The Chinese Communist Revolution, officially known as the Chinese People's War of Liberation in the People's Republic of
China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's most populous country, with a population exceeding 1.4 billion, slightly ahead of India. China spans the equivalent of five time zones and ...
(PRC) and also known as the National Protection War against the Communist Rebellion in the
Republic of China
Taiwan, officially the Republic of China (ROC), is a country in East Asia, at the junction of the East and South China Seas in the northwestern Pacific Ocean, with the People's Republic of China (PRC) to the northwest, Japan to the northeast ...
(ROC), was a period of
social
Social organisms, including human(s), live collectively in interacting populations. This interaction is considered social whether they are aware of it or not, and whether the exchange is voluntary or not.
Etymology
The word "social" derives from ...
and
political revolution
In political science, a revolution (Latin: ''revolutio'', "a turn around") is a fundamental and relatively sudden change in political power and political organization which occurs when the population revolts against the government, typically due ...
in
China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's most populous country, with a population exceeding 1.4 billion, slightly ahead of India. China spans the equivalent of five time zones and ...
that culminated in the establishment of the
People's Republic of China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's most populous country, with a population exceeding 1.4 billion, slightly ahead of India. China spans the equivalent of five time zones and ...
in 1949. For
the preceding century, China had faced escalating social, economic, and political problems as a result of
Western imperialism
Imperialism is the state policy, practice, or advocacy of extending power and dominion, especially by direct territorial acquisition or by gaining political and economic control of other areas, often through employing hard power (economic and ...
and the decline of the
Qing Dynasty
The Qing dynasty ( ), officially the Great Qing,, was a Manchu-led imperial dynasty of China and the last orthodox dynasty in Chinese history. It emerged from the Later Jin dynasty founded by the Jianzhou Jurchens, a Tungusic-speak ...
. Cyclical famines and an oppressive landlord system kept the large mass of rural peasantry poor and politically disenfranchised. The
Chinese Communist Party
The Chinese Communist Party (CCP), officially the Communist Party of China (CPC), is the founding and One-party state, sole ruling party of the China, People's Republic of China (PRC). Under the leadership of Mao Zedong, the CCP emerged victoriou ...
(CCP) was formed in 1921 by young urban intellectuals inspired by
Europe
Europe is a large peninsula conventionally considered a continent in its own right because of its great physical size and the weight of its history and traditions. Europe is also considered a Continent#Subcontinents, subcontinent of Eurasia ...
an
socialist
Socialism is a left-wing economic philosophy and movement encompassing a range of economic systems characterized by the dominance of social ownership of the means of production as opposed to private ownership. As a term, it describes the e ...
ideas and the success of the
Bolshevik Revolution
The October Revolution,. officially known as the Great October Socialist Revolution. in the Soviet Union, also known as the Bolshevik Revolution, was a revolution in Russia led by the Bolsheviks, Bolshevik Party of Vladimir Lenin that was ...
in
Russia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a List of transcontinental countries, transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and North Asia, Northern Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, largest country in the ...
. The CCP originally allied itself with the
nationalist
Nationalism is an idea and movement that holds that the nation should be congruent with the state. As a movement, nationalism tends to promote the interests of a particular nation (as in a group of people), Smith, Anthony. ''Nationalism: The ...
Kuomintang
The Kuomintang (KMT), also referred to as the Guomindang (GMD), the Nationalist Party of China (NPC) or the Chinese Nationalist Party (CNP), is a major political party in the Republic of China, initially on the Chinese mainland and in Tai ...
party against the
warlords
A warlord is a person who exercises military, economic, and political control over a region in a country without a strong national government; largely because of coercive control over the armed forces. Warlords have existed throughout much of h ...
and foreign imperialism, but the
Shanghai Massacre
The Shanghai massacre of 12 April 1927, the April 12 Purge or the April 12 Incident as it is commonly known in China, was the violent suppression of Chinese Communist Party (CCP) organizations and leftist elements in Shanghai by forces supportin ...
of Communists ordered by KMT leader
Chiang Kai-shek
Chiang Kai-shek (31 October 1887 – 5 April 1975), also known as Chiang Chung-cheng and Jiang Jieshi, was a Chinese Nationalist politician, revolutionary, and military leader who served as the leader of the Republic of China (ROC) from 1928 ...
in 1927 forced them into the
Chinese Civil War
The Chinese Civil War was fought between the Kuomintang-led government of the Republic of China and forces of the Chinese Communist Party, continuing intermittently since 1 August 1927 until 7 December 1949 with a Communist victory on m ...
.
Early Nationalist military dominance forced the Communists to abandon their strategy of appealing to the urban
proletariat
The proletariat (; ) is the social class of wage-earners, those members of a society whose only possession of significant economic value is their labour power (their capacity to work). A member of such a class is a proletarian. Marxist philo ...
, instead basing themselves in the countryside as advocated by
Mao Zedong
Mao Zedong pronounced ; also romanised traditionally as Mao Tse-tung. (26 December 1893 – 9 September 1976), also known as Chairman Mao, was a Chinese communist revolutionary who was the founder of the People's Republic of China (PRC) ...
. Mao rose to become the Chairman of CCP during the
Long March
The Long March (, lit. ''Long Expedition'') was a military retreat undertaken by the Chinese Red Army, Red Army of the Chinese Communist Party (CCP), the forerunner of the People's Liberation Army, to evade the pursuit of the National Revolut ...
while the CCP narrowly avoided complete destruction. The Communists led by Mao once again formed a United Front with the Kuomintang to fight the
Japanese occupation of China
The Second Sino-Japanese War (1937–1945) or War of Resistance (Chinese term) was a military conflict that was primarily waged between the Republic of China and the Empire of Japan. The war made up the Chinese theater of the wider Pacific The ...
beginning in 1936. The CCP made effective use of situation to rebuild their movement around the Chinese peasantry. Following the Japanese surrender in 1945, China became an early hot spot in the
Cold War
The Cold War is a term commonly used to refer to a period of geopolitical tension between the United States and the Soviet Union and their respective allies, the Western Bloc and the Eastern Bloc. The term '' cold war'' is used because the ...
. The
United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territorie ...
continued to funnel large amounts of money and weapons to Chiang Kai-shek, but corruption and low morale fatally undermined the
Nationalist army
The National Revolutionary Army (NRA; ), sometimes shortened to Revolutionary Army () before 1928, and as National Army () after 1928, was the military arm of the Kuomintang (KMT, or the Chinese Nationalist Party) from 1925 until 1947 in China ...
. The
Soviet Union
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, it was nominally a federal union of fifteen national ...
's decision to let the CCP take control of Japanese weapons and supplies left behind in Manchuria, on the other hand, proved decisive. The Communists were able to mobilize a massive army of peasants with their program of radical
land reform
Land reform is a form of agrarian reform involving the changing of laws, regulations, or customs regarding land ownership. Land reform may consist of a government-initiated or government-backed property redistribution, generally of agricultural ...
and gradually began winning open battles against the KMT. In 1948 and 1949 the Communist
People's Liberation Army
The People's Liberation Army (PLA) is the principal military force of the People's Republic of China and the armed wing of the Chinese Communist Party (CCP). The PLA consists of five service branches: the Ground Force, Navy, Air Force, ...
won three major campaigns that forced the Nationalist government to
retreat to Taiwan. On 1 October 1949, Mao
formally proclaimed the creation of the People's Republic of China.
The Communist victory had a major impact on the global balance of power: China became the largest
socialist state
A socialist state, socialist republic, or socialist country, sometimes referred to as a workers' state or workers' republic, is a Sovereign state, sovereign State (polity), state constitutionally dedicated to the establishment of socialism. The ...
by population, and, after the 1956
Sino-Soviet split
The Sino-Soviet split was the breaking of political relations between the People's Republic of China and the Soviet Union caused by doctrinal divergences that arose from their different interpretations and practical applications of Marxism–Len ...
, a third force in the
Cold War
The Cold War is a term commonly used to refer to a period of geopolitical tension between the United States and the Soviet Union and their respective allies, the Western Bloc and the Eastern Bloc. The term '' cold war'' is used because the ...
. The People's Republic offered direct and indirect support to communist movements around the world, and inspired the growth of
Maoist
Maoism, officially called Mao Zedong Thought by the Chinese Communist Party, is a variety of Marxism–Leninism that Mao Zedong developed to realise a socialist revolution in the agricultural, pre-industrial society of the Republic of Ch ...
parties in a number of countries. Shock at the CCP's success and
fear of similar events occurring across
East Asia
East Asia is the eastern region of Asia, which is defined in both geographical and ethno-cultural terms. The modern states of East Asia include China, Japan, Mongolia, North Korea, South Korea, and Taiwan. China, North Korea, South Korea and ...
led the
United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territorie ...
to intervene militarily in
Korea
Korea ( ko, 한국, or , ) is a peninsular region in East Asia. Since 1945, it has been divided at or near the 38th parallel, with North Korea (Democratic People's Republic of Korea) comprising its northern half and South Korea (Republic o ...
and South East Asia (e.g.
Vietnam
Vietnam or Viet Nam ( vi, Việt Nam, ), officially the Socialist Republic of Vietnam,., group="n" is a country in Southeast Asia, at the eastern edge of mainland Southeast Asia, with an area of and population of 96 million, making i ...
). To this day, the Chinese Communist Party remains the governing party of mainland China and the second-largest political party in the world.
Start and End Dates
Many historians agree with the Chinese Communist Party official history that the Chinese Revolution dates to the founding of the Party in 1921. A few consider it to be the latter part of the
Chinese Civil War
The Chinese Civil War was fought between the Kuomintang-led government of the Republic of China and forces of the Chinese Communist Party, continuing intermittently since 1 August 1927 until 7 December 1949 with a Communist victory on m ...
, since it was only after the
Second Sino-Japanese War
The Second Sino-Japanese War (1937–1945) or War of Resistance (Chinese term) was a military conflict that was primarily waged between the Republic of China and the Empire of Japan. The war made up the Chinese theater of the wider Pacific Th ...
that the tide turned decisively in favor of the Communists. That said, it is not entirely clear when the second half of the civil war began. The earliest possible date would be the end of the
Second United Front
The Second United Front ( zh, t=第二次國共合作 , s=第二次国共合作 , first=t ) was the alliance between the ruling Kuomintang (KMT) and the Chinese Communist Party (CCP) to resist the Japanese invasion of China during the Seco ...
in January 1941, when Nationalist forces
ambushed and destroyed the New Fourth Army. Another possible date is the
surrender of Japan
The surrender of the Empire of Japan in World War II was announced by Emperor Hirohito on 15 August and formally signed on 2 September 1945, bringing the war's hostilities to a close. By the end of July 1945, the Imperial Japanese Navy ...
on August 10, 1945, which began a scramble by Communist and Nationalist forces to seize the equipment and territory left behind by the Japanese. However, full-scale warfare between the two sides did not truly recommence until June 26, 1946, when
Chiang Kai-Shek
Chiang Kai-shek (31 October 1887 – 5 April 1975), also known as Chiang Chung-cheng and Jiang Jieshi, was a Chinese Nationalist politician, revolutionary, and military leader who served as the leader of the Republic of China (ROC) from 1928 ...
launched a major offensive against Communist bases in Manchuria.
[Hu, Jubin. (2003). ''Projecting a Nation: Chinese National Cinema Before 1949''. Hong Kong University Press. .] This article is focused on the political and social developments that contributed to the Revolution, rather than the military events of the Civil War, so it begins with the founding of the Communist party.
