Chinese Navy on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The People's Liberation Army Navy (PLAN; ), also known as the People's Navy, Chinese Navy, or PLA Navy, is the
 The PLAN traces its lineage to units of the
The PLAN traces its lineage to units of the
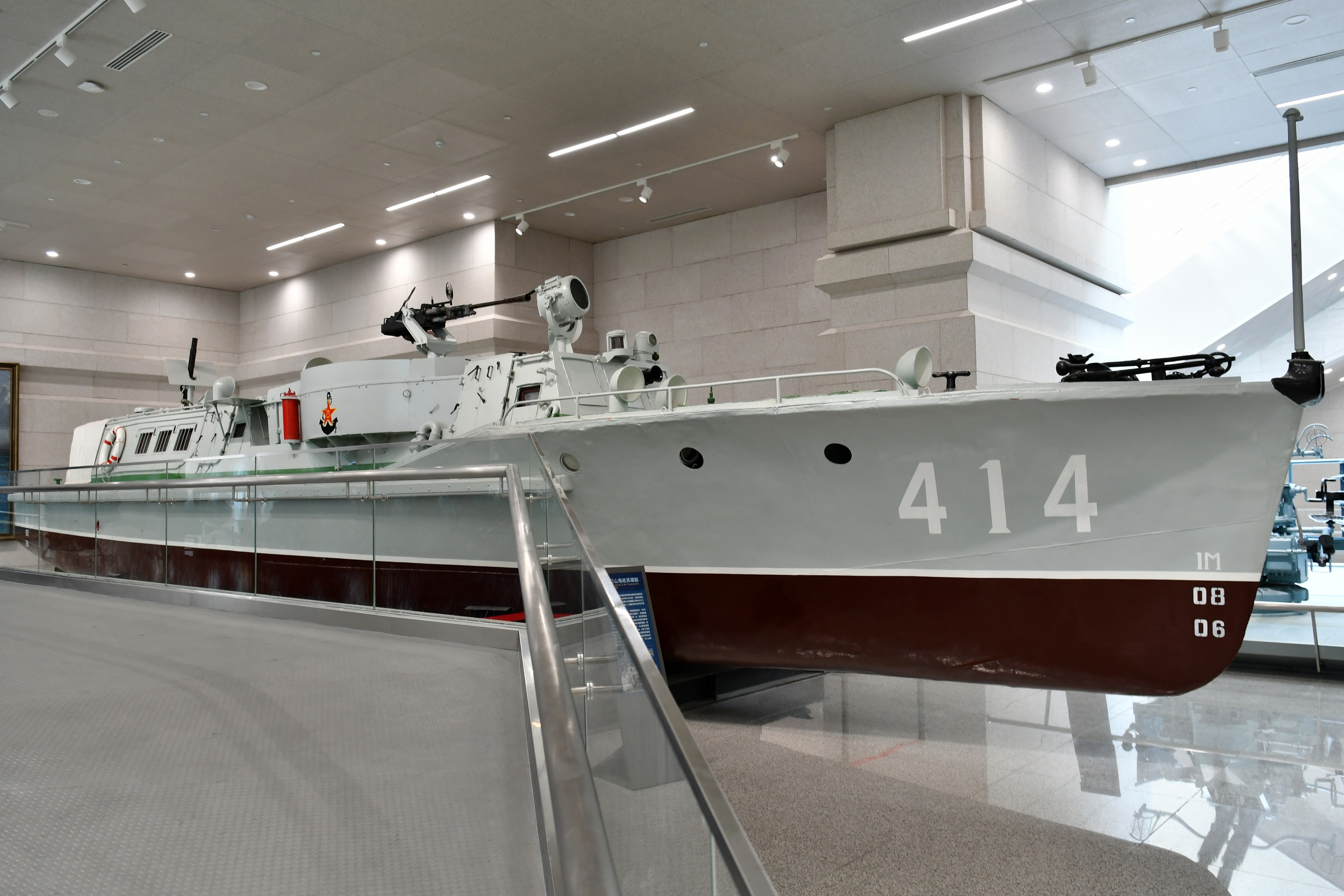
 Beginning in 2009, China ordered 4 Zubr-class LCAC from Ukraine and bought 4 more from the Hellenic Navy (Greece). These hovercraft/LCACs are built to send troops and armored vehicles (tanks, etc.) onto beaches in a fast manner, acting as a landing craft, and were viewed to be a direct threat to Taiwan's pro-independence movement as well as the conflict over
Beginning in 2009, China ordered 4 Zubr-class LCAC from Ukraine and bought 4 more from the Hellenic Navy (Greece). These hovercraft/LCACs are built to send troops and armored vehicles (tanks, etc.) onto beaches in a fast manner, acting as a landing craft, and were viewed to be a direct threat to Taiwan's pro-independence movement as well as the conflict over
 The PLAN is organized into several departments for purposes of command, control and coordination. Main operating forces are organized into fleets, each with its own headquarters, a commander (a Rear Admiral or Vice Admiral) and a Political Commisar. All PLAN headquarters are subordinate to the PLA Joint Staff Department and the Chairman of the Central Military Commission.
The PLAN is organized into several departments for purposes of command, control and coordination. Main operating forces are organized into fleets, each with its own headquarters, a commander (a Rear Admiral or Vice Admiral) and a Political Commisar. All PLAN headquarters are subordinate to the PLA Joint Staff Department and the Chairman of the Central Military Commission.
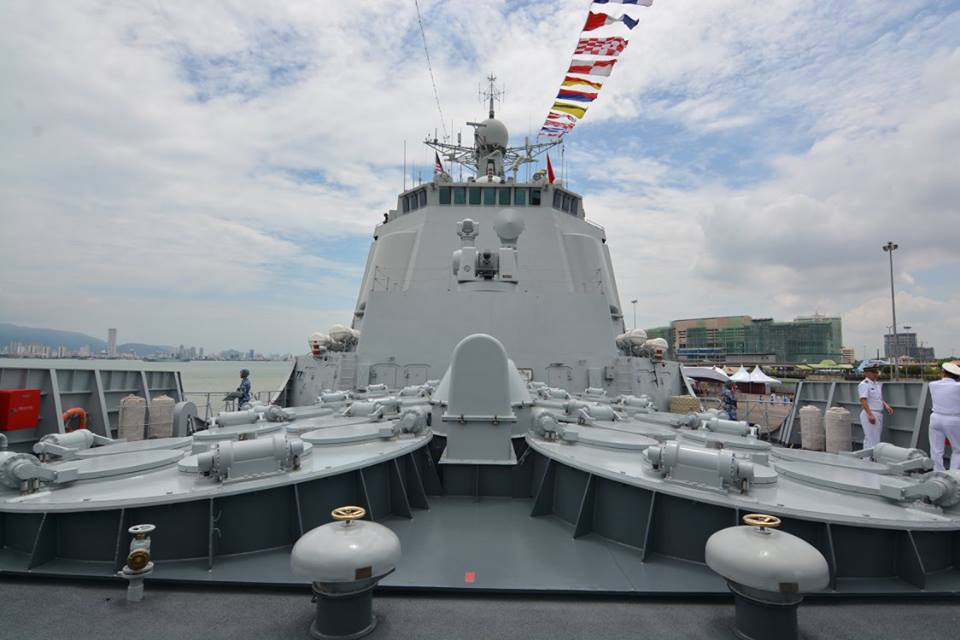
 The People's Liberation Army Surface Force consists of all surface combatant, surface warships in service with the PLAN. They are organised into flotillas spread across the three main fleets.
The People's Liberation Army Surface Force consists of all surface combatant, surface warships in service with the PLAN. They are organised into flotillas spread across the three main fleets.

 The PLAN Marine Corps was originally established in the 1950s and then re-established in 1979 under PLAN organisation. It consists of around 20,000
The PLAN Marine Corps was originally established in the 1950s and then re-established in 1979 under PLAN organisation. It consists of around 20,000
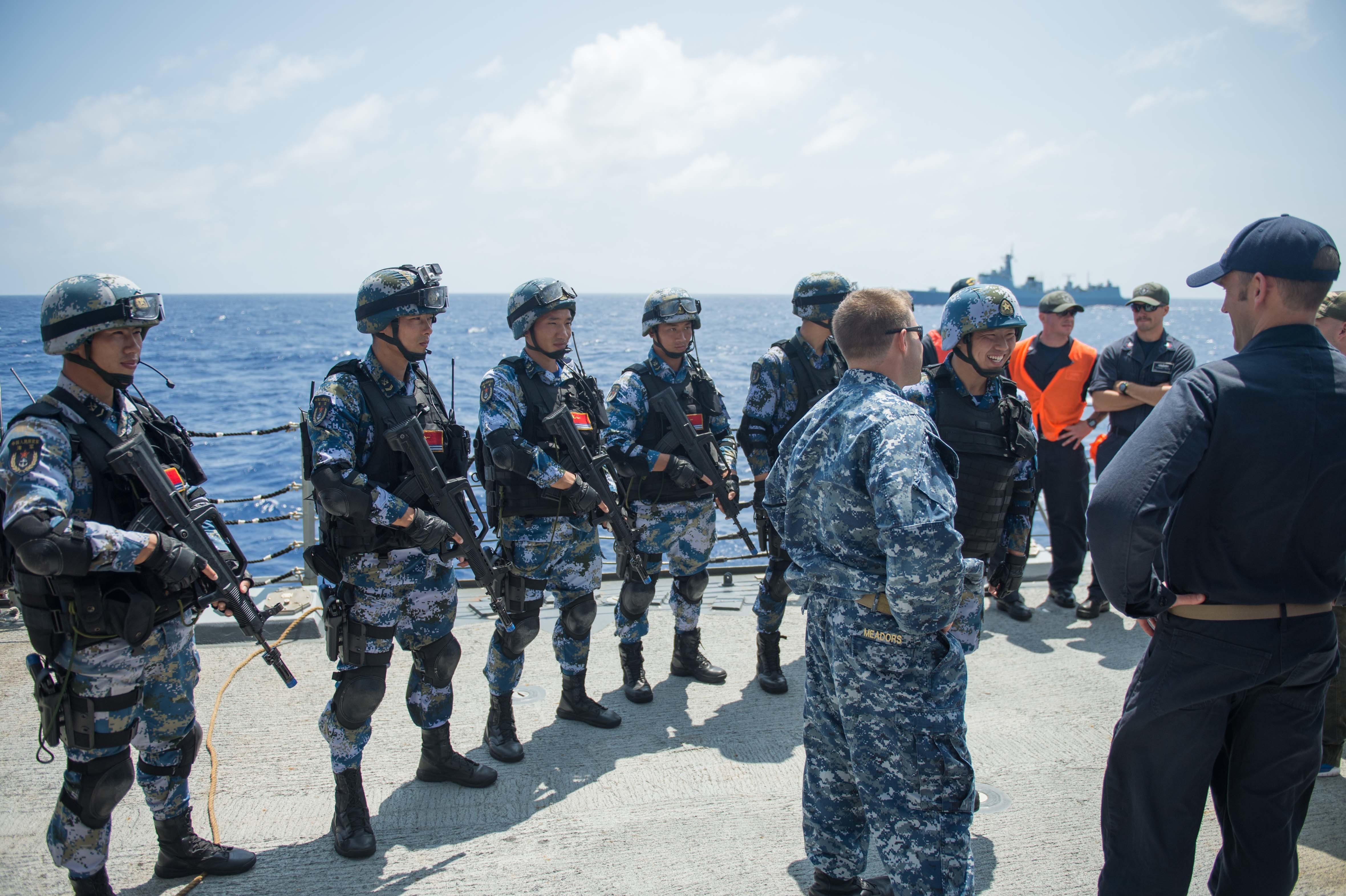
 The People's Liberation Army Navy has become more prominent in recent years owing to a change in Chinese strategic priorities. The new strategic threats include possible conflict with the United States and/or a resurgent Japan in areas such as the Taiwan Strait or the
The People's Liberation Army Navy has become more prominent in recent years owing to a change in Chinese strategic priorities. The new strategic threats include possible conflict with the United States and/or a resurgent Japan in areas such as the Taiwan Strait or the

''BBC News'' 11 September 2012 On some occasions, ships and planes from various Mainland Chinese and Taiwanese government and military agencies have entered the disputed area. In addition to the cases where they escorted fishing and activist vessels, there have been other incursions. In an eight-month period in 2012, over forty maritime incursions and 160 aerial incursions occurred. For example, in July 2012, three Chinese patrol vessels entered the disputed waters around the islands. Military escalation continued in 2013. In February, Minister of Defense (Japan), Japanese Defense Minister Itsunori Onodera claimed that a Chinese frigate had Missile lock-on, locked weapons-targeting radar onto a Japanese destroyer and helicopter on two occasions in January. A Chinese Type 053H3 frigate, Jiangwei II class frigate and a Japanese destroyer were three kilometers apart, and the crew of the latter vessel went to battle stations. The Chinese state media responded that their frigates had been engaged in routine training at the time. In late February 2013, United States Intelligence Community, U.S. intelligence detected China moving road-mobile ballistic missiles closer to the coast near the disputed islands, including medium-range DF-16 anti-ship ballistic missiles. In May, a flotilla of Chinese warships from its
 On 22 July 2011, following its Vietnam port-call, the Indian amphibious assault vessel was reportedly contacted 45 nautical miles from the Vietnamese coast in the disputed South China Sea by a party identifying itself as the Chinese Navy and stating that the Indian warship was entering Chinese waters."China face-off in South China Sea"
On 22 July 2011, following its Vietnam port-call, the Indian amphibious assault vessel was reportedly contacted 45 nautical miles from the Vietnamese coast in the disputed South China Sea by a party identifying itself as the Chinese Navy and stating that the Indian warship was entering Chinese waters."China face-off in South China Sea"
DNA India report According to a spokesperson for the Indian Navy, since there were no Chinese ships or aircraft were visible, the INS ''Airavat'' proceeded on her onward journey as scheduled. The Indian Navy further clarified that "[t]here was no confrontation involving the INS ''Airavat''. India supports freedom of navigation in international waters, including in the South China Sea, and the right of passage in accordance with accepted principles of international law. These principles should be respected by all." On 11 July 2012, the Chinese frigate ''Dongguan'' ran aground on Hasa Hasa Shoal (''pictured'') located 60 Nautical mile, nmi west of Rizal, Palawan, Rizal, which was within the
"China ship runs aground near Phl"
''The Philippine Star''. 14 July 2012. Retrieved 15 July 2012. By 15 July, the frigate had been refloated and was returning to port with no injuries and only minor damage."Stranded naval frigate refloated."
