Chronic Myelogenous Leukaemia on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Chronic myelogenous leukemia (CML), also known as chronic myeloid leukemia, is a cancer of the
 CML was the first cancer to be linked to a clear genetic abnormality, the
CML was the first cancer to be linked to a clear genetic abnormality, the  The fused BCR-ABL protein interacts with the interleukin 3beta(c) receptor subunit. The BCR-ABL transcript is continuously active and does not require activation by other cellular messaging proteins. In turn, BCR-ABL activates a cascade of proteins that control the
The fused BCR-ABL protein interacts with the interleukin 3beta(c) receptor subunit. The BCR-ABL transcript is continuously active and does not require activation by other cellular messaging proteins. In turn, BCR-ABL activates a cascade of proteins that control the

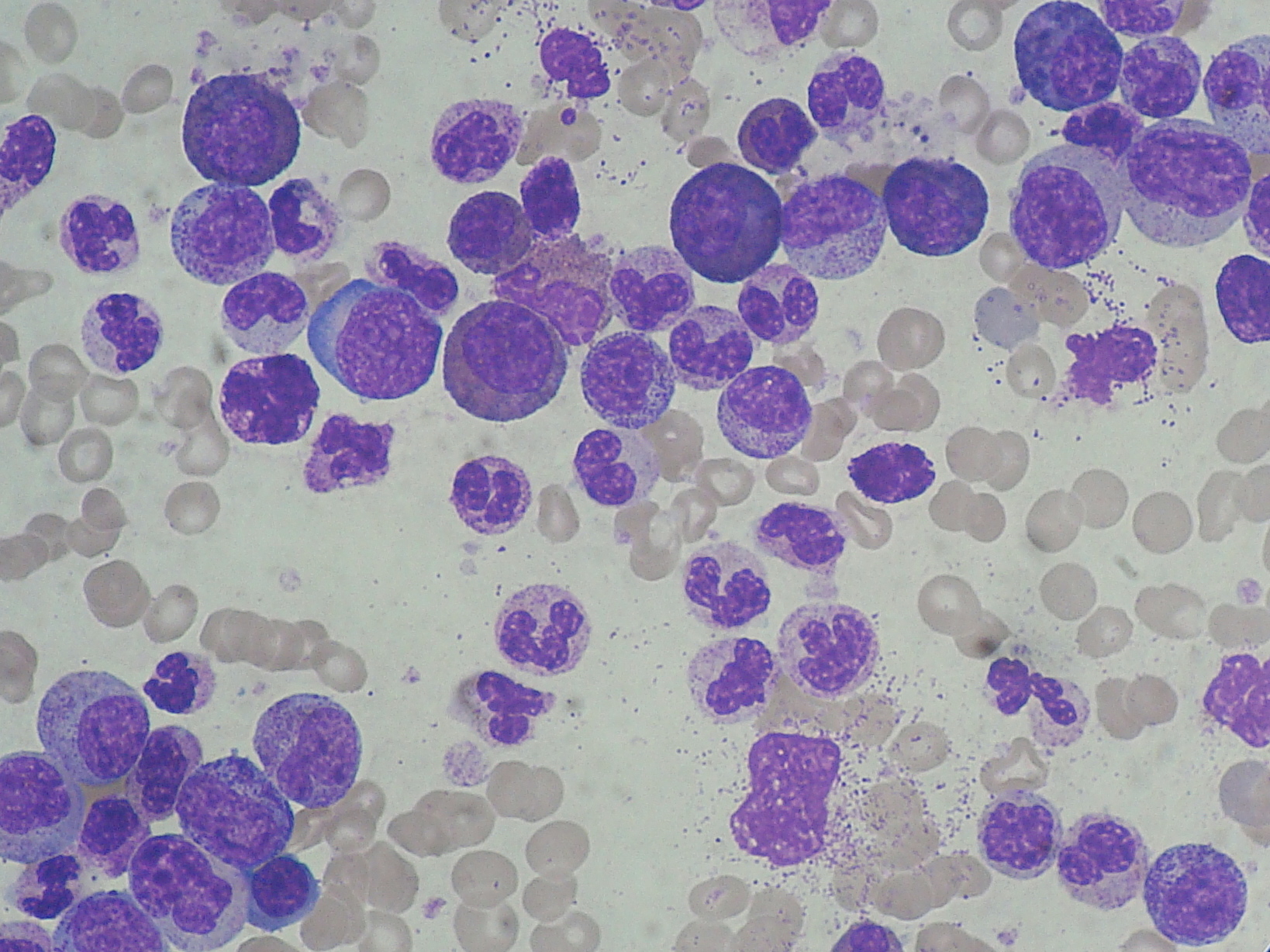
 CML is often suspected on the basis of a
CML is often suspected on the basis of a
Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia Treatment
at the US
Chronic Myelocytic Leukemia (CML)
at '' Merck Manual of Diagnosis and Therapy'' Professional Edition {{DEFAULTSORT:Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia Chronic myeloid leukemia
white blood cell
White blood cells, also called leukocytes or leucocytes, are the cell (biology), cells of the immune system that are involved in protecting the body against both infectious disease and foreign invaders. All white blood cells are produced and de ...
