Commiphora wightii on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
''Commiphora wightii'', with
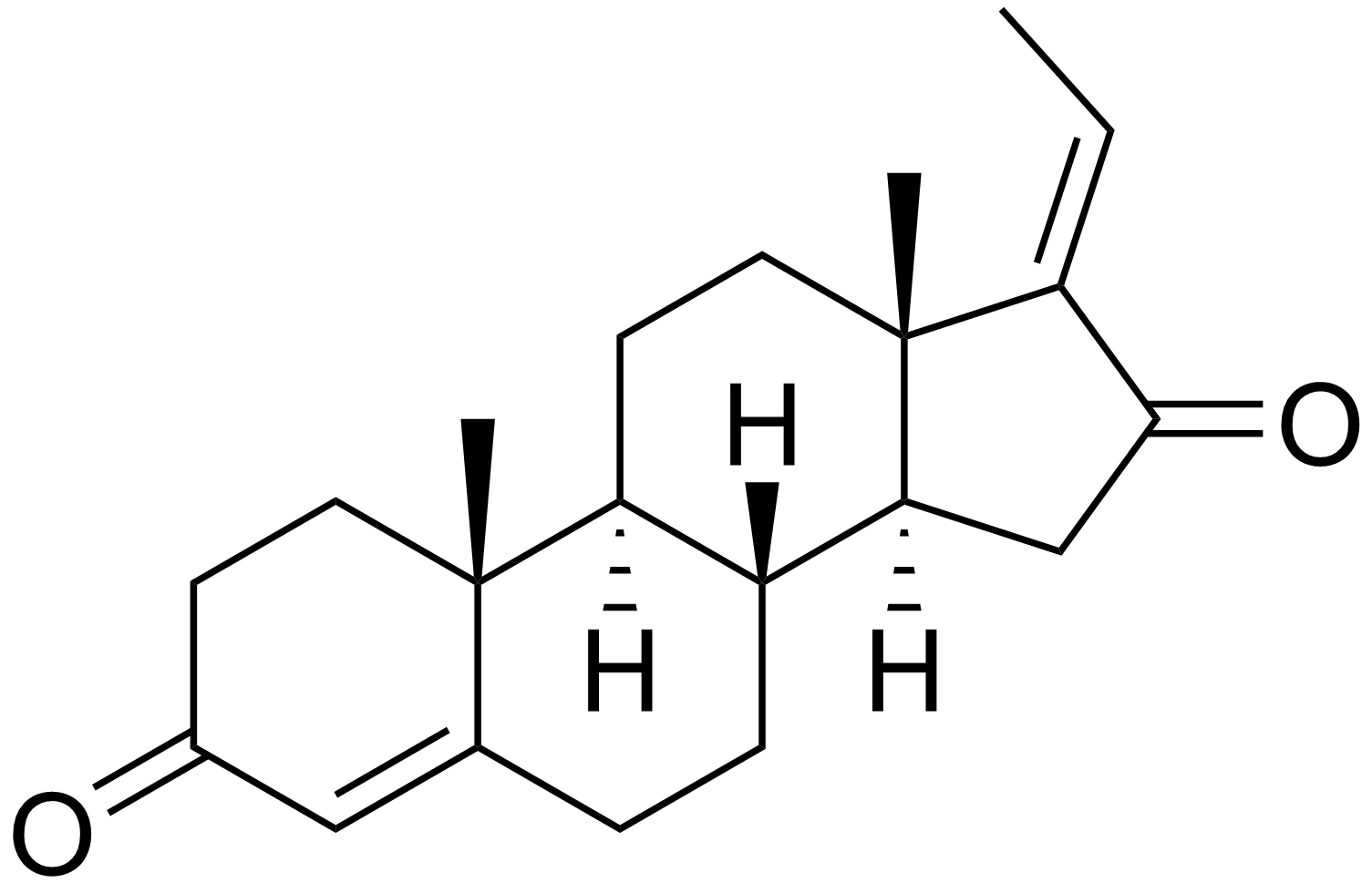 The extract of gum guggul, called gugulipid, guggulipid, or guglipid, has been used in
The extract of gum guggul, called gugulipid, guggulipid, or guglipid, has been used in
 Because of its use in traditional medicine, ''C. wightii'' has been overharvested, and has become so scarce in its two habitats in India—
Because of its use in traditional medicine, ''C. wightii'' has been overharvested, and has become so scarce in its two habitats in India—
"What's Gugul Good For?"
