Circuit Breaker on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]


 A circuit breaker is an electrical safety device designed to protect an
A circuit breaker is an electrical safety device designed to protect an
 Circuit breakers are manufactured in standard sizes, using a system of preferred numbers to cover a range of ratings. Miniature circuit breakers have a fixed trip setting; changing the operating current value requires changing the whole circuit breaker. Larger circuit breakers can have adjustable trip settings, allowing standardized elements to be applied but with a setting intended to improve protection. For example, a circuit breaker with a 400 ampere "frame size" might have its over current detection set to operate at only 300 amperes, to protect a feeder cable.
For low voltage distribution circuit breakers, International Standards, IEC 60898-1 defines the ''rated current'' as the maximum current that the breaker is designed to carry continuously. The commonly available preferred values for the rated current are 1A, 2A, 4A, 6 A, 10 A, 13 A, 16 A, 20 A, 25 A, 32 A, 40 A, 50 A, 63 A, 80 A, 100 A, and 125 A. The circuit breaker is labeled with the rated current in
Circuit breakers are manufactured in standard sizes, using a system of preferred numbers to cover a range of ratings. Miniature circuit breakers have a fixed trip setting; changing the operating current value requires changing the whole circuit breaker. Larger circuit breakers can have adjustable trip settings, allowing standardized elements to be applied but with a setting intended to improve protection. For example, a circuit breaker with a 400 ampere "frame size" might have its over current detection set to operate at only 300 amperes, to protect a feeder cable.
For low voltage distribution circuit breakers, International Standards, IEC 60898-1 defines the ''rated current'' as the maximum current that the breaker is designed to carry continuously. The commonly available preferred values for the rated current are 1A, 2A, 4A, 6 A, 10 A, 13 A, 16 A, 20 A, 25 A, 32 A, 40 A, 50 A, 63 A, 80 A, 100 A, and 125 A. The circuit breaker is labeled with the rated current in
 Many classifications of circuit breakers can be made, based on their features such as voltage class, construction type, interrupting type, and structural features.
Many classifications of circuit breakers can be made, based on their features such as voltage class, construction type, interrupting type, and structural features.
 The
The
 ''Thermal magnetic circuit breakers'', which are the type found in most
''Thermal magnetic circuit breakers'', which are the type found in most
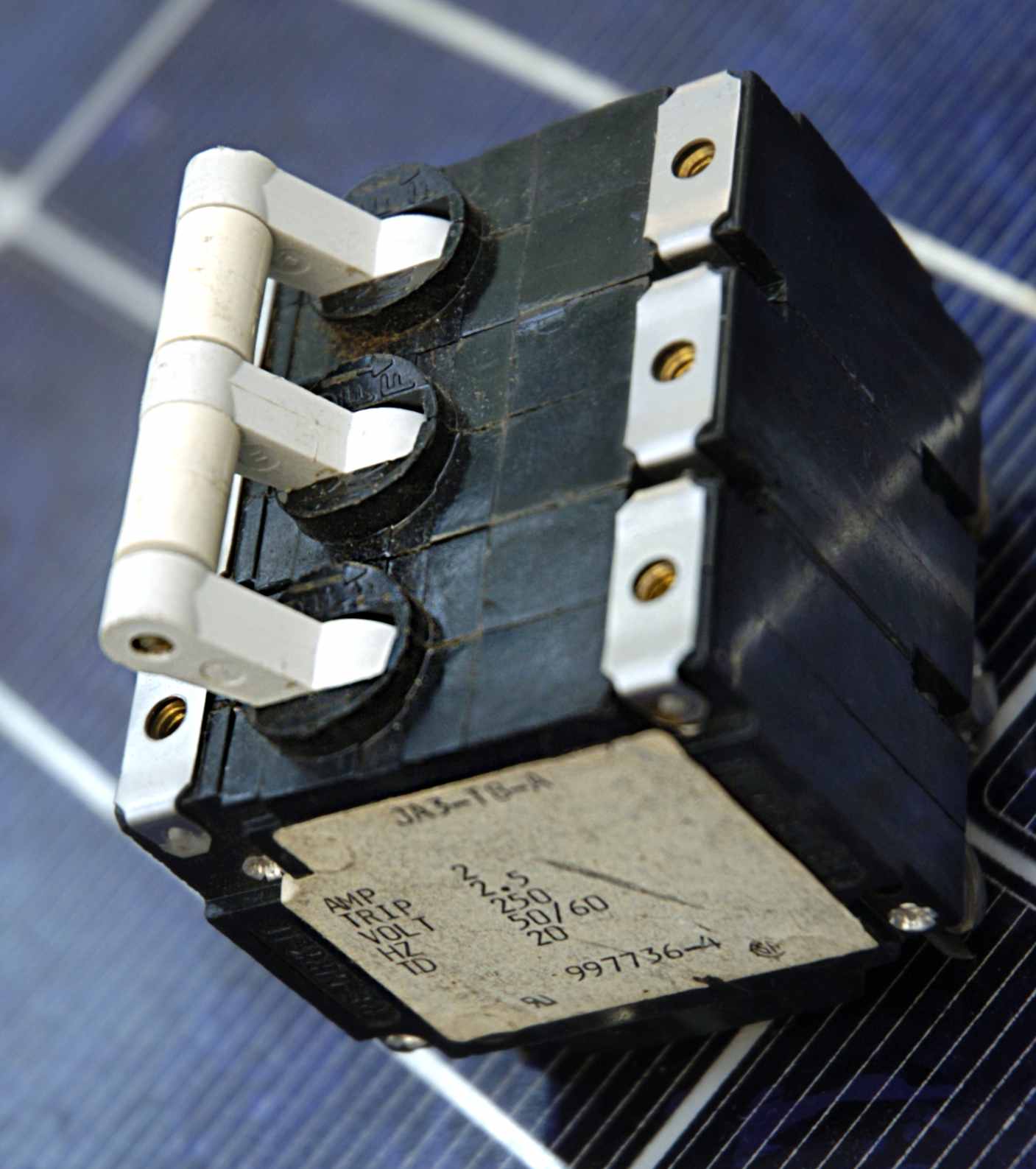 To provide simultaneous breaking on multiple circuits from a fault on any one, circuit breakers may be made as a ganged assembly. This is a very common requirement for 3 phase systems, where breaking may be either 3 or 4 pole (solid or switched neutral). Some makers make ganging kits to allow groups of single phase breakers to be interlinked as required.
