Connaught Hall Courtyard on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Connacht ( ; ga, Connachta or ), is one of the
 Up to the early historic era, Connacht then included County Clare, and was known as Cóiced Ol nEchmacht. Later myths state the Fir Bolg ruled all Ireland before the Tuatha Dé Danann arrived. When the Fir Bolg were defeated, the Tuatha Dé Danann drove them to Connacht. Sites such as the Céide Fields, Knocknarea, Listoghil, Carrowkeel Megalithic Cemetery and Rathcroghan, all demonstrate intensive occupation of Connacht far back into prehistory. Enigmatic artefacts such as the Turoe stone and the Castlestrange stone, whatever their purpose, denote the ambition and achievement of those societies, and their contact with the La Tène culture of mainland Europe. In the early historic era (c. A.D. 300 – c. A.D. 600), Ol nEchmacht was not a united kingdom but a region. It comprised dozens of major and minor túath; rulers of larger túatha ( Maigh Seóla,
Up to the early historic era, Connacht then included County Clare, and was known as Cóiced Ol nEchmacht. Later myths state the Fir Bolg ruled all Ireland before the Tuatha Dé Danann arrived. When the Fir Bolg were defeated, the Tuatha Dé Danann drove them to Connacht. Sites such as the Céide Fields, Knocknarea, Listoghil, Carrowkeel Megalithic Cemetery and Rathcroghan, all demonstrate intensive occupation of Connacht far back into prehistory. Enigmatic artefacts such as the Turoe stone and the Castlestrange stone, whatever their purpose, denote the ambition and achievement of those societies, and their contact with the La Tène culture of mainland Europe. In the early historic era (c. A.D. 300 – c. A.D. 600), Ol nEchmacht was not a united kingdom but a region. It comprised dozens of major and minor túath; rulers of larger túatha ( Maigh Seóla,
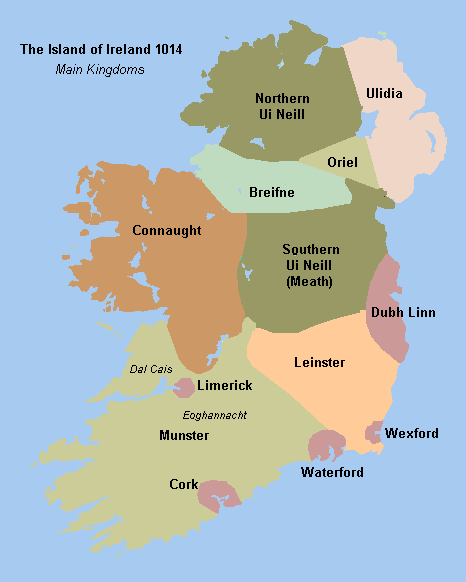 The most successful sept of the
The most successful sept of the
 Under kings Tairrdelbach Ua Conchobair (1088–1156) and his son Ruaidrí Ua Conchobair (c. 1120 – 1198) Connacht became one of the five dominant kingdoms on the island. Tairrdelbach and Ruaidrí became the first men from west of the Shannon to gain the title ''Ard-Rí na hÉireann'' (
Under kings Tairrdelbach Ua Conchobair (1088–1156) and his son Ruaidrí Ua Conchobair (c. 1120 – 1198) Connacht became one of the five dominant kingdoms on the island. Tairrdelbach and Ruaidrí became the first men from west of the Shannon to gain the title ''Ard-Rí na hÉireann'' (
 The town of Galway was the only significant urban area in the province. Its inhabitants governed themselves under charter of the king of England. Its merchant families, The Tribes of Galway, traded not only with the lordships around them and in Lordship of Ireland, Ireland, but with Kingdom of England, England, France, and Spain. Its mayor enjoyed supreme power but only for the length of his office, rarely more than a year. Galway's inhabitants were of mixed descent, its families bearing surnames of Gaelic, French, English, Welsh, Norman and other origins.
Connacht was the site of two of the bloodiest battles in Irish history, the Second Battle of Athenry (1316) and the Battle of Knockdoe (1504). The casualties of both battles were measured in several thousand, unusually high for Irish warfare. A third battle at Aughrim in 1691 resulted in an estimated 10,000 deaths.
All of Connacht's lordships remained in states of full or semi-independence from other Gaelic-Irish and Anglo-Irish rulers until the late 16th century, when the Tudor conquest of Ireland (1534–1603) brought all under the direct rule of King James I of England. The counties were created from c. 1569 onwards.
The town of Galway was the only significant urban area in the province. Its inhabitants governed themselves under charter of the king of England. Its merchant families, The Tribes of Galway, traded not only with the lordships around them and in Lordship of Ireland, Ireland, but with Kingdom of England, England, France, and Spain. Its mayor enjoyed supreme power but only for the length of his office, rarely more than a year. Galway's inhabitants were of mixed descent, its families bearing surnames of Gaelic, French, English, Welsh, Norman and other origins.
Connacht was the site of two of the bloodiest battles in Irish history, the Second Battle of Athenry (1316) and the Battle of Knockdoe (1504). The casualties of both battles were measured in several thousand, unusually high for Irish warfare. A third battle at Aughrim in 1691 resulted in an estimated 10,000 deaths.
