Clan Tartan on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Tartan ( gd, breacan ) is a patterned cloth consisting of criss-crossed, horizontal and vertical bands in multiple colours. Tartans originated in woven wool, but now they are made in other materials. Tartan is particularly associated with Scotland, as Scottish kilts almost always have tartan patterns.
Tartan is made with alternating bands of coloured (pre-dyed) threads woven as both
Tartan ( gd, breacan ) is a patterned cloth consisting of criss-crossed, horizontal and vertical bands in multiple colours. Tartans originated in woven wool, but now they are made in other materials. Tartan is particularly associated with Scotland, as Scottish kilts almost always have tartan patterns.
Tartan is made with alternating bands of coloured (pre-dyed) threads woven as both
 The English and
The English and
File:Tartan diagram (warp and weft) A.svg, Diagram A, the warp
File:Tartan diagram (warp and weft) B.svg, Diagram B, the weft
File:Tartan diagram (warp and weft) C.svg, Diagram C, the tartan. The combining of the warp and weft.
 The shades of colour in tartan can be altered to produce variations of the same tartan. The resulting variations are termed: ''modern'', ''ancient'', and ''muted''."Muted" colours are also called "reproduction" colours. These terms only refer to dye colours.
; Modern colours
: Describes a tartan that is coloured using chemical dye, as opposed to natural dye. In the mid-19th century natural dyes began to be replaced by chemical dyes which were easier to use and were more economic for the booming tartan industry. Chemical dyes tend to produce a very strong, vivid colour compared to natural dyes. In ''modern'' colours, setts made up of blue, black, and green tend to be obscured.
; Ancient colours
: Refers to a lighter shade of tartan. These shades are meant to represent the colours that would result from fabric aging over time.
; Muted colours
: Also called ''reproduction'' colours, refers to tartan which is shade between ''modern'' and ''ancient''. Although this type of colouring is very recent, dating only from the early 1970s, these shades are thought to be the closest match to the colours attained by natural dyes used before the mid-19th century.
The idea that the various colours used in tartan have a specific meaning is purely a modern one. One such myth is that red tartans were "battle tartans", designed so they would not show blood. It is only recently created tartans, such as Canadian provincial and territorial tartans (beginning 1950s) and US state tartans (beginning 1980s), that are designed with certain symbolic meaning for the colours used. For example, the colour ''green'' sometimes represents prairies or forests, ''blue'' can represent lakes and rivers, and the colour ''yellow'' is sometimes used to represent various crops.
The shades of colour in tartan can be altered to produce variations of the same tartan. The resulting variations are termed: ''modern'', ''ancient'', and ''muted''."Muted" colours are also called "reproduction" colours. These terms only refer to dye colours.
; Modern colours
: Describes a tartan that is coloured using chemical dye, as opposed to natural dye. In the mid-19th century natural dyes began to be replaced by chemical dyes which were easier to use and were more economic for the booming tartan industry. Chemical dyes tend to produce a very strong, vivid colour compared to natural dyes. In ''modern'' colours, setts made up of blue, black, and green tend to be obscured.
; Ancient colours
: Refers to a lighter shade of tartan. These shades are meant to represent the colours that would result from fabric aging over time.
; Muted colours
: Also called ''reproduction'' colours, refers to tartan which is shade between ''modern'' and ''ancient''. Although this type of colouring is very recent, dating only from the early 1970s, these shades are thought to be the closest match to the colours attained by natural dyes used before the mid-19th century.
The idea that the various colours used in tartan have a specific meaning is purely a modern one. One such myth is that red tartans were "battle tartans", designed so they would not show blood. It is only recently created tartans, such as Canadian provincial and territorial tartans (beginning 1950s) and US state tartans (beginning 1980s), that are designed with certain symbolic meaning for the colours used. For example, the colour ''green'' sometimes represents prairies or forests, ''blue'' can represent lakes and rivers, and the colour ''yellow'' is sometimes used to represent various crops.
 Today tartan is mostly associated with Scotland; however, the earliest evidence of tartan is found far afield from Britain. According to the textile historian E. J. W. Barber, the
Today tartan is mostly associated with Scotland; however, the earliest evidence of tartan is found far afield from Britain. According to the textile historian E. J. W. Barber, the
 The tartan as we know it today is not thought to have existed in Scotland before the 16th century. By the late 16th century there are numerous references to striped or checkered plaids. It is not until the late 17th or early 18th century that uniformity in tartan is thought to have occurred. Martin Martin, in ''A Description of the Western Islands of Scotland'', published in 1703, wrote that Scottish tartans could be used to distinguish the inhabitants of different regions. He expressly wrote that the inhabitants of various islands and the mainland of the Highlands were not all dressed alike, but that the setts and colours of the various tartans varied from isle to isle. As he does not mention the use of a special pattern by each family, it would appear that such a distinction is a modern one.
For centuries the patterns were loosely associated with the weavers of a particular area, though it was common for highlanders to wear a number of different tartans at the same time. A 1587 charter granted to Hector Maclean of Duart requires feu duty on land paid as 60
The tartan as we know it today is not thought to have existed in Scotland before the 16th century. By the late 16th century there are numerous references to striped or checkered plaids. It is not until the late 17th or early 18th century that uniformity in tartan is thought to have occurred. Martin Martin, in ''A Description of the Western Islands of Scotland'', published in 1703, wrote that Scottish tartans could be used to distinguish the inhabitants of different regions. He expressly wrote that the inhabitants of various islands and the mainland of the Highlands were not all dressed alike, but that the setts and colours of the various tartans varied from isle to isle. As he does not mention the use of a special pattern by each family, it would appear that such a distinction is a modern one.
For centuries the patterns were loosely associated with the weavers of a particular area, though it was common for highlanders to wear a number of different tartans at the same time. A 1587 charter granted to Hector Maclean of Duart requires feu duty on land paid as 60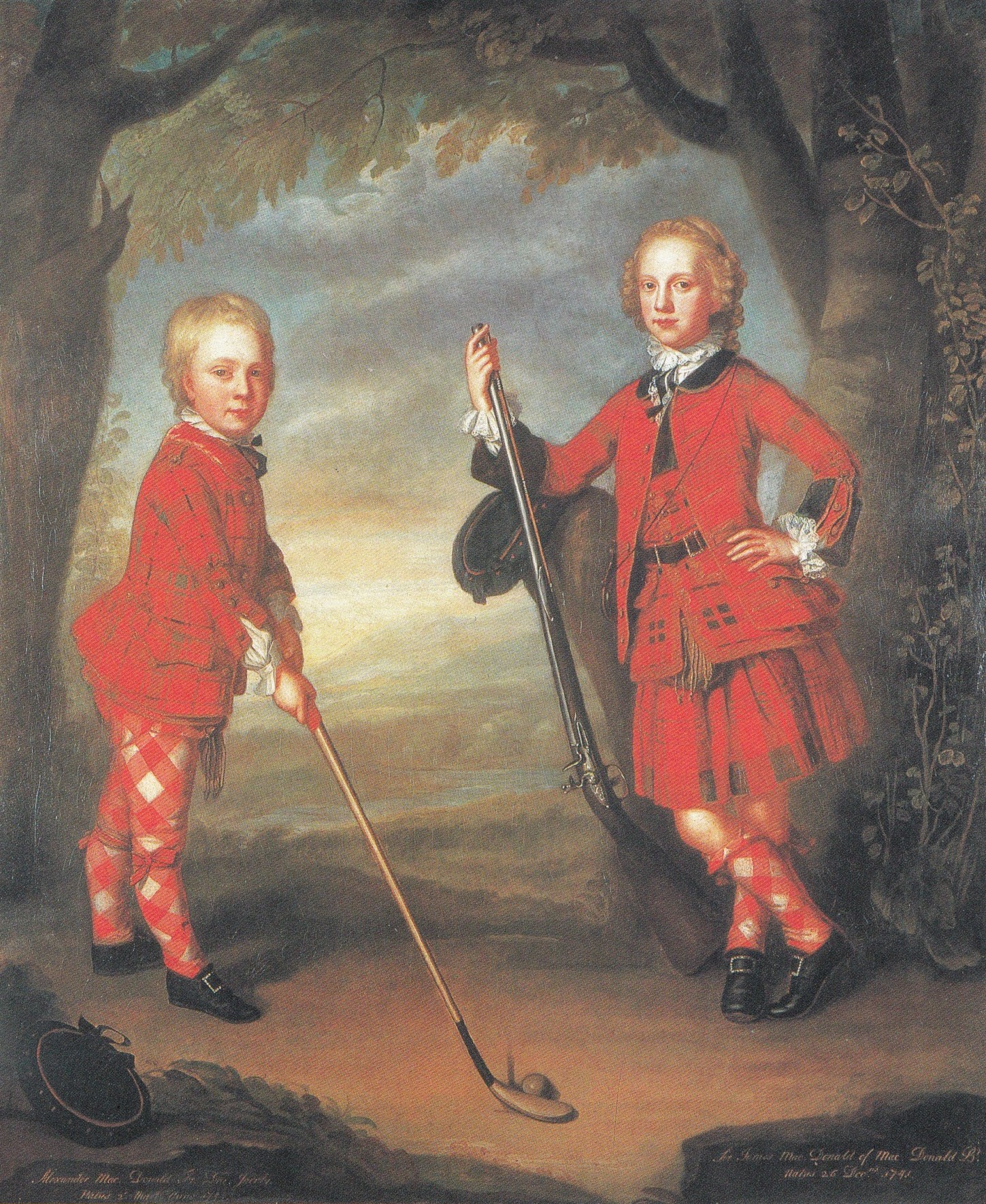  The most effective fighters for Jacobitism were the supporting Scottish clans, leading to an association of tartans with the Jacobite cause. Efforts to pacify the Highlands led to the ''Dress Act of 1746'', banning tartans, except for the Highland regiments of the British army. " was probably their use of it which gave birth to the idea of differentiating tartan by clans; for as the Highland regiments were multiplied ... so their tartan uniforms were differentiated."
