Chinese Battleship Chen Yuan on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
''Zhenyuan'' () was an ironclad battleship built for the Chinese Beiyang Fleet. She was the second and final member of the , which included one other vessel, , both of which were built in Germany in the early 1880s. Delivery of the two ironclads was delayed by the
 Upon her acquisition by
Upon her acquisition by
 ''Zhenyuan'' was ordered in 1881 and was laid down at the AG Vulcan shipyard in
''Zhenyuan'' was ordered in 1881 and was laid down at the AG Vulcan shipyard in 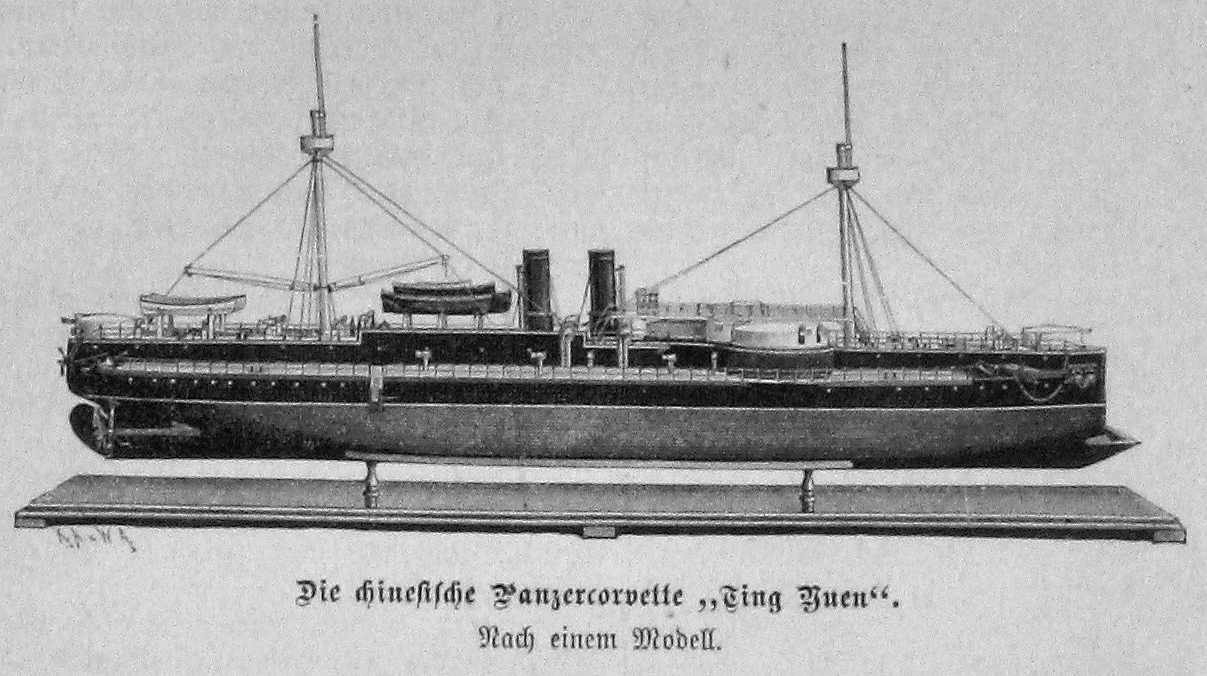 The year 1887 passed less eventfully, with the ships spending the bulk of the year in the Bohai Sea. Late in the year, another group of four European-built cruisers arrived, further strengthening the fleet and necessitating extensive maneuvers in 1888 to familiarize the crews with the rest of the fleet. The Beiyang Fleet adopted the same black, white, and buff paint scheme used by the Royal Navy at the time, repainting their vessels at some point in 1888. In 1889, the fleet was divided into two divisions; ''Dingyuan'' and several cruisers were sent on a tour of Korean ports while ''Zhenyuan'' and the rest of the fleet remained in the Bohai Sea for exercises. The two divisions rendezvoused in Shanghai in December, thereafter proceeding to Hong Kong for ''Zhenyuan'' and ''Dingyuan'' to be drydocked. They then cruised off Korea, where ''Zhenyuan''
The year 1887 passed less eventfully, with the ships spending the bulk of the year in the Bohai Sea. Late in the year, another group of four European-built cruisers arrived, further strengthening the fleet and necessitating extensive maneuvers in 1888 to familiarize the crews with the rest of the fleet. The Beiyang Fleet adopted the same black, white, and buff paint scheme used by the Royal Navy at the time, repainting their vessels at some point in 1888. In 1889, the fleet was divided into two divisions; ''Dingyuan'' and several cruisers were sent on a tour of Korean ports while ''Zhenyuan'' and the rest of the fleet remained in the Bohai Sea for exercises. The two divisions rendezvoused in Shanghai in December, thereafter proceeding to Hong Kong for ''Zhenyuan'' and ''Dingyuan'' to be drydocked. They then cruised off Korea, where ''Zhenyuan''
 Ding took the fleet on a sweep into the
Ding took the fleet on a sweep into the
 While approaching Weihaiwei on 14 November, ''Zhenyuan'' struck a reef as the ship attempted to maneuver around the obstacles that had been erected off the harbor entrance to prevent a Japanese attack. The grounding tore a hole that was long and caused significant flooding, including the port engine room. The vessel remained stuck on the reef for three weeks, listing to port with her main deck awash. The salvage team eventually towed her off the reef and brought the ship into the anchorage at Weihaiwei, where she was run aground to avoid sinking. Divers were sent from Shanghai to patch the hole with concrete. Lin took responsibility for the accident and committed suicide the following day with an overdose of
While approaching Weihaiwei on 14 November, ''Zhenyuan'' struck a reef as the ship attempted to maneuver around the obstacles that had been erected off the harbor entrance to prevent a Japanese attack. The grounding tore a hole that was long and caused significant flooding, including the port engine room. The vessel remained stuck on the reef for three weeks, listing to port with her main deck awash. The salvage team eventually towed her off the reef and brought the ship into the anchorage at Weihaiwei, where she was run aground to avoid sinking. Divers were sent from Shanghai to patch the hole with concrete. Lin took responsibility for the accident and committed suicide the following day with an overdose of
 Competition over control of Korea brought Japan into a second conflict, now with the Russian Empire in 1904. The Russo-Japanese War began on 8 February with a surprise torpedo-boat attack on the Russian First Pacific Squadron that occupied Port Arthur. Now obsolete, ''Chin Yen'' was assigned to the 5th Squadron of 3rd Fleet, the flagship of Vice Admiral
Competition over control of Korea brought Japan into a second conflict, now with the Russian Empire in 1904. The Russo-Japanese War began on 8 February with a surprise torpedo-boat attack on the Russian First Pacific Squadron that occupied Port Arthur. Now obsolete, ''Chin Yen'' was assigned to the 5th Squadron of 3rd Fleet, the flagship of Vice Admiral
Sino-French War
The Sino-French War (, french: Guerre franco-chinoise, vi, Chiến tranh Pháp-Thanh), also known as the Tonkin War and Tonquin War, was a limited conflict fought from August 1884 to April 1885. There was no declaration of war. The Chinese arm ...