All of Connacht's lordships remained in states of full or semi-independence from other Gaelic-Irish and Anglo-Irish rulers until the late 16th century, when the Tudor conquest of Ireland (1534–1603) brought all under the direct rule of King James I of England. The counties were created from c. 1569 onwards.
 Connacht was mainly at peace between 1691 and 1798. In 1798 Connacht was a major backdrop to the Irish Rebellion of 1798 when French forces under General Jean Joseph Amable Humbert, Jean Humbert of the French First Republic, French Republic landed in Killala, County Mayo to link up with the United Irishmen. Together, the French and Irish forces defeat a British garrison at the Races of Castlebar before proclaiming the Irish Republic (1798), Irish Republic, which later became better known as the "Republic of Connacht" as its area of effective control never extended beyond the province. The Republic, and the Rebellion itself, was effectively crushed at the Battle of Ballinamuck.
A population growth, population explosion in the early 18th century was curbed by the Irish Famine (1740–1741), Irish Famine, which led to many deaths and some emigration. Its memory has been overshadowed by the Great Famine (Ireland) one hundred years later.
Connacht was mainly at peace between 1691 and 1798. In 1798 Connacht was a major backdrop to the Irish Rebellion of 1798 when French forces under General Jean Joseph Amable Humbert, Jean Humbert of the French First Republic, French Republic landed in Killala, County Mayo to link up with the United Irishmen. Together, the French and Irish forces defeat a British garrison at the Races of Castlebar before proclaiming the Irish Republic (1798), Irish Republic, which later became better known as the "Republic of Connacht" as its area of effective control never extended beyond the province. The Republic, and the Rebellion itself, was effectively crushed at the Battle of Ballinamuck.
A population growth, population explosion in the early 18th century was curbed by the Irish Famine (1740–1741), Irish Famine, which led to many deaths and some emigration. Its memory has been overshadowed by the Great Famine (Ireland) one hundred years later.
Census 2011 – Galway Gaeltacht statsCensus 2011 – Mayo Gaeltacht statsGaeltacht Comprehensive Language Study 2007Gaelscoil stats
{{Authority control Connacht, Provinces of Ireland
provinces of Ireland
There have been four Provinces of Ireland: Connacht (Connaught), Leinster, Munster, and Ulster. The Irish language, Irish word for this territorial division, , meaning "fifth part", suggests that there were once five, and at times Kingdom_of_ ...
, in the west of Ireland. Until the ninth century it consisted of several independent major Gaelic kingdoms ( Uí Fiachrach, Uí Briúin, Uí Maine
U or u, is the twenty-first and sixth-to-last letter and fifth vowel letter of the Latin alphabet, used in the modern English alphabet, the alphabets of other western European languages and others worldwide. Its name in English is ''u'' (pro ...
, Conmhaícne, and Delbhna).
Between the reigns of Conchobar mac Taidg Mór (died 882) and his descendant, Aedh mac Ruaidri Ó Conchobair (reigned 1228–33), it became a kingdom under the rule of the Uí Briúin Aí dynasty, whose ruling sept adopted the surname Ua Conchobair. At its greatest extent, it incorporated the often independent Kingdom of Breifne, as well as vassalage from the lordships of western Mide and west Leinster. Two of its greatest kings, Tairrdelbach Ua Conchobair (1088–1156) and his son Ruaidri Ua Conchobair (c. 1115–1198) greatly expanded the kingdom's dominance, so much so that both became High King of Ireland
High King of Ireland ( ga, Ardrí na hÉireann ) was a royal title in Gaelic Ireland held by those who had, or who are claimed to have had, lordship over all of Ireland. The title was held by historical kings and later sometimes assigned ana ...
.
The Kingdom of Connacht collapsed in the 1230s because of civil war within the royal dynasty, which enabled widespread Hiberno-Norman
From the 12th century onwards, a group of Normans invaded and settled in Gaelic Ireland. These settlers later became known as Norman Irish or Hiberno-Normans. They originated mainly among Cambro-Norman families in Wales and Anglo-Normans from ...
settlement under Richard Mór de Burgh, 1st Baron of Connaught
Richard Mór de Burgh, 1st Lord of Connacht (; ; c.1194–1242, or 1243), was a Hiberno-Norman aristocrat who was Seneschal of Munster and Justiciar of Ireland (1228–32).
Background
Richard Mór de Burgh, was born towards the end of the ye ...
, and his successors. The Norman colony in Connacht shrank from c. 1300 to c. 1360, with events such as the 1307 battle of Ahascragh (see Donnchad Muimnech Ó Cellaigh), the 1316 Second Battle of Athenry and the murder in June 1333 of William Donn de Burgh, 3rd Earl of Ulster, all leading to Gaelic resurgence and colonial withdrawal to towns such as Ballinrobe, Loughrea, Athenry, and Galway. Well into the 16th century, kingdoms such as Uí Maine and Tír Fhíacrach Múaidhe remained beyond English control, while many Norman families such as de Burgh, de Bermingham, de Exeter, de Staunton, became entirely Gaelicised. Only in the late 1500s, during the Tudor conquest of Ireland, was Connacht shire
Shire is a traditional term for an administrative division of land in Great Britain and some other English-speaking countries such as Australia and New Zealand. It is generally synonymous with county. It was first used in Wessex from the beginn ...
d into its present counties.