''
Medicinal Plants of Conservation Concern: ''Commiphora wightii''
* Contains a detailed monograph on ''Commiphora mukul'' (Guggulu) as well as a discussion of purported health benefits and usage in clinical practice. *, pp. 226–227 {{Authority control wightii Flora of India (region) Flora of Pakistan Incense material Taxa named by George Arnott Walker Arnott
common name
In biology, a common name of a taxon or organism (also known as a vernacular name, English name, colloquial name, country name, popular name, or farmer's name) is a name that is based on the normal language of everyday life; and is often con ...
s Indian bdellium-tree, gugal, guggal, guggul, gugul, or mukul myrrh tree, is a flowering plant
Flowering plants are plants that bear flowers and fruits, and form the clade Angiospermae (). The term angiosperm is derived from the Ancient Greek, Greek words (; 'container, vessel') and (; 'seed'), meaning that the seeds are enclosed with ...
in the family Burseraceae
The Burseraceae are a moderate-sized family of 17-19 genera and about 540 species of woody flowering plants. The actual numbers given in taxonomic sources differ according to taxonomic revision at the time of writing. The Burseraceae are also ...
, which
produces a fragrant resin called gugal, guggul or gugul, that is used in incense
Incense is an aromatic biotic material that releases fragrant smoke when burnt. The term is used for either the material or the aroma. Incense is used for aesthetic reasons, religious worship, aromatherapy, meditation, and ceremonial reasons. It ...
and vedic medicine (or ayurveda
Ayurveda (; ) is an alternative medicine system with historical roots in the Indian subcontinent. It is heavily practised throughout India and Nepal, where as much as 80% of the population report using ayurveda. The theory and practice of ayur ...
). The species is native to western India, from where it was introduced westward to southern Pakistan and the middle-east. It prefers arid
Aridity is the condition of geographical regions which make up approximately 43% of total global available land area, characterized by low annual precipitation, increased temperatures, and limited water availability.Perez-Aguilar, L. Y., Plata ...
and semi-arid
A semi-arid climate, semi-desert climate, or steppe climate is a aridity, dry climate sub-type. It is located on regions that receive precipitation below Evapotranspiration#Potential evapotranspiration, potential evapotranspiration, but not as l ...
climates and is tolerant of poor soil.
Description
''Commiphora wightii'' grows as ashrub
A shrub or bush is a small to medium-sized perennial woody plant. Unlike herbaceous plants, shrubs have persistent woody stems above the ground. Shrubs can be either deciduous or evergreen. They are distinguished from trees by their multiple ...
or small tree
In botany, a tree is a perennial plant with an elongated stem, or trunk, usually supporting branches and leaves. In some usages, the definition of a tree may be narrower, e.g., including only woody plants with secondary growth, only ...
, reaching a maximum height of , with thin papery bark
Bark may refer to:
Common meanings
* Bark (botany), an outer layer of a woody plant such as a tree or stick
* Bark (sound), a vocalization of some animals (which is commonly the dog)
Arts and entertainment
* ''Bark'' (Jefferson Airplane album), ...
. The branches are thorny. The leaves
A leaf (: leaves) is a principal appendage of the stem of a vascular plant, usually borne laterally above ground and specialized for photosynthesis. Leaves are collectively called foliage, as in "autumn foliage", while the leaves, stem, ...
are simple or trifoliate, the leaflets ovate, long, broad, and irregularly toothed. It is gynodioecious, with some plants bearing bisexual and male flower
Flowers, also known as blooms and blossoms, are the reproductive structures of flowering plants ( angiosperms). Typically, they are structured in four circular levels, called whorls, around the end of a stalk. These whorls include: calyx, m ...
s, and others with female flowers. The individual flowers are red to pink, with four small petals. The small round fruit are red when ripe.
Cultivation and uses
''Commiphora wightii'' is sought for its gummyresin
A resin is a solid or highly viscous liquid that can be converted into a polymer. Resins may be biological or synthetic in origin, but are typically harvested from plants. Resins are mixtures of organic compounds, predominantly terpenes. Commo ...
