Confidential Computing on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Confidential computing is a security and privacy-enhancing computational technique focused on protecting data in use. Confidential computing can be used in conjunction with storage and network encryption, which protect data at rest and data in transit respectively. It is designed to address software, protocol, cryptographic, and basic physical and supply-chain attacks, although some critics have demonstrated architectural and
Confidential Computing Consortium
Data protection
side-channel attack
In computer security, a side-channel attack is a type of security exploit that leverages information inadvertently leaked by a system—such as timing, power consumption, or electromagnetic or acoustic emissions—to gain unauthorized access to ...
s effective against the technology.
The technology protects data in use by performing computations in a hardware-based trusted execution environment (TEE). Confidential data is released to the TEE only once it is assessed to be trustworthy. Different types of confidential computing define the level of data isolation used, whether virtual machine
In computing, a virtual machine (VM) is the virtualization or emulator, emulation of a computer system. Virtual machines are based on computer architectures and provide the functionality of a physical computer. Their implementations may involve ...
, application, or function, and the technology can be deployed in on-premise data centers, edge locations, or the public cloud. It is often compared with other privacy-enhancing computational techniques such as fully homomorphic encryption, secure multi-party computation, and Trusted Computing.
Confidential computing is promoted by the Confidential Computing Consortium (CCC) industry group, whose membership includes major providers of the technology.
Properties
Trusted execution environments (TEEs) "prevent unauthorized access or modification of applications and data while they are in use, thereby increasing the security level of organizations that manage sensitive and regulated data". Trusted execution environments can be instantiated on a computer's processing components such as acentral processing unit
A central processing unit (CPU), also called a central processor, main processor, or just processor, is the primary Processor (computing), processor in a given computer. Its electronic circuitry executes Instruction (computing), instructions ...
(CPU) or a graphics processing unit
A graphics processing unit (GPU) is a specialized electronic circuit designed for digital image processing and to accelerate computer graphics, being present either as a discrete video card or embedded on motherboards, mobile phones, personal ...
(GPU). In their various implementations, TEEs can provide different levels of isolation including virtual machine
In computing, a virtual machine (VM) is the virtualization or emulator, emulation of a computer system. Virtual machines are based on computer architectures and provide the functionality of a physical computer. Their implementations may involve ...
, individual application, or compute functions.
Typically, data in use in a computer's compute components and memory exists in a decrypted state and can be vulnerable to examination or tampering by unauthorized software or administrators. According to the CCC, confidential computing protects data in use through a minimum of three properties:
*Data confidentiality: "Unauthorized entities cannot view data while it is in use within the TEE".
*Data integrity
Data integrity is the maintenance of, and the assurance of, data accuracy and consistency over its entire Information Lifecycle Management, life-cycle. It is a critical aspect to the design, implementation, and usage of any system that stores, proc ...
: "Unauthorized entities cannot add, remove, or alter data while it is in use within the TEE".
*Code integrity: "Unauthorized entities cannot add, remove, or alter code executing in the TEE".
In addition to trusted execution environments, remote cryptographic
Cryptography, or cryptology (from "hidden, secret"; and ''graphein'', "to write", or '' -logia'', "study", respectively), is the practice and study of techniques for secure communication in the presence of adversarial behavior. More gen ...
attestation is an essential part of confidential computing. The attestation process assesses the trustworthiness of a system and helps ensure that confidential data is released to a TEE only after it presents verifiable evidence that it is genuine and operating with an acceptable security posture. It allows the verifying party to assess the trustworthiness of a confidential computing environment through an "authentic, accurate, and timely report about the software and data state" of that environment. "Hardware-based attestation schemes rely on a trusted hardware component and associated firmware
In computing
Computing is any goal-oriented activity requiring, benefiting from, or creating computer, computing machinery. It includes the study and experimentation of algorithmic processes, and the development of both computer hardware, h ...
to execute attestation routines in a secure environment". Without attestation, a compromised system could deceive others into trusting it, claim it is running certain software in a TEE, and potentially compromise the confidentiality or integrity of the data being processed or the integrity of the trusted code.