In the US, where split phase supplies are common, in branch circuits with more than one live conductor, each live conductor must be protected by a breaker pole. To ensure that all live conductors are interrupted when any pole trips, a "common trip" breaker must be used. These may either contain two or three tripping mechanisms within one case, or for small breakers, may externally tie the poles together via their operating handles. Two-pole common trip breakers are common on 120/240-volt systems where 240 volt loads (including
To provide simultaneous breaking on multiple circuits from a fault on any one, circuit breakers may be made as a ganged assembly. This is a very common requirement for 3 phase systems, where breaking may be either 3 or 4 pole (solid or switched neutral). Some makers make ganging kits to allow groups of single phase breakers to be interlinked as required.
In the US, where split phase supplies are common, in branch circuits with more than one live conductor, each live conductor must be protected by a breaker pole. To ensure that all live conductors are interrupted when any pole trips, a "common trip" breaker must be used. These may either contain two or three tripping mechanisms within one case, or for small breakers, may externally tie the poles together via their operating handles. Two-pole common trip breakers are common on 120/240-volt systems where 240 volt loads (including
 Medium-voltage circuit breakers rated between 1 and 72kV may be assembled into metal-enclosed switchgear line ups for indoor use, or may be individual components installed outdoors in a substation. Air-break circuit breakers replaced oil-filled units for indoor applications, but are now themselves being replaced by vacuum circuit breakers (up to about 40.5kV). Like the high voltage circuit breakers described below, these are also operated by current sensing protective
Medium-voltage circuit breakers rated between 1 and 72kV may be assembled into metal-enclosed switchgear line ups for indoor use, or may be individual components installed outdoors in a substation. Air-break circuit breakers replaced oil-filled units for indoor applications, but are now themselves being replaced by vacuum circuit breakers (up to about 40.5kV). Like the high voltage circuit breakers described below, these are also operated by current sensing protective

 Electrical
Electrical
 The following types are described in separate articles.
* Breakers for protections against earth faults too small to trip an over-current device:
**
The following types are described in separate articles.
* Breakers for protections against earth faults too small to trip an over-current device:
**
Circuit Breaker

 A circuit breaker is an electrical safety device designed to protect an
A circuit breaker is an electrical safety device designed to protect an electrical circuit
An electrical network is an interconnection of electrical components (e.g., batteries, resistors, inductors, capacitors, switches, transistors) or a model of such an interconnection, consisting of electrical elements (e.g., voltage sour ...
from damage caused by overcurrent. Its basic function is to interrupt current flow to protect equipment and to prevent the risk of fire
Fire is the rapid oxidation of a material (the fuel) in the exothermic chemical process of combustion, releasing heat, light, and various reaction Product (chemistry), products.
At a certain point in the combustion reaction, called the ignition ...
. Unlike a fuse
Fuse or FUSE may refer to:
Devices
* Fuse (electrical), a device used in electrical systems to protect against excessive current
** Fuse (automotive), a class of fuses for vehicles
* Fuse (hydraulic), a device used in hydraulic systems to prote ...
, which operates once and then must be replaced, a circuit breaker can be reset (either manually or automatically) to resume normal operation.
Circuit breakers are made in varying sizes, from small devices that protect low-current circuits or individual household appliances, to large switchgear
In an electric power system, a switchgear is composed of electrical disconnect switches, fuses or circuit breakers used to control, protect and isolate electrical equipment. Switchgear is used both to de-energize equipment to allow work to be ...
designed to protect high voltage
High voltage electricity refers to electrical potential large enough to cause injury or damage. In certain industries, ''high voltage'' refers to voltage above a certain threshold. Equipment and conductors that carry high voltage warrant spe ...
circuits feeding an entire city. The generic function of a circuit breaker, or fuse
Fuse or FUSE may refer to:
Devices
* Fuse (electrical), a device used in electrical systems to protect against excessive current
** Fuse (automotive), a class of fuses for vehicles
* Fuse (hydraulic), a device used in hydraulic systems to prote ...
, as an automatic means of removing power from a faulty system, is often abbreviated as OCPD (Over Current Protection Device).
Origins
An early form of circuit breaker was described byThomas Edison
Thomas Alva Edison (February 11, 1847October 18, 1931) was an American inventor and businessman. He developed many devices in fields such as electric power generation, mass communication, sound recording, and motion pictures. These invent ...
in an 1879 patent application, although his commercial power distribution system used fuses
Fuse or FUSE may refer to:
Devices
* Fuse (electrical), a device used in electrical systems to protect against excessive current
** Fuse (automotive), a class of fuses for vehicles
* Fuse (hydraulic), a device used in hydraulic systems to protect ...
. Its purpose was to protect lighting circuit wiring from accidental short circuits and overloads. A modern miniature circuit breaker similar to the ones now in use was patented by Brown, Boveri & Cie
Brown, Boveri & Cie. (Brown, Boveri & Company; BBC) was a Swiss group of electrical engineering companies.
It was founded in Zürich, in 1891 by Charles Eugene Lancelot Brown and Walter Boveri who worked at the Maschinenfabrik Oerlikon. In ...
in 1924. Hugo Stotz, an engineer who had sold his company to BBC #REDIRECT BBC
Here i going to introduce about the best teacher of my life b BALAJI sir. He is the precious gift that I got befor 2yrs . How has helped and thought all the concept and made my success in the 10th board exam. ...
, was credited as the inventor on DRP (''Deutsches Reichspatent'') 458392. Stotz's invention was the forerunner of the modern thermal-magnetic breaker commonly used in household load centers to this day.
Interconnection of multiple generator sources into an electrical grid required the development of circuit breakers with increasing voltage ratings and increased ability to safely interrupt the increasing short-circuit currents produced by networks. Simple air-break manual switches produced hazardous arcs when interrupting high voltages; these gave way to oil-enclosed contacts, and various forms using the directed flow of pressurized air, or pressurized oil, to cool and interrupt the arc. By 1935, the specially constructed circuit breakers used at the Boulder Dam project used eight series breaks and pressurized oil flow to interrupt faults of up to 2,500 MVA, in three cycles of the AC power frequency.
