Colosseum (band) Compilation Albums on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
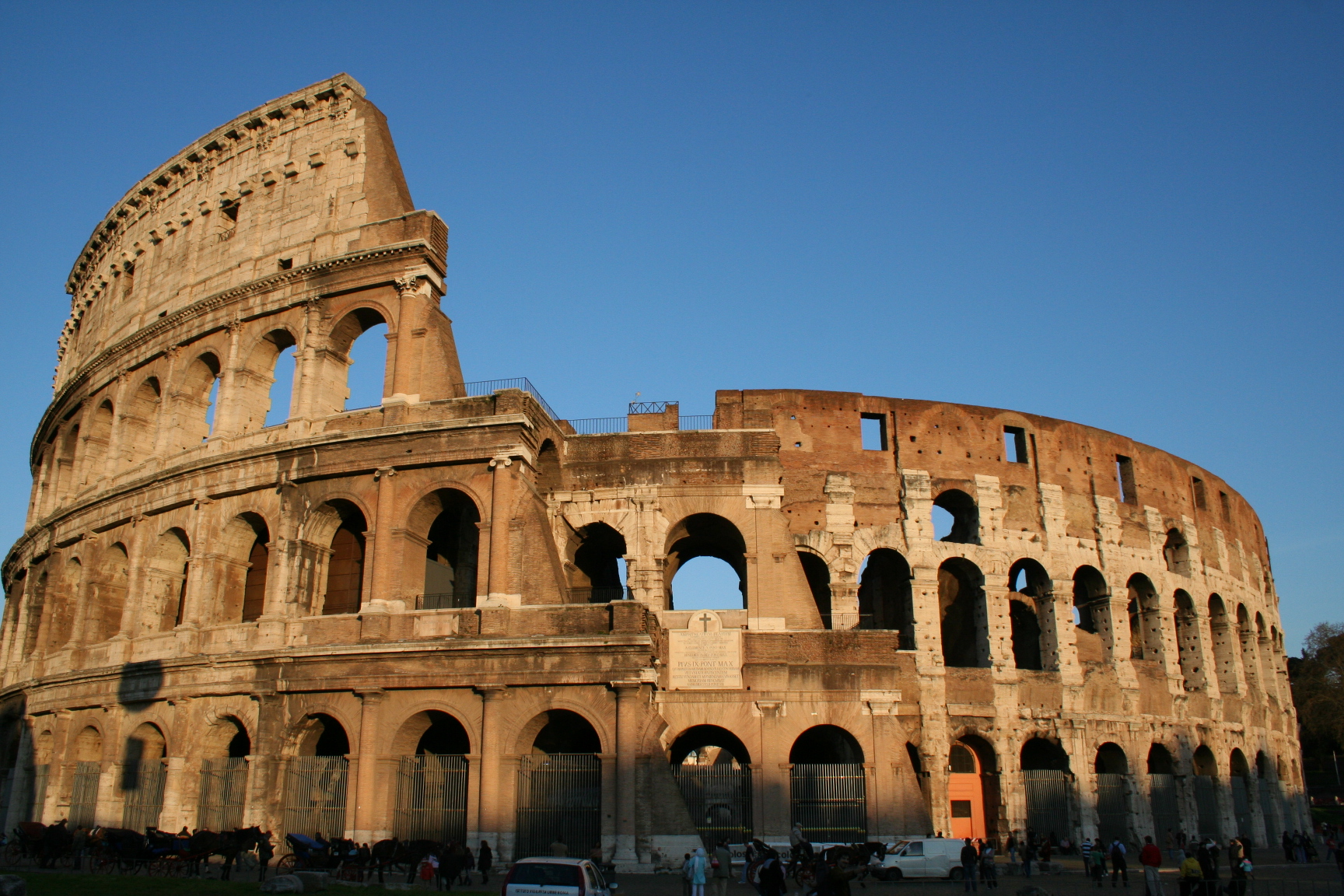
The Colosseum ( ; it, Colosseo ) is an oval
 The earliest citation for the name Colosseum in
The earliest citation for the name Colosseum in

 The site chosen was a flat area on the floor of a low valley between the
The site chosen was a flat area on the floor of a low valley between the  Although the Colossus was preserved, much of the Domus Aurea was torn down. The lake was filled in and the land reused as the location for the new Flavian Amphitheatre. Gladiatorial schools and other support buildings were constructed nearby within the former grounds of the Domus Aurea. Vespasian's decision to build the Colosseum on the site of Nero's lake can be seen as a populist gesture of returning to the people an area of the city which Nero had appropriated for his own use. In contrast to many other amphitheatres, which were on the outskirts of a city, the Colosseum was constructed in the city centre, in effect, placing it both symbolically and precisely at the heart of Rome.
Construction was funded by the opulent spoils taken from the Jewish Temple after the
Although the Colossus was preserved, much of the Domus Aurea was torn down. The lake was filled in and the land reused as the location for the new Flavian Amphitheatre. Gladiatorial schools and other support buildings were constructed nearby within the former grounds of the Domus Aurea. Vespasian's decision to build the Colosseum on the site of Nero's lake can be seen as a populist gesture of returning to the people an area of the city which Nero had appropriated for his own use. In contrast to many other amphitheatres, which were on the outskirts of a city, the Colosseum was constructed in the city centre, in effect, placing it both symbolically and precisely at the heart of Rome.
Construction was funded by the opulent spoils taken from the Jewish Temple after the
 The Colosseum underwent several radical changes of use. By the late 6th century a small chapel had been built into the structure of the amphitheater, though this apparently did not confer any particular religious significance on the building as a whole. The arena was converted into a cemetery. The numerous vaulted spaces in the arcades under the seating were converted into housing and workshops, and are recorded as still being rented out as late as the 12th century. Around 1200 the Frangipani family took over the Colosseum and fortified it, apparently using it as a castle. In the early to mid 14th century, the Pope's relocation to Avignon caused a population decline in Rome that left the region insecure. The colosseum was largely abandoned by the public and became a popular den for bandits.
Severe damage was inflicted on the Colosseum by the great earthquake in 1349, causing the outer south side, lying on a less stable
The Colosseum underwent several radical changes of use. By the late 6th century a small chapel had been built into the structure of the amphitheater, though this apparently did not confer any particular religious significance on the building as a whole. The arena was converted into a cemetery. The numerous vaulted spaces in the arcades under the seating were converted into housing and workshops, and are recorded as still being rented out as late as the 12th century. Around 1200 the Frangipani family took over the Colosseum and fortified it, apparently using it as a castle. In the early to mid 14th century, the Pope's relocation to Avignon caused a population decline in Rome that left the region insecure. The colosseum was largely abandoned by the public and became a popular den for bandits.
Severe damage was inflicted on the Colosseum by the great earthquake in 1349, causing the outer south side, lying on a less stable
Names the order: ''Arciconfraternita del SS. Salvatore ad Sancta Sanctorum'', aka ''del Gonfalone''. Co-tenants: the Roman Senate and the Camera Apostolica. "In 1519 The Confraternita built the little chapel of Santa Maria della Pietà inside the Colosseum." The interior of the amphitheater was extensively stripped of stone, which was reused elsewhere, or (in the case of the marble façade) was burned to make quicklime. The iron clamps which held the stonework together were pried or hacked out of the walls, leaving numerous pockmarks which still scar the building today.

 During the 16th and 17th century, Church officials sought a productive role for the Colosseum. Pope Sixtus V (1585–1590) planned to turn the building into a wool factory to provide employment for Rome's prostitutes, though this proposal fell through with his premature death. In 1671 Cardinal Altieri authorized its use for
During the 16th and 17th century, Church officials sought a productive role for the Colosseum. Pope Sixtus V (1585–1590) planned to turn the building into a wool factory to provide employment for Rome's prostitutes, though this proposal fell through with his premature death. In 1671 Cardinal Altieri authorized its use for  In 1749,
In 1749,  Later popes initiated various stabilization and restoration projects, removing the extensive vegetation which had overgrown the structure and threatened to damage it further. The façade was reinforced with triangular brick wedges in 1807 and 1827, and the interior was repaired in 1831, 1846 and in the 1930s. The arena substructure was partly excavated in 1810–1814 and 1874 and was fully exposed under Benito Mussolini in the 1930s.
The Colosseum is today one of Rome's most popular tourist attractions, receiving millions of visitors annually. The effects of pollution and general deterioration over time prompted a major restoration programme carried out between 1993 and 2000, at a cost of Lire 40 billion ($19.3m / €20.6m at 2000 prices).
In recent years, the Colosseum has become a symbol of the international campaign against capital punishment, which was abolished in Italy in 1948. Several anti–death penalty demonstrations took place in front of the Colosseum in 2000. Since that time, as a gesture against the death penalty, the local authorities of Rome change the color of the Colosseum's night time illumination from white to gold whenever a person condemned to the death penalty anywhere in the world gets their sentence commuted or is released, or if a jurisdiction abolishes the death penalty. Most recently, the Colosseum was illuminated in gold in November 2012 following the abolishment of capital punishment in the American state of
Later popes initiated various stabilization and restoration projects, removing the extensive vegetation which had overgrown the structure and threatened to damage it further. The façade was reinforced with triangular brick wedges in 1807 and 1827, and the interior was repaired in 1831, 1846 and in the 1930s. The arena substructure was partly excavated in 1810–1814 and 1874 and was fully exposed under Benito Mussolini in the 1930s.
The Colosseum is today one of Rome's most popular tourist attractions, receiving millions of visitors annually. The effects of pollution and general deterioration over time prompted a major restoration programme carried out between 1993 and 2000, at a cost of Lire 40 billion ($19.3m / €20.6m at 2000 prices).
In recent years, the Colosseum has become a symbol of the international campaign against capital punishment, which was abolished in Italy in 1948. Several anti–death penalty demonstrations took place in front of the Colosseum in 2000. Since that time, as a gesture against the death penalty, the local authorities of Rome change the color of the Colosseum's night time illumination from white to gold whenever a person condemned to the death penalty anywhere in the world gets their sentence commuted or is released, or if a jurisdiction abolishes the death penalty. Most recently, the Colosseum was illuminated in gold in November 2012 following the abolishment of capital punishment in the American state of
 Unlike Roman theatres that were built into hillsides, the Colosseum is an entirely free-standing structure. It derives its basic exterior and interior architecture from that of two theatres back to back. It is elliptical in plan and is 189 meters (615 ft / 640 Roman feet) long, and 156 meters (510 ft / 528 Roman feet) wide, with a base area of . The height of the outer wall is 48 meters (157 ft / 165 Roman feet). The perimeter originally measured 545 meters (1,788 ft / 1,835 Roman feet). The central arena is an oval 87 m (287 ft) long and 55 m (180 ft) wide, surrounded by a wall 5 m (15 ft) high, above which rose tiers of seating.
The outer wall is estimated to have required over of
Unlike Roman theatres that were built into hillsides, the Colosseum is an entirely free-standing structure. It derives its basic exterior and interior architecture from that of two theatres back to back. It is elliptical in plan and is 189 meters (615 ft / 640 Roman feet) long, and 156 meters (510 ft / 528 Roman feet) wide, with a base area of . The height of the outer wall is 48 meters (157 ft / 165 Roman feet). The perimeter originally measured 545 meters (1,788 ft / 1,835 Roman feet). The central arena is an oval 87 m (287 ft) long and 55 m (180 ft) wide, surrounded by a wall 5 m (15 ft) high, above which rose tiers of seating.
The outer wall is estimated to have required over of  The surviving part of the outer wall's monumental façade comprises three superposed storeys surmounted by a
The surviving part of the outer wall's monumental façade comprises three superposed storeys surmounted by a  The Colosseum's huge crowd capacity made it essential that the venue could be filled or evacuated quickly. Its architects adopted solutions very similar to those used in modern stadia to deal with the same problem. The amphitheatre was ringed by eighty entrances at ground level, 76 of which were used by ordinary spectators. Each entrance and exit was numbered, as was each staircase. The northern main entrance was reserved for the Roman Emperor and his aides, whilst the other three axial entrances were most likely used by the elite. All four axial entrances were richly decorated with painted stucco reliefs, of which fragments survive. Many of the original outer entrances have disappeared with the collapse of the perimeter wall, but entrances XXIII (23) to LIIII (54) survive.
Spectators were given tickets in the form of numbered pottery shards, which directed them to the appropriate section and row. They accessed their seats via '' vomitoria'' (singular ''vomitorium''), passageways that opened into a tier of seats from below or behind. These quickly dispersed people into their seats and, upon conclusion of the event or in an emergency evacuation, could permit their exit within only a few minutes. The name ''vomitoria'' derived from the Latin word for a rapid discharge, from which English derives the word vomit.