Technical approaches
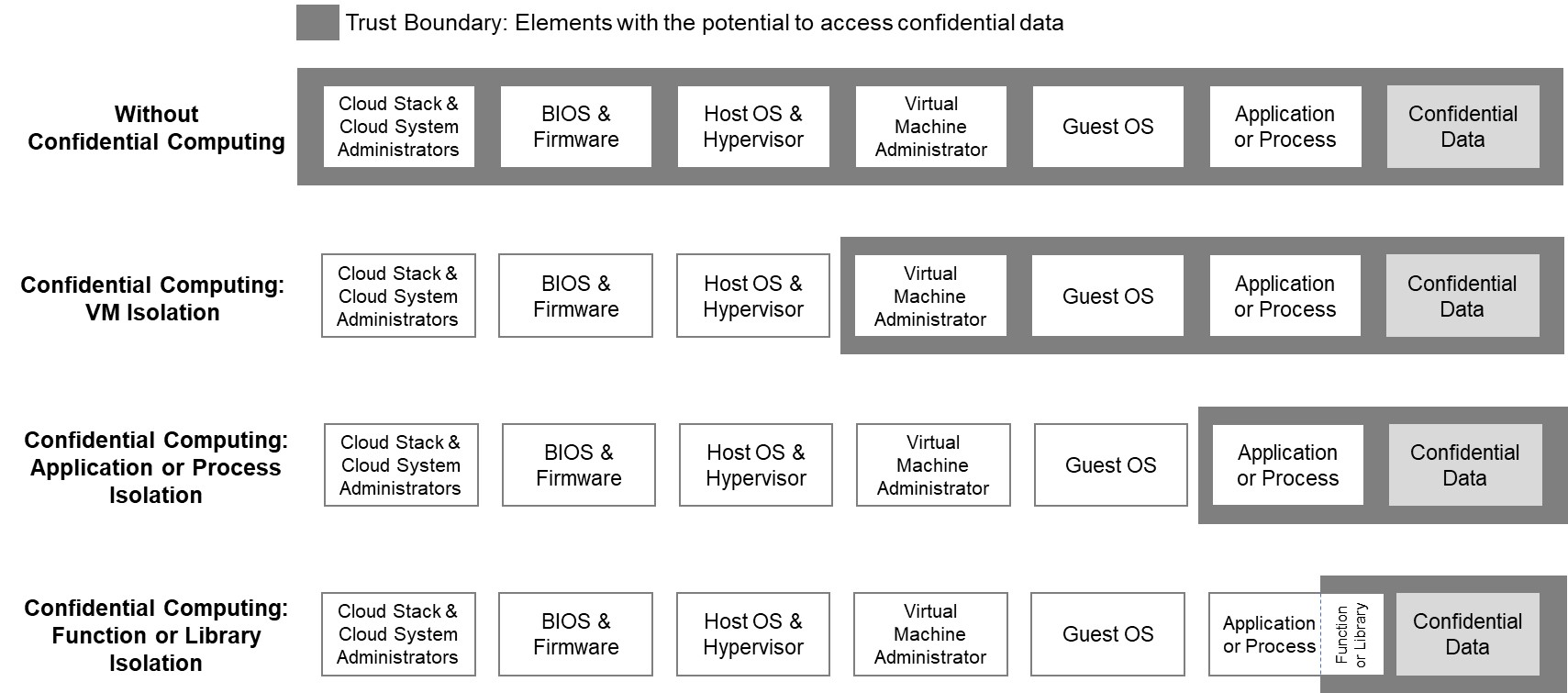
Technical approaches to confidential computing may vary in which software, infrastructure and administrator elements are allowed to access confidential data. The "trust boundary," which circumscribes a trusted computing base (TCB), defines which elements have the potential to access confidential data, whether they are acting benignly or maliciously. Confidential computing implementations enforce the defined trust boundary at a specific level of data isolation. The three main types of confidential computing are: *Virtual machine
In computing, a virtual machine (VM) is the virtualization or emulator, emulation of a computer system. Virtual machines are based on computer architectures and provide the functionality of a physical computer. Their implementations may involve ...
isolation
* Application isolation, also known as process
A process is a series or set of activities that interact to produce a result; it may occur once-only or be recurrent or periodic.