The exact end of the Revolution is also a bit unclear. The most common date used, and the one used here, is the
Proclamation of the People's Republic of China
The founding of the People's Republic of China was formally proclaimed by Mao Zedong, the Chairman of the Chinese Communist Party (CCP), on October 1, 1949, at 3:00 pm in Tiananmen Square in Peking, now Beijing (formerly Beiping), the new ca ...
on October 1, 1949.
Nonetheless, the Nationalist Government had not evacuated to
Taiwan
Taiwan, officially the Republic of China (ROC), is a country in East Asia, at the junction of the East and South China Seas in the northwestern Pacific Ocean, with the People's Republic of China (PRC) to the northwest, Japan to the nort ...
until December, and significant fighting (such as
the conquest of Hainan) continued well into 1950 and the
takeover
In business, a takeover is the purchase of one company (the ''target'') by another (the ''acquirer'' or ''bidder''). In the UK, the term refers to the acquisition of a public company whose shares are listed on a stock exchange, in contrast to t ...
of the de facto state of
Tibet
Tibet (; ''Böd''; ) is a region in East Asia, covering much of the Tibetan Plateau and spanning about . It is the traditional homeland of the Tibetan people. Also resident on the plateau are some other ethnic groups such as Monpa people, ...
in 1951.
[Cook, Chris Cook. Stevenson, John. ]005
''005'' is a 1981 arcade game by Sega. They advertised it as the first of their RasterScan Convert-a-Game series, designed so that it could be changed into another game in minutes "at a substantial savings". It is one of the first examples of a ...
(2005). The Routledge Companion to World History Since 1914. Routledge. . p. 376. Although it never posed a serious threat to the People's Republic, the
Kuomintang Islamic insurgency
The Kuomintang Islamic insurgency () was a continuation of the Chinese Civil War by Chinese Muslim nationalist Kuomintang Republic of China Army forces mainly in Northwest China, in the provinces of Gansu, Qinghai, Ningxia, and Xinjiang, an ...
continued until as late as 1958 in the provinces of
Gansu
Gansu (, ; alternately romanized as Kansu) is a province in Northwest China. Its capital and largest city is Lanzhou, in the southeast part of the province.
The seventh-largest administrative district by area at , Gansu lies between the Tibet ...
,
Qinghai
Qinghai (; alternately romanized as Tsinghai, Ch'inghai), also known as Kokonor, is a landlocked province in the northwest of the People's Republic of China. It is the fourth largest province of China by area and has the third smallest po ...
,
Ningxia
Ningxia (,; , ; alternately romanized as Ninghsia), officially the Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region (NHAR), is an autonomous region in the northwest of the People's Republic of China. Formerly a province, Ningxia was incorporated into Gansu in ...
,
Xinjiang
Xinjiang, SASM/GNC: ''Xinjang''; zh, c=, p=Xīnjiāng; formerly romanized as Sinkiang (, ), officially the Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region (XUAR), is an autonomous region of the People's Republic of China (PRC), located in the northwest ...
, and
Yunnan
Yunnan , () is a landlocked Provinces of China, province in Southwest China, the southwest of the People's Republic of China. The province spans approximately and has a population of 48.3 million (as of 2018). The capital of the province is ...
. ROC soldiers who had fled into the mountains of
Burma
Myanmar, ; UK pronunciations: US pronunciations incl. . Note: Wikipedia's IPA conventions require indicating /r/ even in British English although only some British English speakers pronounce r at the end of syllables. As John Wells explai ...
and
Thailand
Thailand ( ), historically known as Siam () and officially the Kingdom of Thailand, is a country in Southeast Asia, located at the centre of the Indochinese Peninsula, spanning , with a population of almost 70 million. The country is bo ...
worked with the CIA and Kuomintang to finance anti-Communist activities with drug trafficking well into the 1980s. Because no formal peace between the
Republic of China
Taiwan, officially the Republic of China (ROC), is a country in East Asia, at the junction of the East and South China Seas in the northwestern Pacific Ocean, with the People's Republic of China (PRC) to the northwest, Japan to the northeast ...
and the People's Republic was ever negotiated, a formal conclusion to the civil war has never been reached.
Causes and Background
The landlord system
Historians disagree on the fundamental causes of the Chinese Communist Revolution. One explanation offered is the extreme exploitation of the Chinese peasantry by the landlord system. Prior to the revolution, the majority of agricultural land in rural China was owned by a class of landlords and wealthy peasants, with the between 50 and 65 percent of peasants owning little or no land and thus needing to rent additional land from landlords. This disparity in land ownership differed by region, and was more extreme in southern China where the commercialization of agriculture was more developed. For example, in
Guangdong
Guangdong (, ), alternatively romanized as Canton or Kwangtung, is a coastal province in South China on the north shore of the South China Sea. The capital of the province is Guangzhou. With a population of 126.01 million (as of 2020) ...
more than half the rural population owned no land at all. Poor peasants owned an average of only .87 ''
mu'' (about .14 acres) and so spent most of their time working rented land. Even in north China, where most peasants owned at least some land, the plots they owned were so small and
infertile
Infertility is the inability of a person, animal or plant to reproduce by natural means. It is usually not the natural state of a healthy adult, except notably among certain eusocial species (mostly haplodiploid insects). It is the normal state ...
that they remained on the edge of starvation.
Periodic famines were common during both the
Qing Dynasty
The Qing dynasty ( ), officially the Great Qing,, was a Manchu-led imperial dynasty of China and the last orthodox dynasty in Chinese history. It emerged from the Later Jin dynasty founded by the Jianzhou Jurchens, a Tungusic-speak ...
and the later
Chinese Republic. Between 1900 and the end of WWII, China experienced no less than six major
famine
A famine is a widespread scarcity of food, caused by several factors including war, natural disasters, crop failure, Demographic trap, population imbalance, widespread poverty, an Financial crisis, economic catastrophe or government policies. Th ...
s, costing tens of millions of lives.
Depending on the system of tenancy, peasants renting land might have been expected to pay in kind or in cash, either as a fixed amount or as a
proportion of the harvest. Where a share of the harvest was paid, as in much of north China, rates of 40%, 50%, and 60% were common. A system of
sharecropping
Sharecropping is a legal arrangement with regard to agricultural land in which a landowner allows a tenant to use the land in return for a share of the crops produced on that land.
Sharecropping has a long history and there are a wide range ...
prevailed in much of
Shanxi
Shanxi (; ; formerly romanised as Shansi) is a landlocked province of the People's Republic of China and is part of the North China region. The capital and largest city of the province is Taiyuan, while its next most populated prefecture-lev ...
where landlords owned all agricultural capital and expected 80% of the harvest as rent. The amount of fixed rents varied, but in most areas averaged about $4 a year per ''mu''. Proponents of peasant exploitation as a cause of the Chinese Communist Revolution argue that these rents were often exorbitant and contributed to the extreme poverty of the peasantry.
Agricultural economist
Agricultural economics is an applied field of economics concerned with the application of economic theory in optimizing the production and distribution of food and fiber products.
Agricultural economics began as a branch of economics that specif ...
John Lossing Buck
John Lossing Buck (27 November 189027 September 1975,See the photo of Find a Grave Memorial no. 28263596, citing Pleasant Valley Cemetery, Pleasant Valley, Dutchess County, New York, USA adopted the Chinese name ) was an American agricultural e ...
disagreed, arguing that landlords' return on investment was not especially high in comparison to the standard rates of interest in China at the time.
Other forms of rural exploitation
According to
William H. Hinton
William Howard Hinton (; February 2, 1919 – May 15, 2004) was an American Maoist intellectual, best known for his work on Communism in China. A Marxist, he is best known for his book ''Fanshen'', published in 1966, a "documentary of revolu ...
, author of
a case study on how the Revolution impacted a village in north China:
The land held by the landlords and rich peasants, while ample, was not enough in itself to make them the dominant group in the village. It served primarily as a solid foundation for other forms of open and concealed exploitation which taken together raised a handful of families far above the rest of the inhabitants economically and hence politically and socially as well.
Landlords utilized forms of exploitation such as
usury
Usury () is the practice of making unethical or immoral monetary loans that unfairly enrich the lender. The term may be used in a moral sense—condemning taking advantage of others' misfortunes—or in a legal sense, where an interest rate is ch ...
,
corruption
Corruption is a form of dishonesty or a criminal offense which is undertaken by a person or an organization which is entrusted in a position of authority, in order to acquire illicit benefits or abuse power for one's personal gain. Corruption m ...
, and the theft of public funds to enrich themselves and their families. They ran side businesses with the profits from farming to shore up their finances and isolate themselves from the effects of bad harvests. On holidays, funerals, and other important events, landlords had they right to demand their tenants act as servants, reinforcing the social divide and engendering resentment from the peasants.
Agnes Smedley
Agnes Smedley (February 23, 1892 – May 6, 1950) was an American journalist, writer, and activist who supported the Indian Independence Movement and the Chinese Communist Revolution. Raised in a poverty-stricken miner's family in Missouri and Co ...
observed how even within a short distance from Shanghai, rural landlords operated essentially as feudal lords, paying for private armies, dominating local politics, and keeping numerous
concubines
Concubinage is an interpersonal and sexual relationship between a man and a woman in which the couple does not want, or cannot enter into a full marriage. Concubinage and marriage are often regarded as similar but mutually exclusive.
Concubin ...
.
Anti-imperialism
Some historians emphasize the role of
anti-imperialism
Anti-imperialism in political science and international relations is a term used in a variety of contexts, usually by nationalist movements who want to secede from a larger polity (usually in the form of an empire, but also in a multi-ethnic so ...
in the Chinese Communist Revolution. Richard Harris argues that that
imperialist
Imperialism is the state policy, practice, or advocacy of extending power and dominion, especially by direct territorial acquisition or by gaining political and economic control of other areas, often through employing hard power (economic and ...
pressure by the
Western powers
The Western world, also known as the West, primarily refers to the various nations and states in the regions of Europe, North America, and Oceania. and the Japanese led to a "
Century of Humiliation" that stoked
nationalism
Nationalism is an idea and movement that holds that the nation should be congruent with the State (polity), state. As a movement, nationalism tends to promote the interests of a particular nation (as in a in-group and out-group, group of peo ...
,
class consciousness
In Marxism, class consciousness is the set of beliefs that a person holds regarding their social class or economic rank in society, the structure of their class, and their class interests. According to Karl Marx, it is an awareness that is key to ...
, and
leftism
Left-wing politics describes the range of political ideologies that support and seek to achieve social equality and egalitarianism, often in opposition to social hierarchy. Left-wing politics typically involve a concern for those in soci ...
.
Other causes
The French historian
Lucien Bianco
Lucien André Bianco (born 19 April 1930) is a French people, French history, historian and sinologist specializing in the history of the Chinese peasantry in the twentieth century. He is the author of a reference book on the origins of the Chines ...
, in ''
Origins of the Chinese Revolution, 1915–1949'', is among those who question whether imperialism and "feudalism" explain the revolution. He points out that the CCP did not have great success until the
Japanese invasion of China after 1937. Before the war, he argues that the peasantry was not ready for revolution; economic reasons were not enough to mobilize them. More important was nationalism: "It was the war that brought the Chinese peasantry and China to revolution; at the very least, it considerably accelerated the rise of the CCP to power." The Communist revolutionary movement had a doctrine, long-term objectives, and a clear political strategy that allowed it to adjust to changes in the situation. He adds that the most important aspect of the Chinese communist movement is that it was armed.
