Colombo Museum Rajendra Chola II Inscription, 1054-1063 AD on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Colombo ( ; si, කොළඹ, translit=Koḷam̆ba, ; ta, கொழும்பு, translit=Koḻumpu, ) is the executive and judicial
Colombo Hotels and City Guide
This coincides with
 In 1638 the
In 1638 the
 Although the British captured Colombo in 1796, it remained a
Although the British captured Colombo in 1796, it remained a
 This era of colonialism ended peacefully in 1948 when Ceylon gained independence from Britain.
Due to the tremendous impact this caused on the city's inhabitants and on the country as a whole, the changes that resulted at the end of the colonial period were drastic. An entire new culture took root. Changes in laws and customs, clothing styles, religions and
This era of colonialism ended peacefully in 1948 when Ceylon gained independence from Britain.
Due to the tremendous impact this caused on the city's inhabitants and on the country as a whole, the changes that resulted at the end of the colonial period were drastic. An entire new culture took root. Changes in laws and customs, clothing styles, religions and
Embassies located in Sri Lanka
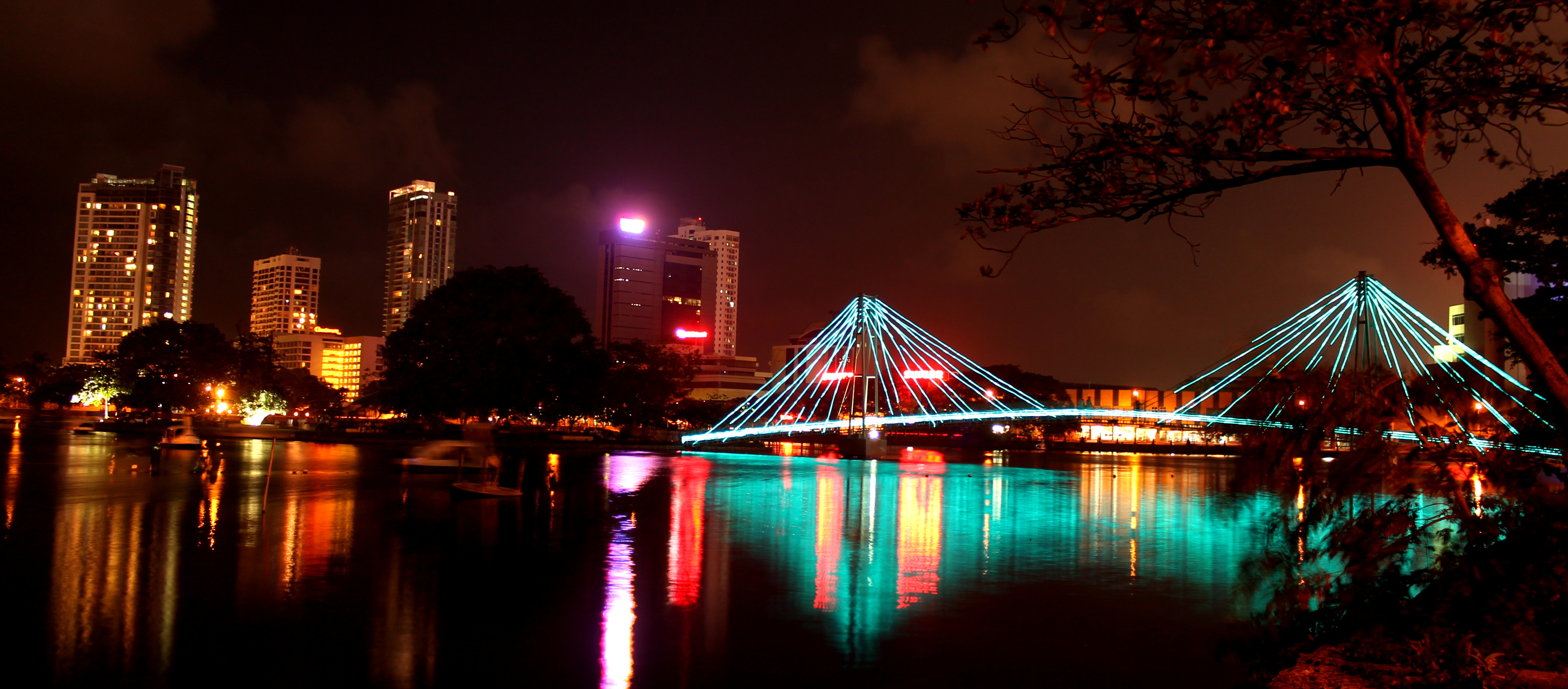 Colombo's geography is a mix of land and water. The city has many canals and, in the heart of the city, the
Colombo's geography is a mix of land and water. The city has many canals and, in the heart of the city, the
, ''Lanka Library'' The lake is one of the most distinctive landmarks of Colombo and was used for centuries by colonists to defend the city. It remains a tourist attraction, hosting


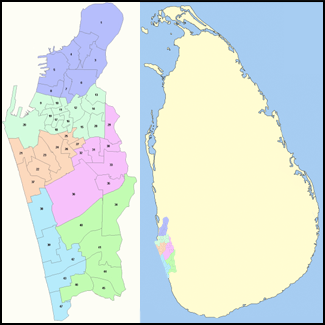
 Colombo is divided into 15 numbered areas for the purposes of postal services. Within these areas are the suburbs with their corresponding post office.
Colombo is divided into 15 numbered areas for the purposes of postal services. Within these areas are the suburbs with their corresponding post office.
 The great majority of Sri Lankan corporations have their head offices in Colombo including Aitken Spence, Ceylinco Consolidated, Ceylinco Corporation, Stassen group of companies, John Keells Holdings, Cargills (Ceylon), Cargills, Hemas Holdings and Akbar Brothers. Some of the industries include chemicals, textiles, glass, cement, leather goods, furniture and jewellery. In the city centre is the World Trade Center Colombo, World Trade Centre. The 40-story Twin Tower complex is the centre of important commercial establishments, in the Fort district, the city's nerve centre. Right outside the Fort area is Pettah which is derived from the Sinhala word ''pita'' which means 'out' or 'outside'.
The great majority of Sri Lankan corporations have their head offices in Colombo including Aitken Spence, Ceylinco Consolidated, Ceylinco Corporation, Stassen group of companies, John Keells Holdings, Cargills (Ceylon), Cargills, Hemas Holdings and Akbar Brothers. Some of the industries include chemicals, textiles, glass, cement, leather goods, furniture and jewellery. In the city centre is the World Trade Center Colombo, World Trade Centre. The 40-story Twin Tower complex is the centre of important commercial establishments, in the Fort district, the city's nerve centre. Right outside the Fort area is Pettah which is derived from the Sinhala word ''pita'' which means 'out' or 'outside'.
 The Colombo Metropolitan area has a GDP (PPP) of $122 billion or 40% of the GDP, making it the most important aspect of the Sri Lankan economy. The per capita income of the Colombo Metro area stood at US$8623 and purchasing power per capita of $25,117, making it one of the most prosperous regions in South Asia. The Colombo Metropolitan (CM) area is the most important industrial, commercial and administrative centre in Sri Lanka. A major share of the country's export-oriented manufacturing takes place in the CM area, which is the engine of growth for Sri Lanka.
The Colombo Metropolitan area has a GDP (PPP) of $122 billion or 40% of the GDP, making it the most important aspect of the Sri Lankan economy. The per capita income of the Colombo Metro area stood at US$8623 and purchasing power per capita of $25,117, making it one of the most prosperous regions in South Asia. The Colombo Metropolitan (CM) area is the most important industrial, commercial and administrative centre in Sri Lanka. A major share of the country's export-oriented manufacturing takes place in the CM area, which is the engine of growth for Sri Lanka.
 The Western province contributes less than 40% to the GDP and about 80% of industrial value additions although it accounts for only 5.7% of the country's geographic area and 25% of the national population. Given its importance as the primary international gateway for Sri Lanka and as the main economic driver of the country, the government of Sri Lanka (GoSL) has launched an ambitious program to transform Colombo and its area into a metropolis of international standards. Bottlenecks are preventing the Colombo metropolitan area from realizing its full economic potential. To facilitate the transformation of Colombo, the government has to address these bottlenecks which have for long been obstructing economic and physical urban regeneration.
Pettah is more crowded than the Fort area. Pettah's roads are always packed and Sidewalk, pavements are full of small stalls selling items from delicious sharbat to shirts. Main Street consists mostly of clothes shops and the crossroads, which are known as Cross-Streets where each of the five streets specialises in a specific business. For example, First Cross Street is mostly electronics, electronic goods shops, the Second cellular phones and fancy goods. Most of these businesses are dominated by Muslim traders. At the end of Main Street further away from Fort is Sea Street – Sri Lanka's gold market – dominated by Tamil interests. This mile-long street is full of jewellery shops, including the former head office of SriLankan Airlines.
The Western province contributes less than 40% to the GDP and about 80% of industrial value additions although it accounts for only 5.7% of the country's geographic area and 25% of the national population. Given its importance as the primary international gateway for Sri Lanka and as the main economic driver of the country, the government of Sri Lanka (GoSL) has launched an ambitious program to transform Colombo and its area into a metropolis of international standards. Bottlenecks are preventing the Colombo metropolitan area from realizing its full economic potential. To facilitate the transformation of Colombo, the government has to address these bottlenecks which have for long been obstructing economic and physical urban regeneration.
Pettah is more crowded than the Fort area. Pettah's roads are always packed and Sidewalk, pavements are full of small stalls selling items from delicious sharbat to shirts. Main Street consists mostly of clothes shops and the crossroads, which are known as Cross-Streets where each of the five streets specialises in a specific business. For example, First Cross Street is mostly electronics, electronic goods shops, the Second cellular phones and fancy goods. Most of these businesses are dominated by Muslim traders. At the end of Main Street further away from Fort is Sea Street – Sri Lanka's gold market – dominated by Tamil interests. This mile-long street is full of jewellery shops, including the former head office of SriLankan Airlines.
 The Sri Lanka Police, the main law enforcement agency of the island, liaise with the municipal council but is under the control of the Ministry of Defence (Sri Lanka), Ministry of Defence of the central government. Policing in Colombo and its suburbs falls within the ''Metropolitan Range'' headed by the Deputy Inspector General of Police (Metropolitan), this also includes the Colombo Crime Division. As with most Sri Lankan cities, the magistrate court handles felony crimes, the district court handles civil cases.
As in other large cities around the world, Colombo experiences certain levels of street crime and bribery. Indeed, the corruption extends to the very top, US reports show. In addition, in the period from the 1980s to 2009, there have been a number of major terrorist attacks. The LTTE has been linked to most of the bombings and assassinations in the city. Welikada Prison is situated in Colombo and it is one of the largest maximum-security prisons in the country.
The Sri Lanka Police, the main law enforcement agency of the island, liaise with the municipal council but is under the control of the Ministry of Defence (Sri Lanka), Ministry of Defence of the central government. Policing in Colombo and its suburbs falls within the ''Metropolitan Range'' headed by the Deputy Inspector General of Police (Metropolitan), this also includes the Colombo Crime Division. As with most Sri Lankan cities, the magistrate court handles felony crimes, the district court handles civil cases.
As in other large cities around the world, Colombo experiences certain levels of street crime and bribery. Indeed, the corruption extends to the very top, US reports show. In addition, in the period from the 1980s to 2009, there have been a number of major terrorist attacks. The LTTE has been linked to most of the bombings and assassinations in the city. Welikada Prison is situated in Colombo and it is one of the largest maximum-security prisons in the country.
 Colombo has most of the amenities that a modern city has. Compared to other parts of the country, Colombo has the highest degree of infrastructure. Electricity, water and transport to street lights and phone booths are to a considerably good standard. The majority of the major shopping malls in Sri Lanka are in the city, of which all are Wi-Fi enabled. Apart from that, many luxurious hotels, clubs and restaurants are in the city. In recent times there has been an outpour of high-rise condominiums, mainly due to the very high land prices.
Colombo has most of the amenities that a modern city has. Compared to other parts of the country, Colombo has the highest degree of infrastructure. Electricity, water and transport to street lights and phone booths are to a considerably good standard. The majority of the major shopping malls in Sri Lanka are in the city, of which all are Wi-Fi enabled. Apart from that, many luxurious hotels, clubs and restaurants are in the city. In recent times there has been an outpour of high-rise condominiums, mainly due to the very high land prices.
 Port of Colombo, Colombo Harbour is the largest and one of the busiest ports in Sri Lanka. Colombo was established primarily as a port city during the colonial era, with an artificial harbour that has been expanded over the years. The Sri Lanka Navy maintains a naval base, ''SLNS Rangalla'', within the harbour.