Things called a process include:
Business and management
* Business process, activities that produce a specific s ...
isolation
* Function isolation, also known as library
A library is a collection of Book, books, and possibly other Document, materials and Media (communication), media, that is accessible for use by its members and members of allied institutions. Libraries provide physical (hard copies) or electron ...
isolation
Virtual machine isolation removes the elements controlled by the computer infrastructure or cloud provider, but allows potential data access by elements inside a virtual machine running on the infrastructure. Application or process isolation permits data access only by authorized software applications or processes. Function or library isolation is designed to permit data access only by authorized subroutine
In computer programming, a function (also procedure, method, subroutine, routine, or subprogram) is a callable unit of software logic that has a well-defined interface and behavior and can be invoked multiple times.
Callable units provide a ...
s or modules within a larger application, blocking access by any other system element, including unauthorized code in the larger application.

Threat model
As confidential computing is concerned with the protection of data in use, only certainthreat model
Threat modeling is a process by which potential threats, such as structural vulnerabilities or the absence of appropriate safeguards, can be identified and enumerated, and countermeasures prioritized. The purpose of threat modeling is to provide d ...
s can be addressed by this technique. Other types of attacks are better addressed by other privacy-enhancing technologies.
In scope
The following threat vectors are generally considered in scope for confidential computing: *Software attacks: including attacks on the host’s software and firmware. This may include theoperating system
An operating system (OS) is system software that manages computer hardware and software resources, and provides common daemon (computing), services for computer programs.
Time-sharing operating systems scheduler (computing), schedule tasks for ...
, hypervisor
A hypervisor, also known as a virtual machine monitor (VMM) or virtualizer, is a type of computer software, firmware or hardware that creates and runs virtual machines. A computer on which a hypervisor runs one or more virtual machines is called ...
, BIOS
In computing, BIOS (, ; Basic Input/Output System, also known as the System BIOS, ROM BIOS, BIOS ROM or PC BIOS) is a type of firmware used to provide runtime services for operating systems and programs and to perform hardware initialization d ...
, other software and workloads.
*Protocol attacks: including "attacks on protocols associated with attestation as well as workload and data transport". This includes vulnerabilities in the "provisioning or placement of the workload" or data that could cause a compromise.
*Cryptographic attacks: including "vulnerabilities found in cipher
In cryptography, a cipher (or cypher) is an algorithm for performing encryption or decryption—a series of well-defined steps that can be followed as a procedure. An alternative, less common term is ''encipherment''. To encipher or encode i ...
s and algorithm
In mathematics and computer science, an algorithm () is a finite sequence of Rigour#Mathematics, mathematically rigorous instructions, typically used to solve a class of specific Computational problem, problems or to perform a computation. Algo ...
s due to a number of factors, including mathematical breakthroughs, availability of computing power and new computing approaches such as quantum computing
A quantum computer is a computer that exploits quantum mechanical phenomena. On small scales, physical matter exhibits properties of wave-particle duality, both particles and waves, and quantum computing takes advantage of this behavior using s ...
". The CCC notes several caveats in this threat vector, including relative difficulty of upgrading cryptographic algorithms in hardware and recommendations that software and firmware be kept up-to-date. A multi-faceted, defense-in-depth
Defence in depth (also known as deep defence or elastic defence) is a military strategy that seeks to delay rather than prevent the advance of an attacker, buying time and causing additional casualties by yielding space. Rather than defeating a ...
strategy is recommended as a best practice.
*Basic physical attacks: including cold boot attack
In computer security, a cold boot attack (or to a lesser extent, a platform reset attack) is a type of side channel attack in which an attacker with physical access to a computer performs a memory dump of a computer's random-access memory (RAM) ...
s, bus and cache snooping and plugging attack devices into an existing port, such as a PCI Express slot or USB port.
*Basic upstream supply-chain attacks: including attacks that would compromise TEEs through changes such as added debugging ports.
The degree and mechanism of protection against these threats varies with specific confidential computing implementations.