Origins of the communist movement in China

In the first decade of the twentieth century, young Chinese
intellectuals
An intellectual is a person who engages in critical thinking
Critical thinking is the analysis of available facts, evidence, observations, and arguments to form a judgement. The subject is complex; several different definitions exist, ...
such as
Ma Junwu
Ma Junwu 馬君武 (1881 in Guilin – 1940 in Guilin) was a celebrated scientist and educator in China and first president of Guangxi University.
Biography
Ma Junwu was born in Guilin in 1881 and enlisted in one of the new schools for higher ed ...
,
Liang Qichao
Liang Qichao (Chinese: 梁啓超 ; Wade–Giles, Wade-Giles: ''Liang2 Chʻi3-chʻao1''; Yale romanization of Cantonese, Yale: ''Lèuhng Kái-chīu'') (February 23, 1873 – January 19, 1929) was a Chinese politician, social and political act ...
, and Zhao Bizhen were the first to translate and summarize
socialist
Socialism is a left-wing economic philosophy and movement encompassing a range of economic systems characterized by the dominance of social ownership of the means of production as opposed to private ownership. As a term, it describes the e ...
and
Marxist
Marxism is a Left-wing politics, left-wing to Far-left politics, far-left method of socioeconomic analysis that uses a Materialism, materialist interpretation of historical development, better known as historical materialism, to understand S ...
ideas into Chinese. However, this happened on a very small scale, and had no immediate impacts. This would change following the
1911 Revolution
The 1911 Revolution, also known as the Xinhai Revolution or Hsinhai Revolution, ended China's last imperial dynasty, the Manchu-led Qing dynasty, and led to the establishment of the Republic of China. The revolution was the culmination of a d ...
, which saw
military
A military, also known collectively as armed forces, is a heavily armed, highly organized force primarily intended for warfare. It is typically authorized and maintained by a sovereign state, with its members identifiable by their distinct ...
and popular revolts overthrow the
Qing Dynasty
The Qing dynasty ( ), officially the Great Qing,, was a Manchu-led imperial dynasty of China and the last orthodox dynasty in Chinese history. It emerged from the Later Jin dynasty founded by the Jianzhou Jurchens, a Tungusic-speak ...
.
[Li, Xiaobing. 007(2007). ''A History of the Modern Chinese Army''. University Press of Kentucky. , . pp. 13, 26–27.][Reilly, Thomas. ]997
Year 997 (Roman numerals, CMXCVII) was a common year starting on Friday (link will display the full calendar) of the Julian calendar.
Events
By place
Japan
* 1 February: Empress Teishi gives birth to Princess Shushi - she is the first ...
(1997). ''Science and Football III'', Volume 3. Taylor & Francis publishing. , . pp. 105–106, 277–278. The failure of the new
Chinese Republic to improve social conditions or modernize the country led scholars to take a greater interest in Western ideas such as socialism. The
New Culture Movement
The New Culture Movement () was a movement in China in the 1910s and 1920s that criticized classical Chinese ideas and promoted a new Chinese culture based upon progressive, modern and western ideals like democracy and science. Arising out of ...
was especially strong in cities like
Shanghai
Shanghai (; , , Standard Mandarin pronunciation: ) is one of the four direct-administered municipalities of the People's Republic of China (PRC). The city is located on the southern estuary of the Yangtze River, with the Huangpu River flow ...
, where
Chen Duxiu
Chen Duxiu ( zh, t=陳獨秀, w=Ch'en Tu-hsiu; 8 October 187927 May 1942) was a Chinese revolutionary socialist, educator, philosopher and author, who co-founded the Chinese Communist Party (CCP) with Li Dazhao in 1921. From 1921 to 1927, he ser ...
began to publish the left-leaning journal ''
New Youth
''New Youth'' (french: La Jeunesse, lit=The Youth; ) was a Chinese literary magazine founded by Chen Duxiu and published between 1915 and 1926. It strongly influenced both the New Culture Movement and the later May Fourth Movement. Publishi ...
'' in 1915.
''New Youth'' quickly became the most popular and widely distributed journal amongst the intelligentsia during this period.

In May 1919, news reached China that the
Versailles Peace Conference
The Palace of Versailles ( ; french: Château de Versailles ) is a former royal residence built by King Louis XIV located in Versailles, about west of Paris, France. The palace is owned by the French Republic and since 1995 has been managed, u ...
had decided to give
German
German(s) may refer to:
* Germany (of or related to)
**Germania (historical use)
* Germans, citizens of Germany, people of German ancestry, or native speakers of the German language
** For citizens of Germany, see also German nationality law
**Ger ...
-occupied province of
Shandong
Shandong ( , ; ; alternately romanized as Shantung) is a coastal province of the People's Republic of China and is part of the East China region.
Shandong has played a major role in Chinese history since the beginning of Chinese civilizati ...
to
Japan
Japan ( ja, 日本, or , and formally , ''Nihonkoku'') is an island country in East Asia. It is situated in the northwest Pacific Ocean, and is bordered on the west by the Sea of Japan, while extending from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north ...
rather than returning it to China. The Chinese public saw this not only as a betrayal by
the Western allies, but also as a failure by the Chinese Republican government to properly defend the country against imperialism. In what became known as the
May Fourth Movement
The May Fourth Movement was a Chinese anti-imperialist, cultural, and political movement which grew out of student protests in Beijing on May 4, 1919. Students gathered in front of Tiananmen (The Gate of Heavenly Peace) to protest the Chinese ...
, large protests erupted in major cities across China. Although led by students, these protests were significant because they included the first mass participation by those outside the traditional intellectual and cultural elites.
Mao Zedong
Mao Zedong pronounced ; also romanised traditionally as Mao Tse-tung. (26 December 1893 – 9 September 1976), also known as Chairman Mao, was a Chinese communist revolutionary who was the founder of the People's Republic of China (PRC) ...
later reflected that the May Fourth Movement "marked a new stage in China's bourgeois-democratic revolution against imperialism and feudalism...a powerful camp made its appearance in the bourgeois-democratic revolution, a camp consisting of the working class, the student masses and the new national bourgeoisie." Many political, and social leaders of the next five decades emerged at this time, including those of the Chinese Communist Party.
Many of the May Fourth protests were led and organized by students, who had become increasingly radical in the past few years. The
October Revolution
The October Revolution,. officially known as the Great October Socialist Revolution. in the Soviet Union, also known as the Bolshevik Revolution, was a revolution in Russia led by the Bolshevik Party of Vladimir Lenin that was a key moment ...
in
Russia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a List of transcontinental countries, transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and North Asia, Northern Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, largest country in the ...
had inspired many of them to join study groups centered on Marxist theory.
Soviet Russia
The Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic, Russian SFSR or RSFSR ( rus, Российская Советская Федеративная Социалистическая Республика, Rossíyskaya Sovétskaya Federatívnaya Soci ...
offered a unique and compelling model of modernization and revolutionary social change in semi-colonial nation. One of the most influential study groups was led by Li Dazhao, head librarian at Peking University. His study group included Mao Zedong and Chen Duxiu, the latter of who was now working as dean at the university. As the editor of ''New Youth'', Chen used his journal to publish a series of Marxist articles, including an entire issue devoted to the subject in 1919.
By 1920, Li and Chen had fully converted to Marxism, and Li founded the Peking Socialist Youth Corps in Beijing.
Chen had moved back to Shanghai, where he also founded a small Communist group.
Cooperation with the Nationalists
Foundation of the Chinese Communist Party

By 1920, "skepticism about
[study groups'] suitability as vehicles for reform had become widespread." Instead, most Chinese Marxists had determined to follow the Leninism, Leninist model, which they understood as organizing a Vanguardism, vanguard party around a core group of professional revolutionaries.
The Chinese Communist Party was founded on 23 July 1921 in Shanghai, at the 1st National Congress of the Chinese Communist Party, 1st National Congress of the CCP. The dozen delegates resolved to affiliate with the Communist International (Comintern), although the CCP would only formally become a member at its 2nd National Congress of the Chinese Communist Party, second congress. Chen was elected in absentia to be the first General Secretary of the Chinese Communist Party, General Secretary.
The Chinese Communist Party grew slowly in its first few years. The party had 50 members at the beginning of 1921, 200 in 1922, and 2,428 in 1925. In contrast, the Kuomintang had 50,000 members already in 1923.
[Fairbank, John King. [1994] (1994). China: A New History. Harvard University Press. .] The CCP continued to be dominated by students and urban intellectuals living in China's large cities, where exposure to Marxist ideas was strongest: three of the first four party congresses were held in Shanghai, the other in Guangzhou. One exception was Peng Pai, who became the first CCP leader to seriously engage with the peasants. In Haifeng County in rural Guangdong, he organized a powerful peasant association that campaigned for lower rents, led anti-landlord boycotts, and organized welfare activities. By 1923, it claimed a membership of about 100,000, or one-quarter of the population of the entire county. Later that year, Peng worked with the KMT to establish a joint "Peasant Movement Training Institute" to train young idealists to work in rural areas, which slowly increased both parties' awareness of and engagement with the peasants and their issues.
First United Front
At the same time as CCP was developing in Shanghai, in Guangzhou the seasoned revolutionary Sun Yat-sen was building the Chinese Nationalist Party, or
Kuomintang
The Kuomintang (KMT), also referred to as the Guomindang (GMD), the Nationalist Party of China (NPC) or the Chinese Nationalist Party (CNP), is a major political party in the Republic of China, initially on the Chinese mainland and in Tai ...
(KMT). Although not a communist, Sun admired the success of the Russian Revolution and sought help from the Soviet Union. The Sun–Joffe Manifesto issued in January 1923 formalized cooperation between the KMT and the Soviet Union.
[Tung, William L. [1968] (1968). The political institutions of modern China. Springer publishing. . p 92. P106.] The CCP's 3rd National Congress of the Chinese Communist Party, Third Party Congress was held in Guangzhou later that year, and the Comintern instructed the CCP to disband and join the KMT as individuals.
This was justified in view of the "two-stage theory" of revolution, which postulated that "feudal" societies such as China's needed to undergo a period of capitalist development before they could experience a successful socialist revolution. Although the CCP did agree to allow members to join the KMT, it did not disband. Sun encouraged this decision by offering praise for Vladimir Lenin and calling his Three Principles of the People, principle of livelihood "a form of communism".
This was the basis of the First United Front, which in effect turned the CCP into the left-wing of the larger KMT. The KMT ratified this First United Front, United Front at its 1st National Congress of the Kuomintang, First National Congress in 1924. The Soviets began sending the support the KMT needed for its planned expansion out of Guangdong. Military advisors Mikhail Borodin and Vasily Blyukher arrived in May to oversee the construction of the Whampoa Military Academy, financed with Soviet funds.
Chiang Kai-shek
Chiang Kai-shek (31 October 1887 – 5 April 1975), also known as Chiang Chung-cheng and Jiang Jieshi, was a Chinese Nationalist politician, revolutionary, and military leader who served as the leader of the Republic of China (ROC) from 1928 ...
, who the year prior had spent three months in the Soviet Union, was appointed commandant of the new National Revolutionary Army (NRA).
On 30 May 1925, Chinese students in
Shanghai
Shanghai (; , , Standard Mandarin pronunciation: ) is one of the four direct-administered municipalities of the People's Republic of China (PRC). The city is located on the southern estuary of the Yangtze River, with the Huangpu River flow ...
gathered at the Shanghai International Settlement, International Settlement, and held May Thirtieth Movement, demonstrations in opposition to foreign interference in China. Specifically, with the support of the KMT, they called for the boycott of foreign goods and an end to the Settlement, which was Concessions in China, governed by the British and Americans. The Shanghai Municipal Police, largely operated by the British, opened fire on the crowd of demonstrators. This incident sparked outrage throughout China, culminating in the Canton–Hong Kong strike, which began on 18 June, and proved a fertile recruiting ground for the CCP. Membership was catapulted to over 20,000, almost ten times what it had been earlier in the year.
