Cima Dome on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Cima volcanic field is a
File:Mojave cinder cones 2.jpg,
File:Mojave cinder cones 3.jpg,
 The cones have given rise to about 60
The cones have given rise to about 60
volcanic field
A volcanic field is an area of Earth's crust that is prone to localized volcanic activity. The type and number of volcanoes required to be called a "field" is not well-defined. Volcanic fields usually consist of clusters of up to 100 volcanoes ...
in San Bernardino County
San Bernardino County (), officially the County of San Bernardino, is a county located in the southern portion of the U.S. state of California, and is located within the Inland Empire area. As of the 2020 U.S. Census, the population was 2,181, ...
, California
California is a U.S. state, state in the Western United States, located along the West Coast of the United States, Pacific Coast. With nearly 39.2million residents across a total area of approximately , it is the List of states and territori ...
, close to the border with Nevada
Nevada ( ; ) is a U.S. state, state in the Western United States, Western region of the United States. It is bordered by Oregon to the northwest, Idaho to the northeast, California to the west, Arizona to the southeast, and Utah to the east. N ...
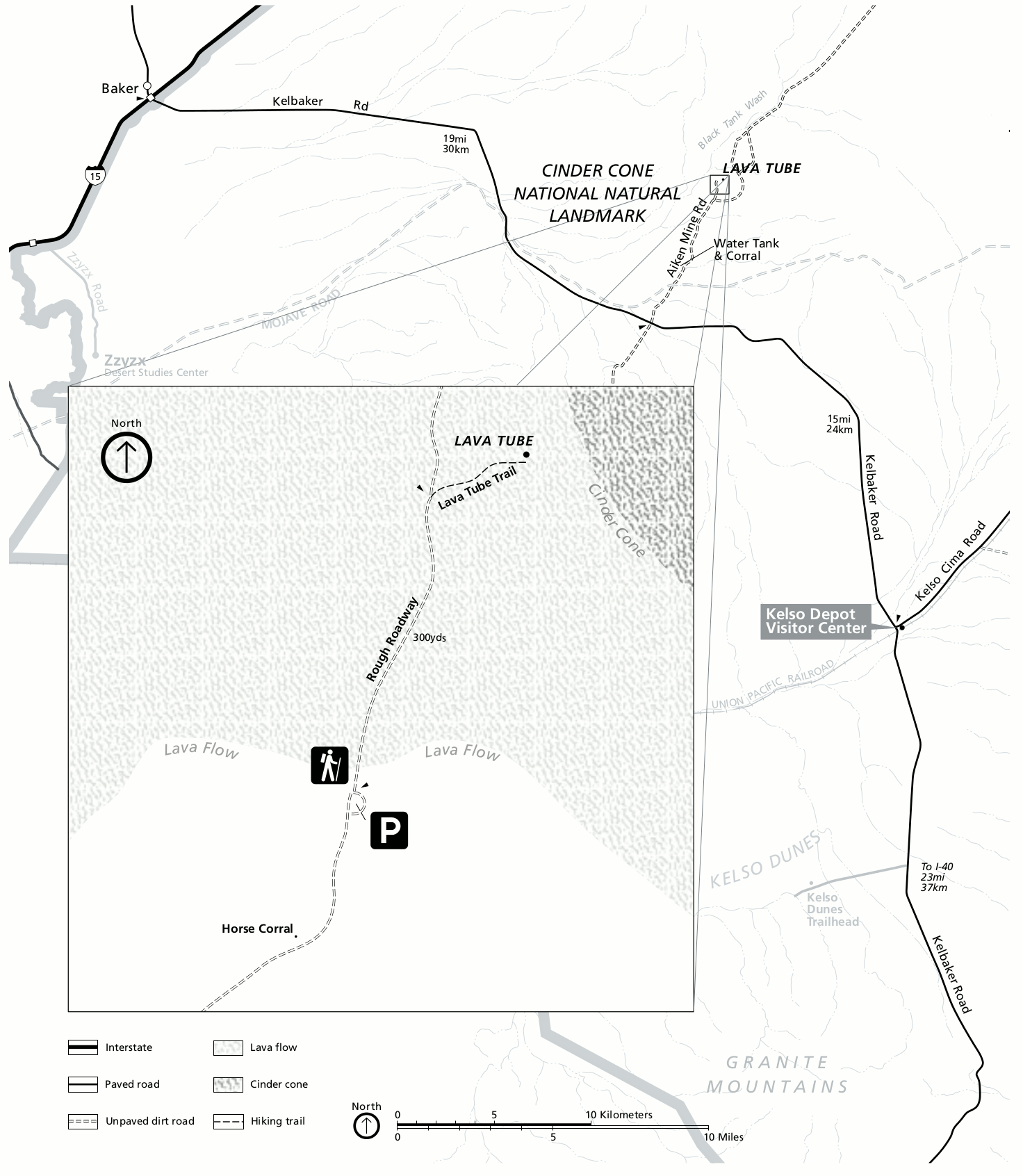
. The volcanic field covers a surface area of within the Mojave National Preserve
Mojave National Preserve is a United States National Preserve located in the Mojave Desert of San Bernardino County, California, USA, between Interstate 15 in California, Interstate 15 and Interstate 40. The preserve was established October 31 ...