The Port of Colombo handled 3.75 million twenty-foot equivalent units in 2008, 10.6% up on 2007 (which itself was 9.7% up on 2006), bucking the global economic trend. Of those, 817,000 were local shipments with the rest transshipments. With a capacity of 5.7 million TEUs and a dredged depth of over 15 m (49 ft), the Colombo Harbour is one of the busiest ports in the world and ranks among the top 25 ports (23rd).
Colombo is part of the 21st Century Maritime Silk Road that runs from the Chinese coast to the Upper Adriatic region with its rail connections to Central Europe, Central and Eastern Europe.
Port of Colombo, Colombo Harbour is the largest and one of the busiest ports in Sri Lanka. Colombo was established primarily as a port city during the colonial era, with an artificial harbour that has been expanded over the years. The Sri Lanka Navy maintains a naval base, ''SLNS Rangalla'', within the harbour.
The Port of Colombo handled 3.75 million twenty-foot equivalent units in 2008, 10.6% up on 2007 (which itself was 9.7% up on 2006), bucking the global economic trend. Of those, 817,000 were local shipments with the rest transshipments. With a capacity of 5.7 million TEUs and a dredged depth of over 15 m (49 ft), the Colombo Harbour is one of the busiest ports in the world and ranks among the top 25 ports (23rd).
Colombo is part of the 21st Century Maritime Silk Road that runs from the Chinese coast to the Upper Adriatic region with its rail connections to Central Europe, Central and Eastern Europe.
 Train transport Sri Lanka Railways#Commuter Rail, in the city is limited since most trains are meant for transport to and from the city rather than within it and are often overcrowded. However, the Central Bus Stand and Fort Railway Station (Colombo), Fort Railway Station function as the island's primary hub for bus and rail transport respectively. Up until the 1970s, the city had
Train transport Sri Lanka Railways#Commuter Rail, in the city is limited since most trains are meant for transport to and from the city rather than within it and are often overcrowded. However, the Central Bus Stand and Fort Railway Station (Colombo), Fort Railway Station function as the island's primary hub for bus and rail transport respectively. Up until the 1970s, the city had
 Ratmalana Airport is the city's airport, located south of the city centre. It commenced operating in 1935 and was the country's first international airport until it was replaced by Bandaranaike Airport in 1967. Ratmalana Airport now primarily services domestic flights, aviation training and international corporate flights.
Ratmalana Airport is the city's airport, located south of the city centre. It commenced operating in 1935 and was the country's first international airport until it was replaced by Bandaranaike Airport in 1967. Ratmalana Airport now primarily services domestic flights, aviation training and international corporate flights.
 The two World Trade Center Colombo, World Trade Centre towers used to be the most recognised landmarks of the city. Before they were completed in 1997, the adjacent Bank of Ceylon tower was the tallest structure and the most prominent city landmark. Before the skyscrapers were built, the Old Parliament Building that stood in the Fort district with the Old Colombo Lighthouse close to it used to be the tallest building. Another important landmark is the Independence Commemoration Hall (Sri Lanka), Independence Hall at Independence Square in Cinnamon Gardens.
Even before the parliament was built some claim that the Jami Ul-Alfar Mosque was recognised as the landmark of Colombo by sailors approaching the port. The mosque is still one of the most visited tourist sites in Colombo.
Another landmark is St.Paul's Church Milagiriya, one of the oldest church (building), churches in Sri Lanka, first built by the Portuguese and rebuilt by the British in 1848. The Cargills & Millers building in Fort is also a protected building of historical significance.
The Galle Face Green is the city's largest promenade. Lined with coconut trees and adjacent to the coast. The Green frequently hosts international and local concerts and performances, such as the World Drum Festival.
Cannons that were once mounted on the rampart of the old fort of Colombo were laid out for observance and prestige at the Green. The colonial styled Galle Face Hotel, known as Asia's Emerald on the Green since 1864, is adjacent to Galle Face Green. The hotel has played host to guests such as the British Royal Family and other royal family, royal guests and celebrities. After a stay at the hotel, Alexandra, Countess of Frederiksborg, Princess Alexandra of Denmark commented that "the peacefulness and generosity encountered at the Galle Face Hotel cannot be matched." Also facing Galle Face Green is the Ceylon Inter-Continental Hotel.
The two World Trade Center Colombo, World Trade Centre towers used to be the most recognised landmarks of the city. Before they were completed in 1997, the adjacent Bank of Ceylon tower was the tallest structure and the most prominent city landmark. Before the skyscrapers were built, the Old Parliament Building that stood in the Fort district with the Old Colombo Lighthouse close to it used to be the tallest building. Another important landmark is the Independence Commemoration Hall (Sri Lanka), Independence Hall at Independence Square in Cinnamon Gardens.
Even before the parliament was built some claim that the Jami Ul-Alfar Mosque was recognised as the landmark of Colombo by sailors approaching the port. The mosque is still one of the most visited tourist sites in Colombo.
Another landmark is St.Paul's Church Milagiriya, one of the oldest church (building), churches in Sri Lanka, first built by the Portuguese and rebuilt by the British in 1848. The Cargills & Millers building in Fort is also a protected building of historical significance.
The Galle Face Green is the city's largest promenade. Lined with coconut trees and adjacent to the coast. The Green frequently hosts international and local concerts and performances, such as the World Drum Festival.
Cannons that were once mounted on the rampart of the old fort of Colombo were laid out for observance and prestige at the Green. The colonial styled Galle Face Hotel, known as Asia's Emerald on the Green since 1864, is adjacent to Galle Face Green. The hotel has played host to guests such as the British Royal Family and other royal family, royal guests and celebrities. After a stay at the hotel, Alexandra, Countess of Frederiksborg, Princess Alexandra of Denmark commented that "the peacefulness and generosity encountered at the Galle Face Hotel cannot be matched." Also facing Galle Face Green is the Ceylon Inter-Continental Hotel.
 Education institutions in Colombo have a long history. Colombo has many of the prominent Public school (UK), public schools in the country, some of them government-owned and others private. Most of the prominent schools in the city date back to the 1800s when they were established during the British colonial rule, such as the Royal College Colombo established in 1835. Certain urban schools of Sri Lanka have some religious alignment; this is partly due to the influence of the British, who established Christian missionary schools. These include the Anglican, Bishop's College (Sri Lanka), Bishop's College(1875); the Methodist, Wesley College Colombo (1874); the Buddhist, Ananda College (1886); the Muslim, Zahira College, Colombo, Zahira College (1892); the St. Benedict's College, Colombo (1985), the Catholic Church, Catholic, St. Joseph's College, Colombo, St. Joseph's College (1896). The religious alignments do not affect the curriculum of the school except for the demographics of the student population. Colombo has many International Schools that have come up in recent years.
Higher education in the city has a long history, beginning with the establishment of the Colombo Medical School (1870), the Sri Lanka Law College, Colombo Law College (1875), the School of Agriculture (1884) and the Government Technical College (1893). The first step in the creation of a university in Colombo was taken in 1913 with the establishment of the University College Colombo which prepared students for the University of London External System, external examinations of the University of London. This was followed by the establishment of the University of Ceylon in Colombo. Today the
Education institutions in Colombo have a long history. Colombo has many of the prominent Public school (UK), public schools in the country, some of them government-owned and others private. Most of the prominent schools in the city date back to the 1800s when they were established during the British colonial rule, such as the Royal College Colombo established in 1835. Certain urban schools of Sri Lanka have some religious alignment; this is partly due to the influence of the British, who established Christian missionary schools. These include the Anglican, Bishop's College (Sri Lanka), Bishop's College(1875); the Methodist, Wesley College Colombo (1874); the Buddhist, Ananda College (1886); the Muslim, Zahira College, Colombo, Zahira College (1892); the St. Benedict's College, Colombo (1985), the Catholic Church, Catholic, St. Joseph's College, Colombo, St. Joseph's College (1896). The religious alignments do not affect the curriculum of the school except for the demographics of the student population. Colombo has many International Schools that have come up in recent years.
Higher education in the city has a long history, beginning with the establishment of the Colombo Medical School (1870), the Sri Lanka Law College, Colombo Law College (1875), the School of Agriculture (1884) and the Government Technical College (1893). The first step in the creation of a university in Colombo was taken in 1913 with the establishment of the University College Colombo which prepared students for the University of London External System, external examinations of the University of London. This was followed by the establishment of the University of Ceylon in Colombo. Today the
 Colombo has widely varying architecture that spans centuries and depicts many styles. colonial architecture, Colonial buildings influenced by the Architecture of Portugal, Portuguese, Architecture of the Netherlands, Dutch and Architecture of the United Kingdom, British exist alongside structures built in Buddhist architecture, Buddhist, Hindu architecture, Hindu, Islamic architecture, Islamic, Architecture of India, Indian and Contemporary architecture, Contemporary architectural styles. No other place is this more evident than in the Fort area. Here, one may find new, towering skyscrapers as well as historic buildings dating far back as the 1700s.Colombo Fort
Colombo has widely varying architecture that spans centuries and depicts many styles. colonial architecture, Colonial buildings influenced by the Architecture of Portugal, Portuguese, Architecture of the Netherlands, Dutch and Architecture of the United Kingdom, British exist alongside structures built in Buddhist architecture, Buddhist, Hindu architecture, Hindu, Islamic architecture, Islamic, Architecture of India, Indian and Contemporary architecture, Contemporary architectural styles. No other place is this more evident than in the Fort area. Here, one may find new, towering skyscrapers as well as historic buildings dating far back as the 1700s.Colombo Fort
. Kermeey.blogspot.com (2006-02-19). Retrieved on 2011-10-17.
File:SL Colombo asv2020-01 img25 Cargills Building.jpg, The historical Cargills & Millers building continues as the headquarters of Cargills
File:Old Parliament Building, Colombo.JPG, The Old Parliament Building, Colombo, Old Parliament Building near the Galle Face Green, now the Presidential Secretariat (Sri Lanka), Presidential Secretariat
File:SL Colombo asv2020-01 img10 National Museum.jpg, The Neoclassical architecture, Neoclassical style Colombo National Museum
 Colombo's most popular festival is the celebration of Gautama Buddha, Buddha's birth, enlightenment and death all falling on the same day. In Sinhala this is known as ''Vesak''.
During this festival, much of the city is decorated with lanterns, lights and special displays of light (known as ''thoran''). The festival falls in mid-May and lasts a week. Many Sri Lankans visit the city to see the lantern competitions and decorations. During this week people distribute, rice, drinks and other food items for free in ''dunsal'' which means charity place. These ''dunsal'' are popular amongst visitors from the suburbs.
Since there is a large number of Muslims in Colombo. Eid Ul Fitr and Eid Ul Adha are two Islamic festivals that are celebrated in Colombo. Many businesses flourish during the eventual countdown for Eid Ul Fitr which is a major Islamic festival celebrated by Muslims after a month-long fasting. Colombo is generally very busy on the eve of the festivals as people do their last-minute shopping.
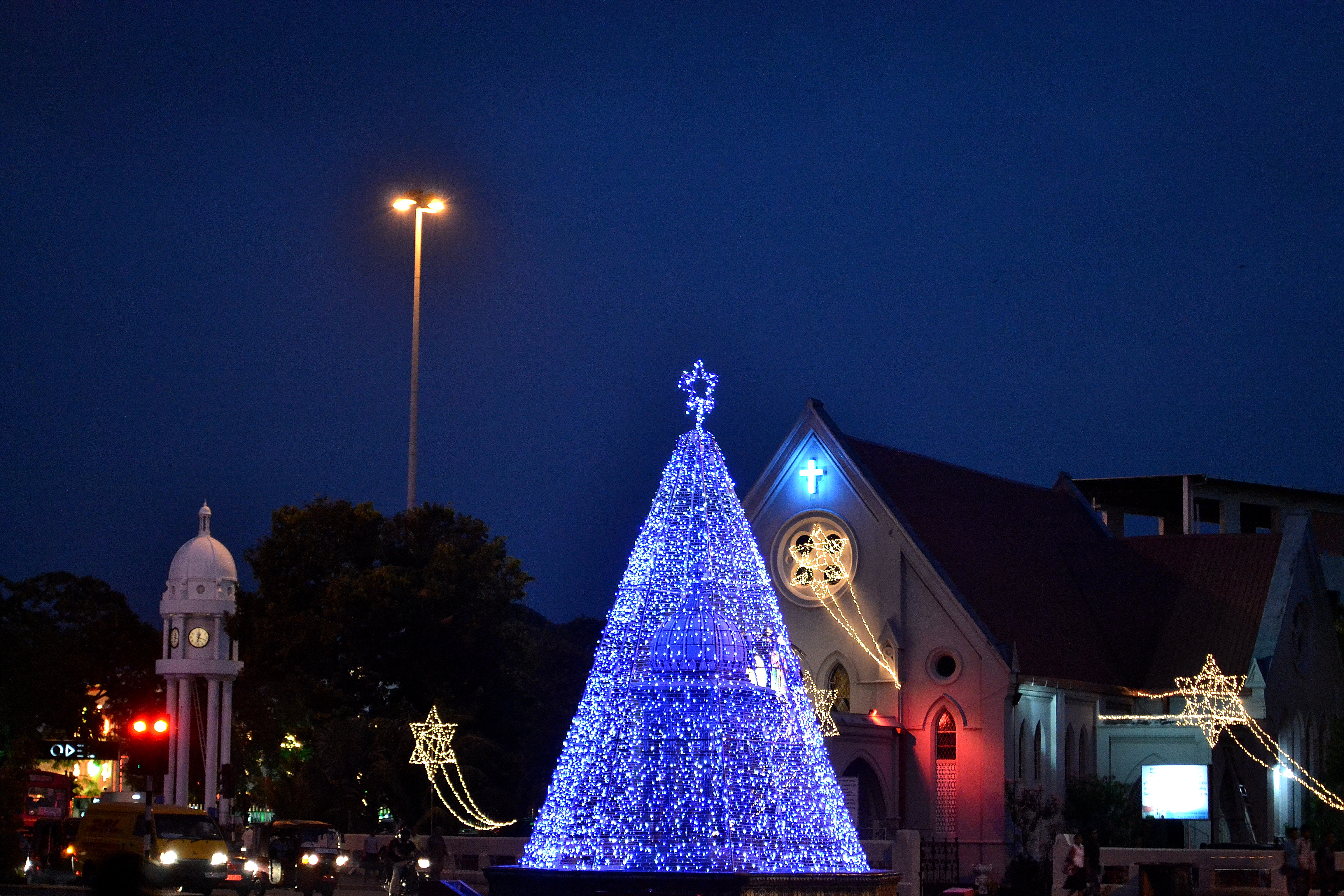
Christmas is another major festival. Although Sri Lanka's Christians make up only just over 7% of the population, Christmas is one of the island's biggest festivals. Most streets and commercial buildings light up from the beginning of December and festive sales begin at all shopping centres and department stores. Caroling and nativity plays are frequent sights during the season.
