and the left ma ...
and right coronary artery
In the blood supply of the heart, the right coronary artery (RCA) is an artery originating above the right cusp of the aortic valve, at the right aortic sinus in the heart. It travels down the right coronary sulcus, towards the crux of the hear ...
. The arteries can additionally be categorized based on the area of the heart for which they provide circulation. These categories are called ''epicardial'' (above the epicardium
The pericardium, also called pericardial sac, is a double-walled sac containing the heart and the roots of the great vessels. It has two layers, an outer layer made of strong connective tissue (fibrous pericardium), and an inner layer made of ...
, or the outermost tissue of the heart) and ''microvascular'' (close to the endocardium
The endocardium is the innermost layer of tissue that lines the chambers of the heart. Its cells are embryologically and biologically similar to the endothelial cells that line blood vessels. The endocardium also provides protection to the va ...
, or the innermost tissue of the heart).
Reduced function of the coronary arteries can lead to decreased flow of oxygen and nutrients to the heart. Not only does this affect supply to the heart muscle itself, but it also can affect the ability of the heart to pump blood throughout the body. Therefore, any disorder or disease of the coronary arteries can have a serious impact on health, possibly leading to angina
Angina, also known as angina pectoris, is chest pain or pressure, usually caused by ischemia, insufficient blood flow to the Cardiac muscle, heart muscle (myocardium). It is most commonly a symptom of coronary artery disease.
Angina is typical ...
, a heart attack
A myocardial infarction (MI), commonly known as a heart attack, occurs when blood flow decreases or stops to the coronary artery of the heart, causing damage to the heart muscle. The most common symptom is chest pain or discomfort which may tr ...
, and even death.
Structure
The coronary arteries are mainly composed of the left and right coronary arteries, both of which give off several branches, as shown in the 'coronary artery flow' figure. *
Aorta
The aorta ( ) is the main and largest artery in the human body, originating from the left ventricle of the heart and extending down to the abdomen, where it splits into two smaller arteries (the common iliac arteries). The aorta distributes ...
**Left coronary artery
The left coronary artery (LCA) is a coronary artery that arises from the aorta above the left cusp of the aortic valve, and feeds blood to the left side of the heart muscle. It is also known as the left main coronary artery (LMCA) and the left ma ...
***Left anterior descending artery
The left anterior descending artery (also LAD, anterior interventricular branch of left coronary artery, or anterior descending branch) is a branch of the left coronary artery. Blockage of this artery is often called the ''widow-maker infarction' ...
***Left circumflex artery
The circumflex branch of left coronary artery, or left circumflex artery or circumflex artery, is a branch of the left coronary artery.
Description
The left circumflex artery follows the left part of the coronary sulcus, running first to the l ...
***Posterior descending artery
In the coronary circulation, the posterior interventricular artery (PIV, PIA, or PIVA), most often called the posterior descending artery (PDA), is an artery running in the posterior interventricular sulcus to the apex of the heart where it meets ...
***Ramus or intermediate artery
**Right coronary artery
In the blood supply of the heart, the right coronary artery (RCA) is an artery originating above the right cusp of the aortic valve, at the right aortic sinus in the heart. It travels down the right coronary sulcus, towards the crux of the hear ...
***Right marginal artery
The right marginal branch of right coronary artery (or right marginal artery) is the largest marginal branch of the right coronary artery. It follows the acute margin of the heart. It supplies blood to both surfaces of the right ventricle.
Stru ...
***Posterior descending artery
In the coronary circulation, the posterior interventricular artery (PIV, PIA, or PIVA), most often called the posterior descending artery (PDA), is an artery running in the posterior interventricular sulcus to the apex of the heart where it meets ...
The left coronary artery
The left coronary artery (LCA) is a coronary artery that arises from the aorta above the left cusp of the aortic valve, and feeds blood to the left side of the heart muscle. It is also known as the left main coronary artery (LMCA) and the left ma ...
arises from the aorta
The aorta ( ) is the main and largest artery in the human body, originating from the left ventricle of the heart and extending down to the abdomen, where it splits into two smaller arteries (the common iliac arteries). The aorta distributes ...
within the left cusp of the aortic valve
The aortic valve is a valve in the heart of humans and most other animals, located between the left ventricle and the aorta. It is one of the four valves of the heart and one of the two semilunar valves, the other being the pulmonary valve. The ...
and feeds blood to the left side of the heart
The heart is a muscular organ in most animals. This organ pumps blood through the blood vessels of the circulatory system. The pumped blood carries oxygen and nutrients to the body, while carrying metabolic waste such as carbon dioxide t ...