Connacht's population was 1,418,859 in 1841. Then came the Great Famine of the 1840s, which began a 120-year decline to under 400,000. The province has a population of just under 590,000 according to the preliminary results of the 2022 census.
British cultural imperialism was weaker in the west of Ireland, and Connacht today has the highest number of Irish language
Irish ( Standard Irish: ), also known as Gaelic, is a Goidelic language of the Insular Celtic branch of the Celtic language family, which is a part of the Indo-European language family. Irish is indigenous to the island of Ireland and was ...
speakers among the four Irish provinces. Currently, the total percentage of people who consider themselves as Irish speakers in Connacht is 39.8% (more than 202,000 persons). There are Gaeltacht areas in Counties Galway and Mayo.
The province of Connacht has no official function for local government purposes, but it is an officially recognised subdivision of the Irish state. It is listed on ISO-3166-2
ISO 3166-2 is part of the ISO 3166 standard published by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO), and defines codes for identifying the principal subdivisions (e.g., provinces or states) of all countries coded in ISO 3166-1. The of ...
as one of the four provinces of Ireland and "IE-C" is attributed to Connacht as its country sub-division code. Along with counties from other provinces, Connacht lies in the Midlands–North-West constituency for elections to the European Parliament.
Name
The name comes from the medieval ruling dynasty, the ''Connacht'', laterConnachta
The Connachta are a group of medieval Irish dynasties who claimed descent from the legendary High King Conn Cétchathach (Conn of the Hundred Battles). The modern western province of Connacht (Irish ''Cúige Chonnacht'', province, literally "f ...
, whose name means "descendants of Conn", from the mythical king Conn of the Hundred Battles
Conn Cétchathach (; "of the Hundred Battles"), son of Fedlimid Rechtmar, was a semi-legendary High King of Ireland and the ancestor of the Connachta, and, through his descendant Niall Noígiallach, the Uí Néill dynasties, which dominated Irela ...
. The name of the province in the Irish language is ''Connachta''. Originally ''Connacht'' was a singular collective noun, but it came to be used only in the plural ''Connachta'', partly by analogy with plural names of other dynastic territories like Ulaid and Laigin, and partly because the Connachta split into different branches. Before the Connachta dynasty, the province (''cúige'', "fifth") was known as Cóiced Ol nEchmacht. In Modern Irish, the province is usually called ''Cúige Chonnacht'', "the Province of Connacht", where ''Chonnacht'' is plural genitive case
In grammar, the genitive case (abbreviated ) is the grammatical case that marks a word, usually a noun, as modifying another word, also usually a noun—thus indicating an attributive relationship of one noun to the other noun. A genitive can al ...
with lenition of the ''C'' to ''Ch''.
The usual English spelling in Ireland since the Gaelic revival
The Gaelic revival ( ga, Athbheochan na Gaeilge) was the late-nineteenth-century Romantic nationalism, national revival of interest in the Irish language (also known as Gaelic) and Irish Gaelic culture (including Irish folklore, folklore, Iri ...
is ''Connacht'', the spelling of the disused Irish singular. The official English spelling during English and British rule was the anglicisation
Anglicisation is the process by which a place or person becomes influenced by English culture or British culture, or a process of cultural and/or linguistic change in which something non-English becomes English. It can also refer to the influen ...
Connaught, pronounced or . This was used for the Connaught Rangers in the British Army; in the title of Queen Victoria's son Arthur, Duke of Connaught; and the Connaught Hotel, London, named after the Duke in 1917. Usage of the Connaught spelling is now in decline. State bodies use ''Connacht'', for example in Central Statistics Office census reports since 1926, and the name of the Connacht–Ulster European Parliament constituency of 1979–2004, although ''Connaught'' occurs in some statutes. Among newspapers, the ''Connaught Telegraph
''The Connaught Telegraph'' is a weekly local newspaper published in Castlebar, County Mayo
County Mayo (; ga, Contae Mhaigh Eo, meaning "Plain of the Taxus baccata, yew trees") is a Counties of Ireland, county in Republic of Ireland, Irel ...
'' (founded 1830) retains the anglicised spelling in its name, whereas the '' Connacht Tribune'' (founded 1909) uses the Gaelic. Connacht Rugby
Connacht Rugby ( ga, Rugbaí Connachta) is one of the four professional provincial rugby teams from the island of Ireland. Connacht competes in the United Rugby Championship and the European Rugby Champions Cup. The team represents the IRFU Con ...
who represent the region and are based in Galway, use the Gaelic spelling also.
Geography and political divisions
The province is divided into five traditional counties, the fewest of any province. These are: Galway, Leitrim, Mayo, Roscommon andSligo
Sligo ( ; ga, Sligeach , meaning 'abounding in shells') is a coastal seaport and the county town of County Sligo, Ireland, within the western province of Connacht. With a population of approximately 20,000 in 2016, it is the List of urban areas ...
. Connacht is the smallest of the four Irish provinces both in terms of size and population. Galway is the only official city in the province.