west of the Cima Dome and consists of about 40 volcanic cone
Volcanic cones are among the simplest volcanic landforms. They are built by ejecta from a volcanic vent, piling up around the vent in the shape of a cone with a central crater. Volcanic cones are of different types, depending upon the nature and ...
s with about 60 lava
Lava is molten or partially molten rock (magma) that has been expelled from the interior of a terrestrial planet (such as Earth) or a moon onto its surface. Lava may be erupted at a volcano or through a fracture in the crust, on land or un ...
flows. The volcanic cones range from simple cones over multi-cratered mountains to eroded hills, and lava flows are up to long. At least one lava tube
A lava tube, or pyroduct, is a natural conduit formed by flowing lava from a volcanic vent that moves beneath the hardened surface of a lava flow. If lava in the tube empties, it will leave a cave.
Formation
A lava tube is a type of lava ca ...
exists in the field and can be visited.
Volcanic activity in the field commenced in the Late Miocene
The Late Miocene (also known as Upper Miocene) is a sub-epoch of the Miocene epoch (geology), Epoch made up of two faunal stage, stages. The Tortonian and Messinian stages comprise the Late Miocene sub-epoch, which lasted from 11.63 Ma (million ye ...
and after a pause between 3 and 1 million years ago continued into the latest Pleistocene
The Pleistocene ( , often referred to as the ''Ice age'') is the geological Epoch (geology), epoch that lasted from about 2,580,000 to 11,700 years ago, spanning the Earth's most recent period of repeated glaciations. Before a change was fina ...
. The youngest cone is known as the Black Tank cone and formed about 15,000 years before present, although it is possible that it was formed through two separate eruption events; formerly it was considered to be of historical
History (derived ) is the systematic study and the documentation of the human activity. The time period of event before the invention of writing systems is considered prehistory. "History" is an umbrella term comprising past events as well ...
age.
Geography and geology
The Cima volcanic field lies in the easternMojave Desert
The Mojave Desert ( ; mov, Hayikwiir Mat'aar; es, Desierto de Mojave) is a desert in the rain shadow of the Sierra Nevada mountains in the Southwestern United States. It is named for the indigenous Mojave people. It is located primarily in ...
of California
California is a U.S. state, state in the Western United States, located along the West Coast of the United States, Pacific Coast. With nearly 39.2million residents across a total area of approximately , it is the List of states and territori ...
, between the Shadow Valley in the northeast, the Cima Dome in the east and the Soda Lake Valley in the southwest. Southwest of the field is Kelbaker Road
Kelbaker Road is a Road surface, paved road in San Bernardino County, California, that serves as the primary and busiest route through the Mojave National Preserve. It also connects the communities of Kelso, California, Kelso and Baker, Californi ...
which crosses some lava flows, and dirt road
A dirt road or track is a type of unpaved road not paved with asphalt, concrete, brick, or stone; made from the native material of the land surface through which it passes, known to highway engineers as subgrade material. Dirt roads are suitable ...
s such as the Indian Springs Trail and the Aiken Mine Road crisscross between the volcanoes.
Interstate 15
Interstate 15 (I-15) is a major Interstate Highway System, Interstate Highway in the western United States, running through Southern California and the Intermountain West. I-15 begins near the Mexico–United States border, Mexican border i ...
passes north of the field and just south of older volcanic units, while California State Route 127
State Route 127 (SR 127) is a state highway in the U.S. state of California that connects Interstate 15 in Baker to Nevada State Route 373 at the Nevada state line, passing near the eastern boundary of Death Valley National Park. The entire lengt ...
runs west and southwest of the field, The city of Las Vegas
Las Vegas (; Spanish for "The Meadows"), often known simply as Vegas, is the 25th-most populous city in the United States, the most populous city in the state of Nevada, and the county seat of Clark County. The city anchors the Las Vegas ...
is northeast of the area. The Cima volcanoes are part of the Mojave National Preserve
Mojave National Preserve is a United States National Preserve located in the Mojave Desert of San Bernardino County, California, USA, between Interstate 15 in California, Interstate 15 and Interstate 40. The preserve was established October 31 ...
and since 1973 they make up the Cinder Cones National Natural Landmark
Cinder is an alternate term for scoria.