Agence-France Presse, AFP. 15 July 2012 During this incident, the 2012 Association of Southeast Asian Nations, ASEAN summit took place in Phnom Penh, Cambodia, amid the rising regional tensions.
 As of 2018, the Chinese navy operates over 496 combat ships and 232 various auxiliary vessels and counts 255,000 seamen in its ranks. The Chinese Navy also employ more than 710 naval aircraft, including fighters, bombers and electronic warfare aircraft. China has large amount of artillery, torpedoes, and missiles included in their combat assets.
As of 2018, the Chinese navy operates over 496 combat ships and 232 various auxiliary vessels and counts 255,000 seamen in its ranks. The Chinese Navy also employ more than 710 naval aircraft, including fighters, bombers and electronic warfare aircraft. China has large amount of artillery, torpedoes, and missiles included in their combat assets.
 The PLAN's ambitions include operating out to the first and second island chains, as far as the South Pacific near Australia, and spanning to the Aleutian islands, and operations extending to the Straits of Malacca near the Indian Ocean.Annual Report to Congress, ''Military Power of the People's Republic of China''. Retrieved 22 May 2008 The future PLAN fleet will be composed of a balance of combatant assets aimed at maximising the PLAN's fighting effectiveness.
On the high end, there would be modern destroyers, such as stealth guided missile destroyers equipped with long-range air defense missiles and anti-submarine capabilities (Type 055 destroyer, Type 055). There would be modern destroyers equipped with long-range air defense missiles (Type 052B destroyer, Type 052B, Type 052C destroyer, Type 052C, Type 052D destroyer, Type 052D and Type 051C destroyer, Type 051C, and destroyers armed with supersonic anti-ship missiles (Sovremenny class destroyer, ''Sovremenny'' class).
There would be advanced nuclear-powered attack and ballistic missile submarines (Type 093 submarine, Type 093, Type 095 submarine, Type 095, Type 094 submarine, Type 094, Type 096 submarine, Type 096), advanced conventional attack submarines (Kilo class submarine, ''Kilo'' and Type 041 submarine, ''Yuan'' classes), aircraft carriers (Chinese aircraft carrier Liaoning, Type 001, Type 002 aircraft carrier, Type 002 and Type 003 aircraft carrier, Type 003), and helicopter carriers (Type 075 landing helicopter dock, Type 075) and large amphibious warfare vessels (Type 071 amphibious transport dock, Type 071) capable of mobilizing troops at long distances.
On the medium and low end, there would be more economical multi-role capable frigates and destroyers (Type 052 destroyer, ''Luhu'', Type 053H3 frigate, ''Jiangwei II'' and Type 054A frigate, ''Jiangkai'' classes), corvettes (Type 056 corvette, ''Jiangdao'' class), fast littoral missile attack craft (Type 037-II class missile boat, ''Houjian'', Type 037-IG class missile boat, ''Houxin'' and Houbei class missile boat, ''Houbei'' classes), various landing ships and light craft, and conventionally powered coastal patrol submarines (Type 039 submarine, ''Song'' class). The obsolete combat ships (based on 1960s designs) will be phased out in the coming decades as more modern designs enter full production.
It may take a decade for the bulk of these older ships to be retired. Until then, they will serve principally on the low end, as multi-role patrol/escort platforms. Their use could be further enhanced in the future by being used as fast transports or fire support platforms. This system of phasing out would see a reversal in the decline in quantity of PLAN vessels by 2015, and cuts in inventory after the end of the Cold War could be made up for by 2020.
Between 2001–2006 there was a rapid building and acquisition program, a trend which continued. There were more than a dozen new classes of ships built in those five years, totaling some 60 brand new ships (including landing ships and auxiliaries). Simultaneously, dozens of other ships have been either phased out of service or refitted with new equipment.
Submarines play a significant role in the development of the PLAN's future fleet. This is made evident by the construction of a new type of nuclear
The PLAN's ambitions include operating out to the first and second island chains, as far as the South Pacific near Australia, and spanning to the Aleutian islands, and operations extending to the Straits of Malacca near the Indian Ocean.Annual Report to Congress, ''Military Power of the People's Republic of China''. Retrieved 22 May 2008 The future PLAN fleet will be composed of a balance of combatant assets aimed at maximising the PLAN's fighting effectiveness.
On the high end, there would be modern destroyers, such as stealth guided missile destroyers equipped with long-range air defense missiles and anti-submarine capabilities (Type 055 destroyer, Type 055). There would be modern destroyers equipped with long-range air defense missiles (Type 052B destroyer, Type 052B, Type 052C destroyer, Type 052C, Type 052D destroyer, Type 052D and Type 051C destroyer, Type 051C, and destroyers armed with supersonic anti-ship missiles (Sovremenny class destroyer, ''Sovremenny'' class).
There would be advanced nuclear-powered attack and ballistic missile submarines (Type 093 submarine, Type 093, Type 095 submarine, Type 095, Type 094 submarine, Type 094, Type 096 submarine, Type 096), advanced conventional attack submarines (Kilo class submarine, ''Kilo'' and Type 041 submarine, ''Yuan'' classes), aircraft carriers (Chinese aircraft carrier Liaoning, Type 001, Type 002 aircraft carrier, Type 002 and Type 003 aircraft carrier, Type 003), and helicopter carriers (Type 075 landing helicopter dock, Type 075) and large amphibious warfare vessels (Type 071 amphibious transport dock, Type 071) capable of mobilizing troops at long distances.
On the medium and low end, there would be more economical multi-role capable frigates and destroyers (Type 052 destroyer, ''Luhu'', Type 053H3 frigate, ''Jiangwei II'' and Type 054A frigate, ''Jiangkai'' classes), corvettes (Type 056 corvette, ''Jiangdao'' class), fast littoral missile attack craft (Type 037-II class missile boat, ''Houjian'', Type 037-IG class missile boat, ''Houxin'' and Houbei class missile boat, ''Houbei'' classes), various landing ships and light craft, and conventionally powered coastal patrol submarines (Type 039 submarine, ''Song'' class). The obsolete combat ships (based on 1960s designs) will be phased out in the coming decades as more modern designs enter full production.
It may take a decade for the bulk of these older ships to be retired. Until then, they will serve principally on the low end, as multi-role patrol/escort platforms. Their use could be further enhanced in the future by being used as fast transports or fire support platforms. This system of phasing out would see a reversal in the decline in quantity of PLAN vessels by 2015, and cuts in inventory after the end of the Cold War could be made up for by 2020.
Between 2001–2006 there was a rapid building and acquisition program, a trend which continued. There were more than a dozen new classes of ships built in those five years, totaling some 60 brand new ships (including landing ships and auxiliaries). Simultaneously, dozens of other ships have been either phased out of service or refitted with new equipment.
Submarines play a significant role in the development of the PLAN's future fleet. This is made evident by the construction of a new type of nuclear
Al Jazeera English website
Retrieved 2 May 2021.
Chinese naval aircraft in service
PLAN – Chinese Defence Today
{{People's Liberation Army People's Liberation Army Navy, People's Liberation Army branches, 2 1950 establishments in China
maritime
Maritime may refer to:
Geography
* Maritime Alps, a mountain range in the southwestern part of the Alps
* Maritime Region, a region in Togo
* Maritime Southeast Asia
* The Maritimes, the Canadian provinces of Nova Scotia, New Brunswick, and Princ ...
service branch
Military branch (also service branch or armed service) is according to common standard a subdivision of the national armed forces of a sovereign nation or state.
Types of branches
Unified armed forces
The Canadian Armed Forces is the unifi ...
of the People's Liberation Army
The People's Liberation Army (PLA) is the principal military force of the People's Republic of China and the armed wing of the Chinese Communist Party (CCP). The PLA consists of five service branches: the Ground Force, Navy, Air Force, ...
.
The PLAN traces its lineage to naval units fighting during the Chinese Civil War
The Chinese Civil War was fought between the Kuomintang-led government of the Republic of China and forces of the Chinese Communist Party, continuing intermittently since 1 August 1927 until 7 December 1949 with a Communist victory on m ...
and was established on 23 April 1949. Throughout the 1950s and early 1960s, the Soviet Union
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, it was nominally a federal union of fifteen national ...
provided assistance to the PLAN in the form of naval advisers and export of equipment and technology.
Until the late 1980s, the PLAN was largely a riverine
A river is a natural flowing watercourse, usually freshwater, flowing towards an ocean, sea, lake or another river. In some cases, a river flows into the ground and becomes dry at the end of its course without reaching another body of wate ...
and littoral
The littoral zone or nearshore is the part of a sea, lake, or river that is close to the shore. In coastal ecology, the littoral zone includes the intertidal zone extending from the high water mark (which is rarely inundated), to coastal areas ...
force (brown-water navy
The term brown-water navy or riverine navy refers in its broadest sense to any navy, naval force capable of military operations in littoral zone waters. The term originated in the United States Navy during the American Civil War, when it refer ...
). In the 1990s, following the fall of the Soviet Union and a shift towards a more forward-oriented foreign and security policy, the leaders of the Chinese military were freed from worrying overland border disputes. Traditionally subordinated to the PLA Ground Force
''Ground Force'' was a British garden makeover television series originally broadcast by the BBC between 1997 and 2005. The series was originally hosted by Alan Titchmarsh, Charlie Dimmock and Tommy Walsh.
Production
The series was created b ...
, PLAN leaders were now able to advocate for a renewed attention towards the seas.