Concerns about the rising power of the leftist faction, and the effect of the strike on the Guangzhou government's ability to raise funds, which was largely dependent on foreign trade, led to increasing tensions within the United Front. When Sun Yat-sen had died on 12 March, his immediate successor as chairman was the moderate Liao Zhongkai, who supported the United Front and the KMT's close relationship with the Soviet Union. On August 20 Hu Hanmin's far-right faction likely orchestrated Liao's assassination. Hu was arrested for his connections to the murderers, leaving Chiang and Wang Jingwei—Sun's former confidant and a leftist sympathizer—as the two main contenders for control of the party. Amidst this backdrop, Chiang began to consolidate power in preparation for an expedition against the northern warlords. On 20 March 1926, he launched a bloodless purge of hardline communists who were opposed to the proposed expedition from the Guangzhou administration and its military, known as the Canton Coup. The rapid replacement of leadership enabled Chiang to effectively end civilian oversight of the military. At the same time, Chiang made conciliatory moves toward the Soviet Union, and attempted to balance the need for Soviet and CCP assistance in the fight against the warlords with his concerns about growing communist influence within the KMT. In the aftermath of the coup, Chiang negotiated a compromise whereby hardline members of the rightist faction, such as Wu Tieh-cheng, were removed from their posts in compensation for the purged leftists. By doing so, Chiang was able to prove his usefulness to the CCP and their Soviet sponsor, Joseph Stalin. Soviet aid to the KMT government would continue, as would co-operation with the CCP. A fragile coalition between KMT rightists, centrists led by Chiang, KMT leftists, and the CCP managed to hold together, laying the groundwork for the Northern Expedition.
The Northern Expedition

By 1926 the
Kuomintang
The Kuomintang (KMT), also referred to as the Guomindang (GMD), the Nationalist Party of China (NPC) or the Chinese Nationalist Party (CNP), is a major political party in the Republic of China, initially on the Chinese mainland and in Tai ...
(KMT) had solidified their control over
Guangdong
Guangdong (, ), alternatively romanized as Canton or Kwangtung, is a coastal province in South China on the north shore of the South China Sea. The capital of the province is Guangzhou. With a population of 126.01 million (as of 2020) ...
province enough to rival the legitimacy of the Beiyang government based in Beijing.
After purging his opponents in the KMT leadership,
Chiang Kai-shek
Chiang Kai-shek (31 October 1887 – 5 April 1975), also known as Chiang Chung-cheng and Jiang Jieshi, was a Chinese Nationalist politician, revolutionary, and military leader who served as the leader of the Republic of China (ROC) from 1928 ...
was appointed Generalissimo of the National Revolutionary Army and set out to defeat the warlords one at a time. The campaign saw massive success against Wu Peifu in Hunan, Hubei, and Henan. Sun Chuanfang put up a stronger resistance, but popular support for the KMT and opposition to the warlords helped the National Revolutionary Army (NRA) make inroads into Jiangxi, Fujian, and Zhejiang. As the NRA advanced, workers in the cities organized themselves into left-leaning trade unions: in Wuhan, for example, more than 300,000 had joined trade unions by the end of the year. The All-China Federation of Labor (ACFL), founded by the Communists in 1925, reached 2.8 million members by 1927.
At the same time as workers organized in the cities, peasants rose up across the countryside of Hunan and Hubei provinces, appropriating the land of the wealthy landowners, who were in many cases killed. Such uprisings angered senior KMT figures, who were themselves landowners, emphasising the growing class and ideological divide within the revolutionary movement. CCP leader Chen Duxiu was also upset, both from doubt in the peasants' revolutionary capabilities and fear that premature revolt would wreck the United Front.
[Xuyin, Guo. "Reconsideration of Chen Duxiu's Attitude toward the Peasant Movement." Chinese Law & Government 17, no. 1-2 (1984): 51-67.] The KMT-CCP leadership dispatched prominent CCP cadre
Mao Zedong
Mao Zedong pronounced ; also romanised traditionally as Mao Tse-tung. (26 December 1893 – 9 September 1976), also known as Chairman Mao, was a Chinese communist revolutionary who was the founder of the People's Republic of China (PRC) ...
to investigate and report on the nature of the unrest. Mao had returned from a previous visit to Shaoshan, his rural home town personally convinced that the peasantry had revolutionary potential, and over the course of 1926 had established himself as an authority on rural issues while lecturing at the Peasant Movement Training Institute, Peasant Training Institute. Mao spent just over a month in Hunan and published his report in March. Rather than condemning the peasant movement, his now-famous Report on an Investigation of the Peasant Movement in Hunan, Hunan Report made the case that a peasant-led revolution was not only justified, but practically possible and even inevitable. Mao predicted that:
In a very short time, in China's central, southern and northern provinces, several hundred million peasants will rise like a mighty storm, like a hurricane, a force so swift and violent that no power, however great, will be able to hold it back. They will smash all the trammels that bind them and rush forward along the road to liberation. They will sweep all the imperialists, warlords, corrupt officials, local tyrants and evil gentry into their graves. Every revolutionary party and every revolutionary comrade will be put to the test, to be accepted or rejected as they decide. There are three alternatives. To march at their head and lead them. To trail behind them, gesticulating and criticizing. Or to stand in their way and oppose them. Every Chinese is free to choose, but events will force you to make the choice quickly.
Wuhan Nationalist Government

After the capture of Wuhan, the Central Committee of the Koumintang voted to move to their government to this more central location. Headed in Chiang's absence by Minister of Justice Xu Qian, the executive committee was a mix of liberals and conservatives who had not been subject to Chiang's purge of leftists. They included Minister of Finance Sun Fo, Minister for Foreign Affairs Eugene Chen, and banker and industrialist T. V. Soong. When they arrived in Wuhan on December 10, the Nationalists found a city gripped by enthusiasm for the revolution. The rapidly-expanding, Communist-led labor movement staged near-constant demonstrations in Wuhan itself and across the nominally KMT-controlled territories. Although still prevented from participating in the KMT government, the CCP established parallel structures of administration in areas liberated by the NRA.
The Wuhan Nationalist government, Wuhan government proved its competency when, in January 1927, violent protests broke out in the British Concessions in China, concession at Hankou. Eugene Chen successfully negotiated its evacuation by the British and handover to the Chinese. The Wuhan administration gradually drifted away from Chiang, becoming a center of leftist power and seeking to reassert civilian control over the military. On 10 March, the Wuhan government, Wuhan leadership nominally stripped Chiang of much of his military authority, though refrained from deposing him as commander-in-chief. At the same time, the Communist Party became an equal partner in the Wuhan government, sharing power with the KMT leftists.
Chiang Kai-shek declined to join the rest of the KMT in Wuhan, wary of the influence the CCP had there. Instead, he stayed at his military headquarters in Nanchang and began to rally anti-Communist elements in the KMT and NRA around him. In February 1927, he launched an offensive on the last and most important cities under Sun Choufang's control: Nanjing and Shanghai. While two of Chiang's columns advanced on Shanghai, Sun was confronted with the defection of his navy and a communist general strike. On 22 March, NRA General Bai Chongxi's forces marched into Shanghai victorious. But the strike continued until Bai ordered its end on 24 March. The general disorder caused by the strike is said to have resulted in the deaths of 322 people, with 2,000 wounded, contributing to KMT feelings of unease with its rising Communist allies. The same day the Shanghai strike ended, nationalist forces entered Nanjing. Almost immediately after arrival of the NRA, mass anti-foreigner riots broke out in the city, in an event that came to be known as the Nanking incident of 1927, Nanjing Incident. British and American naval forces were sent to evacuate their respective citizens, resulting in a naval bombardment that left the city burning and at least forty people dead. He's forces arrived on 25 March, and on the next day, Cheng and He were finally able to put an end to the violence. Although it was a mix of both Nationalists and Communist soldiers within the army who had participated in the riots, Chiang Kai-shek's faction accused Lin Boqu of planning the unrest in order to turn international opinion against the KMT.
Lin, a member of both the CCP and the KMT, had been serving as political commissar of the Sixth Army, part of the forces that captured Nanjing. Whatever was responsible, the Nanjing Incident represented the culmination of tensions within the First United Front.
First phase of the Civil War (1927-1936)
Shanghai Massacre
On April 12, 1927, Chiang Kai-shek and his right-wing faction of the KMT Shanghai Massacre, massacred the Communists in Shanghai. The White Terror (mainland China), White Terror spread nationwide and the United Front collapsed. In Beijing, 19 leading Communists were killed by Zhang Zuolin.
That May, tens of thousands of Communists and those suspected of being communists were killed, and the CCP lost approximately of its members.
Only in Wuhan, where leftist sympathizer Wang Jingwei split from Chiang and proclaimed a rival Government of the Republic of China in Wuhan, nationalist government, were the Communists safe to hold their 5th National Congress of the Chinese Communist Party, Fifth National Congress. However, under pressure from Chiang, Wang eventually July 15 Incident, purged Communists from his government and declared his loyalty to the right-wing government in Nanjing.
[Barnouin, Barbara and Yu Changgen. ''Zhou Enlai: A Political Life.'' Hong Kong: Chinese University of Hong Kong, 2006. p. 38. Retrieved 12 March 2011.]
Failed insurrections and the Chinese Soviet

In 1927, immediately after the collapse of Wang Jingwei's Wuhan Nationalist government, leftist Kuomintang government in Wuhan and Chiang Kai-shek's Shanghai massacre of 1927, suppression of communists, the CCP attempted a series of uprisings and military mutinies in Guangzhou, Nanchang Uprising, Nanchang and Autumn Harvest Uprising, Hunan. Despite initial success they were unable to withstand direct pressure from the KMT's National Revolutionary Army (NRA). The immediate effect was to make it clear to CCP leaders that a formal military apparatus was needed, and during Little Long March, the flight from Nanchang they founded the Chinese Red Army.
The defeat left an opening for machinations within the party leadership. In late 1927, Xiang Zhongfa was sent as the CCP's representative to celebrations of the Bolshevik Revolution's 10th Anniversary. While in Moscow, Xiang was able to convince the Soviet leadership to hold the
CCP's 6th National Congress of the Chinese Communist Party, 6th Party Congress there, rather than in China. With the help of the "28 Bolsheviks" (Chinese students studying Marxism at the Moscow Sun Yat-sen University), Xiang replaced Chen Duxiu as general secretary to the dismay of CCP leaders back in China. Upon his return to Shanghai, Xiang attempted several bureaucratic changes to consolidate centralized power, with mixed success. In 1930, the Comintern began pressuring the CCP to conduct more "anti-rightist" actions and Li Lisan was promoted to propanganda chief. Li grew to become the effective paramount leader with support from Xiang and advocated for an immediate armed uprising in the cities. This was attempted in July 1930, but failed and again led to heavy losses.

Under pressure from Zhou Enlai and many others in the party, the Comintern sent Soviet functionary Pavel Mif to replace Li Lisan and Xiang Zhongfa with members of the 28 Bolsheviks. Bo Gu became nominal party secretary while Wang Ming became the de facto paramount leader. Under the influence of Moscow, the strategy of direct confrontation with the KMT by organizing urban uprisings continued until 1933, when party leadership was finally forced to evacuate to the countryside. They fled to Jiangxi, where Mao Zedong had had considerable success in setting up the Chinese Soviet Republic. Established in November 1931, the Soviet had helped expand CCP membership to over 300,000 and supported 100,000 Red Army soldiers.
