Chromatic Mediant on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 In
In  Chromatic mediants are usually in
Chromatic mediants are usually in  Some chromatic mediants are equivalent to
Some chromatic mediants are equivalent to 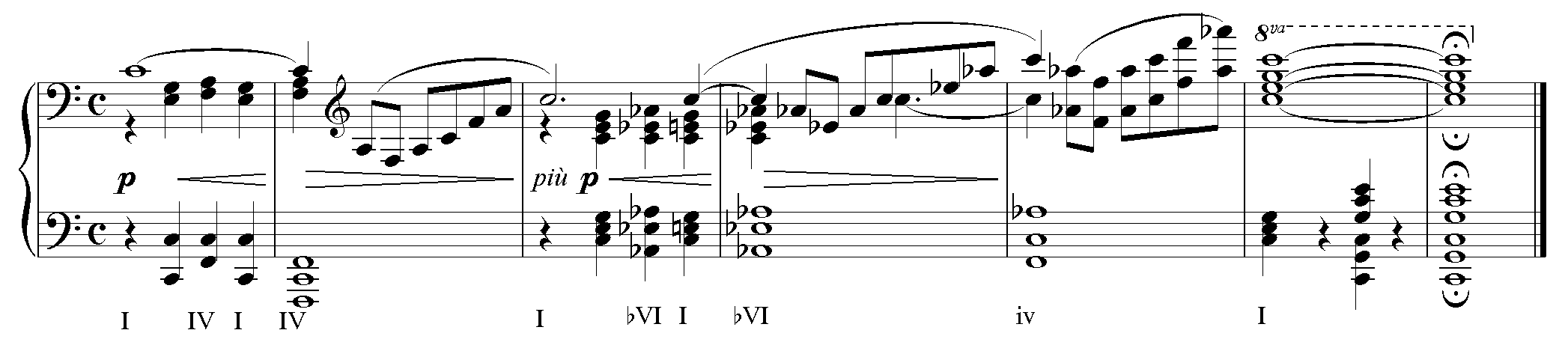
 In
In music
Music is generally defined as the art of arranging sound to create some combination of form, harmony, melody, rhythm or otherwise expressive content. Exact definitions of music vary considerably around the world, though it is an aspect ...
, chromatic mediants are "altered mediant In music, the mediant (''Latin'': to be in the middle) is the third scale degree () of a diatonic scale, being the note halfway between the tonic and the dominant.Benward & Saker (2003), p.32. In the movable do solfège system, the mediant note i ...
and submediant
In music, the submediant is the sixth degree () of a diatonic scale. The submediant ("lower mediant") is named thus because it is halfway between tonic and subdominant ("lower dominant") or because its position below the tonic is symmetrical to t ...
chords
Chord may refer to:
* Chord (music), an aggregate of musical pitches sounded simultaneously
** Guitar chord a chord played on a guitar, which has a particular tuning
* Chord (geometry), a line segment joining two points on a curve
* Chord (as ...
." A chromatic mediant relationship defined conservatively is a relationship between two sections
Section, Sectioning or Sectioned may refer to:
Arts, entertainment and media
* Section (music), a complete, but not independent, musical idea
* Section (typography), a subdivision, especially of a chapter, in books and documents
** Section sig ...
and/or chords whose roots
A root is the part of a plant, generally underground, that anchors the plant body, and absorbs and stores water and nutrients.
Root or roots may also refer to:
Art, entertainment, and media
* ''The Root'' (magazine), an online magazine focusing ...
are related by a major third
In classical music, a third is a musical interval encompassing three staff positions (see Interval number for more details), and the major third () is a third spanning four semitones. Forte, Allen (1979). ''Tonal Harmony in Concept and P ...
or minor third
In music theory, a minor third is a musical interval that encompasses three half steps, or semitones. Staff notation represents the minor third as encompassing three staff positions (see: interval number). The minor third is one of two com ...
