Continuous Glucose Monitoring on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
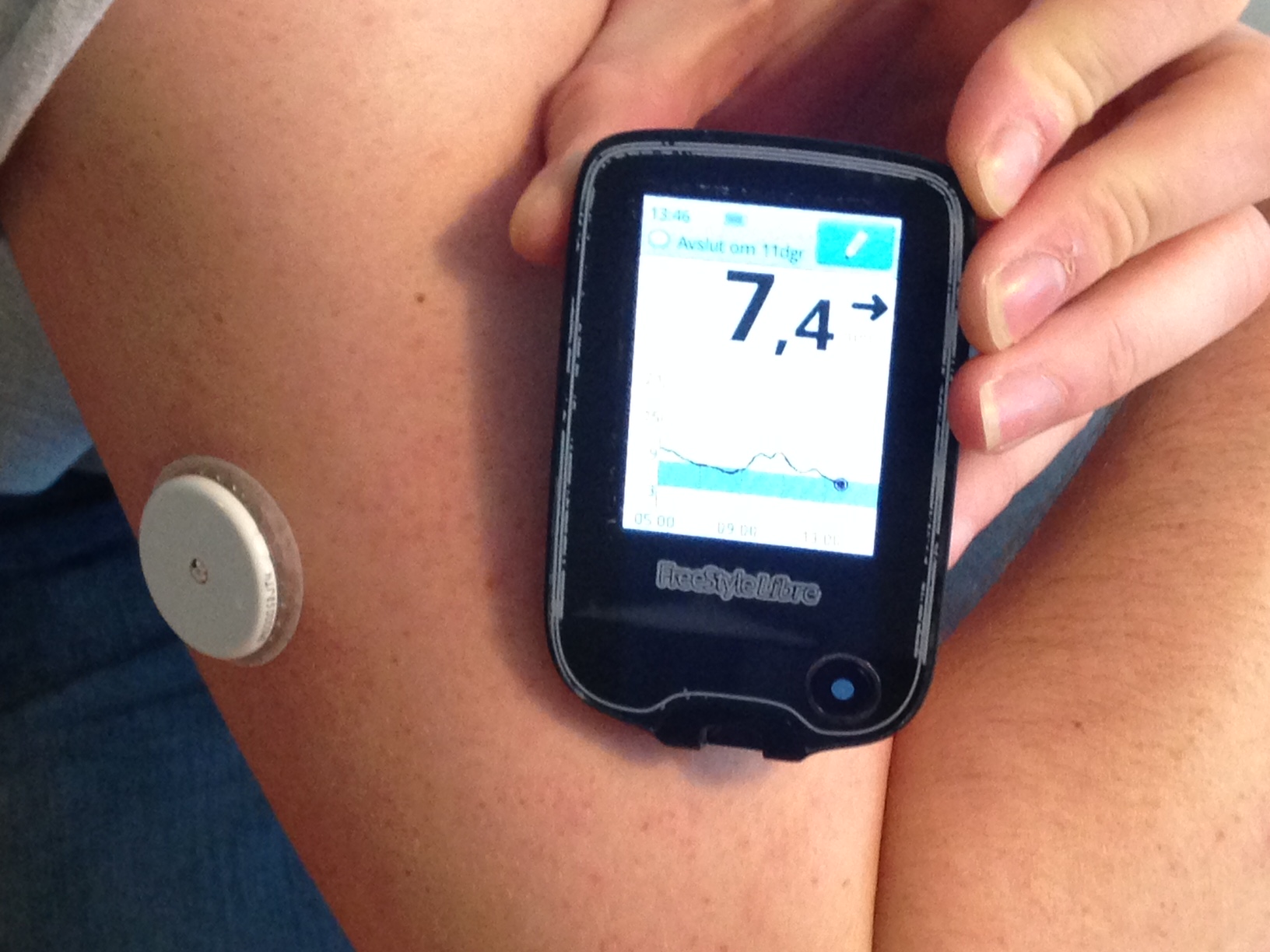 A continuous glucose monitor (CGM) is a device used for monitoring
A continuous glucose monitor (CGM) is a device used for monitoring
blood glucose
Glycaemia, also known as blood sugar level, blood sugar concentration, or blood glucose level is the measure of glucose concentrated in the blood of humans or other animals. Approximately 4 grams of glucose, a simple sugar, is present in the blo ...
on a continual basis by insulin-requiring people with diabetes
Diabetes, also known as diabetes mellitus, is a group of metabolic disorders characterized by a high blood sugar level ( hyperglycemia) over a prolonged period of time. Symptoms often include frequent urination, increased thirst and increased ...