The Sinhalese and Hindu Aluth Awurudda' is a cultural event that takes place on 13 and 14 April. This is the celebration of the Sinhalese and Hindu new year. The festivities include many events and traditions that display a great deal of Sri Lankan culture.
Several old clubs of the city give a glimpse of the British equestrian lifestyle; these include the Colombo Club, Orient Club, the 80 Club, and the Colombo Cricket Club.
Colombo's most popular festival is the celebration of Gautama Buddha, Buddha's birth, enlightenment and death all falling on the same day. In Sinhala this is known as ''Vesak''.
During this festival, much of the city is decorated with lanterns, lights and special displays of light (known as ''thoran''). The festival falls in mid-May and lasts a week. Many Sri Lankans visit the city to see the lantern competitions and decorations. During this week people distribute, rice, drinks and other food items for free in ''dunsal'' which means charity place. These ''dunsal'' are popular amongst visitors from the suburbs.
Since there is a large number of Muslims in Colombo. Eid Ul Fitr and Eid Ul Adha are two Islamic festivals that are celebrated in Colombo. Many businesses flourish during the eventual countdown for Eid Ul Fitr which is a major Islamic festival celebrated by Muslims after a month-long fasting. Colombo is generally very busy on the eve of the festivals as people do their last-minute shopping.
Christmas is another major festival. Although Sri Lanka's Christians make up only just over 7% of the population, Christmas is one of the island's biggest festivals. Most streets and commercial buildings light up from the beginning of December and festive sales begin at all shopping centres and department stores. Caroling and nativity plays are frequent sights during the season.
The Sinhalese and Hindu Aluth Awurudda' is a cultural event that takes place on 13 and 14 April. This is the celebration of the Sinhalese and Hindu new year. The festivities include many events and traditions that display a great deal of Sri Lankan culture.
Several old clubs of the city give a glimpse of the British equestrian lifestyle; these include the Colombo Club, Orient Club, the 80 Club, and the Colombo Cricket Club.
 Colombo has several performing arts centres, which are popular for their musical and theatrical performances, including the Lionel Wendt Art Centre, Lionel Wendt Theatre, the Elphinstone, and Tower Hall, all of which were made for western-style productions. The Navarangahala found in the city is the country's first national theatre (structure), theatre designed and built for Asian and local style musical and theatrical productions.
The Nelum Pokuna Mahinda Rajapaksa Theatre is a world-class theatre that opened in December 2011. Designed in the form of the Lotus Pond in Polonnaruwa, the theatre is a major theatre destination.
Colombo has several performing arts centres, which are popular for their musical and theatrical performances, including the Lionel Wendt Art Centre, Lionel Wendt Theatre, the Elphinstone, and Tower Hall, all of which were made for western-style productions. The Navarangahala found in the city is the country's first national theatre (structure), theatre designed and built for Asian and local style musical and theatrical productions.
The Nelum Pokuna Mahinda Rajapaksa Theatre is a world-class theatre that opened in December 2011. Designed in the form of the Lotus Pond in Polonnaruwa, the theatre is a major theatre destination.
 One of the most popular sports in Sri Lanka is cricket. The country emerged as champions of the 1996 Cricket World Cup and became runners up in 2007 and 2011. In the ICC World Twenty20 they became runners up in 2009 and 2012 and winners in 2014. The sport is played in parks, playgrounds, beaches and even in the streets. Colombo is the home for two of the country's most popular International structure of cricket, international cricket stadiums, Singhalese Sports Club's Cricket Stadium and R. Premadasa Stadium (named after late president Premadasa). Colombo Stars represents the city in Lanka Premier League.
Colombo has the distinction of being the only city in the world to have four cricket test venues in the past: Paikiasothy Saravanamuttu Stadium, Singhalese Sports Club Cricket Ground, Colombo Cricket Club Ground and Ranasinghe Premadasa Stadium. The Sugathadasa Stadium is an international standard stadium for Sport, athletics, swimming (sport), swimming and football (soccer), football, also held the South Asian Games in 1991 and 2006. Situated in Colombo the Royal Colombo Golf Club is one of the oldest in Asia. Other sporting clubs in Colombo include Colombo Swimming Club, Colombo Rowing Club and the Yachting Association of Sri Lanka.
Rugby Union, Rugby is also a popular sport at the club and school levels. Colombo has its local football team Colombo FC and the sport is being developed as a part of the FIFA Goal program.
The Colombo Port City is to include a new Formula One track, constructed in the vicinity of the Colombo Harbour. According to Dr Priyath Wickrama, the Chairman of the Sri Lanka Ports Authority, an eight-lane F1 track will "definitely" be a part of the New Port City. This would host the Sri Lankan Grand Prix.
Colombo Marathon is an internationally recognised marathon established in 1998.
One of the most popular sports in Sri Lanka is cricket. The country emerged as champions of the 1996 Cricket World Cup and became runners up in 2007 and 2011. In the ICC World Twenty20 they became runners up in 2009 and 2012 and winners in 2014. The sport is played in parks, playgrounds, beaches and even in the streets. Colombo is the home for two of the country's most popular International structure of cricket, international cricket stadiums, Singhalese Sports Club's Cricket Stadium and R. Premadasa Stadium (named after late president Premadasa). Colombo Stars represents the city in Lanka Premier League.
Colombo has the distinction of being the only city in the world to have four cricket test venues in the past: Paikiasothy Saravanamuttu Stadium, Singhalese Sports Club Cricket Ground, Colombo Cricket Club Ground and Ranasinghe Premadasa Stadium. The Sugathadasa Stadium is an international standard stadium for Sport, athletics, swimming (sport), swimming and football (soccer), football, also held the South Asian Games in 1991 and 2006. Situated in Colombo the Royal Colombo Golf Club is one of the oldest in Asia. Other sporting clubs in Colombo include Colombo Swimming Club, Colombo Rowing Club and the Yachting Association of Sri Lanka.
Rugby Union, Rugby is also a popular sport at the club and school levels. Colombo has its local football team Colombo FC and the sport is being developed as a part of the FIFA Goal program.
The Colombo Port City is to include a new Formula One track, constructed in the vicinity of the Colombo Harbour. According to Dr Priyath Wickrama, the Chairman of the Sri Lanka Ports Authority, an eight-lane F1 track will "definitely" be a part of the New Port City. This would host the Sri Lankan Grand Prix.
Colombo Marathon is an internationally recognised marathon established in 1998.
File:SL Colombo asv2020-01 img01 Wolvendaal Church.jpg, Colombo's colonial heritage is visible throughout the city, as in the historical Wolvendaal Church, established by the Dutch in 1749
File:Nelum Pokuna (Lotus Pond) Mahinda Rajapaksa Theatre.JPG, The Nelum Pokuna Theatre at night
File:Repub building.jpg, British era Legislative Council Building, Colombo fort. Today it houses the Ministry of Foreign Affairs (Sri Lanka), Ministry of Foreign Affairs
File:Colombo Town Hall 1.JPG, The Town Hall of Colombo at night, it is the headquarters of the Ceylon, the Land of Eternal Charm
Ali Foad Toulba (Asian Educational Services) p.237
File:Viharamahadevi Park incl. Town Hall.jpg, The
capital
Capital may refer to:
Common uses
* Capital city, a municipality of primary status
** List of national capital cities
* Capital letter, an upper-case letter Economics and social sciences
* Capital (economics), the durable produced goods used f ...
and largest city of Sri Lanka
Sri Lanka (, ; si, ශ්රී ලංකා, Śrī Laṅkā, translit-std=ISO (); ta, இலங்கை, Ilaṅkai, translit-std=ISO ()), formerly known as Ceylon and officially the Democratic Socialist Republic of Sri Lanka, is an ...
by population. According to the Brookings Institution
The Brookings Institution, often stylized as simply Brookings, is an American research group founded in 1916. Located on Think Tank Row in Washington, D.C., the organization conducts research and education in the social sciences, primarily in ec ...
, Colombo metropolitan area has a population of 5.6 million, and 752,993 in the Municipality
A municipality is usually a single administrative division having corporate status and powers of self-government or jurisdiction as granted by national and regional laws to which it is subordinate.
The term ''municipality'' may also mean the go ...
. It is the financial centre of the island and a tourist destination. It is located on the west coast of the island and adjacent to the Greater Colombo area
Colombo ( ; si, කොළඹ, translit=Koḷam̆ba, ; ta, கொழும்பு, translit=Koḻumpu, ) is the executive and judicial capital and largest city of Sri Lanka by population. According to the Brookings Institution, Colombo m ...
which includes Sri Jayawardenepura Kotte
Sri Jayawardenepura Kotte, commonly known as Kotte (), is the legislative capital of Sri Lanka. Sri Jayawardenepura Kotte is a satellite city and located within the urban area of Sri Lanka's de facto economic, executive, and judicial capital, ...
, the legislative capital of Sri Lanka, and Dehiwala-Mount Lavinia
Dehiwala-Mount Lavinia ( si, දෙහිවල-ගල්කිස්ස, translit=Dehivala-Galkissa; ta, தெஹிவளை-கல்கிசை, translit=Tehivaḷai-Kalkicai), population 245,974 (2012) is the largest suburb of the City of ...
. Colombo is often referred to as the capital since Sri Jayawardenepura Kotte is itself within the urban/suburban area of Colombo. It is also the administrative capital of the Western Province
Western Province or West Province may refer to:
* Western Province, Cameroon
*Western Province, Rwanda
*Western Province (Kenya)
*Western Province (Papua New Guinea)
*Western Province (Solomon Islands)
*Western Province, Sri Lanka
*Western Provin ...
and the district capital of Colombo District. Colombo is a busy and vibrant city with a mixture of modern life, colonial buildings and monuments.
Due to its large harbour
A harbor (American English), harbour (British English; see spelling differences), or haven is a sheltered body of water where ships, boats, and barges can be docked. The term ''harbor'' is often used interchangeably with ''port'', which is a ...
and its strategic position along the East–West sea trade route
A trade route is a logistical network identified as a series of pathways and stoppages used for the commercial transport of cargo. The term can also be used to refer to trade over bodies of water. Allowing goods to reach distant markets, a sing ...
s, Colombo was known to ancient traders 2,000 years ago. It was made the capital of the island when Sri Lanka was ceded to the British Empire
The British Empire was composed of the dominions, colonies, protectorates, mandates, and other territories ruled or administered by the United Kingdom and its predecessor states. It began with the overseas possessions and trading posts esta ...
in 1815, and its status as capital was retained when the nation became independent
Independent or Independents may refer to:
Arts, entertainment, and media Artist groups
* Independents (artist group), a group of modernist painters based in the New Hope, Pennsylvania, area of the United States during the early 1930s
* Independ ...
in 1948. In 1978, when administrative functions were moved to Sri Jayawardenepura Kotte
Sri Jayawardenepura Kotte, commonly known as Kotte (), is the legislative capital of Sri Lanka. Sri Jayawardenepura Kotte is a satellite city and located within the urban area of Sri Lanka's de facto economic, executive, and judicial capital, ...