The act was repealed in 1782, due to the efforts of the Highland Society of London. William Wilson & Sons of Bannockburn became the foremost weaving manufacturer around 1770 as suppliers of tartan to the military. Wilson corresponded with his agents in the Highlands to get information and samples of cloth from the clan districts to enable him to reproduce "perfectly genuine patterns" and recorded over 200 setts by 1822. The Cockburn Collection of named samples made by William Wilson & Sons was put together between 1810 and 1820 and is now in the Mitchell Library in Glasgow. At this time setts were simply numbered, or given fanciful names such as the " Robin Hood" tartan, not associated with a specific clan.
The most effective fighters for Jacobitism were the supporting Scottish clans, leading to an association of tartans with the Jacobite cause. Efforts to pacify the Highlands led to the ''Dress Act of 1746'', banning tartans, except for the Highland regiments of the British army. " was probably their use of it which gave birth to the idea of differentiating tartan by clans; for as the Highland regiments were multiplied ... so their tartan uniforms were differentiated."
The act was repealed in 1782, due to the efforts of the Highland Society of London. William Wilson & Sons of Bannockburn became the foremost weaving manufacturer around 1770 as suppliers of tartan to the military. Wilson corresponded with his agents in the Highlands to get information and samples of cloth from the clan districts to enable him to reproduce "perfectly genuine patterns" and recorded over 200 setts by 1822. The Cockburn Collection of named samples made by William Wilson & Sons was put together between 1810 and 1820 and is now in the Mitchell Library in Glasgow. At this time setts were simply numbered, or given fanciful names such as the " Robin Hood" tartan, not associated with a specific clan.
 It is generally regarded that "clan tartans" date no earlier than the beginning of the 19th century, and are an example of an invented tradition. Contemporary portraits show that although tartan is of an early date, the pattern worn depended not on the wearer's clan, but rather upon his or her present affiliation, place of origin or current residence, or personal taste.
David Morier's well-known mid-1700s painting of the Highland charge at the
It is generally regarded that "clan tartans" date no earlier than the beginning of the 19th century, and are an example of an invented tradition. Contemporary portraits show that although tartan is of an early date, the pattern worn depended not on the wearer's clan, but rather upon his or her present affiliation, place of origin or current residence, or personal taste.
David Morier's well-known mid-1700s painting of the Highland charge at the
 The popularity of tartan was greatly increased by the royal visit of George IV to Edinburgh in 1822. George IV was the first reigning monarch to visit Scotland in 171 years. Moncreiffe of that Ilk 1967: p. 24. The festivities surrounding the event were originated by Sir Walter Scott who founded the Celtic Society of Edinburgh in 1820. Scott and the Celtic Society urged Scots to attend festivities "all plaided and plumed in their tartan array". One contemporary writer sarcastically described the pomp that surrounded the celebrations as "Sir Walter's Celtified Pagentry". Magnusson 2003: pp. 653–654.
The popularity of tartan was greatly increased by the royal visit of George IV to Edinburgh in 1822. George IV was the first reigning monarch to visit Scotland in 171 years. Moncreiffe of that Ilk 1967: p. 24. The festivities surrounding the event were originated by Sir Walter Scott who founded the Celtic Society of Edinburgh in 1820. Scott and the Celtic Society urged Scots to attend festivities "all plaided and plumed in their tartan array". One contemporary writer sarcastically described the pomp that surrounded the celebrations as "Sir Walter's Celtified Pagentry". Magnusson 2003: pp. 653–654.
 Twenty years after her uncle's visit to Scotland, Queen Victoria and her husband
Twenty years after her uncle's visit to Scotland, Queen Victoria and her husband
 The naming and registration of official clan tartans began on 8 April 1815, when the Highland Society of London (founded 1778) resolved that the clan chiefs each "be respectfully solicited to furnish the Society with as much of the Tartan of his Lordship's Clan as will serve to Show the Pattern and to Authenticate the Same by Attaching Thereunto a Card bearing the Impression of his Lordship's Arms." Many had no idea of what their tartan might be, but were keen to comply and to provide authentic signed and sealed samples. Alexander Macdonald, 2nd Baron Macdonald was so far removed from his Highland heritage that he wrote to the Society: "Being really ignorant of what is exactly The Macdonald Tartan, I request you will have the goodness to exert every Means in your power to Obtain a perfectly genuine Pattern, Such as Will Warrant me in Authenticating it with my Arms."
Today tartan and "clan tartan" is an important part of a Scottish clan. Most Scottish clans have several tartans attributed to their name and some clans have "official" tartans. Although it is possible for anyone to create a tartan and name it any name they wish, the only person with the authority to make a clan's tartan "official" is the chief.
In some cases, following such recognition from the clan chief, the clan tartan is recorded and registered by the Lord Lyon King of Arms. Once approved by the Lord Lyon, after recommendation by the Advisory Committee on Tartan, the clan tartan is then recorded in the Lyon Court Books.Campbell of Airds (2000), pp. 259–261. In at least one instance a clan tartan appears in the heraldry of a clan chief and is considered by the Lord Lyon as the "proper" tartan of the clan.
Modern-day tartans also encompass registered tartans for Irish clans, (for example, the surname Fitzpatrick has two registered tartans) counties, and other Gaelic and Celtic nations, such as the Isle of Man, Wales, and Cornwall.
The naming and registration of official clan tartans began on 8 April 1815, when the Highland Society of London (founded 1778) resolved that the clan chiefs each "be respectfully solicited to furnish the Society with as much of the Tartan of his Lordship's Clan as will serve to Show the Pattern and to Authenticate the Same by Attaching Thereunto a Card bearing the Impression of his Lordship's Arms." Many had no idea of what their tartan might be, but were keen to comply and to provide authentic signed and sealed samples. Alexander Macdonald, 2nd Baron Macdonald was so far removed from his Highland heritage that he wrote to the Society: "Being really ignorant of what is exactly The Macdonald Tartan, I request you will have the goodness to exert every Means in your power to Obtain a perfectly genuine Pattern, Such as Will Warrant me in Authenticating it with my Arms."
Today tartan and "clan tartan" is an important part of a Scottish clan. Most Scottish clans have several tartans attributed to their name and some clans have "official" tartans. Although it is possible for anyone to create a tartan and name it any name they wish, the only person with the authority to make a clan's tartan "official" is the chief.
In some cases, following such recognition from the clan chief, the clan tartan is recorded and registered by the Lord Lyon King of Arms. Once approved by the Lord Lyon, after recommendation by the Advisory Committee on Tartan, the clan tartan is then recorded in the Lyon Court Books.Campbell of Airds (2000), pp. 259–261. In at least one instance a clan tartan appears in the heraldry of a clan chief and is considered by the Lord Lyon as the "proper" tartan of the clan.
Modern-day tartans also encompass registered tartans for Irish clans, (for example, the surname Fitzpatrick has two registered tartans) counties, and other Gaelic and Celtic nations, such as the Isle of Man, Wales, and Cornwall.