Chinese military officials have outlined plans to operate in the first
First or 1st is the ordinal form of the number one (#1).
First or 1st may also refer to:
*World record, specifically the first instance of a particular achievement
Arts and media Music
* 1$T, American rapper, singer-songwriter, DJ, and rec ...
and second island chains, and are working towards blue water
Maritime geography is a collection of terms used by naval military units to loosely define three maritime regions: brown water, green water, and blue water.
Definitions
The elements of maritime geography are loosely defined and their meanings hav ...
capability. Chinese strategists term the development of the PLAN from a green-water navy into "a regional blue-water defensive and offensive navy."Ronald O'Rourke, "China Naval Modernization: Implications for U.S. Navy Capabilities—Background and Issues for Congress", 10 December 2012, page 7 As the PLAN expands into a blue-water navy
A blue-water navy is a maritime force capable of operating globally, essentially across the deep waters of open oceans. While definitions of what actually constitutes such a force vary, there is a requirement for the ability to exercise sea cont ...
, regular exercises and naval patrols in the South China Sea
The South China Sea is a marginal sea of the Western Pacific Ocean. It is bounded in the north by the shores of South China (hence the name), in the west by the Indochinese Peninsula, in the east by the islands of Taiwan and northwestern Phil ...
have been increased, particularly near the Senkaku Islands
The are a group of uninhabited islands in the East China Sea, administered by Japan. They are located northeast of Taiwan, east of China, west of Okinawa Island, and north of the southwestern end of the Ryukyu Islands. They are known in main ...
in the East China Sea
The East China Sea is an arm of the Western Pacific Ocean, located directly offshore from East China. It covers an area of roughly . The sea’s northern extension between mainland China and the Korean Peninsula is the Yellow Sea, separated b ...
and the island of Taiwan
Taiwan, officially the Republic of China (ROC), is a country in East Asia, at the junction of the East and South China Seas in the northwestern Pacific Ocean, with the People's Republic of China (PRC) to the northwest, Japan to the nort ...
, which it claims. The People's Republic of China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's most populous country, with a population exceeding 1.4 billion, slightly ahead of India. China spans the equivalent of five time zones and ...
(PRC) along with the Republic of China
Taiwan, officially the Republic of China (ROC), is a country in East Asia, at the junction of the East and South China Seas in the northwestern Pacific Ocean, with the People's Republic of China (PRC) to the northwest, Japan to the northeast ...
(ROC), Vietnam
Vietnam or Viet Nam ( vi, Việt Nam, ), officially the Socialist Republic of Vietnam,., group="n" is a country in Southeast Asia, at the eastern edge of mainland Southeast Asia, with an area of and population of 96 million, making i ...
, Brunei
Brunei ( , ), formally Brunei Darussalam ( ms, Negara Brunei Darussalam, Jawi alphabet, Jawi: , ), is a country located on the north coast of the island of Borneo in Southeast Asia. Apart from its South China Sea coast, it is completely sur ...
, Malaysia
Malaysia ( ; ) is a country in Southeast Asia. The federation, federal constitutional monarchy consists of States and federal territories of Malaysia, thirteen states and three federal territories, separated by the South China Sea into two r ...
, and the Philippines
The Philippines (; fil, Pilipinas, links=no), officially the Republic of the Philippines ( fil, Republika ng Pilipinas, links=no),
* bik, Republika kan Filipinas
* ceb, Republika sa Pilipinas
* cbk, República de Filipinas
* hil, Republ ...
claims a significant amount of maritime boundary located within the South China Sea.
The People's Liberation Army Navy is composed of five branches; the Submarine Force, the Surface Force
Surface force denoted ''fs'' is the force that acts across an internal or external surface element in a material body. Surface force can be decomposed into two perpendicular components: normal forces and shear forces. A normal force acts normal ...
, the Coastal Defense Force, the Marine Corps
Marines, or naval infantry, are typically a military force trained to operate in littoral zones in support of naval operations. Historically, tasks undertaken by marines have included helping maintain discipline and order aboard the ship (refle ...
and the Naval Air Force
The Naval Air Force ( vi, Binh chủng Không quân Hải quân) is an armed service of the Vietnam People's Navy that has the function of performing tasks at sea or along the coast and islands by means of the air force such as aircraft combat a ...
. With a personnel strength of 240,000 personnel, including 15,000 marines
Marines, or naval infantry, are typically a military force trained to operate in littoral zones in support of naval operations. Historically, tasks undertaken by marines have included helping maintain discipline and order aboard the ship (refle ...
and 26,000 naval air force
The Naval Air Force ( vi, Binh chủng Không quân Hải quân) is an armed service of the Vietnam People's Navy that has the function of performing tasks at sea or along the coast and islands by means of the air force such as aircraft combat a ...
personnel, it is the second largest navy in the world in terms of tonnage which stands at 1,820,222 tonne as of 2019, only behind the United States Navy
The United States Navy (USN) is the maritime service branch of the United States Armed Forces and one of the eight uniformed services of the United States. It is the largest and most powerful navy in the world, with the estimated tonnage ...
, and has the largest number of major surface combatant
Surface combatants (or surface ships or surface vessels) are a subset of naval warships which are designed for warfare on the surface of the water, with their own weapons and armed forces. They are generally ships built to fight other ships, subma ...
s of any navy globally with an overall battle force of approximately 350 surface ship
Surface combatants (or surface ships or surface vessels) are a subset of naval warships which are designed for warfare on the surface of the water, with their own weapons and armed forces. They are generally ships built to fight other ships, subma ...
s and submarine
A submarine (or sub) is a watercraft capable of independent operation underwater. It differs from a submersible, which has more limited underwater capability. The term is also sometimes used historically or colloquially to refer to remotely op ...
s — in comparison, the United States Navy
The United States Navy (USN) is the maritime service branch of the United States Armed Forces and one of the eight uniformed services of the United States. It is the largest and most powerful navy in the world, with the estimated tonnage ...
's battle force is approximately 293 ships.
History
 The PLAN traces its lineage to units of the
The PLAN traces its lineage to units of the Republic of China Navy
The Republic of China Navy (ROCN; ), also called the ROC Navy and colloquially the Taiwan Navy, is the maritime branch of the Republic of China Armed Forces (ROCAF).
The service was formerly commonly just called the Chinese Navy during World Wa ...
(ROCN) who defected to the People's Liberation Army
The People's Liberation Army (PLA) is the principal military force of the People's Republic of China and the armed wing of the Chinese Communist Party (CCP). The PLA consists of five service branches: the Ground Force, Navy, Air Force, ...
towards the end of the Chinese Civil War
The Chinese Civil War was fought between the Kuomintang-led government of the Republic of China and forces of the Chinese Communist Party, continuing intermittently since 1 August 1927 until 7 December 1949 with a Communist victory on m ...
. In 1949, Mao Zedong
Mao Zedong pronounced ; also romanised traditionally as Mao Tse-tung. (26 December 1893 – 9 September 1976), also known as Chairman Mao, was a Chinese communist revolutionary who was the founder of the People's Republic of China (PRC) ...
asserted that "to oppose imperialist aggression, we must build a powerful navy". During the Landing Operation on Hainan Island
The Battle of Hainan Island occurred in 1950 during the final phase of the Chinese Civil War. The People's Republic of China (PRC) conducted an amphibious assault on the island in mid-April, assisted by the independent Hainan Communist movement, w ...
, the communists used wooden junks
A junk (Chinese: 船, ''chuán'') is a type of Chinese sailing ship with fully battened sails. There are two types of junk in China: northern junk, which developed from Chinese river boats, and southern junk, which developed from Austronesian ...
fitted with mountain guns
Mountain guns are artillery pieces designed for use in mountain warfare and areas where usual wheeled transport is not possible. They are generally capable of being taken apart to make smaller loads for transport by horses, humans, mules, tractor ...
as both transport and warships against the ROCN. The navy was established on 23 April 1949 by consolidating regional naval forces under Joint Staff Department command in Jiangyan
Jiangyan District () is one of three urban districts of the city of Taizhou, Jiangsu province, having been, until December 2012, a county-level city. Jiangyan is noted for being the birthplace of the former General Secretary of the Chinese Commun ...
(now in Taizhou, Jiangsu
Tàizhōu is a prefecture-level city in central Jiangsu province in eastern China. Situated on the north bank of the Yangtze River, it borders Nantong to the east, Yancheng to the north and Yangzhou to the west.
The 2020 Chinese census counted ...
).
The Naval Academy was set up at Dalian
Dalian () is a major sub-provincial port city in Liaoning province, People's Republic of China, and is Liaoning's second largest city (after the provincial capital Shenyang) and the third-most populous city of Northeast China. Located on the ...
on 22 November 1949, mostly with Soviet instructors. It then consisted of a motley collection of ships and boats acquired from the Kuomintang
The Kuomintang (KMT), also referred to as the Guomindang (GMD), the Nationalist Party of China (NPC) or the Chinese Nationalist Party (CNP), is a major political party in the Republic of China, initially on the Chinese mainland and in Tai ...
forces. The Naval Air Force
The Naval Air Force ( vi, Binh chủng Không quân Hải quân) is an armed service of the Vietnam People's Navy that has the function of performing tasks at sea or along the coast and islands by means of the air force such as aircraft combat a ...
was added two years later. By 1954 an estimated 2,500 Soviet naval advisers were in China—possibly one adviser to every thirty Chinese naval personnel—and the Soviet Union
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, it was nominally a federal union of fifteen national ...
began providing modern ships.
With Soviet assistance, the navy reorganized in 1954 and 1955 into the North Sea Fleet
The Northern Theater Command Navy (), or the North Sea Fleet (NSF; ) is one of the three fleets of the Chinese People's Liberation Army Navy, under the Northern Theater Command. In September 1950 the Qingdao Army Base was redesignated as a naval ...
, East Sea Fleet
The Eastern Theater Command Navy (), or East Sea Fleet (ESF; ), is one of the three fleets of the People's Liberation Army Navy, operating in the East China Sea under the Eastern Theater Command. It was the first naval force formed by the Peopl ...
, and South Sea Fleet
The Southern Theater Command Navy (), or the South Sea Fleet (SSF; ) is one of the three fleets of the Chinese People's Liberation Army Navy, operating in the South China Sea under the Southern Theater Command. It is headquartered in Zhanjiang, G ...
, and a corps of admirals and other naval officers was established from the ranks of the ground forces. In shipbuilding
Shipbuilding is the construction of ships and other floating vessels. It normally takes place in a specialized facility known as a shipyard. Shipbuilders, also called shipwrights, follow a specialized occupation that traces its roots to befor ...
the Soviets first assisted the Chinese, then the Chinese copied Soviet designs without assistance, and finally the Chinese produced vessels of their own design. Eventually Soviet assistance progressed to the point that a joint Sino-Soviet Pacific Ocean fleet was under discussion.
1950s and 1960s
Through the upheavals of the late 1950s and 1960s the Navy remained relatively undisturbed. Under the leadership of Minister of National DefenseLin Biao
)
, serviceyears = 1925–1971
, branch = People's Liberation Army
, rank = Marshal of the People's Republic of China Lieutenant general of the National Revolutionary Army, Republic of China
, commands ...
, large investments were made in naval construction during the frugal years immediately after the Great Leap Forward
The Great Leap Forward (Second Five Year Plan) of the People's Republic of China (PRC) was an economic and social campaign led by the Chinese Communist Party (CCP) from 1958 to 1962. CCP Chairman Mao Zedong launched the campaign to reconstruc ...
. During the Cultural Revolution
The Cultural Revolution, formally known as the Great Proletarian Cultural Revolution, was a sociopolitical movement in the People's Republic of China (PRC) launched by Mao Zedong in 1966, and lasting until his death in 1976. Its stated goal ...
, a number of top naval commissars and commanders were purged.
Naval forces were used to suppress a revolt in Wuhan
Wuhan (, ; ; ) is the capital of Hubei, Hubei Province in the China, People's Republic of China. It is the largest city in Hubei and the most populous city in Central China, with a population of over eleven million, the List of cities in China ...
in July 1967, but the service largely avoided the turmoil affecting the country. Although it paid lip service to Mao and assigned political commissars aboard ships, the Navy continued to train, build, and maintain the fleets as well the coastal defense and aviation arms, as well as in the performance of its mission.
