Christian Lassen on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Christian Lassen (22 October 1800 – 8 May 1876) was a
Christian Lassen (22 October 1800 – 8 May 1876) was a
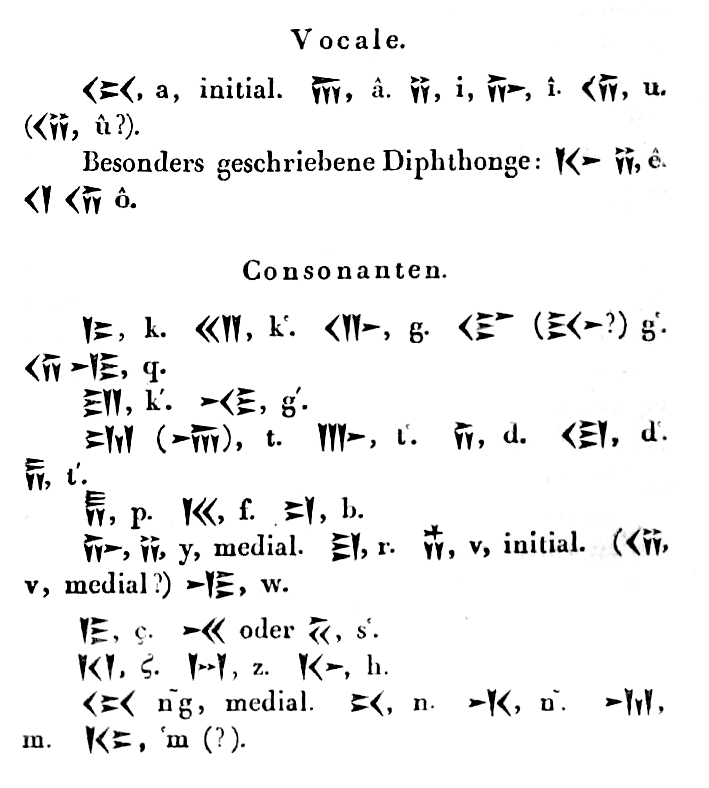 Soon after the appearance of Burnouf's ''Commentaire sur le Yacna'' (1833), Lassen also directed his attention to the
Soon after the appearance of Burnouf's ''Commentaire sur le Yacna'' (1833), Lassen also directed his attention to the
File:AgathoklesCoinage.jpg, Lassen used the bilingual Greek-Brahmi coinage of
 Christian Lassen (22 October 1800 – 8 May 1876) was a
Christian Lassen (22 October 1800 – 8 May 1876) was a Norwegian
Norwegian, Norwayan, or Norsk may refer to:
*Something of, from, or related to Norway, a country in northwestern Europe
*Norwegians, both a nation and an ethnic group native to Norway
*Demographics of Norway
*The Norwegian language, including the ...
-born, German orientalist and Indologist
Indology, also known as South Asian studies, is the academic study of the history and cultures, languages, and literature of the Indian subcontinent, and as such is a subset of Asian studies.
The term ''Indology'' (in German, ''Indologie'') is o ...
. He was a professor of Old Indian language and literature at the University of Bonn
The Rhenish Friedrich Wilhelm University of Bonn (german: Rheinische Friedrich-Wilhelms-Universität Bonn) is a public research university located in Bonn, North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany. It was founded in its present form as the ( en, Rhine U ...
.
Biography
He was born atBergen, Norway
Bergen (), historically Bjørgvin, is a city and municipalities of Norway, municipality in Vestland county on the Western Norway, west coast of Norway. , its population is roughly 285,900. Bergen is the list of towns and cities in Norway, secon ...
where he attended Bergen Cathedral School
Bergen Cathedral School (Norwegian: ''Bergen Katedralskole'', Latin: ''Schola Cathedralis Bergensis'', formerly known as Bergens lærdeskole and Bergen latinskole and colloquially known as Katten) is an upper secondary school in Bergen, Norway. Loc ...
. Having received an education at the University of Oslo
The University of Oslo ( no, Universitetet i Oslo; la, Universitas Osloensis) is a public research university located in Oslo, Norway. It is the highest ranked and oldest university in Norway. It is consistently ranked among the top universit ...
