Shivaji Bhonsale I (; 19 February 1630 – 3 April 1680), also referred to as Chhatrapati Shivaji Maharaj, was an Indian ruler and a member of the
Bhonsle
The Bhonsle (or Bhonsale, Bhosale, Bhosle) are a prominent group within the Maratha clan system of kunbi origin. They claimed descent from the Sisodia Rajputs but were likely Kunbi tiller-plainsmen.
History Earliest members
The earliest a ...
Maratha clan
The Maratha clan system (also referred to as Shahannava Kuli Marathas, 96 Kuli Marathas or 96K), refers to the network of 96 clans of families and essentially their surnames, within the Maratha caste of India. The Marathas primarily reside in th ...
. Shivaji carved out his own independent kingdom from the declining
Adilshahi sultanate
The Adil Shahi or Adilshahi, was a Shia,Salma Ahmed Farooqui, ''A Comprehensive History of Medieval India: From Twelfth to the Mid-Eighteenth Century'', (Dorling Kindersley Pvt Ltd., 2011), 174. and later Sunni Muslim,Muhammad Qasim Firishta's ...
of
Bijapur
Bijapur, officially known as Vijayapura, is the district headquarters of Bijapur district of the Karnataka state of India. It is also the headquarters for Bijapur Taluk. Bijapur city is well known for its historical monuments of architectural ...
which formed the genesis of the
Maratha Empire
The Maratha Empire, also referred to as the Maratha Confederacy, was an early modern Indian confederation that came to dominate much of the Indian subcontinent in the 18th century. Maratha rule formally began in 1674 with the coronation of Shi ...
. In 1674, he was formally crowned the ''
Chhatrapati
Chhatrapati is a royal title from Sanskrit language.The word ‘Chhatrapati’ is a Sanskrit language compound word (tatpurusha in Sanskrit) of ''Chatra (umbrella), chhatra'' (''parasol'' or ''umbrella'') and ''pati'' (''master/lord/ruler''). Th ...
'' of his realm at
Raigad Fort
Raigad is a hill fort situated in Mahad, Raigad district of Maharashtra, India. It is one of the strongest fortresses on the Deccan Plateau. It was previously known as Rairee or Rairy fort.
Many constructions and structures on Raigad were b ...
.
Over the course of his life, Shivaji engaged in both alliances and hostilities with the
Mughal Empire
The Mughal Empire was an early-modern empire that controlled much of South Asia between the 16th and 19th centuries. Quote: "Although the first two Timurid emperors and many of their noblemen were recent migrants to the subcontinent, the d ...
, the
Sultanate of Golkonda,
Sultanate of Bijapur
The Adil Shahi or Adilshahi, was a Shia Islam, Shia,Salma Ahmed Farooqui, ''A Comprehensive History of Medieval India: From Twelfth to the Mid-Eighteenth Century'', (Dorling Kindersley Pvt Ltd., 2011), 174. and later Sunni Muslim,Muhammad Qasim ...
and the
European colonial powers
Colonialism is a practice or policy of control by one people or power over other people or areas, often by establishing colonies and generally with the aim of economic dominance. In the process of colonisation, colonisers may impose their reli ...
. Shivaji's military forces expanded the Maratha sphere of influence, capturing and building forts, and forming a
Maratha navy
The Maratha Navy was the naval wing of the armed forces of the Maratha Empire, which existed from around mid-17th century to mid-18th century in India.
Formative years
Historian Sir Jadunath Sarkar noted:
In medieval India, the Muslim rul ...
. Shivaji established a competent and progressive civil rule with well-structured administrative organisations. He revived ancient Hindu political traditions, court conventions and promoted the usage of the
Marathi
Marathi may refer to:
*Marathi people, an Indo-Aryan ethnolinguistic group of Maharashtra, India
*Marathi language, the Indo-Aryan language spoken by the Marathi people
*Palaiosouda, also known as Marathi, a small island in Greece
See also
*
* ...
and
Sanskrit
Sanskrit (; attributively , ; nominally , , ) is a classical language belonging to the Indo-Aryan branch of the Indo-European languages. It arose in South Asia after its predecessor languages had diffused there from the northwest in the late ...
languages, replacing
Persian
Persian may refer to:
* People and things from Iran, historically called ''Persia'' in the English language
** Persians, the majority ethnic group in Iran, not to be conflated with the Iranic peoples
** Persian language, an Iranian language of the ...
in court and administration.
Shivaji's legacy was to vary by observer and time, but nearly two centuries after his death, he began to take on increased importance with the emergence of the
Indian independence movement
The Indian independence movement was a series of historic events with the ultimate aim of ending British Raj, British rule in India. It lasted from 1857 to 1947.