Operation
All circuit breaker systems have common features in their operation, but details vary substantially depending on the voltage class, current rating and type of the circuit breaker. The circuit breaker must first detect a fault condition. In small mains andlow voltage In electrical engineering, low voltage is a relative term, the definition varying by context. Different definitions are used in electric power transmission and distribution, compared with electronics design. electrical safety codes define "low vol ...
circuit breakers, this is usually done within the device itself. Typically, the heating or magnetic effects of electric current are employed. Circuit breakers for large currents or high voltages are usually arranged with protective relay
In electrical engineering, a protective relay is a relay device designed to trip a circuit breaker when a fault is detected. The first protective relays were electromagnetic devices, relying on coils operating on moving parts to provide detec ...
pilot devices to sense a fault condition and to operate the opening mechanism. These typically require a separate power source, such as a battery
Battery most often refers to:
* Electric battery, a device that provides electrical power
* Battery (crime), a crime involving unlawful physical contact
Battery may also refer to:
Energy source
*Automotive battery, a device to provide power t ...
, although some high-voltage circuit breakers are self-contained with current transformer
A current transformer (CT) is a type of transformer that is used to reduce or multiply an alternating current (AC). It produces a current in its secondary which is proportional to the current in its primary.
Current transformers, along with volt ...
s, protective relay
In electrical engineering, a protective relay is a relay device designed to trip a circuit breaker when a fault is detected. The first protective relays were electromagnetic devices, relying on coils operating on moving parts to provide detec ...
s, and an internal control power source.
Once a fault is detected, the circuit breaker contacts must open to interrupt the circuit; this is commonly done using mechanically stored energy contained within the breaker, such as a spring or compressed air to separate the contacts. Circuit breakers may also use the higher current caused by the fault to separate the contacts, such as thermal expansion or a magnetic field. Small circuit breakers typically have a manual control lever to switch off the load or reset a tripped breaker, while larger units use solenoid
upright=1.20, An illustration of a solenoid
upright=1.20, Magnetic field created by a seven-loop solenoid (cross-sectional view) described using field lines
A solenoid () is a type of electromagnet formed by a helix, helical coil of wire whose ...
s to trip the mechanism, and electric motor
An electric motor is an electrical machine that converts electrical energy into mechanical energy. Most electric motors operate through the interaction between the motor's magnetic field and electric current in a wire winding to generate forc ...
s to restore energy to the springs.
The circuit breaker contacts must carry the load current without excessive heating, and must also withstand the heat of the arc produced when interrupting (opening) the circuit. Contacts are made of copper or copper alloys, silver alloys and other highly conductive materials. Service life of the contacts is limited by the erosion of contact material due to arcing while interrupting the current. Miniature and molded-case circuit breakers are usually discarded when the contacts have worn, but power circuit breakers and high-voltage circuit breakers have replaceable contacts.
When a high current or voltage is interrupted, an arc is generated. The length of the arc is generally proportional to the voltage while the intensity (or heat) is proportional to the current. This arc must be contained, cooled and extinguished in a controlled way, so that the gap between the contacts can again withstand the voltage in the circuit. Different circuit breakers use vacuum
A vacuum is a space devoid of matter. The word is derived from the Latin adjective ''vacuus'' for "vacant" or " void". An approximation to such vacuum is a region with a gaseous pressure much less than atmospheric pressure. Physicists often di ...
, air, insulating gas A dielectric gas, or insulating gas, is a dielectric material in gaseous state. Its main purpose is to prevent or rapidly quench electric discharges. Dielectric gases are used as electrical insulators in high voltage applications, e.g. transformers ...
, or oil
An oil is any nonpolar chemical substance that is composed primarily of hydrocarbons and is hydrophobic (does not mix with water) & lipophilic (mixes with other oils). Oils are usually flammable and surface active. Most oils are unsaturate ...
as the medium the arc forms in. Different techniques are used to extinguish the arc including:
* Lengthening or deflecting the arc
* Intensive cooling (in jet chambers)
* Division into partial arcs
* Zero point quenching (contacts open at the zero current time crossing of the AC waveform, effectively breaking no load current at the time of opening. The zero-crossing occurs at twice the line frequency; i.e., 100 times per second for 50 Hz and 120 times per second for 60 Hz AC.)
* Connecting capacitor
A capacitor is a device that stores electrical energy in an electric field by virtue of accumulating electric charges on two close surfaces insulated from each other. It is a passive electronic component with two terminals.
The effect of a ...
s in parallel with contacts in DC circuits.
Finally, once the fault condition has been cleared, the contacts must again be closed to restore power to the interrupted circuit.
Arc interruption
Low-voltage miniature circuit breakers (MCB) use air alone to extinguish the arc. These circuit breakers contain so-called arc chutes, a stack of mutually insulated parallel metal plates that divide and cool the arc. By splitting the arc into smaller arcs the arc is cooled down while the arc voltage is increased and serves as an additional impedance that limits the current through the circuit breaker. The current-carrying parts near the contacts provide easy deflection of the arc into the arc chutes by a magnetic force of a current path, althoughmagnetic blowout
:''In semiconductor testing, contactors can also be referred to as the specialized socket that connects the device under test.''
:''In process industries, a contactor is a vessel where two streams interact, for example, air and liquid. See Gas- ...
coils or permanent magnets
A magnet is a material or object that produces a magnetic field. This magnetic field is invisible but is responsible for the most notable property of a magnet: a force that pulls on other ferromagnetic materials, such as iron, steel, nickel ...
could also deflect the arc into the arc chute (used on circuit breakers for higher ratings). The number of plates in the arc chute is dependent on the short-circuit rating and nominal voltage of the circuit breaker.
In larger ratings, oil circuit breakers rely upon vaporization of some of the oil to blast a jet of oil through the arc.
Gas (usually sulfur hexafluoride
Sulfur hexafluoride or sulphur hexafluoride ( British spelling) is an inorganic compound with the formula SF6. It is a colorless, odorless, non- flammable, and non-toxic gas. has an octahedral geometry, consisting of six fluorine atoms attach ...