Largest settlements
Physical geography
The highest point of Connacht is Mweelrea (814 m), in County Mayo. The largest island in Connacht (and Ireland) is Achill. The biggest lake isLough Corrib
Lough Corrib ( ; ) is a lake in the west of Ireland. The River Corrib or Galway River connects the lake to the sea at Galway. It is the largest lake within the Republic of Ireland and the second largest on the island of Ireland (after Lough Nea ...
.
Much of the west coast (e.g. Connemara and Erris) is ruggedly inhospitable and not conducive for agriculture. It contains the main mountainous areas in Connacht, including the Twelve Bens, Maumturks, Mweelrea, Croagh Patrick
Croagh Patrick (), nicknamed 'the Reek', is a mountain with a height of and an important site of pilgrimage in County Mayo, Ireland. The mountain has a pyramid-shaped peak and overlooks Clew Bay, rising above the village of Murrisk, several mil ...
, Nephin Beg, Ox Mountains, and Dartry Mountains.
Killary Harbour, one of Ireland's fjords (the others being Carlingford Lough
Carlingford Lough (, Ulster Scots: ''Carlinford Loch'') is a glacial fjord or sea inlet in northeastern Ireland, forming part of the border between Northern Ireland to the north and the Republic of Ireland to the south. On its northern shore i ...
and Lough Swilly), is located at the foot of Mweelrea. Connemara National Park is in County Galway. The Aran Islands, featuring prehistoric forts such as Dún Aonghasa, have been a regular tourist destination since the 19th century.
Inland areas such as east Galway, Roscommon and Sligo have enjoyed greater historical population density due to better agricultural land and infrastructure.
Rivers and lakes include the River Moy, River Corrib, the Shannon, Lough Mask, Lough Melvin
Lough Melvin ( ; ) is a lake in the northwest of the island of Ireland on the border between County Leitrim (in Ireland) and County Fermanagh (in the United Kingdom). It is internationally renowned for its unique range of plants and animals ...
, Lough Allen and Lough Gill.
The largest urban area in Connacht is Galway, with a population of 79,934. Other large towns in Connacht are Sligo
Sligo ( ; ga, Sligeach , meaning 'abounding in shells') is a coastal seaport and the county town of County Sligo, Ireland, within the western province of Connacht. With a population of approximately 20,000 in 2016, it is the List of urban areas ...
(19,199), Castlebar (12,068) and Ballina (10,171).
History
Early history
 Up to the early historic era, Connacht then included County Clare, and was known as Cóiced Ol nEchmacht. Later myths state the Fir Bolg ruled all Ireland before the Tuatha Dé Danann arrived. When the Fir Bolg were defeated, the Tuatha Dé Danann drove them to Connacht. Sites such as the Céide Fields, Knocknarea, Listoghil, Carrowkeel Megalithic Cemetery and Rathcroghan, all demonstrate intensive occupation of Connacht far back into prehistory. Enigmatic artefacts such as the Turoe stone and the Castlestrange stone, whatever their purpose, denote the ambition and achievement of those societies, and their contact with the La Tène culture of mainland Europe. In the early historic era (c. A.D. 300 – c. A.D. 600), Ol nEchmacht was not a united kingdom but a region. It comprised dozens of major and minor túath; rulers of larger túatha ( Maigh Seóla,
Up to the early historic era, Connacht then included County Clare, and was known as Cóiced Ol nEchmacht. Later myths state the Fir Bolg ruled all Ireland before the Tuatha Dé Danann arrived. When the Fir Bolg were defeated, the Tuatha Dé Danann drove them to Connacht. Sites such as the Céide Fields, Knocknarea, Listoghil, Carrowkeel Megalithic Cemetery and Rathcroghan, all demonstrate intensive occupation of Connacht far back into prehistory. Enigmatic artefacts such as the Turoe stone and the Castlestrange stone, whatever their purpose, denote the ambition and achievement of those societies, and their contact with the La Tène culture of mainland Europe. In the early historic era (c. A.D. 300 – c. A.D. 600), Ol nEchmacht was not a united kingdom but a region. It comprised dozens of major and minor túath; rulers of larger túatha ( Maigh Seóla, Uí Maine
U or u, is the twenty-first and sixth-to-last letter and fifth vowel letter of the Latin alphabet, used in the modern English alphabet, the alphabets of other western European languages and others worldwide. Its name in English is ''u'' (pro ...
, Aidhne and Máenmaige) were accorded high-king status, while peoples such as the Gailenga, Corco Moga and Senchineoil were lesser peoples given the status of Déisi. All were termed kingdoms, but according to a graded status, denoting each according the likes of lord, count, earl, king.
Some of the more notable peoples or ethnic groups included the following:
By the 5th century, the pre-historic nations such as the Auteini and Nagnatae
The Nagnatae (Ναγνάται) or Magnatae (Μαγνάται) were a people of ancient Ireland, recorded in Ptolemy's 2nd century ''Geography'' as living in northern Connacht. O'Rahilly suggests a connection between the Nagnatae and the Fir Ó ...