, he moved to Germany and continued his studies at the University of Heidelberg
}
Heidelberg University, officially the Ruprecht Karl University of Heidelberg, (german: Ruprecht-Karls-Universität Heidelberg; la, Universitas Ruperto Carola Heidelbergensis) is a public research university in Heidelberg, Baden-Württemberg, ...
and the University of Bonn
The Rhenish Friedrich Wilhelm University of Bonn (german: Rheinische Friedrich-Wilhelms-Universität Bonn) is a public research university located in Bonn, North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany. It was founded in its present form as the ( en, Rhine U ...
where Lassen acquired a sound knowledge of Sanskrit
Sanskrit (; attributively , ; nominally , , ) is a classical language belonging to the Indo-Aryan branch of the Indo-European languages. It arose in South Asia after its predecessor languages had diffused there from the northwest in the late ...
. He spent three years in Paris
Paris () is the capital and most populous city of France, with an estimated population of 2,165,423 residents in 2019 in an area of more than 105 km² (41 sq mi), making it the 30th most densely populated city in the world in 2020. S ...
and London, engaged in copying and collating manuscripts, and collecting materials for future research, especially with reference to Hindu
Hindus (; ) are people who religiously adhere to Hinduism.Jeffery D. Long (2007), A Vision for Hinduism, IB Tauris, , pages 35–37 Historically, the term has also been used as a geographical, cultural, and later religious identifier for ...
drama and philosophy. During this period he published, jointly with Eugène Burnouf
Eugène Burnouf (; April 8, 1801May 28, 1852) was a French scholar, an Indologist and orientalist. His notable works include a study of Sanskrit literature, translation of the Hindu text ''Bhagavata Purana'' and Buddhist text ''Lotus Sutra''. He ...
, his first work, ''Essai sur le Pâli'' (Paris, 1826).
On his return to Bonn he studied Arabic
Arabic (, ' ; , ' or ) is a Semitic languages, Semitic language spoken primarily across the Arab world.Semitic languages: an international handbook / edited by Stefan Weninger; in collaboration with Geoffrey Khan, Michael P. Streck, Janet C ...
, and took the degree of Ph.D., his dissertation discussing the Arabic notices of the geography of the Punjab
Punjab (; Punjabi: پنجاب ; ਪੰਜਾਬ ; ; also romanised as ''Panjāb'' or ''Panj-Āb'') is a geopolitical, cultural, and historical region in South Asia, specifically in the northern part of the Indian subcontinent, comprising ...
(''Commentario geographica historica de Pentapotamia Indica'', Bonn, 1827). Soon after he was admitted ''Privatdozent
''Privatdozent'' (for men) or ''Privatdozentin'' (for women), abbreviated PD, P.D. or Priv.-Doz., is an academic title conferred at some European universities, especially in German-speaking countries, to someone who holds certain formal qualific ...
'', and in 1830 was appointed extraordinary and in 1840 ordinary professor of Old Indian language and literature. Lassen remained at the University of Bonn to the end of his life. Having been affected with almost total blindness for many years, by 1864 he was allowed to give up lecturing.
He died at Bonn and was buried at Alter Friedhof.Work
In 1829–1831 he brought out, in conjunction withAugust Wilhelm von Schlegel
August Wilhelm (after 1812: von) Schlegel (; 8 September 176712 May 1845), usually cited as August Schlegel, was a German poet, translator and critic, and with his brother Karl Wilhelm Friedrich Schlegel, Friedrich Schlegel the leading influence w ...
, a critical annotated edition of the ''Hitopadeśa''. The appearance of this edition marks the starting-point of the critical study of Sanskrit literature. Lassen assisted von Schlegel in editing and translating the first two cantos of the epic ''Rāmāyana'' (1829-1838). In 1832 he brought out the text of the first act of Bhavabhuti
Bhavabhūti (Devanagari: भवभूति) was an 8th-century scholar of India noted for his plays and poetry, written in Sanskrit. His plays are considered the equal of the works of Kalidasa. Bhavabhuti was born in Padmapura, Vidarbha, in Gond ...
's drama, ''Mālatīmādhava'', and a complete edition, with a Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power of the ...
translation, of the ''Sānkhya-kārikā''. In 1837 followed his edition and translation of Jayadeva
Jayadeva (; born ), also spelt Jaideva, was a Sanskrit poet during the 12th century. He is most known for his epic poem ''Gita Govinda'' which concentrates on Krishna's love with the '' gopi'', Radha, in a rite of spring. This poem, which presen ...