The first nationalistic revolutionary movement for Indian independence emerged ...
, as many Indian nationalists elevated him as a proto-nationalist and hero of the
Hindus
Hindus (; ) are people who religiously adhere to Hinduism.Jeffery D. Long (2007), A Vision for Hinduism, IB Tauris, , pages 35–37 Historically, the term has also been used as a geographical, cultural, and later religious identifier for ...
.
Early life

Shivaji was born in the hill-fort of
Shivneri
Shivneri Fort (Marathi pronunciation: �iʋneɾiː is a 17th-century military fortification located near Junnar in Pune district in Maharashtra, India. It is the birthplace of Shivaji, the emperor and founder of Maratha Empire.
History
Shivneri ...
, near the city of
Junnar
Junnar (Marathi pronunciation: ͡ʒunːəɾ is a city in the Pune district of the Indian state of Maharashtra. The city has history dating back to the first millennium. The nearby fort of Shivneri was the birthplace of Maratha king Chatrapa ...
, which is now in
Pune district
Pune district (Marathi pronunciation: Help:IPA/Marathi, uɳeː is the most populous district in the Indian state of Maharashtra. The district's population was 9,429,408 in the 2011 census, making it the fourth most populous district amongst I ...
. Scholars disagree on his date of birth. The
Government of Maharashtra
The Government of Maharashtra is the state governing authority for the state of Maharashtra, India. It is a democratically elected government with 288 MLAs elected to the Vidhan Sabha for a five-year term.
Maharashtra has a Maharashtra Legisla ...
lists 19 February as a holiday commemorating Shivaji's birth (
Shivaji Jayanti).
Shivaji was named after a local deity, the goddess Shivai. Shivaji's father
Shahaji Bhonsle was a
Maratha
The Marathi people (Marathi: मराठी लोक) or Marathis are an Indo-Aryan ethnolinguistic group who are indigenous to Maharashtra in western India. They natively speak Marathi, an Indo-Aryan language. Maharashtra was formed as a M ...
general who served the
Deccan Sultanates
The Deccan sultanates were five Islamic late-medieval Indian kingdoms—on the Deccan Plateau between the Krishna River and the Vindhya Range—that were ruled by Muslim dynasties: namely Ahmadnagar, Berar, Bidar, Bijapur, and Golconda. Th ...
.
His mother was
Jijabai
Jijabai Bhonsle (or Bhonsale, Bhosale, Bhosle) or Jadhav (12 January 1598 – 17 June 1674), referred to as Rajmata, Rastramata, Jijabai or Jijau, was the mother of Shivaji, founder of the Maratha Empire. She was a daughter of Lakhujirao Ja ...
the daughter of
Lakhuji Jadhavrao
Lakhujiraje Jadhav Rao was a grandee of Sindkhed Raja in the present-day Buldhana district of Maharashtra state during the 16th century. He was maternal Grandfather of Maratha Emperor Shivaji.
Background
Lakhuji Jadhav was a Maratha chief.
...
of
Sindhkhed
Sindkhed Raja is a town and a municipal council in Buldhana district in the Indian state of Maharashtra. It is the birthplace of Rajmata Jijabai, mother of Shivaji. Sindkhed was ruled by Koli Chieftain.
Etymology
There are many legends associa ...
, a Mughal-aligned
sardar
Sardar, also spelled as Sardaar/Sirdar ( fa, سردار, , 'commander', literally 'headmaster'), is a title of royalty and nobility that was originally used to denote princes, noblemen, chiefs, kings and other aristocrats. It has also been u ...
claiming descent from a
Yadav
Yadav refers to a grouping of traditionally non-elite, Quote: "The Yadavs were traditionally a low-to-middle-ranking cluster of pastoral-peasant castes that have become a significant political force in Uttar Pradesh (and other northern state ...
royal family of
Devagiri
Daulatabad Fort, also known as Devagiri Fort or Deogiri Fort, is a historic fortified citadel located in Daulatabad village near Aurangabad, Maharashtra, India. It was the capital of the Yadava dynasty (9th century–14th century CE), for a b ...
.
Shivaji belonged to
Maratha
The Marathi people (Marathi: मराठी लोक) or Marathis are an Indo-Aryan ethnolinguistic group who are indigenous to Maharashtra in western India. They natively speak Marathi, an Indo-Aryan language. Maharashtra was formed as a M ...
family of
Bhonsle
The Bhonsle (or Bhonsale, Bhosale, Bhosle) are a prominent group within the Maratha clan system of kunbi origin. They claimed descent from the Sisodia Rajputs but were likely Kunbi tiller-plainsmen.
