Chieftain tank on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The FV4201 Chieftain was the
 The design of the Chieftain included a heavily sloped hull and turret which greatly increased the effective thickness of the frontal armour – on the glacis (from an actual thickness of ) and on the turret (from ).Richard Ogorkiewicz, ''Cold War, Hot Science: Applied Research in Britain's Defence Laboratories 1945–1990'' (2002), p.128-129, edited by Robert Bud & Philip Gummett, NMSI Trading Ltd, It had a mantletless turret in order to take full advantage of reclining the vehicle up to ten degrees in a hull-down position.
For security reasons early prototypes had a canvas screen covering the mantlet and a sheet metal box mounted over the sloping glacis plate to disguise the configuration of the vehicle.
The driver lay semi-recumbent in the hull when his hatch was closed down which helped to reduce the profile of the forward glacis plate. The commander, gunner and loader were situated in the turret. To the left side of the turret was a large searchlight with infrared capability in an armoured housing.
The design of the Chieftain included a heavily sloped hull and turret which greatly increased the effective thickness of the frontal armour – on the glacis (from an actual thickness of ) and on the turret (from ).Richard Ogorkiewicz, ''Cold War, Hot Science: Applied Research in Britain's Defence Laboratories 1945–1990'' (2002), p.128-129, edited by Robert Bud & Philip Gummett, NMSI Trading Ltd, It had a mantletless turret in order to take full advantage of reclining the vehicle up to ten degrees in a hull-down position.
For security reasons early prototypes had a canvas screen covering the mantlet and a sheet metal box mounted over the sloping glacis plate to disguise the configuration of the vehicle.
The driver lay semi-recumbent in the hull when his hatch was closed down which helped to reduce the profile of the forward glacis plate. The commander, gunner and loader were situated in the turret. To the left side of the turret was a large searchlight with infrared capability in an armoured housing.
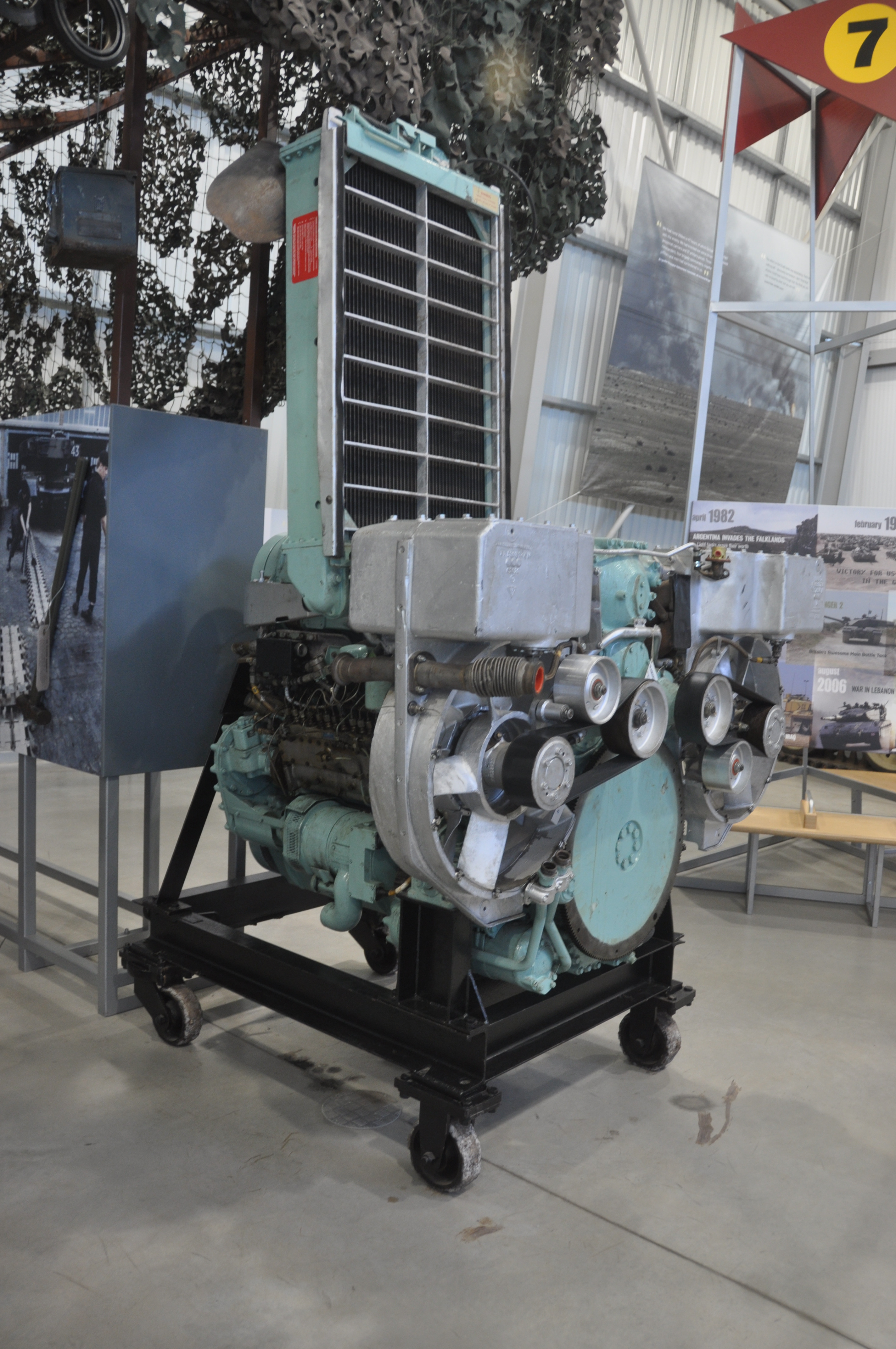 The Leyland L60 engine is a
The Leyland L60 engine is a  The main armament was the 120 mm L11A5 rifled gun. This differed from most contemporary main tank armament as it used projectiles and charges that were loaded separately, as opposed to a single fixed round. The charges were encased in combustible bags. Other tank guns such as the 120mm L1 gun on the Conqueror, needed to store the spent shell cartridges or eject them outside. The combustible charges were stored in 36 recesses surrounded by a pressurised water/glycol mixture – so-called "wet-stowage". In the event of a hit penetrating the fighting compartment, the jacket would rupture soaking the charges and preventing a catastrophic propellant explosion. As there was no shell case, the firing of the charge was by vent tubes automatically loaded from a ten-round magazine on the breech. Due to the length of the gun, which required balancing, and the need for storage space, the turret has a large overhang to the rear. This contains radios, ammunition and fire control equipment and has further stowage externally.
The gun could fire a wide range of ammunition but the most commonly loaded types were high explosive squash head (HESH),
The main armament was the 120 mm L11A5 rifled gun. This differed from most contemporary main tank armament as it used projectiles and charges that were loaded separately, as opposed to a single fixed round. The charges were encased in combustible bags. Other tank guns such as the 120mm L1 gun on the Conqueror, needed to store the spent shell cartridges or eject them outside. The combustible charges were stored in 36 recesses surrounded by a pressurised water/glycol mixture – so-called "wet-stowage". In the event of a hit penetrating the fighting compartment, the jacket would rupture soaking the charges and preventing a catastrophic propellant explosion. As there was no shell case, the firing of the charge was by vent tubes automatically loaded from a ten-round magazine on the breech. Due to the length of the gun, which required balancing, and the need for storage space, the turret has a large overhang to the rear. This contains radios, ammunition and fire control equipment and has further stowage externally.
