Client-side Script on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 A server-side dynamic web page is a web page whose construction is controlled by an
A server-side dynamic web page is a web page whose construction is controlled by an
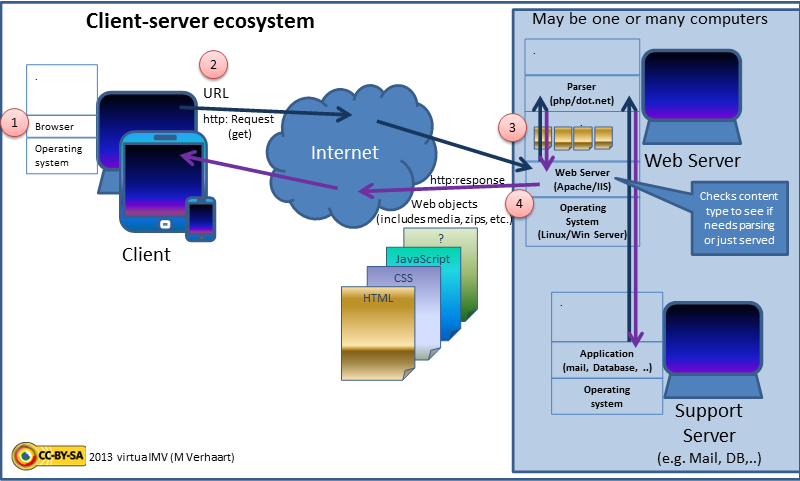 A program running on a
A program running on a
Static versus dynamic web site
from W3.org
Dynamic web sites
using the Relationship Management Method, from W3.org.
Wide analysis of dynamic web pages
from University of Texas, Austin. {{Web interfaces, state=collapsed Web development Web 1.0 Web design Website management
application server
An application server is a server that hosts applications or software that delivers a business application through a communication protocol.
An application server framework is a service layer model. It includes software components available to a ...
processing server-side scripts. In server-side scripting, parameter
A parameter (), generally, is any characteristic that can help in defining or classifying a particular system (meaning an event, project, object, situation, etc.). That is, a parameter is an element of a system that is useful, or critical, when ...
s determine how the assembly of every new web page proceeds, and including the setting up of more client-side processing.
A client-side dynamic web page processes the web page using JavaScript
JavaScript (), often abbreviated as JS, is a programming language that is one of the core technologies of the World Wide Web, alongside HTML and CSS. As of 2022, 98% of Website, websites use JavaScript on the Client (computing), client side ...
running in the browser as it loads. JavaScript
JavaScript (), often abbreviated as JS, is a programming language that is one of the core technologies of the World Wide Web, alongside HTML and CSS. As of 2022, 98% of Website, websites use JavaScript on the Client (computing), client side ...
can interact with the page via Document Object Model, or DOM, to query page state and modify it. Even though a web page can be dynamic on the client-side, it can still be hosted on a static hosting service
An Internet hosting service is a service that runs servers connected to the Internet, allowing organizations and individuals to serve content or host services connected to the Internet.
A common kind of hosting is web hosting. Most hosting provi ...
such as GitHub Pages
GitHub, Inc. () is an Internet hosting service for software development and version control using Git. It provides the distributed version control of Git plus access control, bug tracking, software feature requests, task management, continuou ...
or Amazon S3 as long as there isn't any server-side code included.
A dynamic web page is then reloaded by the user or by a computer program
A computer program is a sequence or set of instructions in a programming language for a computer to execute. Computer programs are one component of software, which also includes documentation and other intangible components.
