clades on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 A clade (), also known as a monophyletic group or natural group, is a group of
A clade (), also known as a monophyletic group or natural group, is a group of
 The idea of a clade did not exist in pre-
The idea of a clade did not exist in pre-
original text w/ figures
/ref> although the term ''clade'' itself would not be coined until 1957 by his grandson,
page 10
Understanding Evolution website. University of California, Berkeley. Retrieved 26 February 2016. Taxonomists have increasingly worked to make the taxonomic system reflect evolution. When it comes to
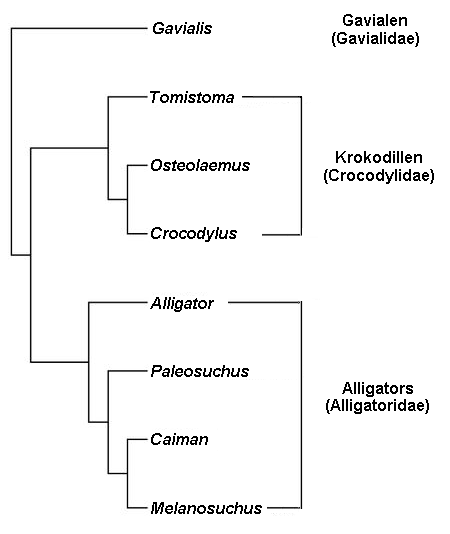 A clade is by definition
A clade is by definition
 The relationship between clades can be described in several ways:
* A clade located within a clade is said to be ''nested'' within that clade. In the diagram, the hominoid clade, i.e. the apes and humans, is nested within the primate clade.
* Two clades are '' sisters'' if they have an immediate common ancestor. In the diagram, lemurs and lorises are sister clades, while humans and tarsiers are not.
* A clade ''A'' is ''
The relationship between clades can be described in several ways:
* A clade located within a clade is said to be ''nested'' within that clade. In the diagram, the hominoid clade, i.e. the apes and humans, is nested within the primate clade.
* Two clades are '' sisters'' if they have an immediate common ancestor. In the diagram, lemurs and lorises are sister clades, while humans and tarsiers are not.
* A clade ''A'' is ''
Evolving Thoughts: "Clade"
* DM Hillis, D Zwickl & R Gutell.
. An unrooted cladogram depicting around 3000 species.
"Phylogenetic systematics, an introductory slide-show on evolutionary trees"
–
organism
In biology, an organism () is any life, living system that functions as an individual entity. All organisms are composed of cells (cell theory). Organisms are classified by taxonomy (biology), taxonomy into groups such as Multicellular o ...
s that are monophyletic
In cladistics for a group of organisms, monophyly is the condition of being a clade—that is, a group of taxa composed only of a common ancestor (or more precisely an ancestral population) and all of its lineal descendants. Monophyletic ...
– that is, composed of a common ancestor and all its lineal descendants – on a phylogenetic tree. Rather than the English term, the equivalent Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power ...
term ''cladus'' (plural ''cladi'') is often used in taxonomical literature.
The common ancestor may be an individual, a population
Population typically refers to the number of people in a single area, whether it be a city or town, region, country, continent, or the world. Governments typically quantify the size of the resident population within their jurisdiction using ...
, or a species
In biology, a species is the basic unit of Taxonomy (biology), classification and a taxonomic rank of an organism, as well as a unit of biodiversity. A species is often defined as the largest group of organisms in which any two individuals of ...
( extinct or extant). Clades are nested, one in another, as each branch in turn splits into smaller branches. These splits reflect evolutionary history as populations diverged and evolved independently. Clades are termed monophyletic (Greek: "one clan") groups.
Over the last few decades, the cladistic approach has revolutionized biological classification and revealed surprising evolutionary relationships among organisms. Increasingly, taxonomists try to avoid naming taxa
In biology, a taxon ( back-formation from '' taxonomy''; plural taxa) is a group of one or more populations of an organism or organisms seen by taxonomists to form a unit. Although neither is required, a taxon is usually known by a particular n ...
that are not clades; that is, taxa that are not monophyletic
In cladistics for a group of organisms, monophyly is the condition of being a clade—that is, a group of taxa composed only of a common ancestor (or more precisely an ancestral population) and all of its lineal descendants. Monophyletic ...
. Some of the relationships between organisms that the molecular biology arm of cladistics has revealed include that fungi
A fungus (plural, : fungi or funguses) is any member of the group of Eukaryote, eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and Mold (fungus), molds, as well as the more familiar mushrooms. These organisms are classified ...
are closer relatives to animals than they are to plants, archaea are now considered different from bacteria
Bacteria (; singular: bacterium) are ubiquitous, mostly free-living organisms often consisting of one biological cell. They constitute a large domain of prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometres in length, bacteria were am ...