Cinder or Cinders may also refer to:
In computing
*Cinder (programming library), a C++ programming library for visualization
*Cinder, OpenStack's block storage component
*Cyber Insider Threat, CINDER, a d ...
.
During the Holocene and until recent times, humans engraved petroglyph
A petroglyph is an image created by removing part of a rock surface by incising, picking, carving, or abrading, as a form of rock art. Outside North America, scholars often use terms such as "carving", "engraving", or other descriptions ...
s into the lava flows. One cinder cone was quarried
A quarry is a type of open-pit mining, open-pit mine in which dimension stone, rock (geology), rock, construction aggregate, riprap, sand, gravel, or slate is excavated from the ground. The operation of quarries is regulated in some juri ...
to obtain materials for road construction. The volcanic field has been the subject of soil science
Soil science is the study of soil as a natural resource on the surface of the Earth including soil formation, classification and mapping; physical, chemical, biological, and fertility properties of soils; and these properties in relation to th ...
s and landscape development research.
Regional
Volcanism is widespread in the western United States and occurs in various forms at various places. Among the better known are theCascade
Cascade, Cascades or Cascading may refer to:
Science and technology Science
*Cascade waterfalls, or series of waterfalls
* Cascade, the CRISPR-associated complex for antiviral defense (a protein complex)
* Cascade (grape), a type of fruit
* Bioc ...
volcanoes created by subduction
Subduction is a geological process in which the oceanic lithosphere is recycled into the Earth's mantle at convergent boundaries. Where the oceanic lithosphere of a tectonic plate converges with the less dense lithosphere of a second plate, the ...
off the western coast of North America, which include the caldera
A caldera ( ) is a large cauldron-like hollow that forms shortly after the emptying of a magma chamber in a volcano eruption. When large volumes of magma are erupted over a short time, structural support for the rock above the magma chamber is ...
of Mount Mazama
Mount Mazama (''Giiwas'' in the Native American language Klamath language, Klamath) is a complex volcano in the state of Oregon, United States, in a segment of the Cascade Volcanoes, Cascade Volcanic Arc and Cascade Range. Most of the mountai ...
(created by a large eruption in the early Holocene
The Holocene ( ) is the current geological epoch. It began approximately 11,650 cal years Before Present (), after the Last Glacial Period, which concluded with the Holocene glacial retreat. The Holocene and the preceding Pleistocene togethe ...
) as well as stratovolcano
A stratovolcano, also known as a composite volcano, is a conical volcano built up by many layers (strata) of hardened lava and tephra. Unlike shield volcanoes, stratovolcanoes are characterized by a steep profile with a summit crater and per ...
es such as Mount St. Helens
Mount St. Helens (known as Lawetlat'la to the indigenous Cowlitz people, and Loowit or Louwala-Clough to the Klickitat) is an active stratovolcano located in Skamania County, Washington, in the Pacific Northwest region of the United St ...
and mafic
A mafic mineral or rock is a silicate mineral or igneous rock rich in magnesium and iron. Most mafic minerals are dark in color, and common rock-forming mafic minerals include olivine, pyroxene, amphibole, and biotite. Common mafic rocks include ...
volcanic fields. Other volcanic centres in the United States are those associated with Yellowstone Caldera
The Yellowstone Caldera, sometimes referred to as the Yellowstone Supervolcano, is a volcanic caldera and supervolcano in Yellowstone National Park in the Western United States. The caldera and most of the park are located in the northwest corn ...
and Snake River Plain
image:Snake River view near Twin Falls, Idaho.jpg, The Snake River cutting through the plain leaves many canyons and Canyon#List of gorges, gorges, such as this one near Twin Falls, Idaho
The Snake River Plain is a geology, geologic feature ...
, those along the margins of the Colorado Plateau
The Colorado Plateau, also known as the Colorado Plateau Province, is a physiographic and desert region of the Intermontane Plateaus, roughly centered on the Four Corners region of the southwestern United States. This province covers an area of ...
, volcanoes linked to the Rio Grande Rift
The Rio Grande rift is a north-trending continental rift zone. It separates the Colorado Plateau in the west from the interior of the North American craton on the east. The rift extends from central Colorado in the north to the state of Chihua ...
and Jemez lineament
The Jemez Lineament is a chain of late Cenozoic volcanic fields, long, reaching from the Springerville and White Mountains volcanic fields in East-Central Arizona to the Raton-Clayton volcanic field in Northeastern New Mexico.
