Chinese Americans are
Americans
Americans are the citizens and nationals of the United States of America.; ; Although direct citizens and nationals make up the majority of Americans, many dual citizens, expatriates, and permanent residents could also legally claim Ame ...
of
Han Chinese
The Han Chinese () or Han people (), are an East Asian ethnic group native to China. They constitute the world's largest ethnic group, making up about 18% of the global population and consisting of various subgroups speaking distinctiv ...
ancestry. Chinese Americans constitute a subgroup of
East Asian Americans
Asian Americans are Americans of Asian ancestry (including naturalized Americans who are immigrants from specific regions in Asia and descendants of such immigrants). Although this term had historically been used for all the indigenous peopl ...
which also constitute a subgroup of
Asian Americans. Many Chinese Americans along with their ancestors trace lineage from
mainland China
"Mainland China" is a geopolitical term defined as the territory governed by the People's Republic of China (including islands like Hainan or Chongming), excluding dependent territories of the PRC, and other territories within Greater China. ...
,
Hong Kong
Hong Kong ( (US) or (UK); , ), officially the Hong Kong Special Administrative Region of the People's Republic of China (abbr. Hong Kong SAR or HKSAR), is a city and special administrative region of China on the eastern Pearl River Delta i ...
,
Macau
Macau or Macao (; ; ; ), officially the Macao Special Administrative Region of the People's Republic of China (MSAR), is a city and special administrative region of China in the western Pearl River Delta by the South China Sea. With a p ...
,
Malaysia
Malaysia ( ; ) is a country in Southeast Asia. The federation, federal constitutional monarchy consists of States and federal territories of Malaysia, thirteen states and three federal territories, separated by the South China Sea into two r ...
,
Singapore
Singapore (), officially the Republic of Singapore, is a sovereign island country and city-state in maritime Southeast Asia. It lies about one degree of latitude () north of the equator, off the southern tip of the Malay Peninsula, bor ...
,
Taiwan
Taiwan, officially the Republic of China (ROC), is a country in East Asia, at the junction of the East and South China Seas in the northwestern Pacific Ocean, with the People's Republic of China (PRC) to the northwest, Japan to the nort ...
, as well as other regions which are inhabited by large populations of the
Chinese diaspora
Overseas Chinese () refers to people of Chinese birth or ethnicity who reside outside Mainland China, Hong Kong, Macau, and Taiwan. As of 2011, there were over 40.3 million overseas Chinese.
Terminology
() or ''Hoan-kheh'' () in Hokkien, re ...
, especially
Southeast Asia
Southeast Asia, also spelled South East Asia and South-East Asia, and also known as Southeastern Asia, South-eastern Asia or SEA, is the geographical south-eastern region of Asia, consisting of the regions that are situated south of mainlan ...
and some other countries such as
Australia,
Canada
Canada is a country in North America. Its ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, covering over , making it the world's second-largest country by tot ...
,
France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic, Pacific and Indian Oceans. Its metropolitan area ...
,
South Africa
South Africa, officially the Republic of South Africa (RSA), is the Southern Africa, southernmost country in Africa. It is bounded to the south by of coastline that stretch along the Atlantic Ocean, South Atlantic and Indian Oceans; to the ...
,
New Zealand
New Zealand ( mi, Aotearoa ) is an island country in the southwestern Pacific Ocean. It consists of two main landmasses—the North Island () and the South Island ()—and over 700 smaller islands. It is the sixth-largest island count ...
, and the
United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Europe, off the north-western coast of the European mainland, continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotlan ...
. Chinese-Americans include Chinese from the Chinese circle and around the world who became naturalized U.S. citizens and their natural-born descendants in the United States.
The Chinese American community is the largest overseas Chinese community outside
Asia
Asia (, ) is one of the world's most notable geographical regions, which is either considered a continent in its own right or a subcontinent of Eurasia, which shares the continental landmass of Afro-Eurasia with Africa. Asia covers an are ...
. It is also the third largest community in the Chinese diaspora, behind the Chinese communities in
Thailand
Thailand ( ), historically known as Siam () and officially the Kingdom of Thailand, is a country in Southeast Asia, located at the centre of the Indochinese Peninsula, spanning , with a population of almost 70 million. The country is b ...
and
Malaysia
Malaysia ( ; ) is a country in Southeast Asia. The federation, federal constitutional monarchy consists of States and federal territories of Malaysia, thirteen states and three federal territories, separated by the South China Sea into two r ...
. The 2016 Community Survey of the US Census estimates a population of Chinese Americans of one or more races to be 5,081,682. According to the 2010 census, the Chinese American population numbered approximately 3.8 million.
In 2010, half of Chinese-born people living in the United States resided in the states of
California
California is a state in the Western United States, located along the Pacific Coast. With nearly 39.2million residents across a total area of approximately , it is the most populous U.S. state and the 3rd largest by area. It is also the m ...
and
New York.
History


Early arrivals, cause for migration
The first Chinese immigrants arrived in 1820, according to U.S. government records. 325 men are known to have arrived before the 1849
California Gold Rush, which drew the first significant number of laborers from China who mined for gold and performed menial labor.
There were 25,000 immigrants by 1852, and 105,465 by 1880, most of whom lived on the
West Coast. They formed over a tenth of California's population. Nearly all of the early Chinese immigrants were young males with varied educational levels from rural villages of
Toisan
Taishan (), alternately romanized in Cantonese as Toishan or Toisan, in local dialect as Hoisan, and formerly known as Xinning or Sunning (), is a county-level city in the southwest of Guangdong province, China. It is administered as part o ...
as well as the
eight districts in
Guangdong Province.
[International World History Project. . Retrieved 14 March 2014.]
The Guangdong province especially
Toisan
Taishan (), alternately romanized in Cantonese as Toishan or Toisan, in local dialect as Hoisan, and formerly known as Xinning or Sunning (), is a county-level city in the southwest of Guangdong province, China. It is administered as part o ...
experienced extreme floods and famine in the mid-nineteenth century. The instability caused by these events led to mass political unrest in the province such as the
Red Turban unrest. Other provinces were similarly afflicted by natural disasters, which prompted many people to migrate to the U.S. The vast majority of the 19th century Chinese immigrants to the U.S. came from a small area of eight districts on the west side of the
Pearl River Delta in Guangdong province. The eight districts consist of three subgroups—the four districts of
Sze Yup
The Siyi (Seiyap or Sze Yup in Cantonese; ) refers to the four former counties of Xinhui (Sunwui), Taishan (Toisan), Kaiping (Hoiping) and Enping (Yanping) on the west side of the Pearl River Delta in Southern Guangdong Province, China.
Geogra ...
, the district of
Chung Shan, and the three districts of
Sam Yup
Sanyi () or Nanpanshun (), also known by Cantonese romanizations such as Sam Yup and Nam Pun Shun, refers to the three districts (former counties) of Nanhai, Panyu and Shunde surrounding Guangzhou and Foshan in Guangdong, China.
Geography
Th ...
—each subgroup speaking a distinct dialect of
Cantonese
Cantonese ( zh, t=廣東話, s=广东话, first=t, cy=Gwóngdūng wá) is a language within the Chinese (Sinitic) branch of the Sino-Tibetan languages originating from the city of Guangzhou (historically known as Canton) and its surrounding ar ...
.
In the U.S., people from Sze Yup generally worked as laborers; Chung Shan people specialized in agriculture; and Sam Yup people worked as entrepreneurs.

These Chinese immigrants were predominantly men. By 1900, only 4,522 of the 89,837 Chinese migrants that lived in the U.S. were women. The lack of women migrants was largely due to the passage of U.S. anti-immigration laws. For example, the
Page Law of 1875 prevented the immigration of all women prostitutes from China. This law was used to limit the immigration of all Chinese women, not just prostitutes. Upon arrival to the U.S. Chinese men and women were separated from each other as they awaited hearings on their immigration status, which often took weeks. During this time the women were subjected to lengthy questioning that focused on their family life and origins. Their responses were then cross examined with others from their village, and any discrepancies were used to justify denial of entry. The stress of being separated from family caused many women to fall ill while they waited for a hearing. Some even committed suicide as they feared being denied access to the country. Once they were approved and allowed into the country, Chinese women migrants faced additional challenges. Many were coerced into prostitution, with over 60% of the adult Chinese women living in California in 1870 working in the trade. Some women were lured to the U.S. with the promise of marriage only to become sex slaves. Despite these challenges Chinese women were often drawn to the U.S. in order to reunite with their families. Ninety percent of the Chinese women who immigrated to the US between 1898 and 1908 did so to join their husband or father who already resided in the U.S. Chinese women migrants, similarly to men, immigrated for economic opportunities as well.
In the 1850s, Chinese workers migrated to the United States, first to work in the gold mines, but also to take agricultural jobs, and factory work, especially in the garment industry. Chinese immigrants were particularly instrumental in building railroads in the U.S. west, and as Chinese laborers grew successful in the United States, a number of them became entrepreneurs in their own right. As the numbers of Chinese laborers increased, so did the strength of anti-Chinese attitude among other workers in the U.S. economy. This finally resulted in legislation that aimed to limit future immigration of Chinese workers to the United States, and threatened to sour diplomatic relations between the United States and China through the
Chinese Exclusion Act
The Chinese Exclusion Act was a United States federal law signed by President Chester A. Arthur on May 6, 1882, prohibiting all immigration of Chinese laborers for 10 years. The law excluded merchants, teachers, students, travelers, and diplo ...
.
California Gold Rush, Central Pacific Railroad construction
The Chinese came to California in large numbers during the California Gold Rush, with 40,400 being recorded as arriving from 1851 to 1860, and again in the 1860s, when the
Central Pacific Railroad recruited large labor gangs, many on five-year contracts, to build its portion of the
Transcontinental Railroad
A transcontinental railroad or transcontinental railway is contiguous railroad trackage, that crosses a continental land mass and has terminals at different oceans or continental borders. Such networks can be via the tracks of either a single ...
. The Chinese laborers worked out well and thousands more were recruited until the railroad's completion in 1869. Chinese labor provided the massive workforce needed to build the majority of the Central Pacific's difficult route through the
Sierra Nevada mountains and across
Nevada
Nevada ( ; ) is a state in the Western region of the United States. It is bordered by Oregon to the northwest, Idaho to the northeast, California to the west, Arizona to the southeast, and Utah to the east. Nevada is the 7th-most extensive, ...
. By 1869, the ethnic Chinese population in the U.S. numbered at least 100,000.
Objections to Chinese immigration, 1882 Chinese Exclusion Act
Nativist objections to Chinese immigration to the U.S. took many forms, and generally stemmed from economic and cultural tensions, as well as ethnic discrimination. Most Chinese laborers who came to the United States did so in order to send money back to China to support their families there. At the same time, they also had to repay loans to the Chinese merchants who paid their passage to North America. These financial pressures left them little choice but to work for whatever wages they could. Non-Chinese laborers often required much higher wages to support their wives and children in the United States, and also generally had a stronger political standing to bargain for higher wages. Therefore, many of the non-Chinese workers in the United States came to resent the Chinese laborers, who might squeeze them out of their jobs. Furthermore, as with most immigrant communities, many Chinese settled in their own neighborhoods, and tales spread of Chinatowns as places where large numbers of Chinese men congregated to visit prostitutes, smoke tobacco, or gamble. Some advocates of anti-Chinese legislation therefore argued that admitting Chinese into the United States lowered the cultural and moral standards of American society. Others used a more overtly racist argument for limiting immigration from East Asia, and expressed concern about the integrity of American racial composition.
To address these rising social tensions, from the 1850s through the 1870s the California state government passed a series of measures aimed at Chinese residents, ranging from requiring special licenses for Chinese businesses or workers to preventing naturalization. Because anti-Chinese discrimination and efforts to stop Chinese immigration violated the 1868
Burlingame-Seward Treaty with China, the federal government was able to negate much of this legislation.