File:Royal Stewart tartan.png, Royal Stewart tartan
File:Black_Watch_or_Campbell_tartan.svg, Black Watch tartan
 In addition to clan tartans, many tartan patterns have been developed for individuals, families, districts, institutions, and corporations. They have also been created for various events and certain
In addition to clan tartans, many tartan patterns have been developed for individuals, families, districts, institutions, and corporations. They have also been created for various events and certain
 Tartans are sometimes differentiated from another with the same name by the label ''dress'', ''hunting'', or rarely ''mourning''.
Dress tartans are based on the ''earasaid'' tartans worn by Highland women in the 17th and 18th centuries. Dress tartans tend to be made by replacing a prominent colour with the colour white. They are commonly used today in Highland dancing.
Hunting tartans also seem to be a Victorian conception, although there is some evidence of early tartans with camouflage colours. These tartans tend to be made up of subdued colours, such as dark blues and greens. Despite the name, hunting tartans have very little to do with actual hunting.
Mourning tartans, though quite rare, are associated with death and funerals. They are usually designed using combinations of black and white, or by replacing bright colors such as reds and yellows in a traditional tartan with black, white, or grey.
Tartans are sometimes differentiated from another with the same name by the label ''dress'', ''hunting'', or rarely ''mourning''.
Dress tartans are based on the ''earasaid'' tartans worn by Highland women in the 17th and 18th centuries. Dress tartans tend to be made by replacing a prominent colour with the colour white. They are commonly used today in Highland dancing.
Hunting tartans also seem to be a Victorian conception, although there is some evidence of early tartans with camouflage colours. These tartans tend to be made up of subdued colours, such as dark blues and greens. Despite the name, hunting tartans have very little to do with actual hunting.
Mourning tartans, though quite rare, are associated with death and funerals. They are usually designed using combinations of black and white, or by replacing bright colors such as reds and yellows in a traditional tartan with black, white, or grey.
 Victorian entrepreneurs not only created new tartans, but new tartan objects called ''tartan-ware''. Tartan was incorporated in an assortment of common household objects, such as snuffboxes, jewellery cases, tableware, sewing accessories, and desk items. Tourists visiting the Scottish Highlands went home with it, and Scottish-based businesses sent tartanware out as gifts to customers. Some of the more popular tartans were the ''Stewart'', ''MacDonald'', ''McGregor'', ''McDuff'', ''MacBeth'', and ''Prince Charlie''. Banks; de la Chapelle (2007) pp. 21–22. Today tartanware is widely collected in England and Scotland.
Numerous Scottish brands use tartan. Founded in 1898, Walkers Shortbread is sold in tartan packaging around the world (especially during Christmas and
Victorian entrepreneurs not only created new tartans, but new tartan objects called ''tartan-ware''. Tartan was incorporated in an assortment of common household objects, such as snuffboxes, jewellery cases, tableware, sewing accessories, and desk items. Tourists visiting the Scottish Highlands went home with it, and Scottish-based businesses sent tartanware out as gifts to customers. Some of the more popular tartans were the ''Stewart'', ''MacDonald'', ''McGregor'', ''McDuff'', ''MacBeth'', and ''Prince Charlie''. Banks; de la Chapelle (2007) pp. 21–22. Today tartanware is widely collected in England and Scotland.
Numerous Scottish brands use tartan. Founded in 1898, Walkers Shortbread is sold in tartan packaging around the world (especially during Christmas and
 For instance, tartan made a resurgence in punk fashion. In the late 1970s, punk music was a way for youth in the British Isles to voice their discontent with the ruling class. The unorthodox use of tartan, which had long been associated with authority and gentility, was then seen as the expression of discontent against modern society. In this way tartan, worn unconventionally, became an anti-establishment symbol. Banks; de la Chapelle (2007), pp. 26–27. Ash; Wright (1988) p. 63.
Popular in the mid 1970s, the Scottish teeny bopper band the
For instance, tartan made a resurgence in punk fashion. In the late 1970s, punk music was a way for youth in the British Isles to voice their discontent with the ruling class. The unorthodox use of tartan, which had long been associated with authority and gentility, was then seen as the expression of discontent against modern society. In this way tartan, worn unconventionally, became an anti-establishment symbol. Banks; de la Chapelle (2007), pp. 26–27. Ash; Wright (1988) p. 63.
Popular in the mid 1970s, the Scottish teeny bopper band the
 Since the Victorian era, authorities on tartan have claimed that there is an
Since the Victorian era, authorities on tartan have claimed that there is an
Tartan Kilt
{{Authority control Textile patterns Textile arts of Scotland Scottish design
 Tartan ( gd, breacan ) is a patterned cloth consisting of criss-crossed, horizontal and vertical bands in multiple colours. Tartans originated in woven wool, but now they are made in other materials. Tartan is particularly associated with Scotland, as Scottish kilts almost always have tartan patterns.
Tartan is made with alternating bands of coloured (pre-dyed) threads woven as both
Tartan ( gd, breacan ) is a patterned cloth consisting of criss-crossed, horizontal and vertical bands in multiple colours. Tartans originated in woven wool, but now they are made in other materials. Tartan is particularly associated with Scotland, as Scottish kilts almost always have tartan patterns.
Tartan is made with alternating bands of coloured (pre-dyed) threads woven as both warp
Warp, warped or warping may refer to:
Arts and entertainment Books and comics
* WaRP Graphics, an alternative comics publisher
* ''Warp'' (First Comics), comic book series published by First Comics based on the play ''Warp!''
* Warp (comics), a ...
and weft at right angle
In geometry and trigonometry, a right angle is an angle of exactly 90 Degree (angle), degrees or radians corresponding to a quarter turn (geometry), turn. If a Line (mathematics)#Ray, ray is placed so that its endpoint is on a line and the ad ...
s to each other. The weft is woven in a simple twill, two over—two under the warp, advancing one thread at each pass. This pattern forms visible diagonal lines where different colours cross, which give the appearance of new colours blended from the original ones. The resulting blocks of colour repeat vertically and horizontally in a distinctive pattern of squares and lines known as a ''sett''. Tartan is often called "plaid" (particularly in North America), because in Scotland, a ''plaid
Plaid () may refer to:
Fabric
* Full plaid, a cloth made with a tartan pattern, wrapped around the waist, cast over the shoulder and fastened at the front
* A synonym for tartan in North America
* A plaid shirt, typically of flannel and worn du ...
'' is a large piece of tartan cloth, worn as a type of kilt or large shawl. The term ''plaid'' is also used in Scotland for an ordinary blanket such as one would have on a bed.
The Dress Act of 1746 attempted to bring the warrior clans under government control by banning the tartan and other aspects of Gaelic culture. When the law was repealed in 1782, it was no longer ordinary Highland dress, but was adopted instead as the symbolic national dress of Scotland, a status that was widely popularised after King George IV wore a tartan kilt in his 1822 visit to Scotland. Until the middle of the nineteenth century, the highland tartans were only associated with either regions or districts, rather than any specific Scottish clan. This was because like other materials, tartan designs were produced by local weavers for local tastes and would usually only use the natural dyes available in that area, as synthetic dye production was non-existent and transportation of other dye materials across long distances was prohibitively expensive. The patterns were simply different regional checked-cloth patterns, chosen by the wearer's preference—in the same way as people nowadays choose what colours and patterns they like in their clothing, without particular reference to propriety. It was not until the mid-nineteenth century that patterns were created and artificially associated with Scottish clans, families, or institutions who were (or wished to be seen as) associated in some way with a Scottish heritage. The Victorians' penchant for ordered taxonomy and the new chemical dyes then available meant that the idea of specific patterns of bright colours, or "dress" tartans, could be created and applied to a nostalgic view of Scottish history. The Irish also wore tartan clothing but to a far lesser degree than their Gaelic cousins in Scotland.
Today ''tartan'' is no longer limited to textiles, but is also used as a name for the pattern itself, appearing on media such as paper, plastics, packaging, and wall coverings. The use of tartan has spread outside the British Isles, particularly to countries who have been influenced by Scottish culture.