1970s and 1980s
In the 1970s, when approximately 20 percent of the defense budget was allocated to naval forces, the Navy grew dramatically. The conventional submarine force increased from 35 to 100 boats, the number ofmissile
In military terminology, a missile is a guided airborne ranged weapon capable of self-propelled flight usually by a jet engine or rocket motor. Missiles are thus also called guided missiles or guided rockets (when a previously unguided rocket i ...
-carrying ships grew from 20 to 200, and the production of larger surface ship
Surface combatants (or surface ships or surface vessels) are a subset of naval warships which are designed for warfare on the surface of the water, with their own weapons and armed forces. They are generally ships built to fight other ships, subma ...
s, including support ships for oceangoing operations, increased. The Navy also began development of nuclear attack submarines (SSN) and nuclear-powered ballistic missile submarine
A ballistic missile submarine is a submarine capable of deploying submarine-launched ballistic missiles (SLBMs) with nuclear warheads. The United States Navy's hull classification symbols for ballistic missile submarines are SSB and SSBN – t ...
s (SSBN).
In the 1980s, under the leadership of Chief Naval Commander Liu Huaqing
Liu Huaqing (; 1 October 1916 – 14 January 2011) was Chinese revolutionary and an admiral of the People's Liberation Army Navy, who served as the third Commander-in-Chief of the Navy from 1982 through 1988. He is considered to have greatly co ...
, the navy developed into a regional naval power, though naval construction continued at a level somewhat below the 1970s rate. Liu Huaqing was an Army Officer who spent most of his career in administrative positions involving science and technology. It was not until 1988 that the People's Liberation Army Navy was led by a Naval Officer
An officer is a person who holds a position of authority as a member of an armed force or uniformed service.
Broadly speaking, "officer" means a commissioned officer, a non-commissioned officer, or a warrant officer. However, absent context ...
. Liu was also very close to Deng Xiaoping
Deng Xiaoping (22 August 1904 – 19 February 1997) was a Chinese revolutionary leader, military commander and statesman who served as the paramount leader of the People's Republic of China (PRC) from December 1978 to November 1989. After CC ...
as his modernization efforts were very much in keeping with Deng's national policies.Cole, Bernard D. ''The Great Wall at Sea'' Annapolis: Naval Institute Press, 2001
While under his leadership Naval construction yards produced fewer ships than the 1970s, greater emphasis was placed on technology and qualitative improvement. Modernization efforts also encompassed higher educational and technical standards for personnel; reformulation of the traditional coastal defense doctrine and force structure in favor of more green-water operations; and training in naval combined-arms
Combined arms is an approach to warfare that seeks to integrate different combat arms of a military to achieve mutually complementary effects (for example by using infantry and armour in an urban environment in which each supports the other) ...
operations involving submarine, surface, naval aviation
Naval aviation is the application of military air power by navies, whether from warships that embark aircraft, or land bases.
Naval aviation is typically projected to a position nearer the target by way of an aircraft carrier. Carrier-based a ...
, and coastal defense forces.
Examples of the expansion of China's capabilities were the 1980 recovery of an intercontinental ballistic missile
An intercontinental ballistic missile (ICBM) is a ballistic missile with a range greater than , primarily designed for nuclear weapons delivery (delivering one or more thermonuclear warheads). Conventional, chemical, and biological weapons c ...
(ICBM) in the Western Pacific by a twenty-ship fleet, extended naval operations in the South China Sea
The South China Sea is a marginal sea of the Western Pacific Ocean. It is bounded in the north by the shores of South China (hence the name), in the west by the Indochinese Peninsula, in the east by the islands of Taiwan and northwestern Phil ...
in 1984 and 1985, and the visit of two naval ships to three South Asian nations in 1985. In 1982 the navy conducted a successful test of an underwater-launched ballistic missile
A ballistic missile is a type of missile that uses projectile motion to deliver warheads on a target. These weapons are guided only during relatively brief periods—most of the flight is unpowered. Short-range ballistic missiles stay within the ...
. The navy also had some success in developing a variety of surface-to-surface
A surface-to-surface missile (SSM) or ground-to-ground missile (GGM) is a missile designed to be launched from the ground or the sea and strike targets on land or at sea. They may be fired from hand-held or vehicle mounted devices, from fixed ins ...
and air-to-surface missile
An air-to-surface missile (ASM) or air-to-ground missile (AGM) is a missile designed to be launched from military aircraft at targets on land or sea. There are also unpowered guided glide bombs not considered missiles. The two most common prop ...
s, improving basic capabilities.
In 1986 the Navy's order of battle
In modern use, the order of battle of an armed force participating in a military operation or campaign shows the hierarchical organization, command structure, strength, disposition of personnel, and equipment of units and formations of the armed ...
included two ''Xia''-class SSBN
A ballistic missile submarine is a submarine capable of deploying submarine-launched ballistic missiles (SLBMs) with nuclear warheads. The United States Navy's hull classification symbols for ballistic missile submarines are SSB and SSBN – ...
s armed with twelve CSS-N-3 missiles and three Han-class SSNs armed with six SY-2
The SY (), and HY () series were early anti-ship cruise missiles (ASCM) developed by the People's Republic of China from the Soviet P-15 Termit missile. They entered service in the late 1960s and remained the main ASCMs deployed by the People's L ...
cruise missile
A cruise missile is a guided missile used against terrestrial or naval targets that remains in the atmosphere and flies the major portion of its flight path at approximately constant speed. Cruise missiles are designed to deliver a large warhe ...
s. In the late 1980s, major deficiencies reportedly remained in anti-submarine warfare
Anti-submarine warfare (ASW, or in older form A/S) is a branch of underwater warfare that uses surface warships, aircraft, submarines, or other platforms, to find, track, and deter, damage, or destroy enemy submarines. Such operations are t ...
, mine warfare Mine warfare refers to the use of different types of explosive devices:
*Land mine, a weight-triggered explosive device intended to maim or kill people or to disable or destroy vehicles
*Minelaying, deployment of explosive mines at sea
**Naval mine ...
, naval electronics (including electronic countermeasures
An electronic countermeasure (ECM) is an electrical or electronic device designed to trick or deceive radar, sonar, or other detection systems, like infrared (IR) or lasers. It may be used both offensively and defensively to deny targeting info ...
equipment), and naval aviation
Naval aviation is the application of military air power by navies, whether from warships that embark aircraft, or land bases.
Naval aviation is typically projected to a position nearer the target by way of an aircraft carrier. Carrier-based a ...
capabilities.
The PLA Navy was ranked in 1987 as the third largest navy in the world, although naval personnel had comprised only 12 percent of PLA strength. In 1987 the Navy consisted (as it does now) of the naval headquarters in Beijing; three fleet commands – the North Sea Fleet
The Northern Theater Command Navy (), or the North Sea Fleet (NSF; ) is one of the three fleets of the Chinese People's Liberation Army Navy, under the Northern Theater Command. In September 1950 the Qingdao Army Base was redesignated as a naval ...
, based at Qingdao
Qingdao (, also spelled Tsingtao; , Mandarin: ) is a major city in eastern Shandong Province. The city's name in Chinese characters literally means " azure island". Located on China's Yellow Sea coast, it is a major nodal city of the One Belt ...
, Shandong; the East Sea Fleet
The Eastern Theater Command Navy (), or East Sea Fleet (ESF; ), is one of the three fleets of the People's Liberation Army Navy, operating in the East China Sea under the Eastern Theater Command. It was the first naval force formed by the Peopl ...
, based at Ningbo
Ningbo (; Ningbonese: ''gnin² poq⁷'' , Standard Mandarin pronunciation: ), formerly romanized as Ningpo, is a major sub-provincial city in northeast Zhejiang province, People's Republic of China. It comprises 6 urban districts, 2 sate ...
; and the South Sea Fleet
The Southern Theater Command Navy (), or the South Sea Fleet (SSF; ) is one of the three fleets of the Chinese People's Liberation Army Navy, operating in the South China Sea under the Southern Theater Command. It is headquartered in Zhanjiang, G ...
, based at Zhanjiang
Zhanjiang (), historically spelled Tsamkong, is a prefecture-level city at the southwestern end of Guangdong province, People's Republic of China, facing Haikou city to the south.
As of the 2020 census, its population was 6,981,236 (6,994,832 ...
, Guangdong – and about 1,000 ships of which only approximately 350 are ocean going. The rest are small patrol or support craft.
The 350,000-person Navy included Naval Air Force units of 34,000 men, the Coastal Defense Forces of 38,000, and the Marine Corps of 56,500. Navy Headquarters, which controlled the three fleet commands, was subordinate to the PLA General Staff Department. In 1987, China's 1,500 km coastline
The coast, also known as the coastline or seashore, is defined as the area where land meets the ocean, or as a line that forms the boundary between the land and the coastline. The Earth has around of coastline. Coasts are important zones in n ...
was protected by approximately 70 diesel-powered Romeo
Romeo Montague () is the male protagonist of William Shakespeare's tragedy ''Romeo and Juliet''. The son of Lord Montague and his wife, Lady Montague, he secretly loves and marries Juliet, a member of the rival House of Capulet, through a priest ...
- and Whiskey
Whisky or whiskey is a type of distilled alcoholic beverage made from fermented grain mash. Various grains (which may be malted) are used for different varieties, including barley, corn, rye, and wheat. Whisky is typically aged in wooden cask ...
-class submarines, which could remain at sea only a limited time.
Inside this protective ring and within range of shore-based aircraft were destroyers
In navy, naval terminology, a destroyer is a fast, manoeuvrable, long-endurance warship intended to escort
larger vessels in a Naval fleet, fleet, convoy or Carrier battle group, battle group and defend them against powerful short range attack ...
and frigates
A frigate () is a type of warship. In different eras, the roles and capabilities of ships classified as frigates have varied somewhat.
The name frigate in the 17th to early 18th centuries was given to any full-rigged ship built for speed and ...
mounting Styx
In Greek mythology, Styx (; grc, Στύξ ) is a river that forms the boundary between Earth (Gaia) and the Underworld. The rivers Acheron, Cocytus, Lethe, Phlegethon, and Styx all converge at the centre of the underworld on a great marsh, whic ...
anti-ship missiles, depth-charge projector
A depth charge is an anti-submarine warfare (ASW) weapon. It is intended to destroy a submarine by being dropped into the water nearby and detonating, subjecting the target to a powerful and destructive hydraulic shock. Most depth charges use ...
s, and guns up to 130 mm. Any invader penetrating the destroyer and frigate protection would have been swarmed by almost 900 fast-attack craft. Stormy weather limited the range of these small boats, however, and curtailed air support
In military tactics, close air support (CAS) is defined as air action such as air strikes by fixed or rotary-winged aircraft against hostile targets near friendly forces and require detailed integration of each air mission with fire and movement ...
. Behind the inner ring were Coastal Defense Force personnel operating naval shore batteries of Styx missiles and guns, backed by ground force units deployed in depth.
1990s and 2000s
As the 21st century approached, the PLAN began to transition to an off-shore defensive strategy that entailed more out-of-area operations away from its traditional territorial waters. Between 1989 and 1993, the training ship ''Zhenghe'' paid ports visits to Hawaii, Thailand, Bangladesh, Pakistan, and India. PLAN vessels visited Vladivostok in 1993, 1994, 1995, and 1996. PLAN task groups also paid visits to Indonesia in 1995; North Korea in 1997; New Zealand, Australia, and the Philippines in 1998; Malaysia, Tanzania, South Africa, the United States, and Canada in 2000; and India, Pakistan, France, Italy, Germany, Britain, Hong Kong, Australia, and New Zealand in 2001. In March 1997, the ''Luhu''-class guided missile destroyer ''Harbin'', the ''Luda''-class guided missile destroyer ''Zhuhai
Zhuhai (, ; Yale: ''Jyūhói''), also known as Chuhai is a prefecture-level city located on the west bank of Pearl River estuary on the central coast of southern Guangdong province, People's Republic of China, on the southeastern edge of Pearl ...