The Chinese population rose from 2,716 in 1851 to 63,000 by 1871. In the decade 1861–70, 64,301 were recorded as arriving, followed by 123,201 in 1871–80 and 61,711 in 1881–1890. 77% were located in California, with the rest scattered across the
American West, the South, and
New England
New England is a region comprising six states in the Northeastern United States: Connecticut, Maine, Massachusetts, New Hampshire, Rhode Island, and Vermont. It is bordered by the state of New York (state), New York to the west and by the Can ...
.
Most came from
Toisan
Taishan (), alternately romanized in Cantonese as Toishan or Toisan, in local dialect as Hoisan, and formerly known as Xinning or Sunning (), is a county-level city in the southwest of Guangdong province, China. It is administered as part o ...
looking for a better life to escape a starvation and economic hardships.
In 1879, advocates of immigration restriction succeeded in introducing and passing legislation in Congress to limit the number of Chinese arriving to fifteen per ship or vessel. Republican
President Rutherford B. Hayes
Rutherford Birchard Hayes (; October 4, 1822 – January 17, 1893) was an American lawyer and politician who served as the 19th president of the United States from 1877 to 1881, after serving in the U.S. House of Representatives and as governor ...
vetoed the bill because it violated U.S. treaty agreements with China. Nevertheless, it was still an important victory for advocates of exclusion. Democrats, led by supporters in the West, advocated for all-out exclusion of Chinese immigrants. Although Republicans were largely sympathetic to western concerns, they were committed to a platform of free immigration. In order to placate the western states without offending China, President Hayes sought a revision of the Burlingame-Seward Treaty in which China agreed to limit immigration to the United States.
In 1880, the Hayes Administration appointed U.S. diplomat
James B. Angell to negotiate a new treaty with China. The resulting
Angell Treaty permitted the United States to restrict, but not completely prohibit, Chinese immigration. In 1882, Congress passed the Chinese Exclusion Act, which, per the terms of the Angell Treaty, suspended the immigration of Chinese laborers (skilled or unskilled) for a period of 10 years. The Act also required every Chinese person traveling in or out of the country to carry a certificate identifying his or her status as a laborer, scholar, diplomat, or merchant. The 1882 Act was the first in American history to place broad restrictions on immigration.
For American presidents and Congressmen addressing the question of Chinese exclusion, the challenge was to balance domestic attitudes and politics, which dictated an anti-Chinese policy, while maintaining good diplomatic relations with China, where exclusion would be seen as an affront and a violation of treaty promises. The domestic factors ultimately trumped international concerns. In 1888, Congress took exclusion even further and passed the
Scott Act, which made reentry to the United States after a visit to China impossible, even for long-term legal residents. The Chinese Government considered this act a direct insult, but was unable to prevent its passage. In 1892, Congress voted to renew exclusion for ten years in the
Geary Act
The Geary Act was a United States law that extended the Chinese Exclusion Act of 1882 by adding onerous new requirements. It was written by California Representative Thomas J. Geary and was passed by Congress on .
The law required all Chinese r ...
, and in 1902, the prohibition was expanded to cover Hawaii and the Philippines, all over strong objections from the Chinese Government and people. Congress later extended the Exclusion Act indefinitely.
The initial immigration group may have been as high as 90% male due to the Chinese Exclusion act, resulting in most immigrants coming with the thought of earning money, and then returning to China to start a family. Those that stayed in America faced the lack of suitable Chinese brides, because Chinese women were not allowed to immigrate to the US in significant numbers after 1872. As a result, many isolated mostly-bachelor communities slowly aged in place with very low Chinese birth rates. Later, as a result of the
Fourteenth Amendment and the 1898 ''
United States v. Wong Kim Ark'' Supreme Court decision, ethnic Chinese born in the United States became
American citizens.
The Chinese Exclusion Acts were not repealed until 1943, and then only in the interests of aiding the morale of a wartime ally during World War II. With relations already complicated by the Treaties of Wangxia and Tianjian, the increasingly harsh restrictions on Chinese immigration, combined with the
rising discrimination against Chinese living in the United States in the 1870s-early 1900s, placed additional strain on the diplomatic relationship between the United States and China.
Integration, interracial marriage
In the mid-1850s, 70 to 150 Chinese were living in New York City and 11 of them married Irish women. In 1906, ''
The New York Times
''The New York Times'' (''the Times'', ''NYT'', or the Gray Lady) is a daily newspaper based in New York City with a worldwide readership reported in 2020 to comprise a declining 840,000 paid print subscribers, and a growing 6 million paid d ...
'' reported that 300 white women (
Irish Americans
, image = Irish ancestry in the USA 2018; Where Irish eyes are Smiling.png
, image_caption = Irish Americans, % of population by state
, caption = Notable Irish Americans
, population =
36,115,472 (10.9%) alone ...
) were married to Chinese men in New York, with many more cohabited. In 1900, based on Liang research, of the 120,000 men in more than 20 Chinese communities in the United States, he estimated that one out of every twenty Chinese (
Cantonese
Cantonese ( zh, t=廣東話, s=广东话, first=t, cy=Gwóngdūng wá) is a language within the Chinese (Sinitic) branch of the Sino-Tibetan languages originating from the city of Guangzhou (historically known as Canton) and its surrounding ar ...
) men was married to white women. In the 1960s census showed 3500 Chinese men married to white women and 2900 Chinese women married to white men. Originally at the start of the 20th century there was a 55% rate of Chinese men in New York engaging in interracial marriage which was maintained in the 1920s but in the 1930s it slid to 20%.
During and after
World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposing ...
, severe immigration restrictions were eased as the United States allied with China against
Japanese
Japanese may refer to:
* Something from or related to Japan, an island country in East Asia
* Japanese language, spoken mainly in Japan
* Japanese people, the ethnic group that identifies with Japan through ancestry or culture
** Japanese diaspor ...
expansionism. Later reforms in the 1960s placed increasing value on family unification, allowing relatives of U.S. citizens to receive preference in immigration.
Museums
There are a number of museums in the United States specifically focusing on and documenting the Chinese American experience including the
Museum of Chinese in America
The Museum of Chinese in America (; abbreviated MOCA) is a museum in New York City which exhibits Chinese American history. It is a nonprofit 501(c)(3) education and cultural institution that presents the living history, heritage, culture, and d ...
in
Manhattan's Chinatown established in 1980, the
Chinese American Museum
The Chinese American Museum (Chinese: 華美 博物館; abbreviated CAM) is a museum located in Downtown Los Angeles as a part of the El Pueblo de Los Angeles Historic Monument. It is dedicated to the history and experience of Chinese America ...
in Los Angeles, the
Chinese American Museum of Chicago, the
Chinese Historical Society of America
The Chinese Historical Society of America (; abbreviated CHSA) is the oldest and largest archive and history center documenting the Chinese American experience in the United States. It is based in the Chinatown neighborhood of San Francisco, Cali ...
in San Francisco, and the
Chinese American Museum in Washington, D.C.

.
Demographics
Population
The chart on the right shows the total number of ethnic Chinese in the United States since 1850.
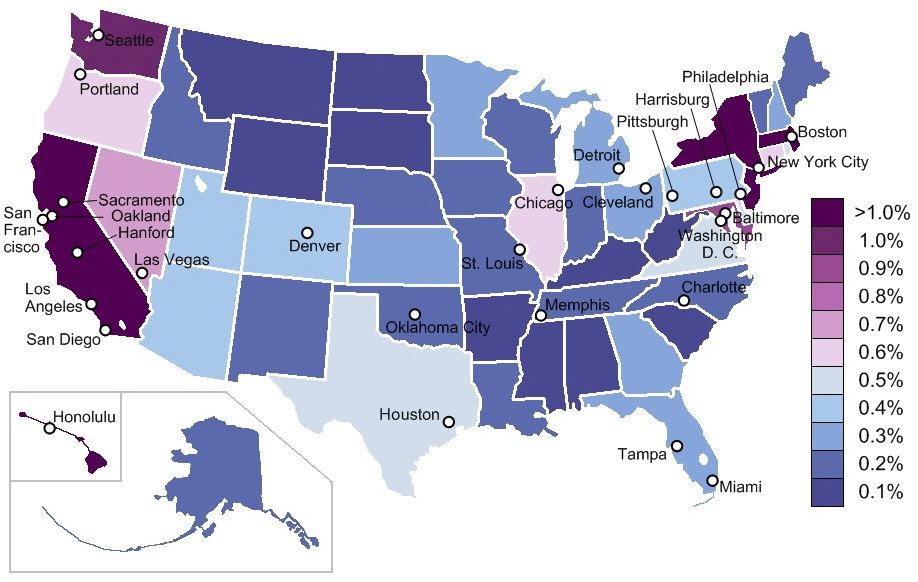
States with the largest estimated Chinese American populations
The states with the largest estimated Chinese American populations, according to the
2010 Census, were
California
California is a state in the Western United States, located along the Pacific Coast. With nearly 39.2million residents across a total area of approximately , it is the most populous U.S. state and the 3rd largest by area. It is also the m ...
(1,253,100; 3.4%),
New York (577,000; 3.0%),
Texas
Texas (, ; Spanish: ''Texas'', ''Tejas'') is a state in the South Central region of the United States. At 268,596 square miles (695,662 km2), and with more than 29.1 million residents in 2020, it is the second-largest U.S. state by ...
(157,000; 0.6%),
New Jersey
New Jersey is a state in the Mid-Atlantic and Northeastern regions of the United States. It is bordered on the north and east by the state of New York; on the east, southeast, and south by the Atlantic Ocean; on the west by the Delaware ...
(134,500; 1.5%),
Massachusetts
Massachusetts (Massachusett: ''Muhsachuweesut Massachusett_writing_systems.html" ;"title="nowiki/> məhswatʃəwiːsət.html" ;"title="Massachusett writing systems">məhswatʃəwiːsət">Massachusett writing systems">məhswatʃəwiːsət'' En ...
(123,000; 1.9%),
Illinois
Illinois ( ) is a state in the Midwestern United States. Its largest metropolitan areas include the Chicago metropolitan area, and the Metro East section, of Greater St. Louis. Other smaller metropolitan areas include, Peoria and Rockf ...
(104,200; 0.8%),
Washington
Washington commonly refers to:
* Washington (state), United States
* Washington, D.C., the capital of the United States
** A metonym for the federal government of the United States
** Washington metropolitan area, the metropolitan area centered o ...
(94,200; 1.4%),
Pennsylvania
Pennsylvania (; ( Pennsylvania Dutch: )), officially the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania, is a state spanning the Mid-Atlantic, Northeastern, Appalachian, and Great Lakes regions of the United States. It borders Delaware to its southeast, ...
(85,000; 0.7%),
Maryland
Maryland ( ) is a state in the Mid-Atlantic region of the United States. It shares borders with Virginia, West Virginia, and the District of Columbia to its south and west; Pennsylvania to its north; and Delaware and the Atlantic Ocean to ...
(69,400; 1.2%),
Virginia
Virginia, officially the Commonwealth of Virginia, is a state in the Mid-Atlantic and Southeastern regions of the United States, between the Atlantic Coast and the Appalachian Mountains. The geography and climate of the Commonwealth ar ...
(59,800; 0.7%), and
Ohio
Ohio () is a state in the Midwestern region of the United States. Of the fifty U.S. states, it is the 34th-largest by area, and with a population of nearly 11.8 million, is the seventh-most populous and tenth-most densely populated. The sta ...
(51,033; 0.5%). The state of
Hawaii
Hawaii ( ; haw, Hawaii or ) is a state in the Western United States, located in the Pacific Ocean about from the U.S. mainland. It is the only U.S. state outside North America, the only state that is an archipelago, and the only state ...
has the highest concentration of Chinese Americans at 4.0%, or 55,000 people.