A computer program ...
to change some variable content. The updating information could come from the server, or from changes made to that page's DOM. This may or may not truncate the browsing history or create a saved version to go back to, but a ''dynamic web page update'' using AJAX technologies will neither create a page to go back to, nor truncate the web browsing history forward of the displayed page. Using AJAX, the end user
Ancient Egyptian roles
* User (ancient Egyptian official), an ancient Egyptian nomarch (governor) of the Eighth Dynasty
* Useramen, an ancient Egyptian vizier also called "User"
Other uses
* User (computing), a person (or software) using an ...
gets one dynamic page managed as a single page in the web browser
A web browser is application software for accessing websites. When a user requests a web page from a particular website, the browser retrieves its files from a web server and then displays the page on the user's screen. Browsers are used on ...
while the actual web content rendered on that page can vary. The AJAX engine sits only on the browser requesting parts of its DOM, ''the'' DOM, for its client, from an application server. A particular application server could offer a standardized REST style interface to offer services to the web application.
DHTML is the umbrella term for technologies and methods used to create web pages that are not static web pages, though it has fallen out of common use since the popularization of AJAX, a term which is now itself rarely used. Client-side-scripting, server-side scripting, or a combination of these make for the dynamic web experience in a browser.
Basic concepts
Classicalhypertext
Hypertext is E-text, text displayed on a computer display or other electronic devices with references (hyperlinks) to other text that the reader can immediately access. Hypertext documents are interconnected by hyperlinks, which are typi ...
navigation, with HTML
The HyperText Markup Language or HTML is the standard markup language for documents designed to be displayed in a web browser. It can be assisted by technologies such as Cascading Style Sheets (CSS) and scripting languages such as JavaScri ...
or XHTML
Extensible HyperText Markup Language (XHTML) is part of the family of XML markup languages. It mirrors or extends versions of the widely used HyperText Markup Language (HTML), the language in which Web pages are formulated.
While HTML, prior ...
alone, provides "static" content, meaning that the user requests a web page and simply views the page and the information on that page.
However, a web page can also provide a "live", "dynamic", or "interactive" user experience. Content (text, images, form fields, etc.) on a web page can change, in response to different contexts or conditions.
There are two ways to create this kind of effect:
* Using client-side scripting to change interface behaviors ''within'' a specific web page, in response to mouse or keyboard actions or at specified timing events. In this case the dynamic behavior occurs within the presentation.
* Using server-side scripting to change the supplied page source ''between'' pages, adjusting the sequence or reload of the web pages or web content supplied to the browser. Server responses may be determined by such conditions as data in a posted HTML form, parameters in the URL
A Uniform Resource Locator (URL), colloquially termed as a web address, is a reference to a web resource that specifies its location on a computer network and a mechanism for retrieving it. A URL is a specific type of Uniform Resource Identifie ...
, the type of browser being used, the passage of time, or a database or server state.
Web pages that use client-side scripting must use presentation technology broadly called rich interfaced pages. Client-side scripting language
A scripting language or script language is a programming language that is used to manipulate, customize, and automate the facilities of an existing system. Scripting languages are usually interpreted at runtime rather than compiled.
A scripting ...
s like JavaScript
JavaScript (), often abbreviated as JS, is a programming language that is one of the core technologies of the World Wide Web, alongside HTML and CSS. As of 2022, 98% of Website, websites use JavaScript on the Client (computing), client side ...
or ActionScript
ActionScript is an object-oriented programming language originally developed by Macromedia Inc. (later acquired by Adobe). It is influenced by HyperTalk, the scripting language for HyperCard. It is now an implementation of ECMAScript (meaning i ...
, used for Dynamic HTML (DHTML) and Flash
Flash, flashes, or FLASH may refer to:
Arts, entertainment, and media
Fictional aliases
* Flash (DC Comics character), several DC Comics superheroes with super speed:
** Flash (Barry Allen)
** Flash (Jay Garrick)
** Wally West, the first Kid ...
technologies respectively, are frequently used to orchestrate media types (sound, animations, changing text, etc.) of the presentation. The scripting also allows use of remote scripting Remote scripting is a technology which allows scripts and programs that are running inside a browser to exchange information with a server. The local scripts can invoke scripts on the remote side and process the returned information.
The earliest ...