'', and the replenishment oiler
A replenishment oiler or replenishment tanker is a naval auxiliary ship with fuel tanks and dry cargo holds which can supply both fuel and dry stores during underway replenishment (UNREP) at sea. Many countries have used replenishment oilers.
The ...
''Nancang'' began the PLA Navy's first circumnavigation of the Pacific Ocean, a 98-day voyage with port visits to Mexico, Peru, Chile, and the United States, including Pearl Harbor
Pearl Harbor is an American lagoon harbor on the island of Oahu, Hawaii, west of Honolulu. It was often visited by the Naval fleet of the United States, before it was acquired from the Hawaiian Kingdom by the U.S. with the signing of the Re ...
and San Diego
San Diego ( , ; ) is a city on the Pacific Ocean coast of Southern California located immediately adjacent to the Mexico–United States border. With a 2020 population of 1,386,932, it is the List of United States cities by population, eigh ...
. The flotilla was under the command of Vice Admiral Wang Yongguo, the commander-in-chief of the South Sea Fleet.
The ''Luhu''-class guided missile destroyer ''Qingdao'' and the replenishment oiler
A replenishment oiler or replenishment tanker is a naval auxiliary ship with fuel tanks and dry cargo holds which can supply both fuel and dry stores during underway replenishment (UNREP) at sea. Many countries have used replenishment oilers.
The ...
''Taicang'' completed the PLA Navy's first circumnavigation of the world ''(pictured)'', a 123-day voyage covering between 15 May – 23 September 2002. Port visits included Changi, Singapore; Alexandria, Egypt
Alexandria ( or ; ar, ٱلْإِسْكَنْدَرِيَّةُ ; grc-gre, Αλεξάνδρεια, Alexándria) is the second largest city in Egypt, and the largest city on the Mediterranean coast. Founded in by Alexander the Great, Alexandria ...
; Aksis, Turkey
Turkey ( tr, Türkiye ), officially the Republic of Türkiye ( tr, Türkiye Cumhuriyeti, links=no ), is a list of transcontinental countries, transcontinental country located mainly on the Anatolia, Anatolian Peninsula in Western Asia, with ...
; Sevastopol, Ukraine
Sevastopol (; uk, Севасто́поль, Sevastópolʹ, ; gkm, Σεβαστούπολις, Sevastoúpolis, ; crh, Акъя́р, Aqyár, ), sometimes written Sebastopol, is the largest city in Crimea, and a major port on the Black Sea ...
; Piraeus, Greece
Piraeus ( ; el, Πειραιάς ; grc, Πειραιεύς ) is a port city within the Athens urban area ("Greater Athens"), in the Attica region of Greece. It is located southwest of Athens' city centre, along the east coast of the Saronic ...
; Lisbon, Portugal
Lisbon (; pt, Lisboa ) is the capital and largest city of Portugal, with an estimated population of 544,851 within its administrative limits in an area of 100.05 km2. Lisbon's urban area extends beyond the city's administrative limits w ...
; Fortaleza, Brazil; Guayaquil, Ecuador; Callao, Peru; and Papeete in French Polynesia. The PLA naval vessels participated in naval exercises with the French Navy, French frigates Nivôse (F 732), ''Nivôse'' and Prairial (F 731), ''Prairial'', as well as exercises with the Peruvian Navy. The flotilla was under the command of Vice Admiral Ding Yiping, the commander-in-chief of the North Sea Fleet, and Xiao (rank), Captain Li Yujie was the commanding officer of the ''Qingdao''.
Overall, between 1985 and 2006, PLAN naval vessels visited 18 Asian-Pacific nations, 4 South American nations, 8 European nations, 3 African nations, and 3 North American nations. In 2003, the PLAN conducted its first joint naval exercises during separate visits to Pakistan and India. Bi-lateral naval exercises were also carried out with exercises with the French, British, Australian, Canadian, Philippine, and United States navies.
On 26 December 2008, the PLAN dispatched a task group consisting of the Type 052C destroyer, guided missile destroyer ''Haikou'' (flagship), the Type 052B destroyer, guided missile destroyer ''Wuhan'', and the supply ship Qiandaohu class replenishment ship, ''Weishanhu'' to the Gulf of Aden to participate in Piracy in Somalia, anti-piracy operations off the coast of Somalia. A team of 16 People's Liberation Army Special Operations Forces, Chinese Special Forces members from its Marine Corps armed with attack helicopters were on board. Since then, China has maintained a three-ship flotilla of two warships and one supply ship in the Gulf of Aden by assigning ships to the Gulf of Aden on a three monthly basis. Other recent PLAN incidents include the 2001 Hainan Island incident, a Chinese submarine 361, major submarine accident in 2003, and naval incidents involving the U.S. Military Sealift Command, MSC-operated ocean surveillance ships and during 2009. At the occasion of the 60th anniversary of the PLAN, 52 to 56 vessels were shown in manoeuvres off Qingdao in April 2009 including previously unseen nuclear submarines.
The demonstration was seen as a sign of the growing status of China, while the Chairman of the Central Military Commission (China), CMC Chairman, Hu Jintao, indicated that China is neither seeking regional hegemony nor entering an arms race.
Predictions by Western analysts that the PLAN would outnumber the USN submarine force as early as 2011 have failed to come true because the PRC curtailed both imports and domestic production of submarines.
2010s and 2020s

 Beginning in 2009, China ordered 4 Zubr-class LCAC from Ukraine and bought 4 more from the Hellenic Navy (Greece). These hovercraft/LCACs are built to send troops and armored vehicles (tanks, etc.) onto beaches in a fast manner, acting as a landing craft, and were viewed to be a direct threat to Taiwan's pro-independence movement as well as the conflict over
Beginning in 2009, China ordered 4 Zubr-class LCAC from Ukraine and bought 4 more from the Hellenic Navy (Greece). These hovercraft/LCACs are built to send troops and armored vehicles (tanks, etc.) onto beaches in a fast manner, acting as a landing craft, and were viewed to be a direct threat to Taiwan's pro-independence movement as well as the conflict over Senkaku Islands
The are a group of uninhabited islands in the East China Sea, administered by Japan. They are located northeast of Taiwan, east of China, west of Okinawa Island, and north of the southwestern end of the Ryukyu Islands. They are known in main ...
. China is continually shifting the power balance in Asia by building up the Navy's Submarines, Amphibious warfare, and surface warfare capabilities.
Between 5–12 July 2013, a seven-ship task force from the North Sea Fleet
The Northern Theater Command Navy (), or the North Sea Fleet (NSF; ) is one of the three fleets of the Chinese People's Liberation Army Navy, under the Northern Theater Command. In September 1950 the Qingdao Army Base was redesignated as a naval ...
joined warships from the Russian Pacific Fleet to participate in Joint Sea 2013, bilateral naval maneuvers held in the Peter the Great Bay of the Sea of Japan. To date, Joint Sea 2013 was the largest naval drill yet undertaken by the People's Liberation Army Navy with a foreign navy.
On 2 April 2015, during the aftermath of the 2014–15 Yemeni coup d'état, violent aftermath of a 2014–15 Yemeni coup d'état, coup d'état in Yemen and amid an 2015 military intervention in Yemen, international bombing campaign, the PLAN helped ten countries get their citizens out of Yemen safely, evacuating them aboard a missile frigate from the Southern Yemen offensive (2015), besieged port city of Aden. The operation was described by Reuters as "the first time that China's military has helped other countries evacuate their people during an international crisis".
China's participation in international maritime exercises is also increasing. In Exercise RIMPAC#RIMPAC 2014, RIMPAC 2014, China was invited to send ships from their People's Liberation Army Navy; marking not only the first time China participated in a RIMPAC exercise but also the first time China participated in a large-scale United States-led naval drill. On 9 June 2014, China confirmed it would be sending four ships to the exercise, a destroyer, frigate, supply ship, & hospital ship. In April 2016, the People's Republic of China was also invited to RIMPAC 2016 despite the tension in South China Sea.
PRC military expert Yin Zhuo said that due to present weaknesses in the PLAN's ability to replenish their ships at sea, their future aircraft carriers will be forced to operate in pairs.
In a TV interview, Zhang Zhaozhong (military official), Zhang Zhaozhong suggest otherwise, saying China is "unlikely to put all her eggs in one basket" and that the navy will likely rotate between carriers rather than deploy them all at once.
The PLAN continued its expansion into the 2020s, increasing its operational capacity, commissioning new ships, and constructing naval facilities. Observers note that the PLAN's ongoing modernization is intended to build up the Chinese surface fleet and fix existing issues that limit the capability of the PLAN. Observers have noted that the PLAN's expansion will allow it to project Chinese power in the South China Sea and allow for the navy to counter the USN's operations in Asia. Chinese naval capability increased substantially in the 2010s and 2020s. According to the US-based think tank RAND Corporation, PLAN enjoyed major advantages in terms of naval technologies, missiles, and tonnage against regional rivals such as Taiwan, Japan, Vietnam, the Philippines, and India. And analysts believe China will further improve its power projection capability to challenge the United State Navy in the Western Pacific Ocean, western Pacific.
Organization
 The PLAN is organized into several departments for purposes of command, control and coordination. Main operating forces are organized into fleets, each with its own headquarters, a commander (a Rear Admiral or Vice Admiral) and a Political Commisar. All PLAN headquarters are subordinate to the PLA Joint Staff Department and the Chairman of the Central Military Commission.
The PLAN is organized into several departments for purposes of command, control and coordination. Main operating forces are organized into fleets, each with its own headquarters, a commander (a Rear Admiral or Vice Admiral) and a Political Commisar. All PLAN headquarters are subordinate to the PLA Joint Staff Department and the Chairman of the Central Military Commission.
Fleets
The People's Liberation Army Navy is divided into three fleets: * TheNorth Sea Fleet
The Northern Theater Command Navy (), or the North Sea Fleet (NSF; ) is one of the three fleets of the Chinese People's Liberation Army Navy, under the Northern Theater Command. In September 1950 the Qingdao Army Base was redesignated as a naval ...
, based in the Yellow Sea and headquartered in Qingdao
Qingdao (, also spelled Tsingtao; , Mandarin: ) is a major city in eastern Shandong Province. The city's name in Chinese characters literally means " azure island". Located on China's Yellow Sea coast, it is a major nodal city of the One Belt ...
, Shandong Province.
* The East Sea Fleet
The Eastern Theater Command Navy (), or East Sea Fleet (ESF; ), is one of the three fleets of the People's Liberation Army Navy, operating in the East China Sea under the Eastern Theater Command. It was the first naval force formed by the Peopl ...
, based in the East China Sea
The East China Sea is an arm of the Western Pacific Ocean, located directly offshore from East China. It covers an area of roughly . The sea’s northern extension between mainland China and the Korean Peninsula is the Yellow Sea, separated b ...
and headquartered in Ningbo
Ningbo (; Ningbonese: ''gnin² poq⁷'' , Standard Mandarin pronunciation: ), formerly romanized as Ningpo, is a major sub-provincial city in northeast Zhejiang province, People's Republic of China. It comprises 6 urban districts, 2 sate ...
, Zhejiang Province.
* The South Sea Fleet
The Southern Theater Command Navy (), or the South Sea Fleet (SSF; ) is one of the three fleets of the Chinese People's Liberation Army Navy, operating in the South China Sea under the Southern Theater Command. It is headquartered in Zhanjiang, G ...
, based in the South China Sea
The South China Sea is a marginal sea of the Western Pacific Ocean. It is bounded in the north by the shores of South China (hence the name), in the west by the Indochinese Peninsula, in the east by the islands of Taiwan and northwestern Phil ...
and headquartered in Zhanjiang
Zhanjiang (), historically spelled Tsamkong, is a prefecture-level city at the southwestern end of Guangdong province, People's Republic of China, facing Haikou city to the south.
As of the 2020 census, its population was 6,981,236 (6,994,832 ...