Population centers of Chinese Americans
According to the 2012 Census estimates, the three
metropolitan areas
A metropolitan area or metro is a region that consists of a densely populated urban agglomeration and its surrounding territories sharing industries, commercial areas, transport network, infrastructures and housing. A metro area usually ...
with the largest Chinese American populations were the
Greater New York Combined Statistical Area
Combined statistical area (CSA) is a United States Office of Management and Budget (OMB) term for a combination of adjacent metropolitan (MSA) and micropolitan statistical areas (µSA) across the 50 US states and the territory of Puerto Ric ...
at 735,019 people, the
San Jose-San Francisco-Oakland Combined Statistical Area at 629,243 people, and the
Los Angeles Area
Greater Los Angeles is the second-largest metropolitan region in the United States with a population of 18.5 million in 2021, encompassing five counties in Southern California extending from Ventura County in the west to San Bernardino Cou ...
Combined Statistical Area at about 566,968 people.
New York City
New York, often called New York City or NYC, is the most populous city in the United States. With a 2020 population of 8,804,190 distributed over , New York City is also the most densely populated major city in the Un ...
contains by far the highest ethnic Chinese population of any individual city outside Asia, estimated at 628,763 as of 2017.
The Los Angeles County city of
Monterey Park has the highest percentage of Chinese Americans of any municipality, at 43.7% of its population, or 24,758 people.
The
New York metropolitan area
The New York metropolitan area, also commonly referred to as the Tri-State area, is the largest metropolitan area in the world by urban landmass, at , and one of the most populous urban agglomerations in the world. The vast metropolitan area ...
, consisting of
New York City
New York, often called New York City or NYC, is the most populous city in the United States. With a 2020 population of 8,804,190 distributed over , New York City is also the most densely populated major city in the Un ...
,
Long Island, and nearby areas within the states of
New York,
New Jersey
New Jersey is a state in the Mid-Atlantic and Northeastern regions of the United States. It is bordered on the north and east by the state of New York; on the east, southeast, and south by the Atlantic Ocean; on the west by the Delaware ...
,
Connecticut
Connecticut () is the southernmost state in the New England region of the Northeastern United States. It is bordered by Rhode Island to the east, Massachusetts to the north, New York to the west, and Long Island Sound to the south. Its capita ...
and
Pennsylvania
Pennsylvania (; ( Pennsylvania Dutch: )), officially the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania, is a state spanning the Mid-Atlantic, Northeastern, Appalachian, and Great Lakes regions of the United States. It borders Delaware to its southeast, ...
, is home to the largest Chinese American population of any
metropolitan area within the United States and the largest Chinese population outside of China, enumerating an estimated 893,697 in 2017
and including at least 12
Chinatowns. Continuing significant
immigration from Mainland China, both legal and illegal
in origin, has spurred the ongoing rise of the Chinese American population in the New York metropolitan area; this immigration continues to be fueled by New York's status as an alpha global city, its high population density, its extensive mass transit system, and the New York metropolitan area's enormous economic marketplace. The
Manhattan Chinatown
Manhattan's Chinatown () is a neighborhood in Lower Manhattan, New York City, bordering the Lower East Side to its east, Little Italy to its north, Civic Center to its south, and Tribeca to its west. With an estimated population of 90,000 to 1 ...
contains the largest concentration of ethnic Chinese in the
Western hemisphere
The Western Hemisphere is the half of the planet Earth that lies west of the prime meridian (which crosses Greenwich, London, United Kingdom) and east of the antimeridian. The other half is called the Eastern Hemisphere. Politically, the te ...
;
[*
*
*
*
* ] while the
Flushing Chinatown in
Queens
Queens is a borough of New York City, coextensive with Queens County, in the U.S. state of New York. Located on Long Island, it is the largest New York City borough by area. It is bordered by the borough of Brooklyn at the western tip of Long ...
has become the world's largest Chinatown.
Also on the
East Coast,
Greater Boston
Greater Boston is the metropolitan region of New England encompassing the municipality of Boston (the capital of the U.S. state of Massachusetts and the most populous city in New England) and its surrounding areas. The region forms the northern a ...
and the
Philadelphia metropolitan area
Philadelphia, often called Philly, is the largest city in the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania, the sixth-largest city in the U.S., the second-largest city in both the Northeast megalopolis and Mid-Atlantic regions after New York City. Since 1 ...
have significant Chinese American communities, with Chinatowns in
Boston
Boston (), officially the City of Boston, is the state capital and most populous city of the Commonwealth of Massachusetts, as well as the cultural and financial center of the New England region of the United States. It is the 24th- mo ...
and
Philadelphia
Philadelphia, often called Philly, is the List of municipalities in Pennsylvania#Municipalities, largest city in the Commonwealth (U.S. state), Commonwealth of Pennsylvania, the List of United States cities by population, sixth-largest city i ...
hosting important and diverse cultural centers. Significant populations can also be found in the
Washington metropolitan area
The Washington metropolitan area, also commonly referred to as the National Capital Region, is the metropolitan area centered on Washington, D.C. The metropolitan area includes all of Washington, D.C. and parts of the states of Maryland, Virgi ...
, with
Montgomery County,
Maryland
Maryland ( ) is a state in the Mid-Atlantic region of the United States. It shares borders with Virginia, West Virginia, and the District of Columbia to its south and west; Pennsylvania to its north; and Delaware and the Atlantic Ocean to ...
and
Fairfax County
Fairfax County, officially the County of Fairfax, is a County (United States), county in the Commonwealth (U.S. state), Commonwealth of Virginia. It is part of Northern Virginia and borders both the city of Alexandria, Virginia, Alexandria and ...
,
Virginia
Virginia, officially the Commonwealth of Virginia, is a state in the Mid-Atlantic and Southeastern regions of the United States, between the Atlantic Coast and the Appalachian Mountains. The geography and climate of the Commonwealth ar ...
, being 3.9% and 2.4% Chinese American, respectively.
Boston's Chinatown is the only historical Chinese neighborhood within
New England
New England is a region comprising six states in the Northeastern United States: Connecticut, Maine, Massachusetts, New Hampshire, Rhode Island, and Vermont. It is bordered by the state of New York (state), New York to the west and by the Can ...
. The Boston suburb of
Quincy also has a prominent Chinese American population, especially within the
North Quincy area.
San Francisco
San Francisco (; Spanish for " Saint Francis"), officially the City and County of San Francisco, is the commercial, financial, and cultural center of Northern California. The city proper is the fourth most populous in California and 17th ...
, California has the highest
per capita
''Per capita'' is a Latin phrase literally meaning "by heads" or "for each head", and idiomatically used to mean "per person". The term is used in a wide variety of social sciences and statistical research contexts, including government statistic ...
concentration of Chinese Americans of any major city in the United States, at an estimated 21.4%, or 172,181 people, and contains the second-largest total number of Chinese Americans of any U.S. city. San Francisco's
Chinatown was established in the 1840s, making it the oldest Chinatown in
North America and one of the largest neighborhoods of Chinese people outside of Asia, composed in large part by immigrants hailing from
Guangdong province and also many from
Hong Kong
Hong Kong ( (US) or (UK); , ), officially the Hong Kong Special Administrative Region of the People's Republic of China (abbr. Hong Kong SAR or HKSAR), is a city and special administrative region of China on the eastern Pearl River Delta i ...
. The San Francisco neighborhoods of
Sunset District and
Richmond District also contain significant Chinese populations.
In addition to the big cities, smaller pockets of Chinese Americans are also dispersed in rural towns, often university-college towns, throughout the United States. For example, the number of Chinese Americans, including college professors, doctors, professionals, and students, has increased over 200% from 2005 to 2010 in
Providence, Rhode Island
Providence is the capital and most populous city of the U.S. state of Rhode Island. One of the oldest cities in New England, it was founded in 1636 by Roger Williams, a Reformed Baptist theologian and religious exile from the Massachusetts ...
, a small city with a large number of colleges.
Income and social status
Income and social status of these Chinese-American locations vary widely. about 333,333 people living in the United States with a Chinese background are not United States citizens. Although many Chinese Americans in
Chinatowns of large cities are often members of an impoverished working class, others are well-educated upper-class people living in affluent suburbs. The upper and lower-class Chinese are also widely separated by social status and class discrimination. In California's
San Gabriel Valley, for example, the cities of
Monterey Park and
San Marino
San Marino (, ), officially the Republic of San Marino ( it, Repubblica di San Marino; ), also known as the Most Serene Republic of San Marino ( it, Serenissima Repubblica di San Marino, links=no), is the fifth-smallest country in the world an ...
are both Chinese American communities lying geographically close to each other but they are separated by a large socioeconomic gap.
Cultural centers
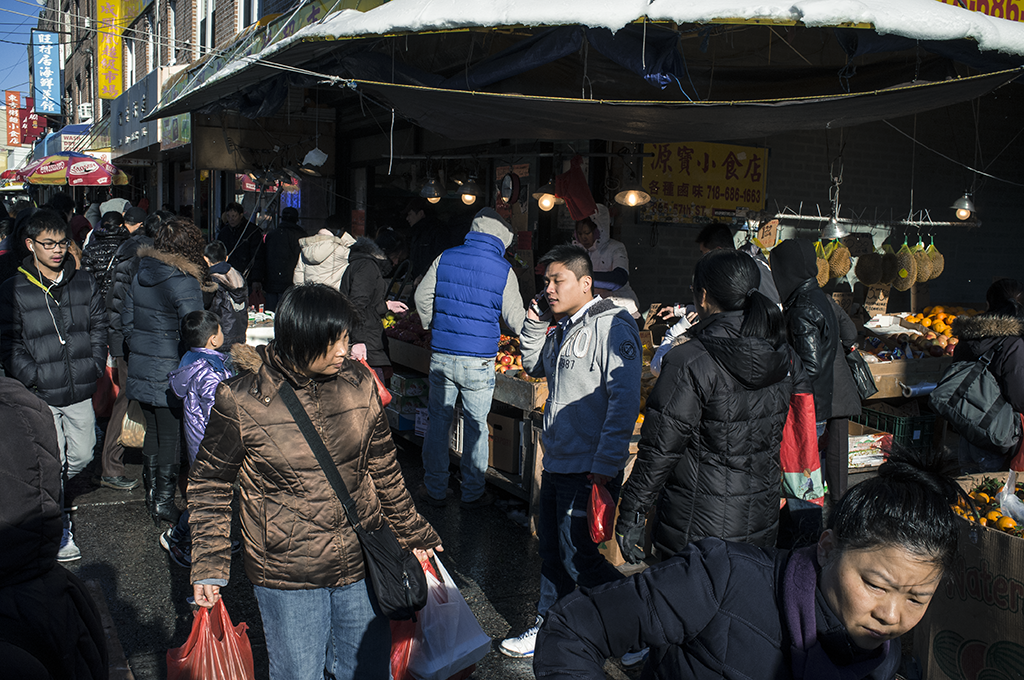

A list of large cities (250,000+ residents) with a Chinese-American population in excess of 1% of the general population in 2010.
Social status and assimilation
Some noteworthy historical Chinese contributions include building the western half of the
Transcontinental Railroad
A transcontinental railroad or transcontinental railway is contiguous railroad trackage, that crosses a continental land mass and has terminals at different oceans or continental borders. Such networks can be via the tracks of either a single ...
, and levees in the
Sacramento River Delta
)
, image_map = Sacramento County California Incorporated and Unincorporated areas Sacramento Highlighted.svg
, mapsize = 250x200px
, map_caption = Location within Sacramento ...
; the popularization of
Chinese American food; deep oil extraction in Texas; and the introduction of Chinese and
East Asian culture to America, such as
Buddhism
Buddhism ( , ), also known as Buddha Dharma and Dharmavinaya (), is an Indian religions, Indian religion or Indian philosophy#Buddhist philosophy, philosophical tradition based on Pre-sectarian Buddhism, teachings attributed to the Buddha. ...
,
Taoism
Taoism (, ) or Daoism () refers to either a school of philosophical thought (道家; ''daojia'') or to a religion (道教; ''daojiao''), both of which share ideas and concepts of Chinese origin and emphasize living in harmony with the '' Ta ...
, and
Kung fu
Chinese martial arts, often called by the umbrella terms kung fu (; ), kuoshu () or wushu (), are multiple fighting styles that have developed over the centuries in Greater China. These fighting styles are often classified according to commo ...