, which is harvested from the plant's bark through the process of tapping
Tapping is a playing technique that can be used on any stringed instrument, but which is most commonly used on guitar. The technique involves a string being fretted and set into vibration as part of a single motion. This is in contrast to stand ...
. In India
India, officially the Republic of India, is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, seventh-largest country by area; the List of countries by population (United Nations), most populous country since ...
and Pakistan
Pakistan, officially the Islamic Republic of Pakistan, is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by population, fifth-most populous country, with a population of over 241.5 million, having the Islam by country# ...
, guggul is cultivated commercially. The resin of ''C. wightii'', known as ''gum guggulu'', has a fragrance
An aroma compound, also known as an odorant, aroma, fragrance, flavoring or flavor, is a chemical compound that has a smell or odor. For an individual chemical or class of chemical compounds to impart a smell or fragrance, it must be sufficien ...
nearly identical to myrrh
Myrrh (; from an unidentified ancient Semitic language, see '' § Etymology'') is a gum-resin extracted from a few small, thorny tree species of the '' Commiphora'' genus, belonging to the Burseraceae family. Myrrh resin has been used ...
, (which is a close relative the bdellium tree), and also closely resembles fragrance of the Opopanax resin (from the Commiphora Erythrea or Commiphora Guidottii trees, also closely related to Indian Bdellium). It is the same product that was known in Hebrew
Hebrew (; ''ʿÎbrit'') is a Northwest Semitic languages, Northwest Semitic language within the Afroasiatic languages, Afroasiatic language family. A regional dialect of the Canaanite languages, it was natively spoken by the Israelites and ...
, ancient Greek
Ancient Greek (, ; ) includes the forms of the Greek language used in ancient Greece and the classical antiquity, ancient world from around 1500 BC to 300 BC. It is often roughly divided into the following periods: Mycenaean Greek (), Greek ...
and Latin
Latin ( or ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally spoken by the Latins (Italic tribe), Latins in Latium (now known as Lazio), the lower Tiber area aroun ...
sources as bdellium, commonly used in incense and perfumes for centuries.
Guggul is also used in Ayurveda
Ayurveda (; ) is an alternative medicine system with historical roots in the Indian subcontinent. It is heavily practised throughout India and Nepal, where as much as 80% of the population report using ayurveda. The theory and practice of ayur ...
remedies and it is mentioned in Ayurvedic texts dating back to 600 BC. It is often sold as a herbal supplement.
The gum can be purchased in a loosely packed form called ''dhoop'', an incense from India, which is burned over hot coals. This produces a fragrant, dense smoke. It is also sold in the form of incense sticks and dhoop cones which can be burned directly.
Chemical composition
Over a hundredmetabolite
In biochemistry, a metabolite is an intermediate or end product of metabolism.
The term is usually used for small molecules. Metabolites have various functions, including fuel, structure, signaling, stimulatory and inhibitory effects on enzymes, c ...
s of various chemical compositions were reported from the leaves, stem, latex, root and fruit samples. High concentrations of quinic acid
Quinic acid is an organic compound with the formula . The compound is classified as a cyclitol, a cyclic polyol, and a cyclohexanecarboxylic acid. It is a colorless solid that can be extracted from plant sources. Quinic acid is implicated in the p ...
and myo-inositol
In biochemistry, medicine, and related sciences, inositol generally refers to ''myo''-inositol (formerly ''meso''-inositol), the most important stereoisomer of the chemical compound cyclohexane-1,2,3,4,5,6-hexol. Its formula is ; the molecule has ...
were found in fruits and leaves.
Traditional medicinal use
''Commiphora wightii'' has been a key component in ancient IndianAyurvedic
Ayurveda (; ) is an alternative medicine system with historical roots in the Indian subcontinent. It is heavily practised throughout India and Nepal, where as much as 80% of the population report using ayurveda. The theory and practice of ayur ...
system of medicine.