Out of scope
Threats generally defined as out of scope for confidential computing include: *Sophisticated physical attacks: including physical attacks that "require long-term and/or invasive access to hardware" such as chip scraping techniques and electron microscope probes. *Upstream hardware supply-chain attacks: including attacks on the CPU manufacturing process, CPU supply chain in key injection/generation during manufacture. Attacks on components of a host system that are not directly providing the capabilities of the trusted execution environment are also generally out-of-scope. *Availability attacks: confidential computing is designed to protect the confidentiality and integrity of protected data and code. It does not addressavailability
In reliability engineering, the term availability has the following meanings:
* The degree to which a system, subsystem or equipment is in a specified operable and committable state at the start of a mission, when the mission is called for at ...
attacks such as Denial of Service
In computing, a denial-of-service attack (DoS attack) is a cyberattack in which the perpetrator seeks to make a machine or network resource unavailable to its intended users by temporarily or indefinitely disrupting services of a host co ...
or Distributed Denial of Service attacks.
Use cases
Confidential computing can be deployed in the public cloud, on-premise data centers, or distributed "edge" locations, including network nodes, branch offices, industrial systems and others.Data privacy and security
Confidential computing protects theconfidentiality
Confidentiality involves a set of rules or a promise sometimes executed through confidentiality agreements that limits the access to or places restrictions on the distribution of certain types of information.
Legal confidentiality
By law, la ...
and integrity
Integrity is the quality of being honest and having a consistent and uncompromising adherence to strong moral and ethical principles and values.
In ethics, integrity is regarded as the honesty and Honesty, truthfulness or of one's actions. Integr ...
of data and code from the infrastructure provider, unauthorized or malicious software and system administrators, and other cloud tenants, which may be a concern for organizations seeking control over sensitive or regulated data. The additional security capabilities offered by confidential computing can help accelerate the transition of more sensitive workloads to the cloud or edge locations.
Multi-party analytics
Confidential computing can enable multiple parties to engage in joint analysis using confidential or regulated data inside a TEE while preserving privacy and regulatory compliance. In this case, all parties benefit from the shared analysis, but no party's sensitive data or confidential code is exposed to the other parties or system host. Examples include multiple healthcare organizations contributing data to medical research, or multiple banks collaborating to identify financial fraud ormoney laundering
Money laundering is the process of illegally concealing the origin of money obtained from illicit activities (often known as dirty money) such as drug trafficking, sex work, terrorism, corruption, and embezzlement, and converting the funds i ...
.
Oxford University researchers proposed the alternative paradigm called "Confidential Remote Computing" (CRC), which supports confidential operations in Trusted Execution Environments across endpoint computers considering multiple stakeholders as mutually distrustful data, algorithm and hardware providers.
Confidential generative AI
Confidential computing technologies can be applied to various stages of a generative AI deployments to help increase data or model privacy, security, and regulatory compliance. TEEs and remote attestation can protect the integrity of data during AI model training, keep non-public data confidential during inference or Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG), and protect the AI model itself from various adversarial attacks or theft.
Regulatory compliance
Confidential computing assists in data protection and regulatory compliance by limiting which software and people may access regulated data, as well as providing greater assurance of data and code integrity. In addition, TEEs can assist with data governance by providing evidence of steps taken to mitigate risks and demonstrate that these were appropriate. In 2021, theEuropean Union Agency for Cybersecurity
The European Union Agency for Cybersecurity – self-designation ENISA from the abbreviation of its original name – is an agency of the European Union. It is fully operational since September 1, 2005. The Agency is located in Athens, Greece a ...
(ENISA) classifies confidential computing as a "State of the Art" technology with respect to protecting data under the European Union's General Data Protection Regulation
The General Data Protection Regulation (Regulation (EU) 2016/679), abbreviated GDPR, is a European Union regulation on information privacy in the European Union (EU) and the European Economic Area (EEA). The GDPR is an important component of ...
and Germany's IT Security Act (ITSiG).