The gun could fire a wide range of ammunition but the most commonly loaded types were high explosive squash head (HESH),
 Chieftain equipped British units of the
Chieftain equipped British units of the  The first model was introduced in 1967. Chieftains were supplied to at least six countries, including
The first model was introduced in 1967. Chieftains were supplied to at least six countries, including
 ; Khalid: Also known as "4030 Phase 2 Jordan". The sale of 274 MBTs was negotiated with Jordan in June 1979 following the cancellation of the Iranian contract. The Khalid tank is based on the Shir 1 design with the addition of the Integrated Fire Control System (IFCS), Tank Laser Sight (TLS) and the No 84 Day/Night Sight. The first 125 were reworked Shir 1's and the remaining 149 were new production tanks. The order has been completed, the first being delivered in July 1981.
;FV4030/3 Shir 2: Also known as "'4030 Phase 3'" Iranian variant. The Shir 2 represented a completely new-MBT incorporating Chobham armour (renamed "Pageant" to avoid diplomatic incident with the US government) to the hull and turret, with the rear of the hull similar in design to the Shir 1. The fire control, gun control and automotive systems were the same as Shir 1 with the following exceptions: Automotive - the option of adopting hydrogas suspension and command & control, the new No 84 commander's (PPE) day/night sight. The project began in 1974 and the first vehicle ran in October 1978. The production order was for 1,200 MBTs and production release given for 250 before cancellation in February 1979. Not delivered, the Shir 2 tanks became FV4030/4 Challenger 1 tanks after reworking at ROF Leeds.
;
; Khalid: Also known as "4030 Phase 2 Jordan". The sale of 274 MBTs was negotiated with Jordan in June 1979 following the cancellation of the Iranian contract. The Khalid tank is based on the Shir 1 design with the addition of the Integrated Fire Control System (IFCS), Tank Laser Sight (TLS) and the No 84 Day/Night Sight. The first 125 were reworked Shir 1's and the remaining 149 were new production tanks. The order has been completed, the first being delivered in July 1981.
;FV4030/3 Shir 2: Also known as "'4030 Phase 3'" Iranian variant. The Shir 2 represented a completely new-MBT incorporating Chobham armour (renamed "Pageant" to avoid diplomatic incident with the US government) to the hull and turret, with the rear of the hull similar in design to the Shir 1. The fire control, gun control and automotive systems were the same as Shir 1 with the following exceptions: Automotive - the option of adopting hydrogas suspension and command & control, the new No 84 commander's (PPE) day/night sight. The project began in 1974 and the first vehicle ran in October 1978. The production order was for 1,200 MBTs and production release given for 250 before cancellation in February 1979. Not delivered, the Shir 2 tanks became FV4030/4 Challenger 1 tanks after reworking at ROF Leeds.
; ; FV4204 ARV/ARRV: Armoured Recovery Vehicle, Armoured Recovery and Repair Vehicle.
; FV4205 AVLB Mk5: Bridge-laying vehicle
; FV4204 ARV/ARRV: Armoured Recovery Vehicle, Armoured Recovery and Repair Vehicle.
; FV4205 AVLB Mk5: Bridge-laying vehicle
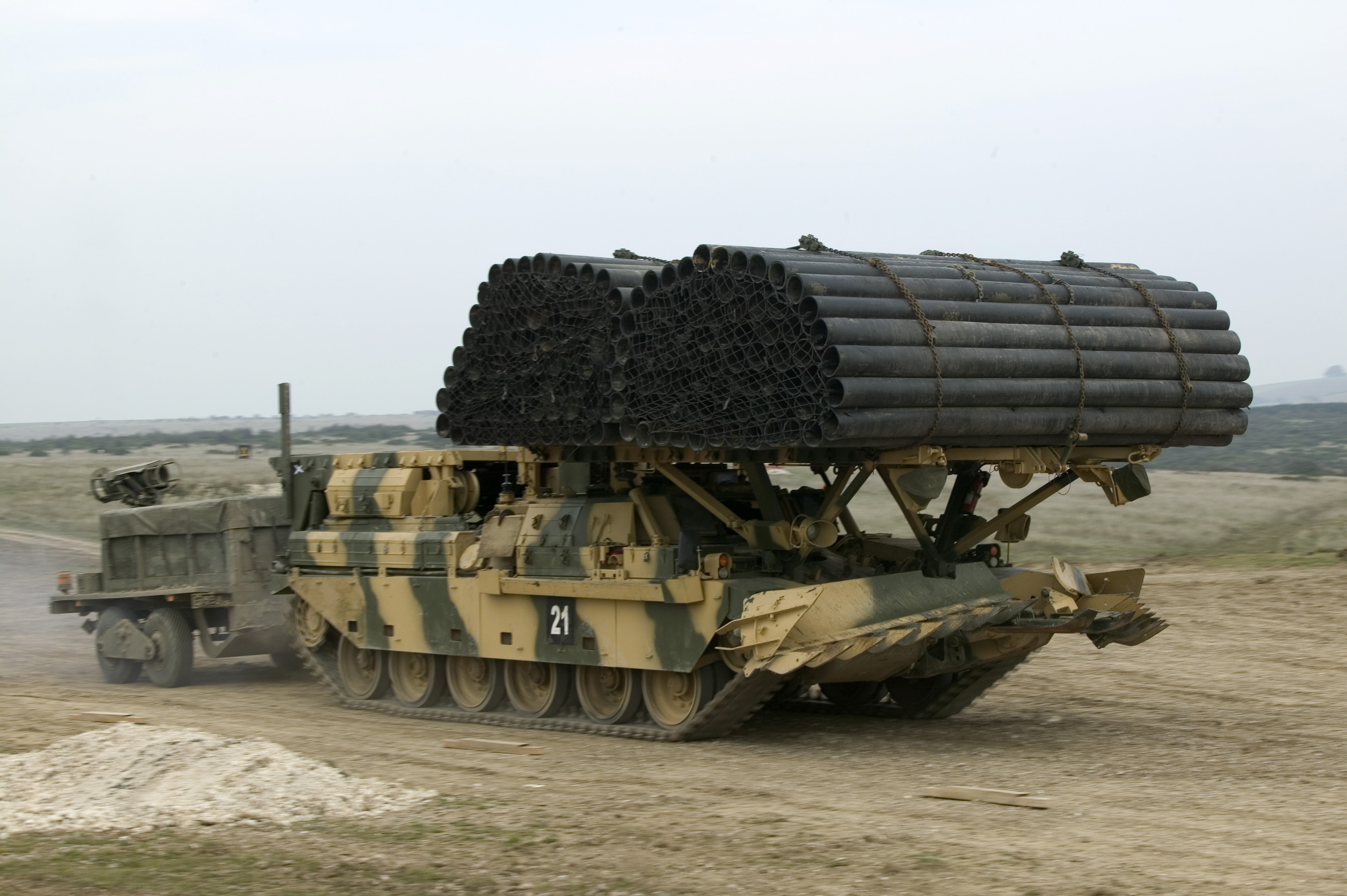 ; Chieftain AVRE (CHAVRE): Armoured Vehicle Royal Engineers, twelve early "Willich Chieftain AVRE" vehicles converted by 32 Armoured Engineer Regiment and 21 Engineer Base Workshop of the Royal Engineers, Willich, 1987, remaining 48 ex MBTs converted by Vickers Defence Ltd, 1991, to be a British Army combat engineering variant used by the Royal Engineers.