Etymology and terminology
 The English and
The English and Scots
Scots usually refers to something of, from, or related to Scotland, including:
* Scots language, a language of the West Germanic language family native to Scotland
* Scots people, a nation and ethnic group native to Scotland
* Scoti, a Latin na ...
word "tartan" is most likely derived from the French
French (french: français(e), link=no) may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to France
** French language, which originated in France, and its various dialects and accents
** French people, a nation and ethnic group identified with Franc ...
' meaning "Tartar
Tartar may refer to:
Places
* Tartar (river), a river in Azerbaijan
* Tartar, Switzerland, a village in the Grisons
* Tərtər, capital of Tartar District, Azerbaijan
* Tartar District, Azerbaijan
* Tartar Island, South Shetland Islands, Ant ...
cloth". It has also been suggested that "tartan" may be derived from modern Scottish Gaelic ', Banks; de la Chapelle 2007: p. 57. meaning "across". Today "tartan" usually refers to coloured patterns, though originally a tartan did not have to be made up of a pattern at all. As late as the 1830s tartan was sometimes described as "plain coloured ... without pattern". Patterned cloth from the Gaelic-speaking Scottish Highlands was called ', meaning many colours. Over time the meanings of ''tartan'' and ' were combined to describe certain type of pattern on a certain type of cloth. The pattern of a tartan is called a ''sett''. The sett is made up of a series of woven threads which cross at right angle
In geometry and trigonometry, a right angle is an angle of exactly 90 Degree (angle), degrees or radians corresponding to a quarter turn (geometry), turn. If a Line (mathematics)#Ray, ray is placed so that its endpoint is on a line and the ad ...
s.
Today ''tartan'' is generally used to describe the pattern, not limited to textiles. In North America the term ''plaid'' is commonly used to describe ''tartan''. The word ''plaid'', derived from the Scottish Gaelic ', meaning "blanket", was first used of any rectangular garment, sometimes made up of tartan, particularly that which preceded the modern kilt (see: belted plaid). In time, ''plaid'' was used to describe blankets themselves.
Construction
Each thread in thewarp
Warp, warped or warping may refer to:
Arts and entertainment Books and comics
* WaRP Graphics, an alternative comics publisher
* ''Warp'' (First Comics), comic book series published by First Comics based on the play ''Warp!''
* Warp (comics), a ...
crosses each thread in the weft at right angles. Where a thread in the warp crosses a thread of the same colour in the weft they produce a solid colour on the tartan, while a thread crossing another of a different colour produces an equal mixture of the two colours. Thus, a set of two base colours produces three different colours including one mixture, increasing quadratically with the number of base colours so a set of six base colours produces fifteen mixtures and a total of twenty-one different colours. This means that the more stripes and colours used, the more blurred and subdued the tartan's pattern becomes. Banks; de la Chapelle 2007: p. 61.
The sequence of threads, known as the sett, starts at an edge and either repeats or reverses on what are called ''pivot'' points. In ''diagram A'', the sett reverses at the first pivot, then repeats, then reverses at the next pivot, and will carry on in this manner horizontally. In ''diagram B'', the sett reverses and repeats in the same way as the warp, and also carries on in the same manner vertically. The diagrams left illustrate the construction of a "symmetrical" tartan. However, on an "asymmetrical" tartan, the sett does not reverse at the pivots, it just repeats at the pivots. Also, some tartans (very few) do not have exactly the same sett for the warp and weft. This means the warp and weft will have alternate ''thread counts''.
Tartan is recorded by counting the threads of each colour that appear in the sett. The ''thread count'' not only describes the width of the stripes on a sett, but also the colours used. For example, the thread count "K4 R24 K24 Y4" corresponds to 4 ''black'' threads, 24 ''red'' threads, 24 ''black'' threads, 4 ''yellow'' threads. Usually the thread count is an even number to assist in manufacture. The first and last threads of the thread count are the pivot points. Though thread counts are indeed quite specific, they can be modified in certain circumstances, depending on the desired size of the tartan. For example, the sett of a tartan (about 6 inches) may be too large to fit upon the face of a necktie
A necktie, or simply a tie, is a piece of cloth worn for decorative purposes around the neck, resting under the shirt collar and knotted at the throat, and often draped down the chest.
Variants include the ascot, bow, bolo, zipper tie, cra ...
. In this case the thread count has to be reduced ''in proportion'' (about 3 inches).
Colour: shades and meaning
 The shades of colour in tartan can be altered to produce variations of the same tartan. The resulting variations are termed: ''modern'', ''ancient'', and ''muted''."Muted" colours are also called "reproduction" colours. These terms only refer to dye colours.
; Modern colours
: Describes a tartan that is coloured using chemical dye, as opposed to natural dye. In the mid-19th century natural dyes began to be replaced by chemical dyes which were easier to use and were more economic for the booming tartan industry. Chemical dyes tend to produce a very strong, vivid colour compared to natural dyes. In ''modern'' colours, setts made up of blue, black, and green tend to be obscured.
; Ancient colours
: Refers to a lighter shade of tartan. These shades are meant to represent the colours that would result from fabric aging over time.
; Muted colours
: Also called ''reproduction'' colours, refers to tartan which is shade between ''modern'' and ''ancient''. Although this type of colouring is very recent, dating only from the early 1970s, these shades are thought to be the closest match to the colours attained by natural dyes used before the mid-19th century.
The idea that the various colours used in tartan have a specific meaning is purely a modern one. One such myth is that red tartans were "battle tartans", designed so they would not show blood. It is only recently created tartans, such as Canadian provincial and territorial tartans (beginning 1950s) and US state tartans (beginning 1980s), that are designed with certain symbolic meaning for the colours used. For example, the colour ''green'' sometimes represents prairies or forests, ''blue'' can represent lakes and rivers, and the colour ''yellow'' is sometimes used to represent various crops.
The shades of colour in tartan can be altered to produce variations of the same tartan. The resulting variations are termed: ''modern'', ''ancient'', and ''muted''."Muted" colours are also called "reproduction" colours. These terms only refer to dye colours.
; Modern colours
: Describes a tartan that is coloured using chemical dye, as opposed to natural dye. In the mid-19th century natural dyes began to be replaced by chemical dyes which were easier to use and were more economic for the booming tartan industry. Chemical dyes tend to produce a very strong, vivid colour compared to natural dyes. In ''modern'' colours, setts made up of blue, black, and green tend to be obscured.
; Ancient colours
: Refers to a lighter shade of tartan. These shades are meant to represent the colours that would result from fabric aging over time.
; Muted colours
: Also called ''reproduction'' colours, refers to tartan which is shade between ''modern'' and ''ancient''. Although this type of colouring is very recent, dating only from the early 1970s, these shades are thought to be the closest match to the colours attained by natural dyes used before the mid-19th century.
The idea that the various colours used in tartan have a specific meaning is purely a modern one. One such myth is that red tartans were "battle tartans", designed so they would not show blood. It is only recently created tartans, such as Canadian provincial and territorial tartans (beginning 1950s) and US state tartans (beginning 1980s), that are designed with certain symbolic meaning for the colours used. For example, the colour ''green'' sometimes represents prairies or forests, ''blue'' can represent lakes and rivers, and the colour ''yellow'' is sometimes used to represent various crops.
History
Pre-medieval origins
 Today tartan is mostly associated with Scotland; however, the earliest evidence of tartan is found far afield from Britain. According to the textile historian E. J. W. Barber, the
Today tartan is mostly associated with Scotland; however, the earliest evidence of tartan is found far afield from Britain. According to the textile historian E. J. W. Barber, the Hallstatt culture
The Hallstatt culture was the predominant Western Europe, Western and Central European Archaeological culture, culture of Late Bronze Age Europe, Bronze Age (Hallstatt A, Hallstatt B) from the 12th to 8th centuries BC and Early Iron Age Europe ...
of Central Europe, which is linked with ancient Celtic populations and flourished between the 8th and 6th centuries BC, produced tartan-like textiles. Some of them were discovered in 2004, remarkably preserved, in the Hallstatt salt mines near Salzburg, Austria. Textile analysis of fabric from the Tarim mummies in Xinjiang, northwestern China has also shown it to be similar to that of the Iron Age Hallstatt culture. Tartan-like leggings were found on the " Cherchen Man", a 3,000 year-old mummy found in the Taklamakan Desert. Similar finds have been made in central Europe and Scandinavia.
The earliest documented tartan in Britain, known as the "Falkirk" tartan, dates from the 3rd century AD. It was uncovered at Falkirk
Falkirk ( gd, An Eaglais Bhreac, sco, Fawkirk) is a large town in the Central Lowlands of Scotland, historically within the county of Stirlingshire. It lies in the Forth Valley, northwest of Edinburgh and northeast of Glasgow.
Falkirk had a ...
in Stirlingshire, Scotland, near the Antonine Wall
The Antonine Wall, known to the Romans as ''Vallum Antonini'', was a turf fortification on stone foundations, built by the Romans across what is now the Central Belt of Scotland, between the Firth of Clyde and the Firth of Forth. Built some twe ...