, Colombo was designated as the commercial capital of Sri Lanka.
Like many cities, Colombo's urban area extends well beyond the boundaries of a single local authority, encompassing other municipal
A municipality is usually a single administrative division having corporate status and powers of self-government or jurisdiction as granted by national and regional laws to which it is subordinate.
The term ''municipality'' may also mean the go ...
and urban councils such as Sri Jayawardenepura Kotte Municipal Council, Dehiwala Mount Lavinia Municipal Council, Kolonnawa Urban Council, Kaduwela Municipal Council, and Kotikawatte Mulleriyawa Pradeshiya Sabha. The main city is home to a majority of Sri Lanka's corporate offices, restaurants, and entertainment venues. Famous landmarks in Colombo include Galle Face Green
Galle Face is a ocean-side urban park, which stretches for along the coast, in the heart of Colombo, the financial and business capital of Sri Lanka. The promenade was initially laid out in 1859 by Governor Sir Henry George Ward, although t ...
, Viharamahadevi Park
Viharamahadevi Park ( si, විහාරමහාදේවී උද්යානය; formerly Victoria Park, si, වික්ටෝරියා පාක්) is a public park located in Cinnamon Gardens, Colombo, situated in front of the colon ...
, Beira Lake
Beira Lake (/bˈɐjɾɐ/; Sinhalese: බේරේ වැව, translit. ''Bērē væva''; Tami: பேரே ஏரி, translit. ''Pērē ēri'') is a lake in the centre of the city of Colombo in Sri Lanka. The lake is surrounded by many large b ...
, Colombo Racecourse
Colombo Racecourse ( si, කොළඹ තුරඟ තරඟ පිටිය) is a historical harness racing course in the Cinnamon Gardens, Colombo. During the Second World War, it was used as a temporary airfield. In 2012, it was redeveloped ...
, Planetarium
A planetarium ( planetariums or ''planetaria'') is a theatre built primarily for presenting educational and entertaining shows about astronomy and the night sky, or for training in celestial navigation.
A dominant feature of most planetarium ...
, University of Colombo
(Buddhih Sarvatra Bhrajate)
, mottoeng = ''Wisdom Enlightens''
, established =
, endowment = Sri Lankan rupee, LKR 1.461 1,000,000,000 (number), billion
, Mount Lavinia beach, Dehiwala Zoological Garden, Nelum Pokuna Theatre
The Nelum Pokuna Mahinda Rajapaksa Theatre ( si, නෙළුම් පොකුණ මහින්ද රාජපක්ෂ රඟහල, ''nelum pokuna Mahinda Rajapaksa rangahala''; often known as Nelum Pokuna; previously the National Performin ...
, One Galle Face
One Galle Face is a mixed-use complex of buildings currently being built near the Galle Face Green in Colombo, Sri Lanka. It is also Sri Lanka's first internationally and developed and managed mixed use project and was officially opened on 8 Nov ...
, Gangaramaya Temple
Gangaramaya Temple ( Sinhala: ශ්රී ගංගාරාම මහාවිහාරය ''śrī gangārāma mahāvihāraya'', Tamil: ஸ்ரீ கங்காராம மகாவிகாரம் ''Srī Gaṅgārāma Makāvikāram' ...
, Dutch Museum, Colombo Lotus Tower
Lotus Tower ( si, නෙළුම් කුළුණ; ta, தாமரைக் கோபுரம்), also referred to as Colombo Lotus Tower, is a tall tower, located in Colombo, Sri Lanka. It has been called a symbolic landmark of Sri La ...
as well as the National Museum
A national museum is a museum maintained and funded by a national government. In many countries it denotes a museum run by the central government, while other museums are run by regional or local governments. In other countries a much greater numb ...
.
Etymology
The name 'Colombo', first introduced by the Portuguese in 1505, is believed to be derived from the classical Sinhala name ''Kolon thota'', meaning "port on the river Kelani". Another belief is that the name is derived from the Sinhala name ''Kola-amba-thota'' which means 'Harbour with leafy/green mango trees'.''World Executive'Colombo Hotels and City Guide
This coincides with
Robert Knox
Robert Knox (4 September 1791 – 20 December 1862) was a Scottish anatomist and ethnologist best known for his involvement in the Burke and Hare murders. Born in Edinburgh, Scotland, Knox eventually partnered with anatomist and former teache ...
's history of the island while he was a prisoner in Kandy. He writes that "On the West, the City of Columbo, so-called from a Tree the Natives call Ambo, (which bears the Mango-fruit) growing in that place; but this never bear fruit, but only leaves, which in their Language is Cola and thence they called the Tree Colambo: which the Christians in honour of Columbus
Columbus is a Latinized version of the Italian surname "''Colombo''". It most commonly refers to:
* Christopher Columbus (1451-1506), the Italian explorer
* Columbus, Ohio, capital of the U.S. state of Ohio
Columbus may also refer to:
Places ...
turned to Columbo."
The author of the oldest Sinhala grammar, ''Sidatsangarava,'' written in the 13th century wrote about a category of words that exclusively belonged to early Sinhala. It lists ''naramba'' (to see) and ''kolamba'' (ford or harbour) as deriving from the indigenous Vedda language
Vedda is an endangered language that is used by the indigenous Vedda people of Sri Lanka. Additionally, communities such as Coast Veddas and Anuradhapura Veddas who do not strictly identify as Veddas also use words from the Vedda language in par ...
. ''Kolamba'' may also be the source of the name of the commercial capital Colombo.
History
As Colombo possesses a natural harbour, it was known toIndian
Indian or Indians may refer to:
Peoples South Asia
* Indian people, people of Indian nationality, or people who have an Indian ancestor
** Non-resident Indian, a citizen of India who has temporarily emigrated to another country
* South Asia ...
, Greek
Greek may refer to:
Greece
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group.
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family.
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor ...
, Persia
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran, and also called Persia, is a country located in Western Asia. It is bordered by Iraq and Turkey to the west, by Azerbaijan and Armenia to the northwest, by the Caspian Sea and Turkmeni ...
n, Roman
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
*Rome, the capital city of Italy
*Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
*Roman people, the people of ancient Rome
*''Epistle to the Romans'', shortened to ''Romans'', a letter ...
, Arab
The Arabs (singular: Arab; singular ar, عَرَبِيٌّ, DIN 31635: , , plural ar, عَرَب, DIN 31635: , Arabic pronunciation: ), also known as the Arab people, are an ethnic group mainly inhabiting the Arab world in Western Asia, ...
and Chinese
Chinese can refer to:
* Something related to China
* Chinese people, people of Chinese nationality, citizenship, and/or ethnicity
**''Zhonghua minzu'', the supra-ethnic concept of the Chinese nation
** List of ethnic groups in China, people of ...
traders over 2,000 years ago. Traveller Ibn Battuta
Abu Abdullah Muhammad ibn Battutah (, ; 24 February 13041368/1369),; fully: ; Arabic: commonly known as Ibn Battuta, was a Berbers, Berber Maghrebi people, Maghrebi scholar and explorer who travelled extensively in the lands of Afro-Eurasia, ...
who visited the island in the 14th century, referred to it as ''Kalanpu''. Arabs, whose prime interests were trade, began to settle in Colombo around the eighth century AD mostly because the port helped their business by the way of controlling much of the trade between the Sinhalese
Sinhala may refer to:
* Something of or related to the Sinhalese people of Sri Lanka
* Sinhalese people
* Sinhala language, one of the three official languages used in Sri Lanka
* Sinhala script, a writing system for the Sinhala language
** Sinha ...
kingdoms and the outside world. Their descendants now comprise the local Sri Lankan Moor
Sri Lankan Moors ( ta, இலங்கைச் சோனகர், translit=Ilaṅkaic Cōṉakar; si, ලංකා යෝනක, translit=Lanka Yonaka; formerly Ceylon Moors; colloquially referred to as Sri Lankan Muslims) are an ethnic minorit ...
community.
Portuguese era
Portuguese
Portuguese may refer to:
* anything of, from, or related to the country and nation of Portugal
** Portuguese cuisine, traditional foods
** Portuguese language, a Romance language
*** Portuguese dialects, variants of the Portuguese language
** Portu ...
explorers led by Dom Lourenço de Almeida
Lourenço de Almeida (c.1480 - March 1508) was a Portuguese explorer and military commander.
He was born in Martim, Kingdom of Portugal, the son of Francisco de Almeida, first viceroy of Portuguese India. Acting under his father, Lourenço dist ...
first arrived in Sri Lanka in 1505. During their initial visit they made a treaty with the King of Kotte, Parakramabahu VIII (1484–1518), which enabled them to trade in the island's crop of cinnamon
Cinnamon is a spice obtained from the inner bark of several tree species from the genus ''Cinnamomum''. Cinnamon is used mainly as an aromatic condiment and flavouring additive in a wide variety of cuisines, sweet and savoury dishes, breakfa ...
, which lay along with the coastal areas of the island, including in Colombo. As part of the treaty, the Portuguese were given full authority over the coastline in exchange for the promise of guarding the coast against invaders. They were allowed to establish a trading post
A trading post, trading station, or trading house, also known as a factory, is an establishment or settlement where goods and services could be traded.
Typically the location of the trading post would allow people from one geographic area to tr ...
in Colombo. Within a short time, however, they expelled the Muslim
Muslims ( ar, المسلمون, , ) are people who adhere to Islam, a monotheistic religion belonging to the Abrahamic tradition. They consider the Quran, the foundational religious text of Islam, to be the verbatim word of the God of Abrah ...
inhabitants of Colombo and began to build a fort
A fortification is a military construction or building designed for the defense of territories in warfare, and is also used to establish rule in a region during peacetime. The term is derived from Latin ''fortis'' ("strong") and ''facere'' ...
in 1517.
The Portuguese soon realised that control of Sri Lanka was necessary for the protection of their coastal establishments in India and they began to manipulate the rulers of the Kotte kingdom to gain control of the area. After skilfully exploiting rivalries within the royal family, they took control of a large area of the kingdom and the Sinhalese King Mayadunne established a new kingdom at Sitawaka, a domain in the Kotte kingdom. Before long he annexed much of the Kotte kingdom and forced the Portuguese to retreat to Colombo, which was repeatedly besieged by Mayadunne and the later kings of Sitawaka, forcing them to seek reinforcement from their major base in Goa
Goa () is a state on the southwestern coast of India within the Konkan region, geographically separated from the Deccan highlands by the Western Ghats. It is located between the Indian states of Maharashtra to the north and Karnataka to the ...
, India. Following the fall of the kingdom in 1593, the Portuguese were able to establish complete control over the coastal area, with Colombo as their capital.
This part of Colombo is still known as Fort
A fortification is a military construction or building designed for the defense of territories in warfare, and is also used to establish rule in a region during peacetime. The term is derived from Latin ''fortis'' ("strong") and ''facere'' ...
and houses the presidential palace and the majority of Colombo's five star
Five Star (also styled as 5 Star) are a British pop group, formed in 1983 and comprising siblings Stedman, Lorraine, Denise, Doris and Delroy Pearson. Between 1985 and 1988, Five Star had four top 20 albums and 15 top 40 singles in the UK ...
hotels. The area immediately outside Fort is known as Pettah
Pettah may refer to:
* Pettah of Ahmednagar, a fortified town outside the Fort of Ahmednagar stormed by British soldiers in 1803 during Second Anglo-Maratha War
* Pettah, Colombo, a neighborhood in Colombo, Sri Lanka located east of the City centr ...
( si, පිට කොටුව ''piṭa koṭuva'', "outer fort") and is a commercial hub.
Dutch era
 In 1638 the
In 1638 the Dutch
Dutch commonly refers to:
* Something of, from, or related to the Netherlands
* Dutch people ()
* Dutch language ()
Dutch may also refer to:
Places
* Dutch, West Virginia, a community in the United States
* Pennsylvania Dutch Country
People E ...
signed a treaty with King Rajasinha II of Kandy which assured the king assistance in his war against the Portuguese in exchange for a monopoly of the island's major trade goods. The Portuguese resisted the Dutch and the Kandyans but were gradually defeated in their strongholds beginning in 1639. The Dutch captured Colombo in 1656 after an epic siege, at the end of which a mere 93 Portuguese survivors were given safe conduct
Safe conduct, safe passage, or letters of transit, is the situation in time of international conflict or war where one state, a party to such conflict, issues to a person (usually an enemy state's subject) a pass or document to allow the enemy ...
out of the fort. Although the Dutch (e.g., Rijcklof van Goens
Rijcklof Volckertsz. van Goens (24 June 1619 – 14 November 1682) was the Governor of Zeylan and Governor-General of the Dutch East Indies. He was the Governor of Zeylan from 12 May 1660 to 1661, then in 1663 and finally from 19 November 16 ...