) circuit breakers sometimes stretch the arc using a magnetic field, and then rely upon the dielectric strength
In physics, the term dielectric strength has the following meanings:
*for a pure electrically insulating material, the maximum electric field that the material can withstand under ideal conditions without undergoing electrical breakdown and bec ...
of the sulfur hexafluoride (SF6) to quench the stretched arc.
Vacuum
A vacuum is a space devoid of matter. The word is derived from the Latin adjective ''vacuus'' for "vacant" or " void". An approximation to such vacuum is a region with a gaseous pressure much less than atmospheric pressure. Physicists often di ...
circuit breakers have minimal arcing (as there is nothing to ionize other than the contact material). The arc quenches when it is stretched a very small amount (less than ). Vacuum circuit breakers are frequently used in modern medium-voltage switch gear to 38,000 volts.
Air circuit breakers may use compressed air to blow out the arc, or alternatively, the contacts are rapidly swung into a small sealed chamber, the escaping of the displaced air thus blowing out the arc.
Circuit breakers are usually able to terminate all current very quickly: typically the arc is extinguished between 30 ms and 150 ms after the mechanism has been tripped, depending upon age and construction of the device. The maximum current value and let-through energy determine the quality of the circuit breakers.
Short circuit
Circuit breakers are rated both by the normal current that they are expected to carry, and the maximum short-circuit current that they can safely interrupt. This latter figure is the ampere interrupting capacity (AIC) of the breaker. Under short-circuit conditions, the calculated or measured maximumprospective short-circuit current
The prospective short-circuit current (PSCC), available fault current, or short-circuit making current is the highest electric current which can exist in a particular electrical system under short-circuit conditions. It is determined by the voltag ...
may be many times the normal, rated current of the circuit. When electrical contacts open to interrupt a large current, there is a tendency for an arc to form between the opened contacts, which would allow the current to continue. This condition can create conductive ionized gases and molten or vaporized metal, which can cause the further continuation of the arc, or creation of additional short circuits, potentially resulting in the explosion of the circuit breaker and the equipment that it is installed in. Therefore, circuit breakers must incorporate various features to divide and extinguish the arc.
The maximum short-circuit current that a breaker can interrupt is determined by testing. Application of a breaker in a circuit with a prospective short-circuit current higher than the breaker's interrupting capacity rating may result in failure of the breaker to safely interrupt a fault. In a worst-case scenario, the breaker may successfully interrupt the fault, only to explode when reset.
Typical domestic panel circuit breakers are rated to interrupt () short-circuit current.
Miniature circuit breakers used to protect control circuits or small appliances may not have sufficient interrupting capacity to use at a panel board; these circuit breakers are called "supplemental circuit protectors" to distinguish them from distribution-type circuit breakers.
Standard current ratings
ampere
The ampere (, ; symbol: A), often Clipping (morphology), shortened to amp,SI supports only the use of symbols and deprecates the use of abbreviations for units. is the unit of electric current in the International System of Units (SI). One amp ...
s prefixed by a letter, which indicates the ''instantaneous tripping current'' that causes the circuit breaker to trip without intentional time delay expressed in multiples of the rated current:
Circuit breakers are also rated by the maximum fault current that they can interrupt; this allows use of more economical devices on systems unlikely to develop the high short-circuit current found on, for example, a large commercial building distribution system.
In the United States, Underwriters Laboratories
The UL enterprise is a global safety science company headquartered in Northbrook, Illinois, composed of three organizations, UL Research Institutes, UL Standards & Engagement and UL Solutions.
Established in 1894, the UL enterprise was founded as ...
(UL) certifies equipment ratings, called Series Ratings (or "integrated equipment ratings") for circuit breaker equipment used for buildings. Power circuit breakers and medium- and high-voltage circuit breakers used for industrial or electric power systems are designed and tested to ANSI
The American National Standards Institute (ANSI ) is a private non-profit organization that oversees the development of voluntary consensus standards for products, services, processes, systems, and personnel in the United States. The organ ...
or IEEE
The Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) is a 501(c)(3) professional association for electronic engineering and electrical engineering (and associated disciplines) with its corporate office in New York City and its operati ...
standards in the C37 series. For example, standard C37.16 lists preferred frame size current ratings for power circuit breakers in the range of 600 to 5000 amperes. Trip current settings dn time-current characteristics of these breakers are generally adjustable.
For medium and high voltage circuit breakers used in switchgear
In an electric power system, a switchgear is composed of electrical disconnect switches, fuses or circuit breakers used to control, protect and isolate electrical equipment. Switchgear is used both to de-energize equipment to allow work to be ...
or substations and generating stations, relatively few standard frame sizes are generally manufactured. These circuit breakers are usually controlled by separate protective relay
In electrical engineering, a protective relay is a relay device designed to trip a circuit breaker when a fault is detected. The first protective relays were electromagnetic devices, relying on coils operating on moving parts to provide detec ...
systems, offering adjustable tripping current and time settings as well as allowing for more complex protection schemes.
Types
 Many classifications of circuit breakers can be made, based on their features such as voltage class, construction type, interrupting type, and structural features.
Many classifications of circuit breakers can be made, based on their features such as voltage class, construction type, interrupting type, and structural features.
Low-voltage
Low-voltage (less than 1,000 VAC) types are common in domestic, commercial and industrial application, and include: * Miniature circuit breaker (MCB)—rated current up to 125 A. Trip characteristics normally not adjustable. Thermal or thermal-magnetic operation. Breakers illustrated above are in this category. * Molded Case Circuit Breaker (MCCB)—rated current up to 1,600 A. Thermal or thermal-magnetic operation. Trip current may be adjustable in larger ratings. * Low-voltage power circuit breakers can be mounted in multi-tiers in low-voltage switchboards orswitchgear
In an electric power system, a switchgear is composed of electrical disconnect switches, fuses or circuit breakers used to control, protect and isolate electrical equipment. Switchgear is used both to de-energize equipment to allow work to be ...
cabinets.
The characteristics of low-voltage circuit breakers are given by international standards such as IEC 947. These circuit breakers are often installed in draw-out enclosures that allow removal and interchange without dismantling the switchgear.
Large low-voltage molded case and power circuit breakers may have electric motor operators so they can open and close under remote control. These may form part of an automatic transfer switch system for standby power.