The lineament ...
, and finally volcanoes in the western Basin and Range Province
The Basin and Range Province is a vast physiographic region covering much of the inland Western United States and northwestern Mexico. It is defined by unique basin and range topography, characterized by abrupt changes in elevation, alternating ...
such as the Cima volcanic field.
Generally, volcanic activity was widespread in the dry regions of the western United States during the Tertiary
Tertiary ( ) is a widely used but obsolete term for the geologic period from 66 million to 2.6 million years ago.
The period began with the demise of the non-avian dinosaurs in the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event, at the start ...
and Quaternary
The Quaternary ( ) is the current and most recent of the three periods of the Cenozoic Era in the geologic time scale of the International Commission on Stratigraphy (ICS). It follows the Neogene Period and spans from 2.58 million years ...
, forming several volcanic fields. An earlier phase of felsic
In geology, felsic is a modifier describing igneous rocks that are relatively rich in elements that form feldspar and quartz.Marshak, Stephen, 2009, ''Essentials of Geology,'' W. W. Norton & Company, 3rd ed. It is contrasted with mafic rocks, whi ...
volcanism during the Tertiary was followed during the Quaternary by more basaltic
Basalt (; ) is an aphanitic (fine-grained) extrusive igneous rock formed from the rapid cooling of low-viscosity lava rich in magnesium and iron (mafic lava) exposed at or very near the surface of a rocky planet or moon. More than 90% of a ...
volcanism, often in the form of short-lived volcanic vents. Examples of this kind of volcanism are the Cima volcanic field, the San Francisco volcanic field
The San Francisco volcanic field is an area of volcanoes in northern Arizona, north of Flagstaff, US. The field covers 1,800 square miles (4,700 km²) of the southern boundary of the Colorado Plateau. The field contains 600 volcanoes rang ...
(Arizona
Arizona ( ; nv, Hoozdo Hahoodzo ; ood, Alĭ ṣonak ) is a state in the Southwestern United States. It is the 6th largest and the 14th most populous of the 50 states. Its capital and largest city is Phoenix. Arizona is part of the Fou ...
), the Southwest Nevada volcanic field
The points of the compass are a set of horizontal, Radius, radially arrayed compass directions (or Azimuth#In navigation, azimuths) used in navigation and cartography. A compass rose is primarily composed of four cardinal directions—north, east ...
(Nevada) and the Zuni-Bandera volcanic field
Zuni-Bandera volcanic field (also known as Bandera lava field, Grants Badlands, Malpais and Malpais volcanic field) is a volcanic field located in the state of New Mexico, United States.
The volcanic field has been considered for Geothermal powe ...
(New Mexico
)
, population_demonym = New Mexican ( es, Neomexicano, Neomejicano, Nuevo Mexicano)
, seat = Santa Fe
, LargestCity = Albuquerque
, LargestMetro = Tiguex
, OfficialLang = None
, Languages = English, Spanish ( New Mexican), Navajo, Ker ...
).
The Cima volcanic field is part of the Mojave Desert
The Mojave Desert ( ; mov, Hayikwiir Mat'aar; es, Desierto de Mojave) is a desert in the rain shadow of the Sierra Nevada mountains in the Southwestern United States. It is named for the indigenous Mojave people. It is located primarily in ...
, which in turn belongs to the Basin and Range Province
The Basin and Range Province is a vast physiographic region covering much of the inland Western United States and northwestern Mexico. It is defined by unique basin and range topography, characterized by abrupt changes in elevation, alternating ...
and features both mountains exceeding height which trend in southeast–northwest direction, with broad valleys between the mountains.
Local
There are about 40 cones in the Cima volcanic field. The cones are as much as wide and high, and are concentrated between elevations of on a south-southwest tilting slope. Some cones are well preserved with intactcrater
Crater may refer to:
Landforms
*Impact crater, a depression caused by two celestial bodies impacting each other, such as a meteorite hitting a planet
*Explosion crater, a hole formed in the ground produced by an explosion near or below the surfac ...
s, while others have been reduced to hills by erosion. Some cones have more than one crater. North of the main field lie two outcrops of older volcanic rocks (Miocene to Pliocene); other than this separate older outcrop volcanic activity appears to have occurred without any preferential alignment. Several washes such as Willow Wash, Black Tank Wash and Indian Creek cross through the field and have eroded lava flows.