, e.g. people with type I, type II diabetes
Type 2 diabetes, formerly known as adult-onset diabetes, is a form of diabetes mellitus that is characterized by high blood sugar, insulin resistance, and relative lack of insulin. Common symptoms include increased thirst, frequent urinatio ...
or other types of diabetes (e.g. gestational diabetes
Gestational diabetes is a condition in which a woman without diabetes develops high blood sugar levels during pregnancy. Gestational diabetes generally results in few symptoms; however, it increases the risk of pre-eclampsia, depression, and of ...
). A continuous glucose monitor consists of three parts: a small electrode placed under the skin, a transmitter sending readings at regular intervals (ranging from every 5 to 15 min), and a separate receiver. Currently approved CGMs use an enzymatic technology which reacts with glucose molecules in the interstitial fluid
In cell biology, extracellular fluid (ECF) denotes all body fluid outside the cells of any multicellular organism. Total body water in healthy adults is about 60% (range 45 to 75%) of total body weight; women and the obese typically have a lower ...
generating an electric current. This electric current (proportional to the glucose concentration) is then relayed from a transmitter attached to the sensor out to a reader which displays the data to the patient.
Traditional fingerprick
In medicine, some blood tests are conducted on capillary blood obtained by fingerstick (or fingerprick) (or, for neonates, by an analogous heelprick). The site, free of surface arterial flow, where the blood is to be collected is sterilized with ...
testing of blood glucose level
Glycaemia, also known as blood sugar level, blood sugar concentration, or blood glucose level is the measure of glucose concentrated in the blood of humans or other animals. Approximately 4 grams of glucose, a simple sugar, is present in the bl ...
s measures the level at a single point in time. CGM use allows trends in blood glucose to be displayed over time. Some CGM devices have to be periodically calibrated by users with traditional blood glucose measurements, while some do not require user calibration.
CGM is an increasingly adopted technology which has shown to have benefits for people with diabetes. Some studies have demonstrated reduced time spent in hypoglycemia
Hypoglycemia, also called low blood sugar, is a fall in blood sugar to levels below normal, typically below 70 mg/dL (3.9 mmol/L). Whipple's triad is used to properly identify hypoglycemic episodes. It is defined as blood glucose bel ...
or a lower glycated hemoglobin
Glycated hemoglobin, also known as HbA1c, glycohemoglobin, hemoglobin A1c, A1C, is a form of hemoglobin (Hb) that is chemically linked to a sugar. Most monosaccharides, including glucose, galactose and fructose, spontaneously (i.e. non-enzymat ...
, both favorable outcomes.
A Cochrane systematic review found that there is limited and conflicting evidence of the effectiveness of continuous glucose monitoring systems in children, adults or patients with poorly controlled diabetes. However, the use of continuous glucose monitors appears to lower hemoglobin A1c levels, more than just monitoring through capillary blood testing, particularly when used by individuals with poorly controlled diabetes together with an integrated insulin pump. However, there are important limitations: CGM systems are not sufficiently accurate for detecting hypoglycemia, a common side-effect of diabetes treatment. This is especially problematic as some devices offer alarm functions to warn of hypoglycemic episodes and people might rely on those alarms. Still, on the Cochrane systematic review mentioned above, the use of continuous glucose monitors did not increase the risk of hypoglycaemia
Hypoglycemia, also called low blood sugar, is a fall in blood sugar to levels below normal, typically below 70 mg/dL (3.9 mmol/L). Whipple's triad is used to properly identify hypoglycemic episodes. It is defined as blood glucose bel ...
or ketoacidosis. Some manufacturers warn users of relying only on CGM-measurements and the National Institute for Health and Care Excellence
The National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE) is an executive non-departmental public body of the Department of Health and Social Care in England that publishes guidelines in four areas:
* the use of health technologies withi ...
recommends to validate hypoglycaemic values via fingerprick
In medicine, some blood tests are conducted on capillary blood obtained by fingerstick (or fingerprick) (or, for neonates, by an analogous heelprick). The site, free of surface arterial flow, where the blood is to be collected is sterilized with ...
testing of blood glucose level
Glycaemia, also known as blood sugar level, blood sugar concentration, or blood glucose level is the measure of glucose concentrated in the blood of humans or other animals. Approximately 4 grams of glucose, a simple sugar, is present in the bl ...
.
Another limitation is that glucose levels are taken from the interstitial fluid
In cell biology, extracellular fluid (ECF) denotes all body fluid outside the cells of any multicellular organism. Total body water in healthy adults is about 60% (range 45 to 75%) of total body weight; women and the obese typically have a lower ...
rather than the blood. As it takes time for glucose to travel from the bloodstream into the interstitial fluid, there is an inherent lag behind the current blood glucose level and the level measured by the CGM. This lag time varies based on the person and the device, and is generally 5–20 minutes.