Low-voltage circuit breakers are also made for direct-current (DC) applications, such as DC for subway lines. Direct current requires special breakers because the arc is continuous—unlike an AC arc, which tends to go out on each half cycle, direct current circuit breaker has blow-out coils that generate a magnetic field that rapidly stretches the arc. Small circuit breakers are either installed directly in equipment, or are arranged in a breaker panel
A distribution board (also known as panelboard, breaker panel, electric panel, DB board or DB box) is a component of an electricity supply system that divides an electrical power feed into subsidiary circuits while providing a protective fuse ...
.
 The
The DIN rail
A DIN rail is a metal rail of a standard type widely used for mounting circuit breakers and industrial control equipment inside equipment racks. These products are typically made from cold rolled carbon steel sheet with a zinc-plated or chroma ...
-mounted thermal-magnetic miniature circuit breaker is the most common style in modern domestic consumer unit
A consumer unit is a type of distribution board (a component of an electrical power system within which an electrical power feed provides supply to subsidiary circuits).
UK
The IET defines a consumer unit, also known as a consumer control ...
s and commercial electrical distribution board
A distribution board (also known as panelboard, breaker panel, electric panel, DB board or DB box) is a component of an electricity supply system that divides an electrical power feed into subsidiary circuits while providing a protective fus ...
s throughout Europe
Europe is a large peninsula conventionally considered a continent in its own right because of its great physical size and the weight of its history and traditions. Europe is also considered a subcontinent of Eurasia and it is located enti ...
. The design includes the following components:
# Actuator lever
A lever is a simple machine consisting of a beam or rigid rod pivoted at a fixed hinge, or '' fulcrum''. A lever is a rigid body capable of rotating on a point on itself. On the basis of the locations of fulcrum, load and effort, the lever is d ...
- used to manually trip and reset the circuit breaker. Also indicates the status of the circuit breaker (On or Off/tripped). Most breakers are designed so they can still trip even if the lever is held or locked in the "on" position. This is sometimes referred to as "free trip" or "positive trip" operation.
# Actuator mechanism - forces the contacts together or apart.
# Contacts - allow current when touching and break the current when moved apart.
# Terminals
# Bimetallic strip - separates contacts in response to smaller, longer-term overcurrents
# Calibration screw
A screw and a bolt (see '' Differentiation between bolt and screw'' below) are similar types of fastener typically made of metal and characterized by a helical ridge, called a ''male thread'' (external thread). Screws and bolts are used to fa ...
- allows the manufacturer
Manufacturing is the creation or production of goods with the help of equipment, labor, machines, tools, and chemical or biological processing or formulation. It is the essence of secondary sector of the economy. The term may refer to a ...
to precisely adjust the trip current of the device after assembly.
# Solenoid - separates contacts rapidly in response to high overcurrents
# Arc divider/extinguisher
Solid state
''Solid-state circuit breakers'', also known as ''digital circuit breakers'' are a technological innovation which promises advance circuit breaker technology out of the mechanical level, into the electrical. This promises several advantages, such as cutting the circuit in fractions of microseconds, better monitoring of circuit loads and longer lifetimes.Magnetic
''Magnetic circuit breakers'' use asolenoid
upright=1.20, An illustration of a solenoid
upright=1.20, Magnetic field created by a seven-loop solenoid (cross-sectional view) described using field lines
A solenoid () is a type of electromagnet formed by a helix, helical coil of wire whose ...
(electromagnet
An electromagnet is a type of magnet in which the magnetic field is produced by an electric current. Electromagnets usually consist of wire wound into a coil. A current through the wire creates a magnetic field which is concentrated in the ...
) whose pulling force increases with the current
Currents, Current or The Current may refer to:
Science and technology
* Current (fluid), the flow of a liquid or a gas
** Air current, a flow of air
** Ocean current, a current in the ocean
*** Rip current, a kind of water current
** Current (stre ...
. Certain designs utilize electromagnetic forces in addition to those of the solenoid. The circuit breaker contacts are held closed by a latch. As the current in the solenoid increases beyond the rating of the circuit breaker, the solenoid's pull releases the latch, which lets the contacts open by spring action. They are the most commonly used circuit breakers in the United States.
Thermal-magnetic
 ''Thermal magnetic circuit breakers'', which are the type found in most
''Thermal magnetic circuit breakers'', which are the type found in most distribution board
A distribution board (also known as panelboard, breaker panel, electric panel, DB board or DB box) is a component of an electricity supply system that divides an electrical power feed into subsidiary circuits while providing a protective fus ...
s in Europe and countries with a similar wiring arrangements, incorporate both techniques with the electromagnet responding instantaneously to large surges in current (short circuits) and the bimetallic strip responding to less extreme but longer-term over-current conditions. The thermal portion of the circuit breaker provides a time response feature, that trips the circuit breaker sooner for larger over currents but allows smaller overloads to persist for a longer time. This allows short current spikes such as are produced when a motor or other non-resistive load is switched on. With very large over-currents during a short circuit, the magnetic element trips the circuit breaker with no intentional additional delay.
Magnetic-hydraulic
A ''magnetic-hydraulic'' circuit breaker uses a solenoid coil to provide operating force to open the contacts. Magnetic-hydraulic breakers incorporate a hydraulic time delay feature using a viscous fluid. A spring restrains the core until the current exceeds the breaker rating. During an overload, the speed of the solenoid motion is restricted by the fluid. The delay permits brief current surges beyond normal running current for motor starting, energizing equipment, etc. Short-circuit currents provide sufficient solenoid force to release the latch regardless of core position thus bypassing the delay feature. Ambient temperature affects the time delay but does not affect the current rating of a magnetic breaker. Large power circuit breakers, applied in circuits of more than 1000 volts, may incorporate hydraulic elements in the contact operating mechanism. Hydraulic energy may be supplied by a pump, or stored in accumulators. These form a distinct type from oil-filled circuit breakers where oil is the arc extinguishing medium.Common trip (ganged) breakers
 To provide simultaneous breaking on multiple circuits from a fault on any one, circuit breakers may be made as a ganged assembly. This is a very common requirement for 3 phase systems, where breaking may be either 3 or 4 pole (solid or switched neutral). Some makers make ganging kits to allow groups of single phase breakers to be interlinked as required.