. The fragment, held in the National Museums of Scotland, was stuffed into the mouth of an earthenware pot containing almost 2,000 Roman coins. The Falkirk tartan has a simple check design, of natural light and dark wool. Early forms of tartan like this are thought to have been invented in pre-Roman times, and would have been popular among the inhabitants of the northern Roman provinces as well as in other parts of Northern Europe
The northern region of Europe has several definitions. A restrictive definition may describe Northern Europe as being roughly north of the southern coast of the Baltic Sea, which is about 54th parallel north, 54°N, or may be based on other g ...
such as Jutland, where the same pattern was prevalent.
Early modern
 The tartan as we know it today is not thought to have existed in Scotland before the 16th century. By the late 16th century there are numerous references to striped or checkered plaids. It is not until the late 17th or early 18th century that uniformity in tartan is thought to have occurred. Martin Martin, in ''A Description of the Western Islands of Scotland'', published in 1703, wrote that Scottish tartans could be used to distinguish the inhabitants of different regions. He expressly wrote that the inhabitants of various islands and the mainland of the Highlands were not all dressed alike, but that the setts and colours of the various tartans varied from isle to isle. As he does not mention the use of a special pattern by each family, it would appear that such a distinction is a modern one.
For centuries the patterns were loosely associated with the weavers of a particular area, though it was common for highlanders to wear a number of different tartans at the same time. A 1587 charter granted to Hector Maclean of Duart requires feu duty on land paid as 60
The tartan as we know it today is not thought to have existed in Scotland before the 16th century. By the late 16th century there are numerous references to striped or checkered plaids. It is not until the late 17th or early 18th century that uniformity in tartan is thought to have occurred. Martin Martin, in ''A Description of the Western Islands of Scotland'', published in 1703, wrote that Scottish tartans could be used to distinguish the inhabitants of different regions. He expressly wrote that the inhabitants of various islands and the mainland of the Highlands were not all dressed alike, but that the setts and colours of the various tartans varied from isle to isle. As he does not mention the use of a special pattern by each family, it would appear that such a distinction is a modern one.
For centuries the patterns were loosely associated with the weavers of a particular area, though it was common for highlanders to wear a number of different tartans at the same time. A 1587 charter granted to Hector Maclean of Duart requires feu duty on land paid as 60 ell
An ell (from Proto-Germanic *''alinō'', cognate with Latin ''ulna'') is a northwestern European unit of measurement, originally understood as a cubit (the combined length of the forearm and extended hand). The word literally means "arm", and ...
s of cloth of white, black and green colours. A witness of the 1689 Battle of Killiecrankie describes "McDonnell
The McDonnell Aircraft Corporation was an American aerospace manufacturer based in St. Louis, Missouri. The company was founded on July 6, 1939, by James Smith McDonnell, and was best known for its military fighters, including the F-4 Phantom II ...
's men in their triple stripes". From 1725 the government force of the ''Highland Independent Companies'' introduced a standardised tartan chosen to avoid association with a particular clan, and this was formalised when they became the Black Watch regiment in 1739.
 The most effective fighters for Jacobitism were the supporting Scottish clans, leading to an association of tartans with the Jacobite cause. Efforts to pacify the Highlands led to the ''Dress Act of 1746'', banning tartans, except for the Highland regiments of the British army. " was probably their use of it which gave birth to the idea of differentiating tartan by clans; for as the Highland regiments were multiplied ... so their tartan uniforms were differentiated."
The act was repealed in 1782, due to the efforts of the Highland Society of London. William Wilson & Sons of Bannockburn became the foremost weaving manufacturer around 1770 as suppliers of tartan to the military. Wilson corresponded with his agents in the Highlands to get information and samples of cloth from the clan districts to enable him to reproduce "perfectly genuine patterns" and recorded over 200 setts by 1822. The Cockburn Collection of named samples made by William Wilson & Sons was put together between 1810 and 1820 and is now in the Mitchell Library in Glasgow. At this time setts were simply numbered, or given fanciful names such as the " Robin Hood" tartan, not associated with a specific clan.
The most effective fighters for Jacobitism were the supporting Scottish clans, leading to an association of tartans with the Jacobite cause. Efforts to pacify the Highlands led to the ''Dress Act of 1746'', banning tartans, except for the Highland regiments of the British army. " was probably their use of it which gave birth to the idea of differentiating tartan by clans; for as the Highland regiments were multiplied ... so their tartan uniforms were differentiated."
The act was repealed in 1782, due to the efforts of the Highland Society of London. William Wilson & Sons of Bannockburn became the foremost weaving manufacturer around 1770 as suppliers of tartan to the military. Wilson corresponded with his agents in the Highlands to get information and samples of cloth from the clan districts to enable him to reproduce "perfectly genuine patterns" and recorded over 200 setts by 1822. The Cockburn Collection of named samples made by William Wilson & Sons was put together between 1810 and 1820 and is now in the Mitchell Library in Glasgow. At this time setts were simply numbered, or given fanciful names such as the " Robin Hood" tartan, not associated with a specific clan.
Absence of early clan use
 It is generally regarded that "clan tartans" date no earlier than the beginning of the 19th century, and are an example of an invented tradition. Contemporary portraits show that although tartan is of an early date, the pattern worn depended not on the wearer's clan, but rather upon his or her present affiliation, place of origin or current residence, or personal taste.
David Morier's well-known mid-1700s painting of the Highland charge at the
It is generally regarded that "clan tartans" date no earlier than the beginning of the 19th century, and are an example of an invented tradition. Contemporary portraits show that although tartan is of an early date, the pattern worn depended not on the wearer's clan, but rather upon his or her present affiliation, place of origin or current residence, or personal taste.
David Morier's well-known mid-1700s painting of the Highland charge at the Battle of Culloden
The Battle of Culloden (; gd, Blàr Chùil Lodair) was the final confrontation of the Jacobite rising of 1745. On 16 April 1746, the Jacobite army of Charles Edward Stuart was decisively defeated by a British government force under Prince Wi ...
(right) shows the clansmen wearing various tartans. The setts painted differ from one another and very few of those painted resemble today's clan tartans. The method of identifying friend from foe was not through tartans but by the colour of ribbon worn upon the bonnet.
The idea of groups of men wearing the same tartan is thought to originate from the military units in the 18th century. Evidence suggests that in 1725 the Independent Highland Companies
The Independent Highland Companies were irregular militia raised from the Scottish clans of the Scottish Highlands by order of the Government between 1603 and 1760 in order to help keep the peace and enforce the law in the Highlands and were reco ...
may have worn a uniform tartan.
Modern use
By the 19th century the Highland romantic revival, inspired by James Macpherson'sOssian
Ossian (; Irish Gaelic/Scottish Gaelic: ''Oisean'') is the narrator and purported author of a cycle of epic poems published by the Scottish poet James Macpherson, originally as ''Fingal'' (1761) and ''Temora'' (1763), and later combined under t ...
poems and the writings of Sir Walter Scott, led to wider interest, with clubs like the Celtic Society of Edinburgh welcoming Lowlanders. The pageantry invented for the 1822 visit of King George IV to Scotland brought a sudden demand for tartan cloth and made it the national dress of the whole of Scotland, rather than just the Highlands and Islands, with the invention of new clan-specific tartans to suit. Moncreiffe of that Ilk 1967: p. 24.
Georgian royal patronage
 The popularity of tartan was greatly increased by the royal visit of George IV to Edinburgh in 1822. George IV was the first reigning monarch to visit Scotland in 171 years. Moncreiffe of that Ilk 1967: p. 24. The festivities surrounding the event were originated by Sir Walter Scott who founded the Celtic Society of Edinburgh in 1820. Scott and the Celtic Society urged Scots to attend festivities "all plaided and plumed in their tartan array". One contemporary writer sarcastically described the pomp that surrounded the celebrations as "Sir Walter's Celtified Pagentry". Magnusson 2003: pp. 653–654.
The popularity of tartan was greatly increased by the royal visit of George IV to Edinburgh in 1822. George IV was the first reigning monarch to visit Scotland in 171 years. Moncreiffe of that Ilk 1967: p. 24. The festivities surrounding the event were originated by Sir Walter Scott who founded the Celtic Society of Edinburgh in 1820. Scott and the Celtic Society urged Scots to attend festivities "all plaided and plumed in their tartan array". One contemporary writer sarcastically described the pomp that surrounded the celebrations as "Sir Walter's Celtified Pagentry". Magnusson 2003: pp. 653–654.