of 1884–1885. The ships were armed with a main battery of four guns in a pair of gun turrets, making them the most powerful warships in East Asian waters at the time.
In the 1880s and early 1890s, the Beiyang Fleet conducted a routine of training exercises and cruises abroad, with emphasis placed on visits to Japan
Japan ( ja, 日本, or , and formally , ''Nihonkoku'') is an island country in East Asia. It is situated in the northwest Pacific Ocean, and is bordered on the west by the Sea of Japan, while extending from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north ...
to intimidate the country. The latter resulted in the Nagasaki Incident
The , also known as the Nagasaki―Qing Navy Incident (長崎清国水兵事件), was an August 1886 riot involving Chinese Beiyang Fleet sailors in Nagasaki.
Outline
On 1 August 1886 ( Meiji 19), the Qing dynasty's Beiyang Fleet, consistin ...
in 1886 and contributed to a rise in hostility between the two countries that culminated in the First Sino-Japanese War in 1894. She saw action at the Battle of the Yalu River on 17 September, where the Japanese Combined Fleet sank much of the Beiyang Fleet, though both ''Zhenyuan'' and ''Dingyuan'' survived despite numerous hits. The survivors then retreated to Port Arthur for repairs, but after that city was threatened by the Japanese army, fled to Weihaiwei. While entering the port, ''Zhenyuan'' struck an uncharted rock and was badly damaged; she was used as a stationary artillery battery during the Battle of Weihaiwei in February 1895, but Japanese forces captured the city's fortifications, which forced the Chinese to surrender the fleet.
''Zhenyuan'' was seized as a war prize, repaired, and commissioned into the Imperial Japanese Navy as ''Chin Yen''. She frequently toured Japan in the late 1890s and early 1900s to celebrate Japan's victory over China. Obsolescent by the time of the Russo-Japanese War, she nevertheless saw action at the Battle of the Yellow Sea in August 1904 and the Battle of Tsushima
The Battle of Tsushima (Japanese:対馬沖海戦, Tsushimaoki''-Kaisen'', russian: Цусимское сражение, ''Tsusimskoye srazheniye''), also known as the Battle of Tsushima Strait and the Naval Battle of Sea of Japan (Japanese: 日 ...
in May 1905. She also supported the invasion of Sakhalin in July 1905. After the war, ''Chin Yen'' became a training ship, serving in that role until 1911, thereafter being sold to ship breaker
''Ship Breaker'' is a 2010 young adult novel by Paolo Bacigalupi set in a post-apocalyptic future. Human civilization is in decline for ecological reasons. The polar ice caps have melted and New Orleans is underwater. On the Gulf Coast n ...
s in 1912.
Design
left, An overview of the layout of a ''Dingyuan''-class ironclad Following the direct intervention of the imperialist European powers in the mid-19th century, including the First andSecond Opium War
The Second Opium War (), also known as the Second Anglo-Sino War, the Second China War, the Arrow War, or the Anglo-French expedition to China, was a colonial war lasting from 1856 to 1860, which pitted the British Empire and the French Emp ...
s, where their superior steam-powered fleets overwhelmed the small Imperial Chinese Navy that still relied on traditional junks
A junk (Chinese: 船, ''chuán'') is a type of Chinese sailing ship with fully battened sails. There are two types of junk in China: northern junk, which developed from Chinese river boats, and southern junk, which developed from Austronesian ...
, the Chinese began a naval construction program in the 1880s to meet these threats more effectively. They enlisted British and German assistance, and two s were ordered from Germany.
''Zhenyuan'' was long overall, with a beam of and a draft of . She displaced normally and up to at full load. She was powered by a pair of compound steam engines that each drove a screw propeller. Steam was provided by eight coal-fired fire-tube boiler
A fire-tube boiler is a type of boiler in which hot gases pass from a fire through one or more tubes running through a sealed container of water. The heat of the gases is transferred through the walls of the tubes by thermal conduction, heating t ...
s that were ducted into a pair of funnels
A funnel is a tube or pipe that is wide at the top and narrow at the bottom, used for guiding liquid or powder into a small opening.
Funnels are usually made of stainless steel, aluminium, glass, or plastic. The material used in its constr ...
amidships. She was capable of a top speed of from . Her crew consisted of 350 officers and enlisted men.
The ship carried a main battery of four 20-caliber
In guns, particularly firearms, caliber (or calibre; sometimes abbreviated as "cal") is the specified nominal internal diameter of the gun barrel Gauge (firearms) , bore – regardless of how or where the bore is measured and whether the f ...
breech-loading guns in two twin- gun turrets that were placed en echelon forward. These were supported by a secondary battery of two guns in a pair of single turrets, one at the bow and the other at the stern. For defense against torpedo boats, she carried a pair of 3-pounder, Hotchkiss revolver cannon
The Hotchkiss gun can refer to different products of the Hotchkiss arms company starting in the late 19th century. It usually refers to the 1.65-inch (42 mm) light mountain gun; there were also a navy (47 mm) and a 3-inch (76&nbs ...
and eight Maxim-Nordenfelt quick-firing guns in casemate
A casemate is a fortified gun emplacement or armored structure from which artillery, guns are fired, in a fortification, warship, or armoured fighting vehicle.Webster's New Collegiate Dictionary
When referring to Ancient history, antiquity, th ...
s. She was also equipped with three or torpedo tubes.