s. It is a form of leukemia
Leukemia ( also spelled leukaemia and pronounced ) is a group of blood cancers that usually begin in the bone marrow and result in high numbers of abnormal blood cells. These blood cells are not fully developed and are called ''blasts'' or ' ...
characterized by the increased and unregulated growth of myeloid
Myeloid tissue, in the bone marrow sense of the word '' myeloid'' ('' myelo-'' + ''-oid''), is tissue of bone marrow, of bone marrow cell lineage, or resembling bone marrow, and myelogenous tissue (''myelo-'' + '' -genous'') is any tissue of, ...
cells in the bone marrow
Bone marrow is a semi-solid tissue found within the spongy (also known as cancellous) portions of bones. In birds and mammals, bone marrow is the primary site of new blood cell production (or haematopoiesis). It is composed of hematopoietic ce ...
and the accumulation of these cells in the blood. CML is a clonal bone marrow stem cell
In multicellular organisms, stem cells are undifferentiated or partially differentiated cells that can differentiate into various types of cells and proliferate indefinitely to produce more of the same stem cell. They are the earliest type o ...
disorder in which a proliferation of mature granulocyte
Granulocytes are
cells in the innate immune system characterized by the presence of specific granules in their cytoplasm. Such granules distinguish them from the various agranulocytes. All myeloblastic granulocytes are polymorphonuclear. They ha ...
s (neutrophil
Neutrophils (also known as neutrocytes or heterophils) are the most abundant type of granulocytes and make up 40% to 70% of all white blood cells in humans. They form an essential part of the innate immune system, with their functions varying in ...
s, eosinophils and basophils) and their precursors is found. It is a type of myeloproliferative neoplasm associated with a characteristic chromosomal translocation
In genetics, chromosome translocation is a phenomenon that results in unusual rearrangement of chromosomes. This includes balanced and unbalanced translocation, with two main types: reciprocal-, and Robertsonian translocation. Reciprocal translo ...
called the Philadelphia chromosome
The Philadelphia chromosome or Philadelphia translocation (Ph) is a specific genetic abnormality in chromosome 22 of leukemia cancer cells (particularly chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) cells). This chromosome is defective and unusually short becaus ...
.
CML is largely treated with targeted drugs called tyrosine-kinase inhibitor
A tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI) is a pharmaceutical drug that inhibits tyrosine kinases. Tyrosine kinases are enzymes responsible for the activation of many proteins by signal transduction cascades. The proteins are activated by adding a phosph ...
s (TKIs) which have led to dramatically improved long-term survival rates since 2001. These drugs have revolutionized treatment of this disease and allow most patients to have a good quality of life when compared to the former chemotherapy drugs. In Western countries, CML accounts for 15–25% of all adult leukemias and 14% of leukemias overall (including the pediatric population, where CML is less common).