; Chieftain Fascine Layer: Four turret-less vehicles specially converted for laying
; Chieftain AVRE (CHAVRE): Armoured Vehicle Royal Engineers, twelve early "Willich Chieftain AVRE" vehicles converted by 32 Armoured Engineer Regiment and 21 Engineer Base Workshop of the Royal Engineers, Willich, 1987, remaining 48 ex MBTs converted by Vickers Defence Ltd, 1991, to be a British Army combat engineering variant used by the Royal Engineers.
; Chieftain Fascine Layer: Four turret-less vehicles specially converted for laying

FAS.org
Chieftain Tank
Military Factory article
{{Authority control Main battle tanks of the United Kingdom Cold War tanks of the United Kingdom Military vehicles introduced in the 1960s Main battle tanks of the Cold War History of the tank
main battle tank
A main battle tank (MBT), also known as a battle tank or universal tank, is a tank that fills the role of armor-protected direct fire and maneuver in many modern armies. Cold War-era development of more powerful engines, better suspension s ...
of the United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Europe, off the north-western coast of the European mainland, continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotlan ...
during the 1960s–1990s.
A development of the Centurion
A centurion (; la, centurio , . la, centuriones, label=none; grc-gre, κεντυρίων, kentyríōn, or ) was a position in the Roman army during classical antiquity, nominally the commander of a century (), a military unit of around 80 le ...
, the Chieftain introduced the supine (reclining) driver position to British design allowing a heavily sloped hull with reduced height. A new powerpack and improved transmission gave it higher speed than the Centurion despite being heavier due to major upgrades to armour protection and the armament; this allowed it to replace both the Conqueror and Centurion
A centurion (; la, centurio , . la, centuriones, label=none; grc-gre, κεντυρίων, kentyríōn, or ) was a position in the Roman army during classical antiquity, nominally the commander of a century (), a military unit of around 80 le ...
while performing their roles effectively. It remained in service until replaced by the Challenger 1 which shared many of the Chieftain's features.
Development
The Chieftain was an evolutionary development of the successful cruiser line of tanks that had emerged at the end of theSecond World War
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the World War II by country, vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great power ...
. Its predecessor, the Centurion
A centurion (; la, centurio , . la, centuriones, label=none; grc-gre, κεντυρίων, kentyríōn, or ) was a position in the Roman army during classical antiquity, nominally the commander of a century (), a military unit of around 80 le ...
main battle tank (MBT), is widely considered to be one of the most successful of post-war MBT designs. However, the introduction of the Soviet IS-3
The IS-3 (also known as Object 703) is a Soviet heavy tank developed in late 1944. Its semi-hemispherical cast turret (resembling that of an upturned soup bowl), became the hallmark of post-war Soviet tanks. Its pike nose design would also be ...
/ IS-4 heavy tank along with Soviet T-54/T-55
The T-54 and T-55 tanks are a series of Soviet main battle tanks introduced in the years following the Second World War. The first T-54 prototype was completed at Nizhny Tagil by the end of 1945.Steven Zaloga, T-54 and T-55 Main Battle Tan ...
forced the introduction of the Conqueror heavy tank armed with a gun. A single design combining the firepower of the Conqueror's 120 mm gun with the mobility and general usefulness of the Centurion was seen as the ideal combination.
Leyland, who had been involved in the Centurion tank, had built their own prototypes of a new tank design in 1956. Several aspects of the design were trialled by the production of the FV4202 "40-ton Centurion" with a reclined driver position and mantletless gun mounting. In effect, the FV4202 was a shorter Centurion chassis with a prototype of what would become the Chieftain turret, but armed with the 20pdr gun.
This work led to a War Office
The War Office was a department of the British Government responsible for the administration of the British Army between 1857 and 1964, when its functions were transferred to the new Ministry of Defence (United Kingdom), Ministry of Defence (MoD ...
specification for a new tank. The General Staff specification drew on the experience of Centurion tanks in the Korean War
{{Infobox military conflict
, conflict = Korean War
, partof = the Cold War and the Korean conflict
, image = Korean War Montage 2.png
, image_size = 300px
, caption = Clockwise from top: ...
as well as that of the Conqueror tank. The tank was expected to be able to engage the enemy at long range, from defensive positions, and be proof against medium artillery. To this end, the gun was to have a greater angle of depression than the 8 degrees of Conqueror and would be equipped with better frontal armour. The tank was expected to achieve a firing rate of 10 rounds per minute in the first minute and six per minute for the following four.
The first few prototypes were provided for troop trials from 1959 which identified a number of changes. Improvements to address engine vibration and cooling resulted in a redesign of the rear hull. This increased the design weight to nearly 50 tons and accordingly the suspension (which had been designed for 45 tons) was strengthened. Trackpads had to be fitted to protect roads from damage and the ground clearance increased. The design was accepted in the early 1960s.
Britain and Israel had collaborated on the development in its latter stages with a view to Israel purchasing and domestically producing the vehicle. Two prototypes were delivered as part of a four-year trial. However, it was eventually decided not to sell the marque to the Israelis (since, at that period of time in the late 1960s, the UK was more friendly towards the Arab states and Jordan than to Israel), which prompted them to follow their own development programme.
In 1957, NATO had specified that its forces should use multi-fuel engines. The early Leyland engine delivered around to the sprocket, which meant a top road speed of around and cross-country performance was limited. This was further hampered by the Horstmann coil spring suspension, which made it a challenge to drive cross country and provide the crew with a comfortable ride. Due to the cylinder linings being pressure fitted, coolant leaks within the cylinder block were common, resulting in white smoke billowing from the exhaust.
In the late 1970s, engine design changed with the introduction of Belzona which was used to improve the lining seals. Engine output also increased, with later engines delivering some to the sprocket. This meant better performance and an increased speed. However, cross-country performance remained limited.
Design
 The design of the Chieftain included a heavily sloped hull and turret which greatly increased the effective thickness of the frontal armour – on the glacis (from an actual thickness of ) and on the turret (from ).Richard Ogorkiewicz, ''Cold War, Hot Science: Applied Research in Britain's Defence Laboratories 1945–1990'' (2002), p.128-129, edited by Robert Bud & Philip Gummett, NMSI Trading Ltd, It had a mantletless turret in order to take full advantage of reclining the vehicle up to ten degrees in a hull-down position.
For security reasons early prototypes had a canvas screen covering the mantlet and a sheet metal box mounted over the sloping glacis plate to disguise the configuration of the vehicle.
The driver lay semi-recumbent in the hull when his hatch was closed down which helped to reduce the profile of the forward glacis plate. The commander, gunner and loader were situated in the turret. To the left side of the turret was a large searchlight with infrared capability in an armoured housing.
The design of the Chieftain included a heavily sloped hull and turret which greatly increased the effective thickness of the frontal armour – on the glacis (from an actual thickness of ) and on the turret (from ).Richard Ogorkiewicz, ''Cold War, Hot Science: Applied Research in Britain's Defence Laboratories 1945–1990'' (2002), p.128-129, edited by Robert Bud & Philip Gummett, NMSI Trading Ltd, It had a mantletless turret in order to take full advantage of reclining the vehicle up to ten degrees in a hull-down position.
For security reasons early prototypes had a canvas screen covering the mantlet and a sheet metal box mounted over the sloping glacis plate to disguise the configuration of the vehicle.