History Earliest members
The earliest a ...
clan.
His paternal grandfather
Maloji
Maloji Bhosale was a Maratha sardar (general) who served the Ahmadnagar Sultanate in Malik Ambar's army. He was the father of Shahaji and the grandfather of Shivaji, the founder of the Maratha Empire.
Early life
Maloji was born in 1552 to Bab ...
(1552–1597) was an influential general of
Ahmadnagar Sultanate
The Ahmadnagar Sultanate was a late medieval Indian Muslim kingdom located in the northwestern Deccan, between the sultanates of Gujarat and Bijapur. Malik Ahmed, the Bahmani governor of Junnar after defeating the Bahmani army led by general Ja ...
, and was awarded the epithet of "Raja". He was given ''
deshmukh
Deshmukh (IAST:Dēśamukh), is a historical title conferred to the rulers of a . It is used as a surname in certain regions of India, specifically in the states of Maharashtra, Karnataka, Telangana and Andhra Pradesh whose family received it as a ...
i'' rights of Pune, Supe, Chakan and Indapur for military expenses. He was also given Fort Shivneri for his family's residence ().
At the time of Shivaji's birth, power in the Deccan was shared by three Islamic sultanates:
Bijapur
Bijapur, officially known as Vijayapura, is the district headquarters of Bijapur district of the Karnataka state of India. It is also the headquarters for Bijapur Taluk. Bijapur city is well known for its historical monuments of architectural ...
,
Ahmednagar
Ahmednagar (), is a city located in the Ahmednagar district in the state of Maharashtra, India, about 120 km northeast of Pune and 114 km from Aurangabad. Ahmednagar takes its name from Ahmad Nizam Shah I, who founded the town in 1494 ...
, and
Golkonda
Fort (Telugu: గోల్కొండ, romanized: ''Gōlkōnḍa'') is a historic fortress and ruined city located in Hyderabad, Telangana, India. It was originally called Mankal. The fort was originally built by Kakatiya ruler Pratāparud ...
. Shahaji often changed his loyalty between the
Nizamshahi
The Ahmadnagar Sultanate was a late medieval Indian Muslim kingdom located in the northwestern Deccan, between the sultanates of Gujarat and Bijapur. Malik Ahmed, the Bahmani governor of Junnar after defeating the Bahmani army led by general J ...
of Ahmadnagar, the
Adilshah
The Adil Shahi or Adilshahi, was a Shia,Salma Ahmed Farooqui, ''A Comprehensive History of Medieval India: From Twelfth to the Mid-Eighteenth Century'', (Dorling Kindersley Pvt Ltd., 2011), 174. and later Sunni Muslim,Muhammad Qasim Firishta's ...
of Bijapur and the Mughals, but always kept his ''
jagir
A jagir ( fa, , translit=Jāgir), also spelled as jageer, was a type of feudal land grant in the Indian subcontinent at the foundation of its Jagirdar (Zamindar) system. It developed during the Islamic rule era of the Indian subcontinent, start ...
'' (fiefdom) at
Pune
Pune (; ; also known as Poona, (List of renamed Indian cities and states#Maharashtra, the official name from 1818 until 1978) is one of the most important industrial and educational hubs of India, with an estimated population of 7.4 million ...
and his small army.
Background and context
In 1636, the
Adil Shahi sultanate of Bijapur invaded the kingdoms to its south. The sultanate had recently become a tributary state of the
Mughal empire
The Mughal Empire was an early-modern empire that controlled much of South Asia between the 16th and 19th centuries. Quote: "Although the first two Timurid emperors and many of their noblemen were recent migrants to the subcontinent, the d ...
. It was being helped by Shahaji, who at the time was a chieftain in the
Maratha uplands of western India. Shahaji was looking for opportunities of rewards of ''
jagir
A jagir ( fa, , translit=Jāgir), also spelled as jageer, was a type of feudal land grant in the Indian subcontinent at the foundation of its Jagirdar (Zamindar) system. It developed during the Islamic rule era of the Indian subcontinent, start ...
'' land in the conquered territories, the taxes on which he could collect as an annuity.
Shahaji was a rebel from brief Mughal service. Shahaji's campaigns against the Mughals, supported by the Bijapur government, were generally unsuccessful. He was constantly pursued by the Mughal army and Shivaji and his mother Jijabai had to move from fort to fort.