The Colosseum's huge crowd capacity made it essential that the venue could be filled or evacuated quickly. Its architects adopted solutions very similar to those used in modern stadia to deal with the same problem. The amphitheatre was ringed by eighty entrances at ground level, 76 of which were used by ordinary spectators. Each entrance and exit was numbered, as was each staircase. The northern main entrance was reserved for the Roman Emperor and his aides, whilst the other three axial entrances were most likely used by the elite. All four axial entrances were richly decorated with painted stucco reliefs, of which fragments survive. Many of the original outer entrances have disappeared with the collapse of the perimeter wall, but entrances XXIII (23) to LIIII (54) survive.
Spectators were given tickets in the form of numbered pottery shards, which directed them to the appropriate section and row. They accessed their seats via '' vomitoria'' (singular ''vomitorium''), passageways that opened into a tier of seats from below or behind. These quickly dispersed people into their seats and, upon conclusion of the event or in an emergency evacuation, could permit their exit within only a few minutes. The name ''vomitoria'' derived from the Latin word for a rapid discharge, from which English derives the word vomit.
 According to the Codex-Calendar of 354, the Colosseum could accommodate 87,000 people, although modern estimates put the figure at around 50,000. They were seated in a tiered arrangement that reflected the rigidly stratified nature of Roman society. Special boxes were provided at the north and south ends respectively for the Emperor and the
According to the Codex-Calendar of 354, the Colosseum could accommodate 87,000 people, although modern estimates put the figure at around 50,000. They were seated in a tiered arrangement that reflected the rigidly stratified nature of Roman society. Special boxes were provided at the north and south ends respectively for the Emperor and the 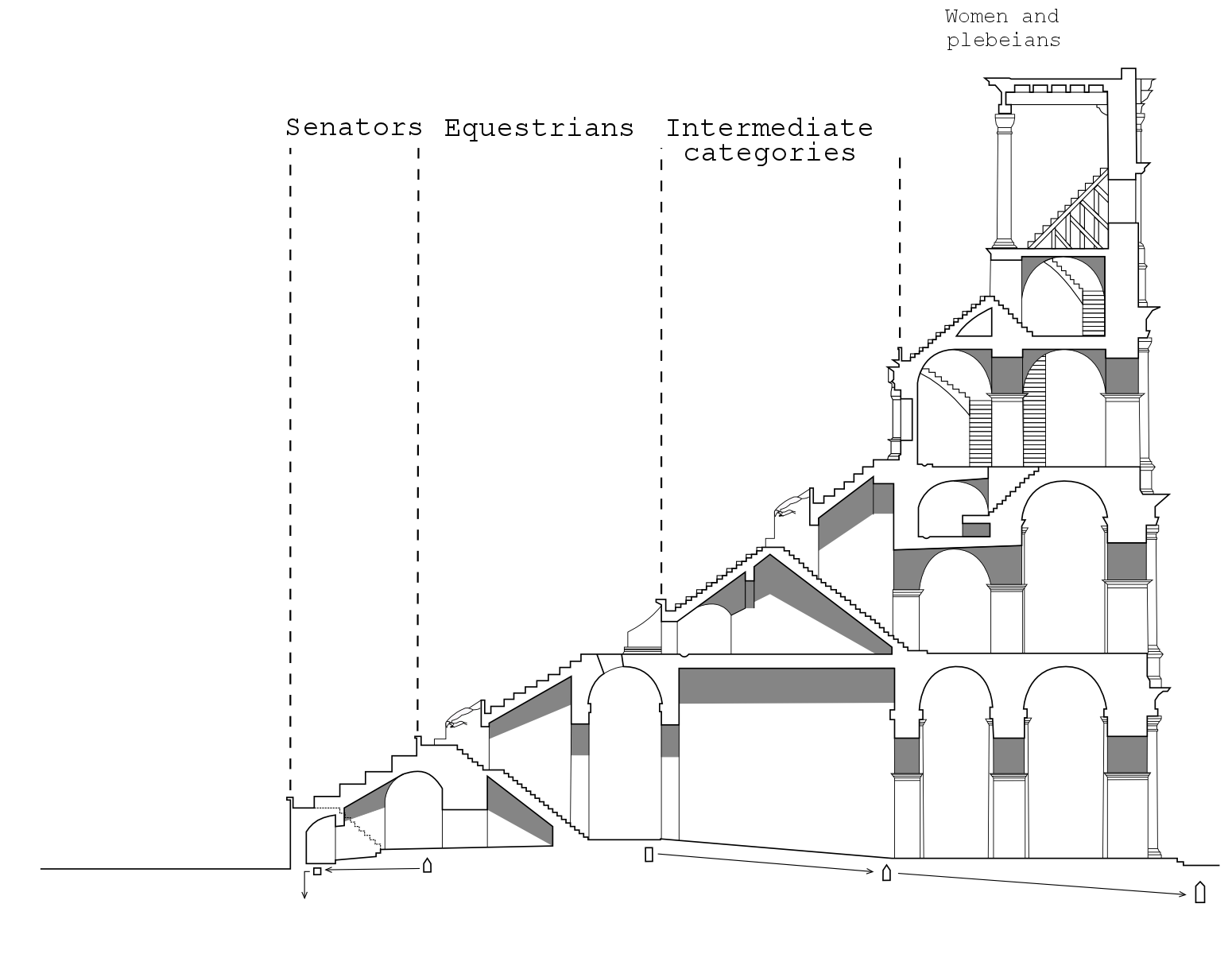 The tier above the senators, known as the ''maenianum primum'', was occupied by the non-senatorial noble class or knights ('' equites''). The next level up, the ''maenianum secundum'', was originally reserved for ordinary Roman citizens (''
The tier above the senators, known as the ''maenianum primum'', was occupied by the non-senatorial noble class or knights ('' equites''). The next level up, the ''maenianum secundum'', was originally reserved for ordinary Roman citizens (''
 The arena itself was 83 meters by 48 meters (272 ft by 157 ft / 280 by 163 Roman feet). It comprised a wooden floor covered by sand (the Latin word for sand is ''harena'' or ''arena''), covering an elaborate underground structure called the ''
The arena itself was 83 meters by 48 meters (272 ft by 157 ft / 280 by 163 Roman feet). It comprised a wooden floor covered by sand (the Latin word for sand is ''harena'' or ''arena''), covering an elaborate underground structure called the '' The ''hypogeum'' was connected by tunnels to a number of points outside the Colosseum. Animals and performers were brought through the tunnel from nearby stables, with the gladiators' barracks at the
The ''hypogeum'' was connected by tunnels to a number of points outside the Colosseum. Animals and performers were brought through the tunnel from nearby stables, with the gladiators' barracks at the
 The Colosseum was used to host gladiatorial shows as well as a variety of other events. The shows, called ''
The Colosseum was used to host gladiatorial shows as well as a variety of other events. The shows, called ''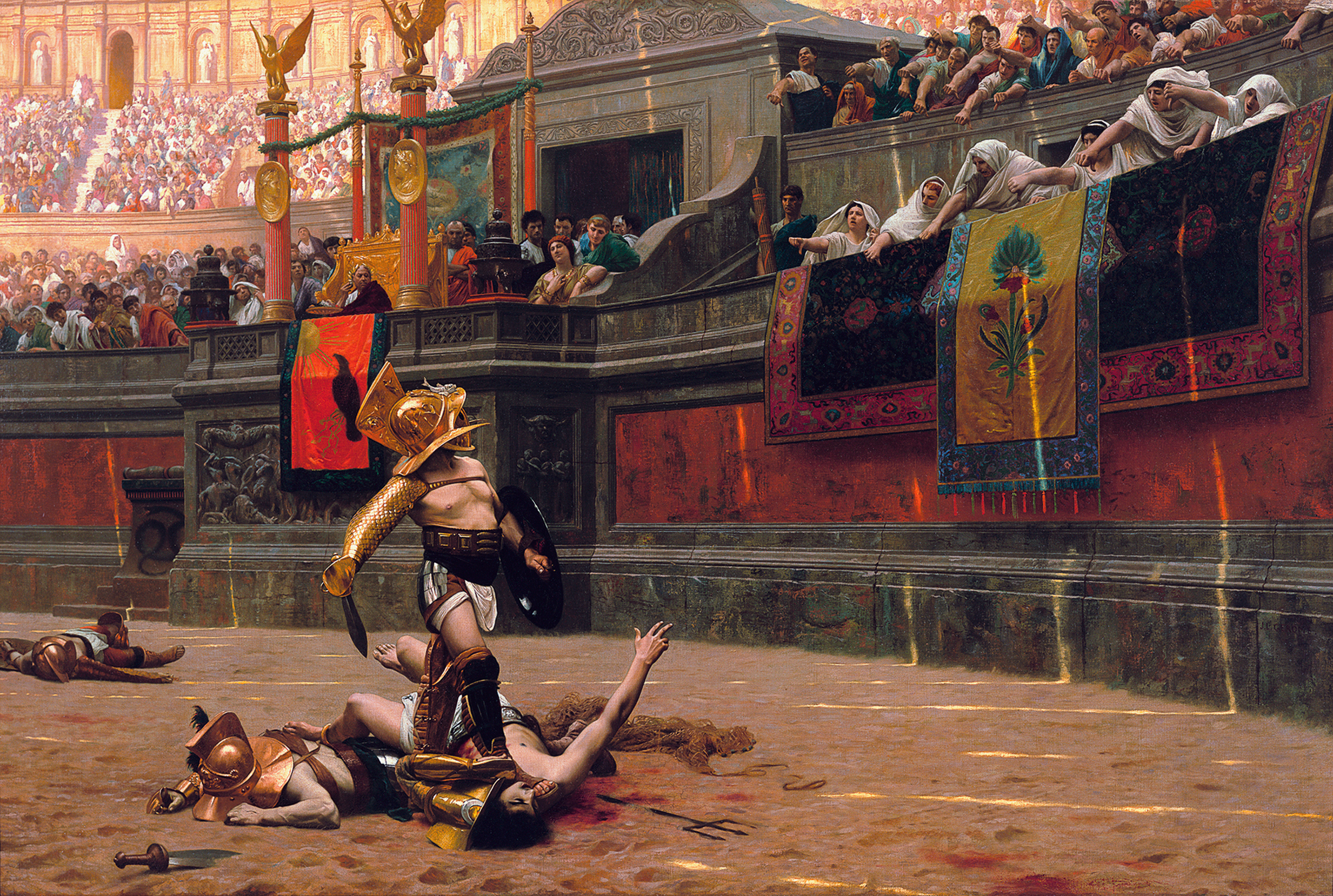 During the early days of the Colosseum, ancient writers recorded that the building was used for ''
During the early days of the Colosseum, ancient writers recorded that the building was used for ''
 The Colosseum today is a major tourist attraction in Rome with thousands of tourists each year entering to view the interior arena. There is now a museum dedicated to
The Colosseum today is a major tourist attraction in Rome with thousands of tourists each year entering to view the interior arena. There is now a museum dedicated to
 In 2011 Diego Della Valle, head of the shoe firm Tod's, entered into an agreement with local officials to sponsor a €25 million restoration of the Colosseum. Work was planned to begin at the end of 2011, taking up to two and a half years. Due to the controversial nature of using a public–private partnership to fund the restoration, work was delayed and began in 2013. The restoration is the first full cleaning and repair in the Colosseum's history. The first stage is to clean and restore the Colosseum's arcaded façade and replace the metal enclosures that block the ground-level arches. After three years, the work was completed on 1 July 2016, when the Italian minister of culture, Dario Franceschini, also announced that the funds have been committed to replace the floors by the end of 2018. These will provide a stage that Franceschini says will be used for "cultural events of the highest level." The project also includes creating a services center and restoring the galleries and underground spaces inside the Colosseum. Since 1 November 2017, the top two levels have been opened for guided visits. The fourth level held the marketplace, and the top fifth tier is where the poorest citizens, the plebeians, gathered and watched the show, bringing picnics for the day-long event.
In 2011 Diego Della Valle, head of the shoe firm Tod's, entered into an agreement with local officials to sponsor a €25 million restoration of the Colosseum. Work was planned to begin at the end of 2011, taking up to two and a half years. Due to the controversial nature of using a public–private partnership to fund the restoration, work was delayed and began in 2013. The restoration is the first full cleaning and repair in the Colosseum's history. The first stage is to clean and restore the Colosseum's arcaded façade and replace the metal enclosures that block the ground-level arches. After three years, the work was completed on 1 July 2016, when the Italian minister of culture, Dario Franceschini, also announced that the funds have been committed to replace the floors by the end of 2018. These will provide a stage that Franceschini says will be used for "cultural events of the highest level." The project also includes creating a services center and restoring the galleries and underground spaces inside the Colosseum. Since 1 November 2017, the top two levels have been opened for guided visits. The fourth level held the marketplace, and the top fifth tier is where the poorest citizens, the plebeians, gathered and watched the show, bringing picnics for the day-long event.