The youngest cone () in the southwestern part of the field is called Black Tank cone. The Black Tank cone is the source of a long lava flow, which at first forms a levee-bound channel and then narrows out into a lobate shape. It also shows traces of a lava tube
A lava tube, or pyroduct, is a natural conduit formed by flowing lava from a volcanic vent that moves beneath the hardened surface of a lava flow. If lava in the tube empties, it will leave a cave.
Formation
A lava tube is a type of lava ca ...
and has a volume of . This flow may have been preceded by a previous lava flow which was later buried by the main flow. An older vent lies just south-southwest of the Black Tank Cone.
The field presents black and red volcanic rocks in the form of cinders, exposed feeder dikes
Dyke (UK) or dike (US) may refer to:
General uses
* Dyke (slang), a slang word meaning "lesbian"
* Dike (geology), a subvertical sheet-like intrusion of magma or sediment
* Dike (mythology), ''Dikē'', the Greek goddess of moral justice
* Dikes, ...
and lava bomb
A volcanic bomb or lava bomb is a mass of partially molten rock (tephra) larger than 64 mm (2.5 inches) in diameter, formed when a volcano ejects viscous fragments of lava during an eruption. Because volcanic bombs cool after they l ...
s, as well as agglutinates which are exposed in gullies and eroded vents. Bombs and cinders cover the less eroded cones, which are also sometimes surrounded by base surge
A pyroclastic surge is a fluidised mass of turbulent gas and rock fragments that is ejected during some volcanic eruptions. It is similar to a pyroclastic flow but it has a lower density or contains a much higher ratio of gas to rock, which makes i ...
deposits. At some vents, tuff ring
Phreatomagmatic eruptions are volcanic eruptions resulting from interaction between magma and water. They differ from exclusively magmatic eruptions and phreatic eruptions. Unlike phreatic eruptions, the products of phreatomagmatic eruptions conta ...
s formed through phreatomagmatic
Phreatomagmatic eruptions are volcanic eruptions resulting from interaction between magma and water. They differ from exclusively magmatic eruptions and phreatic eruptions. Unlike phreatic eruptions, the products of phreatomagmatic eruptions cont ...
activity. Erosion
Erosion is the action of surface processes (such as water flow or wind) that removes soil, rock, or dissolved material from one location on the Earth's crust, and then transports it to another location where it is deposited. Erosion is distin ...
has dug gullies
A gully is a landform created by running water, mass movement, or commonly a combination of both eroding sharply into soil or other relatively erodible material, typically on a hillside or in river floodplains or terraces. Gullies resemble lar ...
and larger valleys in the older cones, including one deep gorge
A canyon (from ; archaic British English spelling: ''cañon''), or gorge, is a deep cleft between escarpments or cliffs resulting from weathering and the erosion, erosive activity of a river over geologic time scales. Rivers have a natural tenden ...
.
Volcanic material covers a surface area of about within an area of . The volcanic field was emplaced on a basement of Tertiary age, which comprises both crystalline bedrock and thick gravel deposits. Other rock formations in the area are of Proterozoic
The Proterozoic () is a geological eon spanning the time interval from 2500 to 538.8million years ago. It is the most recent part of the Precambrian "supereon". It is also the longest eon of the Earth's geologic time scale, and it is subdivided ...
Paleozoic
The Paleozoic (or Palaeozoic) Era is the earliest of three geologic eras of the Phanerozoic Eon.
The name ''Paleozoic'' ( ;) was coined by the British geologist Adam Sedgwick in 1838
by combining the Greek words ''palaiós'' (, "old") and ' ...
to Mesozoic
The Mesozoic Era ( ), also called the Age of Reptiles, the Age of Conifers, and colloquially as the Age of the Dinosaurs is the second-to-last era of Earth's geological history, lasting from about , comprising the Triassic, Jurassic and Cretaceo ...
(Teutonia batholith
A batholith () is a large mass of intrusive igneous rock (also called plutonic rock), larger than in area, that forms from cooled magma deep in Earth's crust. Batholiths are almost always made mostly of felsic or intermediate rock types, such ...
) age, and the region is considered to be part of the Ivanpah uplift.