, a technique by which the DHTML page requests additional information from a server, using a hidden Frame, XMLHttpRequest
XMLHttpRequest (XHR) is an API in the form of an object whose methods transfer data between a web browser and a web server. The object is provided by the browser's JavaScript environment. Particularly, retrieval of data from XHR for the purpose o ...
s, or a web service.
Web pages that use server-side scripting are often created with the help of server-side
In the client–server model, server-side refers to programs and operations that run on the server. This is in contrast to client-side programs and operations which run on the client.
General concepts
Typically, a server is a computer application ...
languages such as PHP
PHP is a general-purpose scripting language geared toward web development. It was originally created by Danish-Canadian programmer Rasmus Lerdorf in 1993 and released in 1995. The PHP reference implementation is now produced by The PHP Group ...
, Perl
Perl is a family of two high-level, general-purpose, interpreted, dynamic programming languages. "Perl" refers to Perl 5, but from 2000 to 2019 it also referred to its redesigned "sister language", Perl 6, before the latter's name was offici ...
, ASP
Asp may refer to:
Places
* Asp, part of Densbüren, Aargau, Switzerland
* Aspe (''Asp'' in Valencian), Alicante, Spain
* Asp Lake, a lake in Minnesota
Animals
* Asp (fish)
* Asp (snake), in antiquity, one of several venomous snakes
** ''Cera ...
, ASP.NET
ASP.NET is an open-source, server-side web-application framework designed for web development to produce dynamic web pages. It was developed by Microsoft to allow programmers to build dynamic web sites, applications and services. The name stan ...
, JSP, ColdFusion
Adobe ColdFusion is a commercial rapid web-application development computing platform created by J. J. Allaire in 1995. (The programming language used with that platform is also commonly called ColdFusion, though is more accurately known as CF ...
and other languages. These server-side languages typically use the Common Gateway Interface
In computing, Common Gateway Interface (CGI) is an interface specification that enables web servers to execute an external program, typically to process user requests.
Such programs are often written in a scripting language and are commonly ref ...
(CGI) to produce ''dynamic web pages''. These kinds of pages can also use, on the client-side, the first kind (DHTML, etc.).
History
It is difficult to be precise about "dynamic web page beginnings" or chronology because the precise concept makes sense only after the "widespread development of web pages".HTTP
The Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) is an application layer protocol in the Internet protocol suite model for distributed, collaborative, hypermedia information systems. HTTP is the foundation of data communication for the World Wide Web, ...
has been in use since 1990, HTML
The HyperText Markup Language or HTML is the standard markup language for documents designed to be displayed in a web browser. It can be assisted by technologies such as Cascading Style Sheets (CSS) and scripting languages such as JavaScri ...
, as standard, since 1996. The web browser's rise in popularity started with Mosaic
A mosaic is a pattern or image made of small regular or irregular pieces of colored stone, glass or ceramic, held in place by plaster/mortar, and covering a surface. Mosaics are often used as floor and wall decoration, and were particularly pop ...
in 1993. It is obvious, however, that the concept of dynamically driven websites predates the Internet, and in fact HTML. For example, in 1990, before general public use of the Internet, a dynamically driven remotely accessed menu system was implemented by Susan Biddlecomb, who was Director of Computer Support of the USC Health Care system at the University of Southern California
The University of Southern California (USC, SC, or Southern Cal) is a Private university, private research university in Los Angeles, California, United States. Founded in 1880 by Robert M. Widney, it is the oldest private research university in C ...
BBS
BBS may refer to:
Ammunition
* BBs, BB gun metal bullets
* BBs, airsoft gun plastic pellets
Computing and gaming
* Bulletin board system, a computer server users dial into via dial-up or telnet; precursor to the Internet
* BIOS Boot Specificat ...
on a 16 line TBBS system with TDBS add-on.database. Between 1995 and 1996 Coldfusion
Adobe ColdFusion is a commercial rapid web-application development computing platform created by J. J. Allaire in 1995. (The programming language used with that platform is also commonly called ColdFusion, though is more accurately known as CF ...