Signs and symptoms
The way CML presents depends on the stage of the disease at diagnosis as it has been known to skip stages in some cases. Most patients (~90%) are diagnosed during the chronic stage which is most often asymptomatic. In these cases, it may be diagnosed incidentally with an elevatedwhite blood cell
White blood cells, also called leukocytes or leucocytes, are the cell (biology), cells of the immune system that are involved in protecting the body against both infectious disease and foreign invaders. All white blood cells are produced and de ...
count on a routine laboratory test. It can also present with symptoms indicative of hepatosplenomegaly and the resulting left upper quadrant pain this causes. The enlarged spleen
The spleen is an organ found in almost all vertebrates. Similar in structure to a large lymph node, it acts primarily as a blood filter. The word spleen comes .
may put pressure on the stomach causing a loss of appetite and resulting weight loss. It may also present with mild fever and night sweats due to an elevated basal level of metabolism.
Some (<10%) are diagnosed during the accelerated stage which most often presents bleeding, petechia
A petechia () is a small red or purple spot (≤4 mm in diameter) that can appear on the skin, conjunctiva, retina, and Mucous membrane, mucous membranes which is caused by haemorrhage of capillaries. The word is derived from Italian , 'freckle,' ...
e and ecchymosis. In these patients fevers are most commonly the result of opportunistic infections.
Some patients are initially diagnosed in the blast phase in which the symptoms are most likely fever, bone pain and an increase in bone marrow fibrosis.
Cause
In most cases, no obvious cause for CML can be isolated.Risk factors
CML is more common in males than in females (male to female ratio of 1.4:1) and appears more commonly in the elderly with a median age at diagnosis of 65 years. Exposure to ionising radiation appears to be a risk factor, based on a 50 fold higher incidence of CML in Hiroshima and Nagasaki nuclear bombing survivors. The rate of CML in these individuals seems to peak about 10 years after the exposure.Pathophysiology
chromosomal translocation
In genetics, chromosome translocation is a phenomenon that results in unusual rearrangement of chromosomes. This includes balanced and unbalanced translocation, with two main types: reciprocal-, and Robertsonian translocation. Reciprocal translo ...
known as the Philadelphia chromosome
The Philadelphia chromosome or Philadelphia translocation (Ph) is a specific genetic abnormality in chromosome 22 of leukemia cancer cells (particularly chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) cells). This chromosome is defective and unusually short becaus ...
. This chromosomal abnormality is so named because it was first discovered and described in 1960 by two scientists from Philadelphia, Pennsylvania
Philadelphia, often called Philly, is the largest city in the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania, the sixth-largest city in the U.S., the second-largest city in both the Northeast megalopolis and Mid-Atlantic regions after New York City. Sinc ...
, USA: Peter Nowell of the University of Pennsylvania
The University of Pennsylvania (also known as Penn or UPenn) is a private research university in Philadelphia. It is the fourth-oldest institution of higher education in the United States and is ranked among the highest-regarded universitie ...
and David Hungerford of Fox Chase Cancer Center
Fox Chase Cancer Center is a National Cancer Institute-designated Comprehensive Cancer Center research facility and hospital located in the Fox Chase section of Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, United States. The main facilities of the center are loca ...
.
In this translocation, parts of two chromosomes (the 9th and 22nd) switch places. As a result, part of the BCR ("breakpoint cluster region") gene from chromosome 22 is fused with the ABL gene on chromosome 9. This abnormal "fusion" gene generates a protein of p210 or sometimes p185 weight (p210 is short for 210 kDa protein, a shorthand used for characterizing proteins based solely on size). Because abl carries a domain that can add phosphate
In chemistry, a phosphate is an anion, salt, functional group or ester derived from a phosphoric acid. It most commonly means orthophosphate, a derivative of orthophosphoric acid .
The phosphate or orthophosphate ion is derived from phospho ...
groups to tyrosine residues (a tyrosine kinase
A tyrosine kinase is an enzyme that can transfer a phosphate group from ATP to the tyrosine residues of specific proteins inside a cell. It functions as an "on" or "off" switch in many cellular functions.