The driver lay semi-recumbent in the hull when his hatch was closed down which helped to reduce the profile of the forward glacis plate. The commander, gunner and loader were situated in the turret. To the left side of the turret was a large searchlight with infrared capability in an armoured housing.
 The Leyland L60 engine is a
The Leyland L60 engine is a two-stroke
A two-stroke (or two-stroke cycle) engine is a type of internal combustion engine that completes a power cycle with two strokes (up and down movements) of the piston during one power cycle, this power cycle being completed in one revolution of t ...
opposed piston design intended for multi-fuel use so that it could run on whatever fuel was available. In practice the engine did not deliver the expected power and was unreliable, estimated to have a 90% breakdown rate but improvements were introduced to address this. Primary problems included cylinder liner failure, fan drive problems and perpetual leaks due to vibration and badly routed pipework. However, as the engine power improved the tank itself became heavier.
The tank was steered by conventional tillers hydraulically actuating onto external brake discs. The discs worked via the epicyclic gearbox providing "regenerative" steering. The Merritt-Brown TN12 triple-differential gearbox was operated motorcycle-style with a kick up/kick down "peg" on the left, which actuated electro-hydraulic units in the gearbox, the accelerator cable was operated by the right foot. In the turret, the loader was on the left and the gunner on the right of the gun with the commander situated behind the gunner. The suspension was of the Horstmann bogie type with large side steel plates to protect the tracks and provide stand-off protection from hollow charge attack.
 The main armament was the 120 mm L11A5 rifled gun. This differed from most contemporary main tank armament as it used projectiles and charges that were loaded separately, as opposed to a single fixed round. The charges were encased in combustible bags. Other tank guns such as the 120mm L1 gun on the Conqueror, needed to store the spent shell cartridges or eject them outside. The combustible charges were stored in 36 recesses surrounded by a pressurised water/glycol mixture – so-called "wet-stowage". In the event of a hit penetrating the fighting compartment, the jacket would rupture soaking the charges and preventing a catastrophic propellant explosion. As there was no shell case, the firing of the charge was by vent tubes automatically loaded from a ten-round magazine on the breech. Due to the length of the gun, which required balancing, and the need for storage space, the turret has a large overhang to the rear. This contains radios, ammunition and fire control equipment and has further stowage externally.
The gun could fire a wide range of ammunition but the most commonly loaded types were high explosive squash head (HESH),
The main armament was the 120 mm L11A5 rifled gun. This differed from most contemporary main tank armament as it used projectiles and charges that were loaded separately, as opposed to a single fixed round. The charges were encased in combustible bags. Other tank guns such as the 120mm L1 gun on the Conqueror, needed to store the spent shell cartridges or eject them outside. The combustible charges were stored in 36 recesses surrounded by a pressurised water/glycol mixture – so-called "wet-stowage". In the event of a hit penetrating the fighting compartment, the jacket would rupture soaking the charges and preventing a catastrophic propellant explosion. As there was no shell case, the firing of the charge was by vent tubes automatically loaded from a ten-round magazine on the breech. Due to the length of the gun, which required balancing, and the need for storage space, the turret has a large overhang to the rear. This contains radios, ammunition and fire control equipment and has further stowage externally.
The gun could fire a wide range of ammunition but the most commonly loaded types were high explosive squash head (HESH), armour-piercing discarding sabot
Armour-piercing discarding sabot (APDS) is a type of spin-stabilized kinetic energy projectile for anti-armour warfare. Each projectile consists of a sub-calibre round fitted with a sabot. The combination of a lighter sub-calibre projectile wit ...
(APDS), or practice round equivalents for both types. The Chieftain could store up to 64 projectiles (although the propellant stowage allowed a maximum of 36 charges for APDS rounds). The gun was fully stabilised with a fully computerized integrated control system. The secondary armament consisted of a coaxial L8A1 7.62 mm machine gun and another 7.62 mm machine gun mounted on the commander's cupola. An advantage of using two-part ammunition was that in the case of inert rounds like APDS the loader could reach for the next round and hold it in his lap, ready to load while the gunner was acquiring the target and firing. This practice increases the rate of fire but would be hazardous with one-piece ammunition.
Chieftain had an NBC protection system which Centurion lacked. An infantry telephone was fitted to the rear of the tank to facilitate communication with infantry.
The initial Fire-control system
A fire-control system (FCS) is a number of components working together, usually a gun data computer, a Director (military), director, and radar, which is designed to assist a ranged weapon system to target, track, and hit a target. It performs ...
(FCS) was the Marconi FV/GCE Mk 4. A .50-inch (12.7 mm) ranging gun
A spotting rifle or ranging gun is a small-calibre rifle used as a sighting device for artillery. The ballistics of the spotting rifle are matched to those of the artillery piece, so that if a shot from the spotting rifle lands on the target, it ...
was mounted above the main gun (with 300 rounds available). This fired ranging shots out to a maximum of , at which point the tracer in the ranging rounds burned out although the high explosive tip still created a visible "splash" on impact. The tank commander had a rotating cupola with nine vision blocks -giving all round view, plus the 7.62 mm machine-gun and an infrared (IR) capable projector coaxial with the weapon. The aiming systems were provided for both the gunner and the tank commander; they had 1x or 10x selectable magnification power, increasing to x15 in the Mk5 and beyond, and they were replaceable with IR vision systems for night operations (3x magnification power). The commander could rotate his cupola to bring his sight onto a target and then engage the mechanism that brought the turret round on to the correct bearing so that the gunner could complete the aiming.
The commander's controls had over-ride capability on those of the gunner.
The left side of the turret had a large searchlight with an electrically controlled infrared filter inside an armoured box, with a relatively long range – up to .JP-4 dossier, ''Main Battle Tanks'' (1990), pp.35–36, edited by Ed.Ai. 1990, Florence
From the beginning of the 1970s, the Mk 3/3 version replaced the ranging gun with a Barr and Stroud LF-2 laser rangefinder
A laser rangefinder, also known as a laser telemeter, is a rangefinder that uses a laser beam to determine the distance to an object. The most common form of laser rangefinder operates on the time of flight principle by sending a laser pulse in ...
with a range. This allowed engagements at much longer ranges, and also could be linked to the fire control system, allowing more rapid engagements and changes of target.
On later models, fire control was provided by the Marconi IFCS (Improved Fire Control System), using a digital ballistic computer. The upgrade was not finished until the end of 1980, when some examples (but not the majority) had the IR searchlight replaced with TOGS. Many later examples had Stillbrew armour, intended to defeat Soviet 125 mm tank guns and heavy anti-tank missiles. These became the Mark 11 version.
Service
British Army of the Rhine
There have been two formations named British Army of the Rhine (BAOR). Both were originally occupation forces in Germany, one after the First World War and the other after the Second World War. Both formations had areas of responsibility locate ...
(BAOR) during the Cold War, defended West Germany against possible Warsaw Pact attack.
Like its European competitors, the Chieftain found a large export market in the Middle East
The Middle East ( ar, الشرق الأوسط, ISO 233: ) is a geopolitical region commonly encompassing Arabia (including the Arabian Peninsula and Bahrain), Asia Minor (Asian part of Turkey except Hatay Province), East Thrace (Europ ...
, but unlike the Centurion, it was not adopted by any other NATO
The North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO, ; french: Organisation du traité de l'Atlantique nord, ), also called the North Atlantic Alliance, is an intergovernmental military alliance between 30 member states – 28 European and two No ...
or Commonwealth country.