. It branches into two arteries, the left anterior descending
The left anterior descending artery (also LAD, anterior interventricular branch of left coronary artery, or anterior descending branch) is a branch of the left coronary artery. Blockage of this artery is often called the ''widow-maker infarction' ...
and the left circumflex. The left anterior descending artery perfuses the interventricular septum
The interventricular septum (IVS, or ventricular septum, or during development septum inferius) is the stout wall separating the ventricles, the lower chambers of the heart, from one another.
The ventricular septum is directed obliquely backwar ...
and anterior wall of the left ventricle
A ventricle is one of two large chambers toward the bottom of the heart that collect and expel blood towards the peripheral beds within the body and lungs. The blood pumped by a ventricle is supplied by an atrium, an adjacent chamber in the upper ...
. The left circumflex artery perfuses the left ventricular free wall. In approximately 33% of individuals, the left coronary artery gives rise to the posterior descending artery
In the coronary circulation, the posterior interventricular artery (PIV, PIA, or PIVA), most often called the posterior descending artery (PDA), is an artery running in the posterior interventricular sulcus to the apex of the heart where it meets ...
which perfuses the posterior and inferior walls of the left ventricle. Sometimes a third branch is formed at the fork between left anterior descending and left circumflex arteries, known as a ''ramus'' or ''intermediate artery''.
The right coronary artery
In the blood supply of the heart, the right coronary artery (RCA) is an artery originating above the right cusp of the aortic valve, at the right aortic sinus in the heart. It travels down the right coronary sulcus, towards the crux of the hear ...
(RCA) originates within the right cusp of the aortic valve. It travels down the right coronary sulcus
The coronary sulcus (also called coronary groove, auriculoventricular groove, atrioventricular groove, AV groove) is a groove on the surface of the heart at the base of right auricle that separates the atria from the ventricles. The structure co ...
, towards the crux of the heart. The RCA primarily branches into the right marginal arteries, and, in 67% of individuals, gives place to the posterior descending artery. The right marginal arteries perfuse the right ventricle and the posterior descending artery perfuses the left ventricular posterior and inferior walls.
There is also the conus artery, which is only present in about 45 percent of the human population, and which provides collateral blood flow to the heart when the left anterior descending artery is occluded.
Clinical significance
 Narrowing of the arteries can be caused by a process known as atherosclerosis (most common), arteriosclerosis, or
Narrowing of the arteries can be caused by a process known as atherosclerosis (most common), arteriosclerosis, or arteriolosclerosis
Arteriolosclerosis is a form of cardiovascular disease involving hardening and loss of elasticity of arterioles or small arteries and is most often associated with hypertension and diabetes mellitus.
Types include hyaline arteriolosclerosis and hyp ...
. This occurs when plaques
Plaque may refer to:
Commemorations or awards
* Commemorative plaque, a plate or tablet fixed to a wall to mark an event, person, etc.
* Memorial Plaque (medallion), issued to next-of-kin of dead British military personnel after World War I
* Pla ...
(made up of deposits of cholesterol and other substances) build up over time in the walls of the arteries. Coronary artery disease
Coronary artery disease (CAD), also called coronary heart disease (CHD), ischemic heart disease (IHD), myocardial ischemia, or simply heart disease, involves the reduction of blood flow to the heart muscle due to build-up of atherosclerotic pla ...
(CAD) or ischemic heart disease are the terms used to describe narrowing of the coronary arteries.
As the disease progresses, plaque buildup can partially block blood flow to the heart muscle. Without enough blood supply (ischemia
Ischemia or ischaemia is a restriction in blood supply to any tissue, muscle group, or organ of the body, causing a shortage of oxygen that is needed for cellular metabolism (to keep tissue alive). Ischemia is generally caused by problems wi ...