's charming lyrical drama, ''Gītagovinda'' and his ''Institutiones linguae Pracriticae''. His ''Anthologia Sanscritica'', which came out the following year, contained several hitherto unpublished texts, and did much to stimulate the study of Sanskrit in German universities. In 1846 Lassen brought out an improved edition of Schlegel's text and translation of the "Bhagavad Gita
The Bhagavad Gita (; sa, श्रीमद्भगवद्गीता, lit=The Song by God, translit=śrīmadbhagavadgītā;), often referred to as the Gita (), is a 700- verse Hindu scripture that is part of the epic ''Mahabharata'' (c ...
".
As well as the study of Indian languages, he was a scientific pioneer in other fields of philological inquiry. In his ''Beiträge zur Deutung der Eugubinischen Tafeln'' (1833) he prepared the way for the correct interpretation of the Umbria
it, Umbro (man) it, Umbra (woman)
, population_note =
, population_blank1_title =
, population_blank1 =
, demographics_type1 =
, demographics1_footnotes =
, demographics1_title1 =
, demographics1_info1 =
, ...
n inscriptions; and the ''Zeitschrift für die Kunde des Morgenlandes'' (7 vols., 1837-1850), started and largely conducted by him, contains, among other valuable papers from his pen, grammatical sketches of the Beluchi and Brahui languages, and an essay on the Lycian inscriptions.
Old Persian cuneiform
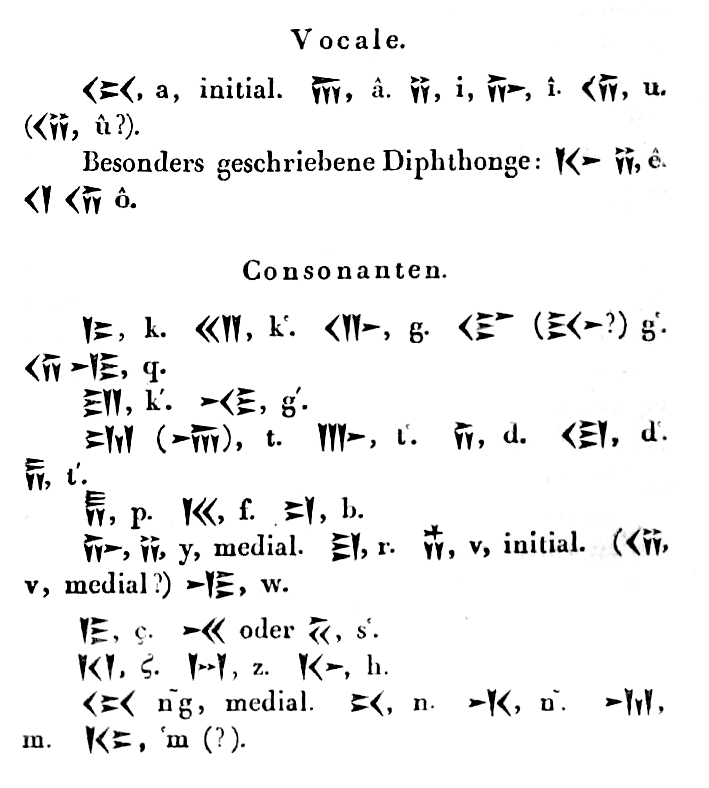 Soon after the appearance of Burnouf's ''Commentaire sur le Yacna'' (1833), Lassen also directed his attention to the
Soon after the appearance of Burnouf's ''Commentaire sur le Yacna'' (1833), Lassen also directed his attention to the Zend language
Avestan (), or historically Zend, is an umbrella term for two Old Iranian languages: Old Avestan (spoken in the 2nd millennium BCE) and Younger Avestan (spoken in the 1st millennium BCE). They are known only from their conjoined use as the scrip ...
, and to Iran
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran, and also called Persia, is a country located in Western Asia. It is bordered by Iraq and Turkey to the west, by Azerbaijan and Armenia to the northwest, by the Caspian Sea and Turkmeni ...
ian studies generally; and in ''Die altpersischen Keilinschriften von Persepolis'' (1836) he greatly improved the knowledge of the Old Persian cuneiform
Old Persian cuneiform is a semi-alphabetic cuneiform script that was the primary script for Old Persian. Texts written in this cuneiform have been found in Iran (Persepolis, Susa, Hamadan, Kharg Island), Armenia, Romania (Gherla), Turkey ( Van Fo ...
inscriptions, following the early efforts of Grotefend
Georg Friedrich Grotefend (9 June 1775 – 15 December 1853) was a German epigraphist and philologist. He is known mostly for his contributions toward the decipherment of cuneiform.