.
Chinese immigrants to the United States brought many of their ideas and values with them. Some of these have continued to influence later generations. Among them are
Confucian
Confucianism, also known as Ruism or Ru classicism, is a system of thought and behavior originating in ancient China. Variously described as tradition, a philosophy, a religion, a humanistic or rationalistic religion, a way of governing, or ...
respect for elders.
[Haiming Liu (2005) "Asian-American Ideas (Cultural Migration)" ''In'' Horowitz, Maryanne Cline (editor) (2005) ''New Dictionary of the History of Ideas'' Charles Scribner's Sons, Detroit, Michigan, volume 1, pp. 158–160, ] Similarly, education and the civil service were the most important path for upward social mobility in China.
The first
Broadway
Broadway may refer to:
Theatre
* Broadway Theatre (disambiguation)
* Broadway theatre, theatrical productions in professional theatres near Broadway, Manhattan, New York City, U.S.
** Broadway (Manhattan), the street
**Broadway Theatre (53rd Stree ...
show about Asian Americans was ''
Flower Drum Song
''Flower Drum Song'' was the eighth musical by the team of Rodgers and Hammerstein. It is based on the 1957 novel, '' The Flower Drum Song'', by Chinese-American author C. Y. Lee. It premiered on Broadway in 1958 and was then performed in the ...
'' which premiered on Broadway in 1958; the hit
''Chinglish'' premiered on Broadway in 2011.
In most American cities with significant Chinese populations, the new year is celebrated with cultural festivals and other celebrations. In
Seattle
Seattle ( ) is a seaport city on the West Coast of the United States. It is the seat of King County, Washington. With a 2020 population of 737,015, it is the largest city in both the state of Washington and the Pacific Northwest regio ...
, the
Chinese Culture and Arts Festival is held every year. Other important festivals include the
Dragon Boat Festival
The Dragon Boat Festival ( zh, s=端午节, t=端午節) is a traditional Chinese holiday which occurs on the fifth day of the fifth month of the Chinese calendar, which corresponds to late May or June in the Gregorian calendar.
Names
The Engl ...
and the
Mid-Autumn Festival.
Discrimination, prejudice, depression and suicide



Perceptions and stereotypes
Analysis indicated that most non-Asian Americans do not differentiate between Chinese Americans and East Asian Americans generally, and perceptions of both groups are nearly identical.
A 2001 survey of Americans' attitudes toward Asian Americans and Chinese Americans indicated that one fourth of the respondents had somewhat or very negative attitude toward Chinese Americans in general.
However, the study did also find several positive perceptions of Chinese Americans: strong family values (91%); honesty as entrepreneurs (77%); high value on education (67%).
Anti-Chinese violence in the United States
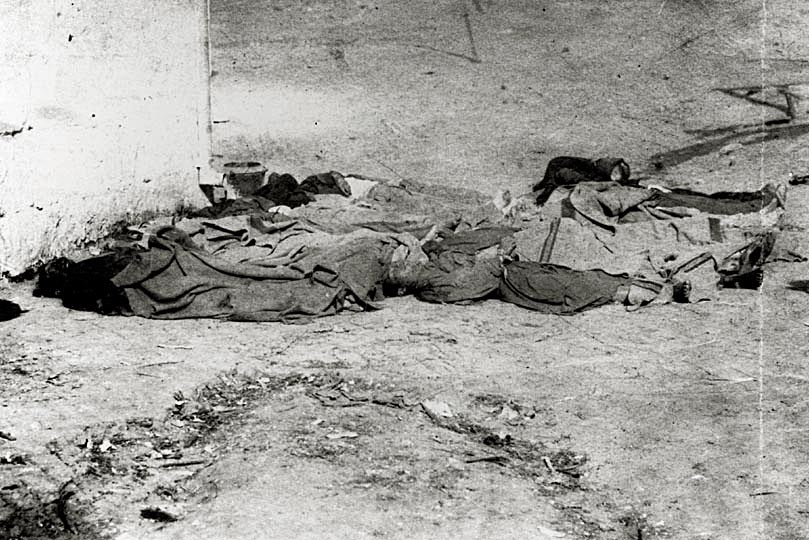
Early Chinese Americans struggled to survive in the United States because of prejudice, discrimination, and violence. In 1871,
17–20 Chinese immigrants were murdered in Los Angeles by a mob of around 500 men. This racially motivated massacre was one of the largest mass-
lynchings in the United States
Lynching was the widespread occurrence of extrajudicial killings which began in the United States' Antebellum South, pre–Civil War South in the 1830s and ended during the civil rights movement in the 1950s and 1960s. Although the victims ...
, and it took place after the accidental killing of Robert Thompson, a local
rancher.
The
Rock Springs massacre
The Rock Springs massacre, also known as the Rock Springs riot, occurred on September 2, 1885, in the present-day United States city of Rock Springs in Sweetwater County, Wyoming. The riot, and resulting massacre of immigrant Chinese miners ...
occurred in 1885, in which at least 28 Chinese immigrants were killed and 15 other Chinese were injured. Many enraged white miners in Sweetwater County felt threatened by the Chinese and they also blamed them for their unemployment. As a result of competition for jobs, white miners expressed their frustration by committing acts of physical violence in which they robbed, shot, and stabbed Chinese in Chinatown. The Chinese quickly tried to flee but in doing so, many of them ended up being burned alive in their homes, starving to death in hiding places, or being exposed to animal predators which lived in the mountains; some of them were successfully rescued by a passing train. A total of 78 homes were burned.
During the
Hells Canyon massacre
The Hells Canyon Massacre (also known as the Snake River Massacre) was a massacre where thirty-four Chinese goldminers were ambushed and murdered in May 1887. In 2005, the area was renamed Chinese Massacre Cove, and a memorial was placed there i ...
of 1887, at least 34 Chinese miners were killed. An accurate account of the event is still unavailable, but it is speculated that the Chinese miners were killed by gunshot during a robbery by a gang of seven armed horse thieves.
Other acts of violence which were committed against Chinese immigrants include the
San Francisco riot of 1877
The San Francisco riot of 1877 was a three-day pogrom waged against Chinese immigrants in San Francisco, California by the city's majority white population from the evening of July 23 through the night of July 25, 1877. The ethnic violence which s ...
, the
Issaquah
Issaquah ( ) is a city in King County, Washington, United States. The population was 40,051 at the 2020 census. Located in a valley and bisected by Interstate 90, the city is bordered by the Sammamish Plateau to the north and the " Issaquah Al ...
and
Tacoma riot of 1885 The Tacoma riot of 1885, also known as the 1885 Chinese expulsion from Tacoma, involved the forceful expulsion of the Chinese population from Tacoma, Washington Territory, on November 3, 1885. City leaders had earlier proposed a November 1 deadline ...
, the
attack on Squak Valley Chinese laborers in 1885, the
Seattle riot of 1886
The Seattle riot of 1886 occurred on February 6–9, 1886, in Seattle, Washington, amidst rising anti-Chinese sentiment caused by intense labor competition and in the context of an ongoing struggle between labor and capital in the Western United S ...
, and the
Pacific Coast race riots of 1907
The Pacific Coast race riots were a series of riots that took place within the United States and Canada. The riots, which resulted in violence, were the result of anti-Asian tension caused by white opposition to the increasing Asian population duri ...
. With the spread of the
COVID-19 pandemic
The COVID-19 pandemic, also known as the coronavirus pandemic, is an ongoing global pandemic of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). The novel virus was first identi ...
, which is believed to have started in the city of Wuhan, China,
numerous incidents of xenophobia and racism against Chinese people and people who are perceived to be Chinese have been reported.
Depression and suicide
In 2008, researchers Georg Hsu and Yu Mui Wan published a paper citing severe stigma of mental illness in the Chinese-American community as a barrier to diagnosis and treatment. In a 1998 study of 29 diagnosed depressive Chinese American immigrants, more than half of respondents avoided labeling their symptoms as depression.
While patients were able to accurately identify and report depressive symptoms such as "irritability" and "rumination," patients were more likely to attribute their depression to somatic and physical symptoms than as a psychological state.
Among Asian-American youth in 1980, suicide accounted for 15.1% of Chinese-American male deaths.
Among females, it constituted 20.8% of deaths.
The study also reported that suicide rates among Chinese-American elderly were higher than that of the national suicide rate for African-American, Hispanic, and Native-American.
A study published in the ''Journal of Aging and Health,'' stated that 18% to 29.4% of older Chinese adults in North America had at least a mild level of depression which was higher than other ethnic groups.
Further, the study reported that these depressive symptoms among older Chinese adults "tend to remain untreated."
Languages
According to the
United States Census Bureau
The United States Census Bureau (USCB), officially the Bureau of the Census, is a principal agency of the U.S. Federal Statistical System, responsible for producing data about the American people and economy. The Census Bureau is part of t ...
, the various
varieties of Chinese
Chinese, also known as Sinitic, is a branch of the Sino-Tibetan language family consisting of hundreds of local varieties, many of which are not mutually intelligible. Variation is particularly strong in the more mountainous southeast of ma ...
, collectively referred to as just
Chinese
Chinese can refer to:
* Something related to China
* Chinese people, people of Chinese nationality, citizenship, and/or ethnicity
**''Zhonghua minzu'', the supra-ethnic concept of the Chinese nation
** List of ethnic groups in China, people of ...
, is the third most-spoken language in the United States. It is almost completely spoken within Chinese American populations and by immigrants or the descendants of immigrants, especially in
California
California is a state in the Western United States, located along the Pacific Coast. With nearly 39.2million residents across a total area of approximately , it is the most populous U.S. state and the 3rd largest by area. It is also the m ...
.
In 2002, over 2 million Americans speak some variety or dialect of Chinese, with
Standard Chinese (Mandarin) becoming increasingly common due to immigration from China and supplanting the previous widespread
Cantonese
Cantonese ( zh, t=廣東話, s=广东话, first=t, cy=Gwóngdūng wá) is a language within the Chinese (Sinitic) branch of the Sino-Tibetan languages originating from the city of Guangzhou (historically known as Canton) and its surrounding ar ...
and
Taishanese
Taishanese (), alternatively romanized in Cantonese as Toishanese or Toisanese, in local dialect as Hoisanese or Hoisan-wa, is a dialect of Yue Chinese native to Taishan, Guangdong. Although it is related to Cantonese, Taishanese has littl ...
.
In
New York City
New York, often called New York City or NYC, is the most populous city in the United States. With a 2020 population of 8,804,190 distributed over , New York City is also the most densely populated major city in the Un ...
at least, although
Standard Chinese (Mandarin) was spoken as a native language among only 10% of
American-born Chinese speakers, it is used as a secondary dialect to English. In addition, the immigration from
Fuzhou,
Fujian
Fujian (; alternately romanized as Fukien or Hokkien) is a province on the southeastern coast of China. Fujian is bordered by Zhejiang to the north, Jiangxi to the west, Guangdong to the south, and the Taiwan Strait to the east. Its cap ...
brings in a significant populace of
Fuzhou people
Fuzhou people (; Foochow Romanized: ''Hók-ciŭ-nè̤ng''), also known as, Foochowese, Hokchew, Hokchia, Hokchiu, Fuzhou Shiyi people (), Eastern Min or Mindong refer to Chinese who originate from the Fuzhou and Mindong regions and the Gutian a ...
(
Eastern Min
Eastern Min or Min Dong (, Foochow Romanized: Mìng-dĕ̤ng-ngṳ̄), is a branch of the Min group of Sinitic languages of China. The prestige form and most-cited representative form is the Fuzhou dialect, the speech of the capital of Fujian.
G ...
), particularly
Changle dialect speakers to major cities like New York City, San Francisco, and Boston. People who comes from Fujian (
Minnan region
Minnan, Banlam or Minnan Golden Triangle (), refers to the coastal region in Southern Fujian Province, China, which includes the prefecture-level cities of Xiamen, Quanzhou and Zhangzhou. The region accounts for 40 percent of the GDP of Fujian Pr ...