– recorded by Ptolemy (c. AD 90 – c. 168) in '' Geography'' – gave way to dynasties. This is demonstrated in the noun ''moccu'' in names such as Muirchu moccu Machtheni, which indicated a person was ''of the Machtheni people.'' As evidenced by kings such as Mac Cairthinn mac Coelboth (died 446) and Ailill Molt
Ailill mac Nath Í (died c. 482), called Ailill Molt, is included in most lists of the High Kings of Ireland and is also called King of Connacht. His cognomen, ''molt'', means "sheep, ram" but its origin is unknown.
Family
Ailill was said to be ...
(died c. 482), even by the 5th century the gens
In ancient Rome, a gens ( or , ; plural: ''gentes'' ) was a family consisting of individuals who shared the same Roman naming conventions#Nomen, nomen and who claimed descent from a common ancestor. A branch of a gens was called a ''stirps'' (p ...
was giving way to kinship all over Ireland, as both men were identified as of the Uí Enechglaiss and Uí Fiachrach dynasties, not of tribes. By 700, ''moccu'' had been entirely replaced by ''mac'' and ''hua'' (later ''Mac'' and ''Ó'').
During the mid-8th century, what is now County Clare was absorbed into Thomond by the Déisi Tuisceart. It has remained a part of the province of Munster
Munster ( gle, an Mhumhain or ) is one of the provinces of Ireland, in the south of Ireland. In early Ireland, the Kingdom of Munster was one of the kingdoms of Gaelic Ireland ruled by a "king of over-kings" ( ga, rí ruirech). Following the ...
ever since.
The name Connacht arose from the most successful of these early dynasties, The Connachta
The Connachta are a group of medieval Irish dynasties who claimed descent from the legendary High King Conn Cétchathach (Conn of the Hundred Battles). The modern western province of Connacht (Irish ''Cúige Chonnacht'', province, literally "f ...
. By 1050, they had extended their rule from Rathcroghan in north County Roscommon to large areas of what are now County Galway, County Mayo, County Sligo, and County Leitrim. The dynastic term was from then on applied to the overall geographic area containing those counties, and has remained so ever since.
Kingdom of Connacht
 The most successful sept of the
The most successful sept of the Connachta
The Connachta are a group of medieval Irish dynasties who claimed descent from the legendary High King Conn Cétchathach (Conn of the Hundred Battles). The modern western province of Connacht (Irish ''Cúige Chonnacht'', province, literally "f ...
were the Ó Conchobair of Síol Muireadaigh. They derived their surname from Conchobar mac Taidg Mór (c. 800 – 882), from whom all subsequent Ó Conchobair Kings of Connacht descended.
Conchobar was a nominal vassal of Máel Sechnaill mac Máele Ruanaid, High King of Ireland
High King of Ireland ( ga, Ardrí na hÉireann ) was a royal title in Gaelic Ireland held by those who had, or who are claimed to have had, lordship over all of Ireland. The title was held by historical kings and later sometimes assigned ana ...
(died 862). He married Máel Sechnaill's daughter, Ailbe, and had sons Áed mac Conchobair
Áed mac Conchobair (died 888) was a King of Connacht from the Uí Briúin branch of the Connachta. He was the son of Conchobar mac Taidg Mór (died 882), the previous king and was the first of his three sons to rule in succession. He was of the ...
(died 888), Tadg mac Conchobair (died 900) and Cathal mac Conchobair (died 925), all of whom subsequently reigned. Conchobar and his sons' descendants expanded the power of the Síol Muiredhaigh south into Uí Maine
U or u, is the twenty-first and sixth-to-last letter and fifth vowel letter of the Latin alphabet, used in the modern English alphabet, the alphabets of other western European languages and others worldwide. Its name in English is ''u'' (pro ...
, west into Iar Connacht, and north into Uí Fiachrach Muaidhe and Bréifne.
By the reign of Áed in Gai Bernaig (1046–1067), Connacht's kings ruled much what is now the province. Yet the Ó Conchobair's contended for control with their cousins, the Ua Ruairc of Uí Briúin Bréifne. Four Ua Ruairc's achieved rule of the kingdom – Fergal Ua Ruairc (956–967), Art Uallach Ua Ruairc (1030–1046), Áed Ua Ruairc (1067–1087), and Domnall Ua Ruairc (1098–1102). In addition, the usurper Flaithbertaigh Ua Flaithbertaigh gained the kingship in 1092 by the expedient of blinding King Ruaidrí na Saide Buide. After 1102 the Ua Ruairc's and Ua Flaithbertaigh's were suborned and confined to their own kingdoms of Bréifne and Iar Connacht. From then until the death of the last king in 1474, the kingship was held exclusively by the Ó Conchobair's.
The single most substantial sub-kingdom in Connacht was Uí Maine
U or u, is the twenty-first and sixth-to-last letter and fifth vowel letter of the Latin alphabet, used in the modern English alphabet, the alphabets of other western European languages and others worldwide. Its name in English is ''u'' (pro ...
, which at it maximum extant enclosed central and south County Roscommon, central, east-central and south County Galway, along with the territory of Lusmagh in Munster
Munster ( gle, an Mhumhain or ) is one of the provinces of Ireland, in the south of Ireland. In early Ireland, the Kingdom of Munster was one of the kingdoms of Gaelic Ireland ruled by a "king of over-kings" ( ga, rí ruirech). Following the ...