The Chieftain proved itself capable in combat and able to be upgraded, both for overall improvement and to meet local requirements. It was continuously upgraded until the early 1990s, when it was replaced by Challenger 1. The final Chieftain version, which was used by the British Army until 1995, incorporated "Stillbrew" armour named after Colonel Still and John Brewer from the Military Vehicles and Engineering Establishment (MVEE), the Improved Fire Control System (IFCS) and the Thermal Observation Gunnery Sight (TOGS). The last British Regiment equipped with Chieftains was the 1st Royal Tank Regiment, which was based at Aliwal Barracks Aliwal may refer to:
*Aliwal, Taran Taran, a village in the Indian state of Punjab
* Aliwal, Jalandhar, a village in the Indian state of Punjab
* Battle of Aliwal fought in 1846 between the British and the Sikhs
* Aliwal North
Aliwal North (off ...
, Tidworth.
 The first model was introduced in 1967. Chieftains were supplied to at least six countries, including
The first model was introduced in 1967. Chieftains were supplied to at least six countries, including Iran
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran, and also called Persia, is a country located in Western Asia. It is bordered by Iraq and Turkey to the west, by Azerbaijan and Armenia to the northwest, by the Caspian Sea and Turkm ...
, Kuwait
Kuwait (; ar, الكويت ', or ), officially the State of Kuwait ( ar, دولة الكويت '), is a country in Western Asia. It is situated in the northern edge of Eastern Arabia at the tip of the Persian Gulf, bordering Iraq to the no ...
, Oman
Oman ( ; ar, عُمَان ' ), officially the Sultanate of Oman ( ar, سلْطنةُ عُمان ), is an Arabian country located in southwestern Asia. It is situated on the southeastern coast of the Arabian Peninsula, and spans the mouth of ...
and Jordan
Jordan ( ar, الأردن; tr. ' ), officially the Hashemite Kingdom of Jordan,; tr. ' is a country in Western Asia. It is situated at the crossroads of Asia, Africa, and Europe, within the Levant region, on the East Bank of the Jordan Ri ...
. An agreement for sales to Israel
Israel (; he, יִשְׂרָאֵל, ; ar, إِسْرَائِيل, ), officially the State of Israel ( he, מְדִינַת יִשְׂרָאֵל, label=none, translit=Medīnat Yīsrāʾēl; ), is a country in Western Asia. It is situated ...
and local production was cancelled by the British Government in 1969, despite considerable Israeli technical and tactical input into the development of the tank, especially the capacity to operate successfully in desert environments, and the provision for the tank to make good use of hull-down
In sailing and warfare, hull-down means that the upper part of a vessel or vehicle is visible, but the main, lower body (hull) is not; the term hull-up means that all of the body is visible. The terms originated with sailing and naval warfare i ...
positioning. Two examples were delivered to, and extensively trialled by, the Israeli Armoured Corps. This experience spurred the creation of the indigenous Israeli Merkava, the development programme was led by General Israel Tal, who had worked closely with the British in the Anglo-Israeli Chieftain project. The largest foreign sale was to Iran, who, at the recommendation of General Tal, took delivery of 707 Mk-3P and Mk-5P (the letter P standing for Persia), as well as 187 FV4030-1, 41 ARV and 14 AVLB before the 1979 revolution. Further planned deliveries of the more capable FV4030-2 (Shir 1) and FV4030-3 (Shir 2) series were cancelled at that point.
It was in the Middle East that the Chieftain was to see all of its operational experience. It was first used extensively by Iran, during the Iran–Iraq War
The Iran–Iraq War was an armed conflict between Iran and Iraq that lasted from September 1980 to August 1988. It began with the Iraqi invasion of Iran and lasted for almost eight years, until the acceptance of United Nations Security Counci ...
of 1980–88, including the largest tank battle of the war, with mixed results as the Chieftain Mk 3/5 suffered from chronic engine problems and low power-to-weight ratio, making it unreliable and slow when manoeuvering over harsh terrain, which in turn made it prone to breakdowns in the midst of battle or a sluggish target and thus vulnerable to enemy tank fire. After the tank battle at Susangerd, captured Chieftains of the Iranian 92nd Armoured Division were taken back to Baghdad for trials. According to Aladdin Makki, the Iraqi Army Corps chief of staff, in a post-war interview, Iraqi sabot rounds "Went through the front Armour of the Chieftain and came out the backside". This as well as the Chieftain's poor off-road capability influenced the Iraqis to reject British arms sale propositions, who were at the time courting Iraq for arms sales that included Chieftain MBT's. According to Makki, when the British telephoned the Iraqi director of Armor, Salah Askar, he responded with "We don't want your stupid tanks!". Ra'ad Al-Hamdani, an Iraqi general in the Iraqi Republican Guard, also expressed negative opinion on the Chieftain's performance in combat, stating "The 16th Iranian Armored Division, which was equipped with Chieftain tanks, lost a battle against the 10th Iraqi Armored Brigade with T-72
The T-72 is a family of Soviet/Russian main battle tanks that entered production in 1969. The T-72 was a development of the T-64, which was troubled by high costs and its reliance on immature developmental technology. About 25,000 T-72 tanks ...
tanks. It is hard for an armored brigade to destroy a division in 12 hours but it happened; it was a disaster for the Iranians". Out of the 894 Chieftain tanks that had started the war only 200 were left by the war's end.
The Chieftain remains in service in Iran, the Mobarez tank
Mobarez (Persian: مبارز; meaning "Warrior") is a domestically upgraded version of the British Chieftain tank by Iran.
Changes
The hull of the tank has been modified at the back and sides. The fuel tank has been replaced by a new, repairabl ...
being a locally upgraded version.
Kuwait and the Battle of the Bridges
Kuwait had 143 Chieftains on the eve of the 1990 IraqiInvasion of Kuwait
The Iraqi invasion of Kuwait was an operation conducted by Iraq on 2 August 1990, whereby it invaded the neighboring State of Kuwait, consequently resulting in a seven-month-long Iraqi military occupation of the country. The invasion and Ira ...
. Thirty-seven Chieftains of the Kuwaiti 35th Armored Brigade fought at the Battle of the Bridges against elements of the Iraqi Hammurabi and Medina divisions before withdrawing over the Saudi border. None of the brigade's tanks were lost in the battle, and the 35th Armored Brigade (known as Al-Fatah) became part of '' Joint Command Forces East'' during the 1991 Gulf War
The Gulf War was a 1990–1991 armed campaign waged by a Coalition of the Gulf War, 35-country military coalition in response to the Iraqi invasion of Kuwait. Spearheaded by the United States, the coalition's efforts against Ba'athist Iraq, ...
and was able to return into Kuwait undefeated.
Besides those of the 35th Armored Brigade, the rest of the Kuwaiti Armed Forces' Chieftains (136 tanks) were either destroyed or captured by the invading forces after they had been abandoned by their Kuwaiti crews when their ammunition ran out. After the liberation of Kuwait, the ageing Chieftains were replaced by the Yugoslav M-84
The M-84 is a Yugoslav main battle tank, a variant of the Soviet T-72. The M-84 is still in service in Croatia, Serbia, Bosnia and Herzegovina and Kuwait.
Development and production
Development
The M-84 is based on the Soviet T-72M (expo ...
.
Specifications (Mk. 5)
* Crew: 4 * Combat weight: 55 tons * Overall length: gun forward * Hull length: * Height: * Width: * Powerplant:Opposed-piston engine
An opposed-piston engine is a piston engine in which each cylinder has a piston at both ends, and no cylinder head. Petrol and diesel opposed-piston engines have been used mostly in large-scale applications such as ships, military tanks, and ...