Data localization, sovereignty and residency
Regulations regarding data localization and residency or data sovereignty may require that sensitive data remain in a specific country or geographic bloc to provide assurance that the data will only be used in compliance with local law. Using confidential computing, only the workload owner holds the encryption keys required to decrypt data for processing inside a verified TEE. This provides a technological safeguard that reduces the risk of data being exfiltrated and processed in plaintext in other countries or jurisdictions without the workload owner's consent. Additional use cases for confidential computing include blockchain applications with enhanced record privacy and code integrity, privacy-preserving advertising technology, confidential databases and more.Criticism
Multiple academic and security research groups have demonstrated architectural andside-channel attack
In computer security, a side-channel attack is a type of security exploit that leverages information inadvertently leaked by a system—such as timing, power consumption, or electromagnetic or acoustic emissions—to gain unauthorized access to ...
s against CPU-based TEEs based on a variety of approaches. These include page fault
In computing, a page fault is an exception that the memory management unit (MMU) raises when a process accesses a memory page without proper preparations. Accessing the page requires a mapping to be added to the process's virtual address space ...
s, caching, and the memory bus, as well as specifically Æpic and SGAxe against Intel SGX, and CIPHERLEAKS against AMD SEV-SNP. Update mechanisms in the hardware, such as Trusted computing base
The trusted computing base (TCB) of a computer system is the set of all hardware, firmware, and/or software components that are critical to its security, in the sense that bugs or vulnerabilities occurring inside the TCB might jeopardize the ...
(TCB) recovery, can mitigate side-channel vulnerabilities as they are discovered.
The definition of confidential computing itself has also been criticized by some academic researchers. Scholars at the Technical University of Dresden, Germany called it, "imprecise, incomplete and even conflicting." Researchers have made recommendations to make it more detailed and exact to facilitate research and comparisons with other security technologies.
"Confidential Remote Computing" (CRC) paradigm, claims to revert confidential computing to original design principles of TEEs and advocate for small enclaves, running in available end-users computers. CRC adds practices and templates for multiple stakeholders, such as different data owners, hardware owners and algorithm owners. CRC extends the broad notion of confidential computing by adding practices and methodologies for individual use.
None of the major microprocessor or GPU providers offer Confidential computing hardware in devices for personal computers anymore, which limits use cases only to server-class platforms. Intel SGX was introduced for PCs in 6th Generation Intel Core ( Skylake) processors in 2015, but deprecated in the 11th Generation Intel Core processors (Rocket Lake
Rocket Lake is Intel's codename for its 11th generation Core microprocessors. Released on March 30, 2021, it is based on the new Cypress Cove microarchitecture, a variant of Sunny Cove (used by Intel's Ice Lake mobile processors) backporte ...
) in 2022.
Comparison with other privacy-enhancing technologies
Confidential computing is often compared to other security or privacy-enhancing technologies, including fully homomorphic encryption, secure multi-party computing and trusted computing.Fully homomorphic encryption
Fullyhomomorphic encryption
Homomorphic encryption is a form of encryption that allows computations to be performed on encrypted data without first having to decrypt it. The resulting computations are left in an encrypted form which, when decrypted, result in an output th ...
(FHE) is a form of encryption that permits users to perform computations on encrypted data without first decrypting it. Confidential computing, in contrast, transfers encrypted data inside a hardware-enforced, access-controlled TEE in the processor and memory, decrypts the data, and performs the required computations. Data may be re-encrypted before exiting the TEE. Compared to each other, FHE performance can suffer from higher computational overhead than confidential computing and require extensive application-specific coding but is less susceptible to side-channel attacks since data is never decrypted. Several researchers have described use cases where confidential computing TEEs and FHE work together to mitigate shortcomings of the technologies acting individually.
Secure multi-party computation
Secure multi-party computation (SMPC) is a privacy-preserving technology that allows multiple parties to jointly compute a task using distributed algorithms while keeping each party's data private from the others. Confidential computing can also be used for privacy-preserving multi-party collaboration. Compared to each other, distributed computing with SMPC can be more expensive in terms of computation and network bandwidth, but less susceptible to side-channel attacks since no party ever holds the complete data set.Trusted computing
Trusted computing is a concept and set of standards published by the Trusted Computing Group that aim to establish trust in computing systems by using standardized hardware-based mechanisms like the Trusted Platform Module (TPM). From a technical perspective, Trusted Computing and confidential computing rely on similar security concepts, such as trust architecture and remote attestation protocols. However, Trusted Computing targets a different set of threat models and large variety of platforms (e.g., phones, laptops, servers, network equipment); confidential computing addresses attack vectors that target confidentiality and integrity of code and data in use, notably through the use of Trusted Execution Environments and memory encryption.Providers
Confidential computing use cases require a combination of hardware and software, often delivered in conjunction with cloud service providers or server manufacturers.Cloud computing providers
Confidential computing technology and services can be accessed via public cloud computing providers, including Alibaba Cloud, Baidu Cloud, Google Cloud,IBM Cloud
IBM Cloud (formerly known as Bluemix) is a set of cloud computing services for business offered by the information technology company IBM.