In the US, where split phase supplies are common, in branch circuits with more than one live conductor, each live conductor must be protected by a breaker pole. To ensure that all live conductors are interrupted when any pole trips, a "common trip" breaker must be used. These may either contain two or three tripping mechanisms within one case, or for small breakers, may externally tie the poles together via their operating handles. Two-pole common trip breakers are common on 120/240-volt systems where 240 volt loads (including
To provide simultaneous breaking on multiple circuits from a fault on any one, circuit breakers may be made as a ganged assembly. This is a very common requirement for 3 phase systems, where breaking may be either 3 or 4 pole (solid or switched neutral). Some makers make ganging kits to allow groups of single phase breakers to be interlinked as required.
In the US, where split phase supplies are common, in branch circuits with more than one live conductor, each live conductor must be protected by a breaker pole. To ensure that all live conductors are interrupted when any pole trips, a "common trip" breaker must be used. These may either contain two or three tripping mechanisms within one case, or for small breakers, may externally tie the poles together via their operating handles. Two-pole common trip breakers are common on 120/240-volt systems where 240 volt loads (including major appliance
A major appliance, also known as a large domestic appliance or large electric appliance or simply a large appliance, large domestic, or large electric, is a non-portable or semi-portable machine used for routine housekeeping tasks such as cooki ...
s or further distribution boards) span the two live wires. Three-pole common trip breakers are typically used to supply three-phase electric power
Three-phase electric power (abbreviated 3φ) is a common type of alternating current used in electricity generation, transmission, and distribution. It is a type of polyphase system employing three wires (or four including an optional neutral ...
to large motors or further distribution boards.
Separate circuit breakers must never be used for live and neutral, because if the neutral is disconnected while the live conductor stays connected, a very dangerous condition arises: the circuit appears de-energized (appliances don't work), but wires remain live and some residual-current device
A residual-current device (RCD), residual-current circuit breaker (RCCB) or ground fault circuit interrupter (GFCI) is an electrical safety device that quickly breaks an electrical circuit with leakage current to ground. It is to protect equip ...
s (RCDs) may not trip if someone touches the live wire (because some RCDs need power to trip). This is why only common trip breakers must be used when neutral wire switching is needed.
Shunt-trip units
A shunt-trip unit appears similar to a normal breaker and the moving actuators are 'ganged' to a normal breaker mechanism to operate together in a similar way, but the shunt trip is a solenoid intended to be operated by an external constant voltage signal, rather than a current, commonly the local mains voltage or DC. These are often used to cut the power when a high risk event occurs, such as a fire or flood alarm, or another electrical condition, such as over voltage detection. Shunt trips may be a user fitted accessory to a standard breaker, or supplied as an integral part of the circuit breaker.Medium-voltage
 Medium-voltage circuit breakers rated between 1 and 72kV may be assembled into metal-enclosed switchgear line ups for indoor use, or may be individual components installed outdoors in a substation. Air-break circuit breakers replaced oil-filled units for indoor applications, but are now themselves being replaced by vacuum circuit breakers (up to about 40.5kV). Like the high voltage circuit breakers described below, these are also operated by current sensing protective
Medium-voltage circuit breakers rated between 1 and 72kV may be assembled into metal-enclosed switchgear line ups for indoor use, or may be individual components installed outdoors in a substation. Air-break circuit breakers replaced oil-filled units for indoor applications, but are now themselves being replaced by vacuum circuit breakers (up to about 40.5kV). Like the high voltage circuit breakers described below, these are also operated by current sensing protective relay
A relay
Electromechanical relay schematic showing a control coil, four pairs of normally open and one pair of normally closed contacts
An automotive-style miniature relay with the dust cover taken off
A relay is an electrically operated swit ...
s operated through current transformer
A current transformer (CT) is a type of transformer that is used to reduce or multiply an alternating current (AC). It produces a current in its secondary which is proportional to the current in its primary.
Current transformers, along with volt ...
s. The characteristics of MV breakers are given by international standards such as IEC 62271. Medium-voltage circuit breakers nearly always use separate current sensors and protective relay
In electrical engineering, a protective relay is a relay device designed to trip a circuit breaker when a fault is detected. The first protective relays were electromagnetic devices, relying on coils operating on moving parts to provide detec ...
s, instead of relying on built-in thermal or magnetic overcurrent sensors.
Medium-voltage circuit breakers can be classified by the medium used to extinguish the arc:
* Vacuum circuit breakers—With rated current up to 6,300A, and higher for generator circuit breakers application (up to 16,000A & 140kA). These breakers interrupt the current by creating and extinguishing the arc in a vacuum container - aka "bottle". Long life bellows are designed to travel the 6–10 mm the contacts must part. These are generally applied for voltages up to about 40,500V, which corresponds roughly to the medium-voltage range of power systems. Vacuum circuit breakers have longer life expectancy between overhaul than do other circuit breakers. In addition their global warming potential
Global warming potential (GWP) is the heat absorbed by any greenhouse gas in the atmosphere, as a multiple of the heat that would be absorbed by the same mass of carbon dioxide (). GWP is 1 for . For other gases it depends on the gas and the time ...
is by far lower than SF6 circuit breaker.
* Air circuit breakers—Rated current up to 6,300A and higher for generator circuit breakers. Trip characteristics are often fully adjustable including configurable trip thresholds and delays. Usually electronically controlled, though some models are microprocessor
A microprocessor is a computer processor where the data processing logic and control is included on a single integrated circuit, or a small number of integrated circuits. The microprocessor contains the arithmetic, logic, and control circu ...
controlled via an integral electronic trip unit. Often used for main power distribution in large industrial plant, where the breakers are arranged in draw-out enclosures for ease of maintenance.
* SF6 circuit breakers extinguish the arc in a chamber filled with sulfur hexafluoride
Sulfur hexafluoride or sulphur hexafluoride ( British spelling) is an inorganic compound with the formula SF6. It is a colorless, odorless, non- flammable, and non-toxic gas. has an octahedral geometry, consisting of six fluorine atoms attach ...
gas.