, Guangdong Province.
Each fleet consists of surface forces (destroyers, frigates, amphibious vessels etc.), submarine forces, coastal defence units, and aircraft.
Branches
PLAN Surface Force
 The People's Liberation Army Surface Force consists of all surface combatant, surface warships in service with the PLAN. They are organised into flotillas spread across the three main fleets.
The People's Liberation Army Surface Force consists of all surface combatant, surface warships in service with the PLAN. They are organised into flotillas spread across the three main fleets.
PLAN Submarine Force
The People's Liberation Army Navy Submarine Force consists of all nuclear submarine, nuclear and diesel-electric submarines in service with the PLAN. They are organised into flotillas spread across the three main fleets. The PRC is the last of the permanent members of the United Nations Security Council which has not conducted an operationalballistic missile submarine
A ballistic missile submarine is a submarine capable of deploying submarine-launched ballistic missiles (SLBMs) with nuclear warheads. The United States Navy's hull classification symbols for ballistic missile submarines are SSB and SSBN – t ...
patrol, because of institutional problems. It operates a fleet of 68 submarines.
PLAN Coastal Defence Force
The PLAN Coastal Defence Force is a land-based branch of the PLAN in charge of coastal defence and fortification, coastal defence, with a strength of around 25,000 personnel. Also known as the coastal defense troops, they serve to defend China's coastal and littoral areas from invasion via landing operation, amphibious landings or Airstrike, air attacks. Between the 1950s and 1960s, the Coastal Defense Force was primarily assigned to repel anyKuomintang
The Kuomintang (KMT), also referred to as the Guomindang (GMD), the Nationalist Party of China (NPC) or the Chinese Nationalist Party (CNP), is a major political party in the Republic of China, initially on the Chinese mainland and in Tai ...
attempts to infiltrate, invade and harass the Chinese coastline. After the Sino-Soviet split and the abandonment of Project National Glory, KMT's plans to recapture the Mainland, the Coastal Defense Force was focused on defending China's coast from a possible Soviet sea-borne invasion throughout the 1960s to 1980s.
With the fall of the Soviet Union, the threat of an amphibious invasion of China has diminished and therefore the branch is often considered to no longer be a vital component of the PLAN, especially as the surface warships of the PLAN continue to improve in terms of anti-ship and air-defence capabilities and the PLAN's power projection begins to extend beyond the first island chain.
Today the primary weapons of the coastal defense troops are the HY-2, YJ-82 and C-602 anti-ship missiles.
PLAN Marine Corps

 The PLAN Marine Corps was originally established in the 1950s and then re-established in 1979 under PLAN organisation. It consists of around 20,000
The PLAN Marine Corps was originally established in the 1950s and then re-established in 1979 under PLAN organisation. It consists of around 20,000 marines
Marines, or naval infantry, are typically a military force trained to operate in littoral zones in support of naval operations. Historically, tasks undertaken by marines have included helping maintain discipline and order aboard the ship (refle ...
, and is based in the South China Sea
The South China Sea is a marginal sea of the Western Pacific Ocean. It is bounded in the north by the shores of South China (hence the name), in the west by the Indochinese Peninsula, in the east by the islands of Taiwan and northwestern Phil ...
with the South Sea Fleet
The Southern Theater Command Navy (), or the South Sea Fleet (SSF; ) is one of the three fleets of the Chinese People's Liberation Army Navy, operating in the South China Sea under the Southern Theater Command. It is headquartered in Zhanjiang, G ...
. The Marine Corps are considered elite troops, and are rapid deployment forces trained primarily in amphibious warfare and sometimes as paratroopers to establish a beachhead or act as a spearhead during assault operations against enemy targets.
The marines are equipped with the standard QBZ-95, Type 95 assault rifles as well as other small arms and personnel equipment, and a blue/littoral camouflage uniform as standard. The marines are also equipped with amphibious vehicle, amphibious armoured fighting vehicles (including amphibious light tanks such as the Type 63 (tank), Type 63, assault gun, assault vehicles such as the Type 05 amphibious fighting vehicle#Variants, ZTD-05 and infantry fighting vehicle, IFVs such as Type 05 amphibious fighting vehicle#Variants, ZBD-05), military helicopter, helicopters, naval artillery, anti-aircraft weapon systems and short range surface-to-air missiles.
With the PLAN's accelerating efforts to expand its capabilities beyond territorial waters, it would be likely for the Marine Corps to play a greater role in terms of being an offshore expeditionary warfare, expeditionary force similar to the United States Marine Corps, USMC and Royal Marines.
PLA Naval Air Force
The People's Liberation Army Naval Air Force (PLANAF) is thenaval aviation
Naval aviation is the application of military air power by navies, whether from warships that embark aircraft, or land bases.
Naval aviation is typically projected to a position nearer the target by way of an aircraft carrier. Carrier-based a ...
branch of the PLAN and has a strength of around 25,000 personnel and 690 aircraft. It operates similar hardwares to the People's Liberation Army Air Force, including fighter aircraft, bombers, attack aircraft, tanker (aircraft), tankers, reconnaissance aircraft, reconnaissance/airborne early warning and control, early warning aircraft, electronic warfare aircraft, maritime patrol aircraft, military transport aircraft, transport aircraft and helicopters of various roles.
The PLA Naval Air Force has traditionally operated from coastal air bases, and received older aircraft than the PLAAF with less ambitious steps towards modernization of the People's Liberation Army, mass modernization. Advancements in new technologies, weaponry and aircraft acquisition were made after 2000. With the introduction of China's first aircraft carrier, ''Chinese aircraft carrier Liaoning, Liaoning'', in 2012, the Naval Air Force is conducting carrier-based aircraft, carrier-based operations for the first time with the goal of building carrier battle group-focused blue water navy, blue water capabilities.
The PLANAF naval air bases include:
* North Sea Fleet: Dalian
Dalian () is a major sub-provincial port city in Liaoning province, People's Republic of China, and is Liaoning's second largest city (after the provincial capital Shenyang) and the third-most populous city of Northeast China. Located on the ...
, Qingdao
Qingdao (, also spelled Tsingtao; , Mandarin: ) is a major city in eastern Shandong Province. The city's name in Chinese characters literally means " azure island". Located on China's Yellow Sea coast, it is a major nodal city of the One Belt ...
, Huludao, Jinxi, Jiyuan, Laiyang, Jiaoxian, Xingtai, Laishan, Anyang, Changzhi, Liangxiang and Shanhaiguan District, Shan Hai Guan
* East Sea Fleet: Danyang, Jiangsu, Danyang, Daishan, Shanghai (Dachang), Ningbo
Ningbo (; Ningbonese: ''gnin² poq⁷'' , Standard Mandarin pronunciation: ), formerly romanized as Ningpo, is a major sub-provincial city in northeast Zhejiang province, People's Republic of China. It comprises 6 urban districts, 2 sate ...
, Luqiao District, Luqiao, Feidong and Shitangqiao
* South Sea Fleet: Foluo, Haikou, Lingshui Li Autonomous County, Lingshui, Sanya, Guiping, Jialaishi and Yongzhou, Lingling
Relationship with other maritime organizations of China
The PLAN is complemented by paramilitary maritime services such as the China Coast Guard. The Chinese Coast Guard was previously not under an independent command, considered part of the People's Armed Police, under the local (provincial) border defense command, prior to its reorganization and consolidation as an unified service. It was formed from the integration of several formerly separate services such as China Marine Surveillance (CMS), General Administration of Customs, Armed Police, Maritime law enforcement agencies in China#Fisheries Law Enforcement Command, China Fishery Law Enforcement and local maritime militia. The CMS performed mostly coastal and ocean search and rescue or patrols, and received quite a few large patrol ships that significantly enhanced their operations; while Customs, militia, Armed Police and Fishery Law Enforcement operated hundreds of small patrol craft. For maritime patrol services, these craft are usually quite well armed with machine guns and 37mm antiaircraft guns. In addition, these services operated their own small aviation fleets to assist their maritime patrol capabilities, with Customs and CMS operating a handful of Harbin Z-9 helicopters, and a maritime patrol aircraft based on the Harbin Y-12 STOL transport. Every coastal province has 1 to 3 Coast Guard squadrons: * 3 Squadrons: Fujian, Guangdong * 2 Squadrons: Liaoning, Shandong, Zhejiang, Hainan, Guangxi * 1 Squadron: Heibei, Tianjin, Jiangsu, ShanghaiRanks
The ranks in the People's Liberation Army Navy are similar to those of the People's Liberation Army Ground Force. The current system of officer ranks and insignia dates from 1988 and is a revision of the ranks and insignia used from 1955 to 1965. The rank of Hai Jun Yi Ji Shang Jiang (First Class Admiral) was never held and was abolished in 1994. With the official introduction of the Type 07 uniforms all officer insignia are on either shoulders or sleeves depending on the type of uniform used. The current system of enlisted ranks and insignia dates from 1998.Commissioned officer ranks
The rank insignia of commissioned officers.Other ranks
The rank insignia of non-commissioned officers and Enlisted rank, enlisted personnel.Commanders
* Xiao Jinguang (January 1950 − January 1980) * Ye Fei (January 1980 – August 1982) *Liu Huaqing
Liu Huaqing (; 1 October 1916 – 14 January 2011) was Chinese revolutionary and an admiral of the People's Liberation Army Navy, who served as the third Commander-in-Chief of the Navy from 1982 through 1988. He is considered to have greatly co ...
(August 1982 – January 1988)
* Zhang Lianzhong (January 1988 – November 1996)
* Shi Yunsheng (November 1996 – June 2003)
* Zhang Dingfa (June 2003 – August 2006)
* Wu Shengli (August 2006 – January 2017)
* Shen Jinlong (January 2017 – September 2021)
* Dong Jun (September 2021 – present)
Contemporary topics
Strategy, plans, priorities

 The People's Liberation Army Navy has become more prominent in recent years owing to a change in Chinese strategic priorities. The new strategic threats include possible conflict with the United States and/or a resurgent Japan in areas such as the Taiwan Strait or the
The People's Liberation Army Navy has become more prominent in recent years owing to a change in Chinese strategic priorities. The new strategic threats include possible conflict with the United States and/or a resurgent Japan in areas such as the Taiwan Strait or the South China Sea
The South China Sea is a marginal sea of the Western Pacific Ocean. It is bounded in the north by the shores of South China (hence the name), in the west by the Indochinese Peninsula, in the east by the islands of Taiwan and northwestern Phil ...
. As part of its overall program of naval modernization, the PLAN has a long-term plan of developing a blue water navy. Robert D. Kaplan has said that it was the collapse of the Soviet Union that allowed China to transfer resources from its army to its navy and other force projection assets.
China is constructing a major underground nuclear submarine, nuclear submarine base near Sanya, Hainan. In December 2007 the first Type 094 submarine was moved to Sanya.
The Daily Telegraph on 1 May 2008 reported that tunnels were being built into hillsides which could be capable of hiding up to 20 nuclear submarines from spy satellites. According to the Western news media the base is reportedly to help China project seapower well into the Pacific Ocean area, including challenging United States naval power.
During a 2008 interview with the BBC, Major General Qian Lihua, a senior Chinese defense official, stated that the PLAN aspired to possess a small number of aircraft carriers to allow it to expand China's air defense perimeter. According to Qian the important issue was not whether China had an aircraft carrier, but what it did with it. On 13 January 2009, Adm. Robert F. Willard, head of the U.S. Pacific Command, called the PLAN's modernization "aggressive," and that it raised concerns in the region. On 15 July 2009, Senator Jim Webb of the Senate Foreign Relations Committee declared that only the "United States has both the stature and the national power to confront the obvious imbalance of power that China brings" to situations such as the claims to the Spratly Islands, Spratly and Paracel Islands, Paracel islands.
Ronald O'Rourke of the Congressional Research Service wrote in 2009 that the PLAN "continues to exhibit limitations or weaknesses in several areas, including capabilities for sustained operations by larger formations in distant waters, joint operations with other parts of China’s military, C4ISR systems, anti-air warfare (AAW), antisubmarine warfare (ASW), MCM, and a dependence on foreign suppliers for certain key ship components."
