Classification Chart on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Classification chart or classification tree is a synopsis of the
Classification chart or classification tree is a synopsis of the
Charts and graphs: An introduction to graphic methods in the control and analysis of statistics
'' Prentice-Hall, 1923, p. 13.
Edward Hitchcock’s Pre-Darwinian (1840) 'Tree of Life'
''Journal of the History of Biology'' (2009) 42:561–592. * In 1840 Edward Hitchcock inserted a paleontological chart in his ''Elementary Geology'' (1840). It shows a branching diagram of the plant and animal kingdom against a geological background. * The tree of life image that appeared in Darwin's ''
 Classification chart or classification tree is a synopsis of the
Classification chart or classification tree is a synopsis of the classification scheme
In information science and ontology, a classification scheme is the product of arranging things into kinds of things (classes) or into ''groups'' of classes; this bears similarity to categorization, but with perhaps a more theoretical bent, as cl ...
, designed to illustrate the structure of any particular field.
Overview
Classification is the process in which ideas and objects are recognized, differentiated, and understood, and classification charts are intended to help create and eventually visualize the outcome. According to Brinton "in a classification chart the facts, data etc. are arranged so that the place of each in relation to all others is readily seen. Quantities need not be given, although a quantitative analysis adds to the value of a classification chart." Willard Cope Brinton, ''Graphic presentation.'' 1939. p. 43Karsten
Karsten or Carsten is a both a given name and a surname. It is believed to be either derived from a Low German form of Christian, or "man from karst". Notable persons with the name include:
Given name
;Carsten:
* Carsten Charles Sabathia (born 1 ...
(1923) explained, that "in all chart-making, the material to be shown must be accurately compiled before it can be charted. For an understanding of the classification chart, we must delve somewhat into the mysteries of the classification and indexing. The art of classification calls into play the power of visualizing a 'whole' together with its 'parts'." Karsten, Karl G. Charts and graphs: An introduction to graphic methods in the control and analysis of statistics
'' Prentice-Hall, 1923, p. 13.
Examples
Early examples of classification chart are: * The illustrations of theCarl Linnaeus
Carl Linnaeus (; 23 May 1707 – 10 January 1778), also known after his ennoblement in 1761 as Carl von Linné Blunt (2004), p. 171. (), was a Swedish botanist, zoologist, taxonomist, and physician who formalised binomial nomenclature, ...
' 1735 classification of animals
Animals are multicellular, eukaryotic organisms in the Kingdom (biology), biological kingdom Animalia. With few exceptions, animals Heterotroph, consume organic material, Cellular respiration#Aerobic respiration, breathe oxygen, are Motilit ...
and his classification Classification is a process related to categorization, the process in which ideas and objects are recognized, differentiated and understood.
Classification is the grouping of related facts into classes.
It may also refer to:
Business, organizat ...
of plant