Mao's guerilla tactics had successfully repulsed three KMT encirclement campaigns. The CCP leadership Ningdu Conference, quickly took over from Mao when they arrived from Shanghai. Following the advice of Otto Braun (communist), they replaced cautious guerilla tactics with a more traditional military strategy. The subsequent Fourth encirclement campaign against the Jiangxi Soviet, fourth encirclement campaign was a disaster for the Communists, and forced them to abandon South China altogether. They began the
Long March
The Long March (, lit. ''Long Expedition'') was a military retreat undertaken by the Chinese Red Army, Red Army of the Chinese Communist Party (CCP), the forerunner of the People's Liberation Army, to evade the pursuit of the National Revolut ...
, a 9,000 kilometer retreat to Northern China, where Chiang Kai-Shek's authority was weaker.
[Zhang, Chunhou. Vaughan, C. Edwin. [2002] (2002). Mao Zedong as Poet and Revolutionary Leader: Social and Historical Perspectives. Lexington books. . p. 65.] In January 1935, the CCP paused the march to hold a Zunyi Conference, conference in Zunyi. Here, Mao Zedong denounced the party leadership for its dogmatic adherence to urban revolution in the face of repeated defeats. He also criticized Otto Braun's conventional tactics. Instead, Mao put forward People's war, a strategy based on rural guerilla warfare that prioritized winning peasant support. This was controversial because it conflicted with traditional party doctrine and the line endorsed by the Comintern. But with the support of Zhou Enlai, Mao defeated the 28 Bolsheviks and Otto Braun, becoming chairman of the Politburo and de facto leader of the party. Although the party survived the Long March, it had lost about 90% of its membership and was on the brink of destruction.
The Communists' Shaan-Gan-Ning Border Region, new base in Yan'an might indeed have been destroyed, but the outbreak of the Second Sino-Japanese War gave them a reprieve.
Second Sino-Japanese War and the Second United Front
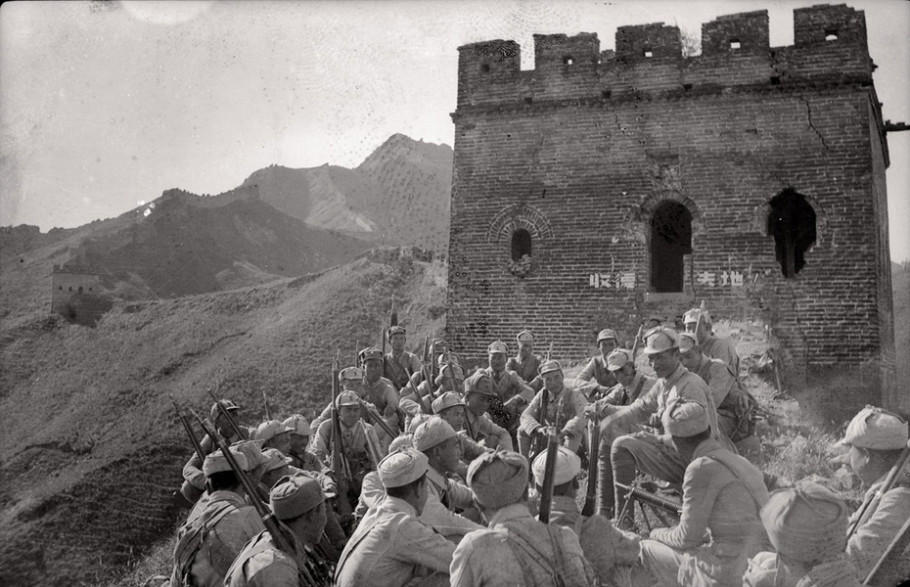

In 1931, the Japanese Kwantung Army, army had Japanese invasion of Manchuria, occupied Manchuria, which had nominally been under Chinese sovereignty. This triggered debates inside China on whether the Nationalist Government of Chiang Kai-Shek, the administration with the strongest claim to national leadership at the time, should declare war on Japan. Chiang, despite popular disapproval, wanted to continue to focus on wiping out the Chinese Communist Party before moving on to Japan.
In 1936, Xian incident, two of Chiang's generals arrested him in Xi'an and forced him to form the Second United Front with the Communists against Japan. In return for the ceasefire, the Communists agreed to dissolve the Red Army and place their units under National Revolutionary Army command. This arrangement did not end tensions between the CCP and KMT. In January 1941, Chiang Kai-shek ordered Nationalist troops to ambush the CCP's New Fourth Army, one of the Communist armies that had been placed under Nationalist command, for alleged insubordination. The New Fourth Army Incident effectively ended any substantive co-operation between the Nationalists and the Communists, although open fighting between the two sides remained sporadic throughout the war.
[Schoppa, R. Keith. (2000). The Columbia Guide to Modern Chinese History. Columbia University Press. .]
The war with Japan and the Second United Front created an enormous opportunity to expand CCP influence, but also created tensions within the party's leadership. The Nationalists' image had been tarnished by Chiang's original reluctance to the take on the Japanese, while the Communists willingly adopted the rhetoric of national resistance against imperialism. Using their experience in rural guerilla warfare, the Communists were able to operate behind the front lines and gain influence among the numerous peasant resistance groups set-up to fight the Japanese. In contrast with the Nationalists, the Communists undertook moderate land reform that made them extremely popular among the poorer peasants. Communist cadres worked tirelessly to organize the local population in each new village they arrived, which had the dual benefits of spreading Communist ideas and allowing for more effective administration. In the eight years of war, the CCP membership rose from 40,000 to 1,200,000. According to historian Chalmers Johnson, by the end of the war the CCP had also won the support of perhaps 100 million peasants in the regions where they had operated. The temporary truce with the Nationalists also made it possible for the Communists to once again target the urban proletariat, a policy advocated by the "internationalist" faction of the party. Led by Wang Ming, this faction advocated mobilizing labor not for revolution, but rather to support to Nationalists (at least until the war was won). Mao, in contrast, advocated continued focus on the peasantry, and ultimately managed to consolidate his position during the Yan'an Rectification Movement.
[Lieberthal, Kenneth. (2003). ''Governing China: From Revolution to Reform,'' W.W. Norton & Co.; Second edition. pp. 45-48]
Second Phase of Civil War (1945-1949)

Postwar situation
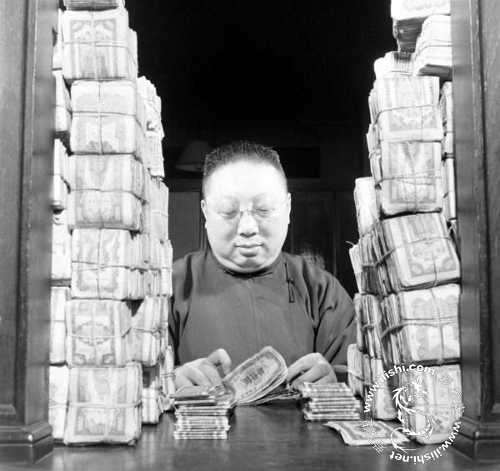
The impact of the war on the social and economics conditions of China had been brutal. An estimated 20 to 25 million Chinese were killed in fighting, massacres, and man-made natural disasters. By 1946, Chinese industries operated at 20 percent capacity and had 25 percent of the output of pre-war China. The influx of cheap American goods forestalled any recovery. In order to coordinate the war effort, the Nationalist government had taken over more than 70% of Chinese industry, a dramatic increase from the 15% it owned before the war. This consolidation of wealth in the regime's hands contributed to the pervasive problem of corruption. The Nationalist currency had been undergoing hyperinflation since the beginning of the war.
By 1945, retail market prices had reached 3,000% of their 1937 levels.
This problem was compounded by the presence of numerous other currencies printed by the Japanese, Communists, and other local authorities.
The Nationalist Government failed to curb inflation after the Japanese surrender and continued to print more currency to pay for the civil war.
Hyperinflation reduced the real wages of peasants, workers, and especially soldiers, and destroyed the savings of the upper-middle class that was Chiang's base of support.
The power of the CCP had grown considerably by the end of the Second Sino-Japanese War. The Eighth Route Army and New Fourth Army—officially still part of the Nationalist Government, Nationalist National Revolutionary Army, NRA but in reality under independent Communist command—counted between 1.2 and 1.27 million men. An additional 1.8 to 2.68 million militia brought the total Communist forces to between 3 million and 4 million.
When the Surrender of Japan, Japanese surrendered, the Communists' "Liberated Zone" grew to contain 19 base areas (mostly in north China), making up one-quarter of the country's territory and one-third of its population. In the south, the New Fourth Army had recovered from the New Fourth Army Incident, attempted massacre of its forces and established a serious Communist presence along the banks of the Yangtze. Nonetheless, the CCP's forces were still numerically inferior to the rest of the NRA, which excluding the Communists counted around 4 million regulars and 1 million militia in its ranks.
This was compounded by the Communists' lack of war material like trucks, artillery, and other heavy weaponry. For most of the war the Communists had operated in rural areas without factories or support from the Allies of World War II, Allies, which the Kuomintang received in abundance.
As
Mao Zedong
Mao Zedong pronounced ; also romanised traditionally as Mao Tse-tung. (26 December 1893 – 9 September 1976), also known as Chairman Mao, was a Chinese communist revolutionary who was the founder of the People's Republic of China (PRC) ...
said to an American Colonel David D. Barrett, the Communists had an army based on "millet plus rifles."
The international situation for the Communists was unfavorable in 1945. At Yalta Conference, Yalta, the Allies had agreed to recognize Russia's claims in the Far East in exchange for a Soviet–Japanese War, Soviet declaration of war on Japan.
These claims included control of Lüshunkou District, Port Arthur and joint control over the Chinese Eastern Railway, which Chiang reluctantly accepted in return for Sino-Soviet Treaty of Friendship and Alliance, Soviet recognition of the KMT as the sole legitimate government of China. In that way, the Communists appeared to have lost their most likely ally. The American Dixie Mission had investigated the possibility of American support for the Communists, but although its findings were favorable, cooperation was stubbornly blocked by American Ambassador Patrick J. Hurley. Hurley and the powerful pro-Nationalist China Lobby orchestrated the recall or dismissal of American "China Hands" who favored cutting ties with the Nationalists or supporting the Communists, including John Service, Joseph Stilwell, and David Barrett.
[Fenby, Jonathan ''Chiang Kai-shek China's Generalissimo and the Nation He Lost'', New York: Carrol & Graf, 2004 page 446.] By mid-1945, the United States was firmly committed to supporting Chiang. According to William Blum, American aid included substantial amounts of mostly surplus military supplies, and loans were made to the KMT. In the two years following the Sino-Japanese War, the KMT had received $4.43 billion from the US—most of which was military aid.
Japanese surrender and attempted negotiations

On August 8, 1945, the
Soviet Union
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, it was nominally a federal union of fifteen national ...
Soviet invasion of Manchuria, invaded Manchuria, immediately altering the military situation in China. The Soviet invasion, among Surrender of Japan, other contemporary developments, made Japan's defeat inevitable.
[Bright, Richard Carl. 007(2007). ''Pain and Purpose in the Pacific: True Reports of War''. Trafford Publishing. .] Both the Kuomintang and the Chinese Communist Party immediately ordered their forces to take as much territory from the Japanese as possible, which would yield not just land, but also weapons and equipment from the defeated Japanese units. Although Chiang Kai-Shek was confident that he was in a strong position to win a civil war against the CCP, he also knew that if the Communists gained control of Japanese war material, the balance of power would change.