Medium-voltage circuit breakers may be connected into the circuit by bolted connections to bus bars or wires, especially in outdoor switchyards. Medium-voltage circuit breakers in switchgear line-ups are often built with draw-out construction, allowing breaker removal without disturbing power circuit connections, using a motor-operated or hand-cranked mechanism to separate the breaker from its enclosure.
High-voltage

 Electrical
Electrical power transmission
Power transmission is the movement of energy from its place of generation to a location where it is applied to perform useful work.
Power is defined formally as units of energy per unit time. In SI units:
:\text = \frac = \frac
Since the deve ...
networks are protected and controlled by high-voltage breakers. The definition of ''high voltage'' varies but in power transmission work is usually thought to be 72.5 kV or higher, according to a recent definition by the International Electrotechnical Commission
The International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC; in French: ''Commission électrotechnique internationale'') is an international standards organization that prepares and publishes international standards for all electrical, electronic and ...
(IEC). High-voltage breakers are nearly always solenoid
upright=1.20, An illustration of a solenoid
upright=1.20, Magnetic field created by a seven-loop solenoid (cross-sectional view) described using field lines
A solenoid () is a type of electromagnet formed by a helix, helical coil of wire whose ...
-operated, with current sensing protective relay
In electrical engineering, a protective relay is a relay device designed to trip a circuit breaker when a fault is detected. The first protective relays were electromagnetic devices, relying on coils operating on moving parts to provide detec ...
s operated through current transformer
A current transformer (CT) is a type of transformer that is used to reduce or multiply an alternating current (AC). It produces a current in its secondary which is proportional to the current in its primary.
Current transformers, along with volt ...
s. In substations the protective relay scheme can be complex, protecting equipment and buses from various types of overload or ground/earth fault.
High-voltage breakers are broadly classified by the medium used to extinguish the arc:
* Bulk oil
* Minimum oil
* Air blast
* Vacuum
A vacuum is a space devoid of matter. The word is derived from the Latin adjective ''vacuus'' for "vacant" or " void". An approximation to such vacuum is a region with a gaseous pressure much less than atmospheric pressure. Physicists often di ...
* SF6
* CO2
Due to environmental and cost concerns over insulating oil spills, most new breakers use SF6 gas to quench the arc.
Circuit breakers can be classified as ''live tank'', where the enclosure that contains the breaking mechanism is at line potential, or ''dead tank'' with the enclosure at earth potential. High-voltage AC circuit breakers are routinely available with ratings up to 765 kV. 1,200kV breakers were launched by Siemens in November 2011, followed by ABB in April the following year.
High-voltage circuit breakers used on transmission systems may be arranged to allow a single pole of a three-phase line to trip, instead of tripping all three poles; for some classes of faults this improves the system stability and availability.
High-voltage direct current
A high-voltage direct current (HVDC) electric power transmission system (also called a power superhighway or an electrical superhighway) uses direct current (DC) for electric power transmission, in contrast with the more common alternating curre ...
circuit breakers are still a field of research as of 2015. Such breakers would be useful to interconnect HVDC transmission systems.
Sulfur hexafluoride (SF6) high-voltage
A sulfur hexafluoride circuit breaker uses contacts surrounded by sulfur hexafluoride gas to quench the arc. They are most often used for transmission-level voltages and may be incorporated into compact gas-insulated switchgear. In cold climates, supplemental heating or different gas mixtures are used for high voltage circuit breakers, due to liquefaction of the SF6 gas. In some northern power grids, gaz mixtures of N2 and SF6, or CF4 and SF6 are installed in puffer-type HVCB to quench the arc without any liquefaction of the gas. https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/abstract/document/4080767. The minimum temperature ratings of these models are as low as -50 °C for some northern substations.Disconnecting circuit breaker (DCB)
The disconnecting circuit breaker (DCB) was introduced in 2000 and is a high-voltage circuit breaker modeled after the SF6-breaker. It presents a technical solution where the disconnecting function is integrated in the breaking chamber, eliminating the need for separate disconnectors. This increases theavailability
In reliability engineering, the term availability has the following meanings:
* The degree to which a system, subsystem or equipment is in a specified operable and committable state at the start of a mission, when the mission is called for at ...
, since open-air disconnecting switch main contacts need maintenance every 2–6 years, while modern circuit breakers have maintenance intervals of 15 years. Implementing a DCB solution also reduces the space requirements within the substation, and increases the reliability
Reliability, reliable, or unreliable may refer to:
Science, technology, and mathematics Computing
* Data reliability (disambiguation), a property of some disk arrays in computer storage
* High availability
* Reliability (computer networking), ...
, due to the lack of separate disconnectors.
In order to further reduce the required space of substation, as well as simplifying the design and engineering of the substation, a fiber optic current sensor
A fiber-optic current sensor (FOCS) is a current sensor for measuring direct current. By using a single-ended optical fiber around the current conductor that utilizes the magneto-optic effect (Faraday effect), FOCS measures uni- or bidirectional ...
(FOCS) can be integrated with the DCB. A 420 kV DCB with integrated FOCS can reduce a substation's footprint
Footprints are the impressions or images left behind by a person walking or running. Hoofprints and pawprints are those left by animals with hooves or paws rather than feet, while "shoeprints" is the specific term for prints made by shoes. T ...
with over 50% compared to a conventional solution of live tank breakers with disconnector
In electrical engineering, a disconnector, disconnect switch or isolator switch is used to ensure that an electrical circuit is completely de-energized for service or maintenance. They are often found in electrical distribution and industrial a ...
s and current transformer
A current transformer (CT) is a type of transformer that is used to reduce or multiply an alternating current (AC). It produces a current in its secondary which is proportional to the current in its primary.
Current transformers, along with volt ...
s, due to reduced material and no additional insulation medium.
Carbon dioxide (CO2) high-voltage
In 2012, ABB presented a 75kV high-voltage breaker that uses carbon dioxide as the medium to extinguish the arc. The carbon dioxide breaker works on the same principles as an SF6 breaker and can also be produced as a disconnecting circuit breaker. By switching from SF6 to CO2, it is possible to reduce the CO2 emissions by 10 tons during the product's life cycle."Smart" circuit breakers
Several firms have looked at adding monitoring for appliances via electronics or using a digital circuit breaker to monitor the breakers remotely. Utility companies in the United States have been reviewing use of the technology to turn on and off appliances, as well as potentially turning off charging of electric cars during periods of high electrical grid load. These devices under research and testing would have wireless capability to monitor the electrical usage in a house via a smartphone app or other means.Other breakers
 The following types are described in separate articles.