Flash glucose monitoring
The Freestyle Libre product introduced by Abbott Diabetes Care in 2015 was billed as "Flash glucose monitoring," and featured a sensor that was factory calibrated, not requiring recalibration against a finger-stick glucose test during use. The sensor with a probe under the skin, as in other CGM sensors, continuously measures the glucose level ofinterstitial fluid
In cell biology, extracellular fluid (ECF) denotes all body fluid outside the cells of any multicellular organism. Total body water in healthy adults is about 60% (range 45 to 75%) of total body weight; women and the obese typically have a lower ...
s (as a proxy for blood sugar levels), but these readings (averaged over each 15 minute period) are rather stored in the sensor unit itself. So instead of a wireless link (such as using Bluetooth
Bluetooth is a short-range wireless technology standard that is used for exchanging data between fixed and mobile devices over short distances and building personal area networks (PANs). In the most widely used mode, transmission power is limi ...
) to an external device, as used by other CGM systems, data stored in the sensor is only transmitted on-demand to a "reader" held within 1-2 centimeters of the sensor unit, employing near-field communication
Near-field communication (NFC) is a set of communication protocols that enables communication between two electronic devices over a distance of 4 cm (1 in) or less. NFC offers a low-speed connection through a simple setup that can be u ...
(NFC) technology. This can be done by the user at any time to obtain a contemporaneous reading, and must be done at least once in 8 hours to avoid a period of missing data, due to the limited memory
Memory is the faculty of the mind by which data or information is encoded, stored, and retrieved when needed. It is the retention of information over time for the purpose of influencing future action. If past events could not be remembered ...
in the sensor unit.
Differences in insurance coverage favoring "flash glucose monitoring" over "continuous glucose monitoring" were an advantage to early adoption of Abbott's less expensive system.
The updated Freestyle Libre 2 version of Abbott's device, however ''does'' have wireless communications capabilities but only to transmit an "alarm" signal using Bluetooth to a nearby device (up to about 10m) in order to warn of an impending low blood sugar level (hypoglycemia
Hypoglycemia, also called low blood sugar, is a fall in blood sugar to levels below normal, typically below 70 mg/dL (3.9 mmol/L). Whipple's triad is used to properly identify hypoglycemic episodes. It is defined as blood glucose bel ...
) or a high blood sugar reading, as programmed by the user. The subsequent Freestyle Libre 3 features a reduced size and simply transmits its readings wirelessly (using bluetooth), as with other manufacturers' models, typically to a smart phone
A smartphone is a portable computer device that combines mobile telephone and computing functions into one unit. They are distinguished from feature phones by their stronger hardware capabilities and extensive mobile operating systems, which ...
.
History
United States
The first CGM system was approved by theFDA
The United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA or US FDA) is a federal agency of the Department of Health and Human Services. The FDA is responsible for protecting and promoting public health through the control and supervision of food ...
in 1999. Continued development has extended the length of time sensors can be worn, options for receiving and reading data, and settings for alerting users of high and low glucose levels.
The first iteration of the Medtronic
Medtronic plc is an American medical device company. The company's operational and executive headquarters are in Minneapolis, Minnesota, and its legal headquarters are in Ireland due to its acquisition of Irish-based Covidien in 2015. While it ...
MiniMed took glucose readings every ten seconds with average readings reported every five minutes. Sensors could be worn for up to 72 hours.
A second system, developed by Dexcom
DexCom, Inc. is a company that develops, manufactures, produces, and distributes continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) systems for diabetes management. It operates internationally with headquarters in San Diego, California, and has a manufacturing ...
, was approved in 2006. The sensor was approved for use for up to 72 hours, and the receiver needed to be within five feet for transmission of data.
In 2008, the third model was approved, Abbott Laboratories
Abbott Laboratories is an American multinational medical devices and health care company with headquarters in Abbott Park, Illinois, United States. The company was founded by Chicago physician Wallace Calvin Abbott in 1888 to formulate known dr ...
' Freestyle Navigator. Sensors could be worn for up to five days.
In 2012, Dexcom released a new device that allowed for the sensor to be worn for seven days and had a transmission distance of 20 feet. Dexcom later introduced an app allowing data from the sensor to be transmitted to an iPhone. This system was approved for paediatric use in 2015.
In September 2017, the FDA approved the first CGM that does not require calibration with fingerstick measurement, the FreeStyle Libre. The Libre is considered a "flash monitoring" system (FGM), and thus not a true ("real-time") CGM system. This device could be worn for up to ten days, but required 12 hours to start readings. and was followed by an updated device that could be worn for up to 14 days, and needed only one hour to start a new sensor. The FreeStyle Libre 2 was approved in Europe in October 2018, and enabled configuration of alerts when glucose is out of range.
