Commodore REU on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Commodore RAM Expansion Unit (REU) is a range of external
 Although the C128 could access more than of RAM through
Although the C128 could access more than of RAM through
REU Games & UtilitiesREU Programming documentationSource code of RAMDOS, a RAM disk program for the Commodore RAM Expansion UnitREU Programming - by Robin Harbron
{{DEFAULTSORT:Commodore Reu Memory expansion
RAM
Ram, ram, or RAM most commonly refers to:
* A male sheep
* Random-access memory, computer memory
* Ram Trucks, US, since 2009
** List of vehicles named Dodge Ram, trucks and vans
** Ram Pickup, produced by Ram Trucks
Ram, ram, or RAM may also ref ...
add-ons.
At the time of introduction of the Commodore 128
The Commodore 128, also known as the C128, is the last 8-bit home computer that was commercially released by Commodore Business Machines (CBM). Introduced in January 1985 at the CES in Las Vegas, it appeared three years after its predecessor, t ...
home computer
Home computers were a class of microcomputers that entered the market in 1977 and became common during the 1980s. They were marketed to consumers as affordable and accessible computers that, for the first time, were intended for the use of a s ...
, two REUs were announced for that model; the 1700 (128 KB) and 1750 () REUs. Later, Commodore introduced a third model, for their Commodore 64
The Commodore 64, also known as the C64, is an 8-bit computing, 8-bit home computer introduced in January 1982 by Commodore International (first shown at the Consumer Electronics Show, January 7–10, 1982, in Las Vegas). It has been listed in ...
model: the 1764 ()
The need for the REU came about when Commodore management decided to not use the final version of the custom Memory Management Unit (MMU) which then limited the size of memory in spite of early discussion of a larger memory map. Engineers traveling to the 1985 Consumer Electronics Show
CES (; formerly an initialism for Consumer Electronics Show) is an annual trade show organized by the Consumer Technology Association (CTA). Held in January at the Las Vegas Convention Center in Winchester, Nevada, United States, the event typi ...
(CES) were confronted with flyers and billboards advertising a memory size that was no longer supported and finally the top management asked where the additional memory (up to ) would plug in.
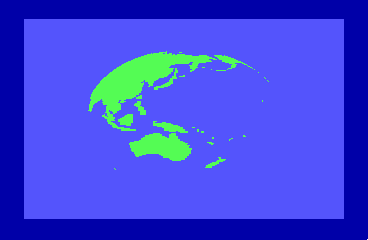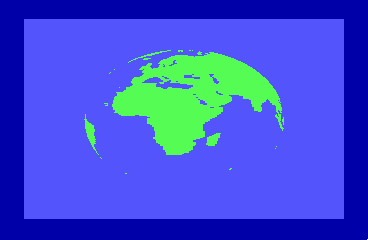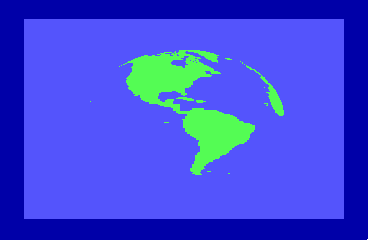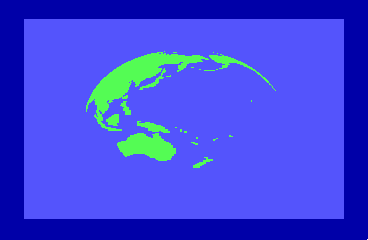
By the time of the 1985 CES show in Chicago, the engineers were able to display a spinning globe of the earth as a demonstration of Direct Memory Access (DMA) by the new REU units.
The REU hardware was designed by Frank Palia and the dedicated RAM Expansion Controller (REC) integrated circuit (IC) was designed by Victor Andrade. Fred Bowen and Terry Ryan adapted the C128's KERNAL
KERNAL is Commodore's name for the ROM-resident operating system core in its 8-bit home computers; from the original PET of 1977, followed by the extended but related versions used in its successors: the VIC-20, Commodore 64, Plus/4, Commodore ...
and BASIC
Basic or BASIC may refer to:
Science and technology
* BASIC, a computer programming language
* Basic (chemistry), having the properties of a base
* Basic access authentication, in HTTP
Entertainment
* Basic (film), ''Basic'' (film), a 2003 film
...
to accommodate the REU natively and Hedley Davis wrote the globe spinning demo which was an impressive display of animation in the mid-1980s.
Hardware description
 Although the C128 could access more than of RAM through
Although the C128 could access more than of RAM through bank switching
Bank switching is a technique used in computer design to increase the amount of usable memory beyond the amount directly addressable by the Processor (computing), processor instructions. It can be used to configure a system differently at diffe ...
, the memory inside the REU could only be accessed by memory-transfers (STORE/LOAD/SWAP/COMPAREs) between the main memory and the REU memory. Additionally, the C128's built-in BASIC 7.0 had three statements, STASH, FETCH, and SWAP, for storing and retrieving data from the REU.
Officially, only the 1700 and 1750 were supported on the C128. The model, the 1764, was released for the C64 at the same time. There were only minor differences between the three models. The original C64 power supply could not support the additional load presented by the 1764 so a 2.5 ampere C64 power supply was included.
The 1700 uses sixteen 4164 64kx1 DRAM
Dram, DRAM, or drams may refer to:
Technology and engineering
* Dram (unit), a unit of mass and volume, and an informal name for a small amount of liquor, especially whisky or whiskey
* Dynamic random-access memory, a type of electronic semicondu ...
ICs, the 1764 has eight 41256 256kx1 DRAMs, and the 1750 has sixteen 41256 DRAMs.