Tyrosine kinases belong to a larger cla ...
), the ''bcr-abl'' fusion gene product is also a tyrosine kinase.
cell cycle
The cell cycle, or cell-division cycle, is the series of events that take place in a cell that cause it to divide into two daughter cells. These events include the duplication of its DNA (DNA replication) and some of its organelles, and subs ...
, speeding up cell division. Moreover, the BCR-ABL protein inhibits DNA repair
DNA repair is a collection of processes by which a cell identifies and corrects damage to the DNA molecules that encode its genome. In human cells, both normal metabolic activities and environmental factors such as radiation can cause DNA dam ...
, causing genomic instability and making the cell more susceptible to developing further genetic abnormalities. The action of the BCR-ABL protein is the pathophysiologic cause of chronic myelogenous leukemia. With improved understanding of the nature of the BCR-ABL protein and its action as a tyrosine kinase, targeted therapies
Targeted therapy or molecularly targeted therapy is one of the major modalities of medical treatment (pharmacotherapy) for cancer, others being hormonal therapy and cytotoxic chemotherapy. As a form of molecular medicine, targeted therapy blocks t ...
(the first of which was imatinib
Imatinib, sold under the brand names Gleevec and Glivec (both marketed worldwide by Novartis) among others, is an oral chemotherapy medication used to treat cancer. Imatinib is a small molecule inhibitor targeting multiple receptor tyrosine kin ...
) that specifically inhibit the activity of the BCR-ABL protein have been developed. These tyrosine kinase inhibitors can induce complete remissions in CML, confirming the central importance of bcr-abl as the cause of CML.
Diagnosis

 CML is often suspected on the basis of a
CML is often suspected on the basis of a complete blood count
A complete blood count (CBC), also known as a full blood count (FBC), is a set of medical laboratory tests that provide cytometry, information about the cells in a person's blood. The CBC indicates the counts of white blood cells, red blood cell ...
, which shows increased granulocyte
Granulocytes are
cells in the innate immune system characterized by the presence of specific granules in their cytoplasm. Such granules distinguish them from the various agranulocytes. All myeloblastic granulocytes are polymorphonuclear. They ha ...
s of all types, typically including mature myeloid cells
A myelocyte is a young cell of the granulocytic series, occurring normally in bone marrow (can be found in circulating blood when caused by certain diseases).
Structure
When stained with the usual dyes, the cytoplasm is distinctly basophilic ...
. Basophils and eosinophils are almost universally increased; this feature may help differentiate CML from a leukemoid reaction
The term leukemoid reaction describes an increased
white blood cell count (> 50,000 cells/μL), which is a physiological response to stress or infection (as opposed to a primary blood malignancy, such as leukemia). It often describes the presence o ...
. A bone marrow biopsy is often performed as part of the evaluation for CML, and CML is diagnosed by cytogenetics that detects the translocation t(9;22)(q34;q11.2) which involves the ABL1 gene in chromosome 9 and the BCR gene in chromosome 22. As a result of this translocation, the chromosome looks smaller than its homologue chromosome, and this appearance is known as the Philadelphia chromosome chromosomal abnormality
A chromosomal abnormality, chromosomal anomaly, chromosomal aberration, chromosomal mutation, or chromosomal disorder, is a missing, extra, or irregular portion of chromosomal DNA. These can occur in the form of numerical abnormalities, where ther ...
. Thus, this abnormality can be detected by routine cytogenetics, and the involved genes BCR-ABL1 can be detected by fluorescent in situ hybridization
Fluorescence ''in situ'' hybridization (FISH) is a molecular cytogenetic technique that uses fluorescent probes that bind to only particular parts of a nucleic acid sequence with a high degree of sequence complementarity. It was developed ...
, as well as by PCR PCR or pcr may refer to:
Science
* Phosphocreatine, a phosphorylated creatine molecule
* Principal component regression, a statistical technique
Medicine
* Polymerase chain reaction
** COVID-19 testing, often performed using the polymerase chain r ...
.