Lava flows
 The cones have given rise to about 60
The cones have given rise to about 60 lava flow
Lava is molten or partially molten rock (magma) that has been expelled from the interior of a terrestrial planet (such as Earth) or a moon onto its surface. Lava may be erupted at a volcano or through a fracture in the crust, on land or und ...
s. Lava flows reach lengths of , thicknesses of and have surface features similar to pahoehoe
Lava is molten or partially molten rock (magma) that has been expelled from the interior of a terrestrial planet (such as Earth) or a moon onto its surface. Lava may be erupted at a volcano or through a fracture in the crust, on land or und ...
or aa lava
Lava is molten or partially molten rock (magma) that has been expelled from the interior of a terrestrial planet (such as Earth) or a moon onto its surface. Lava may be erupted at a volcano or through a fracture in the crust, on land or und ...
depending on how steep the slopes they flowed down were. The lava flows display structures like levees, finger-like and lobe-like edges at the lava flow margins, spines and spires and material from the cones that was rafted away by the lavas. One can distinguish between long, gently sloping flows which dominate the field, and shorter, steeper rougher flows covered by blocks with sizes of up to . One major lava tube
A lava tube, or pyroduct, is a natural conduit formed by flowing lava from a volcanic vent that moves beneath the hardened surface of a lava flow. If lava in the tube empties, it will leave a cave.
Formation
A lava tube is a type of lava ca ...
lies in the Cima field and is accessible through a skylight
A skylight (sometimes called a rooflight) is a light-permitting structure or window, usually made of transparent or translucent glass, that forms all or part of the roof space of a building for daylighting and ventilation purposes.
History
Open ...
; it is long and wide. In some places flows surrounded basement outcrops, forming kipukas. In accordance to the slope of the area, most lavas flowed westward.
Younger flows often show crisp lava flow features while older flows are almost always mantled with younger material and have lost their original surface features. The oldest flows have flat or gentle surfaces and their source vents are heavily degraded. Lava flows are also in part covered by wind-transported or erosional material and desert varnish
Desert varnish or rock varnish is an orange-yellow to black coating found on exposed rock surfaces in arid environments. Desert varnish is approximately one micrometer thick and exhibits nanometer-scale layering. Rock rust and desert patina are ot ...
.
Composition
The field has eruptedalkali basalt
Alkali basalt or alkali olivine basalt is a dark-colored, porphyritic volcanic rock usually found in oceanic and continental areas associated with volcanic activity, such as oceanic islands, continental rifts and volcanic fields. Alkali basalt ...
, basanite
Basanite () is an igneous, volcanic (extrusive) rock with aphanitic to porphyritic texture. It is composed mostly of feldspathoids, pyroxenes, olivine, and plagioclase and forms from magma low in silica and enriched in alkali metal oxides that s ...
and hawaiite
Hawaiite is an olivine basalt with a composition between alkali basalt and mugearite. It was first used as a name for some lavas found on the island of Hawaii.
It occurs during the later stages of volcanic activity on oceanic islands such as Haw ...
. Phenocryst
300px, feldspathic phenocrysts. This granite, from the Switzerland">Swiss side of the Mont Blanc massif, has large white plagioclase phenocrysts, triclinic minerals that give trapezoid shapes when cut through). 1 euro coins, 1 euro coin (diameter ...
s include clinopyroxene
The pyroxenes (commonly abbreviated to ''Px'') are a group of important rock-forming inosilicate minerals found in many igneous and metamorphic rocks. Pyroxenes have the general formula , where X represents calcium (Ca), sodium (Na), iron (Fe II) ...
, olivine
The mineral olivine () is a magnesium iron silicate with the chemical formula . It is a type of nesosilicate or orthosilicate. The primary component of the Earth's upper mantle, it is a common mineral in Earth's subsurface, but weathers quickl ...
and plagioclase
Plagioclase is a series of tectosilicate (framework silicate) minerals within the feldspar group. Rather than referring to a particular mineral with a specific chemical composition, plagioclase is a continuous solid solution series, more prope ...
. There are also xenolith
A xenolith ("foreign rock") is a rock fragment (country rock) that becomes enveloped in a larger rock during the latter's development and solidification. In geology, the term ''xenolith'' is almost exclusively used to describe inclusions in igne ...
s including dunite
Dunite (), also known as olivinite (not to be confused with the mineral olivenite), is an intrusive igneous rock of ultramafic composition and with phaneritic (coarse-grained) texture. The mineral assemblage is greater than 90% olivine, with mi ...
, gabbro
Gabbro () is a phaneritic (coarse-grained), mafic intrusive igneous rock formed from the slow cooling of magnesium-rich and iron-rich magma into a holocrystalline mass deep beneath the Earth's surface. Slow-cooling, coarse-grained gabbro is che ...
, granite
Granite () is a coarse-grained (phaneritic) intrusive igneous rock composed mostly of quartz, alkali feldspar, and plagioclase. It forms from magma with a high content of silica and alkali metal oxides that slowly cools and solidifies undergro ...
, and notably ultramafic
Ultramafic rocks (also referred to as ultrabasic rocks, although the terms are not wholly equivalent) are igneous and meta-igneous rocks with a very low silica content (less than 45%), generally >18% MgO, high FeO, low potassium, and are composed ...
to mafic xenoliths. The rock composition has not changed much during the history of the Cima volcanoes. Temperatures of have been estimated for the lava erupted by the Black Tank cone.