),
Chaoshan
Chaoshan or Teoswa (; peng'im: ''Dio5suan1'' i̯o˥˥꜖꜖.sũ̯ã˧˧ is a cultural-linguistic region in the east of Guangdong, China. It is the origin of the Min Nan Chaoshan dialect (). The region, also known as Chiushan in Cantonese, c ...
,
Taiwan
Taiwan, officially the Republic of China (ROC), is a country in East Asia, at the junction of the East and South China Seas in the northwestern Pacific Ocean, with the People's Republic of China (PRC) to the northwest, Japan to the nort ...
and
Southeast Asia
Southeast Asia, also spelled South East Asia and South-East Asia, and also known as Southeastern Asia, South-eastern Asia or SEA, is the geographical south-eastern region of Asia, consisting of the regions that are situated south of mainlan ...
mainly use Southern Min dialect (Hokkien and Teochew dialect, Teochew) as their mother tongue. Varieties of Wu Chinese, particularly Shanghainese and the mutually unintelligible Wenzhounese, are now spoken by a minority of recent Chinese immigrants hailing from Jiangsu, Zhejiang, and Shanghai.
Although Chinese Americans grow up learning English language, English, some teach their children to speak Chinese for a variety of reasons: preservation of an ancient civilization, preservation of a group identity, preservation of their cultural ancestry, desire for easy communication with each other and their relatives, and the perception that Chinese is a very useful language, regardless of China's economic strength. The official standard for United States public notices and signage is Traditional Chinese.
Religion
The Chinese American community is different from the rest of the population in that the majority of Chinese Americans do not report a religious affiliation. 43% of Chinese Americans switched to a different religion and 54% stayed within their childhood religion within their lifetime. According to the Pew Research Center's 2012 Asian-American Survey, 52% of Chinese Americans aged 15 and over said that they did not have any religious affiliation. This is also compared with the religious affiliation of Asian American average of 26% and a national average of 19%.
Of the survey respondents, 15% were Buddhist, 8% were Catholic, and 22% belonged to a Protestant denomination. Fully half of Chinese Americans (52%)—including 55% of those born in the U.S. and 51% of those born overseas—describe themselves as religiously unaffiliated. Because Chinese Americans are the largest subgroup of Asian Americans, nearly half of all religiously unaffiliated Asians in the U.S. are of Chinese descent (49%).
There are also many Chinese who identify as Jewish due to intermarriage with Jews. Some posit that Judaism has similar habits to Confucianism such as the emphasis on scholarship.
There is a significantly higher percentage of Chinese Christians in the United States than there is in China, as a large amount of Chinese Christians fled and are still fleeing to the United States under Communist persecution.
List of Chinese temples in the United States
Politics

Chinese Americans are divided among many subgroups based on factors such as age, nativity, and socioeconomic status and politics between China and the United States, or about Chinese nationalism. Different subgroups of Chinese Americans also have radically different and sometimes very conflicting political priorities and goals.
In 2013, Chinese Americans were the least likely Asian American ethnicity to be affiliated with a political party.
Nonetheless, Chinese Americans are clustered in majority-Democratic Party (United States), Democratic states and have increasingly voted Democratic in recent presidential elections, following the trend for Asian Americans in general, excluding the Vietnamese Americans. Polling just before the 2004 United States presidential election, 2004 U.S. Presidential Election found John Kerry was favored by 58% of Chinese Americans and George W. Bush by only 23%,
as compared with a 54/44 split in United States presidential election in California, 2004, California, a 58/40 split in United States presidential election in New York, 2004, New York, and a 48/51 split in 2004 United States presidential election, America as a whole on Election Day itself. In the 2012 United States presidential election, 2012 presidential election, 81% of Chinese American voters selected Barack Obama over Mitt Romney.
Immigration
Economic growth in the People's Republic of China has given mainland Chinese more opportunities to Chinese emigration, emigrate. A 2011 survey showed that 60% of Chinese millionaires were planning to emigrate, with 40% of Chinese millionaires selecting the United States as the top destination for immigration.
The EB-5 visa, EB-5 Investment Visa allows many Chinese to seek U.S. citizenship. It has a yearly quota of around 10,000 applicants or families, and recent reports show that 75% of applicants for this visa in 2011 were Chinese. Under this program, applicants, together with their spouses and unmarried children under 21 years old will be eligible to apply for US permanent residency as a group. Because the EB-5 program allows applicants to apply as a family, it has been reported to be a significant method for Chinese students to obtain authorization to work in the United States. Chinese multimillionaires benefited most from the EB-5 Immigrant Investor Program in the U.S. Now, as long as one has at least US$500,000 to invest in projects listed by United States Citizenship and Immigration Services (USCIS), where it is possible to get an EB-5 green card that comes with permanent U.S. residency rights, but only in states specified by the pilot project. The H-1B visa is also becoming one of the main immigration pathways for the Chinese with 9% of the approved petitions in 2016.
Illegal immigration
Before 1882, there were no limits on immigration to the United States, but with the Chinese Exclusion Act of 1882, Chinese Exclusion Act, for the first time in American history immigration was deemed illegal. This legislation was partially repealed in 1943 with the Magnuson Act, and only fully repealed in 1965. The history of Illegal immigration to the United States, illegal immigration of Chinese people to the United States go back to the 19th century. Smuggling of immigrants without authorization increased during 1990s following policy changes by the American government, but by the 21st century some have returned to China due to its growing economy. By 2017, it is estimated that more than a quarter million immigrants reside in the United States without authorization from China. In 2015, there were about 39,000 Chinese nationals who were supposed to be Deportation and removal from the United States, deported; however, the People's Republic of China government had not provided paperwork to verify their citizenship. In 2017, China was described as having become one of the leading sources of new immigrants without authorization.
Socioeconomics
Educational attainment
Overall, as a demographic group, Chinese Americans have a higher educational attainment, have a higher percentage of people working in select white collar and professional occupations, and earn higher median household incomes when compared to other demographic groups in the United States. Educational achievements of Chinese in the United States are one of the highest among Asian Americans and also among all ethnic groups in the United States. Chinese Americans often have some of the highest averages in tests such as SAT, ACT (test), ACT, Graduate Record Examination, GRE etc. in the United States. Although verbal scores lag somewhat due to the influx of new immigrants, combined SAT scores have also been higher than for most Americans. With their above average SAT and ACT scores as well as GPA's, Chinese Americans are more likely to apply to competitively elite higher education institutions.
China sends the most international students to the U.S., with Chinese students comprising 33.2% of the international student population. In the 2017–2018 school year, there were close to 363,000 enrolled students in higher education. Chinese students also make up 32.2% of the undergraduate students and 48.8% of the graduate students.
International students
International students studying at various higher education institutions around the United States account for a significant percentage of the international student body. According to a Brookings Institution report analyzing foreign student visa approvals from 2008 to 2012, Michigan State University has the highest enrollment of Chinese international students in the United States, with roughly 4,700 Chinese citizens enrolled during the period of the study making up 62 percent of the 7,568 international students enrolled at MSU. International undergraduates, who make up 38 percent of Purdue University, Purdue's undergraduate body, come from China more than any other country. International Chinese students make up 49.8 percent of all international students at the University of Southern California. International Chinese students also comprise 60 percent of the 6039 international students enrolled at Ohio State University. Mainland China is the top sending country of international students to the United States. After the 1970s, the globalization and Chinese Reform and Opening-Up Act resulted in a growing economy, more middle-class families from China are able to afford American college tuition, bringing an influx of Chinese students to study abroad in the United States. With a more diverse educational background and higher level of English proficiency, international Chinese students also value American degrees, as it gives them a notable advantage over their college-educated counterparts in China by the time they return to their native country to seek employment.
Choice of institution
Due to cultural factors, many Chinese international students are brand name conscious, choosing nationally ranked elite higher education institutes throughout the United States as their target schools.
International Chinese students are also widely found at many elite liberal arts colleges such as Barnard College and Mount Holyoke College. Students from China gravitate towards Americans colleges and universities for their high quality and the style of education which stresses interdisciplinary approaches, creativity, student participation and critical thinking.
Subject choice
Chinese international students tend to gravitate towards technical and scientific majors that involve heavy use of mathematics, engineering and the natural sciences. 27.5% of international Chinese students study business management, finance, or economics, 19.2% study engineering, 11.5% study the life sciences and 10.6% study math or computer science.
Largely driven by educational immigration, among American PhD recipients in fields related to science and engineering, 25% of the recipients are ethnic Chinese.
Level of education
According to the 2017 U.S. Census Bureau of Labor Statistics, 55.3% of all Chinese Americans have attained at least a bachelor's degree, compared with 32.0% nationally and 53.8% for all Asian American groups. The Census reports that 57.8% of Chinese American men attained a bachelor's degree and 53.2% of Chinese American women attained a bachelor's degree. In addition, 28.4% of all Chinese Americans in the United States possess a master's, doctorate or other professional degree, compared to 23.6% for all Asian Americans, and is roughly two times above the national average of 12.3%.
Employment

Perceptions and change
There has been a significant change in the perceptions about Chinese Americans. In as little as 100 years of American history, Stereotypes of East Asians in the Western world, stereotypes of Chinese Americans have changed to portraying a hard working and educated minority. Most Chinese Americans work as White-collar worker, white collar professionals, many of whom are highly educated, salaried professionals whose work is largely self-directed in management, professional, and related occupations such as engineering, medicine, investment banking, law, and academia. 56.2% of Chinese Americans work in white collar professions compared with 52.1% for all Asian Americans and a national average of 38.2%.
Chinese Americans also make up a third of the Asian American high tech professional workforce and a tenth of the entire Silicon Valley workforce. Chinese Americans also hold lower unemployment rates than the population average with a figure of 4.7% compared to a national rate of 5.9% in 2010.
Medicine
Between 2008 and 2017, the number of Chinese-educated physicians practicing in the United States rose by 38.1%, and the total number of Chinese-educated physicians actively practicing in the United States was about 0.6% of the active physician workforce in 2017.
Technology sector
Many Chinese Americans have turned to the high tech center to jump-start potential computer science and programming startups to capitalize on the region's wealth of venture capital, business expertise, and cultural and financial incentives for innovation. Ethnic Chinese have been successful in starting new firms in technology centers across the United States, including California's Silicon Valley. Chinese Americans have been disproportionately successful in high technology sectors, as evidenced by the 2010 Goldsea 100 Compilation of America's Most Successful Asian Entrepreneurs. Chinese Americans accounted for 4% of people listed in the 1998 Forbes Hi Tech 100 List.
Annalee Saxenian, a UC Berkeley professor, whose research interests include the contribution of Chinese immigrants on America's technology concludes that in Silicon Valley, carried out a study that showed that since 1998, one out of five high tech start-ups in Silicon Valley were led by Chinese Americans. During the same year, 5 of the 8 fastest growing companies had Chinese American CEOs, except for Yahoo, whose Jerry Yang (entrepreneur), Jerry Yang was a founder but not a CEO. In Silicon Valley there are at least 2 to 3 dozen Chinese American organizations according to professional interests each with at least 100 members, one prominent organization of which is the Committee of 100 (United States), Committee of 100. Immigrants from mainland China and Taiwan were key founders in 12.8% of all Silicon Valley start-ups between 1995 and 2005. Almost 6% of the immigrants who founded companies in the innovation/manufacturing-related services field are from China.
Research funded by the Public Policy Institute of California indicates that in 1996, 1,786 Silicon Valley technology companies with $12.5 billion in sales and 46,000 employees were run by Indian or Chinese executives. Moreover, the pace of entrepreneurship among local immigrants is increasing rapidly. While Chinese or Indian executives are at the helm of 13% of the Silicon Valley technology businesses started between 1980 and 1985, they are running 27% of the more than 4,000 businesses started between 1991 and 1996. Start-up firms remain a primary source for new ideas and innovation for Chinese American internet entrepreneurs. Many of them are employed or directly engaged in new start-up activities. The proportional share of start-up firms by ethnic Chinese in Silicon Valley skyrocketed from 9% in 1980–1984 to about 20% between 1995 and 1998. By 2006, Chinese American internet entrepreneurs continued to start 20% of all Silicon Valley start-up firms, leading 2000 Silicon Valley companies, and employing 58,000 workers.