She was protected by compound armor
Compound armour was a type of armour used on warships in the 1880s, developed in response to the emergence of armor-piercing shells and the continual need for reliable protection with the increasing size in naval ordnance. Compound armour was a no ...
that was 14 in for the armor belt, which covered the central part of the ship were the ammunition magazines and propulsion machinery spaces were located. An armor deck that was thick provided horizontal protection. Her conning tower
A conning tower is a raised platform on a ship or submarine, often armored, from which an officer in charge can conn the vessel, controlling movements of the ship by giving orders to those responsible for the ship's engine, rudder, lines, and gro ...
was covered with of armor plate on the sides. The barbettes for the gun turrets were 12–14 in thick. A strake of armor that was 8 in thick protected the casemate guns.
Modifications
 Upon her acquisition by
Upon her acquisition by Japan
Japan ( ja, 日本, or , and formally , ''Nihonkoku'') is an island country in East Asia. It is situated in the northwest Pacific Ocean, and is bordered on the west by the Sea of Japan, while extending from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north ...
in 1895, the ship was significantly modernized, including new fire-control director
A fire-control system (FCS) is a number of components working together, usually a gun data computer, a director, and radar, which is designed to assist a ranged weapon system to target, track, and hit a target. It performs the same task as a hu ...
s for the main battery and more powerful secondary and tertiary batteries. The Japanese had initially considered replacing the main battery guns, but the project proved to be beyond the capabilities of Japanese shipyards at the time.
The old, slow-firing 5.9 in guns were replaced with quick-firing guns; the forward turret was retained, but the stern mount was replaced with an open mount with a gun shield
A U.S. Marine manning an M240 machine gun equipped with a gun shield
A gun shield is a flat (or sometimes curved) piece of armor designed to be mounted on a crew-served weapon such as a machine gun, automatic grenade launcher, or artillery piece ...
. Two more of the guns were installed abreast of the main mast, both in the same shielded mount as the stern gun. The ''Dingyuan''-class ships suffered from trim problems as a result of their heavy main battery turrets being placed forward, which caused them to nose down and ship water; it also hampered their steering ability. The addition of the 6-inch guns further aft helped to counterbalance the weight of the main battery, significantly improving both defects. The light battery was revised to a pair of 6-pounder Hotchkiss guns and eight of the Hotchkiss 3-pounders, all in individual mounts.
Displacement and other dimensions remained the same, but by that time, the propulsion system was only capable of producing for a speed of . Her crew was reduced significantly, despite the addition of the 6-inch guns, to 250 officers and enlisted men.
Service history
Chinese service
 ''Zhenyuan'' was ordered in 1881 and was laid down at the AG Vulcan shipyard in
''Zhenyuan'' was ordered in 1881 and was laid down at the AG Vulcan shipyard in Stettin
Szczecin (, , german: Stettin ; sv, Stettin ; Latin language, Latin: ''Sedinum'' or ''Stetinum'') is the capital city, capital and largest city of the West Pomeranian Voivodeship in northwestern Poland. Located near the Baltic Sea and the Po ...
, Germany in March 1882; her name means "striking from afar" in Chinese. Work proceeded quickly and she was launched on 28 November 1882, though fitting-out work continued into early 1884. She was completed in April that year, but the outbreak of the Sino-French War
The Sino-French War (, french: Guerre franco-chinoise, vi, Chiến tranh Pháp-Thanh), also known as the Tonkin War and Tonquin War, was a limited conflict fought from August 1884 to April 1885. There was no declaration of war. The Chinese arm ...
in August prevented both ''Dingyuan''-class ships from being delivered until 1885. Both vessels were manned by German crews, sailing on 3 July 1885 under the German flag in company with the also German-built protected cruiser . The three ships arrived in Tianjin in November, where they were transferred to Chinese control. Li Hongzhang, the Viceroy of Zhili and director of China's naval construction program, inspected the vessels following their arrival. The two ironclads were then commissioned into the Beiyang Fleet, which was based in Port Arthur. The ships steamed south to Shanghai for the winter of 1885–1886.
In the 1880s, the Beiyang Fleet was occupied with an annual routine of winter training cruises to the South China Sea, often in company with the Nanyang Fleet. This cruise typically involved visits to Zhejiang, Fujian, and Guangdong provinces, and sometimes went as far south as stops in Southeast Asia. The rest of the year was spent in northern waters off Zhili, Shandong
Shandong ( , ; ; alternately romanized as Shantung) is a coastal province of the People's Republic of China and is part of the East China region.
Shandong has played a major role in Chinese history since the beginning of Chinese civilizati ...
, and Fengtian Fengtian (; postal: Fengtien; Manchu: ''Abkai imiyangga fu'') is:
* Shenyang, largest city and provincial capital of Liaoning province, which was formerly administered under Fengtian Fu, which was abolished in 1910
* Liaoning, the province formerl ...
provinces, conducting training exercises. Training cruises to foreign ports were conducted in the mid-1880s and early 1890s, both to train navigational skills on voyages far from shore and to show the flag. Discipline aboard the ships of the Beiyang Fleet was poor, which contributed to a low state of readiness of the ships. During this period, the fleet was commanded by Admiral Ding Ruchang, while ''Zhenyuan'' was captained by Lin Taizeng
Lin or LIN may refer to:
People
*Lin (surname) (normally ), a Chinese surname
*Lin (surname) (normally 蔺), a Chinese surname
* Lin (''The King of Fighters''), Chinese assassin character
*Lin Chow Bang, character in Fat Pizza
Places
*Lin, Iran, ...
, who was promoted to the rank of rear admiral shortly after taking command in 1885. Lin served as Ding's deputy through 1894. At the time, China lacked dry dock
A dry dock (sometimes drydock or dry-dock) is a narrow basin or vessel that can be flooded to allow a load to be floated in, then drained to allow that load to come to rest on a dry platform. Dry docks are used for the construction, maintenance, ...
s large enough to handle ''Zhenyuan'' and ''Dingyuan'', forcing the navy to rely on shipyards in Japan or in British Hong Kong
Hong Kong was a colony and later a dependent territory of the British Empire from 1841 to 1997, apart from a period of occupation under the Japanese Empire from 1941 to 1945 during the Pacific War. The colonial period began with the Briti ...
for periodic maintenance.