The magma
Magma () is the molten or semi-molten natural material from which all igneous rocks are formed. Magma is found beneath the surface of the Earth, and evidence of magmatism has also been discovered on other terrestrial planets and some natural sa ...
erupted in the field ultimately appears to originate from the lithospheric
A lithosphere () is the rigid, outermost rocky shell of a terrestrial planet or natural satellite. On Earth, it is composed of the crust and the portion of the upper mantle that behaves elastically on time scales of up to thousands of years o ...
or asthenospheric
The asthenosphere () is the mechanically weak and ductile region of the upper mantle of Earth. It lies below the lithosphere, at a depth between ~ below the surface, and extends as deep as . However, the lower boundary of the asthenosphere is not ...
mantle with little contribution of crustal components, unlike earlier felsic
In geology, felsic is a modifier describing igneous rocks that are relatively rich in elements that form feldspar and quartz.Marshak, Stephen, 2009, ''Essentials of Geology,'' W. W. Norton & Company, 3rd ed. It is contrasted with mafic rocks, whi ...
volcanism. Upwelling
Upwelling is an oceanographic phenomenon that involves wind-driven motion of dense, cooler, and usually nutrient-rich water from deep water towards the ocean surface. It replaces the warmer and usually nutrient-depleted surface water. The nutr ...
of asthenosphere material appears to be responsible for the volcanism at the end, possibly associated with the change in the tectonics of the region from subduction-dominated to tectonics of a transform boundary
A transform fault or transform boundary, is a fault along a plate boundary where the motion is predominantly horizontal. It ends abruptly where it connects to another plate boundary, either another transform, a spreading ridge, or a subductio ...
. Fractional crystallization Fractional crystallization may refer to:
* Fractional crystallization (chemistry), a process to separate different solutes from a solution
* Fractional crystallization (geology)
Fractional crystallization, or crystal fractionation, is one of the ...
, magma ponding in the crust, differences in the mantle sources and partial melting
Partial melting occurs when only a portion of a solid is melted. For mixed substances, such as a rock containing several different minerals or a mineral that displays solid solution, this melt can be different from the bulk composition of the solid ...
processes have been invoked to explain certain compositional differences in the erupted rocks.
Climate and vegetation
The climate of the area is warm and dry with average temperatures of and average precipitation amounting to . Most precipitation falls during winter, with only small amounts of rain falling during summer asmonsoon
A monsoon () is traditionally a seasonal reversing wind accompanied by corresponding changes in precipitation but is now used to describe seasonal changes in atmospheric circulation and precipitation associated with annual latitudinal oscil ...
al rainfall. Before the beginning of the Holocene, the climate was wetter and this facilitated the development of soils on lava flows. During the Holocene, playas became sources for wind-blown dust which accumulates on the lava.
Vegetation in the area is classified as scrub, with plants including brittle bush
''Encelia farinosa'' (commonly known as brittlebush, brittlebrush, or incienso), is a common desert shrub of the southwestern United States and northern Mexico. It has a variety of historical uses.
Description
Brittlebush grows up to tall, ...
, creosote bush
''Larrea tridentata'', called creosote bush and greasewood as a plant, chaparral as a medicinal herb, and ''gobernadora'' (Spanish language, Spanish for "governess") in Mexico, due to its ability to secure more water by inhibiting the growth of n ...
, Mormon tea
''Ephedra'' is a genus of gymnosperm shrubs. The various species of ''Ephedra'' are widespread in many arid regions of the world, ranging across southwestern North America, southern Europe, northern Africa, southwest and central Asia, northern ...
and white bursage
''Ambrosia dumosa'', the burro-weed or white bursage, a North American species of plants in the family Asteraceae. It is a common constituent of the creosote-bush scrub community throughout the Mojave desert of California, Nevada, and Utah and ...
. Joshua tree
''Yucca brevifolia'' is a plant species belonging to the genus ''Yucca''. It is tree-like in habit, which is reflected in its common names: Joshua tree, yucca palm, tree yucca, and palm tree yucca.
This monocotyledonous tree is native to the ar ...
s grow at higher elevations. Some of these species arrived during the Holocene
The Holocene ( ) is the current geological epoch. It began approximately 11,650 cal years Before Present (), after the Last Glacial Period, which concluded with the Holocene glacial retreat. The Holocene and the preceding Pleistocene togethe ...