. Their rulers bore the family name Kelly (surname), Ó Ceallaigh; its spelling sometimes varying slightly from scribe to scribe.
Though the Ó Ceallaigh's were never elevated to the provincial kingship, Uí Maine existed as a semi-independent kingdom both before and after the demise of the Connacht kingship.
Kings and High Kings
 Under kings Tairrdelbach Ua Conchobair (1088–1156) and his son Ruaidrí Ua Conchobair (c. 1120 – 1198) Connacht became one of the five dominant kingdoms on the island. Tairrdelbach and Ruaidrí became the first men from west of the Shannon to gain the title ''Ard-Rí na hÉireann'' (
Under kings Tairrdelbach Ua Conchobair (1088–1156) and his son Ruaidrí Ua Conchobair (c. 1120 – 1198) Connacht became one of the five dominant kingdoms on the island. Tairrdelbach and Ruaidrí became the first men from west of the Shannon to gain the title ''Ard-Rí na hÉireann'' (High King of Ireland
High King of Ireland ( ga, Ardrí na hÉireann ) was a royal title in Gaelic Ireland held by those who had, or who are claimed to have had, lordship over all of Ireland. The title was held by historical kings and later sometimes assigned ana ...
). In the latter's case, he was recognised all over the island in 1166 as ''Rí Éireann'', or King of Ireland.
Tairrdelbach was highly innovative, building the first stone castles in Ireland, and more controversially, introducing the policy of primogeniture to a hostile Gaelic polity. Castles were built in the 1120s at Galway (where he based his Naval fleet, fleet), Dunmore, County Galway, Dunmore, Sligo
Sligo ( ; ga, Sligeach , meaning 'abounding in shells') is a coastal seaport and the county town of County Sligo, Ireland, within the western province of Connacht. With a population of approximately 20,000 in 2016, it is the List of urban areas ...
and Ballinasloe, where he dug a new six-mile canal to divert the river Suck around the castle of Dun Ló. Churches, monasteries and dioceses were re-founded or created, works such as the Corpus Missal, the High Cross of Tuam and the Cross of Cong were sponsored by him.
Tairrdelbach annexed the Kingdom of Mide; its rulers, the Clann Cholmáin, became his vassals. This brought two of Ireland's five main kingdoms under the direct control of Connacht. He also asserted control over Dublin, which was even then being recognised as a kind of national capital.
His son, Ruaidrí, became king of Connacht ''"without any opposition"'' in 1156. One of his first acts as king was arresting three of his twenty-two brothers, ''"Brian Breifneach, Brian Luighneach, and Muircheartach Muimhneach"'' to prevent them from usurping him. He blinded Brian Breifneach as an extra precaution.
Ruaidrí was compelled to recognise Muirchertach Mac Lochlainn as Ard-Rí, though he went to war with him in 1159. Mac Lochlainn's murder in 1166 left Ruaidrí the unopposed ruler of all Ireland. He was crowned in 1166 at Dublin, ''"took the kingship of Ireland ...[and was] inaugurated king as honourably as any king of the Gaeidhil was ever inaugurated;"'' He was the first and last native ruler who was recognised by the Gaelic-Irish as full King of Ireland.
However, his expulsion of Dermot MacMurrough later that year brought about the Norman invasion of Ireland in 1169. Ruaidrí's inept response to events led to rebellion by his sons in 1177, and his deposition by Conchobar Maenmaige Ua Conchobair in 1183. Ruaidrí died at Cong, County Mayo, Cong in 1198, noted as the annals as late ''"King of Connacht and of All Ireland, both the Irish and the English."''
High medieval era
Connacht was first raided by the Anglo-Normans in 1177 but not until 1237 did encastellation begin under Richard Mor de Burgh (c. 1194 – 1242). New towns were founded ( Athenry, Headford, Castlebar) or former settlements expanded (Sligo
Sligo ( ; ga, Sligeach , meaning 'abounding in shells') is a coastal seaport and the county town of County Sligo, Ireland, within the western province of Connacht. With a population of approximately 20,000 in 2016, it is the List of urban areas ...
, Roscommon, Loughrea, Ballymote). Both ''Gael and Gall'' acknowledged the supreme lordship of the Earl of Ulster; after the murder of the last earl in 1333, the Anglo-Irish split into different factions, the most powerful emerging as Bourke of Mac William Eighter in north Connacht, and House of Burke, Burke of Clanricarde in the south. They were regularly in and out of alliance with equally powerful Gaels, Gaelic lords and kings such as Conor, Ó Conchobair of Síol Muireadaigh, Kelly (surname), Ó Cellaigh of Uí Maine
U or u, is the twenty-first and sixth-to-last letter and fifth vowel letter of the Latin alphabet, used in the modern English alphabet, the alphabets of other western European languages and others worldwide. Its name in English is ''u'' (pro ...
and MacDermot, Mac Diarmata of Moylurg, in addition to extraprovincial powers such as O'Brian, Ó Briain of Thomond, FitzGerald dynasty, FitzGerald of Kildare, O'Donnell dynasty, Ó Domhnaill of Tyrconnell, Tír Chonaill.