They still continue to own about 20% of all information technology companies that were founded in Silicon Valley since 1980.
Numerous professional organizations in perspective in the 1990s as a support network for fellow Chinese American high tech start-ups in the valley. Between 1980 and 1999, 17% of the 11,443 high-tech firms in Silicon Valley – including some 40 publicly traded firms were controlled by ethnic Chinese. In 1990, Chinese Americans made up a third of the Asian American high tech professional workforce or 11% of the entire Silicon Valley professional workforce. In 1998, Chinese Americans managed 2001 firms, employing 41,684 workers, and ran up 13.2 billion in sales. They also account for 17% of all Silicon Valley firm owners, 10% of the professional workforce in the Valley, and 13.5% of the total sales accounting for less than 1% of the U.S. population at the time.
Self-employment and entrepreneurship
Chinese Americans are also noted for their high rates of self-employment, as they have an extensive history of self-employment dating back to the
California Gold Rush in the 1880s. However, as more Chinese Americans seek higher education to elevate themselves socioeconomically, rates of self-employment are generally lower than population average. In 2007, there were over 109,614 Chinese-owned employer firms, employing more than 780,000 workers, and generating more than $128 billion in revenue.
Among Chinese-owned U.S. firms, 40% were in the professional, scientific, and technical services sector, the accommodation and food services sector, and the repair, maintenance, personal, and laundry services sector. Chinese-owned U.S. firms comprised 2% of all U.S. businesses in these sectors. Wholesale trade and accommodation and food services accounted for 50.4% of Chinese-owned business revenue. 66,505 or 15.7% of Chinese-owned firms had receipts of $250,000 or more compared with 2% for all U.S. businesses.
Economics
With their above average educational attainment rates, Chinese Americans from all socioeconomic backgrounds have achieved significant advances in their educational levels, income, life expectancy, and other social indicators as the financial and socioeconomic opportunities offered by the United States have lifted many Chinese Americans out of poverty, bringing them into the ranks of America's American middle class, middle class, Upper middle class in the United States, upper middle class, as well as the enjoyment of substantial quality of life, well being.
However, Chinese-American wealth vary greatly by region: For instance, in New York City, 22% of Chinese-Americans live in poverty.
Chinese Americans are more likely to own homes than the general American population. According to the 2000 U.S. Census, 65% of Chinese Americans owned a home, higher than the total population's rate of 54%. In 2003, real estate economist Gary Painter of the University of Southern California Lusk Center for Real Estate Research found out that when comparing homeowners with similar income levels Los Angeles, the Chinese-American home-ownership rate is 20% higher than White American, Whites; in
San Francisco
San Francisco (; Spanish for " Saint Francis"), officially the City and County of San Francisco, is the commercial, financial, and cultural center of Northern California. The city proper is the fourth most populous in California and 17th ...
, 23% higher; and in the
New York metropolitan area
The New York metropolitan area, also commonly referred to as the Tri-State area, is the largest metropolitan area in the world by urban landmass, at , and one of the most populous urban agglomerations in the world. The vast metropolitan area ...
, 18% higher. A 2008 Asian Real Estate Association of America report released on behalf of the American community survey, Chinese Americans living in the states of
Texas
Texas (, ; Spanish: ''Texas'', ''Tejas'') is a state in the South Central region of the United States. At 268,596 square miles (695,662 km2), and with more than 29.1 million residents in 2020, it is the second-largest U.S. state by ...
,
New York, and
California
California is a state in the Western United States, located along the Pacific Coast. With nearly 39.2million residents across a total area of approximately , it is the most populous U.S. state and the 3rd largest by area. It is also the m ...
all had high home ownership rates that were significantly near or above the general population average.
According to the 2017 U.S. Census, Chinese American men had a full-time median income of $71,096 and Chinese American women had a median income of $60,157. Chinese Americans also have one of the highest median household incomes among most demographic groups in the United States, which is almost 30% higher than the national average but is slightly lower compared with the Asian American population.
Despite positive economic indicators, a number of economic deterrents have been noted to afflict the Chinese American community including institutionalized discrimination against STEM researchers and scientists. While median income remains above some ethnic groups in the United States, studies in the wake of the 2008 financial crisis revealed that Asian men have the highest rate of persistent long-term unemployment. In addition, studies have shown that Asian Americans have been discriminated in companies with lower pay grades; even in larger corporate settings such as Google.
Genetics
Studies on the genetics of Chinese Americans
A research on the whole genome patterns of common DNA variation in different human populations (African-American, Asian-American and European American) finds some common single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) in these three populations with diverse ancestry. In the samples of Han Chinese in America, 74% of the total SNPs have two alleles, and majority of the segregating SNPs have a minor allele frequency (MAF) greater than 10%. Another noticeable point is that MAFs show similar distributions in European-American and Han Chinese populations. Besides, rarer haplotype is found to be absent in the samples of Han Chinese, and they also possess a high level of redundancy.
A study analyzing East Asian Genetic Substructure using genome-wide SNP arrays is carried out with greater than 200,000 genotypes from people of East Asian ancestry. The continental populations are from the Human Genome Diversity Panel (Cambodian, Yi, Daur, Mongolian, Lahu, Dai, Hezhen, Miaozu, Naxi, Oroqen, She, Tu, Tujia, Naxi, Xibo, and Yakut), HapMap (Han Chinese and Japanese), as well as East Asian or East Asian American subjects of Vietnamese, Korean, Filipino and Chinese ancestry. A clear understanding of the genetic substructure of any population helps in the studies of complex diseases, as well as the design and execution of association tests. Results of this study have identified markers that can not only reduce type 1 errors in future genetic disease studies, but also identify homogeneous groups and hence make this study more powerful.
The group of Chinese Americans in the same study consists of subjects with origins from North China, South China and Taiwan. This group is paired with Han Chinese from Beijing, and results indicate that the population differentiation values was small (<0.0025). There is substantially less genetic substructure between Han Chinese and Chinese American, compared with that between Han Chinese, Japanese and Korean groups, yet there is still a substructure in principal component, according to the split half reliability test.
Another study aiming to estimate cardiometabolic risk profile of Chinese adults with diabetes is also useful to reveal the personal genomics of Chinese Americans. In this study, all subjects are over 18 years old and non-institutionalized. Results derived from a complex, multistage, probability sampling design show that 12,607 out of 98,658 Chinese adults are suffering from diabetes, based on the criteria of 2010 American Diabetes Association. In addition, the study reaches a conclusion that for those Chinese adults defined with diabetes, cardiometabolic risk factors are highly prevalent, including metabolic syndrome, systolic blood pressure that is higher than 140mmHg, low fruit and vegetable intake, low-density lipoprotein cholesterol that is higher than 110 mg/dL.
Diabetes
The circumstance of Asian American population is informative in a way that some knowledge about Chinese American can be inferred from it. The statistics of diabetes in Asian American population reveals that approximately 10% of the entire population are diabetic, and in which 90–95% are type 2 diabetes. The current situation is that there are some challenges in diagnosing diabetes in many Asian Americans. The main obstacle is that many clinical features along with risks factors associated with diabetes are obtained from studies that focus on Caucasian populations, which might result in misdiagnoses between type 1 and type 2 diabetes for Asian Americans. In fact, the reason why classic features of type 1 and type 2 diabetes in America might not apply to Asian American population is about shared absence of common HLA DR-DQ genotype, low prevalence of positive anti-islet antibodies and low BMI in both types of diabetes.
Some other studies have pointed out that for people of Asian descent and without diabetes, their insulin resistance levels are higher than non-diabetic people of Caucasian descent. Thus, Asian Americans are relatively more predisposed to develop type 2 diabetes. This suggests that insulin resistance, rather than body mass index (BMI) should be targeted while making diagnoses. A potential biomarker to identify diabetes in young Asian American population is adipocyte fatty acid binding protein that has a strong association with insulin resistance but is independent of adiposity. Nevertheless, more research studies should be carried out in order to confirm such finding. With further applying the above outcome on the population of Chinese Americans, it is rational that there is a higher tendency for type 2 diabetes among this group of people, who also face the challenge of correct diagnosis in America.
Mental illness

Genetic mental illness is stigmatized in China. A study compares the attitude of Chinese American towards mental illness with genetic causes and that of European American. It finds out that there is a perception of eugenics existing among Chinese Americans. Consequently, in order to reduce the stigma in the society, more efforts should be devoted to this population.
Stigma and eugenics
The journal launched by the above study highlights the idea of genetic essentialism, namely, genes are largely deterministic of individual characteristics and behavior. There is a separation between the normal and the deviant, which drives the process of stigma labeling. On the other hand, since genetic diseases can be passed on from one generation to another, some mental illnesses are shared in a family, stigmatizing all members involved. Another viewpoint relevant to genetic essentialism is that, since genes are perceived by the common people as difficult to modify, genetic mental illness is likely to persist, and so is the stigma. As a result, the mindset of many Chinese Americans is formulated as diseases with genetic causes being more serious than those without.
The same journal also delivers some hypotheses made on the basis of the long history of eugenics in China. First, Chinese Americans are more in favor of eugenic policies than European Americans. Secondly, more stigma would be generated towards genetic attributions of any diseases in Chinese American population. China used to implement restrictions on marriage licenses to people with genetic illnesses, which has made the attitude of Chinese American towards premarital genetic screening more supportive, especially when facing a chance of genetic defects. Moreover, from the perspective of this group of people, knowing whether a marriage partner has family history of mental illness with genetic basis is fairly important.
Notable Chinese Americans
* Iris Chang (28 March 1968 – 9 November 2004), a historian, her publishings included: ''Thread of the Silkworm'' (1995), ''The Rape of Nanking (book), The Rape of Nanking: The Forgotten Holocaust of World War Two'' (1997)
* Charles Kuen Kao, physicist, winner of Nobel Prize in Physics in 2009 for the work on fiber optics, using laser to transmit digital data through glass fiber.
* Bruce Lee, martial artist and actor, founder of Jeet Kune Do.
*Tsung-Dao Lee, physicist, won the Nobel Prize in Physics (1957) with Yang Chen-Ning for their work on the violation of the parity law in weak interactions.
*Jeremy Shu-How Lin, professional basketball player, played in NBA for several years and a Harvard University, Harvard graduate.
*Gary Locke, politician and diplomat, the 10th United States ambassador to China (2011–2014), 21st Governor of Washington (1997–2005) and served in the Obama administration as United States Secretary of Commerce (2009–11).
*Amy Ruth Tan, writer, author of The Joy Luck Club (novel), The Joy Luck Club.
*Samuel Chao Chung Ting, physicist, one of the two winners of Nobel Prize in Physics in 1976 for the work on the discovery of J/ψ meson.
*Daniel Chee Tsui, physicist, one of the winners of Nobel Prize in Physics in 1998 for the work on the discovery of a new form of quantum fluid with fractionally charged excitations.
*Donnie Yen actor, martial artist, former Wushu tournament champion, film director, producer, action director, and fight choreographer. Yen is one of Hong Kong's top action stars.
*Charles B. Wang, businessman, a co-founder and CEO of Computer Associates International, Inc. (later renamed to CA Technologies).
*Chien-Shiung Wu, physicist who was called by scientists, "The First Lady of Physics" for her experimental discovery of parity violation in weak interaction proposed by Chen-Ning Yang and Tsung-Dao Lee, both of whom won Nobel Prize. She also made the crucial study that showed the problem with Xenon in nuclear reactors for the Manhattan Project. Her work was not publicly recognized except by top scientists until 1978 when she was given the Wolf Prize.
* Michelle Wu First Asian American mayor of Boston, Michelle born in USA, her grandparents were from mainland China.
*Andrew Yang, entrepreneur, politician, lawyer, and 2020 Democratic Party presidential primaries, 2020 Democratic presidential candidate.