, while others became established during the Pleistocene
The Pleistocene ( , often referred to as the ''Ice age'') is the geological Epoch (geology), epoch that lasted from about 2,580,000 to 11,700 years ago, spanning the Earth's most recent period of repeated glaciations. Before a change was fina ...
or appeared and disappeared repeatedly. Vegetation grows in clusters separated by soil covered by desert pavement
A desert pavement, also called reg (in the western Sahara), serir (eastern Sahara), gibber (in Australia), or saï (central Asia) is a desert surface covered with closely packed, interlocking angular or rounded rock fragments of pebble and cob ...
. The youngest cone is unvegetated and little vegetation has developed on other recent volcanic vents and lava flows.
Eruptive history
Early research postulated a Pleistocene age for the northern part of the field and a Holocene age for the southern; laterradiometric
Radiometry is a set of techniques for measuring electromagnetic radiation, including visible light. Radiometric techniques in optics characterize the distribution of the radiation's power in space, as opposed to photometric techniques, which cha ...
dates indicated Miocene ages for the northern parts of the field. More recent research showed Miocene ages for the northern volcanics and Pleistocene ages for the southern. An eruption rate of 8 events per 100,000 years and a magma output of has been estimated for the Cima field.
According to potassium-argon dating, volcanic activity started in the Miocene and continued to the end of the Pleistocene. Activity has been subdivided into five phases, the first between 7.6 and 6.5 million years ago, the second between 5.1 and 3.6 million years ago, the third between 1.1 and 0.6 million years ago, the fourth between 750,000 and 200,000 years ago and the fifth and last between 200,000 and 10,000 years ago. The radiometric ages have been corroborated by morphological and paleomagnetic
Paleomagnetism (or palaeomagnetismsee ), is the study of magnetic fields recorded in rocks, sediment, or archeological materials. Geophysicists who specialize in paleomagnetism are called ''paleomagnetists.''
Certain magnetic minerals in rock ...
information. Volcanic activity paused between 3 and 1 million years ago.
The oldest volcanic phase left a heavily dissected volcano in the southeastern part of the field, while the subsequent phase involved lava flows in the northern part of the field that take the form of eroded mesa
A mesa is an isolated, flat-topped elevation, ridge or hill, which is bounded from all sides by steep escarpments and stands distinctly above a surrounding plain. Mesas characteristically consist of flat-lying soft sedimentary rocks capped by ...
s. The final three phases formed lava flows and the volcanoes in the southern part of the field. Eruptions commenced as maar
A maar is a broad, low-relief volcanic crater caused by a phreatomagmatic eruption (an explosion which occurs when groundwater comes into contact with hot lava or magma). A maar characteristically fills with water to form a relatively shallow ...
-forming eruptions and continued with the growth of cinder cone
A cinder cone (or scoria cone) is a steep conical hill of loose pyroclastic fragments, such as volcanic clinkers, volcanic ash, or scoria that has been built around a volcanic vent. The pyroclastic fragments are formed by explosive eruptions o ...
s and lava flows. Unlike regular cinder cones which usually erupt only once, some cones at Cima experienced more than one eruption and were active over hundreds of thousands of years.
The Black Tank cone, the youngest cone in the field, has been dated to 15,000 ± 5,000 years before present by several methods. Some evidence suggested a historical age for one of the southern lava flows, with earlier radiocarbon dating
Radiocarbon dating (also referred to as carbon dating or carbon-14 dating) is a method for determining the age of an object containing organic material by using the properties of radiocarbon, a radioactive isotope of carbon.
The method was dev ...
yielding an age of 330–480 years. Several chronological data imply that the lava flow was formed during two separate eruptive episodes, one 20,000 years ago and the other 11,500 - 13,000 years ago. The lava flow was probably laid down in less than a week of time, and the growth of the cone was influenced by wind, which transported tephra
Tephra is fragmental material produced by a volcanic eruption regardless of composition, fragment size, or emplacement mechanism.
Volcanologists also refer to airborne fragments as pyroclasts. Once clasts have fallen to the ground, they rem ...
east-southeastwards where it fell out and formed a tephra blanket.
See also
* Aiken's Wash *List of volcanoes in the United States
A list of volcanoes in the United States and its territories.
Alaska
American Samoa
Arizona
California
Colorado
Hawaii
/[./[Https://www.sci.news/geology/puhahonu-shield-volcano-08435.html Puhahonu ...
Notes
References
Sources
* * * * * * * * * * * * * * * {{authority control Volcanoes of San Bernardino County, California Mojave National Preserve Natural history of the Mojave Desert Protected areas of the Mojave Desert Protected areas of San Bernardino County, California Volcanic fields of California Volcanoes of California