, WebObjects, PHP
PHP is a general-purpose scripting language geared toward web development. It was originally created by Danish-Canadian programmer Rasmus Lerdorf in 1993 and released in 1995. The PHP reference implementation is now produced by The PHP Group ...
and Active Server Pages
Active Server Pages (ASP) is Microsoft's first server-side scripting language and engine for dynamic web pages.
It was first released in December 1996, before being superseded in January 2002 by ASP.NET.
History
Initially released as an add ...
were introduced to the market.
The introduction of JavaScript (then known as LiveScript) enabled the production of client-side dynamic web pages, with JavaScript code executed in the client's browser.
. The letter "J" in the term AJAX originally indicated the use of JavaScript, as well as XML
Extensible Markup Language (XML) is a markup language and file format for storing, transmitting, and reconstructing arbitrary data. It defines a set of rules for encoding documents in a format that is both human-readable and machine-readable. T ...
. With the rise of server side JavaScript processing, for example, Node.js
Node.js is an open-source server environment. Node.js is cross-platform and runs on Windows, Linux, Unix, and macOS. Node.js is a back-end JavaScript runtime environment. Node.js runs on the V8 JavaScript Engine and executes JavaScript code ou ...
, originally developed in 2009, JavaScript is also used to dynamically create pages on the server that are sent fully formed to clients.
MediaWiki
MediaWiki is a free and open-source wiki software. It is used on Wikipedia and almost all other Wikimedia websites, including Wiktionary, Wikimedia Commons and Wikidata; these sites define a large part of the requirement set for MediaWiki ...
, the content management system
A content management system (CMS) is computer software used to manage the creation and modification of digital content (content management).''Managing Enterprise Content: A Unified Content Strategy''. Ann Rockley, Pamela Kostur, Steve Manning. New ...
that powers Wikipedia, is an example for an originally server-side dynamic web page, interacted with through form submissions and URL parameters. Throughout time, progressively enhancing extensions such as the visual editor
A visual editor is computer software for editing text files using a textual or graphical user interface that normally renders the content (text) in accordance with embedded markup code, e.g., HTML, Wikitext, rather than displaying the raw text. E ...
have also added elements that are dynamic on the client side, while the original dynamic server-side elements such as the classic edit form remain available to be fallen back on (graceful degradation
Fault tolerance is the property that enables a system to continue operating properly in the event of the failure of one or more faults within some of its components. If its operating quality decreases at all, the decrease is proportional to the ...
) in case of error or incompatibility.
Server-side scripting
 A program running on a
A program running on a web server
A web server is computer software and underlying hardware that accepts requests via HTTP (the network protocol created to distribute web content) or its secure variant HTTPS. A user agent, commonly a web browser or web crawler, initiate ...
( server-side scripting) is used to generate the web content on various web pages, manage user sessions, and control workflow. Server responses may be determined by such conditions as data in a posted HTML form, parameters in the URL
A Uniform Resource Locator (URL), colloquially termed as a web address, is a reference to a web resource that specifies its location on a computer network and a mechanism for retrieving it. A URL is a specific type of Uniform Resource Identifie ...
, the type of browser being used, the passage of time, or a database or server state.
Such web pages are often created with the help of server-side
In the client–server model, server-side refers to programs and operations that run on the server. This is in contrast to client-side programs and operations which run on the client.
General concepts
Typically, a server is a computer application ...
languages such as ASP
Asp may refer to:
Places
* Asp, part of Densbüren, Aargau, Switzerland
* Aspe (''Asp'' in Valencian), Alicante, Spain
* Asp Lake, a lake in Minnesota
Animals
* Asp (fish)
* Asp (snake), in antiquity, one of several venomous snakes
** ''Cera ...
, ColdFusion
Adobe ColdFusion is a commercial rapid web-application development computing platform created by J. J. Allaire in 1995. (The programming language used with that platform is also commonly called ColdFusion, though is more accurately known as CF ...