[Lilley, James. ''China hands: nine decades of adventure, espionage, and diplomacy in Asia''. PublicAffairs, New York, 2004] In order to buy time, and under American pressure to negotiate, Chiang Kai-shek reached out to Mao Zedong with a request that the latter fly to Chongqing to negotiate.
At first, Mao demanded that Chiang grant the CCP certain conditions, but sustained pressure from Joseph Stalin made him realize the extent of the CCP's international isolation.
On August 23, Mao told the Politburo of the Chinese Communist Party, Politburo that without Soviet backing, the CCP would have to make concessions to Chiang.
Meanwhile, military forces on all sides continued their maneuvers. On the 20th, the last Japanese units in Manchuria surrendered to the Soviet Red Army. On the 26th, the CCP authorized army units and cadres to begin infiltrating the Manchurian countryside (a move tolerated by the Soviets).
CCP dominance in northern China seriously concerned Chiang, who was not in a position to stop the CCP from taking Beijing, Beiping or Tianjin. Chiang Kai-shek ordered the Japanese troops to remain at their post to receive the Kuomintang and not surrender their arms to the Communists.
[Zarrow, Peter Gue. (2005). ''China in War and Revolution, 1895–1949''. Routledge. . p. 338.] Chiang called on the Americans for assistance, and the
United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territorie ...
Operation Beleaguer, landed more than 50,000 marines in northern China to occupy the major cities until the Nationalists could arrive.
Although greeted with enthusiasm, incidents such as the Shen Chong case, rape of a Chinese student quickly turned the population against the Americans and contributed to growing support for the Communists. The Americans were anxious to have the Nationalists take over their duties, and so Albert Coady Wedemeyer, General Wedemeyer further ordered the airlifting of 100,000 Nationalist troops into Northern China. As Nationalist troops moved in to formerly occupied territories, looting and large-scale corruption were common. Under the pretext of "receiving the Japanese surrender," business interests within the KMT government occupied most of the banks, factories and commercial properties, which had previously been seized by the Imperial Japanese Army.
They also conscripted troops at an accelerated pace from the civilian population and hoarded supplies, preparing for a resumption of war with the Communists. These harsh and unpopular measures caused great hardship for the residents of cities such as Shanghai, where the unemployment rate rose dramatically to 37.5%.
The Communists abstained from trying to take and hold any major cities (with the exception of Jinzhou, Chinchow), focusing instead on gaining control over the countryside.
Nevertheless, as Mao left for negotiations he simultaneously ordered the Shangdang Campaign to defeat as many KMT units in
Shanxi
Shanxi (; ; formerly romanised as Shansi) is a landlocked province of the People's Republic of China and is part of the North China region. The capital and largest city of the province is Taiyuan, while its next most populated prefecture-lev ...
as possible and thereby gain a stronger hand at the negotiating table.
During negotiations, Chiang's main offer was to move from the second stage of Sun Yat-Sen's stages of unification (KMT tutelage) to the third stage (constitutional government). Mao and Zhou Enlai, on the other hand, were willing to recognize Chiang as ''de jure'' President of China in return for ''de facto'' autonomy in the provinces of Shanxi, Shandong, Hebei, Rehe, and Chahar Province, Chahar. They would be willing to join and support a KMT-led coalition government, but wanted to maintain separate armed forces in their provinces.
Both sides criticized the other as unreasonable. Chiang viewed the degree of local autonomy requested by the Communists as a regression to the Warlord Era, and was not willing to sacrifice his goal of reunification.
The Communists, on the other hand, suspected they would be massacred if they laid down their arms.
Both sides eventually signed the Double Tenth Agreement, but this was mostly for show and the major issues were left unresolved.
[Xu, Guangqiu. [2001] (2001). ''War Wings: The United States and Chinese Military Aviation, 1929–1949''. Greenwood Publishing Group. . p. 201.] Negotiations between Chiang and Zhou would continue in Nanking, but Mao returned to
Yunnan
Yunnan , () is a landlocked Provinces of China, province in Southwest China, the southwest of the People's Republic of China. The province spans approximately and has a population of 48.3 million (as of 2018). The capital of the province is ...
.
The outbreak of fighting in Manchuria (see next section) proved to Ambassador Patrick J. Hurley, Hurley that negotiations had failed, and he resigned in disgust. He was replaced by General George Marshall, who arrived in China on 20 December 1945. The goal of the Marshall Mission was to bring both parties into a coalition government, with the hope that a strong, non-Communist China would act as a bulwark against the encroachment of the Soviet Union. Marshall drew both sides into negotiations which would drag on for more than a year. No significant agreements were reached, as both sides used the time to further prepare themselves for the ensuing conflict.
Manchurian Campaigns, 1946-1948

By the time that Nationalist units had been able to arrive in the major cities of Manchuria, Communist forces commanded by Lin Biao were already in firm control of most of the countryside and surrounding areas, including the city of Jinzhou, Chinchow. On 15 November 1945, the Nationalists began a campaign to roll back these gains. Chiang Kai-shek's forces pushed as far as Chinchow by 26 November 1945, meeting with little resistance. Rather than confront the advancing Nationalists head on, Lin Biao avoided decisive confrontations, and in doing so was able to preserve the strength of his army. The Nationalist advance also prompted Stalin, who did not want the CCP entirely crushed, to command Marshal Rodion Malinovsky to give most captured Japanese weapons to the CCP.
This was decisive; from this point onwards the Communist forces were no longer just an army of "millet plus rifles".
In March 1946, despite repeated requests from Chiang Kai-Shek, the Soviet Red Army under the command of Marshal of the Soviet Union, Marshal Rodion Malinovsky continued to delay pulling out of Manchuria, while Malinovsky secretly told the CCP forces to move in behind them. Mao quickly seized the opportunity, ordering Lin Biao and Zhu De to begin taking key cities, including Battle of Siping, Siping and Harbin.
[Lew 36] These favorable conditions also facilitated many changes inside the Communist leadership: the more radical faction who wanted a complete military take-over of China finally gained the upper hand and defeated the careful opportunists. By May 3, all Soviet troops had withdrawn, and fighting between local Communist and Nationalist forces had broken out in earnest.
The conflict would escalate to the scale of a nation-wide civil war over the summer, as Chiang Kai-shek launched a large-scale assault on Communist territory in North China with 113 brigades (a total of 1.6 million troops).
[Hu, Jubin. (2003). ''Projecting a Nation: Chinese National Cinema Before 1949''. Hong Kong University Press. .]
Knowing their disadvantages in manpower and equipment, the CCP adopted a "passive defense" strategy. It avoided the strong points of the KMT army and was prepared to abandon territory in order to preserve its forces. In most cases the surrounding countryside and small towns had come under Communist influence long before the cities. The CCP also attempted to wear out the KMT forces as much as possible. This tactic seemed to be successful; after a year, the power balance became more favorable to the CCP. They wiped out 1.12 million KMT troops, while their strength grew to about two million men.
In March 1947 the KMT achieved a symbolic victory by seizing the CCP capital of Yan'an. The Communists counterattacked soon afterwards; on 30 June 1947 CCP troops crossed the Yellow River and moved to the Dabie Mountains area, restored and developed the Central Plain (China), Central Plain. At the same time, Communist forces also began to counterattack in Northeastern China, North China and East China.
The Three Campaigns, 1948-1949

In late 1948, the CCP and the newly rechristened "
People's Liberation Army
The People's Liberation Army (PLA) is the principal military force of the People's Republic of China and the armed wing of the Chinese Communist Party (CCP). The PLA consists of five service branches: the Ground Force, Navy, Air Force, ...
" (PLA) launched the decisive Liaoshen Campaign. The PLA finally captured for good the northern cities of Shenyang and Changchun and consolidated control of the Northeast.
[Westad, Odd Arne. [2003] (2003). Decisive Encounters: The Chinese Civil War, 1946–1950. Stanford University Press. . pp. 192–193.] The New 1st Army, regarded as the best KMT army, was forced to surrender after the CCP conducted a brutal six-month siege of Changchun that resulted in more than 150,000 civilian deaths from starvation.
[Pomfret, John. "Red Army Starved 150,000 Chinese Civilians, Books Says]
Seattle Times 2 October 2009
Accessed: 2009-10-02. Archive
WebSite
/ref>
The conscripted peasants who filled the Nationalist ranks also were beginning to defect to the PLA in larger and larger numbers, drawn by the promise of land and much better treatment by Communist officers. The defection and capture of large numbers of well-trained KMT troops finally gave the PLA material superiority over the Nationalist army. Manpower continued to grow as well; during the Huaihai Campaign alone the CCP was able to mobilize 5,430,000 peasants to fight against the KMT forces.
Now with tanks, heavy artillery, and other combined-arms assets, the PLA was prepared to execute offensive operations south of the Great Wall. In April 1948 the city of Luoyang fell, cutting the KMT army off from Xi'an.[Elleman, Bruce A. Modern Chinese Warfare, 1795–1989. Routledge. .] Following a fierce battle, the CCP captured Jinan and Shandong province on 24 September 1948. The Huaihai Campaign of late 1948 and early 1949 secured east-central China for the CCP.[Finkelstein, David Michael. Ryan, Mark A. McDevitt, Michael. [2003] (2003). Chinese Warfighting: The PLA Experience Since 1949. M.E. Sharpe. China. . p. 63.] The PLA suffered heavy casualties while securing Zhangjiakou, Tianjin along with its port and garrison at Taku Forts, Dagu and Beijing, Beiping. After achieving decisive victory at Liaoshen, Huaihai and Pingjin campaigns, the CCP wiped out 144 regular and 29 irregular KMT divisions, including 1.54 million veteran KMT troops, which significantly reduced the strength of Nationalist forces.
After achieving decisive victory at Liaoshen, Huaihai and Pingjin campaigns, the CCP wiped out 144 regular and 29 irregular KMT divisions, including 1.54 million veteran KMT troops, which significantly reduced the strength of Nationalist forces.
Establishment of the People's Republic
The founding of the Central People's Government of the People's Republic of China (1949–1954), Central People's Government of China was formally proclaimed by Chairman of the Chinese Communist Party, Chairman Mao Zedong
Mao Zedong pronounced ; also romanised traditionally as Mao Tse-tung. (26 December 1893 – 9 September 1976), also known as Chairman Mao, was a Chinese communist revolutionary who was the founder of the People's Republic of China (PRC) ...
on October 1, 1949, at 3:00 pm in Tiananmen Square in Beijing, the new capital. The new Flag of China, national flag of the People's Republic of China (the Five-starred Red Flag) was officially unveiled and hoisted to a 21-gun salute. The ceremony was followed by a PLA military parade. Commanded by Nie Rongzhen, the Commander of the Northern China Military Region and inspected by Zhu De, the Commander-in-Chief of the PLA, the parade involved around 16,000 PLA officers and personnel. The parade, which was approved in June 1949, was the first large-scale and modern Chinese military parade, with the country having never done a public review of troops before under previous governments. Liu Bocheng proposed to parade directors Yang Chengwu and Tang Yanjie be organized in the Soviet format, having personally witnessed a military parade on Red Square in Moscow. The Central Military Band of the People's Liberation Army of China, Northern Military Region Band (now the Central Military Band of the PLA) provided musical accompaniment which included the ''Military Anthem of the People's Liberation Army'' and new national anthem of China, the ''March of the Volunteers''.[s:Resolution on the Capital, Calendar, National Anthem and National Flag of the People's Republic of China, Resolution on the Capital, Calendar, National Anthem, and National Flag of the People's Republic of China. 1st Chinese People's Political Consultative Conference (Beijing), 27 September 1949. Hosted at s:Main Page, Wikisource.]