, and multicellular organisms may have evolved from archaea.
The term "clade" is also used with a similar meaning in other fields besides biology, such as historical linguistics
Historical linguistics, also termed diachronic linguistics, is the scientific study of language change over time. Principal concerns of historical linguistics include:
# to describe and account for observed changes in particular languages
# ...
; see Cladistics § In disciplines other than biology.
Naming and etymology
The term "clade" was coined in 1957 by the biologistJulian Huxley
Sir Julian Sorell Huxley (22 June 1887 – 14 February 1975) was an English evolutionary biologist, eugenicist, and internationalist. He was a proponent of natural selection, and a leading figure in the mid-twentieth century modern synthes ...
to refer to the result of cladogenesis, the evolutionary splitting of a parent species into two distinct species, a concept Huxley borrowed from Bernhard Rensch.
Many commonly named groups – rodent
Rodents (from Latin , 'to gnaw') are mammals of the Order (biology), order Rodentia (), which are characterized by a single pair of continuously growing incisors in each of the upper and lower jaws. About 40% of all mammal species are roden ...
s and insect
Insects (from Latin ') are pancrustacean hexapod invertebrates of the class Insecta. They are the largest group within the arthropod phylum. Insects have a chitinous exoskeleton, a three-part body (head, thorax and abdomen), three pairs ...
s, for example – are clades because, in each case, the group consists of a common ancestor with all its descendant branches. Rodents, for example, are a branch of mammals that split off after the end of the period when the clade Dinosaur
Dinosaurs are a diverse group of reptiles of the clade Dinosauria. They first appeared during the Triassic period, between 243 and 233.23 million years ago (mya), although the exact origin and timing of the evolution of dinosaurs is t ...
ia stopped being the dominant terrestrial vertebrate
Vertebrates () comprise all animal taxon, taxa within the subphylum Vertebrata () (chordates with vertebral column, backbones), including all mammals, birds, reptiles, amphibians, and fish. Vertebrates represent the overwhelming majority of the ...
s 66 million years ago. The original population and all its descendants are a clade. The rodent clade corresponds to the order Rodentia, and insects to the class Insecta. These clades include smaller clades, such as chipmunk or ant, each of which consists of even smaller clades. The clade "rodent" is in turn included in the mammal, vertebrate
Vertebrates () comprise all animal taxon, taxa within the subphylum Vertebrata () (chordates with vertebral column, backbones), including all mammals, birds, reptiles, amphibians, and fish. Vertebrates represent the overwhelming majority of the ...
and animal clades.
History of nomenclature and taxonomy
 The idea of a clade did not exist in pre-
The idea of a clade did not exist in pre-Darwinian
Darwinism is a theory of biological evolution developed by the English naturalist Charles Darwin (1809–1882) and others, stating that all species of organisms arise and develop through the natural selection of small, inherited variations that ...
Linnaean taxonomy
Linnaean taxonomy can mean either of two related concepts:
# The particular form of biological classification (taxonomy) set up by Carl Linnaeus, as set forth in his ''Systema Naturae'' (1735) and subsequent works. In the taxonomy of Linnaeus t ...
, which was based by necessity only on internal or external morphological similarities between organisms. Many of the better known animal groups in Linnaeus' original ''Systema Naturae
' (originally in Latin written ' with the ligature æ) is one of the major works of the Swedish botanist, zoologist and physician Carl Linnaeus (1707–1778) and introduced the Linnaean taxonomy. Although the system, now known as binomial nom ...
'' (mostly vertebrate
Vertebrates () comprise all animal taxon, taxa within the subphylum Vertebrata () (chordates with vertebral column, backbones), including all mammals, birds, reptiles, amphibians, and fish. Vertebrates represent the overwhelming majority of the ...
groups) do represent clades. The phenomenon of convergent evolution
Convergent evolution is the independent evolution of similar features in species of different periods or epochs in time. Convergent evolution creates analogous structures that have similar form or function but were not present in the last com ...
is responsible for many cases of misleading similarities in the morphology of groups that evolved from different lineages.
With the increasing realization in the first half of the 19th century that species had changed and split through the ages, classification increasingly came to be seen as branches on the evolutionary tree of life
The tree of life is a fundamental archetype in many of the world's mythological, religious, and philosophical traditions. It is closely related to the concept of the sacred tree.Giovino, Mariana (2007). ''The Assyrian Sacred Tree: A Histo ...