Controversy exists over so-called ''Ph-negative'' CML, or cases of suspected CML in which the Philadelphia chromosome cannot be detected. Many such patients in fact have complex chromosomal abnormalities that mask the (9;22) translocation, or have evidence of the translocation by FISH
Fish are aquatic, craniate, gill-bearing animals that lack limbs with digits. Included in this definition are the living hagfish, lampreys, and cartilaginous and bony fish as well as various extinct related groups. Approximately 95% of li ...
or RT-PCR
Reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) is a laboratory technique combining reverse transcription of RNA into DNA (in this context called complementary DNA or cDNA) and amplification of specific DNA targets using polymerase cha ...
in spite of normal routine karyotyping. The small subset of patients without detectable molecular evidence of BCR-ABL1 fusion may be better classified as having an undifferentiated myelodysplastic/myeloproliferative disorder, as their clinical course tends to be different from patients with CML.
CML must be distinguished from a leukemoid reaction
The term leukemoid reaction describes an increased
white blood cell count (> 50,000 cells/μL), which is a physiological response to stress or infection (as opposed to a primary blood malignancy, such as leukemia). It often describes the presence o ...
, which can have a similar appearance on a blood smear
A blood smear, peripheral blood smear or blood film is a thin layer of blood smeared on a glass microscope slide and then stained in such a way as to allow the various blood cells to be examined microscopically. Blood smears are examined in the ...
.
Classification
CML is often divided into three phases based on clinical characteristics and laboratory findings. In the absence of intervention, CML typically begins in the ''chronic'' phase, and over the course of several years progresses to an ''accelerated'' phase and ultimately to a ''blast crisis''. Blast crisis is the terminal phase of CML and clinically behaves like an acute leukemia. Drug treatment will usually stop this progression if started early. One of the drivers of the progression from chronic phase through acceleration and blast crisis is the acquisition of new chromosomal abnormalities (in addition to the Philadelphia chromosome). Some patients may already be in the accelerated phase or blast crisis by the time they are diagnosed.Chronic phase
Approximately 85% of patients with CML are in the chronic phase at the time of diagnosis. During this phase, patients are usually asymptomatic or have only mild symptoms of fatigue, left side pain, joint and/or hip pain, or abdominal fullness. The duration of chronic phase is variable and depends on how early the disease was diagnosed as well as the therapies used. In the absence of treatment, the disease progresses to an accelerated phase. Precise patient staging based on clinical markers and personal genomic profile will likely prove beneficial in the assessment of disease history with respect to progression risk.Accelerated phase
Criteria for diagnosing transition into the accelerated phase are somewhat variable; the most widely used criteria are those put forward by investigators at M.D. Anderson Cancer Center, by Sokal et al., and theWorld Health Organization
The World Health Organization (WHO) is a specialized agency of the United Nations responsible for international public health. The WHO Constitution states its main objective as "the attainment by all peoples of the highest possible level of h ...
. The WHO criteria are perhaps most widely used, and define the accelerated phase by the presence of ≥1 of the following haematological/cytogenetic criteria or provisional criteria concerning response to tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI) therapy
* ''Haematological/cytogenetic criteria''
** Persistent or increasing high white blood cell count (> 10 × 109/L), unresponsive to therapy
** Persistent or increasing splenomegaly, unresponsive to therapy
** Persistent thrombocytosis
Thrombocythemia is a condition of high platelet (thrombocyte) count in the blood. Normal count is in the range of 150x109 to 450x109 platelets per liter of blood, but investigation is typically only considered if the upper limit exceeds 750x109/L. ...
(> 1000 × 109/L), unresponsive to therapy
** Persistent thrombocytopenia
Thrombocytopenia is a condition characterized by abnormally low levels of platelets, also known as thrombocytes, in the blood. It is the most common coagulation disorder among intensive care patients and is seen in a fifth of medical patients an ...
