Class Of Accuracy In Electrical Measurements on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 In electrical engineering class of accuracy is a figure which represents the error tolerance of a measuring device.
In electrical engineering class of accuracy is a figure which represents the error tolerance of a measuring device.
 In electrical engineering class of accuracy is a figure which represents the error tolerance of a measuring device.
In electrical engineering class of accuracy is a figure which represents the error tolerance of a measuring device.
Class of accuracy
Measuring devices are labelled for the class of accuracy. This figure is the percentage of the inherent error of the measuring device with respect to full scale deflection. For example, if the class of accuracy is 2 that means an error of 2 volts in a full scale 100 volt reading.Measurement
In electrical engineering, characteristics likecurrent
Currents, Current or The Current may refer to:
Science and technology
* Current (fluid), the flow of a liquid or a gas
** Air current, a flow of air
** Ocean current, a current in the ocean
*** Rip current, a kind of water current
** Current (stre ...
or voltage
Voltage, also known as electric pressure, electric tension, or (electric) potential difference, is the difference in electric potential between two points. In a static electric field, it corresponds to the work needed per unit of charge to m ...
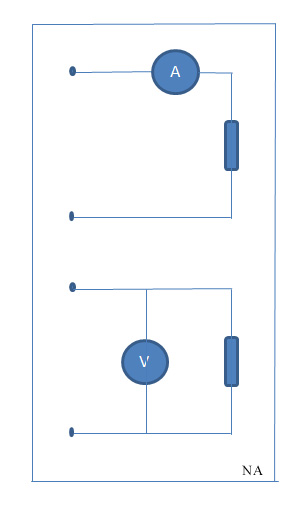
can be measured by an ammeter
An ammeter (abbreviation of ''Ampere meter'') is an instrument used to measure the current in a circuit. Electric currents are measured in amperes (A), hence the name. For direct measurement, the ammeter is connected in series with the circuit ...
, a voltmeter
A voltmeter is an instrument used for measuring electric potential difference between two points in an electric circuit. It is connected in parallel. It usually has a high resistance so that it takes negligible current from the circuit.
Ana ...
, a multimeter
A multimeter is a measuring instrument that can measure multiple electrical properties. A typical multimeter can measure voltage, resistance, and current, in which case it is also known as a volt-ohm-milliammeter (VOM), as the unit is equipped w ...
, etc. The ammeter is used in series with the load, so the same current flows through the load and the ammeter. The voltmeter is used in parallel with the load, so the voltage between the two terminals of the load is equal to the voltage between the two terminals of the voltmeter. Ideally the measuring device should not affect the circuit parameters i.e., the internal impedance of the ammeter should be zero (no voltage drop over the ammeter) and the internal impedance of the voltmeter should be infinite (no current through the voltmeter). However, in actual case, ammeters have a low but non zero impedance and voltmeters have a high but not infinite internal impedance. Thus the measured parameters are somewhat altered during the measurements.
Example
Let V be the voltage (EMF) of the source R be the resistance of the load and r be the resistance of the ammeter. The current through the load is I : When the ammeter is connected in series with the load the current I2 is : The difference introduced by the measuring device is then, : The ratio of the difference to the actual value is Georg Rose: ''Elektroteknik ve Elektronik Formüller'' (translation: Haluk Erna), İnkılap and Aka Bookhouses, İstanbul, 1975, p.175 :References