The two ''Dingyuan''-class ships began their training routine in April 1886 in joint maneuvers with the units of the Nanyang Fleet, which culminated in a naval review in Port Arthur. They received the British vessels of the China Station from 19 to 20 May. ''Zhenyuan'', ''Dingyuan'', and four cruisers began the first of their overseas cruises in August 1886, which included stops in Hong Kong, Busan and Wonsan in Korea, Vladivostok, Russia, and Nagasaki, Japan. While at the latter port in August, Chinese crewmen became involved in an altercation with Japanese locals that resulted in the deaths of eight Chinese sailors and two Japanese police, with forty-two Chinese and twenty-nine Japanese injured. The so-called Nagasaki Incident
The , also known as the Nagasaki―Qing Navy Incident (長崎清国水兵事件), was an August 1886 riot involving Chinese Beiyang Fleet sailors in Nagasaki.
Outline
On 1 August 1886 ( Meiji 19), the Qing dynasty's Beiyang Fleet, consistin ...
was characterized by the Japanese press as an attempt by China to intimidate Japan, leading to calls for naval expansion to counter the Beiyang Fleet. The Japanese government ordered three protected cruisers in response. The Japanese also refused to allow the Chinese ironclads to return for repairs in their shipyards, hampering the ability of the Beiyang Fleet to keep the vessels operational.
 The year 1887 passed less eventfully, with the ships spending the bulk of the year in the Bohai Sea. Late in the year, another group of four European-built cruisers arrived, further strengthening the fleet and necessitating extensive maneuvers in 1888 to familiarize the crews with the rest of the fleet. The Beiyang Fleet adopted the same black, white, and buff paint scheme used by the Royal Navy at the time, repainting their vessels at some point in 1888. In 1889, the fleet was divided into two divisions; ''Dingyuan'' and several cruisers were sent on a tour of Korean ports while ''Zhenyuan'' and the rest of the fleet remained in the Bohai Sea for exercises. The two divisions rendezvoused in Shanghai in December, thereafter proceeding to Hong Kong for ''Zhenyuan'' and ''Dingyuan'' to be drydocked. They then cruised off Korea, where ''Zhenyuan''
The year 1887 passed less eventfully, with the ships spending the bulk of the year in the Bohai Sea. Late in the year, another group of four European-built cruisers arrived, further strengthening the fleet and necessitating extensive maneuvers in 1888 to familiarize the crews with the rest of the fleet. The Beiyang Fleet adopted the same black, white, and buff paint scheme used by the Royal Navy at the time, repainting their vessels at some point in 1888. In 1889, the fleet was divided into two divisions; ''Dingyuan'' and several cruisers were sent on a tour of Korean ports while ''Zhenyuan'' and the rest of the fleet remained in the Bohai Sea for exercises. The two divisions rendezvoused in Shanghai in December, thereafter proceeding to Hong Kong for ''Zhenyuan'' and ''Dingyuan'' to be drydocked. They then cruised off Korea, where ''Zhenyuan'' ran aground
Ship grounding or ship stranding is the impact of a ship on seabed or
waterway side. It may be intentional, as in beaching to land crew or cargo, and careening, for maintenance or repair, or unintentional, as in a marine accident. In accidenta ...
in November 1890, forcing another return to Hong Kong for repairs.
Another visit to Japan came in June and July 1891, the first since the Nagasaki Incident; the fleet stopped in Kobe
Kobe ( , ; officially , ) is the capital city of Hyōgo Prefecture Japan. With a population around 1.5 million, Kobe is Japan's seventh-largest city and the third-largest port city after Tokyo and Yokohama. It is located in Kansai region, whic ...
on 30 June and Yokohama on 14 July. At the latter port, a large Japanese delegation of senior military commanders and members of the imperial family received the ships. Another voyage to Japan took place the following year. Coupled with the Nagasaki Incident, these voyages contributed to the growing tensions between China and Japan, since Hongzhang intended them to make clear Chinese naval strength at a time the Japanese fleet was small and poorly developed. At the core of the dispute was control over Korea, which since the Convention of Tientsin of 1884, was treated as a co-protectorate of China and Japan.
First Sino-Japanese War
In early 1894, the Donghak Peasant Revolution broke out in Korea, prompting China to send an expedition of 28,000 to suppress the rebels. Japan viewed this as a violation of the Tientsin Convention and deployed 8,000 troops in response, leading to the outbreak of the First Sino-Japanese War on 1 August. The Chinese fleet was no match for the new Combined Fleet of Japan, as years of insufficient naval budgets had not allowed Hongzhang to update the vessels—funds he had planned to use to add new quick-firing guns to ''Zhenyuan'' and ''Dingyuan'' were instead appropriated for the 60th birthday of the Dowager Empress Cixi—and the Chinese lacked effective commanders and sufficiently trained crews. At the time, the American naval officerPhilo McGiffen
Philo Norton McGiffin (December 12/13, 1860 – February 11, 1897) was an American soldier of fortune serving in Chinese service as a naval advisor during the First Sino-Japanese War. Although primarily skilled as an instructor and administrat ...
served as the ship's executive officer to advise Lin. And to add to China's disadvantages during the war, the Japanese had broken the Chinese diplomatic codes in 1888, giving them access to China's internal communications.
As the Chinese made preparations in August for action, they removed the gun shields from the main battery turrets. Experience at the Battle of Pungdo had revealed the thin shields created numerous splinters when struck by enemy fire, and these fragments had inflicted numerous casualties to the gun crews of the cruiser ''Jiyuan'' at Pungdo. The crews also placed bags of coal around the gun batteries as a form of improvised armor. The ships were repainted light gray to make them more difficult to observe at sea. The ships of the Beiyang Fleet then steamed to Taku to take on supplies, thereafter doing little for the next month.