(< 100 × 109/L), unrelated to therapy
** ≥ 20% basophils in the peripheral blood
** 10―19% blasts in the peripheral blood and/or bone marrow
** Additional clonal chromosomal abnormalities in Philadelphia (Ph) chromosome-positive (Ph+) cells at diagnosis, including so-called major route abnormalities (a second Ph chromosome, trisomy 8, isochromosome 17q, trisomy 19), complex karyotype, and abnormalities of 3q26.2
** Any new clonal chromosomal abnormality in Ph+ cells that occurs during therapy
* ''Provisional response-to-TKI criteria''
** Haematological resistance (or failure to achieve a complete haematological response d) to the first TKI
** Any haematological, cytogenetic, or molecular indications of resistance to two sequential TKIs
** Occurrence of two or more mutations in the BCR-ABL1 fusion gene during TKI therapy
The patient is considered to be in the accelerated phase if any of the above are present. The accelerated phase is significant because it signals that the disease is progressing and transformation to blast crisis is imminent. Drug treatment often becomes less effective in the advanced stages.
Blast crisis
Blast crisis is the final phase in the evolution of CML, and behaves like an acute leukemia, with rapid progression and short survival. Blast crisis is diagnosed if any of the following are present in a patient with CML: * >20% blasts in the blood or bone marrow * The presence of an extramedullary proliferation of blastsTreatment
The only curative treatment for CML is a bone marrow transplant or an allogeneic stem cell transplant. Other than this there are four major mainstays of treatment in CML: treatment with tyrosine kinase inhibitors, myelosuppressive or leukopheresis therapy (to counteract the leukocytosis during early treatment), splenectomy andinterferon alfa-2b
Interferon alfa-2b is an antiviral or antineoplastic drug. It is a recombinant form of the protein Interferon alpha-2 that was originally sequenced and produced recombinantly in '' E. coli'' in the laboratory of Charles Weissmann at the Univers ...
treatment. Due to the high median age of patients with CML it is relatively rare for CML to be seen in pregnant women, despite this, however, chronic myelogenous leukemia can be treated with relative safety at any time during pregnancy with the cytokine
Cytokines are a broad and loose category of small proteins (~5–25 kDa) important in cell signaling. Cytokines are peptides and cannot cross the lipid bilayer of cells to enter the cytoplasm. Cytokines have been shown to be involved in autocrin ...
Interferon-alpha.
Chronic phase
In the past, antimetabolites (e.g.,cytarabine
Cytarabine, also known as cytosine arabinoside (ara-C), is a chemotherapy medication used to treat acute myeloid leukemia (AML), acute lymphocytic leukemia (ALL), chronic myelogenous leukemia (CML), and non-Hodgkin's lymphoma. It is given by in ...
, hydroxyurea
Hydroxycarbamide, also known as hydroxyurea, is a medication used in sickle-cell disease, essential thrombocythemia, chronic myelogenous leukemia, polycythemia vera, and cervical cancer. In sickle-cell disease it increases fetal hemoglobin and ...
), alkylating agent
Alkylation is the transfer of an alkyl group from one molecule to another. The alkyl group may be transferred as an alkyl carbocation, a free radical, a carbanion, or a carbene (or their equivalents). Alkylating agents are reagents for effecting al ...
s, interferon alfa 2b, and steroid
A steroid is a biologically active organic compound with four rings arranged in a specific molecular configuration. Steroids have two principal biological functions: as important components of cell membranes that alter membrane fluidity; and a ...
s were used as treatments of CML in the chronic phase, but since the 2000s have been replaced by Bcr-Abl tyrosine-kinase inhibitor
Bcr-Abl tyrosine-kinase inhibitors (TKI) are the first-line therapy for most patients with chronic myelogenous leukemia (CML). More than 90% of CML cases are caused by a chromosomal abnormality that results in the formation of a so-called Philadel ...
s drugs that specifically target BCR-ABL, the constitutively activated tyrosine kinase fusion protein caused by the Philadelphia chromosome
The Philadelphia chromosome or Philadelphia translocation (Ph) is a specific genetic abnormality in chromosome 22 of leukemia cancer cells (particularly chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) cells). This chromosome is defective and unusually short becaus ...
translocation. Despite the move to replacing cytotoxic antineoplastics (standard anticancer drugs) with tyrosine kinase inhibitors sometimes hydroxyurea is still used to counteract the high leukocyte counts encountered during treatment with tyrosine kinase inhibitors like imatinib; in these situations it may be the preferred myelosuppressive agent due to its relative lack of leukemogenic effects and hence the relative lack of potential for secondary haematologic malignancies to result from treatment. IRIS, an international study that compared interferon/cytarabine combination and the first of these new drugs imatinib, with long-term follow up, demonstrated the clear superiority of tyrosine-kinase-targeted inhibition over existing treatments.