. The publication of Darwin's theory of evolution in 1859 gave this view increasing weight. Thomas Henry Huxley
Thomas Henry Huxley (4 May 1825 – 29 June 1895) was an English biologist and anthropologist specialising in comparative anatomy. He has become known as "Darwin's Bulldog" for his advocacy of Charles Darwin's theory of evolution.
The stor ...
, an early advocate of evolutionary theory, proposed a revised taxonomy based on a concept strongly resembling clades,Huxley, T.H. (1876): Lectures on Evolution. ''New York Tribune''. Extra. no 36. In Collected Essays IV: pp 46-13original text w/ figures
/ref> although the term ''clade'' itself would not be coined until 1957 by his grandson,
Julian Huxley
Sir Julian Sorell Huxley (22 June 1887 – 14 February 1975) was an English evolutionary biologist, eugenicist, and internationalist. He was a proponent of natural selection, and a leading figure in the mid-twentieth century modern synthes ...
. For example, the elder Huxley grouped birds with reptiles, based on fossil evidence.
German biologist Emil Hans Willi Hennig
Emil Hans Willi Hennig (20 April 1913 – 5 November 1976) was a German biologist and zoologist who is considered the founder of phylogenetic systematics, otherwise known as cladistics. In 1945 as a prisoner of war, Hennig began work on his theo ...
(1913–1976) is considered to be the founder of cladistics
Cladistics (; ) is an approach to biological classification in which organisms are categorized in groups (" clades") based on hypotheses of most recent common ancestry. The evidence for hypothesized relationships is typically shared derived ch ...
.
He proposed a classification system that represented repeated branchings of the family tree, as opposed to the previous systems, which put organisms on a "ladder", with supposedly more "advanced" organisms at the top.”Evolution 101"page 10
Understanding Evolution website. University of California, Berkeley. Retrieved 26 February 2016. Taxonomists have increasingly worked to make the taxonomic system reflect evolution. When it comes to
naming
Naming is assigning a name to something.
Naming may refer to:
* Naming (parliamentary procedure), a procedure in certain parliamentary bodies
* Naming ceremony, an event at which an infant is named
* Product naming, the discipline of deciding ...
, this principle is not always compatible with the traditional rank-based nomenclature (in which only taxa associated with a rank can be named) because not enough ranks exist to name a long series of nested clades. For these and other reasons, phylogenetic nomenclature has been developed; it is still controversial.
As an example, see the full current classification of '' Anas platyrhynchos'' (the mallard duck) with 40 clades from '' Eukaryota'' down by following this Wikispecies link and clicking on "Expand".
The name of a clade is conventionally a plural, where the singular refers to each member individually. A unique exception is the reptile clade Dracohors
Dinosauromorpha is a clade of avemetatarsalian archosaurs (reptiles closer to birds than to crocodilians) that includes the Dinosauria (dinosaurs) and some of their close relatives. It was originally defined to include dinosauriforms and lager ...
, which was made by haplology from Latin "draco" and "cohors", i.e. "the dragon cohort"; its form with a suffix added should be e.g. "dracohortian".
Definition
monophyletic
In cladistics for a group of organisms, monophyly is the condition of being a clade—that is, a group of taxa composed only of a common ancestor (or more precisely an ancestral population) and all of its lineal descendants. Monophyletic ...
, meaning that it contains one ancestor (which can be an organism, a population, or a species) and all its descendants.
A semantic case has been made that the name should be "holophyletic", but this term has not acquired widespread use. For more information, see '' holophyly''. The ancestor can be known or unknown; any and all members of a clade can be extant or extinct.
Clades and phylogenetic trees
The science that tries to reconstruct phylogenetic trees and thus discover clades is calledphylogenetics
In biology, phylogenetics (; from Greek φυλή/ φῦλον [] "tribe, clan, race", and wikt:γενετικός, γενετικός [] "origin, source, birth") is the study of the evolutionary history and relationships among or within groups ...
or cladistics
Cladistics (; ) is an approach to biological classification in which organisms are categorized in groups (" clades") based on hypotheses of most recent common ancestry. The evidence for hypothesized relationships is typically shared derived ch ...
, the latter term coined by Ernst Mayr (1965), derived from "clade". The results of phylogenetic/cladistic analyses are tree-shaped diagrams called ''cladogram
A cladogram (from Greek ''clados'' "branch" and ''gramma'' "character") is a diagram used in cladistics to show relations among organisms. A cladogram is not, however, an evolutionary tree because it does not show how ancestors are related to ...
s''; they, and all their branches, are phylogenetic hypotheses.
Three methods of defining clades are featured in phylogenetic nomenclature: node-, stem-, and apomorphy-based (see Phylogenetic nomenclature§Phylogenetic definitions of clade names for detailed definitions).