 At the insistence of St. Leonard of Port Maurice, Pope Benedict XIV (1740–1758) forbade the quarrying of the Colosseum and erected Stations of the Cross around the arena, which remained until February 1874. Benedict Joseph Labre spent the later years of his life within the walls of the Colosseum, living on alms, before he died in 1783. Several 19th century popes funded repair and restoration work on the Colosseum, and it still retains its Christian connection today. A Christian cross stands in the Colosseum, with a plaque, stating:
At the insistence of St. Leonard of Port Maurice, Pope Benedict XIV (1740–1758) forbade the quarrying of the Colosseum and erected Stations of the Cross around the arena, which remained until February 1874. Benedict Joseph Labre spent the later years of his life within the walls of the Colosseum, living on alms, before he died in 1783. Several 19th century popes funded repair and restoration work on the Colosseum, and it still retains its Christian connection today. A Christian cross stands in the Colosseum, with a plaque, stating:
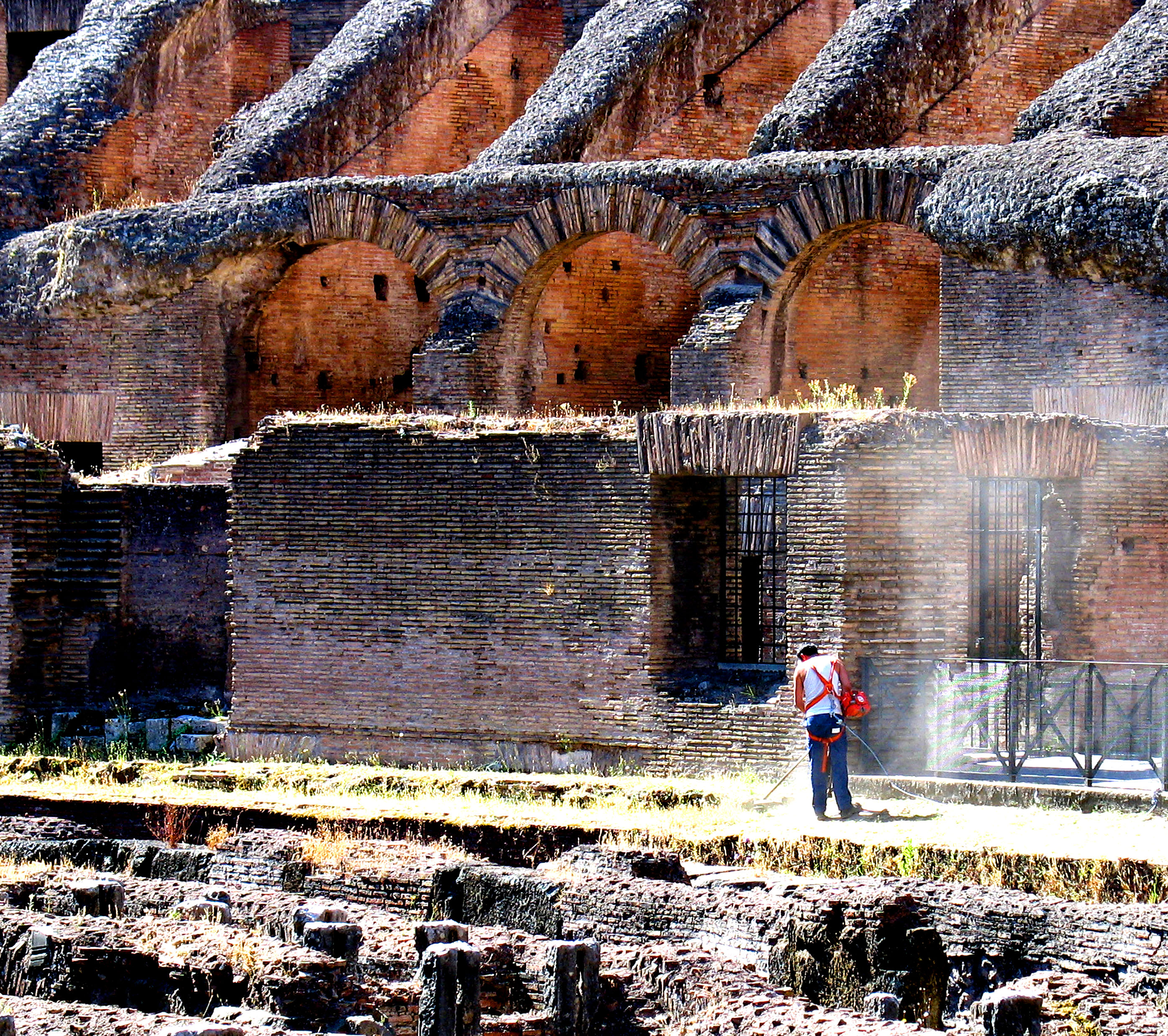 The Colosseum has a wide and well-documented history of Flora (plants), flora ever since Domenico Panaroli made the first catalogue of its plants in 1643. Since then, 684 species have been identified there. The peak was in 1855 (420 species). Attempts were made in 1871 to eradicate the vegetation, because of concerns over the damage that was being caused to the masonry, but much of it has returned. 242 species have been counted today and of the species first identified by Panaroli, 200 remain.
The variation of plants can be explained by the change of climate in Rome through the centuries. Additionally, bird migration, flower blooming, and the growth of Rome that caused the Colosseum to become embedded within the modern city centre rather than on the outskirts of the ancient city, as well as deliberate transport of species, are also contributing causes. Another reason often given is their seeds being unwittingly transported either on the fur or in the feces of animals brought there from all corners of the empire.
The Colosseum has a wide and well-documented history of Flora (plants), flora ever since Domenico Panaroli made the first catalogue of its plants in 1643. Since then, 684 species have been identified there. The peak was in 1855 (420 species). Attempts were made in 1871 to eradicate the vegetation, because of concerns over the damage that was being caused to the masonry, but much of it has returned. 242 species have been counted today and of the species first identified by Panaroli, 200 remain.
The variation of plants can be explained by the change of climate in Rome through the centuries. Additionally, bird migration, flower blooming, and the growth of Rome that caused the Colosseum to become embedded within the modern city centre rather than on the outskirts of the ancient city, as well as deliberate transport of species, are also contributing causes. Another reason often given is their seeds being unwittingly transported either on the fur or in the feces of animals brought there from all corners of the empire.
File:Rom Colosseum Sept 2021 2.jpg, The Colosseum in 2021
File:Colosseum and Arch of Constantine seen from Palatine.jpg, Colosseum and the Arch of Constantine seen from Palatine
File:Colosseum (8474551096).jpg, Interior
File:Colosseum 1000689.jpg, Interior
File:Colosseo - Through my lens 2.jpg, Colosseum at night
File:The Colosseum (9554989427).jpg, Seating tiers at the east entrance
File:Rome (IT), Kolosseum -- 2013 -- 3400.jpg, Colosseum 2013
Virtual tour of the Colosseum
A 3D model of Colosseum on Sketchfab
* *
3D model of the past and present of the colosseum – The Only Progress is Human
{{DEFAULTSORT:Flavian Amphitheatre Amphitheatres in Rome Building projects of the Flavian dynasty Roman archaeology Ruins in Italy National museums of Italy Round buildings Roman amphitheatres in Italy 1st-century establishments in Italy 80s establishments in the Roman Empire Rome R. XIX Celio Titus Vespasian 80 Buildings and structures completed in the 1st century World Heritage Sites in Italy Outdoor arenas
amphitheatre
An amphitheatre (British English) or amphitheater (American English; both ) is an open-air venue used for entertainment, performances, and sports. The term derives from the ancient Greek ('), from ('), meaning "on both sides" or "around" and ...
in the centre of the city of Rome
, established_title = Founded
, established_date = 753 BC
, founder = King Romulus (legendary)
, image_map = Map of comune of Rome (metropolitan city of Capital Rome, region Lazio, Italy).svg
, map_caption ...
, Italy
Italy ( it, Italia ), officially the Italian Republic, ) or the Republic of Italy, is a country in Southern Europe. It is located in the middle of the Mediterranean Sea, and its territory largely coincides with the homonymous geographical ...
, just east of the Roman Forum. It is the largest ancient amphitheatre ever built, and is still the largest standing amphitheatre in the world today, despite its age. Construction began under the emperor Vespasian
Vespasian (; la, Vespasianus ; 17 November AD 9 – 23/24 June 79) was a Roman emperor who reigned from AD 69 to 79. The fourth and last emperor who reigned in the Year of the Four Emperors, he founded the Flavian dynasty that ruled the Empi ...
() in 72 and was completed in 80 AD under his successor and heir, Titus
Titus Caesar Vespasianus ( ; 30 December 39 – 13 September 81 AD) was Roman emperor from 79 to 81. A member of the Flavian dynasty, Titus succeeded his father Vespasian upon his death.
Before becoming emperor, Titus gained renown as a mili ...
(). Further modifications were made during the reign of Domitian
Domitian (; la, Domitianus; 24 October 51 – 18 September 96) was a Roman emperor who reigned from 81 to 96. The son of Vespasian and the younger brother of Titus, his two predecessors on the throne, he was the last member of the Fl ...
(). The three emperors that were patrons of the work are known as the Flavian dynasty
The Flavian dynasty ruled the Roman Empire between AD 69 and 96, encompassing the reigns of Vespasian (69–79), and his two sons Titus (79–81) and Domitian (81–96). The Flavians rose to power during the civil war of 69, known ...
, and the amphitheatre was named the Flavian Amphitheatre ( la, Amphitheatrum Flavium; it, Anfiteatro Flavio ) by later classicists
Classics or classical studies is the study of classical antiquity. In the Western world, classics traditionally refers to the study of Classical Greek and Roman literature and their related original languages, Ancient Greek and Latin. Classics ...
and archaeologists for its association with their family name (Flavius
The gens Flavia was a plebeian family at ancient Rome. Its members are first mentioned during the last three centuries of the Republic. The first of the Flavii to achieve prominence was Marcus Flavius, tribune of the plebs in 327 and 323 BC; ...
).
The Colosseum is built of travertine
Travertine ( ) is a form of terrestrial limestone deposited around mineral springs, especially hot springs. It often has a fibrous or concentric appearance and exists in white, tan, cream-colored, and even rusty varieties. It is formed by a p ...
limestone, tuff
Tuff is a type of rock made of volcanic ash ejected from a vent during a volcanic eruption. Following ejection and deposition, the ash is lithified into a solid rock. Rock that contains greater than 75% ash is considered tuff, while rock ...
(volcanic rock), and brick-faced concrete
Concrete is a composite material composed of fine and coarse aggregate bonded together with a fluid cement (cement paste) that hardens (cures) over time. Concrete is the second-most-used substance in the world after water, and is the most wid ...
. It could hold an estimated 50,000 to 80,000 spectators at various points in its history, having an average audience of some 65,000; it was used for gladiatorial
A gladiator ( la, gladiator, "swordsman", from , "sword") was an armed combatant who entertained audiences in the Roman Republic and Roman Empire in violent confrontations with other gladiators, wild animals, and condemned criminals. Some gla ...
contests and public spectacles including animal hunts, executions, re-enactments of famous battles, and dramas based on Roman mythology
Roman mythology is the body of myths of ancient Rome as represented in the literature and visual arts of the Romans. One of a wide variety of genres of Roman folklore, ''Roman mythology'' may also refer to the modern study of these representa ...
, and briefly mock sea battles. The building ceased to be used for entertainment in the early medieval
The Early Middle Ages (or early medieval period), sometimes controversially referred to as the Dark Ages, is typically regarded by historians as lasting from the late 5th or early 6th century to the 10th century. They marked the start of the Mi ...
era. It was later reused for such purposes as housing, workshops, quarters for a religious order, a fortress, a quarry
A quarry is a type of open-pit mine in which dimension stone, rock, construction aggregate, riprap, sand, gravel, or slate is excavated from the ground. The operation of quarries is regulated in some jurisdictions to reduce their envir ...
, and a Christian shrine.