, Go, JavaScript
JavaScript (), often abbreviated as JS, is a programming language that is one of the core technologies of the World Wide Web, alongside HTML and CSS. As of 2022, 98% of Website, websites use JavaScript on the Client (computing), client side ...
, Perl
Perl is a family of two high-level, general-purpose, interpreted, dynamic programming languages. "Perl" refers to Perl 5, but from 2000 to 2019 it also referred to its redesigned "sister language", Perl 6, before the latter's name was offici ...
, PHP
PHP is a general-purpose scripting language geared toward web development. It was originally created by Danish-Canadian programmer Rasmus Lerdorf in 1993 and released in 1995. The PHP reference implementation is now produced by The PHP Group ...
, Ruby
A ruby is a pinkish red to blood-red colored gemstone, a variety of the mineral corundum ( aluminium oxide). Ruby is one of the most popular traditional jewelry gems and is very durable. Other varieties of gem-quality corundum are called sa ...
, Python
Python may refer to:
Snakes
* Pythonidae, a family of nonvenomous snakes found in Africa, Asia, and Australia
** ''Python'' (genus), a genus of Pythonidae found in Africa and Asia
* Python (mythology), a mythical serpent
Computing
* Python (pro ...
, WebDNA and other languages, by a support server that can run on the same hardware as the web server. These server-side languages often use the Common Gateway Interface
In computing, Common Gateway Interface (CGI) is an interface specification that enables web servers to execute an external program, typically to process user requests.
Such programs are often written in a scripting language and are commonly ref ...
(CGI) to produce dynamic web pages. Two notable exceptions are ASP.NET
ASP.NET is an open-source, server-side web-application framework designed for web development to produce dynamic web pages. It was developed by Microsoft to allow programmers to build dynamic web sites, applications and services. The name stan ...
, and JSP, which reuse CGI concepts in their APIs but actually dispatch all web requests into a shared virtual machine.
The server-side languages are used to embed tags or markers within the source file of the web page on the web server. When a user on a client computer requests that web page, the web server interprets these tags or markers to perform actions on the server. For example, the server may be instructed to insert information from a database or information such as the current date.
Dynamic web pages are often cached when there are few or no changes expected and the page is anticipated to receive considerable amount of web traffic that would wastefully strain the server and slow down page loading if it had to generate the pages on the fly for each request.
Client-side scripting
Client-side scripting is changing interface behaviors within a specific web page in response to input device actions, or at specified timing events. In this case, the dynamic behavior occurs within the presentation. The client-side content is generated on the user's local computer system. Such web pages use presentation technology called rich interfaced pages. Client-side scripting languages likeJavaScript
JavaScript (), often abbreviated as JS, is a programming language that is one of the core technologies of the World Wide Web, alongside HTML and CSS. As of 2022, 98% of Website, websites use JavaScript on the Client (computing), client side ...
or ActionScript
ActionScript is an object-oriented programming language originally developed by Macromedia Inc. (later acquired by Adobe). It is influenced by HyperTalk, the scripting language for HyperCard. It is now an implementation of ECMAScript (meaning i ...
, used for Dynamic HTML (DHTML) and Flash
Flash, flashes, or FLASH may refer to:
Arts, entertainment, and media
Fictional aliases
* Flash (DC Comics character), several DC Comics superheroes with super speed:
** Flash (Barry Allen)
** Flash (Jay Garrick)
** Wally West, the first Kid ...
technologies respectively, are frequently used to orchestrate media types (sound, animations, changing text, etc.) of the presentation. Client-side scripting also allows the use of remote scripting Remote scripting is a technology which allows scripts and programs that are running inside a browser to exchange information with a server. The local scripts can invoke scripts on the remote side and process the returned information.
The earliest ...