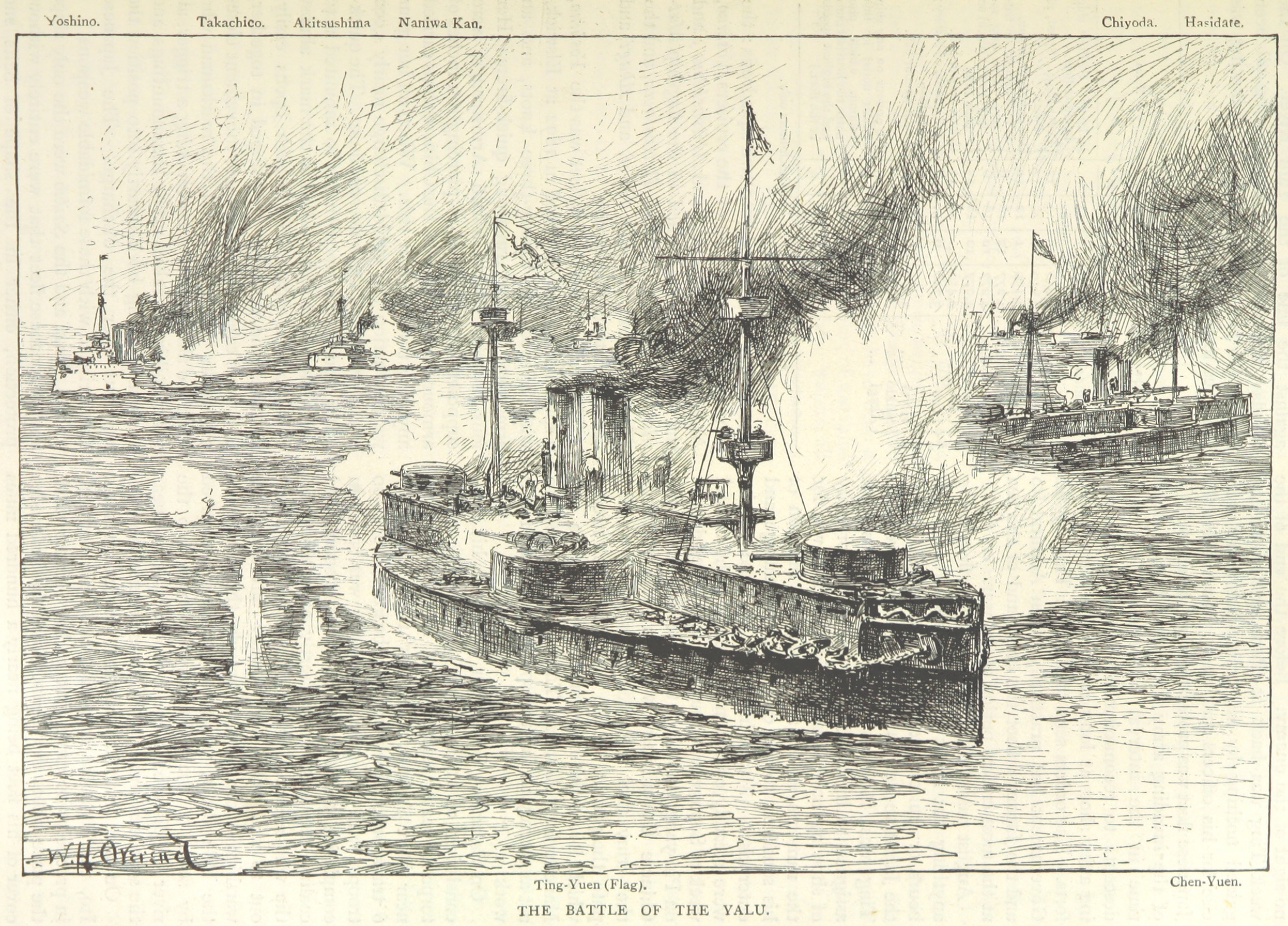
=Battle of the Yalu River
= Ding took the fleet on a sweep into the
Ding took the fleet on a sweep into the Korea Bay
The Korea Bay, sometimes the West Korea Bay (; ; or ), is a bight and the northern extension of the Yellow Sea, between the southeastern coastline of China's Liaoning province and the western coastline of North Korea's North Pyongan, South P ...
on 12 September to clear the way for a convoy of troopships scheduled to deliver reinforcements to Korea. While on the way to the bay, he received faulty reports indicating the presence of Japanese warships off the Shandong Peninsula, prompting him to change course to search for them. Finding no enemy vessels, he took the fleet to Weihaiwei (modern Weihai), and on 15 September, the fleet rendezvoused with the convoy to cover its approach to the mouth of the Yalu River, where the transports deposited the men and supplies on 16 September. During the unloading process, ''Zhenyuan'' and the bulk of the fleet remained underway to provide distant support and avoid presenting themselves as stationary targets to Japanese torpedo boats known to be in the area. While the Chinese were on the way back to Port Arthur, the Combined Fleet under Vice Admiral Itō Sukeyuki intercepted them on 17 September, leading to the Battle of the Yalu River. The poorly trained Beiyang Fleet sailed in a disorganized line abreast
Galley tactics were the dominant form of naval tactics used from antiquity to the late 16th century when sailing ships began to replace oared ships as the principal form of warships. Throughout antiquity and the Middle Ages until the 16th centur ...
formation, while the Japanese approached them from the south in line ahead
The line of battle is a tactic in naval warfare in which a fleet of ships forms a line end to end. The first example of its use as a tactic is disputed—it has been variously claimed for dates ranging from 1502 to 1652. Line-of-battle tacti ...
; the Chinese ships steamed at around and the Japanese at .
Itō turned his ships to port to pass in front of the oncoming Beiyang Fleet. ''Dingyuan'' opened fire first, at about 12:20, at the extreme range of , far in excess of what fire-control equipment
A fire-control system (FCS) is a number of components working together, usually a gun data computer, a director, and radar, which is designed to assist a ranged weapon system to target, track, and hit a target. It performs the same task as a hu ...
was capable of accurately directing at the time. The blast effect from ''Dingyuan''s initial salvo
A salvo is the simultaneous discharge of artillery or firearms including the firing of guns either to hit a target or to perform a salute. As a tactic in warfare, the intent is to cripple an enemy in one blow and prevent them from fighting b ...
destroyed her own bridge, collapsing it and trapping Ding and his staff for the duration of the action, depriving the Beiyang Fleet of central control. The rest of the Chinese fleet quickly followed ''Dingyuan'', but failed to score any hits as their opponents passed in front. The Japanese ships returned fire at 12:25, having divided into two squadrons and turned back to starboard to encircle the Chinese. Concentrating their fire on the cruisers on the Chinese right flank, they quickly destroyed the Chinese cruisers and . The battle quickly devolved into a melee at close range, and the Chinese cruisers and were sunk. In return, the Chinese warships inflicted serious damage on the old ironclad , which had been unable to keep pace with the rest of Itō's fleet, and was eventually forced to disengage and flee. ''Zhenyuan'' and ''Dingyuan'' hit the auxiliary cruiser '' Saikyō Maru'' with four 12-inch shells and inflicted significant damage.