Terminology
basal
Basal or basilar is a term meaning ''base'', ''bottom'', or ''minimum''.
Science
* Basal (anatomy), an anatomical term of location for features associated with the base of an organism or structure
* Basal (medicine), a minimal level that is nec ...
'' to a clade ''B'' if ''A'' branches off the lineage leading to ''B'' before the first branch leading only to members of ''B''. In the adjacent diagram, the strepsirrhine
Strepsirrhini or Strepsirhini (; ) is a Order (biology), suborder of primates that includes the Lemuriformes, lemuriform primates, which consist of the lemurs of Fauna of Madagascar, Madagascar, galagos ("bushbabies") and pottos from Fauna of A ...
/ prosimian clade, is basal to the hominoids/ ape clade. In this example, both Haplorrhine as prosimians should be considered as most basal groupings. It is better to say that the prosimians are the sister group to the rest of the primates. This way one also avoids unintended and misconceived connotations about evolutionary advancement, complexity, diversity, ancestor status, and ancienity e.g. due to impact of sampling diversity and extinction. Basal clades should not be confused with stem groupings, as the latter is associated with paraphyletic or unresolved groupings.
Age
The age of a clade can be described based on two different reference points, crown age and stem age. The crown age of a clade refers to the age of the most recent common ancestor of all of the species in the clade. The stem age of a clade refers to the time that the ancestral lineage of the clade diverged from its sister clade. A clade's stem age is either the same as or older than its crown age. Note that ages of clades cannot be directly observed. They are inferred, either fromstratigraphy
Stratigraphy is a branch of geology concerned with the study of rock layers ( strata) and layering (stratification). It is primarily used in the study of sedimentary and layered volcanic rocks.
Stratigraphy has three related subfields: lithost ...
of fossil
A fossil (from Classical Latin , ) is any preserved remains, impression, or trace of any once-living thing from a past geological age. Examples include bones, shells, exoskeletons, stone imprints of animals or microbes, objects preserved ...
s, or from molecular clock
The molecular clock is a figurative term for a technique that uses the mutation rate of biomolecules to deduce the time in prehistory when two or more life forms diverged. The biomolecular data used for such calculations are usually nucleo ...
estimates.
In popular culture
''Clade'' is the title of a novel by James Bradley, who chose it both because of its biological meaning and also because of the larger implications of the word. An episode of '' Elementary'' is titled " Dead Clade Walking" and deals with a case involving a rare fossil.See also
* Adaptive radiation *Binomial nomenclature
In taxonomy, binomial nomenclature ("two-term naming system"), also called nomenclature ("two-name naming system") or binary nomenclature, is a formal system of naming species of living things by giving each a name composed of two parts, b ...
* Biological classification
In biology, taxonomy () is the scientific study of naming, defining ( circumscribing) and classifying groups of biological organisms based on shared characteristics. Organisms are grouped into taxa (singular: taxon) and these groups are giv ...
* Cladistics
Cladistics (; ) is an approach to biological classification in which organisms are categorized in groups (" clades") based on hypotheses of most recent common ancestry. The evidence for hypothesized relationships is typically shared derived ch ...
* Crown group
* Monophyly
In cladistics for a group of organisms, monophyly is the condition of being a clade—that is, a group of taxa composed only of a common ancestor (or more precisely an ancestral population) and all of its lineal descendants. Monophyletic gr ...
* Paraphyly
* Phylogenetic network
A phylogenetic network is any graph used to visualize evolutionary relationships (either abstractly or explicitly) between nucleotide sequences, genes, chromosomes, genomes, or species. They are employed when reticulation events such as hybrid ...
* Phylogenetic nomenclature
* Phylogenetics
In biology, phylogenetics (; from Greek φυλή/ φῦλον [] "tribe, clan, race", and wikt:γενετικός, γενετικός [] "origin, source, birth") is the study of the evolutionary history and relationships among or within groups ...
* Polyphyly
A polyphyletic group is an assemblage of organisms or other evolving elements that is of mixed evolutionary origin. The term is often applied to groups that share similar features known as homoplasies, which are explained as a result of conver ...
Notes
References
Bibliography
*External links
Evolving Thoughts: "Clade"
* DM Hillis, D Zwickl & R Gutell.
. An unrooted cladogram depicting around 3000 species.
"Phylogenetic systematics, an introductory slide-show on evolutionary trees"
–
University of California, Berkeley
The University of California, Berkeley (UC Berkeley, Berkeley, Cal, or California) is a public land-grant research university in Berkeley, California. Established in 1868 as the University of California, it is the state's first land-grant u ...
{{Evolution
Biology terminology
Philosophy of biology
Phylogenetics
1950s neologisms