, a technique by which the DHTML page requests additional information from a server, using a hidden frame, XMLHttpRequest
XMLHttpRequest (XHR) is an API in the form of an object whose methods transfer data between a web browser and a web server. The object is provided by the browser's JavaScript environment. Particularly, retrieval of data from XHR for the purpose o ...
s, or a Web service.
The first widespread use of JavaScript was in 1997, when the language was standardized as ECMAScript
ECMAScript (; ES) is a JavaScript standard intended to ensure the interoperability of web pages across different browsers. It is standardized by Ecma International in the documenECMA-262
ECMAScript is commonly used for client-side scripting o ...
and implemented in Netscape 3.
; Example
The client-side content is generated on the client's computer. The web browser retrieves a page from the server, then processes the code embedded in the page (typically written in JavaScript
JavaScript (), often abbreviated as JS, is a programming language that is one of the core technologies of the World Wide Web, alongside HTML and CSS. As of 2022, 98% of Website, websites use JavaScript on the Client (computing), client side ...
) and displays the retrieved page's content to the user.
The innerHTML property (or write command) can illustrate the client-side dynamic page generation: two distinct pages, A and B, can be regenerated (by an "event response dynamic") as document.innerHTML = A and document.innerHTML = B; or "on load dynamic" by document.write(A) and document.write(B).
Combination technologies
All of the client and server components that collectively build a dynamic web page are called aweb application
A web application (or web app) is application software that is accessed using a web browser. Web applications are delivered on the World Wide Web to users with an active network connection.
History
In earlier computing models like client-serve ...
. Web applications manage user interactions, state, security, and performance.
Ajax uses a combination of both client-side scripting and server-side requests. It is a web application development technique for dynamically interchanging content, and it sends requests to the server for data in order to do so. The server returns the requested data which is then processed by a client-side script. This technique can reduce server load time because the client does not request the entire webpage to be regenerated by the server's language parser; only the content that will change is transmitted. Google Maps
Google Maps is a web mapping platform and consumer application offered by Google. It offers satellite imagery, aerial photography, street maps, 360° interactive panoramic views of streets ( Street View), real-time traffic conditions, and rou ...
is an example of a web application that uses Ajax techniques.
A web client
A web browser is application software for accessing websites. When a user requests a web page from a particular website, the browser retrieves its files from a web server and then displays the page on the user's screen. Browsers are used on ...
, such as a web browser, can act as its own server, accessing data from many different servers, such as Gopher, FTP, NNTP (Usenet) and HTTP, to build a page. HTTP
The Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) is an application layer protocol in the Internet protocol suite model for distributed, collaborative, hypermedia information systems. HTTP is the foundation of data communication for the World Wide Web, ...
supports uploading documents from the client back to the server. There are several HTTP methods for doing this.
See also
* Static web page * Dynamic HTML * Responsive Web Design * Deep web (search indexing) * Web template system *Solution stack
In computing, a solution stack or software stack is a set of software subsystems or components needed to create a complete Computing platform, platform such that no additional software is needed to support applications. Applications are said to " ...
s to serve dynamic web pages
** LAMP (software bundle)
** LYME (software bundle)
** LYCE (software bundle)
LYME and LYCE are software stacks composed entirely of free and open-source software to build high-availability heavy duty dynamic web pages. The stacks are composed of:
* Linux, the operating system;
* Yaws, the web server;
* Mnesia or Couc ...
* Content management system
A content management system (CMS) is computer software used to manage the creation and modification of digital content (content management).''Managing Enterprise Content: A Unified Content Strategy''. Ann Rockley, Pamela Kostur, Steve Manning. New ...
* Web content management system
* Personalization management system
A personalization management system (PMS) is an integrated software solution that enables users in an organization to manage and deliver personalized messages, campaigns, and interactive experiences to consumers across different communications cha ...
References
External links
Static versus dynamic web site
from W3.org
Dynamic web sites
using the Relationship Management Method, from W3.org.
Wide analysis of dynamic web pages
from University of Texas, Austin. {{Web interfaces, state=collapsed Web development Web 1.0 Web design Website management