''Zhenyuan''s heavy citadel armor proved to be impervious to the Japanese shellfire directed against it, though the large-caliber Canet guns mounted on the ''Matsushima''-class cruisers proved to be nearly useless and the other Japanese cruisers were engaged with their Chinese counterparts. At 15:30, ''Zhenyuan'' scored a hit with her main battery on the Japanese flagship , striking her forward barbette. The shell disabled the forward main gun, set the ship on fire, disabled four of ''Matsushima''s secondary guns, and inflicted heavy casualties. Itō was forced to shift his flag as a result. ''Zhenyuan'' caught fire several times during the action, but her crew was able to quickly suppress the fires. By around 17:00, both sides were low on ammunition and the Chinese began to reform their surviving vessels into line-ahead formation. The Japanese eventually broke off at around 17:30 and withdrew. The battered Beiyang Fleet, by then reduced to the two ''Dingyuan''-class ships and four smaller vessels, limped back to Port Arthur, arriving there the next day.
In the course of the action, ''Zhenyuan'' had expended all of her 5.9-inch ammunition and most of her 12-inch shells, having just twenty-four solid steel shells remaining. She had taken some 220 hits, but none penetrated her belt and only a small number pierced the deck. Repairs to the damaged ships began immediately, and fresh supplies and ammunition were sent to ready the vessels for action. By late October, the Japanese Army
The Japan Ground Self-Defense Force ( ja, 陸上自衛隊, Rikujō Jieitai), , also referred to as the Japanese Army, is the land warfare branch of the Japan Self-Defense Forces. Created on July 1, 1954, it is the largest of the three service b ...
had begun to approach the port, forcing the Chinese to withdraw the Beiyang Fleet across the Bohai Strait to Weihaiwei on 20 October. ''Zhenyuan'' remained in Port Arthur while the rest of the fleet left so that repairs could continue to be made, but by early November, the Japanese were poised to seize the port, prompting her to join the rest of the fleet at Weihaiwei.
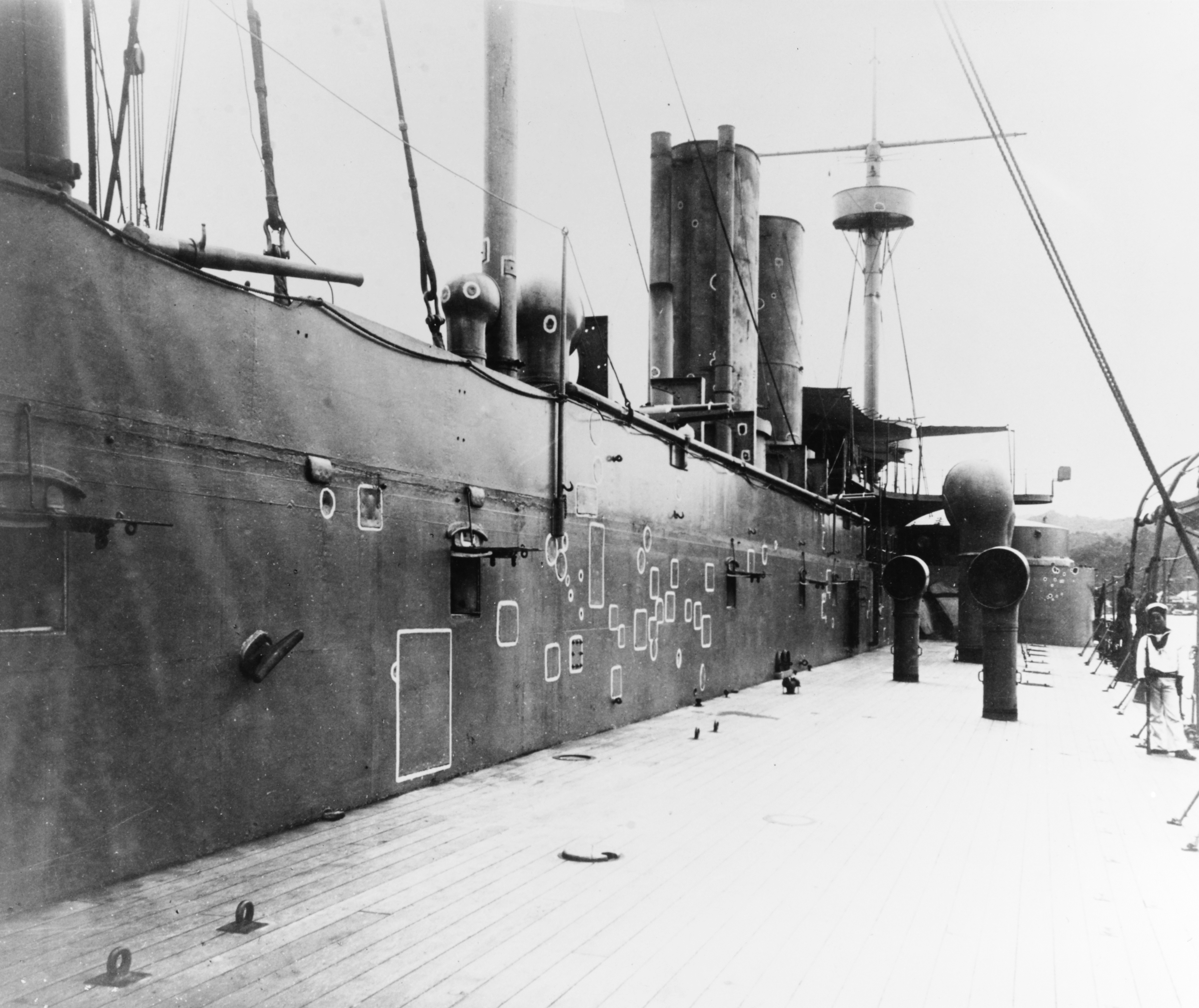
=Battle of Weihaiwei
= While approaching Weihaiwei on 14 November, ''Zhenyuan'' struck a reef as the ship attempted to maneuver around the obstacles that had been erected off the harbor entrance to prevent a Japanese attack. The grounding tore a hole that was long and caused significant flooding, including the port engine room. The vessel remained stuck on the reef for three weeks, listing to port with her main deck awash. The salvage team eventually towed her off the reef and brought the ship into the anchorage at Weihaiwei, where she was run aground to avoid sinking. Divers were sent from Shanghai to patch the hole with concrete. Lin took responsibility for the accident and committed suicide the following day with an overdose of
While approaching Weihaiwei on 14 November, ''Zhenyuan'' struck a reef as the ship attempted to maneuver around the obstacles that had been erected off the harbor entrance to prevent a Japanese attack. The grounding tore a hole that was long and caused significant flooding, including the port engine room. The vessel remained stuck on the reef for three weeks, listing to port with her main deck awash. The salvage team eventually towed her off the reef and brought the ship into the anchorage at Weihaiwei, where she was run aground to avoid sinking. Divers were sent from Shanghai to patch the hole with concrete. Lin took responsibility for the accident and committed suicide the following day with an overdose of opium
Opium (or poppy tears, scientific name: ''Lachryma papaveris'') is dried latex obtained from the seed capsules of the opium poppy ''Papaver somniferum''. Approximately 12 percent of opium is made up of the analgesic alkaloid morphine, which i ...