, and contain one common tone (thereby sharing the same quality, i.e. major or minor). For example, in the key of C major
Major (commandant in certain jurisdictions) is a military rank of commissioned officer status, with corresponding ranks existing in many military forces throughout the world. When used unhyphenated and in conjunction with no other indicators ...
the diatonic
Diatonic and chromatic are terms in music theory that are most often used to characterize Scale (music), scales, and are also applied to musical instruments, Interval (music), intervals, Chord (music), chords, Musical note, notes, musical sty ...
mediant In music, the mediant (''Latin'': to be in the middle) is the third scale degree () of a diatonic scale, being the note halfway between the tonic and the dominant.Benward & Saker (2003), p.32. In the movable do solfège system, the mediant note i ...
and submediant are E minor
Minor may refer to:
* Minor (law), a person under the age of certain legal activities.
** A person who has not reached the age of majority
* Academic minor, a secondary field of study in undergraduate education
Music theory
*Minor chord
** Barb ...
and A minor respectively. Their parallel majors are ''E major'' and ''A major''. The mediants of the parallel minor of C major (C minor) are ''E major'' and ''A major''. Thus, by this conservative definition, C major
Major (commandant in certain jurisdictions) is a military rank of commissioned officer status, with corresponding ranks existing in many military forces throughout the world. When used unhyphenated and in conjunction with no other indicators ...
has four chromatic mediants: ''E major'', ''A major'', ''E major'', and ''A major''.
There is not complete agreement on the definition of chromatic mediant relationships. Theorists such as Allen Forte Allen, Allen's or Allens may refer to:
Buildings
* Allen Arena, an indoor arena at Lipscomb University in Nashville, Tennessee
* Allen Center, a skyscraper complex in downtown Houston, Texas
* Allen Fieldhouse, an indoor sports arena on the Univer ...
define chromatic mediants conservatively, only allowing chromatic mediant chords of the same quality (major or minor) as described above. However, he describes an even more distant "doubly-chromatic mediant" relationship shared by two chords of the opposite mode, with roots a third apart and no common tones; for example C major and ''E'' or ''A minor'', and A minor and ''C'' or ''F major''. Other less conservative theorists, such as Benward and Saker, include these additional chords of opposite quality and no shared tones in their default definition of chromatic mediants. Thus, by this more permissive definition, C major
Major (commandant in certain jurisdictions) is a military rank of commissioned officer status, with corresponding ranks existing in many military forces throughout the world. When used unhyphenated and in conjunction with no other indicators ...
has six chromatic mediants: ''E major'', ''A major'', ''E major'', ''A major'', ''E minor'' and ''A minor''.
When a conservative chromatic mediant relationship involves seventh chords, "...the triad portions of the chords are both major or both minor." This pertains to the more permissive definition of chromatic mediant relationships as well.
 Chromatic mediants are usually in
Chromatic mediants are usually in root position
The root position of a chord is the voicing of a triad, seventh chord, or ninth chord in which the root of the chord is the bass note and the other chord factors are above it. In the root position, uninverted, of a C-major triad, the bass is C ...
, may appear in either major or minor keys, usually provide color and interest while prolonging the tonic harmony, proceed from and to the tonic or less often the dominant, sometimes are preceded or followed by their own secondary dominant
A secondary chord is an analytical label for a specific harmonic device that is prevalent in the tonal idiom of Western music beginning in the common practice period: the use of diatonic functions for tonicization.
Secondary chords are a typ ...
s, or sometimes create a complete modulation
In electronics and telecommunications, modulation is the process of varying one or more properties of a periodic waveform, called the ''carrier signal'', with a separate signal called the ''modulation signal'' that typically contains informatio ...
.