Although substantially ruined by earthquakes and stone robbers taking ''spolia
''Spolia'' (Latin: 'spoils') is repurposed building stone for new construction or decorative sculpture reused in new monuments. It is the result of an ancient and widespread practice whereby stone that has been quarried, cut and used in a built ...
'', the Colosseum is still an iconic symbol of Imperial Rome
The Roman Empire ( la, Imperium Romanum ; grc-gre, Βασιλεία τῶν Ῥωμαίων, Basileía tôn Rhōmaíōn) was the post-Republican period of ancient Rome. As a polity, it included large territorial holdings around the Mediterr ...
and was listed as one of the New 7 Wonders of the World
The New 7 Wonders of the World was a campaign started in 2000 to choose Wonders of the World from a selection of 200 existing monuments. The popularity poll via free Web-based voting and small amounts of telephone voting was led by Canadian-Swiss ...
. It is one of Rome's most popular tourist attraction
A tourist attraction is a place of interest that tourists visit, typically for its inherent or an exhibited natural or cultural value, historical significance, natural or built beauty, offering leisure and amusement.
Types
Places of natural ...
s and also has links to the Roman Catholic Church
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics worldwide . It is among the world's oldest and largest international institutions, and has played a ...
, as each Good Friday the Pope
The pope ( la, papa, from el, πάππας, translit=pappas, 'father'), also known as supreme pontiff ( or ), Roman pontiff () or sovereign pontiff, is the bishop of Rome (or historically the patriarch of Rome), head of the worldwide Cathol ...
leads a torchlit "Way of the Cross" procession that starts in the area around the Colosseum. The Colosseum is depicted on the Italian version of the five-cent euro coin.
Name
Originally, the building's Latin name was simply the . Though the modern name Flavian Amphitheatre () is often used, there is no evidence it was used inclassical antiquity
Classical antiquity (also the classical era, classical period or classical age) is the period of cultural history between the 8th century BC and the 5th century AD centred on the Mediterranean Sea, comprising the interlocking civilizations of ...
. This name refers to the patronage of the Flavian dynasty
The Flavian dynasty ruled the Roman Empire between AD 69 and 96, encompassing the reigns of Vespasian (69–79), and his two sons Titus (79–81) and Domitian (81–96). The Flavians rose to power during the civil war of 69, known ...
, during whose reigns the building was constructed, but the structure is better known as the Colosseum. In antiquity, Romans may have referred to the Colosseum by the unofficial name ''Amphitheatrum Caesareum'' (with ''Caesareum'' an adjective pertaining to the title ''Caesar
Gaius Julius Caesar (; ; 12 July 100 BC – 15 March 44 BC), was a Roman general and statesman. A member of the First Triumvirate, Caesar led the Roman armies in the Gallic Wars before defeating his political rival Pompey in a civil war, an ...
''), but this name may have been strictly poetic as it was not exclusive to the Colosseum; Vespasian and Titus, builders of the Colosseum, also constructed a Flavian Amphitheatre
The Colosseum ( ; it, Colosseo ) is an oval amphitheatre in the centre of the city of Rome, Italy, just east of the Roman Forum. It is the largest ancient amphitheatre ever built, and is still the largest standing amphitheatre in the world to ...
in Puteoli
Pozzuoli (; ; ) is a city and ''comune'' of the Metropolitan City of Naples, in the Italian region of Campania. It is the main city of the Phlegrean Peninsula.
History
Pozzuoli began as the Greek colony of ''Dicaearchia'' ( el, Δικα ...
(modern Pozzuoli).
The name ''Colosseum'' is believed to be derived from a colossal statue of Nero on the model of the Colossus of Rhodes. The giant bronze sculpture of Nero as a solar deity was moved to its position beside the amphitheatre by the emperor Hadrian (). The word ''colosseum'' is a neuter Latin noun
Latin declension is the set of patterns according to which Latin words are declined—that is, have their endings altered to show grammatical case, number and gender. Nouns, pronouns, and adjectives are declined (verbs are conjugated), and a gi ...
formed from the adjective
In linguistics, an adjective (abbreviated ) is a word that generally modifies a noun or noun phrase or describes its referent. Its semantic role is to change information given by the noun.
Traditionally, adjectives were considered one of the ma ...
''colosseus'', meaning "gigantic" or "colossean". By the year 1000 the Latin name "Colosseum" had been coined to refer to the amphitheatre from the nearby "Colossus Solis".
The spelling was sometimes altered in and ''coliseum'' are attested from the 12th and 14th centuries respectively. In the 12th century, the structure was recorded as the . In the High Middle Ages
The High Middle Ages, or High Medieval Period, was the period of European history that lasted from AD 1000 to 1300. The High Middle Ages were preceded by the Early Middle Ages and were followed by the Late Middle Ages, which ended around AD 150 ...
, the Flavian amphitheatre is attested as the late 13th-century , and in by the early 16th century, by which time the word could be applied to any amphitheatre. From derived the , in use by the middle of the 15th century and employed by John Capgrave
John Capgrave (21 April 1393 – 12 August 1464) was an English historian, hagiographer and scholastic theologian, remembered chiefly for ''Nova Legenda Angliae'' (New Reading from England). This was the first comprehensive collection of lives o ...
in his ''Solace of Pilgrims'', in which he remarked: . An English translation by John Bourchier, 2nd Baron Berners
John Bourchier, 2nd Baron Berners (1467 – 19 March 1533) was an English soldier, statesman and translator.
Family
John Bourchier, born about 1467, was the only son of Sir Humphrey Bourchier (d.1471 at the Battle of Barnet) and Elizabeth T ...
, of Antonio de Guevara
Antonio de Guevara (c. 1481 – 3 April 1545) was a Spanish bishop and author. In 1527 he was named royal chronicler to Charles V, Holy Roman Emperor. His first book ''Libro áureo'' first appeared in pirated editions the following year. This pseu ...
's biography of Marcus Aurelius
Marcus Aurelius Antoninus (Latin: áːɾkus̠ auɾέːli.us̠ antɔ́ːni.us̠ English: ; 26 April 121 – 17 March 180) was Roman emperor from 161 to 180 AD and a Stoic philosopher. He was the last of the rulers known as the Five Good ...
() in about 1533 referred to .... Similarly, the , or , are attested as referring first to the amphitheatre in Rome, and then to any amphitheatre (as in 1367). By 1460, an equivalent existed in ; by 1495 had appeared the , and by 1548 the .
 The earliest citation for the name Colosseum in
The earliest citation for the name Colosseum in Early Modern English
Early Modern English or Early New English (sometimes abbreviated EModE, EMnE, or ENE) is the stage of the English language from the beginning of the Tudor period to the English Interregnum and Restoration, or from the transition from Middle E ...
is the 1600 translation, by Philemon Holland
Philemon Holland (1552 – 9 February 1637) was an English schoolmaster, physician and translator. He is known for the first English translations of several works by Livy, Pliny the Elder, and Plutarch, and also for translating William Camden's ...
, of the ''Urbis Romae topographia'' of Bartolomeo Marliani, which he used in the preparation of his translation of Livy
Titus Livius (; 59 BC – AD 17), known in English as Livy ( ), was a Roman historian. He wrote a monumental history of Rome and the Roman people, titled , covering the period from the earliest legends of Rome before the traditional founding in ...
's Augustan era ''Ab Urbe Condita Libri
The work called ( en, From the Founding of the City), sometimes referred to as (''Books from the Founding of the City''), is a monumental history of ancient Rome, written in Latin between 27 and 9 BC by Livy, a Roman historian. The wor ...
''. The text states: "This Amphitheatre was commonly called Colosseum, of Neroes Colossus, which was set up in the porch of Neroes house." Similarly, John Evelyn
John Evelyn (31 October 162027 February 1706) was an English writer, landowner, gardener, courtier and minor government official, who is now best known as a diarist. He was a founding Fellow of the Royal Society.
John Evelyn's diary, or ...
, translating the used by the architectural theorist Roland Fréart de Chambray
Roland Fréart, sieur de Chambray (13 July 1606 – 11 December 1676)Asfour 1996. was a French writer, collector, and a theorist of architecture and the arts. Though not a practitioner himself, his two major publications, ''Parallèle de l'archite ...
, wrote "And 'tis indeed a kind of miracle to see that the Colosseum … and innumerable other Structures which seemed to have been built for Eternity, should be at present so ruinous and dilapidated".
Related to the Colossus of Nero statue
After Nero's suicide and the civil wars of theYear of the Four Emperors
The Year of the Four Emperors, AD 69, was the first civil war of the Roman Empire, during which four emperors ruled in succession: Galba, Otho, Vitellius, and Vespasian. It is considered an important interval, marking the transition from the ...
, the Colossus of Nero
The Colossus of Nero (''Colossus Neronis'') was a bronze statue that the Emperor Nero (37–68 AD) created in the vestibule of his Domus Aurea, the imperial villa complex which spanned a large area from the north side of the Palatine Hill, acro ...
statue was remodeled by the condemned emperor's successors into the likeness of Helios (''Sol'') or Apollo
Apollo, grc, Ἀπόλλωνος, Apóllōnos, label=genitive , ; , grc-dor, Ἀπέλλων, Apéllōn, ; grc, Ἀπείλων, Apeílōn, label= Arcadocypriot Greek, ; grc-aeo, Ἄπλουν, Áploun, la, Apollō, la, Apollinis, label ...
, the sun god, by adding the appropriate solar crown. It was then commonly referred to as the "Colossus solis". Nero's head was also replaced several times with the heads of succeeding emperors. Despite its pagan links, the statue remained standing well into the medieval era and was credited with magical powers. The emperor Constantine the Great
Constantine I ( , ; la, Flavius Valerius Constantinus, ; ; 27 February 22 May 337), also known as Constantine the Great, was Roman emperor from AD 306 to 337, the first one to convert to Christianity. Born in Naissus, Dacia Mediterran ...
remodeled the statue's face as his own.
In the 8th century, an epigram attributed to the Venerable Bede
Bede ( ; ang, Bǣda , ; 672/326 May 735), also known as Saint Bede, The Venerable Bede, and Bede the Venerable ( la, Beda Venerabilis), was an English monk at the monastery of St Peter and its companion monastery of St Paul in the Kingdom o ...
celebrated the symbolic significance of the statue in a prophecy that is variously quoted: ''Quamdiu stat Colisæus, stat et Roma; quando cadet colisæus, cadet et Roma; quando cadet Roma, cadet et mundus'' ("as long as the Colossus stands, so shall Rome; when the Colossus falls, Rome shall fall; when Rome falls, so falls the world").; the form quoted from the Pseudo-Bede is that printed in Migne
Jacques Paul Migne (; 25 October 1800 – 24 October 1875) was a French priest who published inexpensive and widely distributed editions of theological works, encyclopedias, and the texts of the Church Fathers, with the goal of providing a ...
, ''Pat. Lat'' 94 (Paris), 1862:543, noted in F. Schneider, ''Rom und Romgedanke im Mittelalter'' (Munich) 1926:66f, 251, and in Roberto Weiss, ''The Renaissance Discovery of Classical Antiquity'' (Oxford:Blackwell) 1973:8 and note 5. This is often mistranslated to refer to the Colosseum rather than the Colossus (as in, for instance, Byron
George Gordon Byron, 6th Baron Byron (22 January 1788 – 19 April 1824), known simply as Lord Byron, was an English romantic poet and peer. He was one of the leading figures of the Romantic movement, and has been regarded as among the ...
's poem '' Childe Harold's Pilgrimage''). However, at the time that the Pseudo-Bede wrote, the masculine noun ''coliseus'' was applied to the statue rather than to the amphitheatre.
The Colossus did eventually fall, possibly being pulled down to reuse its bronze. The statue itself was largely forgotten and only its base survives, between the Colosseum and the nearby Temple of Venus and Roma
The Temple of Venus and Roma (Latin: ''Templum Veneris et Romae'') is thought to have been the largest temple in Ancient Rome. Located on the Velian Hill, between the eastern edge of the Forum Romanum and the Colosseum, in Rome, it was dedicated ...
.
History
Construction, inauguration, and Roman renovations
 The site chosen was a flat area on the floor of a low valley between the
The site chosen was a flat area on the floor of a low valley between the Caelian
The Caelian Hill (; la, Collis Caelius; it, Celio ) is one of the famous seven hills of Rome.
Geography
The Caelian Hill is a sort of long promontory about long, to wide, and tall in the park near the Temple of Claudius. The hill over ...
, Esquiline
The Esquiline Hill (; la, Collis Esquilinus; it, Esquilino ) is one of the Seven Hills of Rome. Its southernmost cusp is the ''Oppius'' (Oppian Hill).