Leyland L60 (diesel, multi-fuel compression ignition)
* Range:
* Maximum road speed:
* Cross-country speed:
* Armour: turret front, RHA (60°)
;Armament
* 120 mm L11A5 rifled tank gun
A tank gun is the main armament of a tank. Modern tank guns are high-velocity, large-caliber artilleries capable of firing kinetic energy penetrators, high-explosive anti-tank, and cannon-launched guided projectiles. Anti-aircraft guns can ...
** Rate of fire: 10 rounds per minute for the first minute and 6 thereafter.
** Elevation: -10 to +20 degree
** Laser rangefinder
* Coaxial L8A1 7.62 mm machine gun
A machine gun is a fully automatic, rifled autoloading firearm designed for sustained direct fire with rifle cartridges. Other automatic firearms such as automatic shotguns and automatic rifles (including assault rifles and battle rifl ...
* Cupola-mounted L37A1 7.62mm machine gun
Mark 1 and Mark 2 models had a coaxial Browning .50-inch (12.7 mm) ranging machine guns prior to the introduction of the laser rangefinder
A laser rangefinder, also known as a laser telemeter, is a rangefinder that uses a laser beam to determine the distance to an object. The most common form of laser rangefinder operates on the time of flight principle by sending a laser pulse in ...
.
;Equipment
* Twin Clansman VRC 353 VHF Radio sets (1979 onward)
* 1 C42 1 B47 Larkspur VHF
Very high frequency (VHF) is the ITU designation for the range of radio frequency electromagnetic waves (radio waves) from 30 to 300 megahertz (MHz), with corresponding wavelengths of ten meters to one meter.
Frequencies immediately below VHF ...
radios (pre 1979)
* 2 X 6-barrel smoke dischargers on turret
* Bulldozer blade (optional – fitted to one tank per squadron)
Variants
; FV4201 P1 - FV4201 P7: :Prototypes. Seven built, L60 Mk 1 or L60 Mk 4, initial vehicles had internal exhaust silencers, short hull, small diameter road wheels. In an attempt at reducing the overall height of the vehicle the original design used road wheels of a smaller diameter which gave insufficient ground clearance. They were later replaced with Centurion road wheels of a larger diameter and by careful re-positioning of their mountings along with adjustment of the idler and final drive mountings resulted in a vehicle height only higher than with the original smaller wheels. Initial vehicle weight ; for later vehicles, 1959-1962 ; Chieftain Mk.1 : 40 training vehicles for 1965–1966 with L60 Mk 4 engine, strengthened TN12 gearbox, exhaust silencers moved to external armoured box on hull rear plate, larger 'Centurion' diameter road wheels, re-positioned final drive and idler wheel assemblies, two-piece commander's hatch cover, rubber track pads fitted for road protection inWest Germany
West Germany is the colloquial term used to indicate the Federal Republic of Germany (FRG; german: Bundesrepublik Deutschland , BRD) between its formation on 23 May 1949 and the German reunification through the accession of East Germany on 3 O ...
, resilient rubber coaming around engine rear decking to prevent damage from gun with gun depression when turret traversed to the rear, stowage rack added to left rear of turret, dummy stowage 'bin' on front glacis and canvas cover over turret nose to conceal ballistic shapes, weight , Issued to 1 RTR and 5 RTR for troop trials. All Mk.1 to Mk.1/4 vehicles were subsequently to be based at Bovington Camp
Bovington Camp () is a British Army military base in Dorset, England. Together with Lulworth Camp it forms part of Bovington Garrison.
The garrison is home to The Armour Centre and contains two barracks complexes and two forest and heathland tr ...
and Catterick Garrison
Catterick Garrison is a major garrison and military town south of Richmond, North Yorkshire, England. It is the largest British Army garrison in the world, with a population of around 13,000 in 2017 and covering over 2,400 acres (about ...
. 11 short hull units converted to become Chieftain, Armoured Vehicle-Launched Bridge Mk.6 (CH AVLB Mk 6).
; Chieftain Mk.1/2
: Upgrade of Chieftain Mk.1 to Chieftain Mk.2 standard, fitted with 650 hp L60 Mk 4A2 engine, training use only
; Chieftain Mk.1/3
: Upgrade of Chieftain Mk.1, fitted with 650 hpL60 Mk 5A engine, training use only
; Chieftain Mk.1/4
: Upgrade of Chieftain Mk.1, fitted with 650 hp L60 Mk 6A engine and improved ranging gun, training use only
; Chieftain Mk.2: First service model with 650 hp L60 Mk 4A2 engine, L11A2 or L11A3 main gun, NBC system fitted to rear of turret, revised turret stowage, one-piece commander's hatch cover, armour removed from searchlight cover, rigid flotation panels replaced by facility for deep wading, road speed , range , weight , first vehicles issued to 11th Hussars
The 11th Hussars (Prince Albert's Own) was a cavalry regiment of the British Army established in 1715. It saw service for three centuries including the First World War and Second World War but then amalgamated with the 10th Royal Hussars (Prin ...
at Hohne in West Germany in early 1967, improved L60 Mk 5A engine fitted 1969
; Chieftain Mk.3:Improved 650 hp L60 Mk 6A engine with two-stage air cleaner, improved auxiliary generator (Coventry Climax
Coventry Climax was a British forklift truck, fire pump, racing, and other specialty engine manufacturer.
History
Pre WW1
The company was started in 1903 as Lee Stroyer, but two years later, following the departure of Stroyer, it was reloca ...
H30 ), better stowage, new No. 15 Mk 2 commander's cupola, road speed improved to , range increased to , weight , 1970
; Chieftain Mk 3/2: Fitted with L60 Mk 7A, 1971
; Chieftain Mk 3/3: Fitted with 720 hp L60 Mk 7A, Improved main gun range finding, provision for Barr & Stroud TLS (Tank Laser Sight) LF2 laser range finder, With the LF2, the Chieftain became the first vehicle to be fitted with such a range-finding system. 1971
; Chieftain Mk 3/G: Chieftain Mk.3 with engine induction through fighting compartment. Prototype only
; Chieftain Mk.3/3P: Chieftain Mk 3/3 for Iran
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran, and also called Persia, is a country located in Western Asia. It is bordered by Iraq and Turkey to the west, by Azerbaijan and Armenia to the northwest, by the Caspian Sea and Turkm ...
, 1973
; Chieftain Mk 3/S: Production version of Chieftain Mk 3/G with commander's firing control
; Chieftain Mk.4
:Chieftain Mk.3 with increased fuel capacity for Israel Defense Forces (IDF). Only two built. 1973. The Chieftain Mk.4 project was halted at the behest of the British Government due to the perceived adverse effect the sale of Chieftain to Israel was likely to have on the balance of power within the region. Of the two Mk.4 vehicles built, one was scrapped, the other "02 SP 27" was fitted with an NCK Rapier crane and used at Kirkcudbright Training Area
Kirkcudbright ( ; sco, Kirkcoubrie; gd, Cille Chùithbeirt) is a town, parish and a Royal Burgh from 1455 in Kirkcudbrightshire, of which it is traditionally the county town, within Dumfries and Galloway, Scotland.
The town lies southwest of C ...