Plants are predominantly Photosynthesis, photosynthetic eukaryotes of the Kingdom (biology), kingdom Plantae. Historically, the plant kingdom encompassed all living things that were not animals, and included algae and fungi; however, all curr ...
s in his ''Classes Plantarum'' 1738.
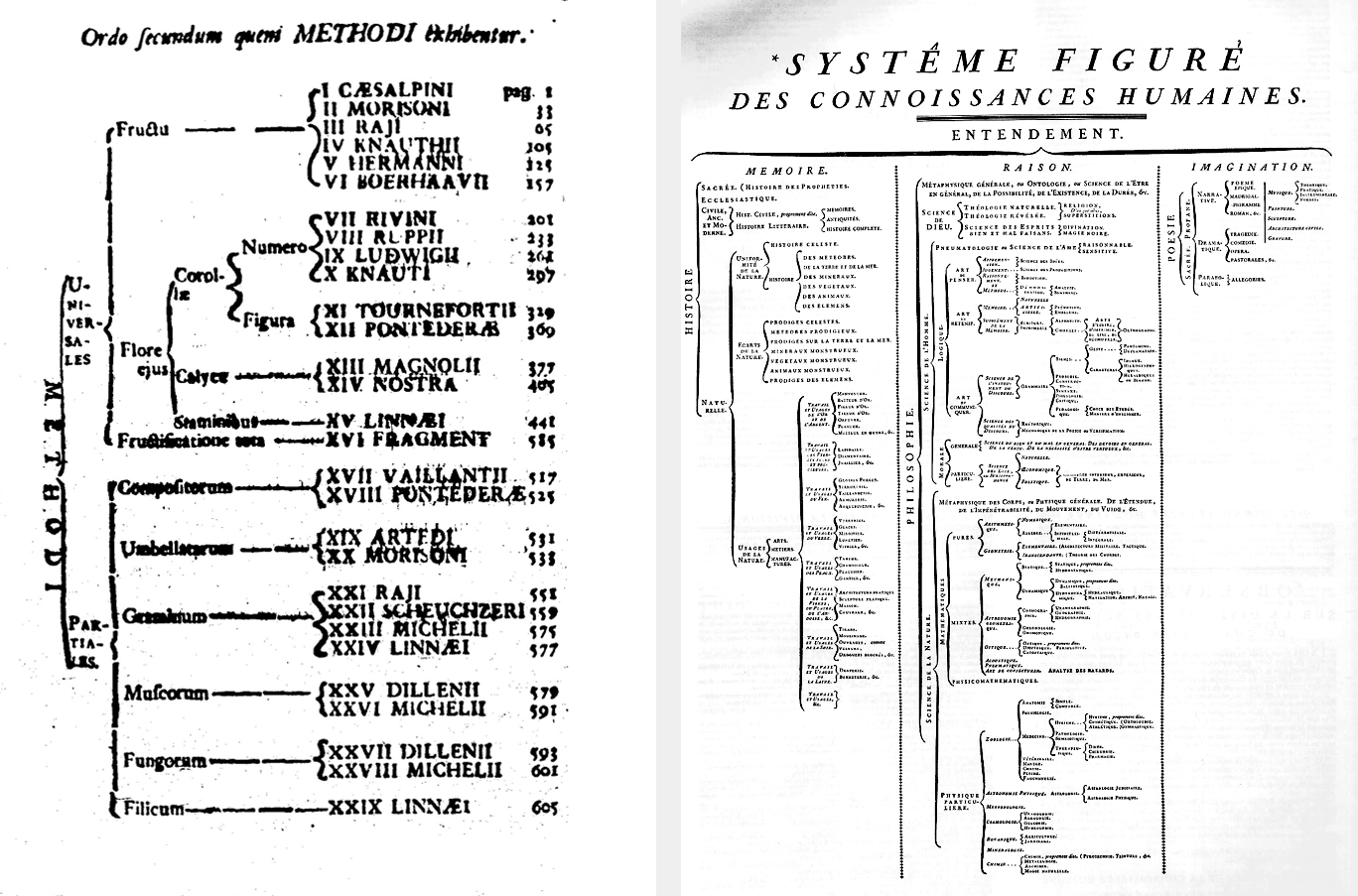
* In 1752 Jean le Rond d'Alembert
Jean-Baptiste le Rond d'Alembert (; ; 16 November 1717 – 29 October 1783) was a French mathematician, mechanician, physicist, philosopher, and music theorist. Until 1759 he was, together with Denis Diderot, a co-editor of the '' Encyclop� ...
and Denis Diderot
Denis Diderot (; ; 5 October 171331 July 1784) was a French philosopher, art critic, and writer, best known for serving as co-founder, chief editor, and contributor to the ''Encyclopédie'' along with Jean le Rond d'Alembert. He was a promine ...
produced a figurative system of human knowledge produced for the ''Encyclopédie
''Encyclopédie, ou dictionnaire raisonné des sciences, des arts et des métiers'' (English: ''Encyclopedia, or a Systematic Dictionary of the Sciences, Arts, and Crafts''), better known as ''Encyclopédie'', was a general encyclopedia publis ...
.''
* Augustin Augier's "Arbre Botanique" (1801)J. David Archibald (2009)Edward Hitchcock’s Pre-Darwinian (1840) 'Tree of Life'
''Journal of the History of Biology'' (2009) 42:561–592. * In 1840 Edward Hitchcock inserted a paleontological chart in his ''Elementary Geology'' (1840). It shows a branching diagram of the plant and animal kingdom against a geological background. * The tree of life image that appeared in Darwin's ''
On the Origin of Species
''On the Origin of Species'' (or, more completely, ''On the Origin of Species by Means of Natural Selection, or the Preservation of Favoured Races in the Struggle for Life''),The book's full original title was ''On the Origin of Species by Me ...
,'' 1859
Early classification chart are often visualized in a tree structure
A tree structure, tree diagram, or tree model is a way of representing the hierarchical nature of a structure in a graphical form. It is named a "tree structure" because the classic representation resembles a tree, although the chart is genera ...
. Modern charts can also be presented in table or as an infographic.
The term "classification chart" came into use in the 20th century. In his 1939 ''Graphic presentation.'' (first edition 1919) Willard Cope Brinton was one of the first to devoted a whole chapter on classification charts.
See also
* Chart *Decision tree
A decision tree is a decision support tool that uses a tree-like model of decisions and their possible consequences, including chance event outcomes, resource costs, and utility. It is one way to display an algorithm that only contains co ...
* Decision tree learning
* Phylogenetic trees
* Tree of life (biology)
The tree of life or universal tree of life is a metaphor, model and research tool used to explore the evolution of life and describe the relationships between organisms, both living and extinct, as described in a famous passage in Charles Dar ...
* Tree structure
A tree structure, tree diagram, or tree model is a way of representing the hierarchical nature of a structure in a graphical form. It is named a "tree structure" because the classic representation resembles a tree, although the chart is genera ...
References
{{reflist Charts Classification systems