In 1998 China purchased the discarded Ukrainian ship Varyag and began retrofitting it for naval deployment. On 25 September 2012, the People's Liberation Army Navy took delivery of China's first aircraft carrier, the Chinese aircraft carrier Liaoning, Liaoning. The 60,000-ton ship can accommodate 33 fixed wing aircraft. It is widely speculated that these aircraft will be the Shenyang J-15, J15 fighter (the Chinese version of Russia's SU-33).
In September 2015, satellite images showed that China may have started constructing its first indigenous Type 002 aircraft carrier. At the time, the layout suggested to be displacement of 50,000 tons and a hull to have a length of about 240 m and a beam of about 35 m. The incomplete bow suggests a length of at least 270 m for the completed hull. In April 2017 the carrier was launched.
Japan has raised concerns about the PLAN's growing capability and the lack of transparency as its naval strength keeps on expanding. China has reportedly entered into service the world's first anti-ship ballistic missile called DF-21D. The potential threat from the DF-21D against U.S. aircraft carriers has reportedly caused major changes in U.S. strategy.
In June 2017 China launched a new type of large destroyer, the Type 055 destroyer. The new destroyer is, with its dimension of 180 meter and over 12,000 tons fully loaded, the second largest destroyer class in the world after the American Zumwalt-class destroyer.
Comparison to US Navy
The strength of PLAN is often compared to that of the US Navy. PLAN is the second largest navy in the world in terms of tonnage which stands at 1,820,222 tonne as of 2019, only behind theUnited States Navy
The United States Navy (USN) is the maritime service branch of the United States Armed Forces and one of the eight uniformed services of the United States. It is the largest and most powerful navy in the world, with the estimated tonnage ...
. PLAN has the largest number of major surface combatant
Surface combatants (or surface ships or surface vessels) are a subset of naval warships which are designed for warfare on the surface of the water, with their own weapons and armed forces. They are generally ships built to fight other ships, subma ...
s of any navy globally with an overall battle force of approximately 350 surface ship
Surface combatants (or surface ships or surface vessels) are a subset of naval warships which are designed for warfare on the surface of the water, with their own weapons and armed forces. They are generally ships built to fight other ships, subma ...
s and submarine
A submarine (or sub) is a watercraft capable of independent operation underwater. It differs from a submersible, which has more limited underwater capability. The term is also sometimes used historically or colloquially to refer to remotely op ...
s — in comparison, the United States Navy
The United States Navy (USN) is the maritime service branch of the United States Armed Forces and one of the eight uniformed services of the United States. It is the largest and most powerful navy in the world, with the estimated tonnage ...
's battle force is approximately 293 ships.
Attempts have been made to compare PLAN's firepower with the USN. A 2019 review found the USN fleet was able to deploy more "battle force missiles" (BFMs), defined as those missiles that contribute to battle missions, than the PLAN: USN fleet could deploy 11,000 BFMs, compared to 5250 BFMs for PLAN and 3326 BFMs for the Russian Navy. A 2016 review concluded that PLAN's missiles had higher firepower than the USN's, measured in terms of "strike-mile", the ability to delivery a warhead using anti-ship missiles (ASM) across a given distance.
The review used the following formula for every ASM the navy had in its inventory:
:Total strike-miles=(Range of an ASM x Warhead weight of an ASM) x Number of such missiles carried by a warship x Number of such warships in the navy
It concluded the total firepower of the PLAN was 77 million strike-miles compared to 17 million strike-miles of the USN.
Territorial disputes
Spratly Islands dispute
The Spratly Islands dispute is a territorial dispute over the ownership of the Spratly Islands, a group of islands located in theSouth China Sea
The South China Sea is a marginal sea of the Western Pacific Ocean. It is bounded in the north by the shores of South China (hence the name), in the west by the Indochinese Peninsula, in the east by the islands of Taiwan and northwestern Phil ...
. States staking claims to various islands are Brunei
Brunei ( , ), formally Brunei Darussalam ( ms, Negara Brunei Darussalam, Jawi alphabet, Jawi: , ), is a country located on the north coast of the island of Borneo in Southeast Asia. Apart from its South China Sea coast, it is completely sur ...
, Malaysia
Malaysia ( ; ) is a country in Southeast Asia. The federation, federal constitutional monarchy consists of States and federal territories of Malaysia, thirteen states and three federal territories, separated by the South China Sea into two r ...
, the Philippines
The Philippines (; fil, Pilipinas, links=no), officially the Republic of the Philippines ( fil, Republika ng Pilipinas, links=no),
* bik, Republika kan Filipinas
* ceb, Republika sa Pilipinas
* cbk, República de Filipinas
* hil, Republ ...
, Republic of China, Taiwan, Vietnam
Vietnam or Viet Nam ( vi, Việt Nam, ), officially the Socialist Republic of Vietnam,., group="n" is a country in Southeast Asia, at the eastern edge of mainland Southeast Asia, with an area of and population of 96 million, making i ...
, and People's Republic of China. All except Brunei occupy some of the islands in dispute. The People's Republic of China conducted naval patrols in the Spratly Islands and established a permanent base.
On 14 March 1988, Chinese and Vietnamese naval forces Johnson South Reef Skirmish, clashed over Johnson South Reef in the Spratly Islands, which involved three PLAN frigates/
In February 2011, the Chinese frigate ''Chinese frigate Dongguan, Dongguan'' fired three shots at Philippine fishing boats in the vicinity of . The shots were fired after the frigate instructed the fishing boats to leave, and one of those boats experienced trouble removing its anchor. In May 2011, the Chinese patrol boats attacked and cut the cable of Vietnamese oil exploration ships near Spratly islands. The incidence sparked several anti-China protests in Vietnam.
In June 2011, the Chinese navy conducted three days of exercises, including live fire drills, in the disputed waters. This was widely seen as a warning to Vietnam, which had also conducted live fire drills near the Spratly Islands. Chinese patrol boats fired repeated rounds at a target on an apparently uninhabited island, as twin fighter jets streaked in tandem overhead. 14 vessels participated in the maneuvers, staging antisubmarine and beach landing drills aimed at "defending atolls and protecting sea lanes."
In May 2013, the Chinese navy's three operational fleets deployed together for the first time since 2010. This combined naval maneuvers in the South China Sea
The South China Sea is a marginal sea of the Western Pacific Ocean. It is bounded in the north by the shores of South China (hence the name), in the west by the Indochinese Peninsula, in the east by the islands of Taiwan and northwestern Phil ...
coincided with the ongoing Spratly Islands dispute between China and the Philippines
The Philippines (; fil, Pilipinas, links=no), officially the Republic of the Philippines ( fil, Republika ng Pilipinas, links=no),
* bik, Republika kan Filipinas
* ceb, Republika sa Pilipinas
* cbk, República de Filipinas
* hil, Republ ...
as well as deployment of the U.S. Navy's Carrier Strike Group Eleven to the U.S. Seventh Fleet.
Senkaku Islands (Diaoyu) dispute
The Senkaku Islands dispute concerns a territorial dispute over a group of Desert island, uninhabited islands known as the Diaoyu Islands in China, theSenkaku Islands
The are a group of uninhabited islands in the East China Sea, administered by Japan. They are located northeast of Taiwan, east of China, west of Okinawa Island, and north of the southwestern end of the Ryukyu Islands. They are known in main ...
in Japan, and Senkaku Islands, Tiaoyutai Islands in Taiwan. Aside from a 1945 to 1972 United States Civil Administration of the Ryukyu Islands, period of administration by the United States, the archipelago has been controlled by Japan since 1895. The People's Republic of China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's most populous country, with a population exceeding 1.4 billion, slightly ahead of India. China spans the equivalent of five time zones and ...
disputed the proposed U.S. handover of authority to Japan in 1971 and has asserted its claims to the islands since that time. Taiwan also has claimed these islands. The disputed territory is close to key shipping lanes and rich fishing grounds, and it may have major oil reserves in the area."Q&A: China-Japan islands row"''BBC News'' 11 September 2012 On some occasions, ships and planes from various Mainland Chinese and Taiwanese government and military agencies have entered the disputed area. In addition to the cases where they escorted fishing and activist vessels, there have been other incursions. In an eight-month period in 2012, over forty maritime incursions and 160 aerial incursions occurred. For example, in July 2012, three Chinese patrol vessels entered the disputed waters around the islands. Military escalation continued in 2013. In February, Minister of Defense (Japan), Japanese Defense Minister Itsunori Onodera claimed that a Chinese frigate had Missile lock-on, locked weapons-targeting radar onto a Japanese destroyer and helicopter on two occasions in January. A Chinese Type 053H3 frigate, Jiangwei II class frigate and a Japanese destroyer were three kilometers apart, and the crew of the latter vessel went to battle stations. The Chinese state media responded that their frigates had been engaged in routine training at the time. In late February 2013, United States Intelligence Community, U.S. intelligence detected China moving road-mobile ballistic missiles closer to the coast near the disputed islands, including medium-range DF-16 anti-ship ballistic missiles. In May, a flotilla of Chinese warships from its
North Sea Fleet
The Northern Theater Command Navy (), or the North Sea Fleet (NSF; ) is one of the three fleets of the Chinese People's Liberation Army Navy, under the Northern Theater Command. In September 1950 the Qingdao Army Base was redesignated as a naval ...
deployed from Qingdao
Qingdao (, also spelled Tsingtao; , Mandarin: ) is a major city in eastern Shandong Province. The city's name in Chinese characters literally means " azure island". Located on China's Yellow Sea coast, it is a major nodal city of the One Belt ...
for training exercises western North Pacific Ocean. It is not known if this deployment is related to the ongoing islands dispute between China and Japan.
Other incidents
 On 22 July 2011, following its Vietnam port-call, the Indian amphibious assault vessel was reportedly contacted 45 nautical miles from the Vietnamese coast in the disputed South China Sea by a party identifying itself as the Chinese Navy and stating that the Indian warship was entering Chinese waters."China face-off in South China Sea"
On 22 July 2011, following its Vietnam port-call, the Indian amphibious assault vessel was reportedly contacted 45 nautical miles from the Vietnamese coast in the disputed South China Sea by a party identifying itself as the Chinese Navy and stating that the Indian warship was entering Chinese waters."China face-off in South China Sea"DNA India report According to a spokesperson for the Indian Navy, since there were no Chinese ships or aircraft were visible, the INS ''Airavat'' proceeded on her onward journey as scheduled. The Indian Navy further clarified that "[t]here was no confrontation involving the INS ''Airavat''. India supports freedom of navigation in international waters, including in the South China Sea, and the right of passage in accordance with accepted principles of international law. These principles should be respected by all." On 11 July 2012, the Chinese frigate ''Dongguan'' ran aground on Hasa Hasa Shoal (''pictured'') located 60 Nautical mile, nmi west of Rizal, Palawan, Rizal, which was within the
Philippines
The Philippines (; fil, Pilipinas, links=no), officially the Republic of the Philippines ( fil, Republika ng Pilipinas, links=no),
* bik, Republika kan Filipinas
* ceb, Republika sa Pilipinas
* cbk, República de Filipinas
* hil, Republ ...
' 200 nmi-Exclusive economic zone, EEZ.Laude, Jamie"China ship runs aground near Phl"
''The Philippine Star''. 14 July 2012. Retrieved 15 July 2012. By 15 July, the frigate had been refloated and was returning to port with no injuries and only minor damage."Stranded naval frigate refloated."
Agence-France Presse, AFP. 15 July 2012 During this incident, the 2012 Association of Southeast Asian Nations, ASEAN summit took place in Phnom Penh, Cambodia, amid the rising regional tensions.