Etymology
The origin of the name ''Esquiline'' is still under much debate. One view is ...
and Palatine Hills, through which a canal
Canals or artificial waterways are waterways or engineered channels built for drainage management (e.g. flood control and irrigation) or for conveyancing water transport vehicles (e.g. water taxi). They carry free, calm surface flo ...
ised stream ran as well as an artificial lake/marsh. By the 2nd century BC the area was densely inhabited. It was devastated by the Great Fire of Rome
The Great Fire of Rome ( la, incendium magnum Romae) occurred in July AD 64. The fire began in the merchant shops around Rome's chariot stadium, Circus Maximus, on the night of 19 July. After six days, the fire was brought under control, but before ...
in 64 AD, following which Nero
Nero Claudius Caesar Augustus Germanicus ( ; born Lucius Domitius Ahenobarbus; 15 December AD 37 – 9 June AD 68), was the fifth Roman emperor and final emperor of the Julio-Claudian dynasty, reigning from AD 54 unti ...
seized much of the area to add to his personal domain. He built the grandiose Domus Aurea
The Domus Aurea (Latin, "Golden House") was a vast landscaped complex built by the Emperor Nero largely on the Oppian Hill in the heart of ancient Rome after the great fire in 64 AD had destroyed a large part of the city.Roth (1993)
It replac ...
on the site, in front of which he created an artificial lake surrounded by pavilions, gardens and porticoes. The existing Aqua Claudia
Aqua Claudia ("the Claudian water") was an ancient Roman aqueduct that, like the Aqua Anio Novus, was begun by Emperor Caligula (37–41 AD) in 38 AD and finished by Emperor Claudius (41–54 AD) in 52 AD.
Together with Aqua Anio Novus, Aqua ...
aqueduct was extended to supply water to the area and the gigantic bronze Colossus of Nero
The Colossus of Nero (''Colossus Neronis'') was a bronze statue that the Emperor Nero (37–68 AD) created in the vestibule of his Domus Aurea, the imperial villa complex which spanned a large area from the north side of the Palatine Hill, acro ...
was set up nearby at the entrance to the Domus Aurea.  Although the Colossus was preserved, much of the Domus Aurea was torn down. The lake was filled in and the land reused as the location for the new Flavian Amphitheatre. Gladiatorial schools and other support buildings were constructed nearby within the former grounds of the Domus Aurea. Vespasian's decision to build the Colosseum on the site of Nero's lake can be seen as a populist gesture of returning to the people an area of the city which Nero had appropriated for his own use. In contrast to many other amphitheatres, which were on the outskirts of a city, the Colosseum was constructed in the city centre, in effect, placing it both symbolically and precisely at the heart of Rome.
Construction was funded by the opulent spoils taken from the Jewish Temple after the
Although the Colossus was preserved, much of the Domus Aurea was torn down. The lake was filled in and the land reused as the location for the new Flavian Amphitheatre. Gladiatorial schools and other support buildings were constructed nearby within the former grounds of the Domus Aurea. Vespasian's decision to build the Colosseum on the site of Nero's lake can be seen as a populist gesture of returning to the people an area of the city which Nero had appropriated for his own use. In contrast to many other amphitheatres, which were on the outskirts of a city, the Colosseum was constructed in the city centre, in effect, placing it both symbolically and precisely at the heart of Rome.
Construction was funded by the opulent spoils taken from the Jewish Temple after the First Jewish–Roman War
The First Jewish–Roman War (66–73 CE), sometimes called the Great Jewish Revolt ( he, המרד הגדול '), or The Jewish War, was the first of three major rebellions by the Jews against the Roman Empire, fought in Roman-controlled ...
in 70 AD led to the Siege of Jerusalem. According to a reconstructed inscription found on the site, "the emperor Vespasian
Vespasian (; la, Vespasianus ; 17 November AD 9 – 23/24 June 79) was a Roman emperor who reigned from AD 69 to 79. The fourth and last emperor who reigned in the Year of the Four Emperors, he founded the Flavian dynasty that ruled the Empi ...
ordered this new amphitheatre to be erected from his general's share of the booty." It is often assumed that Jewish prisoners of war were brought back to Rome and contributed to the massive workforce needed for the construction of the amphitheatre, but there is no ancient evidence for that; it would, nonetheless, be commensurate with Roman practice to add humiliation to the defeated population. Along with this free source of unskilled labor, teams of professional Roman builders, engineers, artists, painters and decorators undertook the more specialized tasks necessary for building the Colosseum. The Colosseum was constructed with several different materials: wood, limestone, tuff
Tuff is a type of rock made of volcanic ash ejected from a vent during a volcanic eruption. Following ejection and deposition, the ash is lithified into a solid rock. Rock that contains greater than 75% ash is considered tuff, while rock ...
, tiles, cement, and mortar.
Construction of the Colosseum began under the rule of Vespasian in around 70–72 AD (73–75 AD according to some sources). The Colosseum had been completed up to the third story by the time of Vespasian's death in 79. The top level was finished by his son, Titus
Titus Caesar Vespasianus ( ; 30 December 39 – 13 September 81 AD) was Roman emperor from 79 to 81. A member of the Flavian dynasty, Titus succeeded his father Vespasian upon his death.
Before becoming emperor, Titus gained renown as a mili ...
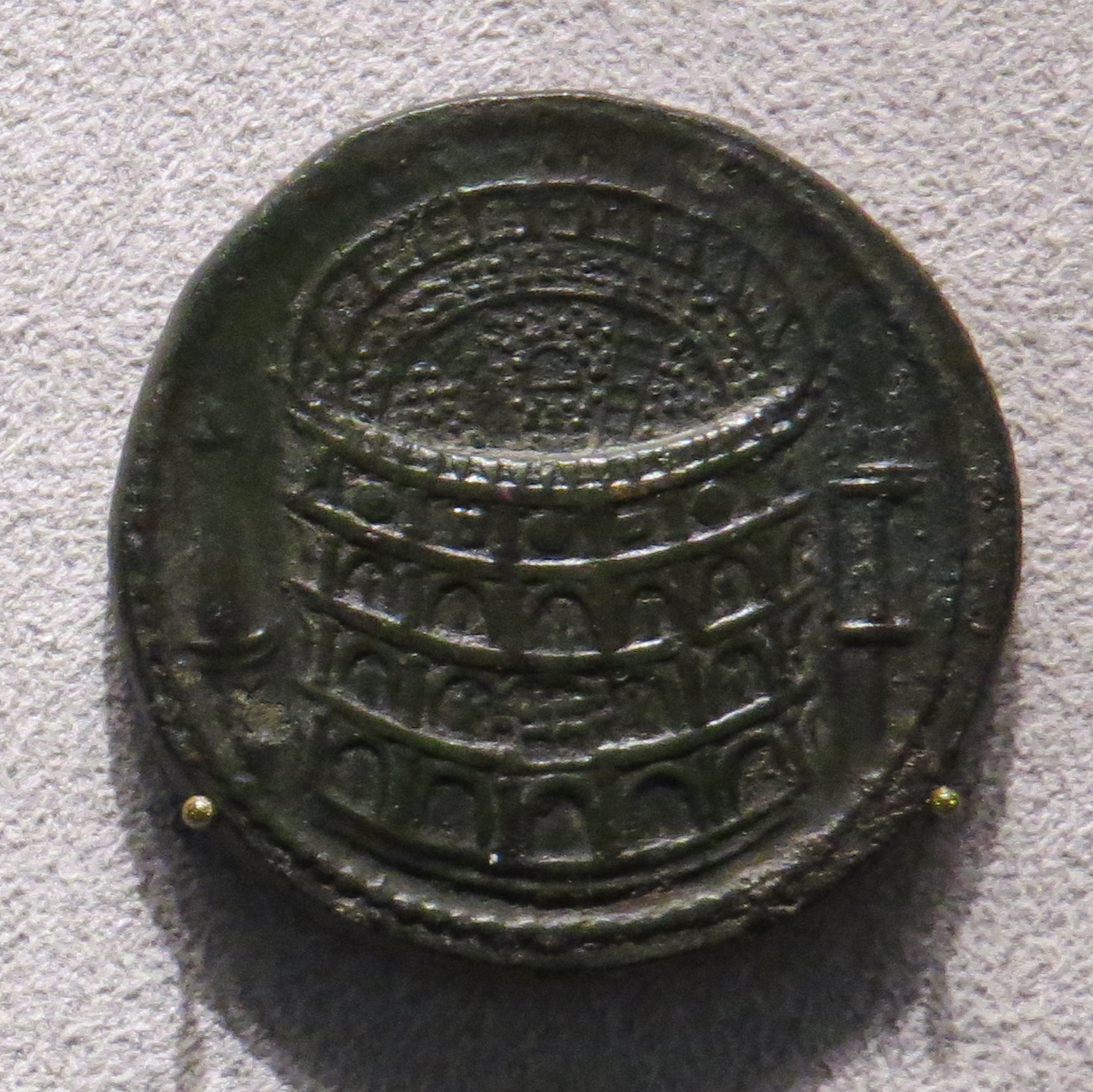
, in 80, and the inaugural games were held in 80 or 81 AD. Dio Cassius recounts that over 9,000 wild animals were killed during the inaugural games of the amphitheatre. Commemorative coinage was issued celebrating the inauguration. The building was remodelled further under Vespasian's younger son, the newly designated Emperor Domitian
Domitian (; la, Domitianus; 24 October 51 – 18 September 96) was a Roman emperor who reigned from 81 to 96. The son of Vespasian and the younger brother of Titus, his two predecessors on the throne, he was the last member of the Fl ...
, who constructed the ''hypogeum
A hypogeum or hypogaeum (plural hypogea or hypogaea, pronounced ; literally meaning "underground", from Greek ''hypo'' (under) and ''ghê'' (earth)) is an underground temple or tomb.
Hypogea will often contain niches for cremated human rem ...
'', a series of tunnels used to house animals and slaves. He also added a gallery to the top of the Colosseum to increase its seating capacity
Seating capacity is the number of people who can be seated in a specific space, in terms of both the physical space available, and limitations set by law. Seating capacity can be used in the description of anything ranging from an automobile that ...
.
In 217, the Colosseum was badly damaged by a major fire (caused by lightning, according to Dio Cassius), which destroyed the wooden upper levels of the amphitheatre's interior. It was not fully repaired until about 240 and underwent further repairs in 250 or 252 and again in 320. Honorius banned the practice of gladiator fights in 399 and again in 404. Gladiatorial fights are last mentioned around 435. An inscription records the restoration of various parts of the Colosseum under Theodosius II
Theodosius II ( grc-gre, Θεοδόσιος, Theodosios; 10 April 401 – 28 July 450) was Roman emperor for most of his life, proclaimed ''augustus'' as an infant in 402 and ruling as the eastern Empire's sole emperor after the death of his ...
and Valentinian III
Valentinian III ( la, Placidus Valentinianus; 2 July 41916 March 455) was Roman emperor in the West from 425 to 455. Made emperor in childhood, his reign over the Roman Empire was one of the longest, but was dominated by powerful generals vying ...
(reigned 425–455), possibly to repair damage caused by a major earthquake in 443; more work followed in 484 and 508. The arena continued to be used for contests well into the 6th century. Animal hunts continued until at least 523, when Anicius Maximus celebrated his consulship with some ''venationes
Venatio ( la, venatio, "hunting", plural ''venationes'') was a type of entertainment in Roman amphitheaters involving the hunting and killing of wild animals.
History
Venatio was first introduced by Marcus Fulvius Nobilior, who celebrated his ...
'', criticised by King Theodoric the Great
Theodoric (or Theoderic) the Great (454 – 30 August 526), also called Theodoric the Amal ( got, , *Þiudareiks; Greek: , romanized: ; Latin: ), was king of the Ostrogoths (471–526), and ruler of the independent Ostrogothic Kingdom of Italy ...
for their high cost.
Medieval
 The Colosseum underwent several radical changes of use. By the late 6th century a small chapel had been built into the structure of the amphitheater, though this apparently did not confer any particular religious significance on the building as a whole. The arena was converted into a cemetery. The numerous vaulted spaces in the arcades under the seating were converted into housing and workshops, and are recorded as still being rented out as late as the 12th century. Around 1200 the Frangipani family took over the Colosseum and fortified it, apparently using it as a castle. In the early to mid 14th century, the Pope's relocation to Avignon caused a population decline in Rome that left the region insecure. The colosseum was largely abandoned by the public and became a popular den for bandits.