Aftermath and Legacy


 On October 1, 1949, Chairman of the Chinese Communist Party, Chairman Mao Zedong officially Proclamation of the People's Republic of China, proclaimed the founding of the
On October 1, 1949, Chairman of the Chinese Communist Party, Chairman Mao Zedong officially Proclamation of the People's Republic of China, proclaimed the founding of the People's Republic of China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's most populous country, with a population exceeding 1.4 billion, slightly ahead of India. China spans the equivalent of five time zones and ...
at Tiananmen Square. Chiang Kai-shek, 600,000 Nationalist troops and about two million Nationalist-sympathizer refugees retreated to the island of Taiwan. After that, resistance to the Communists on the mainland was substantial but scattered, such as in the far south. An attempt to take the Nationalist-controlled island of Kinmen was thwarted in the Battle of Guningtou, Battle of Kuningtou.
In December 1949 Chiang proclaimed Taipei, Taiwan the temporary capital of the Republic, and continued to assert his government as the sole legitimate authority of all China, while the PRC government continued to call for the unification of all China. The last direct fighting between Nationalist and Communist forces ended with the Communist capture of Hainan Island in April 1950, though shelling and guerrilla raids continued for several years.
Starting from June 1950, the outbreak of the Korean War led the American government to place the United States Seventh Fleet in the Taiwan Strait to prevent either side from attacking the other, the cold war era of Taiwan Strait has begun. However, the CCP and Kuomintang kept Cold War in Asia, clashing in Southeast Asia during the cold war.
The Kuomintang also made several last-ditch attempts to use Khampa troops against the Communists in southwest China. The Kuomintang formulated a plan in which three Khampa divisions would be assisted by the Choekyi Gyaltsen, 10th Panchen Lama, Panchen Lama to oppose the Communists. Kuomintang intelligence reported that some Tibetan tusi chiefs and the Khampa Su Yonghe controlled 80,000 troops in Sichuan, Qinghai and Tibet. They hoped to use them against the Communist army.
See also
* Aftermath of World War II
* Long March
The Long March (, lit. ''Long Expedition'') was a military retreat undertaken by the Chinese Red Army, Red Army of the Chinese Communist Party (CCP), the forerunner of the People's Liberation Army, to evade the pursuit of the National Revolut ...
* Loss of China
* John F. Melby
* Cultural Revolution
Notes
References
Citations
Sources
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
Chapter 1, pages 1-26Archive
. -- hosted at CÉRIUM (Centre d’études et de recherches internationales) at the Université de Montréal
*
*
*
* Lew, Christopher R. ''The Third Chinese Revolutionary War, 1945–1949: An Analysis of Communist Strategy and Leadership''. The USA and Canada: Routledge. 2009. .
*
*
*
*
*
* .
* .
*
*
*
*
*
*
* Wolfgang Franke, Franke, Wolfgang, ''A Century of Chinese Revolution, 1851–1949'' (Basil Blackwell, Oxford, 1970).
* .
*
*
{{authority control
20th-century revolutions
Chinese Civil War
Revolutions in China
Communist revolutions
Maoism in China
 In the first decade of the twentieth century, young Chinese
In the first decade of the twentieth century, young Chinese  In May 1919, news reached China that the
In May 1919, news reached China that the  By 1920, "skepticism about
By 1920, "skepticism about  By 1926 the
By 1926 the  After the capture of Wuhan, the Central Committee of the Koumintang voted to move to their government to this more central location. Headed in Chiang's absence by Minister of Justice Xu Qian, the executive committee was a mix of liberals and conservatives who had not been subject to Chiang's purge of leftists. They included Minister of Finance Sun Fo, Minister for Foreign Affairs Eugene Chen, and banker and industrialist T. V. Soong. When they arrived in Wuhan on December 10, the Nationalists found a city gripped by enthusiasm for the revolution. The rapidly-expanding, Communist-led labor movement staged near-constant demonstrations in Wuhan itself and across the nominally KMT-controlled territories. Although still prevented from participating in the KMT government, the CCP established parallel structures of administration in areas liberated by the NRA.
The Wuhan Nationalist government, Wuhan government proved its competency when, in January 1927, violent protests broke out in the British Concessions in China, concession at Hankou. Eugene Chen successfully negotiated its evacuation by the British and handover to the Chinese. The Wuhan administration gradually drifted away from Chiang, becoming a center of leftist power and seeking to reassert civilian control over the military. On 10 March, the Wuhan government, Wuhan leadership nominally stripped Chiang of much of his military authority, though refrained from deposing him as commander-in-chief. At the same time, the Communist Party became an equal partner in the Wuhan government, sharing power with the KMT leftists.
Chiang Kai-shek declined to join the rest of the KMT in Wuhan, wary of the influence the CCP had there. Instead, he stayed at his military headquarters in Nanchang and began to rally anti-Communist elements in the KMT and NRA around him. In February 1927, he launched an offensive on the last and most important cities under Sun Choufang's control: Nanjing and Shanghai. While two of Chiang's columns advanced on Shanghai, Sun was confronted with the defection of his navy and a communist general strike. On 22 March, NRA General Bai Chongxi's forces marched into Shanghai victorious. But the strike continued until Bai ordered its end on 24 March. The general disorder caused by the strike is said to have resulted in the deaths of 322 people, with 2,000 wounded, contributing to KMT feelings of unease with its rising Communist allies. The same day the Shanghai strike ended, nationalist forces entered Nanjing. Almost immediately after arrival of the NRA, mass anti-foreigner riots broke out in the city, in an event that came to be known as the Nanking incident of 1927, Nanjing Incident. British and American naval forces were sent to evacuate their respective citizens, resulting in a naval bombardment that left the city burning and at least forty people dead. He's forces arrived on 25 March, and on the next day, Cheng and He were finally able to put an end to the violence. Although it was a mix of both Nationalists and Communist soldiers within the army who had participated in the riots, Chiang Kai-shek's faction accused Lin Boqu of planning the unrest in order to turn international opinion against the KMT. Lin, a member of both the CCP and the KMT, had been serving as political commissar of the Sixth Army, part of the forces that captured Nanjing. Whatever was responsible, the Nanjing Incident represented the culmination of tensions within the First United Front.
After the capture of Wuhan, the Central Committee of the Koumintang voted to move to their government to this more central location. Headed in Chiang's absence by Minister of Justice Xu Qian, the executive committee was a mix of liberals and conservatives who had not been subject to Chiang's purge of leftists. They included Minister of Finance Sun Fo, Minister for Foreign Affairs Eugene Chen, and banker and industrialist T. V. Soong. When they arrived in Wuhan on December 10, the Nationalists found a city gripped by enthusiasm for the revolution. The rapidly-expanding, Communist-led labor movement staged near-constant demonstrations in Wuhan itself and across the nominally KMT-controlled territories. Although still prevented from participating in the KMT government, the CCP established parallel structures of administration in areas liberated by the NRA.
The Wuhan Nationalist government, Wuhan government proved its competency when, in January 1927, violent protests broke out in the British Concessions in China, concession at Hankou. Eugene Chen successfully negotiated its evacuation by the British and handover to the Chinese. The Wuhan administration gradually drifted away from Chiang, becoming a center of leftist power and seeking to reassert civilian control over the military. On 10 March, the Wuhan government, Wuhan leadership nominally stripped Chiang of much of his military authority, though refrained from deposing him as commander-in-chief. At the same time, the Communist Party became an equal partner in the Wuhan government, sharing power with the KMT leftists.
Chiang Kai-shek declined to join the rest of the KMT in Wuhan, wary of the influence the CCP had there. Instead, he stayed at his military headquarters in Nanchang and began to rally anti-Communist elements in the KMT and NRA around him. In February 1927, he launched an offensive on the last and most important cities under Sun Choufang's control: Nanjing and Shanghai. While two of Chiang's columns advanced on Shanghai, Sun was confronted with the defection of his navy and a communist general strike. On 22 March, NRA General Bai Chongxi's forces marched into Shanghai victorious. But the strike continued until Bai ordered its end on 24 March. The general disorder caused by the strike is said to have resulted in the deaths of 322 people, with 2,000 wounded, contributing to KMT feelings of unease with its rising Communist allies. The same day the Shanghai strike ended, nationalist forces entered Nanjing. Almost immediately after arrival of the NRA, mass anti-foreigner riots broke out in the city, in an event that came to be known as the Nanking incident of 1927, Nanjing Incident. British and American naval forces were sent to evacuate their respective citizens, resulting in a naval bombardment that left the city burning and at least forty people dead. He's forces arrived on 25 March, and on the next day, Cheng and He were finally able to put an end to the violence. Although it was a mix of both Nationalists and Communist soldiers within the army who had participated in the riots, Chiang Kai-shek's faction accused Lin Boqu of planning the unrest in order to turn international opinion against the KMT. Lin, a member of both the CCP and the KMT, had been serving as political commissar of the Sixth Army, part of the forces that captured Nanjing. Whatever was responsible, the Nanjing Incident represented the culmination of tensions within the First United Front.
 In 1927, immediately after the collapse of Wang Jingwei's Wuhan Nationalist government, leftist Kuomintang government in Wuhan and Chiang Kai-shek's Shanghai massacre of 1927, suppression of communists, the CCP attempted a series of uprisings and military mutinies in Guangzhou, Nanchang Uprising, Nanchang and Autumn Harvest Uprising, Hunan. Despite initial success they were unable to withstand direct pressure from the KMT's National Revolutionary Army (NRA). The immediate effect was to make it clear to CCP leaders that a formal military apparatus was needed, and during Little Long March, the flight from Nanchang they founded the Chinese Red Army.
The defeat left an opening for machinations within the party leadership. In late 1927, Xiang Zhongfa was sent as the CCP's representative to celebrations of the Bolshevik Revolution's 10th Anniversary. While in Moscow, Xiang was able to convince the Soviet leadership to hold the
CCP's 6th National Congress of the Chinese Communist Party, 6th Party Congress there, rather than in China. With the help of the "28 Bolsheviks" (Chinese students studying Marxism at the Moscow Sun Yat-sen University), Xiang replaced Chen Duxiu as general secretary to the dismay of CCP leaders back in China. Upon his return to Shanghai, Xiang attempted several bureaucratic changes to consolidate centralized power, with mixed success. In 1930, the Comintern began pressuring the CCP to conduct more "anti-rightist" actions and Li Lisan was promoted to propanganda chief. Li grew to become the effective paramount leader with support from Xiang and advocated for an immediate armed uprising in the cities. This was attempted in July 1930, but failed and again led to heavy losses.
In 1927, immediately after the collapse of Wang Jingwei's Wuhan Nationalist government, leftist Kuomintang government in Wuhan and Chiang Kai-shek's Shanghai massacre of 1927, suppression of communists, the CCP attempted a series of uprisings and military mutinies in Guangzhou, Nanchang Uprising, Nanchang and Autumn Harvest Uprising, Hunan. Despite initial success they were unable to withstand direct pressure from the KMT's National Revolutionary Army (NRA). The immediate effect was to make it clear to CCP leaders that a formal military apparatus was needed, and during Little Long March, the flight from Nanchang they founded the Chinese Red Army.