Lesser lords of both ethnicities included McDonagh, Mac Donnchadha, Costello (surname), Mac Goisdelbh, Mac Bhaldrin, Mac Jordan of Connacht, Mac Siurtain, O'Hara (surname), Ó hEaghra, O'Flaherty, Ó Flaithbeheraigh, Dowd, Ó Dubhda, O'Shaughnessy, Ó Seachnasaigh, Monahan, Ó Manacháin, Joyce (name), Seoighe, O'Malley (surname), Ó Máille, Rourke, Ó Ruairc, Madudan mac Gadhra Mór, Ó Madadháin, Clan Barrett, Bairéad, Mulrooney, Ó Máel Ruanaid, Eidhean mac Cléireach, Ó hEidhin, Finnerty, Ó Finnaghtaigh, Fallon (surname), Ó Fallmhain, Welsh language, Breathneach, Geraghty, Mac Airechtaig, Naughton, Ó Neachtain, Ó hAllmhuráin, Fahy, Ó Fathaigh.
 The town of Galway was the only significant urban area in the province. Its inhabitants governed themselves under charter of the king of England. Its merchant families, The Tribes of Galway, traded not only with the lordships around them and in Lordship of Ireland, Ireland, but with Kingdom of England, England, France, and Spain. Its mayor enjoyed supreme power but only for the length of his office, rarely more than a year. Galway's inhabitants were of mixed descent, its families bearing surnames of Gaelic, French, English, Welsh, Norman and other origins.
Connacht was the site of two of the bloodiest battles in Irish history, the Second Battle of Athenry (1316) and the Battle of Knockdoe (1504). The casualties of both battles were measured in several thousand, unusually high for Irish warfare. A third battle at Aughrim in 1691 resulted in an estimated 10,000 deaths.
All of Connacht's lordships remained in states of full or semi-independence from other Gaelic-Irish and Anglo-Irish rulers until the late 16th century, when the Tudor conquest of Ireland (1534–1603) brought all under the direct rule of King James I of England. The counties were created from c. 1569 onwards.
The town of Galway was the only significant urban area in the province. Its inhabitants governed themselves under charter of the king of England. Its merchant families, The Tribes of Galway, traded not only with the lordships around them and in Lordship of Ireland, Ireland, but with Kingdom of England, England, France, and Spain. Its mayor enjoyed supreme power but only for the length of his office, rarely more than a year. Galway's inhabitants were of mixed descent, its families bearing surnames of Gaelic, French, English, Welsh, Norman and other origins.
Connacht was the site of two of the bloodiest battles in Irish history, the Second Battle of Athenry (1316) and the Battle of Knockdoe (1504). The casualties of both battles were measured in several thousand, unusually high for Irish warfare. A third battle at Aughrim in 1691 resulted in an estimated 10,000 deaths.
All of Connacht's lordships remained in states of full or semi-independence from other Gaelic-Irish and Anglo-Irish rulers until the late 16th century, when the Tudor conquest of Ireland (1534–1603) brought all under the direct rule of King James I of England. The counties were created from c. 1569 onwards.
Confederate and Williamite Wars
During the 17th century representatives from Connacht played leading roles in Confederate Ireland and during the Williamite War in Ireland. Its main town, Galway, endured several sieges (see Sieges of Galway), while warfare, plague (disease), plague, famine and sectarian massacres killed about a third of the population by 1655. One of the last battles fought in pre-20th century Ireland occurred in Connacht, the Battle of Aughrim on 12 July 1691.Early modern era
The Famine to World War One
Connacht was the worst hit area in Ireland during the Great Famine, in particular, counties Mayo and Roscommon. In the Census of 1841, the population of Connacht stood at 1,418,859, the highest ever recorded. By 1851, the population had fallen to 1,010,031 and would continue to decline until the late 20th century.Republic Of Connacht
At the time of the Rebellion of 1798 a force of 1,000 French soldiers under General Jean Joseph Amable Humbert landed at Killala in County Mayo. General Humbert proclaimed the Irish Republic in his declaration to the people upon landing in Ireland on 22 August 1798: After the nascent Republic's victory at the Battle of Castlebar which took place on 27 August 1798, General Humbert, on 31 August 1798, issued the following decree, which ''inter alia'' appointed John Moore (Irish politician), John Moore as the President of the Government of the Province of Connacht: The rebel republic was a client state of the First French Republic, French Republic and was very short lived. Nevertheless, among the things which President Moore did have time to do was to issue "''paper money to a considerable extent...[i]n the name of the French Government''". Despite their general anti-clericalism and hosility to the Bourbon monarchy, the French Directory suggested to the United Irishmen in 1798 restoring the Jacobitism, Jacobite Pretender, Henry Benedict Stuart, as Henry IX, Monarchy of Ireland, King of the Irish. This was on account of General Humbert landing a force in County Mayo for the Irish Rebellion of 1798 and realising the local population were devoutly Catholic (a significant number of Irish priests supported the Rising and had met with Humbert, although Humbert's Army had been veterans of the anti-clerical campaign in Italy). The French Directory hoped this option would allow the creation of a stable French client state in Ireland. However, Wolfe Tone, the Protestant republican leader, scoffed at the suggestion and it was quashed, with an Irish Republic proclaimed.Defeat
On 8 September 1798, just weeks after its proclamation, the republic collapsed after the Battle of Ballinamuck. Moore was captured by a detachment of government troops led by Lieutenant Colonel Crawford in Castlebar, dyring in custody the following year. Humbert and his men were transported by canal to Dublin and exchanged for British prisoners of war. Government forces subsequently slowly spread out into the republic, engaging in numerous skirmishes with rebel holdouts. These sweeps reached their climax in 23 September when Killala was captured by government forces. During these sweeps, suspected rebels were frequently summarily executed while many houses thought to be housing rebels were burnt. Numerous rebels took to the countryside and continued guerrilla operations, which took government forces some months to suppress.Politics
Connacht–Ulster was one of Ireland's four regional constituency, constituencies for elections to the European Parliament until it was superseded in 2004 by the constituency of North-West (European Parliament constituency), North-West.Irish language
TheIrish language
Irish ( Standard Irish: ), also known as Gaelic, is a Goidelic language of the Insular Celtic branch of the Celtic language family, which is a part of the Indo-European language family. Irish is indigenous to the island of Ireland and was ...