) initially restored the captured area back to the Sinhalese kings, they later refused to turn them over and gained control over the island's richest cinnamon lands including Colombo which then served as the capital of the Dutch maritime provinces under the control of the Dutch East India Company
The United East India Company ( nl, Verenigde Oostindische Compagnie, the VOC) was a chartered company established on the 20th March 1602 by the States General of the Netherlands amalgamating existing companies into the first joint-stock ...
until 1796.
British era
 Although the British captured Colombo in 1796, it remained a
Although the British captured Colombo in 1796, it remained a British military
The British Armed Forces, also known as His Majesty's Armed Forces, are the military forces responsible for the defence of the United Kingdom, its Overseas Territories and the Crown Dependencies. They also promote the UK's wider interests, su ...
outpost until the Kandyan Kingdom was ceded to them in 1815 and they made Colombo the capital of their newly created crown colony
A Crown colony or royal colony was a colony administered by The Crown within the British Empire. There was usually a Governor, appointed by the British monarch on the advice of the UK Government, with or without the assistance of a local Counci ...
of British Ceylon
British Ceylon ( si, බ්රිතාන්ය ලංකාව, Britānya Laṃkāva; ta, பிரித்தானிய இலங்கை, Biritthāṉiya Ilaṅkai) was the British Crown colony of present-day Sri Lanka between ...
. Unlike the Portuguese and Dutch before them, whose primary use of Colombo was as a military fort, the British began constructing houses and other civilian structures around the fort, giving rise to the current City of Colombo.
Initially, they placed the administration of the city under a " Collector", and John Macdowell of the Madras
Chennai (, ), formerly known as Madras ( the official name until 1996), is the capital city of Tamil Nadu, the southernmost Indian state. The largest city of the state in area and population, Chennai is located on the Coromandel Coast of th ...
Service was the first to hold the office. Then, in 1833, the Government Agent of the Western Province was charged with the administration of the city. Centuries of colonial rule
Colonialism is a practice or policy of control by one people or power over other people or areas, often by establishing colonies and generally with the aim of economic dominance. In the process of colonisation, colonisers may impose their relig ...
had meant a decline of indigenous administration of Colombo and in 1865 the British conceived a Municipal Council as a means of training the local population in self-governance
__NOTOC__
Self-governance, self-government, or self-rule is the ability of a person or group to exercise all necessary functions of regulation without intervention from an external authority. It may refer to personal conduct or to any form of ...
. The Legislative Council of Ceylon
The Legislative Council of Ceylon was the legislative body of British Ceylon, Ceylon (now Sri Lanka) established in 1833, along with the Executive Council of Ceylon, on the recommendations of the Colebrooke-Cameron Commission. It was the first f ...
constituted the Colombo Municipal Council in 1865 and the Council met for the first time on 16 January 1866. At the time, the population of the region was around 80,000.
During the time they were in control of Colombo, the British were responsible for much of the planning of the present city. In some parts of the city, tram
A tram (called a streetcar or trolley in North America) is a rail vehicle that travels on tramway tracks on public urban streets; some include segments on segregated right-of-way. The tramlines or networks operated as public transport are ...
car tracks and granite flooring laid during the era are still visible today.
After independence
 This era of colonialism ended peacefully in 1948 when Ceylon gained independence from Britain.
Due to the tremendous impact this caused on the city's inhabitants and on the country as a whole, the changes that resulted at the end of the colonial period were drastic. An entire new culture took root. Changes in laws and customs, clothing styles, religions and
This era of colonialism ended peacefully in 1948 when Ceylon gained independence from Britain.
Due to the tremendous impact this caused on the city's inhabitants and on the country as a whole, the changes that resulted at the end of the colonial period were drastic. An entire new culture took root. Changes in laws and customs, clothing styles, religions and proper names
A proper noun is a noun that identifies a single entity and is used to refer to that entity (''Africa'', ''Jupiter'', '' Sarah'', ''Microsoft)'' as distinguished from a common noun, which is a noun that refers to a class of entities (''continent, ...
were a significant result of the colonial era. These cultural changes were followed by the strengthening of the island's economy. Even today, the influence of the Portuguese, the Dutch and the British is visible in Colombo's architecture, names, clothing, food, language and attitudes. Buildings from all three eras stand as reminders of the turbulent past of Colombo. The city and its people show an interesting mix of European clothing and lifestyles together with local customs.
Historically, Colombo referred to the area around the ''Fort
A fortification is a military construction or building designed for the defense of territories in warfare, and is also used to establish rule in a region during peacetime. The term is derived from Latin ''fortis'' ("strong") and ''facere'' ...
'' and ''Pettah Market
The Pettah Market also called Manning Market is an open market in the suburb of Pettah, Sri Lanka, Pettah in the city of Colombo, Sri Lanka.
The entrance to the Pettah Market is marked formally by a tall monument in the centre of a roundabout, kn ...
'' which is known for the variety of products available as well as the Khan Clock Tower
The Khan Clock Tower was built in Colombo, Sri Lanka by the Khan Family of Bombay. The Clock Tower is a popular landmark and marks the entrance to Pettah Market. The Clock Tower was built in the early 20th century by the family of Framjee Bhikhaj ...
, a local landmark. At present, it refers to the city limits of the Colombo Municipal Council
The Colombo Municipal Council is the municipal governing body of Colombo, the largest city and financial centre in Sri Lanka. It consists of a directly elected executive Mayor of Colombo, current elect is Rosy Senanayake, and 119 elected 119 muni ...
. More often, the name is used for the Conurbation
A conurbation is a region comprising a number of metropolises, cities, large towns, and other urban areas which through population growth and physical expansion, have merged to form one continuous urban or industrially developed area. In most ca ...
known as Greater Colombo, which encompasses several Municipal council
A municipal council is the legislative body of a municipality or local government area. Depending on the location and classification of the municipality it may be known as a city council, town council, town board, community council, rural counci ...
s including Kotte, Dehiwela and Colombo.
Although Colombo lost its status as the capital of Sri Lanka in the 1980s to Sri Jayawardanapura, it continues to be the island's commercial centre. Despite the official capital of Sri Lanka moving to the adjacent Sri Jayawardanapura Kotte, most countries still maintain their diplomatic mission
A diplomatic mission or foreign mission is a group of people from a state or organization present in another state to represent the sending state or organization officially in the receiving or host state. In practice, the phrase usually deno ...
s in Colombo.''GoAbroad.com''Embassies located in Sri Lanka
Geography
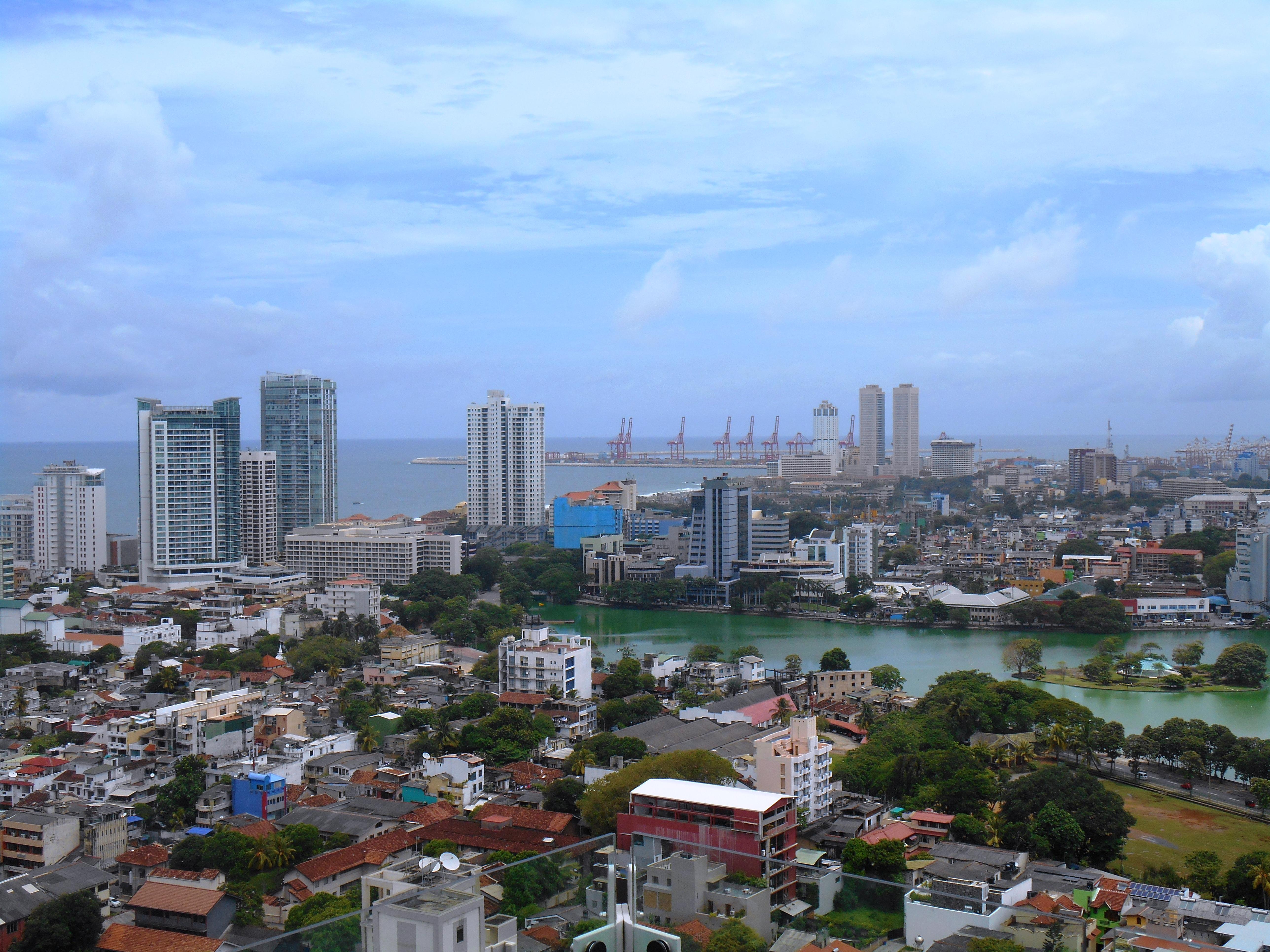
 Colombo's geography is a mix of land and water. The city has many canals and, in the heart of the city, the
Colombo's geography is a mix of land and water. The city has many canals and, in the heart of the city, the Beira Lake
Beira Lake (/bˈɐjɾɐ/; Sinhalese: බේරේ වැව, translit. ''Bērē væva''; Tami: பேரே ஏரி, translit. ''Pērē ēri'') is a lake in the centre of the city of Colombo in Sri Lanka. The lake is surrounded by many large b ...
.The lake in the middle of Colombo, ''Lanka Library'' The lake is one of the most distinctive landmarks of Colombo and was used for centuries by colonists to defend the city. It remains a tourist attraction, hosting
regattas
Boat racing is a sport in which boats, or other types of watercraft, race on water. Boat racing powered by oars is recorded as having occurred in ancient Egypt, and it is likely that people have engaged in races involving boats and other wate ...
, and theatrical events on its shores. The Northern and North-Eastern border of the city of Colombo is formed by the Kelani River
The Kelani River ( si, කැළණි ගඟ) is a river in Sri Lanka. Ranking as the fourth-longest river in the country, it stretches from the Sri Pada Mountain Range to Colombo. It flows through or borders the Sri Lankan districts of Nuwara ...
, which meets the sea in a part of the city known as the Modera (''mōdara'' in Sinhala) which means river delta
A river delta is a landform shaped like a triangle, created by deposition (geology), deposition of sediment that is carried by a river and enters slower-moving or stagnant water. This occurs where a river enters an ocean, sea, estuary, lake, res ...
.
Climate
Colombo features atropical monsoon climate
An area of tropical monsoon climate (occasionally known as a sub-equatorial, tropical wet climate or a tropical monsoon and trade-wind littoral climate) is a tropical climate sub-type that corresponds to the Köppen climate classification category ...
(''Am'') under the Köppen climate classification
The Köppen climate classification is one of the most widely used climate classification systems. It was first published by German-Russian climatologist Wladimir Köppen (1846–1940) in 1884, with several later modifications by Köppen, notabl ...
, falling just short of a tropical rainforest climate
A tropical rainforest climate, humid tropical climate or equatorial climate is a tropical climate sub-type usually found within 10 to 15 degrees latitude of the equator. There are some other areas at higher latitudes, such as the coast of southea ...
(''Af''). Colombo's climate is hot throughout the year. From March to April the average high temperature is around . The only major change in the Colombo weather occurs during the monsoon
A monsoon () is traditionally a seasonal reversing wind accompanied by corresponding changes in precipitation but is now used to describe seasonal changes in atmospheric circulation and precipitation associated with annual latitudinal oscil ...
seasons from April to June and September to November, when heavy rains occur. Colombo sees little relative diurnal range of temperature, although this is more marked in the drier winter months, where minimum temperatures average . Rainfall in the city averages around a year.