*Shing-Tung Yau, mathematician, who won the Fields Medal in 1982 before becoming an American citizen in 1990.
* Eric Yuan, billionaire businessman and founder of Zoom Video Communications.
Media
The World Journal is the most famous Chinese newspapers in the North America.
Newspapers
*World Journal
*Sing Tao Daily
*Ming Pao
Television
*SinoVision
*ETTV America
*Voice of America (Chinese)
*Epoch Times
*New Tang Dynasty Television
*Phoenix Television
*Television Broadcasts Limited (TVB USA)
*Asia Television
Radio
Chinese Radio Seattle (M-T 9:00pm–12:00am Fri-Sun 7:00pm-12:1 m AM1150 KKNW/HD-3 FM 98.9/Mobile App: Chinese Radio Seattle) Studio in Bellevue, WA.
*China Radio International can be heard in the following cities:
**Washington DC on WUST (AM 1120 kHz between 9 a.m.–11 a.m.)
*Chinese American Voice,
heard over a Subsidiary Communications Authority, SCA subcarrier of WACD-FM in the Tri-State Region, New York/New Jersey/Connecticut tri-state area
*Chinese American Voice, heard in
New York City
New York, often called New York City or NYC, is the most populous city in the United States. With a 2020 population of 8,804,190 distributed over , New York City is also the most densely populated major city in the Un ...
24 hours on the Subsidiary Communications Authority, 92 kHz subcarrier of WFAN-FM, WQCD-FM 101.9 MHz.
*Chinese Radio Network]
on WGBB (AM 1240 kHz and the Subsidiary Communications Authority, 67 kHz subcarrier of WCBS-FM 101.1 MHz, Flushing, New York) broadcasts in Mandarin.
*Chung Wah Chinese Broadcasting Company]
heard in
New York City
New York, often called New York City or NYC, is the most populous city in the United States. With a 2020 population of 8,804,190 distributed over , New York City is also the most densely populated major city in the Un ...
24 hours on the Subsidiary Communications Authority, 92 kHz subcarrier of WSKQ-FM 97.9 MHz.
*Multicultural Radio Broadcasting Inc.'s Chinese Media Group broadcasts Chinese programming in the following cities:
**KAHZ, Los Angeles, California, Los Angeles is a Mandarin-dialect station.
**KAZN, Los Angeles, California, Los Angeles is a Mandarin-dialect station.
**KTWR, Guam]
is a shortwave radio station that broadcasts in Mandarin and other languages to the Asia-Pacific region.
**KMRB, Los Angeles, California, Los Angeles is a Cantonese-dialect station.
**Sinocast Radio, national Chinese network, heard in New York City on the Subsidiary Communications Authority, 67 kHz subcarrier of WINS-FM, WXRK-FM 92.3 MHz.
**WKDM, Tri-State Region, New York/New Jersey/Connecticut tri-state area is a Mandarin-dialect station on AM 1380 kHz.
**WZRC, Tri-State Region, New York/New Jersey/Connecticut tri-state area is a Cantonese-dialect station on AM 1480 kHz.
*Radio Taiwan International is broadcast on WYFR from Okeechobee, Florida on shortwave 5950 kHz in the United States sometime after 5 p.m./6 p.m. until early morning. This broadcast can be received virtually through the entire United States using a short wave radio.
KVTO (Sing Tao)on 1400AM in San Francisco.
**KEST, San Francisco, California, San Francisco is a Cantonese-dialect station.
**KSQQ, San Francisco, California, San Francisco is a Mandarin-dialect station.
See also
Notes
References
Bibliography
* Brooks, Charlotte. ''American Exodus: Second-Generation Chinese Americans in China, 1901–1949'' (University of California Press, 2019
online review.
* Chang, Gordon H. ''Ghosts of Gold Mountain: The Epic Story of the Chinese Who Built the Transcontinental Railroad.'' Boston: Houghton Mifflin Harcourt, 2019.
* Chang, Iris. ''The Chinese in America: A Narrative History.'' New York: Viking, 2003.
* Chen, Shehong. ''Being Chinese, Becoming Chinese American'' Urbana, IL: University of Illinois Press, 2002)
* Cheng, Cindy I-Fen. ''Citizens of Asian America: Democracy and Race during the Cold War'' (New York U. Press, 2013). 285p.
* Gillenkirk, Jeff and Motlow, James,
Bitter Melon: Inside America's Last Rural Chinese Town (San Francisco, Nine Mile Press, 2015). 140 pp.
* Madeline Y. Hsu, Hsu, Madeline Y. ''The Good Immigrants: How the Yellow Peril Became the Model Minority.'' Princeton, NJ: Princeton University Press, 2015.
* Isaacs, Harold R. ''Scratches on Our Minds: American Images of China And India'' (1958
online* Kwong, Peter and Dusanka Miscevic. ''Chinese America: The Untold Story of America's Oldest New Community'' (2005)
* Lee, Jonathan H. X. ed. ''Chinese Americans: The History and Culture of a People.'' Santa Monica, CA: ABC-CLIO, 2016.
* Ling, Huping, and Allan W. Austin, eds. ''Asian American History and Culture: An Encyclopedia'' (Routledge, 2015)
* Louie, Vivian S. ''Compelled To Excel: Immigration, Education, And Opportunity Among Chinese Americans'', (Stanford U. Press, 2004) 272 pages,
* McClain, Charles. ''In Search of Equality: The Chinese Struggle Against Discrimination in Nineteenth-Century America'' Berkeley: University of California Press, 1994.
* Meng, Chih. ''Chinese American Understanding: A Sixty-Year Search'', (China Institute in America, 1981, hardcover, 255 pages, OCLC: 8027928
* Miscevic, Dusanka and Peter Kwong, eds. ''Chinese Americans: The Immigrant Experience'', (Hugh Lauter Levin Associates, 2000), 240 pages,
* See, Lisa. ''On Gold Mountain: The One-Hundred-Year Odyssey of My Chinese American Family'', (1996). . See also the website for an exhibition based on this boo
Home from the Smithsonian Asian Pacific American Program.
* Song, Jingyi. ''Shaping and Reshaping Chinese American Identity: New York's Chinese during the Depression and World War II'' (2010)
* Tung, May Pao-May. ''Chinese Americans and Their Immigrant Parents: Conflict, Identity, and Values'', Haworth Press, 2000.
* Wang, Ling-chi. "Chinese Americans." in ''Gale Encyclopedia of Multicultural America,'' edited by Thomas Riggs, (3rd ed., vol. 1, Gale, 2014), pp. 491–506
online
* Xu Guoqi. ''Chinese and Americans: A Shared History.'' Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press, 2014.
* Young, Elliott. ''Alien Nation: Chinese Migration in the Americas from the Coolie Era through World War II.'' Chapel Hill, NC: University of North Carolina Press, 2014.
External links
Factfinder Chinese Americans 2005 American Community SurveyThe Rocky Road to Liberty: A Documented History of Chinese American Immigration and ExclusionMuseum of Chinese in the AmericasChinese Culture Center & Chinese Culture Foundation of San Francisco
Organization of Chinese Americans
Chinese Historical Society of America* [https://www.pbs.org/becomingamerican/ Becoming American: The Chinese Experience] a PBS Bill Moyers special. Thomas F. Lennon, Series Producer.
Chinese American Contribution to Transcontinental Railroad– Central Pacific Railroad Photographic History Museum
Comprehensive list of famous Chinese Americans organized by professions. Includes short biographical notes and Chinese names.
hosts the memoir of the first Chinese American graduate of an American university (Yale 1854).
Chinese American MuseumDocumentary about the Golden Venture tragedyAmericans and Chinese : purpose and fulfillment in great civilizations
{{Overseas Chinese2
American people of Chinese descent
Chinese American,
Asian-American society
East Asian American
Chinese diaspora by country, America
China–United States relations


 These Chinese immigrants were predominantly men. By 1900, only 4,522 of the 89,837 Chinese migrants that lived in the U.S. were women. The lack of women migrants was largely due to the passage of U.S. anti-immigration laws. For example, the Page Law of 1875 prevented the immigration of all women prostitutes from China. This law was used to limit the immigration of all Chinese women, not just prostitutes. Upon arrival to the U.S. Chinese men and women were separated from each other as they awaited hearings on their immigration status, which often took weeks. During this time the women were subjected to lengthy questioning that focused on their family life and origins. Their responses were then cross examined with others from their village, and any discrepancies were used to justify denial of entry. The stress of being separated from family caused many women to fall ill while they waited for a hearing. Some even committed suicide as they feared being denied access to the country. Once they were approved and allowed into the country, Chinese women migrants faced additional challenges. Many were coerced into prostitution, with over 60% of the adult Chinese women living in California in 1870 working in the trade. Some women were lured to the U.S. with the promise of marriage only to become sex slaves. Despite these challenges Chinese women were often drawn to the U.S. in order to reunite with their families. Ninety percent of the Chinese women who immigrated to the US between 1898 and 1908 did so to join their husband or father who already resided in the U.S. Chinese women migrants, similarly to men, immigrated for economic opportunities as well.
In the 1850s, Chinese workers migrated to the United States, first to work in the gold mines, but also to take agricultural jobs, and factory work, especially in the garment industry. Chinese immigrants were particularly instrumental in building railroads in the U.S. west, and as Chinese laborers grew successful in the United States, a number of them became entrepreneurs in their own right. As the numbers of Chinese laborers increased, so did the strength of anti-Chinese attitude among other workers in the U.S. economy. This finally resulted in legislation that aimed to limit future immigration of Chinese workers to the United States, and threatened to sour diplomatic relations between the United States and China through the
These Chinese immigrants were predominantly men. By 1900, only 4,522 of the 89,837 Chinese migrants that lived in the U.S. were women. The lack of women migrants was largely due to the passage of U.S. anti-immigration laws. For example, the Page Law of 1875 prevented the immigration of all women prostitutes from China. This law was used to limit the immigration of all Chinese women, not just prostitutes. Upon arrival to the U.S. Chinese men and women were separated from each other as they awaited hearings on their immigration status, which often took weeks. During this time the women were subjected to lengthy questioning that focused on their family life and origins. Their responses were then cross examined with others from their village, and any discrepancies were used to justify denial of entry. The stress of being separated from family caused many women to fall ill while they waited for a hearing. Some even committed suicide as they feared being denied access to the country. Once they were approved and allowed into the country, Chinese women migrants faced additional challenges. Many were coerced into prostitution, with over 60% of the adult Chinese women living in California in 1870 working in the trade. Some women were lured to the U.S. with the promise of marriage only to become sex slaves. Despite these challenges Chinese women were often drawn to the U.S. in order to reunite with their families. Ninety percent of the Chinese women who immigrated to the US between 1898 and 1908 did so to join their husband or father who already resided in the U.S. Chinese women migrants, similarly to men, immigrated for economic opportunities as well.
In the 1850s, Chinese workers migrated to the United States, first to work in the gold mines, but also to take agricultural jobs, and factory work, especially in the garment industry. Chinese immigrants were particularly instrumental in building railroads in the U.S. west, and as Chinese laborers grew successful in the United States, a number of them became entrepreneurs in their own right. As the numbers of Chinese laborers increased, so did the strength of anti-Chinese attitude among other workers in the U.S. economy. This finally resulted in legislation that aimed to limit future immigration of Chinese workers to the United States, and threatened to sour diplomatic relations between the United States and China through the  .
.

 A list of large cities (250,000+ residents) with a Chinese-American population in excess of 1% of the general population in 2010.
A list of large cities (250,000+ residents) with a Chinese-American population in excess of 1% of the general population in 2010.



 Chinese Americans are divided among many subgroups based on factors such as age, nativity, and socioeconomic status and politics between China and the United States, or about Chinese nationalism. Different subgroups of Chinese Americans also have radically different and sometimes very conflicting political priorities and goals.
In 2013, Chinese Americans were the least likely Asian American ethnicity to be affiliated with a political party.