Imatinib
The first of this new class of drugs wasimatinib mesylate
Imatinib, sold under the brand names Gleevec and Glivec (both marketed worldwide by Novartis) among others, is an oral chemotherapy medication used to treat cancer. Imatinib is a small molecule inhibitor targeting multiple receptor tyrosine kin ...
(marketed as Gleevec or Glivec), approved by the US Food and Drug Administration
The United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA or US FDA) is a List of United States federal agencies, federal agency of the United States Department of Health and Human Services, Department of Health and Human Services. The FDA is respon ...
(FDA) in 2001. Imatinib was found to inhibit the progression of CML in the majority of patients (65–75%) sufficiently to achieve regrowth of their normal bone marrow stem cell population (a cytogenetic response) with stable proportions of maturing white blood cells. Because some leukemic cells (as evaluated by RT-PCR
Reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) is a laboratory technique combining reverse transcription of RNA into DNA (in this context called complementary DNA or cDNA) and amplification of specific DNA targets using polymerase cha ...
) persist in nearly all patients, the treatment has to be continued indefinitely. Since the advent of imatinib, CML has become the first cancer in which a standard medical treatment may give to the patient a normal life expectancy.
Dasatinib, nilotinib, radotinib, bosutinib, and asciminib
To overcome imatinib resistance and to increase responsiveness to TK inhibitors, four novel agents were later developed. The first, dasatinib, blocks several further oncogenic proteins, in addition to more potent inhibition of the BCR-ABL protein, and was approved in 2007, by the U.S.Food and Drug Administration
The United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA or US FDA) is a List of United States federal agencies, federal agency of the United States Department of Health and Human Services, Department of Health and Human Services. The FDA is respon ...
(FDA) to treat CML in people who were either resistant to or intolerant of imatinib. A second TK inhibitor, nilotinib
Nilotinib, sold under the brand name Tasigna marketed worldwide by Novartis, is a medication used to treat chronic myelogenous leukemia (CML) which has the Philadelphia chromosome. It may be used both in initial cases of chronic phase CML as well ...
, was approved by the FDA for the same indication. In 2010, nilotinib and dasatinib were also approved for first-line therapy, making three drugs in this class available for treatment of newly diagnosed CML. In 2012, radotinib
Radotinib (INN; trade name Supect), and sometimes referred to by its investigational name IY5511, is a drug for the treatment of different types of cancer, most notably Philadelphia chromosome-positive (Ph+) chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) with re ...
joined the class of novel agents in the inhibition of the BCR-ABL protein and was approved in South Korea for people resistant to or intolerant of imatinib. Bosutinib
Bosutinib (rINN/USAN; codenamed SKI-606, marketed under the trade name Bosulif) is a small molecule BCR-ABL and src tyrosine kinase inhibitor used for the treatment of chronic myelogenous leukemia.
Originally synthesized by Wyeth, it is being ...
received US FDA and EU European Medicines Agency approval on 4 September 2012, and 27 March 2013, respectively for the treatment of adults with Philadelphia chromosome-positive (Ph+) chronic myelogenous leukemia (CML) with resistance, or intolerance to prior therapy.
Asciminib
Asciminib, sold under the brand name Scemblix, is a medication used to treat Philadelphia chromosome-positive chronic myeloid leukemia (Ph+ CML). Asciminib is a protein kinase inhibitor.
The most common adverse reactions include upper respira ...
(Scemblix) was approved for medical use in the United States in October 2021.