Attractions

Galle Face Green
Galle Face is a ocean-side urban park, which stretches for along the coast, in the heart of Colombo, the financial and business capital of Sri Lanka. The promenade was initially laid out in 1859 by Governor Sir Henry George Ward, although t ...
is located in the heart of the city along the Indian Ocean coast and is a destination for tourists and residents alike. The Galle Face Hotel is a historic landmark on the southern edge of this promenade.
Gangaramaya Temple
Gangaramaya Temple ( Sinhala: ශ්රී ගංගාරාම මහාවිහාරය ''śrī gangārāma mahāvihāraya'', Tamil: ஸ்ரீ கங்காராம மகாவிகாரம் ''Srī Gaṅgārāma Makāvikāram' ...
is one of the most important temples in Colombo. The temple's architecture demonstrates an eclectic mix of Sri Lankan, Thai, Indian and Chinese architecture.
The Viharamahadevi Park
Viharamahadevi Park ( si, විහාරමහාදේවී උද්යානය; formerly Victoria Park, si, වික්ටෝරියා පාක්) is a public park located in Cinnamon Gardens, Colombo, situated in front of the colon ...
(formerly Victoria Park) is an urban park located next to the National Museum of Colombo
The Colombo National Museum, also known as the Sri Lanka National Museum, is a museum in Colombo and the largest in Sri Lanka. Founded in 1877 and maintained by the Department of National Museums, it holds collections of significant importanc ...
and the Town Hall
In local government, a city hall, town hall, civic centre (in the UK or Australia), guildhall, or a municipal building (in the Philippines), is the chief administrative building of a city, town, or other municipality. It usually houses ...
. It is the oldest and largest park in Colombo and features a large Buddha statue.
As part of the Urban Regeneration Program of the Government of Sri Lanka
The Government of Sri Lanka (GoSL) ( si, ශ්රී ලංකා රජය, Śrī Lankā Rajaya; ta, இலங்கை அரசாங்கம்) is a parliamentary system determined by the Sri Lankan Constitution. It administers the is ...
, many old sites and buildings were revamped into modern public recreational spaces and shopping precincts. These include Independence Memorial Hall Square, Pettah Floating Market
The Pettah Floating Markets are located on Bastian Mawatha in Pettah, a neighborhood in Colombo, Sri Lanka, and consist of 92 trade stalls, with a number of the stalls established on boats on Beira Lake. The floating market serves as a tourist ...
and Old Dutch Hospital, among others.
Demographics
Colombo is a multi-religious, multi-ethnic and multi-cultural city. The population of Colombo is a mix of numerous ethnic groups, mainlySinhalese
Sinhala may refer to:
* Something of or related to the Sinhalese people of Sri Lanka
* Sinhalese people
* Sinhala language, one of the three official languages used in Sri Lanka
* Sinhala script, a writing system for the Sinhala language
** Sinha ...
, Sri Lankan Tamils
Sri Lankan Tamils ( or ), also known as Ceylon Tamils or Eelam Tamils, are Tamils native to the South Asian island state of Sri Lanka. Today, they constitute a majority in the Northern Province, live in significant numbers in the Eastern Pro ...
and Sri Lankan Moor
Sri Lankan Moors ( ta, இலங்கைச் சோனகர், translit=Ilaṅkaic Cōṉakar; si, ලංකා යෝනක, translit=Lanka Yonaka; formerly Ceylon Moors; colloquially referred to as Sri Lankan Muslims) are an ethnic minorit ...
. There are also small communities of people with Chinese
Chinese can refer to:
* Something related to China
* Chinese people, people of Chinese nationality, citizenship, and/or ethnicity
**''Zhonghua minzu'', the supra-ethnic concept of the Chinese nation
** List of ethnic groups in China, people of ...
, Portuguese Burgher, Dutch Burgher, Malay
Malay may refer to:
Languages
* Malay language or Bahasa Melayu, a major Austronesian language spoken in Indonesia, Malaysia, Brunei and Singapore
** History of the Malay language, the Malay language from the 4th to the 14th century
** Indonesi ...
and Indian
Indian or Indians may refer to:
Peoples South Asia
* Indian people, people of Indian nationality, or people who have an Indian ancestor
** Non-resident Indian, a citizen of India who has temporarily emigrated to another country
* South Asia ...
origins living in the city, as well as numerous European expatriates. Colombo is the most populous city in Sri Lanka, with 642,163 people living within the city limits., Additional source In 1866 the city had a population of around 80,000.
Government and politics
Local government
Colombo is acharter city
In the United States, a charter city is a city in which the governing system is defined by the city's own charter document rather than solely by general law. In states where city charters are allowed by law, a city can adopt or modify its organ ...
, with a mayor-council government. The mayor and council members are elected through local government elections held once in five years. For the past 50 years the city had been ruled by the United National Party (UNP), a Right-wing politics, right leaning party, whose business-friendly policies resonate with the population of Colombo. However, the UNP nomination list for the 2006 Municipal elections was rejected, and an Independent Group supported by the UNP won the elections. Uvais Mohamed Imitiyas was subsequently appointed Mayor of Colombo.
The city government provides sewer, road and waste management services, in the case of water, electricity and telephone utility services the council liaises with the water supply and drainage board, the Ceylon electricity board and telephone service providers.
National capital status
Colombo was the capital of the coastal areas controlled by the Portuguese, the Dutch and the British from the 1700s to 1815 when the British gained control of the entire island following the Kandyan convention. From then until the 1980s the national capital of the island was Colombo. During the 1980s plans were made to move the administrative capital toSri Jayawardenepura Kotte
Sri Jayawardenepura Kotte, commonly known as Kotte (), is the legislative capital of Sri Lanka. Sri Jayawardenepura Kotte is a satellite city and located within the urban area of Sri Lanka's de facto economic, executive, and judicial capital, ...
and thus move all governmental institutions out of Colombo to make way for commercial activities. As a primary step, the Parliament of Sri Lanka, Parliament was moved to a new complex in Kotte, with several ministries and departments also relocated. However, the move was never completed.
Today, many governmental institutions still remain in Colombo. These include the President's House, Colombo, President's House, Presidential Secretariat (Sri Lanka), Presidential Secretariat, Prime Minister's House (Colombo), Prime Minister's House (Temple Trees), Prime Minister's Office (Colombo), Prime Minister's Office, the Supreme Court of Sri Lanka, Central Bank of Sri Lanka, important government ministries and departments; such as Ministry of Finance and Planning (Sri Lanka), Finance (Treasury), Ministry of Defence (Sri Lanka), Defence, Public Administration & Home affairs, Ministry of Foreign Affairs (Sri Lanka), Foreign affairs, Justice and the Army Headquarters (Sri Lanka), Military headquarters, Naval headquarters (SLNS Parakrama), Air Force headquarters (SLAF Colombo) and Sri Lanka Police, Police national and field force headquarters.
Suburbs and postal codes
City limits
 Colombo is divided into 15 numbered areas for the purposes of postal services. Within these areas are the suburbs with their corresponding post office.
Colombo is divided into 15 numbered areas for the purposes of postal services. Within these areas are the suburbs with their corresponding post office.

Outer suburbs
Economy
 The great majority of Sri Lankan corporations have their head offices in Colombo including Aitken Spence, Ceylinco Consolidated, Ceylinco Corporation, Stassen group of companies, John Keells Holdings, Cargills (Ceylon), Cargills, Hemas Holdings and Akbar Brothers. Some of the industries include chemicals, textiles, glass, cement, leather goods, furniture and jewellery. In the city centre is the World Trade Center Colombo, World Trade Centre. The 40-story Twin Tower complex is the centre of important commercial establishments, in the Fort district, the city's nerve centre. Right outside the Fort area is Pettah which is derived from the Sinhala word ''pita'' which means 'out' or 'outside'.
The great majority of Sri Lankan corporations have their head offices in Colombo including Aitken Spence, Ceylinco Consolidated, Ceylinco Corporation, Stassen group of companies, John Keells Holdings, Cargills (Ceylon), Cargills, Hemas Holdings and Akbar Brothers. Some of the industries include chemicals, textiles, glass, cement, leather goods, furniture and jewellery. In the city centre is the World Trade Center Colombo, World Trade Centre. The 40-story Twin Tower complex is the centre of important commercial establishments, in the Fort district, the city's nerve centre. Right outside the Fort area is Pettah which is derived from the Sinhala word ''pita'' which means 'out' or 'outside'.
 The Colombo Metropolitan area has a GDP (PPP) of $122 billion or 40% of the GDP, making it the most important aspect of the Sri Lankan economy. The per capita income of the Colombo Metro area stood at US$8623 and purchasing power per capita of $25,117, making it one of the most prosperous regions in South Asia. The Colombo Metropolitan (CM) area is the most important industrial, commercial and administrative centre in Sri Lanka. A major share of the country's export-oriented manufacturing takes place in the CM area, which is the engine of growth for Sri Lanka.
The Colombo Metropolitan area has a GDP (PPP) of $122 billion or 40% of the GDP, making it the most important aspect of the Sri Lankan economy. The per capita income of the Colombo Metro area stood at US$8623 and purchasing power per capita of $25,117, making it one of the most prosperous regions in South Asia. The Colombo Metropolitan (CM) area is the most important industrial, commercial and administrative centre in Sri Lanka. A major share of the country's export-oriented manufacturing takes place in the CM area, which is the engine of growth for Sri Lanka.
 The Western province contributes less than 40% to the GDP and about 80% of industrial value additions although it accounts for only 5.7% of the country's geographic area and 25% of the national population. Given its importance as the primary international gateway for Sri Lanka and as the main economic driver of the country, the government of Sri Lanka (GoSL) has launched an ambitious program to transform Colombo and its area into a metropolis of international standards. Bottlenecks are preventing the Colombo metropolitan area from realizing its full economic potential. To facilitate the transformation of Colombo, the government has to address these bottlenecks which have for long been obstructing economic and physical urban regeneration.
Pettah is more crowded than the Fort area. Pettah's roads are always packed and Sidewalk, pavements are full of small stalls selling items from delicious sharbat to shirts. Main Street consists mostly of clothes shops and the crossroads, which are known as Cross-Streets where each of the five streets specialises in a specific business. For example, First Cross Street is mostly electronics, electronic goods shops, the Second cellular phones and fancy goods. Most of these businesses are dominated by Muslim traders. At the end of Main Street further away from Fort is Sea Street – Sri Lanka's gold market – dominated by Tamil interests. This mile-long street is full of jewellery shops, including the former head office of SriLankan Airlines.
The Western province contributes less than 40% to the GDP and about 80% of industrial value additions although it accounts for only 5.7% of the country's geographic area and 25% of the national population. Given its importance as the primary international gateway for Sri Lanka and as the main economic driver of the country, the government of Sri Lanka (GoSL) has launched an ambitious program to transform Colombo and its area into a metropolis of international standards. Bottlenecks are preventing the Colombo metropolitan area from realizing its full economic potential. To facilitate the transformation of Colombo, the government has to address these bottlenecks which have for long been obstructing economic and physical urban regeneration.
Pettah is more crowded than the Fort area. Pettah's roads are always packed and Sidewalk, pavements are full of small stalls selling items from delicious sharbat to shirts. Main Street consists mostly of clothes shops and the crossroads, which are known as Cross-Streets where each of the five streets specialises in a specific business. For example, First Cross Street is mostly electronics, electronic goods shops, the Second cellular phones and fancy goods. Most of these businesses are dominated by Muslim traders. At the end of Main Street further away from Fort is Sea Street – Sri Lanka's gold market – dominated by Tamil interests. This mile-long street is full of jewellery shops, including the former head office of SriLankan Airlines.
Law enforcement and crime
 The Sri Lanka Police, the main law enforcement agency of the island, liaise with the municipal council but is under the control of the Ministry of Defence (Sri Lanka), Ministry of Defence of the central government. Policing in Colombo and its suburbs falls within the ''Metropolitan Range'' headed by the Deputy Inspector General of Police (Metropolitan), this also includes the Colombo Crime Division. As with most Sri Lankan cities, the magistrate court handles felony crimes, the district court handles civil cases.
As in other large cities around the world, Colombo experiences certain levels of street crime and bribery. Indeed, the corruption extends to the very top, US reports show. In addition, in the period from the 1980s to 2009, there have been a number of major terrorist attacks. The LTTE has been linked to most of the bombings and assassinations in the city. Welikada Prison is situated in Colombo and it is one of the largest maximum-security prisons in the country.
The Sri Lanka Police, the main law enforcement agency of the island, liaise with the municipal council but is under the control of the Ministry of Defence (Sri Lanka), Ministry of Defence of the central government. Policing in Colombo and its suburbs falls within the ''Metropolitan Range'' headed by the Deputy Inspector General of Police (Metropolitan), this also includes the Colombo Crime Division. As with most Sri Lankan cities, the magistrate court handles felony crimes, the district court handles civil cases.