is spoken in the Gaeltacht areas of Counties Mayo and Galway, the largest area being in the west of County Galway. The Galway Gaeltacht is the largest Irish-speaking region in Ireland, taking in Gaeltacht Cois Fharraige, Cois Fharraige, parts of Connemara, Conamara Theas, the Aran Islands, Joyce Country, Dúithche Sheoigeach (Joyce Country) and the Galway City Gaeltacht. Irish-speaking areas in County Mayo can be found in Iorras, Acaill and Tourmakeady.
According to the 2016 census, Irish is spoken outside of the education system on a daily basis by 9,455 people in the Galway County Gaeltacht areas.
There are 202,667 Irish speakers in the province, over 84,000 in Galway and more than 55,000 in Mayo. There is also the 4,265 attending the 18 Gaelscoileanna (Irish language primary schools) and three Gaelcholáiste (Irish language secondary schools) outside the Gaeltacht across the province. Between 7% and 10% of the province are either native Irish speakers from the Gaeltacht, in Irish medium education or native Irish speakers who no longer live in Gaeltacht areas but still live in the province.
Sport
Gaelic games
Gaelic football and hurling dominate sport in Connacht with 212 Gaelic Athletic Association affiliated clubs in the province. Gaelic football is played throughout the province with the five counties annually competing in the Connacht Senior Football Championship to determine the provincial champion. Galway GAA, Galway are the most successful side in Connacht with 48 Connacht titles and 9 All-Ireland Senior Football Championship. Mayo GAA, Mayo have been the dominant force in the province in recent years winning a five-in-a-row of Connacht titles from 2011 to 2015, and have regularly reached the semi-finals and finals of the All-Ireland Senior Football Championship. No football team from Connacht has won the All-Ireland since Galway GAA, Galway in 2001 All-Ireland Senior Football Championship, 2001. Hurling in Connacht mostly played in County Galway. Galway GAA, Galway is the only team in the province to compete in the All-Ireland Senior Hurling Championship winning the Liam MacCarthy Cup five times. The Galway GAA, Galway hurling team compete in the Leinster Senior Hurling Championship due to the lack of competition in the province.Rugby union
Connacht is represented byConnacht Rugby
Connacht Rugby ( ga, Rugbaí Connachta) is one of the four professional provincial rugby teams from the island of Ireland. Connacht competes in the United Rugby Championship and the European Rugby Champions Cup. The team represents the IRFU Con ...
in the Pro14 and the Rugby Champions Cup. Connacht home games are played in the Galway Sportsgrounds in Galway. During the 2015/2016 Season of the Pro12, Connacht, for the first time, reached the play off stages of the competition and won the final in Edinburgh against rivals Leinster. It was their first ever Pro12 title.
Connacht-based teams who have played in the All-Ireland League (rugby union), All-Ireland League include Buccaneers RFC, Galway Corinthians RFC, Galwegians RFC, Ballina RFC and Sligo RFC.
Other sports
Some other sports are overseen by provincial bodies, including in association football, where the Connacht Football Association is the governing body for a number of Connacht Senior League (association football), Connacht league and Connacht Senior Cup (association football), cup competitions. Traditionally there have been two main senior men's teams from the province that compete on a national level, Galway United F.C. and Sligo Rovers F.C. Both clubs have won various domestic honours. Cricket is a minor, but growing, sport within the province. The Connacht Cricket Union, founded in 2010, is the governing body for cricket in the province. There are cricket clubs based in Ballaghaderreen, Ballyhaunis, Galway, and Sligo. Connacht does not currently enter a team into the Cricket in Ireland#Domestic cricket, provincial competitions.See also
*Galway city *Connacht Senior Football Championship *Grace O'Malley *Kings of Umaill *Kings of Uí Fiachrach Muaidhe *Kings of Uí Maine *Kings of Luighne Connacht *Kings of Sliabh Lugha *Corca Fhir Trí *List of Cities and Towns in Connacht by population *Coin of Connaught *Connaught Rangers, The Connaught Rangers *Duke of Connaught * Kings of Connacht *Lords of ConnaughtReferences
External links
Census 2011 – Galway Gaeltacht stats
{{Authority control Connacht, Provinces of Ireland