; Chieftain Mk.5: Final production variant, L60 Mark 8A, with upgrades to the NBC protection system, weight , 1975
; Chieftain Mk.5/5P: Chieftain Mk.5 for Iran
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran, and also called Persia, is a country located in Western Asia. It is bordered by Iraq and Turkey to the west, by Azerbaijan and Armenia to the northwest, by the Caspian Sea and Turkm ...
, 1975. Engine later upgraded to L60 Mk 10A, 1977
; Chieftain Mk.5/2K: Chieftain Mk.5 for Kuwait
Kuwait (; ar, الكويت ', or ), officially the State of Kuwait ( ar, دولة الكويت '), is a country in Western Asia. It is situated in the northern edge of Eastern Arabia at the tip of the Persian Gulf, bordering Iraq to the no ...
, 1975
In 1975 all British Army earlier Marks of tanks except Mark 1's were upgraded to Chieftain Mk.5 standard as part of the 1975 "Totem Pole" programme. "Exercise Totem Pole" was carried out in six-to-nine phases depending on the Mark of vehicle being modified (Chieftain Mk.5's already had some of the required changes incorporated at the factory) between 1975 and 1979 and included fitment of the Marconi Improved Fire Control System (IFCS), replacement of the searchlight with the Barr & Stroud Thermal Observation Gunnery System (TOGS), along with modifications for using FSAPDS ammunition. Upon completion of each phase the vehicle received an additional suffix to the designation, e.g., "Chieftain Mk.3/S(Y)2" denoting a Mark 3/S having completed the first three phases of "Totem Pole". including addition of Clansman radios, fitting of TLS, fitment of Muzzle Reference System (MRS) upon replacement of L11A3 barrel with L11A5 barrel, and fitment of 750 hp L60 Mark 8A. These vehicles were re-designated Chieftain Mk's.6 to Mk.8.
; Chieftain Mk.6
:Chieftain Mk.2 upgraded to Chieftain Mk.5 standard, 1975
; Chieftain Mk.7
:Chieftain Mk.3 and Chieftain Mk 3/S upgraded to Chieftain Mk.5 standard, 1975
; Chieftain Mk.7C
:Chieftain Mk.3 upgraded to Chieftain Mk.5 standard for Oman
Oman ( ; ar, عُمَان ' ), officially the Sultanate of Oman ( ar, سلْطنةُ عُمان ), is an Arabian country located in southwestern Asia. It is situated on the southeastern coast of the Arabian Peninsula, and spans the mouth of ...
; Chieftain Mk.8
:Chieftain Mk.3/3 upgraded to Chieftain Mk.5 standard, 1975
In 1977 the engines of all British Army vehicles were upgraded to the 750 hp L60 Mark 9A, followed by further upgrading with the L60 Mark 11A or L60 Mark 12A in 1978 as part of the 1977 "Dark Morn" and the 1978 "Sundance" programmes. "Exercise Sundance" concerned improvements in engine power, reliability, and other power train improvements, and was carried out in five main phases between 1976 and 1979. These, in themselves, had been preceded by "Dark Morn", "High Noon", and the initial "Fleetfoot" engine development programme which had completed in October 1971. Vehicles on which "Sundance" modifications had been carried out received an additional 'Z' suffix appended to their designations, the "Sundance" engines themselves were signified with a distinctive orange/yellow-coloured upper crankcase.
; Chieftain Mk.9
:Chieftain Mk.6 after completing all phases of "Totem Pole", 1979.
; Chieftain Mk.10: Chieftain Mk.7 after completing all phases of "Totem Pole". Later upgraded with addition of Stillbrew Crew Protection Package which added additional armour to the turret front and turret ring to increase turret frontal protection against HEAT
In thermodynamics, heat is defined as the form of energy crossing the boundary of a thermodynamic system by virtue of a temperature difference across the boundary. A thermodynamic system does not ''contain'' heat. Nevertheless, the term is ...
rounds, specifically, the improved variants of the Soviet-made RPG-7, etc., and consisted of conventional steel armour mounted on rubber pads to prevent vibration, 1984–86
; Chieftain Mk.11: Chieftain Mk.8 after completing all phases of "Totem Pole". Later upgraded with Stillbrew, 1984–86
; Chieftain Mk.12: Chieftain Mk.5 after completing all phases of "Totem Pole". Later upgraded with Stillbrew, 1984–86
; Chieftain Mk.12/13: Proposed further upgrades, cancelled when the Challenger 1 was introduced.
; Chieftain 800: Re-engined Iranian FV4030/1 Chieftain Mark 5/3P fitted with the Rolls-Royce CV8 TCA engine and the fully automatic TN12 Mk. 5 transmission.
; Chieftain 900: Two Mk. 5/3 (P) were converted by Royal Ordnance Factories by fitting the Rolls-Royce Condor 900E engine and the fully automatic TN12-1000 version of the Chieftain's gearbox, hence the name of Chieftain 900. The two Chieftain 900 prototypes were built in April 1982 and were exhibited the same year at the British Army Equipment Exhibition (BAEE). They were not fitted with real Chobham armour but were mocked up with cosmetic sheet-metal cladding to simulate the Chobham armour package. The project was abandoned by 1986.
; FV4030/1 Chieftain Mk. 5/3 (P) « Persia » : Also known as "Project 4030 Phase 1" or "Improved Chieftain". The Mk. 5/3P featured the Tank Laser Sight (TLS), the Muzzle Reference System (MRS), a fully automatic controller for the TN12 gearbox, a fuel capacity increase, thickened underbelly mine armour and shock absorbers fitted to the front and rear suspension units. 185 vehicles were built between August 1976 and late 1977/early 1978.
; FV4030/2 Shir (Lion) 1: Also known as "4030 Phase 2". This tank formed Phase 2 of the Iranian contract for the supply of a new generation of MBTs (Phase 1 being for an Improved Chieftain). This project began in 1974. Shir 1 incorporated the Chieftain hull front and turret casting. The rear of the hull was reconfigured to accept a new power pack comprising Rolls-Royce CV12 (a turbocharged V12 four-stroke diesel engine), David Brown TN37 transmission and new cooling group. An improved bogie suspension (Super Horstmann), new final drives and tracks were included. The first vehicle-ran in April 1977 and no production deliveries had taken place when the project was cancelled in February 1979.
 ; Khalid: Also known as "4030 Phase 2 Jordan". The sale of 274 MBTs was negotiated with Jordan in June 1979 following the cancellation of the Iranian contract. The Khalid tank is based on the Shir 1 design with the addition of the Integrated Fire Control System (IFCS), Tank Laser Sight (TLS) and the No 84 Day/Night Sight. The first 125 were reworked Shir 1's and the remaining 149 were new production tanks. The order has been completed, the first being delivered in July 1981.
;FV4030/3 Shir 2: Also known as "'4030 Phase 3'" Iranian variant. The Shir 2 represented a completely new-MBT incorporating Chobham armour (renamed "Pageant" to avoid diplomatic incident with the US government) to the hull and turret, with the rear of the hull similar in design to the Shir 1. The fire control, gun control and automotive systems were the same as Shir 1 with the following exceptions: Automotive - the option of adopting hydrogas suspension and command & control, the new No 84 commander's (PPE) day/night sight. The project began in 1974 and the first vehicle ran in October 1978. The production order was for 1,200 MBTs and production release given for 250 before cancellation in February 1979. Not delivered, the Shir 2 tanks became FV4030/4 Challenger 1 tanks after reworking at ROF Leeds.