As in other large cities around the world, Colombo experiences certain levels of street crime and bribery. Indeed, the corruption extends to the very top, US reports show. In addition, in the period from the 1980s to 2009, there have been a number of major terrorist attacks. The LTTE has been linked to most of the bombings and assassinations in the city. Welikada Prison is situated in Colombo and it is one of the largest maximum-security prisons in the country.
Infrastructure
 Colombo has most of the amenities that a modern city has. Compared to other parts of the country, Colombo has the highest degree of infrastructure. Electricity, water and transport to street lights and phone booths are to a considerably good standard. The majority of the major shopping malls in Sri Lanka are in the city, of which all are Wi-Fi enabled. Apart from that, many luxurious hotels, clubs and restaurants are in the city. In recent times there has been an outpour of high-rise condominiums, mainly due to the very high land prices.
Colombo has most of the amenities that a modern city has. Compared to other parts of the country, Colombo has the highest degree of infrastructure. Electricity, water and transport to street lights and phone booths are to a considerably good standard. The majority of the major shopping malls in Sri Lanka are in the city, of which all are Wi-Fi enabled. Apart from that, many luxurious hotels, clubs and restaurants are in the city. In recent times there has been an outpour of high-rise condominiums, mainly due to the very high land prices.
Harbour
 Port of Colombo, Colombo Harbour is the largest and one of the busiest ports in Sri Lanka. Colombo was established primarily as a port city during the colonial era, with an artificial harbour that has been expanded over the years. The Sri Lanka Navy maintains a naval base, ''SLNS Rangalla'', within the harbour.
The Port of Colombo handled 3.75 million twenty-foot equivalent units in 2008, 10.6% up on 2007 (which itself was 9.7% up on 2006), bucking the global economic trend. Of those, 817,000 were local shipments with the rest transshipments. With a capacity of 5.7 million TEUs and a dredged depth of over 15 m (49 ft), the Colombo Harbour is one of the busiest ports in the world and ranks among the top 25 ports (23rd).
Colombo is part of the 21st Century Maritime Silk Road that runs from the Chinese coast to the Upper Adriatic region with its rail connections to Central Europe, Central and Eastern Europe.
Port of Colombo, Colombo Harbour is the largest and one of the busiest ports in Sri Lanka. Colombo was established primarily as a port city during the colonial era, with an artificial harbour that has been expanded over the years. The Sri Lanka Navy maintains a naval base, ''SLNS Rangalla'', within the harbour.
The Port of Colombo handled 3.75 million twenty-foot equivalent units in 2008, 10.6% up on 2007 (which itself was 9.7% up on 2006), bucking the global economic trend. Of those, 817,000 were local shipments with the rest transshipments. With a capacity of 5.7 million TEUs and a dredged depth of over 15 m (49 ft), the Colombo Harbour is one of the busiest ports in the world and ranks among the top 25 ports (23rd).
Colombo is part of the 21st Century Maritime Silk Road that runs from the Chinese coast to the Upper Adriatic region with its rail connections to Central Europe, Central and Eastern Europe.
Transport
Bus
Colombo has an extensive public transport system based on buses operated both by private operators and the government-owned Sri Lanka Transport Board, Sri Lanka Transport Board (SLTB). The three primary bus terminals – Bastian Mawatha, Central and the Gunasinghapura Bus Terminals – are in Pettah. Bastian Mawatha handles long-distance services whereas Gunasinghapura and Central handle local services.Rail
 Train transport Sri Lanka Railways#Commuter Rail, in the city is limited since most trains are meant for transport to and from the city rather than within it and are often overcrowded. However, the Central Bus Stand and Fort Railway Station (Colombo), Fort Railway Station function as the island's primary hub for bus and rail transport respectively. Up until the 1970s, the city had
Train transport Sri Lanka Railways#Commuter Rail, in the city is limited since most trains are meant for transport to and from the city rather than within it and are often overcrowded. However, the Central Bus Stand and Fort Railway Station (Colombo), Fort Railway Station function as the island's primary hub for bus and rail transport respectively. Up until the 1970s, the city had tram
A tram (called a streetcar or trolley in North America) is a rail vehicle that travels on tramway tracks on public urban streets; some include segments on segregated right-of-way. The tramlines or networks operated as public transport are ...
services, which were discontinued. Other means of transport include auto rickshaws (commonly called "three-wheelers") and taxicabs. Three-wheelers are entirely operated by individuals and hardly regulated whilst cab services are run by private companies and are metered.
* Main Line (Sri Lanka), Main Line – Colombo Fort to Veyangoda; onwards to Kandy, Badulla, Matale, Kurunegala, Anuradhapura, Jaffna, Kankesanturai. Trincomalee railway station, Trincomalee, Batticaloa railway station, Batticaloa, Talaimannar (presently just Mannar Line, Madhu Road).
* Coastal Line (Sri Lanka), Coastal Line – Colombo to Panadura; onwards to Galle, Matara, Sri Lanka, Matara and Beliaththa.
* Puttalam Line – Colombo to Ja-Ela; onwards to Negombo and Puttalam.
* Kelani Valley Line – Colombo to Avissawella.
Roads
Post-war development in the Colombo area also involves the construction of numerous expressway grade arterial road routes. The first of these constructed is the Southern Expressway (Sri Lanka), Southern Expressway, which goes from Kottawa, a southern suburb of Colombo, to Matara, Sri Lanka, Matara City in the south of the country. Expressways constructed in the Colombo metropolitan area include the Colombo–Katunayake Expressway, which was opened in October 2013 and the Colombo orbital bypass Outer Circular Highway (Outer Circular Highway, Arthur C. Clarke Expressway). The Colombo-Katunayake Expressway (E03) runs from Peliyagoda, a northern suburb of Colombo, to Colombo International Airport and it is linked with one of the major commercial hubs and a major tourist destination of the country, the city of Negombo. * A1 highway (Sri Lanka), A1 highway connects Colombo with Kandy. * A2 highway (Sri Lanka), A2 highway connects Colombo with Galle and Matara, Sri Lanka, Matara * A3 highway (Sri Lanka), A3 highway connects Colombo with Negombo and Puttalam * A4 highway (Sri Lanka), A4 highway connects Colombo with Ratnapura and BatticaloaFerry
An international ferry liner, the Scotia Prince, is conducting a ferry service to Tuticorin, India. Ferry services between the two countries have been revived after more than 20 years.Air
 Ratmalana Airport is the city's airport, located south of the city centre. It commenced operating in 1935 and was the country's first international airport until it was replaced by Bandaranaike Airport in 1967. Ratmalana Airport now primarily services domestic flights, aviation training and international corporate flights.
Ratmalana Airport is the city's airport, located south of the city centre. It commenced operating in 1935 and was the country's first international airport until it was replaced by Bandaranaike Airport in 1967. Ratmalana Airport now primarily services domestic flights, aviation training and international corporate flights.
Landmarks
 The two World Trade Center Colombo, World Trade Centre towers used to be the most recognised landmarks of the city. Before they were completed in 1997, the adjacent Bank of Ceylon tower was the tallest structure and the most prominent city landmark. Before the skyscrapers were built, the Old Parliament Building that stood in the Fort district with the Old Colombo Lighthouse close to it used to be the tallest building. Another important landmark is the Independence Commemoration Hall (Sri Lanka), Independence Hall at Independence Square in Cinnamon Gardens.
Even before the parliament was built some claim that the Jami Ul-Alfar Mosque was recognised as the landmark of Colombo by sailors approaching the port. The mosque is still one of the most visited tourist sites in Colombo.
Another landmark is St.Paul's Church Milagiriya, one of the oldest church (building), churches in Sri Lanka, first built by the Portuguese and rebuilt by the British in 1848. The Cargills & Millers building in Fort is also a protected building of historical significance.
The Galle Face Green is the city's largest promenade. Lined with coconut trees and adjacent to the coast. The Green frequently hosts international and local concerts and performances, such as the World Drum Festival.
Cannons that were once mounted on the rampart of the old fort of Colombo were laid out for observance and prestige at the Green. The colonial styled Galle Face Hotel, known as Asia's Emerald on the Green since 1864, is adjacent to Galle Face Green. The hotel has played host to guests such as the British Royal Family and other royal family, royal guests and celebrities. After a stay at the hotel, Alexandra, Countess of Frederiksborg, Princess Alexandra of Denmark commented that "the peacefulness and generosity encountered at the Galle Face Hotel cannot be matched." Also facing Galle Face Green is the Ceylon Inter-Continental Hotel.
The two World Trade Center Colombo, World Trade Centre towers used to be the most recognised landmarks of the city. Before they were completed in 1997, the adjacent Bank of Ceylon tower was the tallest structure and the most prominent city landmark. Before the skyscrapers were built, the Old Parliament Building that stood in the Fort district with the Old Colombo Lighthouse close to it used to be the tallest building. Another important landmark is the Independence Commemoration Hall (Sri Lanka), Independence Hall at Independence Square in Cinnamon Gardens.
Even before the parliament was built some claim that the Jami Ul-Alfar Mosque was recognised as the landmark of Colombo by sailors approaching the port. The mosque is still one of the most visited tourist sites in Colombo.
Another landmark is St.Paul's Church Milagiriya, one of the oldest church (building), churches in Sri Lanka, first built by the Portuguese and rebuilt by the British in 1848. The Cargills & Millers building in Fort is also a protected building of historical significance.
The Galle Face Green is the city's largest promenade. Lined with coconut trees and adjacent to the coast. The Green frequently hosts international and local concerts and performances, such as the World Drum Festival.
Cannons that were once mounted on the rampart of the old fort of Colombo were laid out for observance and prestige at the Green. The colonial styled Galle Face Hotel, known as Asia's Emerald on the Green since 1864, is adjacent to Galle Face Green. The hotel has played host to guests such as the British Royal Family and other royal family, royal guests and celebrities. After a stay at the hotel, Alexandra, Countess of Frederiksborg, Princess Alexandra of Denmark commented that "the peacefulness and generosity encountered at the Galle Face Hotel cannot be matched." Also facing Galle Face Green is the Ceylon Inter-Continental Hotel.
Education
 Education institutions in Colombo have a long history. Colombo has many of the prominent Public school (UK), public schools in the country, some of them government-owned and others private. Most of the prominent schools in the city date back to the 1800s when they were established during the British colonial rule, such as the Royal College Colombo established in 1835. Certain urban schools of Sri Lanka have some religious alignment; this is partly due to the influence of the British, who established Christian missionary schools. These include the Anglican, Bishop's College (Sri Lanka), Bishop's College(1875); the Methodist, Wesley College Colombo (1874); the Buddhist, Ananda College (1886); the Muslim, Zahira College, Colombo, Zahira College (1892); the St. Benedict's College, Colombo (1985), the Catholic Church, Catholic, St. Joseph's College, Colombo, St. Joseph's College (1896). The religious alignments do not affect the curriculum of the school except for the demographics of the student population. Colombo has many International Schools that have come up in recent years.
Higher education in the city has a long history, beginning with the establishment of the Colombo Medical School (1870), the Sri Lanka Law College, Colombo Law College (1875), the School of Agriculture (1884) and the Government Technical College (1893). The first step in the creation of a university in Colombo was taken in 1913 with the establishment of the University College Colombo which prepared students for the University of London External System, external examinations of the University of London. This was followed by the establishment of the University of Ceylon in Colombo. Today the
Education institutions in Colombo have a long history. Colombo has many of the prominent Public school (UK), public schools in the country, some of them government-owned and others private. Most of the prominent schools in the city date back to the 1800s when they were established during the British colonial rule, such as the Royal College Colombo established in 1835. Certain urban schools of Sri Lanka have some religious alignment; this is partly due to the influence of the British, who established Christian missionary schools. These include the Anglican, Bishop's College (Sri Lanka), Bishop's College(1875); the Methodist, Wesley College Colombo (1874); the Buddhist, Ananda College (1886); the Muslim, Zahira College, Colombo, Zahira College (1892); the St. Benedict's College, Colombo (1985), the Catholic Church, Catholic, St. Joseph's College, Colombo, St. Joseph's College (1896). The religious alignments do not affect the curriculum of the school except for the demographics of the student population. Colombo has many International Schools that have come up in recent years.
Higher education in the city has a long history, beginning with the establishment of the Colombo Medical School (1870), the Sri Lanka Law College, Colombo Law College (1875), the School of Agriculture (1884) and the Government Technical College (1893). The first step in the creation of a university in Colombo was taken in 1913 with the establishment of the University College Colombo which prepared students for the University of London External System, external examinations of the University of London. This was followed by the establishment of the University of Ceylon in Colombo. Today the University of Colombo
(Buddhih Sarvatra Bhrajate)
, mottoeng = ''Wisdom Enlightens''
, established =
, endowment = Sri Lankan rupee, LKR 1.461 1,000,000,000 (number), billion
and the University of the Visual & Performing Arts are state universities in the city. The Sri Lanka Institute of Information Technology has a metropolitan campus in the city centre. There are several private higher education institutions in the city.