* Breakers for protections against earth faults too small to trip an over-current device:
**
The following types are described in separate articles.
* Breakers for protections against earth faults too small to trip an over-current device:
** Residual-current device
A residual-current device (RCD), residual-current circuit breaker (RCCB) or ground fault circuit interrupter (GFCI) is an electrical safety device that quickly breaks an electrical circuit with leakage current to ground. It is to protect equip ...
(RCD), or residual-current circuit breaker (RCCB) — detects current imbalance, but does not provide over-current protection. In the United States and Canada, these are called ground fault circuit interrupters (GFCI).
** Residual-current circuit breaker with overcurrent protection (RCBO
A residual-current device (RCD), residual-current circuit breaker (RCCB) or ground fault circuit interrupter (GFCI) is an electrical safety device that quickly breaks an electrical circuit with leakage current to ground. It is to protect equip ...
) — combines the functions of a RCD and a MCB in one package. In the United States and Canada, these are called GFCI breakers.
** Earth leakage circuit breaker
An earth-leakage circuit breaker (ELCB) is a safety device used in electrical installations with high Earth impedance to prevent shock. It detects small stray voltages on the metal enclosures of electrical equipment, and interrupts the circui ...
(ELCB) — This detects current in the earth wire directly rather than detecting imbalance. They are no longer seen in new installations as they cannot detect any dangerous condition where the current is returning to earth by another route - such as via a person on the ground or via plumbing. (also called VOELCB in the UK).
* Recloser
In electric power distribution, automatic circuit reclosers (ACRs) are a class of switchgear designed for use on overhead electricity distribution networks to detect and interrupt transient faults. Also known as reclosers or autoreclosers, ACRs a ...
— A type of circuit breaker that closes automatically after a delay. These are used on overhead electric power distribution
Electric power distribution is the final stage in the delivery of electric power; it carries electricity from the transmission system to individual consumers. Distribution substations connect to the transmission system and lower the transmissi ...
systems, to prevent short duration faults from causing sustained outages.
* Polyswitch (polyfuse) — A small device commonly described as an automatically resetting fuse rather than a circuit breaker.
See also
*Arc-fault circuit interrupter
An arc-fault circuit interrupter (AFCI) or arc-fault detection device (AFDD) is a circuit breaker that breaks the circuit when it detects the electric arcs that are a signature of loose connections in home wiring. Loose connections, which can de ...
* Breaking capacity
Breaking capacity or interrupting rating is the current that a fuse, circuit breaker, or other electrical apparatus is able to interrupt without being destroyed or causing an electric arc with unacceptable duration. The prospective short-circuit cu ...
* Circuit breaker analyzer
* Circuit total limitation
Circuit total limitation (CTL) is one of the present-day standards for electrical panels sold in the United States according to the National Electrical Code. This standard requires an electrical panel to provide a physical mechanism to prevent i ...
(CTL)
* Distribution board
A distribution board (also known as panelboard, breaker panel, electric panel, DB board or DB box) is a component of an electricity supply system that divides an electrical power feed into subsidiary circuits while providing a protective fus ...
(Circuit breaker panel)
* Earthing system
An earthing system (UK and IEC) or grounding system (US) connects specific parts of an electric power system with the ground, typically the Earth's conductive surface, for safety and functional purposes. The choice of earthing system can affec ...
* Ground Fault Circuit Interrupter (GFCI)
* Hybrid switchgear module A hybrid switchgear is one that combines the components of traditional air-insulated switchgear (AIS) and SF6 gas-insulated switchgear (GIS) technologies. It is characterized by a compact and modular design, which encompasses several different fun ...
* Insulation monitoring device An insulation monitoring device monitors the ungrounded system between an active phase conductor and earth. It is intended to give an alert (light and sound) or disconnect the power supply when the resistance
Resistance may refer to:
Arts, ent ...
* Motor control center (MCC)
* Network protector
A network protector is a type of electric protective device used in electricity distribution systems. The network protector automatically disconnect its associated distribution transformer from the secondary network when the power starts flowing ...
* Power distribution center (PDC)
* Power system protection
Power system protection is a branch of electrical power engineering that deals with the protection of electrical power systems from faults through the disconnection of faulted parts from the rest of the electrical network. The objective of a pr ...
* Remote racking system
A remote racking system or remote racking device is a system that allows an operator racking in and out a withdrawable circuit breaker from a remote location. It offers a safe alternative to manually racking circuit breakers, which reduces the requ ...
* Ring Main Unit
* Selectivity (circuit breakers) Selectivity, also known as circuit breaker discrimination, is the coordination of overcurrent protection devices so that a fault in the installation is cleared by the protection device located immediately upstream of the fault. The purpose of sele ...
* Stab-Lok
Stab-Lok is a brand name of electrical circuit breakers that were manufactured primarily by Federal Pacific Electric between 1950-1980.
In June 1980, Reliance Electric, which had purchased FPE, reported to the United States Consumer Product Safet ...
—a popular type of circuit breaker manufactured from 1950 to 1990, now widely deemed unsafe
* Sulfur hexafluoride circuit breaker
* Zener diode
A Zener diode is a special type of diode designed to reliably allow current to flow "backwards" (inverted polarity) when a certain set reverse voltage, known as the ''Zener voltage'', is reached.
Zener diodes are manufactured with a great var ...
—a diode that allows current to flow in reverse direction (to break at certain level of voltage, an opposite effect)
Circuit Breaker
References
Sources
* BS EN 60898-1. Electrical accessories — Circuit breakers for over-current protection for household and similar installations.British Standards Institution
The British Standards Institution (BSI) is the national standards body of the United Kingdom. BSI produces technical standards on a wide range of products and services and also supplies certification and standards-related services to busines ...
, 2003.
{{DEFAULTSORT:Circuit Breaker
Electric power systems components
Electrical wiring
Over-current protection devices
20th-century inventions
fi:Sulake#Palautettavia sulakkeita