Severe damage was inflicted on the Colosseum by the great earthquake in 1349, causing the outer south side, lying on a less stable
The Colosseum underwent several radical changes of use. By the late 6th century a small chapel had been built into the structure of the amphitheater, though this apparently did not confer any particular religious significance on the building as a whole. The arena was converted into a cemetery. The numerous vaulted spaces in the arcades under the seating were converted into housing and workshops, and are recorded as still being rented out as late as the 12th century. Around 1200 the Frangipani family took over the Colosseum and fortified it, apparently using it as a castle. In the early to mid 14th century, the Pope's relocation to Avignon caused a population decline in Rome that left the region insecure. The colosseum was largely abandoned by the public and became a popular den for bandits.
Severe damage was inflicted on the Colosseum by the great earthquake in 1349, causing the outer south side, lying on a less stable alluvial
Alluvium (from Latin ''alluvius'', from ''alluere'' 'to wash against') is loose clay, silt, sand, or gravel that has been deposited by running water in a stream bed, on a floodplain, in an alluvial fan or beach, or in similar settings. All ...
terrain, to collapse. Much of the tumbled stone was reused to build palaces, churches, hospitals and other buildings elsewhere in Rome. In 1377, after the Pope's return to Rome, the Colosseum was restored by a religious order called Arciconfraternita del SS. Salvatore ad Sancta Sanctorum, who then inhabited a northern portion of it until as late as the early 19th century.Names the order: ''Arciconfraternita del SS. Salvatore ad Sancta Sanctorum'', aka ''del Gonfalone''. Co-tenants: the Roman Senate and the Camera Apostolica. "In 1519 The Confraternita built the little chapel of Santa Maria della Pietà inside the Colosseum." The interior of the amphitheater was extensively stripped of stone, which was reused elsewhere, or (in the case of the marble façade) was burned to make quicklime. The iron clamps which held the stonework together were pried or hacked out of the walls, leaving numerous pockmarks which still scar the building today.
Modern

 During the 16th and 17th century, Church officials sought a productive role for the Colosseum. Pope Sixtus V (1585–1590) planned to turn the building into a wool factory to provide employment for Rome's prostitutes, though this proposal fell through with his premature death. In 1671 Cardinal Altieri authorized its use for
During the 16th and 17th century, Church officials sought a productive role for the Colosseum. Pope Sixtus V (1585–1590) planned to turn the building into a wool factory to provide employment for Rome's prostitutes, though this proposal fell through with his premature death. In 1671 Cardinal Altieri authorized its use for bullfight
Bullfighting is a physical contest that involves a bullfighter attempting to subdue, immobilize, or kill a bull, usually according to a set of rules, guidelines, or cultural expectations.
There are several variations, including some forms wh ...
s; a public outcry caused the idea to be hastily abandoned.
 In 1749,
In 1749, Pope Benedict XIV
Pope Benedict XIV ( la, Benedictus XIV; it, Benedetto XIV; 31 March 1675 – 3 May 1758), born Prospero Lorenzo Lambertini, was head of the Catholic Church and ruler of the Papal States from 17 August 1740 to his death in May 1758. Pope Be ...
endorsed the view that the Colosseum was a sacred site where early Christians had been martyr
A martyr (, ''mártys'', "witness", or , ''marturia'', stem , ''martyr-'') is someone who suffers persecution and death for advocating, renouncing, or refusing to renounce or advocate, a religious belief or other cause as demanded by an externa ...
ed. He forbade the use of the Colosseum as a quarry and consecrated the building to the Passion of Christ
In Christianity, the Passion (from the Latin verb ''patior, passus sum''; "to suffer, bear, endure", from which also "patience, patient", etc.) is the short final period in the life of Jesus Christ.
Depending on one's views, the "Passion" m ...
and installed Stations of the Cross, declaring it sanctified by the blood of the Christian martyrs
In Christianity, a martyr is a person considered to have died because of their testimony for Jesus or faith in Jesus. In years of the early church, stories depict this often occurring through death by sawing, stoning, crucifixion, burning at th ...
who perished there (''see Significance in Christianity''). However, there is no historical evidence to support Benedict's claim, nor is there even any evidence that anyone before the 16th century suggested this might be the case; the ''Catholic Encyclopedia
The ''Catholic Encyclopedia: An International Work of Reference on the Constitution, Doctrine, Discipline, and History of the Catholic Church'' (also referred to as the ''Old Catholic Encyclopedia'' and the ''Original Catholic Encyclopedia'') i ...
'' concludes that there are no historical grounds for the supposition, other than the reasonably plausible conjecture that some of the many martyrs may well have been.
 Later popes initiated various stabilization and restoration projects, removing the extensive vegetation which had overgrown the structure and threatened to damage it further. The façade was reinforced with triangular brick wedges in 1807 and 1827, and the interior was repaired in 1831, 1846 and in the 1930s. The arena substructure was partly excavated in 1810–1814 and 1874 and was fully exposed under Benito Mussolini in the 1930s.
The Colosseum is today one of Rome's most popular tourist attractions, receiving millions of visitors annually. The effects of pollution and general deterioration over time prompted a major restoration programme carried out between 1993 and 2000, at a cost of Lire 40 billion ($19.3m / €20.6m at 2000 prices).
In recent years, the Colosseum has become a symbol of the international campaign against capital punishment, which was abolished in Italy in 1948. Several anti–death penalty demonstrations took place in front of the Colosseum in 2000. Since that time, as a gesture against the death penalty, the local authorities of Rome change the color of the Colosseum's night time illumination from white to gold whenever a person condemned to the death penalty anywhere in the world gets their sentence commuted or is released, or if a jurisdiction abolishes the death penalty. Most recently, the Colosseum was illuminated in gold in November 2012 following the abolishment of capital punishment in the American state of
Later popes initiated various stabilization and restoration projects, removing the extensive vegetation which had overgrown the structure and threatened to damage it further. The façade was reinforced with triangular brick wedges in 1807 and 1827, and the interior was repaired in 1831, 1846 and in the 1930s. The arena substructure was partly excavated in 1810–1814 and 1874 and was fully exposed under Benito Mussolini in the 1930s.
The Colosseum is today one of Rome's most popular tourist attractions, receiving millions of visitors annually. The effects of pollution and general deterioration over time prompted a major restoration programme carried out between 1993 and 2000, at a cost of Lire 40 billion ($19.3m / €20.6m at 2000 prices).
In recent years, the Colosseum has become a symbol of the international campaign against capital punishment, which was abolished in Italy in 1948. Several anti–death penalty demonstrations took place in front of the Colosseum in 2000. Since that time, as a gesture against the death penalty, the local authorities of Rome change the color of the Colosseum's night time illumination from white to gold whenever a person condemned to the death penalty anywhere in the world gets their sentence commuted or is released, or if a jurisdiction abolishes the death penalty. Most recently, the Colosseum was illuminated in gold in November 2012 following the abolishment of capital punishment in the American state of Connecticut
Connecticut () is the southernmost state in the New England region of the Northeastern United States. It is bordered by Rhode Island to the east, Massachusetts to the north, New York to the west, and Long Island Sound to the south. Its capita ...
in April 2012.
Because of the ruined state of the interior, it is impractical to use the Colosseum to host large events; only a few hundred spectators can be accommodated in temporary seating. However, much larger concerts have been held just outside, using the Colosseum as a backdrop. Performers who have played at the Colosseum in recent years have included Ray Charles
Ray Charles Robinson Sr. (September 23, 1930 – June 10, 2004) was an American singer, songwriter, and pianist. He is regarded as one of the most iconic and influential singers in history, and was often referred to by contemporaries as "The Ge ...
(May 2002), Paul McCartney
Sir James Paul McCartney (born 18 June 1942) is an English singer, songwriter and musician who gained worldwide fame with the Beatles, for whom he played bass guitar and shared primary songwriting and lead vocal duties with John Lennon. One ...
(May 2003), Elton John (September 2005), and Billy Joel (July 2006).
Physical description
Exterior
 Unlike Roman theatres that were built into hillsides, the Colosseum is an entirely free-standing structure. It derives its basic exterior and interior architecture from that of two theatres back to back. It is elliptical in plan and is 189 meters (615 ft / 640 Roman feet) long, and 156 meters (510 ft / 528 Roman feet) wide, with a base area of . The height of the outer wall is 48 meters (157 ft / 165 Roman feet). The perimeter originally measured 545 meters (1,788 ft / 1,835 Roman feet). The central arena is an oval 87 m (287 ft) long and 55 m (180 ft) wide, surrounded by a wall 5 m (15 ft) high, above which rose tiers of seating.
The outer wall is estimated to have required over of
Unlike Roman theatres that were built into hillsides, the Colosseum is an entirely free-standing structure. It derives its basic exterior and interior architecture from that of two theatres back to back. It is elliptical in plan and is 189 meters (615 ft / 640 Roman feet) long, and 156 meters (510 ft / 528 Roman feet) wide, with a base area of . The height of the outer wall is 48 meters (157 ft / 165 Roman feet). The perimeter originally measured 545 meters (1,788 ft / 1,835 Roman feet). The central arena is an oval 87 m (287 ft) long and 55 m (180 ft) wide, surrounded by a wall 5 m (15 ft) high, above which rose tiers of seating.
The outer wall is estimated to have required over of travertine
Travertine ( ) is a form of terrestrial limestone deposited around mineral springs, especially hot springs. It often has a fibrous or concentric appearance and exists in white, tan, cream-colored, and even rusty varieties. It is formed by a p ...
stone which were set without mortar; they were held together by 300 tons of iron clamps. However, it has suffered extensive damage over the centuries, with large segments having collapsed following earthquakes. The north side of the perimeter wall is still standing; the distinctive triangular brick wedges at each end are modern additions, having been constructed in the early 19th century to shore up the wall. The remainder of the present-day exterior of the Colosseum is in fact the original interior wall.
podium
A podium (plural podiums or podia) is a platform used to raise something to a short distance above its surroundings. It derives from the Greek ''πόδι'' (foot). In architecture a building can rest on a large podium. Podiums can also be used ...
on which stands a tall attic, both of which are pierced by windows interspersed at regular intervals. The arcades are framed by half-columns of the Doric Doric may refer to:
* Doric, of or relating to the Dorians of ancient Greece
** Doric Greek, the dialects of the Dorians
* Doric order, a style of ancient Greek architecture
* Doric mode, a synonym of Dorian mode
* Doric dialect (Scotland)
* Doric ...
, Ionic, and Corinthian Corinthian or Corinthians may refer to:
*Several Pauline epistles, books of the New Testament of the Bible:
**First Epistle to the Corinthians
**Second Epistle to the Corinthians
**Third Epistle to the Corinthians (Orthodox)
*A demonym relating to ...
orders, while the attic is decorated with Corinthian pilaster
In classical architecture, a pilaster is an architectural element used to give the appearance of a supporting column and to articulate an extent of wall, with only an ornamental function. It consists of a flat surface raised from the main wal ...
s.Ian Archibald Richmond, Donald Emrys Strong, Janet DeLaine
Janet DeLaine is Emeritus, Emeritus Fellow at Wolfson College, Oxford and a Fellow of the Society of Antiquaries of London. She is a Roman archaeologist whose research has focused on urban environments, with a particular focus on bath complexes, ...
. "Colosseum", ''The Oxford Companion to Classical Civilization''. Ed. Simon Hornblower and Antony Spawforth. Oxford University Press, 1998. Each of the arches in the second- and third-floor arcades framed statues, probably honoring divinities and other figures from Classical mythology
Classical mythology, Greco-Roman mythology, or Greek and Roman mythology is both the body of and the study of myths from the ancient Greeks and ancient Romans as they are used or transformed by cultural reception. Along with philosophy and poli ...
.
Two hundred and forty mast corbels were positioned around the top of the attic. They originally supported a retractable awning
An awning or overhang is a secondary covering attached to the exterior wall of a building. It is typically composed of canvas woven of acrylic, cotton or polyester yarn, or vinyl laminated to polyester fabric that is stretched tightly over a li ...
, known as the ''velarium
A ("curtain") was a type of awning used in Roman times. It stretched over the whole of the , the seating area in amphitheaters to protect spectators from the sun. Precisely how the awning was supported is a matter of conjecture.Suetonius, '' L ...
'', that kept the sun and rain off spectators. This consisted of a canvas-covered, net-like structure made of ropes, with a hole in the center. It covered two-thirds of the arena, and sloped down towards the center to catch the wind and provide a breeze for the audience. Sailors, specially enlisted from the Roman naval headquarters at Misenum
Miseno is one of the ''frazioni'' of the municipality of Bacoli in the Italian Province of Naples. Known in ancient Roman times as Misenum, it is the site of a great Roman port.