Georgian craze
Following the royal visit, books which documented tartans added to the craze. James Logan's romanticised work ''The Scottish Gael'', published in 1831, was one such publication which led the Scottish tartan industry to invent clan tartans. The first publication showing plates of clan tartans was the '' Vestiarium Scoticum'', published in 1842. The ''Vestiarium'' was the work of two brothers: John Sobieski and Charles Allen Hay. The brothers, who called themselves ''John Sobieski Stolberg Stuart'' and ''Charles Edward Stuart'', first appeared in Scotland in 1822. The two claimed to be grandsons of PrinceCharles Edward Stuart
Charles Edward Louis John Sylvester Maria Casimir Stuart (20 December 1720 – 30 January 1788) was the elder son of James Francis Edward Stuart, grandson of James II and VII, and the Stuart claimant to the thrones of England, Scotland and ...
and his wife Princess Louise of Stolberg, and consequently later became known as the "Sobieski Stuarts
In the 1820s, two English brothers, John Carter Allen (1795–1872) and Charles Manning Allen (1802–1880) adopted the names John Sobieski Stuart and Charles Edward Stuart, moved to Scotland, became Roman Catholics, and about 1839 began to claim ...
". The Sobieski Stuarts claimed that the ''Vestiarium'' was based upon a copy of an ancient manuscript on clan tartans—a manuscript which they never managed to produce. The ''Vestiarium'' was followed by the equally dubious ''The Costume of the Clans'' two years later. Banks; de la Chapelle (2007) pp. 106–108. The romantic enthusiasm that Logan and the Sobieski Stuarts generated with their publications led the way for other tartan books in the 19th century.
Victorian royal patronage
 Twenty years after her uncle's visit to Scotland, Queen Victoria and her husband
Twenty years after her uncle's visit to Scotland, Queen Victoria and her husband Prince Albert
Prince Albert most commonly refers to:
*Albert, Prince Consort (1819–1861), consort of Queen Victoria
*Albert II, Prince of Monaco (born 1958), present head of state of Monaco
Prince Albert may also refer to:
Royalty
* Albert I of Belgium ...
made their first trip to the Scottish Highlands. The Queen and prince bought Balmoral Castle
Balmoral Castle () is a large estate house in Aberdeenshire, Scotland, and a residence of the British royal family. It is near the village of Crathie, west of Ballater and west of Aberdeen.
The estate and its original castle were bought ...
in 1848 and hired a local architect to re-model the estate in " Scots Baronial" style. Prince Albert personally took care of the interior design, where he made great use of tartan. He used the red ''Royal Stewart'' and the green ''Hunting Stewart'' tartans for carpets, while using the ''Dress Stewart'' for curtains and upholstery. The Queen designed the ''Victoria'' tartan, and Prince Albert the ''Balmoral'', still used as a royal tartan today.
Victoria and Albert spent a considerable amount of time at their estate, and in doing so hosted "Highland" activities. Victoria was attended by pipers and her children were attired in Highland dress. Prince Albert himself loved watching the Highland games. Banks; de la Chapelle 2007: pp. 108–109. As the craze swept over Scotland the Highland population suffered grievously from the Highland Clearances
The Highland Clearances ( gd, Fuadaichean nan Gàidheal , the "eviction of the Gaels") were the evictions of a significant number of tenants in the Scottish Highlands and Islands, mostly in two phases from 1750 to 1860.
The first phase resulte ...
, when thousands of Gaelic-speaking Scots from the Highlands and Isles were evicted by landlords (often the very men who would have been their clan chiefs) to make way for sheep.
History of registration
 The naming and registration of official clan tartans began on 8 April 1815, when the Highland Society of London (founded 1778) resolved that the clan chiefs each "be respectfully solicited to furnish the Society with as much of the Tartan of his Lordship's Clan as will serve to Show the Pattern and to Authenticate the Same by Attaching Thereunto a Card bearing the Impression of his Lordship's Arms." Many had no idea of what their tartan might be, but were keen to comply and to provide authentic signed and sealed samples. Alexander Macdonald, 2nd Baron Macdonald was so far removed from his Highland heritage that he wrote to the Society: "Being really ignorant of what is exactly The Macdonald Tartan, I request you will have the goodness to exert every Means in your power to Obtain a perfectly genuine Pattern, Such as Will Warrant me in Authenticating it with my Arms."
Today tartan and "clan tartan" is an important part of a Scottish clan. Most Scottish clans have several tartans attributed to their name and some clans have "official" tartans. Although it is possible for anyone to create a tartan and name it any name they wish, the only person with the authority to make a clan's tartan "official" is the chief.
In some cases, following such recognition from the clan chief, the clan tartan is recorded and registered by the Lord Lyon King of Arms. Once approved by the Lord Lyon, after recommendation by the Advisory Committee on Tartan, the clan tartan is then recorded in the Lyon Court Books.Campbell of Airds (2000), pp. 259–261. In at least one instance a clan tartan appears in the heraldry of a clan chief and is considered by the Lord Lyon as the "proper" tartan of the clan.
Modern-day tartans also encompass registered tartans for Irish clans, (for example, the surname Fitzpatrick has two registered tartans) counties, and other Gaelic and Celtic nations, such as the Isle of Man, Wales, and Cornwall.
The naming and registration of official clan tartans began on 8 April 1815, when the Highland Society of London (founded 1778) resolved that the clan chiefs each "be respectfully solicited to furnish the Society with as much of the Tartan of his Lordship's Clan as will serve to Show the Pattern and to Authenticate the Same by Attaching Thereunto a Card bearing the Impression of his Lordship's Arms." Many had no idea of what their tartan might be, but were keen to comply and to provide authentic signed and sealed samples. Alexander Macdonald, 2nd Baron Macdonald was so far removed from his Highland heritage that he wrote to the Society: "Being really ignorant of what is exactly The Macdonald Tartan, I request you will have the goodness to exert every Means in your power to Obtain a perfectly genuine Pattern, Such as Will Warrant me in Authenticating it with my Arms."
Today tartan and "clan tartan" is an important part of a Scottish clan. Most Scottish clans have several tartans attributed to their name and some clans have "official" tartans. Although it is possible for anyone to create a tartan and name it any name they wish, the only person with the authority to make a clan's tartan "official" is the chief.
In some cases, following such recognition from the clan chief, the clan tartan is recorded and registered by the Lord Lyon King of Arms. Once approved by the Lord Lyon, after recommendation by the Advisory Committee on Tartan, the clan tartan is then recorded in the Lyon Court Books.Campbell of Airds (2000), pp. 259–261. In at least one instance a clan tartan appears in the heraldry of a clan chief and is considered by the Lord Lyon as the "proper" tartan of the clan.
Modern-day tartans also encompass registered tartans for Irish clans, (for example, the surname Fitzpatrick has two registered tartans) counties, and other Gaelic and Celtic nations, such as the Isle of Man, Wales, and Cornwall.
Popular designs
One of the most popular tartans is the Royal Stewart tartan, the personal tartan of Queen Elizabeth II. The sett was first published in 1831 in the book ''The Scottish Gael'' by James Logan. In addition to its use in clothing, such as skirts and scarves, Royal Stewart tartan has also appeared on biscuit tins for Scottish shortbread. Another popular tartan is the Black Watch (also known as Grant Hunting, Universal, and Government). This tartan, a darkened variant of the main Clan Campbell tartan (Ancient or Old Campbell), was used and is still used by military units in the British Army and otherCommonwealth
A commonwealth is a traditional English term for a political community founded for the common good. Historically, it has been synonymous with "republic". The noun "commonwealth", meaning "public welfare, general good or advantage", dates from the ...
forces.
Other uses
 In addition to clan tartans, many tartan patterns have been developed for individuals, families, districts, institutions, and corporations. They have also been created for various events and certain
In addition to clan tartans, many tartan patterns have been developed for individuals, families, districts, institutions, and corporations. They have also been created for various events and certain ethnic group
An ethnic group or an ethnicity is a grouping of people who identify with each other on the basis of shared attributes that distinguish them from other groups. Those attributes can include common sets of traditions, ancestry, language, history, ...
s. Tartan has had a long history with the military and today military units—particularly those within the Commonwealth
A commonwealth is a traditional English term for a political community founded for the common good. Historically, it has been synonymous with "republic". The noun "commonwealth", meaning "public welfare, general good or advantage", dates from the ...
—have tartan dress uniforms. Tartans or tartan-like plaid patterns are also commonly worn as skirts or jumpers / pinafores in Catholic school uniform and other private school uniform
A school uniform is a uniform worn by students primarily for a school or otherwise an educational institution.They are common in primary and secondary schools in various countries.