), the heart is unable to work properly, especially under increased stress. Stable angina is chest pain on exertion that improves with rest. Unstable angina is chest pain that can occur at rest, feels more severe, and/or last longer than stable angina. It is caused by more severe narrowing of the arteries.
 A
A heart attack
A myocardial infarction (MI), commonly known as a heart attack, occurs when blood flow decreases or stops to the coronary artery of the heart, causing damage to the heart muscle. The most common symptom is chest pain or discomfort which may tr ...
results from a sudden plaque rupture and formation of a thrombus (blood clot) that completely blocks blood flow to a portion of the heart, leading to tissue death ( infarct).
CAD can also result in heart failure
Heart failure (HF), also known as congestive heart failure (CHF), is a syndrome, a group of signs and symptoms caused by an impairment of the heart's blood pumping function. Symptoms typically include shortness of breath, excessive fatigue, a ...
or arrhythmias. Heart failure is caused by chronic oxygen deprivation due to reduced blood flow, which weakens the heart over time. Arrhythmias are caused by inadequate blood supply to the heart that interferes with the heart's electric impulse.
The coronary arteries can constrict as a response to various stimuli, mostly chemical. This is known as a coronary reflex Coronary reflex is the change of coronary diameter in response to chemical, neurological or mechanical stimulation of the coronary arteries.
The coronary reflexes are stimulated differently from the rest of the vascular system.
Causes of coronary c ...
.
There is also a rare condition known as spontaneous coronary artery dissection, in which the wall of one of the coronary arteries tears, causing severe pain. Unlike CAD, spontaneous coronary artery dissection is not due to plaque buildup in arteries, and tends to occur in younger individuals, including women who have recently given birth or men who do intense exercise.
Coronary artery dominance is described as the coronary artery that give branches to supply the right posterior descending artery and supplies the inferior wall of the heart. In 80 to 85% of the population, the right coronary artery supplies the posterior descending artery, making it right heart dominant while in 7 to 13% of the population, the left coronary artery supplies the posterior descending artery, making it left heart dominant. In 7 to 8% of the population, both right and left coronary arteries supplies the posterior descending artery, making it right and left co-dominance. Narrowing of coronary arteries is more frequent in those who are left dominant when compared to those who have right dominant or co-dominant hearts.
Name etymology
The word ' is a Latin word meaning "crown", from the Ancient Greek (, “garland, wreath”). It was applied to the coronary arteries because of a notional resemblance (compare the photos). The word ''arterie'' in Anglo-French (' in Old French, and ' in Latin) means "windpipe" and "an artery." It was applied to the coronary arteries because the arteries do not contain blood after death.See also
*Coronary circulation
Coronary circulation is the circulation of blood in the blood vessels that supply the heart muscle (myocardium).
Coronary arteries supply oxygenated blood to the heart muscle. Cardiac veins then drain away the blood after it has been deoxygenat ...
* Left coronary artery
The left coronary artery (LCA) is a coronary artery that arises from the aorta above the left cusp of the aortic valve, and feeds blood to the left side of the heart muscle. It is also known as the left main coronary artery (LMCA) and the left ma ...
* Right coronary artery
In the blood supply of the heart, the right coronary artery (RCA) is an artery originating above the right cusp of the aortic valve, at the right aortic sinus in the heart. It travels down the right coronary sulcus, towards the crux of the hear ...
* Heart
* Cardiology
* Coronary artery disease
Coronary artery disease (CAD), also called coronary heart disease (CHD), ischemic heart disease (IHD), myocardial ischemia, or simply heart disease, involves the reduction of blood flow to the heart muscle due to build-up of atherosclerotic pla ...
* Angina
Angina, also known as angina pectoris, is chest pain or pressure, usually caused by ischemia, insufficient blood flow to the Cardiac muscle, heart muscle (myocardium). It is most commonly a symptom of coronary artery disease.
Angina is typical ...
* Unstable angina
* Heart attack
* Cardiac skeleton
* Coronary sinus
* Foramen ovale There are multiple structures in the human body with the name foramen ovale (plural: ''foramina ovalia''; Latin for "oval hole"):
* Foramen ovale (heart), in the fetal heart, a shunt from the right atrium to left atrium
* Foramen ovale (skull), at ...
Additional images


References
{{Authority control Anatomy Cardiac anatomy