In June 2018, the FDA approved the Eversense CGM system for use in people 18 years of age and older with diabetes. This is the first FDA-approved CGM to include a fully implantable sensor to detect glucose, which can be worn for up to 90 days. The Eversense XL, a 180-day version of the system, was approved in Europe in October 2017.
China
China develops and produces CGM systems. The first CGM system to be approved for the European Union is manufactured by Medtrum Technologies. The sensor's intended use is up to 14 days and measures glucose levels every 2 minutes via a smartphone application. Medtrum was founded in 2008 and is based in Shanghai, China. At the end of 2017, Medtrum Technologies introduced the TouchCare A6 CGM (later A7 or Slim in some countries) which measures glucose levels in the interstitial fluid up to 14 days. The TouchCare system comes with mobile applications, including a remote view application. The TouchCare system has glucose alerts and requires calibration every 24 hours. At the end of 2021, after series of improvements Medtrum announced the launch of its next CGM system - Medtrum Nano. The Nano CGM device is super slim and does not require calibration. The Nano system is approved for up to 14 days use, with customisable glucose alerts. Medtrum Technologies is the first company to offer both CGM and Insulin pumps. The CGM and the Insulin pump are controlled by a single smartphone application where the user can monitor glucose levels and trigger insulin delivery. The goal of Medtrum Technologies is to achieve a Closed loop system for the purpose of simplifying diabetes for patients.United Kingdom
As of March 2022, currentNHS
The National Health Service (NHS) is the umbrella term for the publicly funded healthcare systems of the United Kingdom (UK). Since 1948, they have been funded out of general taxation. There are three systems which are referred to using the " ...
guidelines advise that all Type 1 Diabetic patients should be offered either flash glucose monitoring or CGM. Individuals with Type 2 Diabetes are not automatically eligible, but may be offered flash glucose monitoring or CGM if they use insulin two or more times a day, have recurrent or severe hypoglycaemia, have impaired hypoglycaemia awareness, and can't monitor their own blood sugar levels but could use a scanning device or someone else could scan for them.
Device characteristics
* Continuous vs flash monitoring: Dexcom and Eversense use continuous monitoring where information on the glucose levels are continuously updated. Continuous monitoring allows to set automatic alarms that are triggered when the glucose level goes out of pre-configured thresholds. In contrast, with flash monitoring such as the Freestyle Libre, the glucose level is read automatically by the sensor; however, data is only transmitted to the user on user request. The glucose information store on the sensor contains all the data since the previous read (up to 8 hours). FreeStyle Libre 2 allows configuration of alarms when glucose reaches a pre-determined level. * Implantable sensors: Since the electronics and battery require a relatively large package, most CGM sensors are worn over the skin with the actual sensing probe penetrating the skin. However the Eversense sensor is an actual implant, and receives its power wirelesly from a so-called transmitter worn above the skin. The "transmitter" receives data from the sensor every 5 minutes and forwards that data to a nearby device wirelessly. However unlike the Freestyle Libre, the implanted device is too small to have its own battery and memory, so that no glucose readings are generated during periods in which the transmitter is not being worn. The transmitter must be removed at least once a day for recharging (10 minutes) and replacement of the adhesive.Closed loop system
The CGM is a key element in the development of a "closed-loop" system for the treatment of type I diabetes. A closed-loop system involves blood glucose monitored by CGM and the data sent to aninsulin pump
An insulin pump is a medical device used for the administration of insulin in the treatment of diabetes mellitus, also known as continuous subcutaneous insulin therapy.
The device configuration may vary depending on design. A traditional pump ...
for calculated delivery of insulin without user intervention. A number of insulin pump
An insulin pump is a medical device used for the administration of insulin in the treatment of diabetes mellitus, also known as continuous subcutaneous insulin therapy.
The device configuration may vary depending on design. A traditional pump ...
s currently offer an "auto mode" however this is not yet a fully closed loop system. A number of open source
Open source is source code that is made freely available for possible modification and redistribution. Products include permission to use the source code, design documents, or content of the product. The open-source model is a decentralized sof ...
implementations exist; including the artificial pancreas system and OpenAPS
The Open Artificial Pancreas System (OpenAPS) project is a free and open-source software, free and open-source project that aims to make basic artificial pancreas system (APS) technology available to everyone. The OpenAPS project was designed with ...
.
See also
* Most common smartwatches that are compatible with a CGM device.References
{{Reflist Diabetes-related supplies and medical equipment Medical devices