Services
As of 2021, IBM Cloud contains more than 170 services including compute, storage, networkin ...
, Microsoft Azure
Microsoft Azure, or just Azure ( /ˈæʒər, ˈeɪʒər/ ''AZH-ər, AY-zhər'', UK also /ˈæzjʊər, ˈeɪzjʊər/ ''AZ-ure, AY-zure''), is the cloud computing platform developed by Microsoft. It has management, access and development of ...
, OVHcloud
OVH, legally OVH Groupe SA, is a French cloud computing company which offers VPS, dedicated servers, and other web services. The company was founded in 1999 by the Klaba family and is headquartered in Roubaix, France. In 2019 OVH adopted OVHcl ...
and others.
Application providers
Application software is required to enable most confidential computing use cases. Providers of confidential computing software applications include Anjuna, CanaryBit, Cosmian, CYSEC, Decentriq, Edgeless Systems, Enclaive, Fortanix, IBM Hyper Protect Services, Mithril Security, Oblivious, Opaque Systems, Scontain, Secretarium, Super Protocol, Fr0ntierX, and others.Confidential Computing Consortium
Confidential computing is supported by an advocacy and technical collaboration group called the Confidential Computing Consortium. The CCC was formed in 2019 under theLinux Foundation
The Linux Foundation (LF) is a non-profit organization established in 2000 to support Linux development and open-source software projects.
Background
The Linux Foundation started as Open Source Development Labs in 2000 to standardize and prom ...
. The founding premiere members were Alibaba, Arm, Google Cloud, Huawei
Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. ("Huawei" sometimes stylized as "HUAWEI"; ; zh, c=华为, p= ) is a Chinese multinational corporationtechnology company in Longgang, Shenzhen, Longgang, Shenzhen, Guangdong. Its main product lines include teleco ...
, Intel
Intel Corporation is an American multinational corporation and technology company headquartered in Santa Clara, California, and Delaware General Corporation Law, incorporated in Delaware. Intel designs, manufactures, and sells computer compo ...
, Microsoft
Microsoft Corporation is an American multinational corporation and technology company, technology conglomerate headquartered in Redmond, Washington. Founded in 1975, the company became influential in the History of personal computers#The ear ...
and Red Hat
Red Hat, Inc. (formerly Red Hat Software, Inc.) is an American software company that provides open source software products to enterprises and is a subsidiary of IBM. Founded in 1993, Red Hat has its corporate headquarters in Raleigh, North ...
. The founding general members included SUSE, Baidu
Baidu, Inc. ( ; ) is a Chinese multinational technology company specializing in Internet services and artificial intelligence. It holds a dominant position in China's search engine market (via Baidu Search), and provides a wide variety of o ...
, ByteDance
ByteDance Ltd. is a Chinese internet technology company headquartered in Haidian, Beijing, and incorporated in the Cayman Islands.
Founded by Zhang Yiming, Liang Rubo, and a team of others in 2012, ByteDance developed the video-sharing ap ...
, Decentriq, Fortanix, Kindite, Oasis Labs, Swisscom, Tencent
Tencent Holdings Ltd. ( zh, s=腾讯, p=Téngxùn) is a Chinese Multinational corporation, multinational technology Conglomerate (company), conglomerate and holding company headquartered in Shenzhen. It is one of the highest grossing multimed ...
and VMware. The CCC states its efforts are "focused on projects securing data in use and accelerating the adoption of confidential computing through open collaboration."
Notes
References
{{reflistExternal links
Confidential Computing Consortium
Data protection