. Captain Yang Yung-Lin took his place as the ship's commander. Weihaiwei lacked the dry dock facilities necessary to properly repair ''Zhenyuan'', and the concrete patch, which was completed by January 1895, left her only partially seaworthy, so she was left moored in port. The grounding contributed to a significant decline in morale among the crews of the fleet, since the loss of a fully operational ironclad seriously degraded their ability to resist a Japanese attack.
The Japanese Army had advanced to Weihaiwei by the end of January 1895, launching a major attack on the port on the 30th to begin the Battle of Weihaiwei. They quickly captured the fortifications on the eastern side of the city, which forced the Chinese ships to withdraw to the western portion of the harbor, where they would be out of range for the guns in the fortress. Though ''Zhenyuan'' was unable to get underway, her guns could still be used to support the garrison and disrupt Japanese movements ashore. On 1 February, she fired 119 shells to help repel the Japanese troops. Japanese torpedo boats broke into the harbor on the night of 4/5 February and torpedoed ''Dingyuan'', disabling her and prompting Ding to shift his flag to ''Zhenyuan''. The next night, the torpedo boats made another assault on the Chinese fleet, but they missed ''Zhenyuan'' and instead sank a cruiser, a training ship, and an auxiliary vessel.
On 9 February, ''Zhenyuan'' scored a hit on the cruiser , though the shell failed to detonate. By that time, the Japanese inflicted serious damage on ''Dingyuan'', leading to Ding's decision to scuttle the ship, which provoked many of the senior officers of the Beiyang Fleet to commit suicide, including Yang on 12 February. The next day, the Chinese surrendered, and a party from the Combined Fleet entered the port on 17 February to inspect the vessels in the harbor. They found ''Zhenyuan'' to be in salvageable condition, as the only damage to the hull
Hull may refer to:
Structures
* Chassis, of an armored fighting vehicle
* Fuselage, of an aircraft
* Hull (botany), the outer covering of seeds
* Hull (watercraft), the body or frame of a ship
* Submarine hull
Mathematics
* Affine hull, in affi ...
was from the grounding incident. Seized as a war prize, the ship would be repaired and commissioned into the Japanese fleet.
Japanese service
The Japanese refloated the ship and ''Saikyō Maru'', having been repaired after the Battle of the Yalu River, towed her to Port Arthur. There, she was commissioned into the Japanese Navy on 16 March and renamed ''Chin Yen'', the Japanese version of her original name. She then was dry-docked for temporary repairs that lasted from April to June. During this process, a team inspected the damage that had been inflicted during the war for lessons that could be incorporated into future Japanese warships. The primary observation was that side armor should be strengthened instead of deck armor, given the short battle ranges of the day, since close-range direct fire, with its flat trajectory, would most likely strike the side of a ship, rather than pass over the belt. On 5 July, ''Chin Yen'', the largest vessel in the Japanese fleet and its only capital ship, got underway for a tour of Japan. She first visited Nagasaki from 10 to 16 July, before passing through theSeto Inland Sea
The , sometimes shortened to the Inland Sea, is the body of water separating Honshū, Shikoku, and Kyūshū, three of the four main islands of Japan. It serves as a waterway connecting the Pacific Ocean to the Sea of Japan. It connects to Osaka ...
, where she stopped in Hiroshima
is the capital of Hiroshima Prefecture in Japan. , the city had an estimated population of 1,199,391. The gross domestic product (GDP) in Greater Hiroshima, Hiroshima Urban Employment Area, was US$61.3 billion as of 2010. Kazumi Matsui h ...
, Kure, and Kobe. She arrived in Yokohama on 28 July and was then assigned to the Yokosuka Naval District for a substantial rebuilding as well as permanent repairs to her wartime damage. The main battery could not be updated apart from the installation of fire-control directors, but the secondary battery was substantially improved.
The Meiji Emperor visited the ship at Yokosuka on 25 November 1896, after which ''Chin Yen'' embarked on a tour of Japan to celebrate the country's victory over China. With the of modern pre-dreadnought battleships nearing completion, ''Chin Yen'' was classified as a second class battleship, though she remained in service with the Combined Fleet until 21 March 1898, when she became the flagship of the Reserve Fleet. By that time, both ''Fuji''-class ships had entered service, replacing her as the largest and most powerful vessels in the fleet. Over the next several years, ''Chin Yen'' was occupied with cruises in Japanese waters and visits to numerous ports in the country. During the Boxer Uprising
The Boxer Rebellion, also known as the Boxer Uprising, the Boxer Insurrection, or the Yihetuan Movement, was an anti-foreign, anti-colonial, and anti-Christian uprising in China between 1899 and 1901, towards the end of the Qing dynasty, by ...
in China, she served with the forces of the Eight Nation Alliance during the Battle of Tientsin, helping to break the siege of the city.