An example of a uniform would be requiring button-down shir ...
codes in North America and also in public and private schools in New Zealand.
Regional
In addition to the original Scottish regional tartans and modern district tartans, modern tartans have been created for regions outside of Scotland. Many regional tartans are officially recognised by government bodies. All but two Canadianprovinces and territories
Within the geographical areas of Canada, the ten provinces and three territories are sub-national administrative divisions under the jurisdiction of the Canadian Constitution. In the 1867 Canadian Confederation, three provinces of British North ...
have an official tartan, with the first dating from 1956. Neither Quebec nor Nunavut
Nunavut ( , ; iu, ᓄᓇᕗᑦ , ; ) is the largest and northernmost Provinces and territories of Canada#Territories, territory of Canada. It was separated officially from the Northwest Territories on April 1, 1999, via the ''Nunavut Act'' ...
, Canada's newest territory, have enshrined their tartans in law. Alberta, meanwhile, has two official tartans, including a dress tartan. All but Quebec's are registered with the Court of the Lord Lyon
The Court of the Lord Lyon (the Lyon Court) is a standing court of law, based in New Register House in Edinburgh, which regulates heraldry in Scotland. The Lyon Court maintains the register of grants of arms, known as the Public Register of All A ...
in Scotland. Canada has an official national tartan that was originally designed to commemorate the introduction of its new maple leaf flag, and was made an official national emblem in 2011. Canadian regions (like Labrador and Cape Breton Island
Cape Breton Island (french: link=no, île du Cap-Breton, formerly '; gd, Ceap Breatainn or '; mic, Unamaꞌki) is an island on the Atlantic coast of North America and part of the province of Nova Scotia, Canada.
The island accounts for 18. ...
), counties, municipalities, and institutions also have official tartans.
US states also have official tartans, with the first dating from 1988. In Scotland at least two local government councils have official tartans. Other tartans have been created for Australia, its capital city, Canberra
Canberra ( )
is the capital city of Australia. Founded following the federation of the colonies of Australia as the seat of government for the new nation, it is Australia's largest inland city and the eighth-largest city overall. The ci ...
, each of its States, and some of its local government areas, but only some of those tartans have been officially adopted or recognised by the relevant government in Australia.
Dress, hunting, and mourning
 Tartans are sometimes differentiated from another with the same name by the label ''dress'', ''hunting'', or rarely ''mourning''.
Dress tartans are based on the ''earasaid'' tartans worn by Highland women in the 17th and 18th centuries. Dress tartans tend to be made by replacing a prominent colour with the colour white. They are commonly used today in Highland dancing.
Hunting tartans also seem to be a Victorian conception, although there is some evidence of early tartans with camouflage colours. These tartans tend to be made up of subdued colours, such as dark blues and greens. Despite the name, hunting tartans have very little to do with actual hunting.
Mourning tartans, though quite rare, are associated with death and funerals. They are usually designed using combinations of black and white, or by replacing bright colors such as reds and yellows in a traditional tartan with black, white, or grey.
Tartans are sometimes differentiated from another with the same name by the label ''dress'', ''hunting'', or rarely ''mourning''.
Dress tartans are based on the ''earasaid'' tartans worn by Highland women in the 17th and 18th centuries. Dress tartans tend to be made by replacing a prominent colour with the colour white. They are commonly used today in Highland dancing.
Hunting tartans also seem to be a Victorian conception, although there is some evidence of early tartans with camouflage colours. These tartans tend to be made up of subdued colours, such as dark blues and greens. Despite the name, hunting tartans have very little to do with actual hunting.
Mourning tartans, though quite rare, are associated with death and funerals. They are usually designed using combinations of black and white, or by replacing bright colors such as reds and yellows in a traditional tartan with black, white, or grey.
Corporate and commercial
 Victorian entrepreneurs not only created new tartans, but new tartan objects called ''tartan-ware''. Tartan was incorporated in an assortment of common household objects, such as snuffboxes, jewellery cases, tableware, sewing accessories, and desk items. Tourists visiting the Scottish Highlands went home with it, and Scottish-based businesses sent tartanware out as gifts to customers. Some of the more popular tartans were the ''Stewart'', ''MacDonald'', ''McGregor'', ''McDuff'', ''MacBeth'', and ''Prince Charlie''. Banks; de la Chapelle (2007) pp. 21–22. Today tartanware is widely collected in England and Scotland.
Numerous Scottish brands use tartan. Founded in 1898, Walkers Shortbread is sold in tartan packaging around the world (especially during Christmas and
Victorian entrepreneurs not only created new tartans, but new tartan objects called ''tartan-ware''. Tartan was incorporated in an assortment of common household objects, such as snuffboxes, jewellery cases, tableware, sewing accessories, and desk items. Tourists visiting the Scottish Highlands went home with it, and Scottish-based businesses sent tartanware out as gifts to customers. Some of the more popular tartans were the ''Stewart'', ''MacDonald'', ''McGregor'', ''McDuff'', ''MacBeth'', and ''Prince Charlie''. Banks; de la Chapelle (2007) pp. 21–22. Today tartanware is widely collected in England and Scotland.
Numerous Scottish brands use tartan. Founded in 1898, Walkers Shortbread is sold in tartan packaging around the world (especially during Christmas and Hogmanay
Hogmanay ( , ) is the Scots word for the last day of the old year and is synonymous with the celebration of the New Year in the Scottish manner. It is normally followed by further celebration on the morning of New Year's Day (1 January) or i ...
festivities). Introduced in 1901, Irn-Bru, the best-selling soft drink
A soft drink (see § Terminology for other names) is a drink that usually contains water (often carbonated), a sweetener, and a natural and/or artificial flavoring. The sweetener may be a sugar, high-fructose corn syrup, fruit juice, a su ...
in Scotland, has its own tartan.
Fashion
In the Victorian and Edwardian eras, tartan-clad garments were featured in fashion catalogues. By then, tartan had shifted from being mainly a component of men's clothing to become an important part of women's fashion. In consequence of its association with the British aristocracy and military, tartan developed an air of dignity and exclusivity. Because of this, tartan has made periodic reappearances in the world of fashion. For instance, tartan made a resurgence in punk fashion. In the late 1970s, punk music was a way for youth in the British Isles to voice their discontent with the ruling class. The unorthodox use of tartan, which had long been associated with authority and gentility, was then seen as the expression of discontent against modern society. In this way tartan, worn unconventionally, became an anti-establishment symbol. Banks; de la Chapelle (2007), pp. 26–27. Ash; Wright (1988) p. 63.
Popular in the mid 1970s, the Scottish teeny bopper band the
For instance, tartan made a resurgence in punk fashion. In the late 1970s, punk music was a way for youth in the British Isles to voice their discontent with the ruling class. The unorthodox use of tartan, which had long been associated with authority and gentility, was then seen as the expression of discontent against modern society. In this way tartan, worn unconventionally, became an anti-establishment symbol. Banks; de la Chapelle (2007), pp. 26–27. Ash; Wright (1988) p. 63.
Popular in the mid 1970s, the Scottish teeny bopper band the Bay City Rollers
The Bay City Rollers are a Scottish pop rock band known for their worldwide teen idol popularity in the 1970s. They have been called the "tartan teen sensations from Edinburgh" and one of many acts heralded as the "biggest group since the Beat ...
were described by the '' British Hit Singles & Albums'' reference book as “tartan teen sensations from Edinburgh".
Tartan clothing has appeared in ''Doctor Who
''Doctor Who'' is a British science fiction television series broadcast by the BBC since 1963. The series depicts the adventures of a Time Lord called the Doctor, an extraterrestrial being who appears to be human. The Doctor explores the u ...
''. The Fourth Doctor ( Tom Baker) wore a Clan Wallace tartan scarf on '' Terror of the Zygons'', and the Seventh Doctor ( Sylvester McCoy) wore a crimson and black tartan scarf on '' Time and the Rani''. Clara Oswald ( Jenna Coleman), the companion for the Eleventh Doctor ( Matt Smith) and the Twelfth Doctor ( Peter Capaldi), wore a Clan Campbell tartan dress on '' The Name of the Doctor'' and a Clan Wallace skirt on '' The Time of the Doctor'' and '' Deep Breath''. The Fourteenth Doctor wears a tartan plaid brown suit and navy overcoat
An overcoat is a type of long coat (clothing), coat intended to be worn as the outermost garment, which usually extends below the knee. Overcoats are most commonly used in winter when warmth is more important.