Georg Friedrich Grotefend had a son, named Carl Ludwig Grot ...
(1802) and Saint-Martin (1823). thereby anticipating, by one month, Burnouf's ''Mémoire'' on the same subject, while Sir Henry Rawlinson
Sir Henry Creswicke Rawlinson, 1st Baronet, KLS (5 April 1810 – 5 March 1895) was a British East India Company army officer, politician and Orientalist, sometimes described as the Father of Assyriology. His son, also Henry, was to beco ...
's famous memoir on the Behistun Inscription, though drawn up in Persia, at about the same time, did not reach the Royal Asiatic Society until three years later, 1839.
Subsequently, Lassen published, in the sixth volume of his journal (1845), a collection of all the Old Persian cuneiform inscriptions known up to that date. According to Sayce:
Brahmi script
The first successful attempts at deciphering theBrahmi script
Brahmi (; ; ISO: ''Brāhmī'') is a writing system of ancient South Asia. "Until the late nineteenth century, the script of the Aśokan (non-Kharosthi) inscriptions and its immediate derivatives was referred to by various names such as 'lath' o ...
were made in 1836 by Christian Lassen, who used a bilingual Greek-Brahmi coin of Indo-Greek
The Indo-Greek Kingdom, or Graeco-Indian Kingdom, also known historically as the Yavana Kingdom (Yavanarajya), was a Hellenistic period, Hellenistic-era Ancient Greece, Greek kingdom covering various parts of Afghanistan and the northwestern r ...
king Agathocles Agathocles (Greek: ) is a Greek name, the most famous of which is Agathocles of Syracuse, the tyrant of Syracuse. The name is derived from , ''agathos'', i.e. "good" and , ''kleos'', i.e. "glory".
Other personalities named Agathocles:
*Agathocles, ...
to correctly identify several Brahmi letters. The task was then completed by James Prinsep
James Prinsep FRS (20 August 1799 – 22 April 1840) was an English scholar, orientalist and antiquary. He was the founding editor of the ''Journal of the Asiatic Society of Bengal'' and is best remembered for deciphering the Kharosthi and B ...
, who was able to identify the rest of the Brahmi characters, with the help of Major Cunningham
Major General Sir Alexander Cunningham (23 January 1814 – 28 November 1893) was a British Army engineer with the Bengal Engineer Group who later took an interest in the history and archaeology of India. In 1861, he was appointed to the newly ...
.
Indo-Greek
The Indo-Greek Kingdom, or Graeco-Indian Kingdom, also known historically as the Yavana Kingdom (Yavanarajya), was a Hellenistic period, Hellenistic-era Ancient Greece, Greek kingdom covering various parts of Afghanistan and the northwestern r ...
kings Agathocles Agathocles (Greek: ) is a Greek name, the most famous of which is Agathocles of Syracuse, the tyrant of Syracuse. The name is derived from , ''agathos'', i.e. "good" and , ''kleos'', i.e. "glory".
Other personalities named Agathocles:
*Agathocles, ...
and Pantaleon
Pantaleon, also known as Panteleimon, (Greek: ) was a Greek king who reigned some time between 190–180 BC in Bactria and India. He was a younger contemporary or successor of the Greco-Bactrian king Demetrius, and is sometimes believed to hav ...
to correctly decipher the Brahmi script
Brahmi (; ; ISO: ''Brāhmī'') is a writing system of ancient South Asia. "Until the late nineteenth century, the script of the Aśokan (non-Kharosthi) inscriptions and its immediate derivatives was referred to by various names such as 'lath' o ...
.
File:Announcement of the decipherement of Brahmi letters by Lassen in the JASB in 1836.jpg, Announcement by James Prinsep
James Prinsep FRS (20 August 1799 – 22 April 1840) was an English scholar, orientalist and antiquary. He was the founding editor of the ''Journal of the Asiatic Society of Bengal'' and is best remembered for deciphering the Kharosthi and B ...
of the secure decipherement of the first Brahmi letters by Lassen in the Journal of the Asiatic Society of Bengal
The Asiatic Society is a government of India organisation founded during the Company rule in India to enhance and further the cause of "Oriental research", in this case, research into India and the surrounding regions. It was founded by the p ...