2008 anti-piracy operations
On 18 December 2008, Chinese authorities deployed People's Liberation Army Navy vessels to escort Chinese shipping in the Gulf of Aden. This deployment came after a series of attacks and attempted hijackings on Chinese vessels by Piracy in Somalia, Somali pirates. Reports suggest two destroyers (052C, Type 052C 171 Haikou and 052B, Type 052B 169 Wuhan) and a supply ship are the ones being used. This move was welcomed by the international community as the warships complement a multinational fleet already operating along the coast of Africa. Since this operation PLAN has sought the leadership of the ‘Shared Awareness and Deconfliction (SHADE)' body, which would require an increase in the number of ships contributing to the anti-piracy fleet. This is the first time Chinese warships have deployed outside the Asia-Pacific region for a military operation since Zheng He's Treasure voyages, expeditions in the 15th century. Since then more than 30 People's Liberation Army Navy ships has deployed to the Gulf of Aden in 18 Escort Task Groups.2011 Libyan Civil War
In the lead-up to the 2011 Libyan Civil War, the ''Xuzhou'' (530) was deployed from anti-piracy operations in the Gulf of Aden to help evacuate Chinese nationals from Libya.Yemen Conflict
During the South Yemen insurgency#2015, Yemen conflict, in 2015, the Chinese Navy diverted Anti-piracy measures in Somalia#Vessels in operation, frigates carrying out anti-piracy operations in Somalia to evacuate at least 600 Chinese and 225 foreign citizens working in Yemen. Among the non-Chinese evacuees were 176 Pakistani citizens, with smaller numbers from other countries, such as Ethiopia, Singapore, the UK, Italy, and Germany. Despite the evacuations, the Chinese embassy in Yemen continued to operate.Equipment
 As of 2018, the Chinese navy operates over 496 combat ships and 232 various auxiliary vessels and counts 255,000 seamen in its ranks. The Chinese Navy also employ more than 710 naval aircraft, including fighters, bombers and electronic warfare aircraft. China has large amount of artillery, torpedoes, and missiles included in their combat assets.
As of 2018, the Chinese navy operates over 496 combat ships and 232 various auxiliary vessels and counts 255,000 seamen in its ranks. The Chinese Navy also employ more than 710 naval aircraft, including fighters, bombers and electronic warfare aircraft. China has large amount of artillery, torpedoes, and missiles included in their combat assets.
Ships and submarines
All ships and submarines currently in commission with the People's Liberation Army Navy were built in China, with the exception of the Sovremenny-class destroyers, Kilo-class submarines and the aircraft carrier Liaoning. Those vessels were either imported from, or originated from Russia. As of 2008, English-language official Chinese state media no longer uses the term "People's Liberation Army Navy", instead the term "Chinese Navy" along with the usage of the unofficial prefix "CNS" for "Chinese Navy Ship" is now employed. China employs a wide range of Navy combatants including aircraft carriers, amphibious warfare ships, and destroyers. The Chinese Navy is undergoing modernization rapidly with nearly half of Chinese Navy combat ships built after 2010. China's state-owned shipyards have built 83 ships in just eight years with unprecedented speed. China has its own independent maritime missile defense and naval combat system similar to US Aegis Combat System, Aegis.Aircraft
China operates carrier-based fighter aircraft to secure land, air and sea targets. The Chinese Navy also operates a wide range of helicopters for battlefield logistics, reconnaissance, patrol and medical evacuation.Naval weaponry
The unique QBS-06 is an Underwater firearm, underwater assault rifle with 5.8x42 DBS-06, and is used by Naval frogmen. It is based on the Soviet APS underwater rifle, APS. In early February 2018, pictures of what is claimed to be a Chinese railgun were published online. In pictures the gun is shown mounted on the bow of a Type 072III-class landing ship Haiyang Shan, ''Haiyangshan''. Media is suggesting that the system is or soon will be ready for testing. In March 2018, it was reported that China had confirmed that it had begun testing its electromagnetic rail gun at sea.Future of the People's Liberation Army Navy
 The PLAN's ambitions include operating out to the first and second island chains, as far as the South Pacific near Australia, and spanning to the Aleutian islands, and operations extending to the Straits of Malacca near the Indian Ocean.Annual Report to Congress, ''Military Power of the People's Republic of China''. Retrieved 22 May 2008 The future PLAN fleet will be composed of a balance of combatant assets aimed at maximising the PLAN's fighting effectiveness.
On the high end, there would be modern destroyers, such as stealth guided missile destroyers equipped with long-range air defense missiles and anti-submarine capabilities (Type 055 destroyer, Type 055). There would be modern destroyers equipped with long-range air defense missiles (Type 052B destroyer, Type 052B, Type 052C destroyer, Type 052C, Type 052D destroyer, Type 052D and Type 051C destroyer, Type 051C, and destroyers armed with supersonic anti-ship missiles (Sovremenny class destroyer, ''Sovremenny'' class).
There would be advanced nuclear-powered attack and ballistic missile submarines (Type 093 submarine, Type 093, Type 095 submarine, Type 095, Type 094 submarine, Type 094, Type 096 submarine, Type 096), advanced conventional attack submarines (Kilo class submarine, ''Kilo'' and Type 041 submarine, ''Yuan'' classes), aircraft carriers (Chinese aircraft carrier Liaoning, Type 001, Type 002 aircraft carrier, Type 002 and Type 003 aircraft carrier, Type 003), and helicopter carriers (Type 075 landing helicopter dock, Type 075) and large amphibious warfare vessels (Type 071 amphibious transport dock, Type 071) capable of mobilizing troops at long distances.
On the medium and low end, there would be more economical multi-role capable frigates and destroyers (Type 052 destroyer, ''Luhu'', Type 053H3 frigate, ''Jiangwei II'' and Type 054A frigate, ''Jiangkai'' classes), corvettes (Type 056 corvette, ''Jiangdao'' class), fast littoral missile attack craft (Type 037-II class missile boat, ''Houjian'', Type 037-IG class missile boat, ''Houxin'' and Houbei class missile boat, ''Houbei'' classes), various landing ships and light craft, and conventionally powered coastal patrol submarines (Type 039 submarine, ''Song'' class). The obsolete combat ships (based on 1960s designs) will be phased out in the coming decades as more modern designs enter full production.
It may take a decade for the bulk of these older ships to be retired. Until then, they will serve principally on the low end, as multi-role patrol/escort platforms. Their use could be further enhanced in the future by being used as fast transports or fire support platforms. This system of phasing out would see a reversal in the decline in quantity of PLAN vessels by 2015, and cuts in inventory after the end of the Cold War could be made up for by 2020.
Between 2001–2006 there was a rapid building and acquisition program, a trend which continued. There were more than a dozen new classes of ships built in those five years, totaling some 60 brand new ships (including landing ships and auxiliaries). Simultaneously, dozens of other ships have been either phased out of service or refitted with new equipment.
Submarines play a significant role in the development of the PLAN's future fleet. This is made evident by the construction of a new type of nuclear
The PLAN's ambitions include operating out to the first and second island chains, as far as the South Pacific near Australia, and spanning to the Aleutian islands, and operations extending to the Straits of Malacca near the Indian Ocean.Annual Report to Congress, ''Military Power of the People's Republic of China''. Retrieved 22 May 2008 The future PLAN fleet will be composed of a balance of combatant assets aimed at maximising the PLAN's fighting effectiveness.
On the high end, there would be modern destroyers, such as stealth guided missile destroyers equipped with long-range air defense missiles and anti-submarine capabilities (Type 055 destroyer, Type 055). There would be modern destroyers equipped with long-range air defense missiles (Type 052B destroyer, Type 052B, Type 052C destroyer, Type 052C, Type 052D destroyer, Type 052D and Type 051C destroyer, Type 051C, and destroyers armed with supersonic anti-ship missiles (Sovremenny class destroyer, ''Sovremenny'' class).
There would be advanced nuclear-powered attack and ballistic missile submarines (Type 093 submarine, Type 093, Type 095 submarine, Type 095, Type 094 submarine, Type 094, Type 096 submarine, Type 096), advanced conventional attack submarines (Kilo class submarine, ''Kilo'' and Type 041 submarine, ''Yuan'' classes), aircraft carriers (Chinese aircraft carrier Liaoning, Type 001, Type 002 aircraft carrier, Type 002 and Type 003 aircraft carrier, Type 003), and helicopter carriers (Type 075 landing helicopter dock, Type 075) and large amphibious warfare vessels (Type 071 amphibious transport dock, Type 071) capable of mobilizing troops at long distances.
On the medium and low end, there would be more economical multi-role capable frigates and destroyers (Type 052 destroyer, ''Luhu'', Type 053H3 frigate, ''Jiangwei II'' and Type 054A frigate, ''Jiangkai'' classes), corvettes (Type 056 corvette, ''Jiangdao'' class), fast littoral missile attack craft (Type 037-II class missile boat, ''Houjian'', Type 037-IG class missile boat, ''Houxin'' and Houbei class missile boat, ''Houbei'' classes), various landing ships and light craft, and conventionally powered coastal patrol submarines (Type 039 submarine, ''Song'' class). The obsolete combat ships (based on 1960s designs) will be phased out in the coming decades as more modern designs enter full production.
It may take a decade for the bulk of these older ships to be retired. Until then, they will serve principally on the low end, as multi-role patrol/escort platforms. Their use could be further enhanced in the future by being used as fast transports or fire support platforms. This system of phasing out would see a reversal in the decline in quantity of PLAN vessels by 2015, and cuts in inventory after the end of the Cold War could be made up for by 2020.
Between 2001–2006 there was a rapid building and acquisition program, a trend which continued. There were more than a dozen new classes of ships built in those five years, totaling some 60 brand new ships (including landing ships and auxiliaries). Simultaneously, dozens of other ships have been either phased out of service or refitted with new equipment.
Submarines play a significant role in the development of the PLAN's future fleet. This is made evident by the construction of a new type of nuclear ballistic missile submarine
A ballistic missile submarine is a submarine capable of deploying submarine-launched ballistic missiles (SLBMs) with nuclear warheads. The United States Navy's hull classification symbols for ballistic missile submarines are SSB and SSBN – t ...
, the Type 094 submarine, Type 094 and the Type 093 submarine, Type 093 nuclear attack submarine. This will provide the PLAN with a more modern response for the need of a seaborne nuclear deterrent. The new submarines will also be capable of performing conventional strike and other special warfare requirements.
The European Union has provided much of the propulsion technology for the PLAN's modernization.
Ronald O'Rourke of the Congressional Research Service reported that the long-term goals of PLAN planning include:
* Assert or defend China's claims in maritime territorial disputes and China's interpretation of international laws relating to freedom of navigation in exclusive economic zones (an interpretation at odds with the U.S. interpretation);
* Protect China's sea lines of communications to the Persian Gulf, on which China relies for some of its energy imports.
During the military parade on the 60th anniversary of the People's Republic of China, the C-602, YJ-62 naval cruise missile made its first public appearance; the YJ-62 represents the next generation in naval weapons technology in the PLA.
Following the construction of its two smaller aircraft carriers, China began building the improved Type 003 carrier, which is expected to displace 83,000 tonnes and enable CATOBAR operations by 2022.
The PLAN may also operate from Gwadar or Seychelles for anti-piracy missions and to protect vital trade routes which may endanger China's energy security in the case of a conflict. In 2016, China established her first overseas Chinese naval base in Djibouti, naval base in Djibouti, which provided necessary support for Chinese fleet and troops.
China has reportedly begun testing designs for arsenal ships.
The Pentagon's name for the Chinese sea based militia is the People's Armed Forces Maritime Militia.Their future role is unknown, but war planners have been aware of their history and potential use in naval conflict.Peter Dobbie and Al Jazeera reporters. (1 May 2021). "Video: How China came to dominate the South China Sea"Al Jazeera English website
Retrieved 2 May 2021.
See also
* List of ships of the People's Liberation Army Navy * Chinese aircraft carrier programme * China Coast Guard * Dalian Naval Academy * People's Liberation Army Navy Band * Political Commissar of the People's Liberation Army Navy * Political Department of the People's Liberation Army NavyReferences
Citations
Sources
* *External links
Chinese naval aircraft in service
PLAN – Chinese Defence Today
{{People's Liberation Army People's Liberation Army Navy, People's Liberation Army branches, 2 1950 establishments in China