They are sometimes confused with ...
in the 60th anniversary specials.
A tartan outfit designed by Vivienne Westwood featured on a commemorative UK postage stamp issued by the Royal Mail
, kw, Postya Riel, ga, An Post Ríoga
, logo = Royal Mail.svg
, logo_size = 250px
, type = Public limited company
, traded_as =
, foundation =
, founder = Henry VIII
, location = London, England, UK
, key_people = * Keith Williams ...
in 2012 celebrating Great British Fashion. In 2017, Scottish fashion designer Charles Jeffrey designed a signature tartan for his LOVERBOY label, registering it at the Scottish Register of Tartans.
Registration
Depending upon how "different tartan" is defined, it has been estimated that there are about 3,500 to 7,000 different tartans, with around 150 new designs being created every year. With four ways of presenting the hues in the tartan—"modern", "ancient", "weathered", and "muted" colours—there are thus about 14,000 recognised tartan variations from which to choose. The 7,000 figure above includes many of these variations counted as though they were different tartans. Until the late 20th century, instead of a central official tartan registry, independent organisations located in Scotland, Canada, and the United States documented and recorded tartans. In the 1960s, a Scottish society called the Scottish Tartans Society (now defunct) was created to record and preserve every known tartan design. The society's register, the ''Register of All Publicly Known Tartans'' (''RAPKT''), contains about 2,700 different designs of tartan. The society, however, ran into financial troubles in about the year 2000, and folded. Former members of the society then formed two new Scottish-based organisations – the Scottish Tartans Authority (STA) and the Scottish Tartans World Register (STWR). Both of these societies initially based their databases on the RAPKT. The STA's database, theInternational Tartan Index
The Scottish Tartans Society (STS) was a society committed to the recording and preservation of woven tartan designs from around the world; it maintained the ''Register of All Publicly Known Tartans''. The society was first formed in 1963 and ex ...
(ITI) consists of about 3,500 different tartans (with over 7,000, counting variants), as of 2004. The STWR's self-titled Scottish Tartans World Register database is made up of about 3,000 different designs as of 2004. Both organisations are registered Scottish charities
A charitable organization or charity is an organization whose primary objectives are philanthropy and social well-being (e.g. educational, religious or other activities serving the public interest or common good).
The legal definition of a cha ...
and record new tartans (free in the case of STS and for a fee in the case of STWR) on request.
The Scottish Register of Tartans (SRT) is Scotland's official tartan register. The ''SRT'' is maintained and administrated by the National Archives of Scotland (NAS), a statutory body based in Edinburgh. The aim of the Register is to provide a definitive and accessible resource to promote and preserve tartans. It also aims to be the definitive source for the registration of new tartans (that pass NAS criteria for inclusion). The register itself is made up of the existing registers of the STA and the STWR as they were at the time of the SRT's launch, and new registrations from 5 February 2009 onward. On the Register's website users can register new tartans (for a fee), search for and request the threadcounts of existing tartans and receive notifications of newly registered tartans. One criticism of the SRT and NAS's management of it is that its exclusivity, in both cost and criteria, necessarily means that it cannot actually achieve its goals of definiteness, preservation and open access. The current version of the STA's ITI, for example, already contains a large number of tartans that do not appear in the SRT, and the gulf will only widen under current policy.
Etiquette
etiquette
Etiquette () is the set of norms of personal behaviour in polite society, usually occurring in the form of an ethical code of the expected and accepted social behaviours that accord with the conventions and norms observed and practised by a ...
to wearing tartan, specifically tartan attributed to clans or families. Even so, there are no laws or rules on who can, or cannot, wear a particular tartan. The concept of the entitlement to certain tartans has led to the term of ''universal tartan'', or ''free tartan'', which describes tartan which can be worn by anyone. Traditional examples of such are ''Black Watch'', ''Caledonian'', ''Hunting Stewart'', and ''Jacobite'' tartans, and district or regional tartans. In the same line of opinion, some tartan attributed to the British Royal Family are claimed by some to be "off limits" to non-royalty.
However, some modern tartans are protected by trademark law, and the trademark proprietor can, in certain circumstances, prevent others from selling that tartan. MacDonald (1995) p. 48. The " Burberry Check" of the English fashion house, first designed in early 1920s, is an instantly recognisable tartan that is very well known around the world Haig (2004) p. 143. and is an example of a tartan that is protected.
Books on Scottish clans list such rules and guidelines. One such opinion is that people not bearing a clan surname, or surname claimed as a sept of a clan, should not wear the tartan of their mother's clan. ''The Scottish Clans and Their Tartans'' (2005) p. 14. This opinion is enforced by the fact that in the Scottish clan system, the Lord Lyon states that membership to a clan technically passes through the surname. This means that children who bear their father's surname belong to the father's clan (if any), and that children who bear their mother's surname (her maiden name) belong to their mother's clan (if any). Also, the Lord Lyon states that a clan tartan should only be worn by those who profess allegiance to that clan's chief.
Some clan societies even claim that certain tartans are the personal property of a chief or chieftain, and in some cases they allow their clansfolk "permission" to wear a tartan. According to the Scottish Tartans Authority — which is an establishment of the Scottish tartan industry — the ''Balmoral'' tartan should not be worn by anyone who is not part of the British Royal Family. Even so, some weavers outside of the United Kingdom ignore the "longstanding convention" of the British Royal Family's "right" to this tartan. The society also claims that non-royals who wear this tartan are treated with "great disdain" by the Scottish tartan ''industry''.
Generally, a more liberal attitude is taken by those in the business of selling tartan, stressing that anyone may wear any tartan they like. The claimed "rules" are mere conventions (some of which are recent creations), with different levels of importance depending on the symbolic meaning of the tartan on some particular occasion. For example, when a district tartan is worn at a football game, or a family tartan at a family event, such as the investiture of a new clan chief, the issue of wearing the event's tartan is of greater concern than wearing the same tartan when attending Highland Games where no event is scheduled where the tartan would have special significance. The same rules apply as do to wearing ''any clothing'' that prominently displays colors with national or political significance, such as un-patterned orange or green cloth in Ireland (regardless of whether it is worn as a kilt), or red, white, and blue colors at national events in France or the United States.
See also
* Argyle (pattern) *Carnegie Mellon University
Carnegie Mellon University (CMU) is a private research university in Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania. One of its predecessors was established in 1900 by Andrew Carnegie as the Carnegie Technical Schools; it became the Carnegie Institute of Technology ...
, whose athletic mascot is Scotty the Scottie Dog; their athletic teams are known as "The Tartans"
* Check (pattern)
* District tartans of Australia, registered district tartans of Australia (created since the 1980s)
* Flannel
* List of tartans
* List of U.S. state tartans, officially recognised tartans of states in the US (created since the 1980s)
* Madras (cloth)
* Regional tartans of Canada, officially recognised tartans of the provinces and territories of Canada (created since the 1950s)
* Sillitoe tartan, a chequered pattern properly known as dicing. Introduced by Sir Percy Sillitoe
Sir Percy Joseph Sillitoe KBE DL (22 May 1888 – 5 April 1962) was a chief constable of several police forces. He changed the role of radios, civilian staff, and women police officers within the police. He was later Director General of MI5, ...
for the police in Scotland
Police Scotland ( gd, Poileas Alba), officially the Police Service of Scotland (), is the national police force of Scotland. It was formed in 2013, through the merging of eight regional police forces in Scotland, as well as the specialist service ...
in 1932, it later spread to widespread use for law enforcement throughout the rest of the UK and overseas.
* Sobieski Stuarts
In the 1820s, two English brothers, John Carter Allen (1795–1872) and Charles Manning Allen (1802–1880) adopted the names John Sobieski Stuart and Charles Edward Stuart, moved to Scotland, became Roman Catholics, and about 1839 began to claim ...
* Tartan Army, popular name for the fans of the Scotland football team
* Tartan Day, a day of celebration, in Canada and the US, recognising the influence of Scottish immigration to these countries
* Tartanry
Tartanry is the stereotypical or kitsch representation of traditional Scottish culture, particularly by the emergent Scottish tourist industry in the 18th and 19th centuries, and later by the American film industry. The earliest use of the word ...
* '' Vestiarium Scoticum'', the Victorian forgery that is the source of many of today's clan tartans
Notes
References
Citations
General sources
* (originally published by: W. & A. K. Johnston & G. W. Bacon Ltd., Edinburgh and London, 1944). * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * *External links
* * * *Tartan Kilt
{{Authority control Textile patterns Textile arts of Scotland Scottish design