Geography
Nearby Cape Miseno marks the northwestern end of the Ba ...
and housed in the nearby ''Castra Misenatium'', were used to work the ''velarium
A ("curtain") was a type of awning used in Roman times. It stretched over the whole of the , the seating area in amphitheaters to protect spectators from the sun. Precisely how the awning was supported is a matter of conjecture.Suetonius, '' L ...
''.
 The Colosseum's huge crowd capacity made it essential that the venue could be filled or evacuated quickly. Its architects adopted solutions very similar to those used in modern stadia to deal with the same problem. The amphitheatre was ringed by eighty entrances at ground level, 76 of which were used by ordinary spectators. Each entrance and exit was numbered, as was each staircase. The northern main entrance was reserved for the Roman Emperor and his aides, whilst the other three axial entrances were most likely used by the elite. All four axial entrances were richly decorated with painted stucco reliefs, of which fragments survive. Many of the original outer entrances have disappeared with the collapse of the perimeter wall, but entrances XXIII (23) to LIIII (54) survive.
Spectators were given tickets in the form of numbered pottery shards, which directed them to the appropriate section and row. They accessed their seats via '' vomitoria'' (singular ''vomitorium''), passageways that opened into a tier of seats from below or behind. These quickly dispersed people into their seats and, upon conclusion of the event or in an emergency evacuation, could permit their exit within only a few minutes. The name ''vomitoria'' derived from the Latin word for a rapid discharge, from which English derives the word vomit.
The Colosseum's huge crowd capacity made it essential that the venue could be filled or evacuated quickly. Its architects adopted solutions very similar to those used in modern stadia to deal with the same problem. The amphitheatre was ringed by eighty entrances at ground level, 76 of which were used by ordinary spectators. Each entrance and exit was numbered, as was each staircase. The northern main entrance was reserved for the Roman Emperor and his aides, whilst the other three axial entrances were most likely used by the elite. All four axial entrances were richly decorated with painted stucco reliefs, of which fragments survive. Many of the original outer entrances have disappeared with the collapse of the perimeter wall, but entrances XXIII (23) to LIIII (54) survive.
Spectators were given tickets in the form of numbered pottery shards, which directed them to the appropriate section and row. They accessed their seats via '' vomitoria'' (singular ''vomitorium''), passageways that opened into a tier of seats from below or behind. These quickly dispersed people into their seats and, upon conclusion of the event or in an emergency evacuation, could permit their exit within only a few minutes. The name ''vomitoria'' derived from the Latin word for a rapid discharge, from which English derives the word vomit.
Interior seating
 According to the Codex-Calendar of 354, the Colosseum could accommodate 87,000 people, although modern estimates put the figure at around 50,000. They were seated in a tiered arrangement that reflected the rigidly stratified nature of Roman society. Special boxes were provided at the north and south ends respectively for the Emperor and the
According to the Codex-Calendar of 354, the Colosseum could accommodate 87,000 people, although modern estimates put the figure at around 50,000. They were seated in a tiered arrangement that reflected the rigidly stratified nature of Roman society. Special boxes were provided at the north and south ends respectively for the Emperor and the Vestal Virgins
In ancient Rome, the Vestal Virgins or Vestals ( la, Vestālēs, singular ) were priestesses of Vesta, virgin goddess of Rome's sacred hearth and its flame.
The Vestals were unlike any other public priesthood. They were chosen before puberty ...
, providing the best views of the arena. Flanking them at the same level was a broad platform or ''podium'' for the senatorial
A senate is a deliberative assembly, often the upper house or chamber of a bicameral legislature. The name comes from the ancient Roman Senate (Latin: ''Senatus''), so-called as an assembly of the senior (Latin: ''senex'' meaning "the e ...
class, who were allowed to bring their own chairs. The names of some 5th century senators can still be seen carved into the stonework, presumably reserving areas for their use.
 The tier above the senators, known as the ''maenianum primum'', was occupied by the non-senatorial noble class or knights ('' equites''). The next level up, the ''maenianum secundum'', was originally reserved for ordinary Roman citizens (''
The tier above the senators, known as the ''maenianum primum'', was occupied by the non-senatorial noble class or knights ('' equites''). The next level up, the ''maenianum secundum'', was originally reserved for ordinary Roman citizens (''plebeians
In ancient Rome, the plebeians (also called plebs) were the general body of free Roman citizens who were not patricians, as determined by the census, or in other words " commoners". Both classes were hereditary.
Etymology
The precise origins of ...
'') and was divided into two sections. The lower part (the ''immum'') was for wealthy citizens, while the upper part (the ''summum'') was for poor citizens. Specific sectors were provided for other social groups: for instance, boys with their tutors, soldiers on leave, foreign dignitaries, scribes, heralds, priests and so on. Stone (and later marble) seating was provided for the citizens and nobles, who presumably would have brought their own cushions with them. Inscriptions identified the areas reserved for specific groups.
Another level, the ''maenianum secundum in legneis'', was added at the very top of the building during the reign of Domitian
Domitian (; la, Domitianus; 24 October 51 – 18 September 96) was a Roman emperor who reigned from 81 to 96. The son of Vespasian and the younger brother of Titus, his two predecessors on the throne, he was the last member of the Fl ...
. This comprised a gallery for the common poor, slaves and women. It would have been either standing room only, or would have had very steep wooden benches. Some groups were banned altogether from the Colosseum, notably gravediggers, actors and former gladiators.
Each tier was divided into sections (''maeniana'') by curved passages and low walls (''praecinctiones'' or ''baltei''), and were subdivided into ''cunei'', or wedges, by the steps and aisles from the vomitoria. Each row (''gradus'') of seats was numbered, permitting each individual seat to be exactly designated by its gradus, cuneus, and number.
Arena and hypogeum
hypogeum
A hypogeum or hypogaeum (plural hypogea or hypogaea, pronounced ; literally meaning "underground", from Greek ''hypo'' (under) and ''ghê'' (earth)) is an underground temple or tomb.
Hypogea will often contain niches for cremated human rem ...
'' (literally meaning "underground"). The hypogeum was not part of the original construction but was ordered to be built by Emperor Domitian
Domitian (; la, Domitianus; 24 October 51 – 18 September 96) was a Roman emperor who reigned from 81 to 96. The son of Vespasian and the younger brother of Titus, his two predecessors on the throne, he was the last member of the Fl ...
. Little now remains of the original arena floor, but the ''hypogeum'' is still clearly visible. It consisted of a two-level subterranean network of tunnels and cages beneath the arena where gladiators and animals were held before contests began. Eighty vertical shafts provided instant access to the arena for caged animals and scenery pieces concealed underneath; larger hinged platforms, called ''hegmata'', provided access for elephants and the like. It was restructured on numerous occasions; at least twelve different phases of construction can be seen.
 The ''hypogeum'' was connected by tunnels to a number of points outside the Colosseum. Animals and performers were brought through the tunnel from nearby stables, with the gladiators' barracks at the
The ''hypogeum'' was connected by tunnels to a number of points outside the Colosseum. Animals and performers were brought through the tunnel from nearby stables, with the gladiators' barracks at the Ludus Magnus
The Ludus Magnus (also known as the Great Gladiatorial Training School) was the largest of the gladiatorial schools in Rome. It was built by the emperor Domitian (r. 81–96 C.E.) in the late first century C.E., alongside other building projects u ...
to the east also being connected by tunnels. Separate tunnels were provided for the Emperor and the Vestal Virgins
In ancient Rome, the Vestal Virgins or Vestals ( la, Vestālēs, singular ) were priestesses of Vesta, virgin goddess of Rome's sacred hearth and its flame.
The Vestals were unlike any other public priesthood. They were chosen before puberty ...
to permit them to enter and exit the Colosseum without needing to pass through the crowds.
Substantial quantities of machinery also existed in the ''hypogeum''. Elevators and pulleys raised and lowered scenery and props, as well as lifting caged animals to the surface for release. There is evidence for the existence of major hydraulic
Hydraulics (from Greek: Υδραυλική) is a technology and applied science using engineering, chemistry, and other sciences involving the mechanical properties and use of liquids. At a very basic level, hydraulics is the liquid counte ...
mechanisms and according to ancient accounts, it was possible to flood the arena rapidly, presumably via a connection to a nearby aqueduct. However, the construction of the hypogeum at Domitian's behest put an end to the practise of flooding, and thus also to naval battles, early in the Colosseum's existence.
Supporting buildings
The Colosseum and its activities supported a substantial industry in the area. In addition to the amphitheatre itself, many other buildings nearby were linked to the games. Immediately to the east is the remains of the ''Ludus Magnus
The Ludus Magnus (also known as the Great Gladiatorial Training School) was the largest of the gladiatorial schools in Rome. It was built by the emperor Domitian (r. 81–96 C.E.) in the late first century C.E., alongside other building projects u ...
'', a training school for gladiators. This was connected to the Colosseum by an underground passage, to allow easy access for the gladiators. The ''Ludus Magnus'' had its own miniature training arena, which was itself a popular attraction for Roman spectators. Other training schools were in the same area, including the ''Ludus Matutinus'' (Morning School), where fighters of animals were trained, plus the Dacian and Gallic Schools.
Also nearby were the ''Armamentarium'', comprising an armory to store weapons; the ''Summum Choragium'', where machinery was stored; the ''Sanitarium'', which had facilities to treat wounded gladiators; and the ''Spoliarium'', where bodies of dead gladiators were stripped of their armor and disposed of.
Around the perimeter of the Colosseum, at a distance of 18 m (59 ft) from the perimeter, was a series of tall stone posts, with five remaining on the eastern side. Various explanations have been advanced for their presence; they may have been a religious boundary, or an outer boundary for ticket checks, or an anchor for the ''velarium
A ("curtain") was a type of awning used in Roman times. It stretched over the whole of the , the seating area in amphitheaters to protect spectators from the sun. Precisely how the awning was supported is a matter of conjecture.Suetonius, '' L ...
'' or awning.
Use
 The Colosseum was used to host gladiatorial shows as well as a variety of other events. The shows, called ''
The Colosseum was used to host gladiatorial shows as well as a variety of other events. The shows, called ''munera
Munera is a town and municipality in the province of Albacete, Spain; part of the autonomous community
eu, autonomia erkidegoa
ca, comunitat autònoma
gl, comunidade autónoma
oc, comunautat autonòma
an, comunidat autonoma
ast, comuni ...
'', were always given by private individuals rather than the state. They had a strong religious element but were also demonstrations of power and family prestige, and were immensely popular with the population. Another popular type of show was the animal hunt, or ''venatio
Venatio ( la, venatio, "hunting", plural ''venationes'') was a type of entertainment in Roman amphitheaters involving the hunting and killing of wild animals.
History
Venatio was first introduced by Marcus Fulvius Nobilior, who celebrated his ...
''. This utilized a great variety of wild beasts, mainly imported from Africa and the Middle East, and included creatures such as rhinoceros
A rhinoceros (; ; ), commonly abbreviated to rhino, is a member of any of the five extant species (or numerous extinct species) of odd-toed ungulates in the family Rhinocerotidae. (It can also refer to a member of any of the extinct species ...
, hippopotamus
The hippopotamus ( ; : hippopotamuses or hippopotami; ''Hippopotamus amphibius''), also called the hippo, common hippopotamus, or river hippopotamus, is a large semiaquatic mammal native to sub-Saharan Africa. It is one of only two extan ...
es, elephant
Elephants are the largest existing land animals. Three living species are currently recognised: the African bush elephant, the African forest elephant, and the Asian elephant. They are the only surviving members of the family Elephantidae ...
s, giraffes, aurochs, wisent
The European bison (''Bison bonasus'') or the European wood bison, also known as the wisent ( or ), the zubr (), or sometimes colloquially as the European buffalo, is a European species of bison. It is one of two extant species of bison, along ...
s, Barbary lion
The Barbary lion, also called the North African lion, Berber lion, Atlas lion, and Egyptian lion, is an extinct population of the lion subspecies '' Panthera leo leo''. It lived in the mountains and deserts of the Barbary Coast of North Africa, ...
s, panthers
Panther may refer to:
Large cats
*Pantherinae, the cat subfamily that contains the genera ''Panthera'' and ''Neofelis''
**''Panthera'', the cat genus that contains tigers, lions, jaguars and leopards.
***Jaguar (''Panthera onca''), found in Sout ...
, leopards, bears
Bears are carnivoran mammals of the family Ursidae. They are classified as caniforms, or doglike carnivorans. Although only eight species of bears are extant, they are widespread, appearing in a wide variety of habitats throughout the Nor ...