Architecture
 Colombo has widely varying architecture that spans centuries and depicts many styles. colonial architecture, Colonial buildings influenced by the Architecture of Portugal, Portuguese, Architecture of the Netherlands, Dutch and Architecture of the United Kingdom, British exist alongside structures built in Buddhist architecture, Buddhist, Hindu architecture, Hindu, Islamic architecture, Islamic, Architecture of India, Indian and Contemporary architecture, Contemporary architectural styles. No other place is this more evident than in the Fort area. Here, one may find new, towering skyscrapers as well as historic buildings dating far back as the 1700s.Colombo Fort
Colombo has widely varying architecture that spans centuries and depicts many styles. colonial architecture, Colonial buildings influenced by the Architecture of Portugal, Portuguese, Architecture of the Netherlands, Dutch and Architecture of the United Kingdom, British exist alongside structures built in Buddhist architecture, Buddhist, Hindu architecture, Hindu, Islamic architecture, Islamic, Architecture of India, Indian and Contemporary architecture, Contemporary architectural styles. No other place is this more evident than in the Fort area. Here, one may find new, towering skyscrapers as well as historic buildings dating far back as the 1700s.Colombo Fort. Kermeey.blogspot.com (2006-02-19). Retrieved on 2011-10-17.
Colombo Fort
The Portuguese were the first colonists to settle in Colombo. Establishing a small trading post, they had laid the foundations for a small fort which in time became the largest colonial fort on the island. The Dutch expanded the fort, thus creating a well old fortified harbour. This came into the possession of the British in the late 1700s, and by the late 19th century, seeing no threat to the Colombo Harbour, began demolishing the ramparts to make way for the development of the city. Although now there is nothing left of the fortifications, the area which was once the fort is still referred to as Fort. The area outside is Pettah, Sri Lanka or ''Pitakotuwa'' in Sinhala which means outer fort.
Dutch-era buildings
There are none of the buildings of the Portuguese era and only a few from the Dutch period. These include the oldest building in the fort area, the Old Colombo Dutch Hospital, former Dutch Hospital, the Dutch House which is now the Colombo Dutch Museum and several churches. The President's House, Colombo, President's House (formerly the Queen's House) was originally the Dutch governor's house and successive British governors made it their office and residence. However, it has undergone much change since the Dutch period. Adjoining the President's House are the Gordon Gardens, now off-limits to the public.British-era buildings
Much of the old buildings of the fort area and in other parts of the city date back to British times; these include governmental, commercial buildings, and private houses. Some of the notable government building of British colonial architecture includes the old Parliament building, which is now the Presidential Secretariat (Sri Lanka), Presidential Secretariat; the Republic Building, Colombo, Republic Building, which houses the Ministry of Foreign Affairs (Sri Lanka), Ministry of Foreign affairs but once housed the Ceylon Legislative council; the General Treasury Building; the old General Post Office, Colombo, General Post Office, an Edwardian-style building opposite the President's House; the Prime Minister's Office (Colombo), Prime Minister's Office; the Central Telegraph Office, Colombo, Central Telegraph Office; and the Old Royal College Building, Colombo, Mathematics department of theUniversity of Colombo
(Buddhih Sarvatra Bhrajate)
, mottoeng = ''Wisdom Enlightens''
, established =
, endowment = Sri Lankan rupee, LKR 1.461 1,000,000,000 (number), billion
(formally the Royal College, Colombo). Notable commercial buildings of the British era include the Galle Face Hotel, Cargills and Millers' complex, and the Grand Oriental Hotel.
Culture
Annual cultural events and fairs

Performing arts
Museums and art collections
The Colombo National Museum, National Museum of Colombo, established on 1 January 1877 during the tenure of the British Colonial Governor Sir William Henry Gregory, is in the Cinnamon Gardens area. The museum houses the crown jewels and throne of the last king of the kingdom of Kandy, Sri Vikrama Rajasinha. There is also the Colombo Dutch Museum detailing the Dutch colonial history of the country. Colombo does not boast a very big art gallery. There is a small collection of random Sri Lankan paintings at the Art Gallery in Green Path; next to it is the Natural History Museum.Sports
 One of the most popular sports in Sri Lanka is cricket. The country emerged as champions of the 1996 Cricket World Cup and became runners up in 2007 and 2011. In the ICC World Twenty20 they became runners up in 2009 and 2012 and winners in 2014. The sport is played in parks, playgrounds, beaches and even in the streets. Colombo is the home for two of the country's most popular International structure of cricket, international cricket stadiums, Singhalese Sports Club's Cricket Stadium and R. Premadasa Stadium (named after late president Premadasa). Colombo Stars represents the city in Lanka Premier League.
Colombo has the distinction of being the only city in the world to have four cricket test venues in the past: Paikiasothy Saravanamuttu Stadium, Singhalese Sports Club Cricket Ground, Colombo Cricket Club Ground and Ranasinghe Premadasa Stadium. The Sugathadasa Stadium is an international standard stadium for Sport, athletics, swimming (sport), swimming and football (soccer), football, also held the South Asian Games in 1991 and 2006. Situated in Colombo the Royal Colombo Golf Club is one of the oldest in Asia. Other sporting clubs in Colombo include Colombo Swimming Club, Colombo Rowing Club and the Yachting Association of Sri Lanka.
Rugby Union, Rugby is also a popular sport at the club and school levels. Colombo has its local football team Colombo FC and the sport is being developed as a part of the FIFA Goal program.
The Colombo Port City is to include a new Formula One track, constructed in the vicinity of the Colombo Harbour. According to Dr Priyath Wickrama, the Chairman of the Sri Lanka Ports Authority, an eight-lane F1 track will "definitely" be a part of the New Port City. This would host the Sri Lankan Grand Prix.
Colombo Marathon is an internationally recognised marathon established in 1998.
One of the most popular sports in Sri Lanka is cricket. The country emerged as champions of the 1996 Cricket World Cup and became runners up in 2007 and 2011. In the ICC World Twenty20 they became runners up in 2009 and 2012 and winners in 2014. The sport is played in parks, playgrounds, beaches and even in the streets. Colombo is the home for two of the country's most popular International structure of cricket, international cricket stadiums, Singhalese Sports Club's Cricket Stadium and R. Premadasa Stadium (named after late president Premadasa). Colombo Stars represents the city in Lanka Premier League.
Colombo has the distinction of being the only city in the world to have four cricket test venues in the past: Paikiasothy Saravanamuttu Stadium, Singhalese Sports Club Cricket Ground, Colombo Cricket Club Ground and Ranasinghe Premadasa Stadium. The Sugathadasa Stadium is an international standard stadium for Sport, athletics, swimming (sport), swimming and football (soccer), football, also held the South Asian Games in 1991 and 2006. Situated in Colombo the Royal Colombo Golf Club is one of the oldest in Asia. Other sporting clubs in Colombo include Colombo Swimming Club, Colombo Rowing Club and the Yachting Association of Sri Lanka.
Rugby Union, Rugby is also a popular sport at the club and school levels. Colombo has its local football team Colombo FC and the sport is being developed as a part of the FIFA Goal program.
The Colombo Port City is to include a new Formula One track, constructed in the vicinity of the Colombo Harbour. According to Dr Priyath Wickrama, the Chairman of the Sri Lanka Ports Authority, an eight-lane F1 track will "definitely" be a part of the New Port City. This would host the Sri Lankan Grand Prix.
Colombo Marathon is an internationally recognised marathon established in 1998.
Media
Almost all major media businesses in Sri Lanka operate from Colombo. The state media has its offices in Bullers Road and carries out regional transmissions from there. These include the Sri Lanka Broadcasting Corporation (SLBC), formerly known as Radio Ceylon, and the Sri Lanka Rupavahini Corporation. The SLBC is the oldest radio station in South Asia and the second oldest in the world. Many private broadcasting companies have their offices and transmission stations in or around Colombo. As with most metro areas, radio bands are highly utilised for radio communications. Some of the prominent radio stations broadcasting in the Colombo area are Sirasa FM, FM Derana, Hiru FM, Shakthi FM, Vettri FM, Sooriyan FM, Kiss FM (Sri Lanka), Kiss FM, Lite 89.2, Lite FM, Yes FM, Gold FM (Sri Lanka), Gold FM, Sith FM, Y FM and many more. Television networks operating in the Colombo metro area include the state-owned television broadcasting networks which are broadcast by the Rupavahini Corporation of Sri Lanka, broadcasting television in the official languages Sinhala and Tamil. English language television is also broadcast, more targeted to the demographics of the English speaking Sri Lankans, expatriate communities and tourists. There are as well several private operators. Many of the privately run television station networks were often based upon operational expansions of pre-existing commercial radio networks and broadcast infrastructure.Twin towns and sister cities
Gallery
Colombo Municipal Council
The Colombo Municipal Council is the municipal governing body of Colombo, the largest city and financial centre in Sri Lanka. It consists of a directly elected executive Mayor of Colombo, current elect is Rosy Senanayake, and 119 elected 119 muni ...
and the office of the Mayor of Colombo
File:Old GPO CMB.jpg, The Edwardian architecture, Edwardian style General Post Office, Colombo, old General Post Office
File:SCC Ground Colombo.jpg, A Test match between Sri Lanka and England at the Singhalese Sports Club, SSC Cricket Ground, Colombo, March 2001
File:St. Lucia's Cathedral, Colombo, Sri Lanka.jpg, St. Lucia's Cathedral, the seat of the Archbishop of the Roman Catholic Archdiocese of Colombo
File:Beira Lake and Gangaramaya Temple.jpg, Beira Lake
Beira Lake (/bˈɐjɾɐ/; Sinhalese: බේරේ වැව, translit. ''Bērē væva''; Tami: பேரே ஏரி, translit. ''Pērē ēri'') is a lake in the centre of the city of Colombo in Sri Lanka. The lake is surrounded by many large b ...
and southern side of the Gangaramaya Temple
Gangaramaya Temple ( Sinhala: ශ්රී ගංගාරාම මහාවිහාරය ''śrī gangārāma mahāvihāraya'', Tamil: ஸ்ரீ கங்காராம மகாவிகாரம் ''Srī Gaṅgārāma Makāvikāram' ...
File:SL Colombo asv2020-01 img22 Jami Ul-Alfar Mosque.jpg, The Jami Ul-Alfar Mosque is one of the oldest Mosques in Colombo
File:AngCatSL.JPG, Cathedral of Christ the Living Saviour is the seat of the Anglican Bishop of Colombo
File:CHstatue22.JPG, The statue of Sir Charles Henry de Soysa at De Soysa-Liptons Circus, is the first of a native, in Colombo.Ali Foad Toulba (Asian Educational Services) p.237
Viharamahadevi Park
Viharamahadevi Park ( si, විහාරමහාදේවී උද්යානය; formerly Victoria Park, si, වික්ටෝරියා පාක්) is a public park located in Cinnamon Gardens, Colombo, situated in front of the colon ...
, (formerly Victoria Park) is the oldest and largest park in Colombo
File:LK-colombo-uhrturm.jpg, Built in 1857, the Old Colombo Lighthouse also known as the Colombo Fort Clock Tower is the oldest clock-tower
File:20160122 Sri Lanka 3645 Colombo sRGB (25144304823).jpg, The BMICH Conference Hall
File:Sri Lanka Columbo west coast panorama.png, A clear view of the ocean off Colombo over a green field of grass
See also
* Colombo Town Guard * List of Mayors of Colombo * List of tallest buildings and structures in Sri Lanka * National War Memorial, Colombo * Place names in Sri Lanka * South Asian capitalsReferences
Further reading
The following books contain major components on Colombo: * ''Changing Face of Colombo (1501–1972): Covering the Portuguese, Dutch and British Periods'', by R.L. Brohier, 1984 (Lake House, Colombo) * ''The Port of Colombo 1860–1939'', K. Dharmasena, 1980 (Lake House, Colombo) * ''Decolonizing Ceylon: Colonialism, Nationalism and the Politics of Space in Sri Lanka'', by Nihal Perera, 1999 (Oxford University Press) *''the Essential guide for Colombo and its region'', :fr:Philippe Fabry, Philippe Fabry, Negombo, Viator Publications, 2011, 175 p., ISBN 978-955-8736-09-8 *''The impact of the Tsunami on households and vulnerable groups in two districts in Sri Lanka : Galle and Colombo,'' Swarna Jayaweera, Centre for Women's Research, Colombo, 2005 *''Patterns of Community Structure in Colombo, Sri Lanka, An investigation of Contemporary Urban Life in South Asia'', Neville S. Arachchige-Don, University Press, Maryland, 1994 *''Colombo'', Carl Muller, Penguin Books, New Delhi, 1995 {{Authority control Colombo, Former national capitals Populated places in Western Province, Sri Lanka Portuguese forts