In practice, the difference between the 1764 and the earlier units had little effect on compatibility, and people used 1700s and 1750s successfully with the C64, and 1764s successfully with the C128, although the C64's stock power supply was inadequate to reliably handle the power load of any of them. Some dealers unbundled the 1764 and the power supply in order to sell the power supply to C64 users, and/or upgrade the 1764 to .
The REU model 1750 can be modified to support up to 2MB on memory by installing 2 additional ICs for bank switch. There is only one source of software incompatibility in this modification: software that doesn't set the bits at $DF06 to the same value at all times, or sets the bits to a bank of 512 kb that isn't installed yet, won't work.
During the late 1980s, there was a shortage of DRAM thus 1750s were rare and expensive. However it was comparatively easy to upgrade a 1700 or 1764 to . Several firms did this commercially, either selling upgraded units or upgrading customer-supplied units.
In the early 1990s, DIY modification schemes to increase the capacity of an REU to one megabyte
The megabyte is a multiple of the unit byte for digital information. Its recommended unit symbol is MB. The unit prefix ''mega'' is a multiplier of (106) in the International System of Units (SI). Therefore, one megabyte is one million bytes ...
or higher appeared on various online services.
Model differences
The 1700scircuit board
A printed circuit board (PCB), also called printed wiring board (PWB), is a laminated sandwich structure of conductive and insulating layers, each with a pattern of traces, planes and other features (similar to wires on a flat surface) ...
was identical to that of the 1750, and a trace marked J1 indicated the size of the chips used. On the 1750 and 1764, this trace was cut.
The 1700 and 1750 had a resistor
A resistor is a passive two-terminal electronic component that implements electrical resistance as a circuit element. In electronic circuits, resistors are used to reduce current flow, adjust signal levels, to divide voltages, bias active e ...
at position R4 that, according to Commodore engineer Fred Bowen, compensated for subtle timing differences in the expansion port on the C64 and C128. The 1764 lacked that resistor. Bowen and other CBM engineers recommended against using a 1764 with a C128 unless the resistor was added, or a 1700/1750 with a C64 unless the resistor was removed.
It was possible to check for the presence of a 1750 by reading memory address
In computing, a memory address is a reference to a specific memory location in memory used by both software and hardware. These addresses are fixed-length sequences of digits, typically displayed and handled as unsigned integers. This numeric ...
$DF00's bit
The bit is the most basic unit of information in computing and digital communication. The name is a portmanteau of binary digit. The bit represents a logical state with one of two possible values. These values are most commonly represented as ...
4, which was 1 on a 1750, and 0 on a 1700 or 1764. However, since this procedure would not distinguish between a 1700 and a 1764. To solve this, programmers wrote to, then read from, the REU's RAM to find out the amount of memory installed.
REU software support
A small percentage of software made use of the REUs. Like other add-on products from Commodore, their relatively small installed base relative to the huge number of C64s & C128s made software developers hesitant to invest much time and effort in supporting REUs. The lack of commercial support kept sales lower than they otherwise might have been. Due to its high speed relative to Commodore's floppy drives or even the commercially available hard drives, REUs did see support in the Commodore BBS community. Programs such as Color64 required a REU to minimize load times when switching between sections of the BBS. The REUs came with software to use the extra memory as aRAM disk
A RAM drive (also called a RAM disk) is a block of random-access memory ( primary storage or volatile memory) that a computer's software is treating as if the memory were a disk drive (secondary storage). RAM drives provide high-performance te ...
, but the RAM disk's compatibility with commercial software varied as some commercial software relied heavily on various quirks of the Commodore 1541
The Commodore 1541 (also known as the CBM 1541 and VIC-1541) is a floppy disk drive which was made by Commodore International for the Commodore 64 (C64), Commodore's most popular home computer. The best-known floppy disk drive for the C64, the ...
floppy drive. Additionally, many commercial programs simply overwrote the memory space occupied by the RAM disk software.
The GEOS operating system had built in support for the REU as a RAM disk
A RAM drive (also called a RAM disk) is a block of random-access memory ( primary storage or volatile memory) that a computer's software is treating as if the memory were a disk drive (secondary storage). RAM drives provide high-performance te ...
, as did the C128's version of CP/M
CP/M, originally standing for Control Program/Monitor and later Control Program for Microcomputers, is a mass-market operating system created in 1974 for Intel 8080/Intel 8085, 85-based microcomputers by Gary Kildall of Digital Research, Dig ...
, and some disk copy programs used the REU to facilitate high-speed copying with a single disk drive. GEOS as well as other programs even used the REU for quick memory transfers within the host machine's main memory
Computer data storage or digital data storage is a technology consisting of computer components and recording media that are used to retain digital data. It is a core function and fundamental component of computers.
The central processin ...
by storing a memory block into the REU and then fetching it back to another location. Using this method, only the actual data to be transferred needed to travel on the machine's data bus
In computer architecture, a bus (historically also called a data highway or databus) is a communication system that transfers data between components inside a computer or between computers. It encompasses both hardware (e.g., wires, optical ...
—unlike the ordinary method, which had the computer's CPU do the transfer, thus spending at least three quarters of the bus capacity on instruction fetches and only one quarter or less on payload data.
See also
* Super 1750 Clone * geoRAM *Creative Micro Designs RAMLink * Creative Micro Designs 2 MB REU, (1750 XL)References
External links
REU Games & Utilities
{{DEFAULTSORT:Commodore Reu Memory expansion
REU
Reu or Ragau (; ), according to Genesis in the Hebrew Bible, was the son of Peleg and the father of Serug, thus being Abraham's great-great-grandfather and the ancestor of the Israelites and Ishmaelites.
In scriptures
According to the apo ...
Home computer peripherals
Commodore 64