;
; Khalid: Also known as "4030 Phase 2 Jordan". The sale of 274 MBTs was negotiated with Jordan in June 1979 following the cancellation of the Iranian contract. The Khalid tank is based on the Shir 1 design with the addition of the Integrated Fire Control System (IFCS), Tank Laser Sight (TLS) and the No 84 Day/Night Sight. The first 125 were reworked Shir 1's and the remaining 149 were new production tanks. The order has been completed, the first being delivered in July 1981.
;FV4030/3 Shir 2: Also known as "'4030 Phase 3'" Iranian variant. The Shir 2 represented a completely new-MBT incorporating Chobham armour (renamed "Pageant" to avoid diplomatic incident with the US government) to the hull and turret, with the rear of the hull similar in design to the Shir 1. The fire control, gun control and automotive systems were the same as Shir 1 with the following exceptions: Automotive - the option of adopting hydrogas suspension and command & control, the new No 84 commander's (PPE) day/night sight. The project began in 1974 and the first vehicle ran in October 1978. The production order was for 1,200 MBTs and production release given for 250 before cancellation in February 1979. Not delivered, the Shir 2 tanks became FV4030/4 Challenger 1 tanks after reworking at ROF Leeds.
;Mobarez Tank
Mobarez (Persian: مبارز; meaning "Warrior") is a domestically upgraded version of the British Chieftain tank by Iran.
Changes
The hull of the tank has been modified at the back and sides. The fuel tank has been replaced by a new, repairabl ...
:Iranian upgraded version of Chieftain. :
;Chieftain/ T95: Development of the FV4201 Chieftain allowed for the interchangeability of guns with the U.S. T95 tank by means of exchanging turrets. The project was discontinued because of numerous problems with training crews to master two artillery systems. Equipped with a 90mm T208 (rifled) gun.
;FV4211: Test vehicle using Chieftain automotive sub systems (including the L60 engine), embodied in a new aluminium hull and turret structure incorporating Chobham Armour (CA) for the first time. The project began in October 1969. A feasibility study was completed by February 1970 which led to MVEE being asked to design and produce a prototype within a year. This timescale was achieved, the MVEE produced the first prototype in February 1971. Although the project was officially discontinued in 1972, research work within MVEE continued until 1974. A paper study on a Mk. 2 version was carried out and was considered during the FMBT (Future Main Battle Tank) studies in 1974.
 ; FV4204 ARV/ARRV: Armoured Recovery Vehicle, Armoured Recovery and Repair Vehicle.
; FV4205 AVLB Mk5: Bridge-laying vehicle
; FV4204 ARV/ARRV: Armoured Recovery Vehicle, Armoured Recovery and Repair Vehicle.
; FV4205 AVLB Mk5: Bridge-laying vehicle
 ; Chieftain AVRE (CHAVRE): Armoured Vehicle Royal Engineers, twelve early "Willich Chieftain AVRE" vehicles converted by 32 Armoured Engineer Regiment and 21 Engineer Base Workshop of the Royal Engineers, Willich, 1987, remaining 48 ex MBTs converted by Vickers Defence Ltd, 1991, to be a British Army combat engineering variant used by the Royal Engineers.
; Chieftain Fascine Layer: Four turret-less vehicles specially converted for laying
; Chieftain AVRE (CHAVRE): Armoured Vehicle Royal Engineers, twelve early "Willich Chieftain AVRE" vehicles converted by 32 Armoured Engineer Regiment and 21 Engineer Base Workshop of the Royal Engineers, Willich, 1987, remaining 48 ex MBTs converted by Vickers Defence Ltd, 1991, to be a British Army combat engineering variant used by the Royal Engineers.
; Chieftain Fascine Layer: Four turret-less vehicles specially converted for laying fascine
A fascine is a rough bundle of brushwood or other material used for strengthening an earthen structure, or making a path across uneven or wet terrain. Typical uses are protecting the banks of streams from erosion, covering marshy ground and s ...
s
; Chieftain Marksman: Self-propelled anti-aircraft gun version, equipped with the Marksman twin gun turret.
; Chieftain Mineclearer: Mine-clearing development.
; Chieftain Sabre: Twin 30 mm AA turret.
; Chieftain SID: Chieftain Signature Integration Demonstrator.
:Two vehicles modified from Chieftain Mk.12 for TRIGAT trials aimed at reducing battlefield reflectivity and emissions
; Chieftain Crazy Horse: Mobile Range Hard Target.
:Modified from Chieftain Mk.1 with gun removed and incorporating Skyleader radio control. Remotely controlled range target for use with inert rounds. Used in conjunction with modified Alvis Stormer command vehicle. One built. 1987.
; Weapon Carriers: The Chieftain chassis was adapted to mount air defence weapons ("Marksman" 2 x 35 mm cannon) and a 155 mm howitzer in a number of variants.
Operators

Current operators
* : 707 Mk-3P and Mk-5P, 187 FV4030-1, 41 ARV and 14 AVLB obtained before the 1979 revolution. Further planned deliveries of the more capable FV4030-2 (Shir 1) and FV4030-3 (Shir 2) series were cancelled at that point. 100 in service . (100 in 1990, 250 in 1995, 140 in 2000). * : 274 Khalid delivered between 1981 and 1985 + 90 MK3/5 (captured Iranian tanks) from Iraq. * : 27 delivered 1981–85.Former operators
* : Used from 1965 to 1995. * : 175 in 1976, 143 in 1990, 20 in 1995, 17 in storage in 2000. * : 50-75 tanks, captured from Iran, in service with Iraqi Army in 1990. Most upgraded to Khalid-level, with air-conditioning for the crew and reinforced armour and night vision. * : 2 delivered for the joint Anglo-Israeli developmental project. In Israeli Armored Corps service for trials 1965–69. * : One Chieftain was tested alongside a Leopard between 15 January and 22 March 1968 by the ''Detachement ter Beproeving van Voertuigen'' (“Detachment for Testing of Vehicles”) of theRoyal Netherlands Army
The Royal Netherlands Army ( nl, Koninklijke Landmacht) is the land branch of the Netherlands Armed Forces. Though the Royal Netherlands Army was raised on 9 January 1814, its origins date back to 1572, when the was raised – making the Dut ...
; the tank was allocated British registration number 03 EB 81 and Dutch number KZ-99-65. The Leopard was eventually selected largely because of the Chieftain's poor construction quality, especially the engine, which leaked so much oil that the engine compartment turned black.
See also
Tanks of comparable role, performance and era
* Leopard 1 German main battle tank * Merkava tank (Early models) Israeli main battle tank * M60 tank US main battle tank * T-55M *T-62
The T-62 is a Soviet main battle tank that was first introduced in 1961. As a further development of the T-55 series, the T-62 retained many similar design elements of its predecessor including low profile and thick turret armour. In contras ...
* T-72
The T-72 is a family of Soviet/Russian main battle tanks that entered production in 1969. The T-72 was a development of the T-64, which was troubled by high costs and its reliance on immature developmental technology. About 25,000 T-72 tanks ...
* T-64
The T-64 is a Soviet tank manufactured in Kharkiv, and designed by Kharkiv Morozov Machine Building Design Bureau. The tank was introduced in the early 1960s. It was a more advanced counterpart to the T-62: the T-64 served in tank divisions, whi ...
: Approximate Soviet equivalent main battle tank
Notes
References
;Citations ;Bibliography * *External links
FAS.org
Chieftain Tank
Military Factory article
{{Authority control Main battle tanks of the United Kingdom Cold War tanks of the United Kingdom Military vehicles introduced in the 1960s Main battle tanks of the Cold War History of the tank