Nonetheless, Chinese Americans are clustered in majority-Democratic Party (United States), Democratic states and have increasingly voted Democratic in recent presidential elections, following the trend for Asian Americans in general, excluding the Vietnamese Americans. Polling just before the 2004 United States presidential election, 2004 U.S. Presidential Election found John Kerry was favored by 58% of Chinese Americans and George W. Bush by only 23%, as compared with a 54/44 split in United States presidential election in California, 2004, California, a 58/40 split in United States presidential election in New York, 2004, New York, and a 48/51 split in 2004 United States presidential election, America as a whole on Election Day itself. In the 2012 United States presidential election, 2012 presidential election, 81% of Chinese American voters selected Barack Obama over Mitt Romney.
Chinese Americans are divided among many subgroups based on factors such as age, nativity, and socioeconomic status and politics between China and the United States, or about Chinese nationalism. Different subgroups of Chinese Americans also have radically different and sometimes very conflicting political priorities and goals.
In 2013, Chinese Americans were the least likely Asian American ethnicity to be affiliated with a political party.
Nonetheless, Chinese Americans are clustered in majority-Democratic Party (United States), Democratic states and have increasingly voted Democratic in recent presidential elections, following the trend for Asian Americans in general, excluding the Vietnamese Americans. Polling just before the 2004 United States presidential election, 2004 U.S. Presidential Election found John Kerry was favored by 58% of Chinese Americans and George W. Bush by only 23%, as compared with a 54/44 split in United States presidential election in California, 2004, California, a 58/40 split in United States presidential election in New York, 2004, New York, and a 48/51 split in 2004 United States presidential election, America as a whole on Election Day itself. In the 2012 United States presidential election, 2012 presidential election, 81% of Chinese American voters selected Barack Obama over Mitt Romney.
 Perceptions and change
There has been a significant change in the perceptions about Chinese Americans. In as little as 100 years of American history, Stereotypes of East Asians in the Western world, stereotypes of Chinese Americans have changed to portraying a hard working and educated minority. Most Chinese Americans work as White-collar worker, white collar professionals, many of whom are highly educated, salaried professionals whose work is largely self-directed in management, professional, and related occupations such as engineering, medicine, investment banking, law, and academia. 56.2% of Chinese Americans work in white collar professions compared with 52.1% for all Asian Americans and a national average of 38.2%. Chinese Americans also make up a third of the Asian American high tech professional workforce and a tenth of the entire Silicon Valley workforce. Chinese Americans also hold lower unemployment rates than the population average with a figure of 4.7% compared to a national rate of 5.9% in 2010.
Medicine
Between 2008 and 2017, the number of Chinese-educated physicians practicing in the United States rose by 38.1%, and the total number of Chinese-educated physicians actively practicing in the United States was about 0.6% of the active physician workforce in 2017.
Technology sector
Many Chinese Americans have turned to the high tech center to jump-start potential computer science and programming startups to capitalize on the region's wealth of venture capital, business expertise, and cultural and financial incentives for innovation. Ethnic Chinese have been successful in starting new firms in technology centers across the United States, including California's Silicon Valley. Chinese Americans have been disproportionately successful in high technology sectors, as evidenced by the 2010 Goldsea 100 Compilation of America's Most Successful Asian Entrepreneurs. Chinese Americans accounted for 4% of people listed in the 1998 Forbes Hi Tech 100 List.
Annalee Saxenian, a UC Berkeley professor, whose research interests include the contribution of Chinese immigrants on America's technology concludes that in Silicon Valley, carried out a study that showed that since 1998, one out of five high tech start-ups in Silicon Valley were led by Chinese Americans. During the same year, 5 of the 8 fastest growing companies had Chinese American CEOs, except for Yahoo, whose Jerry Yang (entrepreneur), Jerry Yang was a founder but not a CEO. In Silicon Valley there are at least 2 to 3 dozen Chinese American organizations according to professional interests each with at least 100 members, one prominent organization of which is the Committee of 100 (United States), Committee of 100. Immigrants from mainland China and Taiwan were key founders in 12.8% of all Silicon Valley start-ups between 1995 and 2005. Almost 6% of the immigrants who founded companies in the innovation/manufacturing-related services field are from China.
Research funded by the Public Policy Institute of California indicates that in 1996, 1,786 Silicon Valley technology companies with $12.5 billion in sales and 46,000 employees were run by Indian or Chinese executives. Moreover, the pace of entrepreneurship among local immigrants is increasing rapidly. While Chinese or Indian executives are at the helm of 13% of the Silicon Valley technology businesses started between 1980 and 1985, they are running 27% of the more than 4,000 businesses started between 1991 and 1996. Start-up firms remain a primary source for new ideas and innovation for Chinese American internet entrepreneurs. Many of them are employed or directly engaged in new start-up activities. The proportional share of start-up firms by ethnic Chinese in Silicon Valley skyrocketed from 9% in 1980–1984 to about 20% between 1995 and 1998. By 2006, Chinese American internet entrepreneurs continued to start 20% of all Silicon Valley start-up firms, leading 2000 Silicon Valley companies, and employing 58,000 workers. They still continue to own about 20% of all information technology companies that were founded in Silicon Valley since 1980.
Numerous professional organizations in perspective in the 1990s as a support network for fellow Chinese American high tech start-ups in the valley. Between 1980 and 1999, 17% of the 11,443 high-tech firms in Silicon Valley – including some 40 publicly traded firms were controlled by ethnic Chinese. In 1990, Chinese Americans made up a third of the Asian American high tech professional workforce or 11% of the entire Silicon Valley professional workforce. In 1998, Chinese Americans managed 2001 firms, employing 41,684 workers, and ran up 13.2 billion in sales. They also account for 17% of all Silicon Valley firm owners, 10% of the professional workforce in the Valley, and 13.5% of the total sales accounting for less than 1% of the U.S. population at the time.
Self-employment and entrepreneurship
Chinese Americans are also noted for their high rates of self-employment, as they have an extensive history of self-employment dating back to the California Gold Rush in the 1880s. However, as more Chinese Americans seek higher education to elevate themselves socioeconomically, rates of self-employment are generally lower than population average. In 2007, there were over 109,614 Chinese-owned employer firms, employing more than 780,000 workers, and generating more than $128 billion in revenue.
Among Chinese-owned U.S. firms, 40% were in the professional, scientific, and technical services sector, the accommodation and food services sector, and the repair, maintenance, personal, and laundry services sector. Chinese-owned U.S. firms comprised 2% of all U.S. businesses in these sectors. Wholesale trade and accommodation and food services accounted for 50.4% of Chinese-owned business revenue. 66,505 or 15.7% of Chinese-owned firms had receipts of $250,000 or more compared with 2% for all U.S. businesses.
Perceptions and change
There has been a significant change in the perceptions about Chinese Americans. In as little as 100 years of American history, Stereotypes of East Asians in the Western world, stereotypes of Chinese Americans have changed to portraying a hard working and educated minority. Most Chinese Americans work as White-collar worker, white collar professionals, many of whom are highly educated, salaried professionals whose work is largely self-directed in management, professional, and related occupations such as engineering, medicine, investment banking, law, and academia. 56.2% of Chinese Americans work in white collar professions compared with 52.1% for all Asian Americans and a national average of 38.2%. Chinese Americans also make up a third of the Asian American high tech professional workforce and a tenth of the entire Silicon Valley workforce. Chinese Americans also hold lower unemployment rates than the population average with a figure of 4.7% compared to a national rate of 5.9% in 2010.
Medicine
Between 2008 and 2017, the number of Chinese-educated physicians practicing in the United States rose by 38.1%, and the total number of Chinese-educated physicians actively practicing in the United States was about 0.6% of the active physician workforce in 2017.
Technology sector
Many Chinese Americans have turned to the high tech center to jump-start potential computer science and programming startups to capitalize on the region's wealth of venture capital, business expertise, and cultural and financial incentives for innovation. Ethnic Chinese have been successful in starting new firms in technology centers across the United States, including California's Silicon Valley. Chinese Americans have been disproportionately successful in high technology sectors, as evidenced by the 2010 Goldsea 100 Compilation of America's Most Successful Asian Entrepreneurs. Chinese Americans accounted for 4% of people listed in the 1998 Forbes Hi Tech 100 List.
Annalee Saxenian, a UC Berkeley professor, whose research interests include the contribution of Chinese immigrants on America's technology concludes that in Silicon Valley, carried out a study that showed that since 1998, one out of five high tech start-ups in Silicon Valley were led by Chinese Americans. During the same year, 5 of the 8 fastest growing companies had Chinese American CEOs, except for Yahoo, whose Jerry Yang (entrepreneur), Jerry Yang was a founder but not a CEO. In Silicon Valley there are at least 2 to 3 dozen Chinese American organizations according to professional interests each with at least 100 members, one prominent organization of which is the Committee of 100 (United States), Committee of 100. Immigrants from mainland China and Taiwan were key founders in 12.8% of all Silicon Valley start-ups between 1995 and 2005. Almost 6% of the immigrants who founded companies in the innovation/manufacturing-related services field are from China.
Research funded by the Public Policy Institute of California indicates that in 1996, 1,786 Silicon Valley technology companies with $12.5 billion in sales and 46,000 employees were run by Indian or Chinese executives. Moreover, the pace of entrepreneurship among local immigrants is increasing rapidly. While Chinese or Indian executives are at the helm of 13% of the Silicon Valley technology businesses started between 1980 and 1985, they are running 27% of the more than 4,000 businesses started between 1991 and 1996. Start-up firms remain a primary source for new ideas and innovation for Chinese American internet entrepreneurs. Many of them are employed or directly engaged in new start-up activities. The proportional share of start-up firms by ethnic Chinese in Silicon Valley skyrocketed from 9% in 1980–1984 to about 20% between 1995 and 1998. By 2006, Chinese American internet entrepreneurs continued to start 20% of all Silicon Valley start-up firms, leading 2000 Silicon Valley companies, and employing 58,000 workers. They still continue to own about 20% of all information technology companies that were founded in Silicon Valley since 1980.
Numerous professional organizations in perspective in the 1990s as a support network for fellow Chinese American high tech start-ups in the valley. Between 1980 and 1999, 17% of the 11,443 high-tech firms in Silicon Valley – including some 40 publicly traded firms were controlled by ethnic Chinese. In 1990, Chinese Americans made up a third of the Asian American high tech professional workforce or 11% of the entire Silicon Valley professional workforce. In 1998, Chinese Americans managed 2001 firms, employing 41,684 workers, and ran up 13.2 billion in sales. They also account for 17% of all Silicon Valley firm owners, 10% of the professional workforce in the Valley, and 13.5% of the total sales accounting for less than 1% of the U.S. population at the time.
Self-employment and entrepreneurship
Chinese Americans are also noted for their high rates of self-employment, as they have an extensive history of self-employment dating back to the California Gold Rush in the 1880s. However, as more Chinese Americans seek higher education to elevate themselves socioeconomically, rates of self-employment are generally lower than population average. In 2007, there were over 109,614 Chinese-owned employer firms, employing more than 780,000 workers, and generating more than $128 billion in revenue.
Among Chinese-owned U.S. firms, 40% were in the professional, scientific, and technical services sector, the accommodation and food services sector, and the repair, maintenance, personal, and laundry services sector. Chinese-owned U.S. firms comprised 2% of all U.S. businesses in these sectors. Wholesale trade and accommodation and food services accounted for 50.4% of Chinese-owned business revenue. 66,505 or 15.7% of Chinese-owned firms had receipts of $250,000 or more compared with 2% for all U.S. businesses.
 Genetic mental illness is stigmatized in China. A study compares the attitude of Chinese American towards mental illness with genetic causes and that of European American. It finds out that there is a perception of eugenics existing among Chinese Americans. Consequently, in order to reduce the stigma in the society, more efforts should be devoted to this population.
Genetic mental illness is stigmatized in China. A study compares the attitude of Chinese American towards mental illness with genetic causes and that of European American. It finds out that there is a perception of eugenics existing among Chinese Americans. Consequently, in order to reduce the stigma in the society, more efforts should be devoted to this population.