Circuits Of England And Wales on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
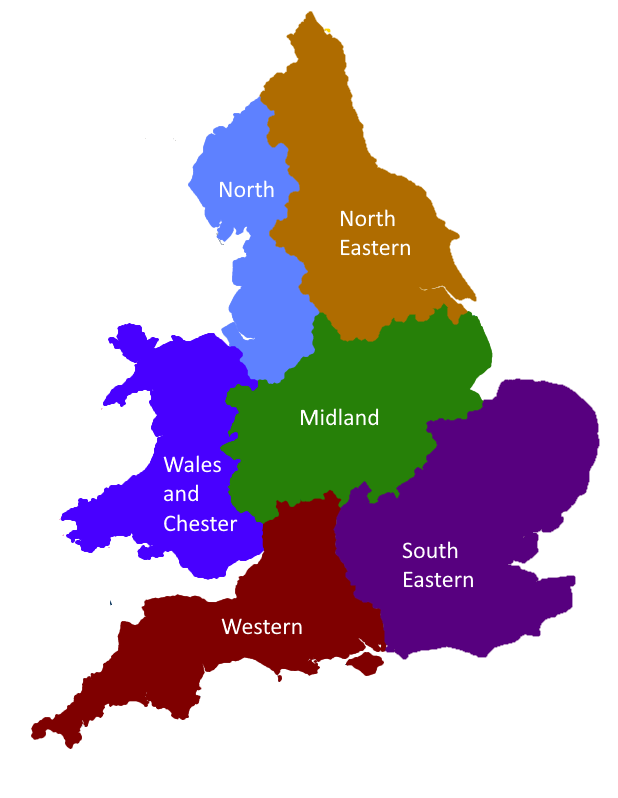 Circuits are the highest-level administrative divisions of the Bar of England and Wales and His Majesty's Courts and Tribunals Service. Today, they serve as professional associations for barristers practicing within their areas, as well as administrative divisions for the purposes of administration of justice.
There are six circuits in total: Midland,
Circuits are the highest-level administrative divisions of the Bar of England and Wales and His Majesty's Courts and Tribunals Service. Today, they serve as professional associations for barristers practicing within their areas, as well as administrative divisions for the purposes of administration of justice.
There are six circuits in total: Midland,
 Circuits are the highest-level administrative divisions of the Bar of England and Wales and His Majesty's Courts and Tribunals Service. Today, they serve as professional associations for barristers practicing within their areas, as well as administrative divisions for the purposes of administration of justice.
There are six circuits in total: Midland,
Circuits are the highest-level administrative divisions of the Bar of England and Wales and His Majesty's Courts and Tribunals Service. Today, they serve as professional associations for barristers practicing within their areas, as well as administrative divisions for the purposes of administration of justice.
There are six circuits in total: Midland, Northern
Northern may refer to the following:
Geography
* North, a point in direction
* Northern Europe, the northern part or region of Europe
* Northern Highland, a region of Wisconsin, United States
* Northern Province, Sri Lanka
* Northern Range, a ra ...
, North Eastern, Western, Wales and Chester, and South Eastern.
There is also the European Circuit, which is an association of barristers with interests in European law. Though it is called a circuit and recognised by the Bar Council, it does not serve any administrative or judicial purposes.
Circuits are divided along local authority area borders.
History
The term "circuit" is derived from the English custom of itinerant courts whose judges periodically travelled on pre-set paths—circuits—to hear cases from different areas. In 1293, a statute was enacted which formally defined four assize circuits. These would change frequently over the next few centuries. By the 1500s, there were six different circuits:Home
A home, or domicile, is a space used as a permanent or semi-permanent residence for one or many humans, and sometimes various companion animals. It is a fully or semi sheltered space and can have both interior and exterior aspects to it. H ...
, Midland, Northern, Oxford, Northern, and Western. This remained largely constant until the 19th century. Twice each year, judges "literally rode each circuit," meaning that a pair of common law judges assigned to a circuit rode on horseback through all the county towns and several other important towns in each circuit and heard cases.
The current circuits originate from the 1969 Beeching Commission, which recommended the merger of the Midland and Oxford circuits. Since then only minor boundary changes have been made, such as in the 1998 Review of Criminal Justice Boundaries.
Functions
As part of the Bar Council
Circuits effectively function as professional associations for barristers. They provide important sources of support, advice and representation for barristers practising in those areas. They liaise closely with the local court service, Crown Prosecution Service and other bodies as well as providing important training and social events for barristers. Each circuit is represented on the Bar Council through its leader and other appointed representatives. Circuits are closely linked with specialist bar associations, who may appoint representatives to each circuit.As part of the judiciary
Circuits also serve a judicial function as judges (except for judges of the Court of Appeal andthe Supreme Court
A supreme court is the highest court within the hierarchy of courts in most legal jurisdictions. Other descriptions for such courts include court of last resort, apex court, and high (or final) court of appeal. Broadly speaking, the decisions of ...
) are appointed to, and will only sit in, a specific circuit. This avoids judges having to travel large distances to hear cases.
The circuits system is overseen by the Lord Chancellor.
Leadership
Each circuit elects a leader to represent it, to serve a three-year term. The current leaders are: Potential leaders must beKing's Counsel
In the United Kingdom and in some Commonwealth countries, a King's Counsel ( post-nominal initials KC) during the reign of a king, or Queen's Counsel (post-nominal initials QC) during the reign of a queen, is a lawyer (usually a barrister or ...
. A circuit may also appoint other leadership positions, such as a circuit junior or treasurer, who will often form its executive committee.
Circuit leaders are entitled to sit on the Bar Council ''ex officio''.
See also
*Assizes
The courts of assize, or assizes (), were periodic courts held around England and Wales until 1972, when together with the quarter sessions they were abolished by the Courts Act 1971 and replaced by a single permanent Crown Court. The assizes e ...
* Circuit riding
In the United States, circuit riding was the practice of a judge, sometimes referred to as a circuit rider, traveling to a judicial district (referred to as a circuit) to preside over court cases there. A defining feature of American federal cour ...
References
{{Legal services in the United Kingdom Bar of England and Wales Judicial districts