Treatment-resistant CML
While capable of producing significantly improved responses compared with the action of imatinib, neither dasatinib nor nilotinib could overcome drug resistance caused by one particular mutation found to occur in the structure of BCR-ABL1 known as the T315I mutation (in other words, where the 315th amino acid is mutated from athreonine
Threonine (symbol Thr or T) is an amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. It contains an α-amino group (which is in the protonated −NH form under biological conditions), a carboxyl group (which is in the deprotonated −COO� ...
residue to an isoleucine
Isoleucine (symbol Ile or I) is an α-amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. It contains an α-amino group (which is in the protonated −NH form under biological conditions), an α-carboxylic acid group (which is in the deprot ...
residue). Two approaches were developed to the treatment of CML as a result:
In 2007, Chemgenex released results of an open-label Phase 2/3 study (CGX-635-CML-202) that investigated the use of a non BCR-ABL targeted agent omacetaxine
Omacetaxine mepesuccinate (INN, trade names Synribo ), formerly named as homoharringtonine or HHT, is a pharmaceutical drug substance that is indicated for treatment of chronic myeloid leukemia (CML).
HHT is a natural plant alkaloid derived from ...
, administered subcutaneously (under the skin) in patients who had failed with imatinib and exhibited T315I kinase domain mutation. This is a study which is ongoing through 2014. In September 2012, the FDA approved omacetaxine for the treatment of CML in the case of resistance to other chemotherapeutic agents.
Independently, ARIAD pharmaceuticals, adapting the chemical structures from first and second-generation TK inhibitors, arrived at a new pan-BCR-ABL1 inhibitor which showed (for the first time) efficacy against T315I, as well as all other known mutations of the oncoprotein. The drug, ponatinib
Ponatinib (trade name Iclusig , previously AP24534) is an oral drug developed by ARIAD Pharmaceuticals for the treatment of chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) and Philadelphia chromosome–positive (Ph+) acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL). It is ...
, gained FDA approval in December 2012 for treatment of patients with resistant or intolerant CML. Just as with second-generation TK inhibitors, early approval is being sought to extend the use of ponatinib to newly diagnosed CML also.
Vaccination
In 2005, encouraging but mixed results ofvaccination
Vaccination is the administration of a vaccine to help the immune system develop immunity from a disease. Vaccines contain a microorganism or virus in a weakened, live or killed state, or proteins or toxins from the organism. In stimulating ...
were reported with the ''BCR/ABL1'' p210 fusion protein in patients with stable disease, with GM-CSF as an adjuvant.
Prognosis
Before the advent of tyrosine kinase inhibitors, the median survival time for CML patients had been about 3–5 years from time of diagnosis. With the use of tyrosine kinase inhibitors, survival rates have improved dramatically. A 2006 follow-up of 553 patients using imatinib (Gleevec) found an overall survival rate of 89% after five years. A 2011 followup of 832 patients using imatinib who achieved a stable cytogenetic response found an overall survival rate of 95.2% after 8 years, which is similar to the rate in the general population. Fewer than 1% of patients died because of leukemia progression.Epidemiology
United Kingdom
CML accounts for 8% of all leukaemias in the UK, and around 680 people were diagnosed with the disease in 2011.United States
The American Cancer Society estimates that in 2014, about 5,980 new cases of chronic myeloid leukemia were diagnosed, and about 810 people died of the disease. This means that a little over 10% of all newly diagnosed leukemia cases will be chronic myeloid leukemia. The average risk of a person getting this disease is 1 in 588. The disease is more common in men than women, and more common in whites than African-Americans. The average age at diagnosis is 64 years, and this disease is rarely seen in children.References
External links
Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia Treatment
at the US
National Cancer Institute
The National Cancer Institute (NCI) coordinates the United States National Cancer Program and is part of the National Institutes of Health (NIH), which is one of eleven agencies that are part of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. T ...
Chronic Myelocytic Leukemia (CML)
at '' Merck Manual of Diagnosis and Therapy'' Professional Edition {{DEFAULTSORT:Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia Chronic myeloid leukemia