 Some chromatic mediants are equivalent to
Some chromatic mediants are equivalent to altered chord
An altered chord is a chord that replaces one or more notes from the diatonic scale with a neighboring pitch from the chromatic scale. By the broadest definition, any chord with a non-diatonic chord tone is an altered chord. The simplest examp ...
s, for example VI is also a borrowed chord
A borrowed chord (also called mode mixture,Romeo, Sheila (1999). ''Complete Rock Keyboard Method: Mastering Rock Keyboard'', p. 42. . Bouchard, Joe and Romeo, Sheila (2007). ''The Total Rock Keyboardist'', p. 120. Alfred Music. . modal mixture, ...
from the parallel minor
In music theory, a major scale and a minor scale that have the same tonic note are called parallel keys and are said to be in a parallel relationship. Forte, Allen (1979). ''Tonal Harmony'', p.9. 3rd edition. Holt, Rinehart, and Wilson. . "When ...
, VI is also a secondary dominant of ii (V/ii), and III is V/vi, with context and analysis
Analysis ( : analyses) is the process of breaking a complex topic or substance into smaller parts in order to gain a better understanding of it. The technique has been applied in the study of mathematics and logic since before Aristotle (38 ...
revealing the distinction.Benward & Saker (2009). ''Music: In Theory and Practice, Vol. II'', pp. 201–204. Eighth edition. . "Always look carefully to determine the function of the chord."
Chromatic mediant chords were rarely used during the baroque
The Baroque (, ; ) is a style of architecture, music, dance, painting, sculpture, poetry, and other arts that flourished in Europe from the early 17th century until the 1750s. In the territories of the Spanish and Portuguese empires including t ...
and classical periods, though the chromatic mediant relationship was occasionally found between sections
Section, Sectioning or Sectioned may refer to:
Arts, entertainment and media
* Section (music), a complete, but not independent, musical idea
* Section (typography), a subdivision, especially of a chapter, in books and documents
** Section sig ...
, but the chords and relationships became much more common during the romantic period
Romanticism (also known as the Romantic movement or Romantic era) was an artistic, literary, musical, and intellectual movement that originated in Europe towards the end of the 18th century, and in most areas was at its peak in the approximate ...
and became even more prominent in post-romantic and impressionistic music. One author describes their use within phrases as, "surprising," even more so than the deceptive cadence
In Western musical theory, a cadence (Latin ''cadentia'', "a falling") is the end of a phrase in which the melody or harmony creates a sense of full or partial resolution, especially in music of the 16th century onwards.Don Michael Randel (199 ...
, in part due to their rarity and in part due to their chromaticism (they come from 'outside' the key), while another says they are so rare that one should first eliminate the possibility that one is looking at a diatonic movement (presumably, borrowing), then make sure that it is not a secondary chord
A secondary chord is an analytical label for a specific harmonic device that is prevalent in the tonal idiom of Western music beginning in the common practice period: the use of diatonic functions for tonicization.
Secondary chords are a typ ...
, and then, "finally," one may consider, "the likeliness of an actual chromatic mediant relationship."Sorce, Richard (1995). ''Music Theory for the Music Professional'', p. 423. Scarecrow. .

See also
*Closely related key
In music, a closely related key (or close key) is one sharing many common tones with an original key, as opposed to a distantly related key (or distant key). In music harmony, there are six of them: five share all, or all except one, pitches wit ...
*Inversion (music)
In music theory, an inversion is a type of change to intervals, chords, voices (in counterpoint), and melodies. In each of these cases, "inversion" has a distinct but related meaning. The concept of inversion also plays an important role in mus ...
*Parallel and counter parallel
Parallel and counter parallel chords are terms derived from the German (''Parallelklang'', ''Gegenparallelklang'') to denote what is more often called in English the "relative", and possibly the "counter relative" chords. In Hugo Riemann' ...
*Relative key
In music, relative keys are the major and minor scales that have the same key signatures ( enharmonically equivalent), meaning that they share all the same notes but are arranged in a different order of whole steps and half steps. A pair of major ...
References
{{Chromaticism Chords Chromaticism