The defeat left an opening for machinations within the party leadership. In late 1927, Xiang Zhongfa was sent as the CCP's representative to celebrations of the Bolshevik Revolution's 10th Anniversary. While in Moscow, Xiang was able to convince the Soviet leadership to hold the
CCP's 6th National Congress of the Chinese Communist Party, 6th Party Congress there, rather than in China. With the help of the "28 Bolsheviks" (Chinese students studying Marxism at the Moscow Sun Yat-sen University), Xiang replaced Chen Duxiu as general secretary to the dismay of CCP leaders back in China. Upon his return to Shanghai, Xiang attempted several bureaucratic changes to consolidate centralized power, with mixed success. In 1930, the Comintern began pressuring the CCP to conduct more "anti-rightist" actions and Li Lisan was promoted to propanganda chief. Li grew to become the effective paramount leader with support from Xiang and advocated for an immediate armed uprising in the cities. This was attempted in July 1930, but failed and again led to heavy losses.
 In 1931, the Japanese Kwantung Army, army had Japanese invasion of Manchuria, occupied Manchuria, which had nominally been under Chinese sovereignty. This triggered debates inside China on whether the Nationalist Government of Chiang Kai-Shek, the administration with the strongest claim to national leadership at the time, should declare war on Japan. Chiang, despite popular disapproval, wanted to continue to focus on wiping out the Chinese Communist Party before moving on to Japan. In 1936, Xian incident, two of Chiang's generals arrested him in Xi'an and forced him to form the Second United Front with the Communists against Japan. In return for the ceasefire, the Communists agreed to dissolve the Red Army and place their units under National Revolutionary Army command. This arrangement did not end tensions between the CCP and KMT. In January 1941, Chiang Kai-shek ordered Nationalist troops to ambush the CCP's New Fourth Army, one of the Communist armies that had been placed under Nationalist command, for alleged insubordination. The New Fourth Army Incident effectively ended any substantive co-operation between the Nationalists and the Communists, although open fighting between the two sides remained sporadic throughout the war.Schoppa, R. Keith. (2000). The Columbia Guide to Modern Chinese History. Columbia University Press. .
The war with Japan and the Second United Front created an enormous opportunity to expand CCP influence, but also created tensions within the party's leadership. The Nationalists' image had been tarnished by Chiang's original reluctance to the take on the Japanese, while the Communists willingly adopted the rhetoric of national resistance against imperialism. Using their experience in rural guerilla warfare, the Communists were able to operate behind the front lines and gain influence among the numerous peasant resistance groups set-up to fight the Japanese. In contrast with the Nationalists, the Communists undertook moderate land reform that made them extremely popular among the poorer peasants. Communist cadres worked tirelessly to organize the local population in each new village they arrived, which had the dual benefits of spreading Communist ideas and allowing for more effective administration. In the eight years of war, the CCP membership rose from 40,000 to 1,200,000. According to historian Chalmers Johnson, by the end of the war the CCP had also won the support of perhaps 100 million peasants in the regions where they had operated. The temporary truce with the Nationalists also made it possible for the Communists to once again target the urban proletariat, a policy advocated by the "internationalist" faction of the party. Led by Wang Ming, this faction advocated mobilizing labor not for revolution, but rather to support to Nationalists (at least until the war was won). Mao, in contrast, advocated continued focus on the peasantry, and ultimately managed to consolidate his position during the Yan'an Rectification Movement.Lieberthal, Kenneth. (2003). ''Governing China: From Revolution to Reform,'' W.W. Norton & Co.; Second edition. pp. 45-48
In 1931, the Japanese Kwantung Army, army had Japanese invasion of Manchuria, occupied Manchuria, which had nominally been under Chinese sovereignty. This triggered debates inside China on whether the Nationalist Government of Chiang Kai-Shek, the administration with the strongest claim to national leadership at the time, should declare war on Japan. Chiang, despite popular disapproval, wanted to continue to focus on wiping out the Chinese Communist Party before moving on to Japan. In 1936, Xian incident, two of Chiang's generals arrested him in Xi'an and forced him to form the Second United Front with the Communists against Japan. In return for the ceasefire, the Communists agreed to dissolve the Red Army and place their units under National Revolutionary Army command. This arrangement did not end tensions between the CCP and KMT. In January 1941, Chiang Kai-shek ordered Nationalist troops to ambush the CCP's New Fourth Army, one of the Communist armies that had been placed under Nationalist command, for alleged insubordination. The New Fourth Army Incident effectively ended any substantive co-operation between the Nationalists and the Communists, although open fighting between the two sides remained sporadic throughout the war.Schoppa, R. Keith. (2000). The Columbia Guide to Modern Chinese History. Columbia University Press. .
The war with Japan and the Second United Front created an enormous opportunity to expand CCP influence, but also created tensions within the party's leadership. The Nationalists' image had been tarnished by Chiang's original reluctance to the take on the Japanese, while the Communists willingly adopted the rhetoric of national resistance against imperialism. Using their experience in rural guerilla warfare, the Communists were able to operate behind the front lines and gain influence among the numerous peasant resistance groups set-up to fight the Japanese. In contrast with the Nationalists, the Communists undertook moderate land reform that made them extremely popular among the poorer peasants. Communist cadres worked tirelessly to organize the local population in each new village they arrived, which had the dual benefits of spreading Communist ideas and allowing for more effective administration. In the eight years of war, the CCP membership rose from 40,000 to 1,200,000. According to historian Chalmers Johnson, by the end of the war the CCP had also won the support of perhaps 100 million peasants in the regions where they had operated. The temporary truce with the Nationalists also made it possible for the Communists to once again target the urban proletariat, a policy advocated by the "internationalist" faction of the party. Led by Wang Ming, this faction advocated mobilizing labor not for revolution, but rather to support to Nationalists (at least until the war was won). Mao, in contrast, advocated continued focus on the peasantry, and ultimately managed to consolidate his position during the Yan'an Rectification Movement.Lieberthal, Kenneth. (2003). ''Governing China: From Revolution to Reform,'' W.W. Norton & Co.; Second edition. pp. 45-48

 On August 8, 1945, the
On August 8, 1945, the  By the time that Nationalist units had been able to arrive in the major cities of Manchuria, Communist forces commanded by Lin Biao were already in firm control of most of the countryside and surrounding areas, including the city of Jinzhou, Chinchow. On 15 November 1945, the Nationalists began a campaign to roll back these gains. Chiang Kai-shek's forces pushed as far as Chinchow by 26 November 1945, meeting with little resistance. Rather than confront the advancing Nationalists head on, Lin Biao avoided decisive confrontations, and in doing so was able to preserve the strength of his army. The Nationalist advance also prompted Stalin, who did not want the CCP entirely crushed, to command Marshal Rodion Malinovsky to give most captured Japanese weapons to the CCP. This was decisive; from this point onwards the Communist forces were no longer just an army of "millet plus rifles".
In March 1946, despite repeated requests from Chiang Kai-Shek, the Soviet Red Army under the command of Marshal of the Soviet Union, Marshal Rodion Malinovsky continued to delay pulling out of Manchuria, while Malinovsky secretly told the CCP forces to move in behind them. Mao quickly seized the opportunity, ordering Lin Biao and Zhu De to begin taking key cities, including Battle of Siping, Siping and Harbin.Lew 36 These favorable conditions also facilitated many changes inside the Communist leadership: the more radical faction who wanted a complete military take-over of China finally gained the upper hand and defeated the careful opportunists. By May 3, all Soviet troops had withdrawn, and fighting between local Communist and Nationalist forces had broken out in earnest. The conflict would escalate to the scale of a nation-wide civil war over the summer, as Chiang Kai-shek launched a large-scale assault on Communist territory in North China with 113 brigades (a total of 1.6 million troops).Hu, Jubin. (2003). ''Projecting a Nation: Chinese National Cinema Before 1949''. Hong Kong University Press. .
Knowing their disadvantages in manpower and equipment, the CCP adopted a "passive defense" strategy. It avoided the strong points of the KMT army and was prepared to abandon territory in order to preserve its forces. In most cases the surrounding countryside and small towns had come under Communist influence long before the cities. The CCP also attempted to wear out the KMT forces as much as possible. This tactic seemed to be successful; after a year, the power balance became more favorable to the CCP. They wiped out 1.12 million KMT troops, while their strength grew to about two million men. In March 1947 the KMT achieved a symbolic victory by seizing the CCP capital of Yan'an. The Communists counterattacked soon afterwards; on 30 June 1947 CCP troops crossed the Yellow River and moved to the Dabie Mountains area, restored and developed the Central Plain (China), Central Plain. At the same time, Communist forces also began to counterattack in Northeastern China, North China and East China.
By the time that Nationalist units had been able to arrive in the major cities of Manchuria, Communist forces commanded by Lin Biao were already in firm control of most of the countryside and surrounding areas, including the city of Jinzhou, Chinchow. On 15 November 1945, the Nationalists began a campaign to roll back these gains. Chiang Kai-shek's forces pushed as far as Chinchow by 26 November 1945, meeting with little resistance. Rather than confront the advancing Nationalists head on, Lin Biao avoided decisive confrontations, and in doing so was able to preserve the strength of his army. The Nationalist advance also prompted Stalin, who did not want the CCP entirely crushed, to command Marshal Rodion Malinovsky to give most captured Japanese weapons to the CCP. This was decisive; from this point onwards the Communist forces were no longer just an army of "millet plus rifles".
In March 1946, despite repeated requests from Chiang Kai-Shek, the Soviet Red Army under the command of Marshal of the Soviet Union, Marshal Rodion Malinovsky continued to delay pulling out of Manchuria, while Malinovsky secretly told the CCP forces to move in behind them. Mao quickly seized the opportunity, ordering Lin Biao and Zhu De to begin taking key cities, including Battle of Siping, Siping and Harbin.Lew 36 These favorable conditions also facilitated many changes inside the Communist leadership: the more radical faction who wanted a complete military take-over of China finally gained the upper hand and defeated the careful opportunists. By May 3, all Soviet troops had withdrawn, and fighting between local Communist and Nationalist forces had broken out in earnest. The conflict would escalate to the scale of a nation-wide civil war over the summer, as Chiang Kai-shek launched a large-scale assault on Communist territory in North China with 113 brigades (a total of 1.6 million troops).Hu, Jubin. (2003). ''Projecting a Nation: Chinese National Cinema Before 1949''. Hong Kong University Press. .
Knowing their disadvantages in manpower and equipment, the CCP adopted a "passive defense" strategy. It avoided the strong points of the KMT army and was prepared to abandon territory in order to preserve its forces. In most cases the surrounding countryside and small towns had come under Communist influence long before the cities. The CCP also attempted to wear out the KMT forces as much as possible. This tactic seemed to be successful; after a year, the power balance became more favorable to the CCP. They wiped out 1.12 million KMT troops, while their strength grew to about two million men. In March 1947 the KMT achieved a symbolic victory by seizing the CCP capital of Yan'an. The Communists counterattacked soon afterwards; on 30 June 1947 CCP troops crossed the Yellow River and moved to the Dabie Mountains area, restored and developed the Central Plain (China), Central Plain. At the same time, Communist forces also began to counterattack in Northeastern China, North China and East China.
 In late 1948, the CCP and the newly rechristened "
In late 1948, the CCP and the newly rechristened "
 On October 1, 1949, Chairman of the Chinese Communist Party, Chairman Mao Zedong officially Proclamation of the People's Republic of China, proclaimed the founding of the
On October 1, 1949, Chairman of the Chinese Communist Party, Chairman Mao Zedong officially Proclamation of the People's Republic of China, proclaimed the founding of the