, Caspian tiger
The Caspian tiger was a ''Panthera tigris tigris'' population native to eastern Turkey, northern Iran, Mesopotamia, the Caucasus around the Caspian Sea, Central Asia to northern Afghanistan, and the Xinjiang region in western China. Until the M ...
s, crocodiles and ostrich
Ostriches are large flightless birds of the genus ''Struthio'' in the order Struthioniformes, part of the infra-class Palaeognathae, a diverse group of flightless birds also known as ratites that includes the emus, rheas, and kiwis. There ...
es. Battles and hunts were often staged amid elaborate sets with movable trees and buildings. Such events were occasionally on a huge scale; Trajan
Trajan ( ; la, Caesar Nerva Traianus; 18 September 539/11 August 117) was Roman emperor from 98 to 117. Officially declared ''optimus princeps'' ("best ruler") by the senate, Trajan is remembered as a successful soldier-emperor who presi ...
is said to have celebrated his victories in Dacia
Dacia (, ; ) was the land inhabited by the Dacians, its core in Transylvania, stretching to the Danube in the south, the Black Sea in the east, and the Tisza in the west. The Carpathian Mountains were located in the middle of Dacia. It ...
in 107 with contests involving 11,000 animals and 10,000 gladiators over the course of 123 days. During lunch intervals, executions '' ad bestias'' would be staged. Those condemned to death would be sent into the arena, naked and unarmed, to face the beasts of death which would literally tear them to pieces. Other performances would also take place by acrobats and magicians, typically during the intervals. During the early days of the Colosseum, ancient writers recorded that the building was used for ''
During the early days of the Colosseum, ancient writers recorded that the building was used for ''naumachia
The naumachia (in Latin , from the Ancient Greek /, literally "naval combat") in the Ancient Roman world referred to both the staging of naval battles as mass entertainment, and the basin or building in which this took place.
Early
The fir ...
e'' (more properly known as ''navalia proelia'') or simulated sea battles. Accounts of the inaugural games held by Titus in AD 80 describe it being filled with water for a display of specially trained swimming horses and bulls. There is also an account of a re-enactment of a famous sea battle between the Corcyrean (Corfiot) Greeks and the Corinthians
The First Epistle to the Corinthians ( grc, Α΄ ᾽Επιστολὴ πρὸς Κορινθίους) is one of the Pauline epistles, part of the New Testament of the Christian Bible. The epistle is attributed to Paul the Apostle and a co-aut ...
. This has been the subject of some debate among historians; although providing the water would not have been a problem, it is unclear how the arena could have been waterproofed, nor would there have been enough space in the arena for the warships to move around. It has been suggested that the reports either have the location wrong or that the Colosseum originally featured a wide floodable channel down its central axis (which would later have been replaced by the hypogeum
A hypogeum or hypogaeum (plural hypogea or hypogaea, pronounced ; literally meaning "underground", from Greek ''hypo'' (under) and ''ghê'' (earth)) is an underground temple or tomb.
Hypogea will often contain niches for cremated human rem ...
).
''Sylvae'' or recreations of natural scenes were also held in the arena. Painters, technicians and architects would construct a simulation of a forest with real trees and bushes planted in the arena's floor, and animals would then be introduced. Such scenes might be used simply to display a natural environment for the urban population, or could otherwise be used as the backdrop for hunts or dramas depicting episodes from mythology. They were also occasionally used for executions in which the hero of the story – played by a condemned person – was killed in one of various gruesome but mythologically authentic ways, such as being mauled by beasts or burned to death.
Modern use
 The Colosseum today is a major tourist attraction in Rome with thousands of tourists each year entering to view the interior arena. There is now a museum dedicated to
The Colosseum today is a major tourist attraction in Rome with thousands of tourists each year entering to view the interior arena. There is now a museum dedicated to Eros
In Greek mythology, Eros (, ; grc, Ἔρως, Érōs, Love, Desire) is the Greek god of love and sex. His Roman counterpart was Cupid ("desire").''Larousse Desk Reference Encyclopedia'', The Book People, Haydock, 1995, p. 215. In the ear ...
in the upper floor of the outer wall of the building. Part of the arena floor has been re-floored. Beneath the Colosseum, a network of subterranean passageways once used to transport wild animals and gladiators to the arena opened to the public in summer 2010.
The Colosseum is also the site of Roman Catholic ceremonies in the 20th and 21st centuries. For instance, Pope Benedict XVI
Pope Benedict XVI ( la, Benedictus XVI; it, Benedetto XVI; german: link=no, Benedikt XVI.; born Joseph Aloisius Ratzinger, , on 16 April 1927) is a retired prelate of the Catholic church who served as the head of the Church and the soverei ...
led the Stations of the Cross called the Scriptural Way of the Cross (which calls for more meditation) at the Colosseum on Good Fridays.
Restoration
 In 2011 Diego Della Valle, head of the shoe firm Tod's, entered into an agreement with local officials to sponsor a €25 million restoration of the Colosseum. Work was planned to begin at the end of 2011, taking up to two and a half years. Due to the controversial nature of using a public–private partnership to fund the restoration, work was delayed and began in 2013. The restoration is the first full cleaning and repair in the Colosseum's history. The first stage is to clean and restore the Colosseum's arcaded façade and replace the metal enclosures that block the ground-level arches. After three years, the work was completed on 1 July 2016, when the Italian minister of culture, Dario Franceschini, also announced that the funds have been committed to replace the floors by the end of 2018. These will provide a stage that Franceschini says will be used for "cultural events of the highest level." The project also includes creating a services center and restoring the galleries and underground spaces inside the Colosseum. Since 1 November 2017, the top two levels have been opened for guided visits. The fourth level held the marketplace, and the top fifth tier is where the poorest citizens, the plebeians, gathered and watched the show, bringing picnics for the day-long event.
In 2011 Diego Della Valle, head of the shoe firm Tod's, entered into an agreement with local officials to sponsor a €25 million restoration of the Colosseum. Work was planned to begin at the end of 2011, taking up to two and a half years. Due to the controversial nature of using a public–private partnership to fund the restoration, work was delayed and began in 2013. The restoration is the first full cleaning and repair in the Colosseum's history. The first stage is to clean and restore the Colosseum's arcaded façade and replace the metal enclosures that block the ground-level arches. After three years, the work was completed on 1 July 2016, when the Italian minister of culture, Dario Franceschini, also announced that the funds have been committed to replace the floors by the end of 2018. These will provide a stage that Franceschini says will be used for "cultural events of the highest level." The project also includes creating a services center and restoring the galleries and underground spaces inside the Colosseum. Since 1 November 2017, the top two levels have been opened for guided visits. The fourth level held the marketplace, and the top fifth tier is where the poorest citizens, the plebeians, gathered and watched the show, bringing picnics for the day-long event.
Significance in Christianity
The Colosseum is generally regarded by Christians as a site of the martyrdom of large numbers of believers during the persecution of Christians in the Roman Empire, as evidenced by Church history and tradition. On the other hand, other scholars believe that the majority of martyrdoms may have occurred at other venues within the city of Rome, rather than at the Colosseum, citing a lack of still-intact physical evidence or historical records. These scholars assert that "some Christians were executed as common criminals in the Colosseum—their crime being refusal to reverence the Roman gods", but most Christian martyrs of the early Church were executed for their faith at the Circus Maximus. According to Irenaeus (died about 202), Ignatius of Antioch was fed to the lions in Rome around 107 A.D and although Irenaeus says nothing about this happening at the Colosseum, tradition ascribes it to that place. In the Middle Ages, the Colosseum was not regarded as a monument, and was used as what some modern sources label a "quarry," which is to say that stones from the Colosseum were taken for the building of other sacred sites. This fact is used to support the idea that, at a time when sites associated with martyrs were highly venerated the Colosseum was not being treated as a sacred site. It was not included in the itineraries compiled for the use of pilgrims nor in works such as the 12th century ''Mirabilia Urbis Romae'' ("Marvels of the City of Rome"), which claims the Circus Flaminius – but not the Colosseum – as the site of martyrdoms. Part of the structure was inhabited by a Religious order#Christian tradition, Christian religious order, but it is not known whether this was for any particular religious reason. Pope Pius V (1566–1572) is said to have recommended that pilgrims gather sand from the arena of the Colosseum to serve as a relic, on the grounds that it was impregnated with the blood of martyrs, although some of his contemporaries did not share his conviction. A century later Fioravante Martinelli listed the Colosseum at the head of a list of places sacred to the martyrs in his 1653 book ''Roma ex ethnica sacra''. Martinelli's book evidently had an effect on public opinion; in response to Cardinal Altieri's proposal some years later to turn the Colosseum into a bullring, Carlo Tomassi published a pamphlet in protest against what he regarded as an act of desecration. The ensuing controversy persuaded Pope Clement X to close the Colosseum's external arcades and declare it a sanctuary.The amphitheater, one consecrated to triumphs, entertainments, and the impious worship of pagan gods, is now dedicated to the sufferings of the martyrs purified from impious superstitions.Other Christian crosses stand in several points around the arena and every Good Friday the Pope leads a Via Crucis procession to the amphitheater.
Flora
 The Colosseum has a wide and well-documented history of Flora (plants), flora ever since Domenico Panaroli made the first catalogue of its plants in 1643. Since then, 684 species have been identified there. The peak was in 1855 (420 species). Attempts were made in 1871 to eradicate the vegetation, because of concerns over the damage that was being caused to the masonry, but much of it has returned. 242 species have been counted today and of the species first identified by Panaroli, 200 remain.
The variation of plants can be explained by the change of climate in Rome through the centuries. Additionally, bird migration, flower blooming, and the growth of Rome that caused the Colosseum to become embedded within the modern city centre rather than on the outskirts of the ancient city, as well as deliberate transport of species, are also contributing causes. Another reason often given is their seeds being unwittingly transported either on the fur or in the feces of animals brought there from all corners of the empire.
The Colosseum has a wide and well-documented history of Flora (plants), flora ever since Domenico Panaroli made the first catalogue of its plants in 1643. Since then, 684 species have been identified there. The peak was in 1855 (420 species). Attempts were made in 1871 to eradicate the vegetation, because of concerns over the damage that was being caused to the masonry, but much of it has returned. 242 species have been counted today and of the species first identified by Panaroli, 200 remain.
The variation of plants can be explained by the change of climate in Rome through the centuries. Additionally, bird migration, flower blooming, and the growth of Rome that caused the Colosseum to become embedded within the modern city centre rather than on the outskirts of the ancient city, as well as deliberate transport of species, are also contributing causes. Another reason often given is their seeds being unwittingly transported either on the fur or in the feces of animals brought there from all corners of the empire.
In popular culture
The Colosseum has appeared in numerous films, artworks and games. It's featured in movies such as ''Roman Holiday'', ''Gladiator (2000 film), Gladiator'', ''The Way of the Dragon'', ''The Core'' and ''Jumper (2008 film), Jumper'' and games like Assassin's Creed: Brotherhood, Ryse: Son of Rome and Forge of Empires. Several architectural works have also been modelled on or inspired by, the Colosseum. These include: * The ''Kongresshalle'', or "Congress Hall", (1935, unfinished) at the Nazi Party Rally grounds, Nuremberg, Germany * The Summer Olympic Games Olympic medal, medal from 1928 to 2000, designed by Giuseppe Cassioli, features a depiction of the Colosseum. At the 2004 Summer Olympics in Athens the Colosseum was replaced by a depiction of the Panathinaiko Stadium * The exterior of the Vancouver Public Library in British Columbia resembles the current state of the Colosseum. It was designed by Moshe Safdie. * The Los Angeles Memorial Coliseum entrance was inspired by the Colosseum. * The Palazzo della Civilta Italiana was very closely modelled on the Colosseum. It was built for Mussolini for the Universal Exhibition of 1942 but the exhibition never happened due to the outbreak of World War II. The architects were Giovanni Guerrini, Ernesto Bruno La Padula, and Mario Romano. * McCaig's Tower, overlooking Oban, Scotland.Gallery
See also
* * *References
Notes
Bibliography
* * *External links
*Virtual tour of the Colosseum
A 3D model of Colosseum on Sketchfab
* *
3D model of the past and present of the colosseum – The Only Progress is Human
{{DEFAULTSORT:Flavian Amphitheatre Amphitheatres in Rome Building projects of the Flavian dynasty Roman archaeology Ruins in Italy National museums of Italy Round buildings Roman amphitheatres in Italy 1st-century establishments in Italy 80s establishments in the Roman Empire Rome R. XIX Celio Titus Vespasian 80 Buildings and structures completed in the 1st century World Heritage Sites in Italy Outdoor arenas