, in 1836.
File:Agathukleyasa Agathokles.jpg, Identical regnal names ''Agathuklayesa'' (Brahmi: 𑀅𑀕𑀣𑀼𑀼𑀓𑁆𑀮𑁂𑀬𑁂𑀲) and ''Agathokles'' (Greek: ΑΓΑΘΟΚΛΕΟΥΣ) on a bilingual coin of Agathocles, used by Christian Lassen to decipher securely the first Brahmi letters.
Kharoshthi
He also was one of the first scholars in Europe who took up, with signal success, the decipherment of the newly discovered Bactrian,Indo-Greek
The Indo-Greek Kingdom, or Graeco-Indian Kingdom, also known historically as the Yavana Kingdom (Yavanarajya), was a Hellenistic period, Hellenistic-era Ancient Greece, Greek kingdom covering various parts of Afghanistan and the northwestern r ...
and Indo-Scythian
Indo-Scythians (also called Indo-Sakas) were a group of nomadic Iranian peoples of Scythian origin who migrated from Central Asia southward into modern day Pakistan and Northwestern India from the middle of the 2nd century BCE to the 4th centur ...
coins with Kharoshthi
The Kharoṣṭhī script, also spelled Kharoshthi (Kharosthi: ), was an ancient Indo-Iranian script used by various Aryan peoples in north-western regions of the Indian subcontinent, more precisely around present-day northern Pakistan and ...
legends, which furnished him the materials for ''Zur Geschichte der griechischen und indoskythsschen Könige in Bakterien, Kabul, und Indien'' (1838). In this, he closely followed the pioneering work of James Prinsep
James Prinsep FRS (20 August 1799 – 22 April 1840) was an English scholar, orientalist and antiquary. He was the founding editor of the ''Journal of the Asiatic Society of Bengal'' and is best remembered for deciphering the Kharosthi and B ...
(1835), and Carl Ludwig Grotefend
Carl Ludwig Grotefend (22 December 1807 – 27 October 1874) was a German epigraphist, philologist and numismat. He played a key role in the decipherment of the Indian Kharoshthi script on the coinage of the Indo-Greek kings, around the same time a ...
(1836).
He contemplated bringing out a critical edition of the ''Vendidad''; but, after publishing the first five fargards (1852), he felt that his whole energies were required for the successful accomplishment of the great undertaking of his life—his ''Indische Altertumskunde''. In this work—completed in four volumes, published respectively in 1847 (2nd ed., 1867), 1849 (2nd ed., 1874), 1858 and 1861—which forms one of the greatest monuments of untiring industry and critical scholarship, everything that could be gathered from native and foreign sources, relative to the political, social and intellectual development of India
India, officially the Republic of India (Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by area, the second-most populous country, and the most populous democracy in the world. Bounded by the Indian Ocean on the so ...
. He was elected a Foreign Honorary Member of the American Academy of Arts and Sciences
The American Academy of Arts and Sciences (abbreviation: AAA&S) is one of the oldest learned societies in the United States. It was founded in 1780 during the American Revolution by John Adams, John Hancock, James Bowdoin, Andrew Oliver, and ...
in 1868.
References
Other sources
* “Christian Lassen,” ''Allgemeine Deutsche Biographie
''Allgemeine Deutsche Biographie'' (ADB, german: Universal German Biography) is one of the most important and comprehensive biographical reference works in the German language.
It was published by the Historical Commission of the Bavarian Aca ...
'', Band 17, Leipzig: Duncker & Humblot, 1883, S. 784–788.
* “Christian Lassen,” ''Meyers Konversations-Lexikon
' or ' was a major encyclopedia in the German language that existed in various editions, and by several titles, from 1839 to 1984, when it merged with the '.
Joseph Meyer (1796–1856), who had founded the publishing house in 1826, intended t ...
'', 4. Auflage von 1888–1890.
*
*
External links
* {{DEFAULTSORT:Lassen, Christian 1800 births 1876 deaths People educated at the Bergen Cathedral School Fellows of the American Academy of Arts and Sciences Recipients of the Pour le Mérite (civil class) Indologists University of Bonn faculty University of Bonn alumni Heidelberg University alumni 20th-century German historians Norwegian emigrants to Germany