Russo-Japanese War
 Competition over control of Korea brought Japan into a second conflict, now with the Russian Empire in 1904. The Russo-Japanese War began on 8 February with a surprise torpedo-boat attack on the Russian First Pacific Squadron that occupied Port Arthur. Now obsolete, ''Chin Yen'' was assigned to the 5th Squadron of 3rd Fleet, the flagship of Vice Admiral
Competition over control of Korea brought Japan into a second conflict, now with the Russian Empire in 1904. The Russo-Japanese War began on 8 February with a surprise torpedo-boat attack on the Russian First Pacific Squadron that occupied Port Arthur. Now obsolete, ''Chin Yen'' was assigned to the 5th Squadron of 3rd Fleet, the flagship of Vice Admiral Kataoka Shichirō
Baron was an early admiral of the Imperial Japanese Navy.
Biography
Early career
Born to a ''samurai'' family in the Satsuma domain (present day Kagoshima prefecture), Kataoka entered the 3rd class of the Imperial Japanese Naval Academy in 187 ...
, along with the three ''Matsushima''-class cruisers. The ships had departed from Sasebo near Nagasaki to join the rest of the fleet in preparation for war already on 6 February.
''Chin Yen'' helped to enforce the blockade of the Russian fleet in Port Arthur, which led to the Battle of the Yellow Sea on 10 August, where she saw action as part of the Main Force under Admiral Tōgō Heihachirō. The battle resulted from a Russian attempt to break the blockade. During the action, which resulted in the Russians being forced back into port, ''Chin Yen'' scored several hits on Russian ships in exchange for suffering two hits that did not inflict serious damage. After resuming the blockade, the Japanese fleet also conducted bombardments of Russian positions in the area. On 6 March, ''Chin Yen'' and several other ships shelled Vladivostok, where another Russian squadron was located. In a forty-minute bombardment, the Japanese vessels failed to inflict any serious damage.
The ship next saw action at the Battle of Tsushima
The Battle of Tsushima (Japanese:対馬沖海戦, Tsushimaoki''-Kaisen'', russian: Цусимское сражение, ''Tsusimskoye srazheniye''), also known as the Battle of Tsushima Strait and the Naval Battle of Sea of Japan (Japanese: 日 ...
on 27–28 May 1905; the Russians had assembled a Second Pacific Squadron from vessels of the Baltic Fleet
, image = Great emblem of the Baltic fleet.svg
, image_size = 150
, caption = Baltic Fleet Great ensign
, dates = 18 May 1703 – present
, country =
, allegiance = (1703–1721) (1721–1917) (1917–1922) (1922–1991)(1991–present)
...
to relieve the ships in Port Arthur and sent it on a very long voyage to Asia. Tōgō intercepted the Russians in the Tsushima Strait and ''Chin Yen'' and the rest of 5th Squadron had formed the rear of his line of battle, tasked with engaging their Russian counterparts. The ships sank the supply ship ''Kamchatka'' and badly damaged the battleship . The next morning, the 5th Squadron ships helped to clear the area of any remaining Russian warships still in action and escorted the seven warships that had surrendered to Japanese ports, where they would be taken as war prizes.
''Chin Yen'' and the rest of 5th Squadron then proceeded to Tsushima Tsushima may refer to:
Places
* Tsushima Island, part of Nagasaki Prefecture
** Tsushima, Nagasaki, a city in Nagasaki Prefecture (coterminous with Tsushima Island)
** Tsushima Province, a historical province, coterminous with modern Tsushima Su ...
, where they arrived on 20 June. From there, ''Chin Yen'' was detached for a refit in Kure and was then reassigned to the Ōminato Guard District in northern Honshu. The ship got underway on 4 July as part of an amphibious assault force that landed on Sakhalin three days later. After the end of the war on 5 September, ''Chin Yen'' went to Port Arthur to escort the armored cruiser , which had been scuttled there during the war and then raised by a Japanese salvage team. A fleet review was held on 23 October to celebrate Japan's victory, which was to be ''Chin Yen''s last activity as part of the active fleet. The review began with a parade of captured Russian warships, followed by ''Chin Yen'' and other former Chinese vessels as part of a display of the spoils the Japanese Navy had seized in the two wars.
Later career
''Chin Yen'' was reclassified as a first-class coastal defense ship on 11 December. For the next five and a half years, she was used as a training ship for naval cadets andnon-commissioned officer
A non-commissioned officer (NCO) is a military officer who has not pursued a commission. Non-commissioned officers usually earn their position of authority by promotion through the enlisted ranks. (Non-officers, which includes most or all enli ...
s. During this period, the ship also took part in training maneuvers with the fleet, as she did in a series of major exercises in October and November 1908 that concluded with a fleet review for the emperor. She was finally decommissioned in April 1911; her training duties were taken by her old opponent ''Itsukushima''. ''Chin Yen'' was employed as a target ship for the new armored cruiser in late 1911 and was later sold to ship breaker
''Ship Breaker'' is a 2010 young adult novel by Paolo Bacigalupi set in a post-apocalyptic future. Human civilization is in decline for ecological reasons. The polar ice caps have melted and New Orleans is underwater. On the Gulf Coast n ...
s in April 1912. The funds raised were used to cover part of the cost of the grand hall at the Naval Academy Etajima in Hiroshima.
Two of the ship's anchors were removed in 1896 during the reconstruction to be preserved in Ueno Park in Tokyo as a monument to Japan's victory. This was a cause of public outrage in China. After Japan's defeat in World War II, the Chinese nationalist government insisted on their return, which was granted by the American occupation authority. The anchors left Tokyo on 1 May 1947 and arrived in Shanghai in October. They were installed at the naval academy in Qingdao
Qingdao (, also spelled Tsingtao; , Mandarin: ) is a major city in eastern Shandong Province. The city's name in Chinese characters literally means " azure island". Located on China's Yellow Sea coast, it is a major nodal city of the One Belt ...
and after the Communist victory in the Chinese Civil War, they were moved to the Military Museum of the Chinese People's Revolution in Beijing.
Citations
References
* * * * * * * * * {{DEFAULTSORT:Zhenyuan Ships built in Stettin 1882 ships Dingyuan-class ironclads Battleships of the Imperial Japanese Navy Russo-Japanese War battleships of Japan Captured ships