 The extract of gum guggul, called gugulipid, guggulipid, or guglipid, has been used in
The extract of gum guggul, called gugulipid, guggulipid, or guglipid, has been used in Unani
Unani or Yunani medicine (Urdu: ''tibb yūnānī'') is Perso-Arabic traditional medicine as practiced in Muslim culture in South Asia and modern day Central Asia. Unani medicine is pseudoscientific.
The term '' Yūnānī'' means 'Greek', ref ...
and Ayurvedic
Ayurveda (; ) is an alternative medicine system with historical roots in the Indian subcontinent. It is heavily practised throughout India and Nepal, where as much as 80% of the population report using ayurveda. The theory and practice of ayur ...
medicine, for nearly 3,000 years in India. One chemical ingredient in the extract is the steroid guggulsterone
Guggulsterone is a phytosteroid found in the resin of the guggul plant, ''Commiphora mukul''. Guggulsterone can exist as either of two stereoisomers, ''E''-guggulsterone and ''Z''-guggulsterone. In humans, it acts as an antagonist of the farnesoi ...
, which acts as an antagonist
An antagonist is a character in a story who is presented as the main enemy or rival of the protagonist and is often depicted as a villain.farnesoid X receptor
The bile acid receptor (BAR), also known as farnesoid X receptor (FXR) or NR1H4 (nuclear receptor subfamily 1, group H, member 4), is a nuclear receptor that is encoded by the ''NR1H4'' gene in humans.
Function
FXR is expressed at high level ...
, once believed to result in decreased cholesterol
Cholesterol is the principal sterol of all higher animals, distributed in body Tissue (biology), tissues, especially the brain and spinal cord, and in Animal fat, animal fats and oils.
Cholesterol is biosynthesis, biosynthesized by all anima ...
synthesis in the liver
The liver is a major metabolic organ (anatomy), organ exclusively found in vertebrates, which performs many essential biological Function (biology), functions such as detoxification of the organism, and the Protein biosynthesis, synthesis of var ...
. However, several studies have been published that indicate no overall reduction in total cholesterol occurs using various dosages of guggulsterone and levels of low-density lipoprotein
Low-density lipoprotein (LDL) is one of the five major groups of lipoprotein that transport all fat molecules around the body in extracellular water. These groups, from least dense to most dense, are chylomicrons (aka ULDL by the overall density ...
("bad cholesterol") increased in many people.
Endangerment and rescue
Gujarat
Gujarat () is a States of India, state along the Western India, western coast of India. Its coastline of about is the longest in the country, most of which lies on the Kathiawar peninsula. Gujarat is the List of states and union territories ...
and Rajasthan
Rajasthan (; Literal translation, lit. 'Land of Kings') is a States and union territories of India, state in northwestern India. It covers or 10.4 per cent of India's total geographical area. It is the List of states and union territories of ...
—that the World Conservation Union
The International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) is an international organization working in the field of nature conservation and sustainable use of natural resources. Founded in 1948, IUCN has become the global authority on the statu ...
(IUCN) has enlisted it in its IUCN Red List
The International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) Red List of Threatened Species, also known as the IUCN Red List or Red Data Book, founded in 1964, is an inventory of the global conservation status and extinction risk of biological ...
of threatened species. Several efforts are in place to address this situation. India's National Medicinal Plants Board launched a project in Kutch District
Kutch district (), officially spelled Kachchh is a district of Gujarat state in western India, with its headquarters (capital) at Bhuj. Covering an area of 45,674 km2, it is the largest district of India. The area of Kutch is larger than ...
to cultivate of guggal, while a grass-roots conservation movement, led by IUCN associate Vineet Soni, has been started to educate guggal growers and harvesters in safe, sustainable harvesting methods.
References
External links
*Bjerklie, David (August 25, 2003)"What's Gugul Good For?"
''
Time
Time is the continuous progression of existence that occurs in an apparently irreversible process, irreversible succession from the past, through the present, and into the future. It is a component quantity of various measurements used to sequ ...
''.Medicinal Plants of Conservation Concern: ''Commiphora wightii''
* Contains a detailed monograph on ''Commiphora mukul'' (Guggulu) as well as a discussion of purported health benefits and usage in clinical practice. *, pp. 226–227 {{Authority control wightii Flora of India (region) Flora of Pakistan Incense material Taxa named by George Arnott Walker Arnott