In 1636, Shahaji joined in the service of Bijapur and obtained
Poona
Pune (; ; also known as Poona, (List of renamed Indian cities and states#Maharashtra, the official name from 1818 until 1978) is one of the most important industrial and educational hubs of India, with an estimated population of 7.4 million ...
as a grant. Shivaji and Jijabai settled in Poona. Shahaji, being deployed in
Bangalore
Bangalore (), officially Bengaluru (), is the capital and largest city of the Indian state of Karnataka. It has a population of more than and a metropolitan population of around , making it the third most populous city and fifth most ...
by the Bijapuri ruler Adilshah, appointed
Dadoji Kondadeo
Dadoji Kondadeo (also spelled as Dadoji Konddev) was an administrator of the Pune jagir and the nearby Kondana fort. He was appointed by Shahaji, a noble and general of the Adilshahi sultanate of Bijapur.
Biography Early life
Kondadeo was born ...
as administrator. Kondadeo died in 1647 and Shivaji took over the administration. One of his first acts directly challenged the Bijapuri government.
Conflict with Bijapur sultanate
In 1646, 16-year-old Shivaji took the
Torna Fort
Torna Fort, also known as Prachandagad, is a large fort located in Pune district, in the Indian state of Maharashtra. It is historically significant because it was the first fort captured by Chhatrapati Shivaji in 1646, at the age of 16. The hill ...
, taking advantage of the confusion prevailing in the Bijapur court due to the ailment of
Sultan Mohammed Adil Shah,
and seized the large treasure he found there.
In the following two years, Shivaji took several important forts near Pune, including
Purandar,
Kondhana
Sinhagad is an ancient hill fortress located at around 49 km southwest of the city of Pune, India.
Previously known as ''Kondhana'', the fort had been the site of many battles, most notably the Battle of Sinhagad in 1670.
The Sinhagad ...
and
Chakan. Also, he brought areas east of Pune around
Supa,
Baramati
Baramati ( aːɾamət̪iː is a city, a tehsil and a municipal council in Pune district in the state of Maharashtra, India. The city is about 100 KM (62 miles) southeast of the city of Pune and about 250 KM from Mumbai.
Baramati is located ...
, and
Indapur
Indapur is a town and a municipal council in Pune district in the Indian state of Maharashtra. Indapur is known for Jahagir of Chhatrapati Shivaji Maharaj's father and grandfather. Chhatrapati Shivaji Maharaj's grandfather Malojiraje died in ba ...
under his direct control. He used the treasure found at Torna to build a new fort named
Rajgad
Rajgad (literal meaning ''Ruling Fort'') is a Hill region fort situated in the Pune district of Maharashtra, India. Formerly known as ''Murumdev'', the fort was the first capital of the Maratha Empire under the rule of Chhatrapati Shivaji for ...
.That fort served as the seat of his government for over a decade.
After this, Shivaji turned west to the
Konkan
The Konkan ( kok, कोंकण) or Kokan () is a stretch of land by the western coast of India, running from Damaon in the north to Karwar in the south; with the Arabian Sea to the west and the Deccan plateau in the east. The hinterland ...
and took possession of the important town of
Kalyan
Kalyan (Pronunciation: Help:IPA/Marathi, əljaːɳ is a city on the banks of Ulhas River in Thane district of Maharashtra state in Konkan division. It is governed by Kalyan-Dombivli Municipal Corporation. Kalyan is a subdivision (Taluka) ...
. Bijapur government took note of these happenings and sought to take action. On 25 July 1648, Shahaji was imprisoned by a fellow Maratha sardar called, Baji Ghorpade under the orders of Bijapur government, in a bid to contain Shivaji.
Shahaji was released in 1649 after the capture of
Jinji secured Adilshah's position in Karnataka. During the period of 1649–1655 Shivaji paused in his conquests and quietly consolidated his gains. Following his father's release, Shivaji resumed raiding, and in 1656, under controversial circumstances, killed
Chandrarao More, a fellow Maratha feudatory of Bijapur, and seized the valley of
Javali, near the present-day hill station of
Mahabaleshwar
Mahabaleshwar () is a small town and a municipal council in Satara district, Maharashtra, India. It is a place of pilgrimage for Hindus because Krishna river has its origin here. The British colonial rulers developed the town as a hill station ...
, from him. In addition to the Bhonsale and the More families, many others including
Sawant
Sawant is a surname of Maratha Caste
Notable people
People with this surname include:
*Abhijeet Sawant, singer
* Arvind Sawant, Ministry of Heavy Industries and Public Enterprises
*Ashlesha Sawant (born 24 September 1972), Indian television ...
of
Sawantwadi
Sawantwadi an aesthetic land of artists, is an integral part of the Konkan region which is in the mid-western coast of India.
The western coast of India since 1510 A.D. has assumed great importance in Indian history and history of internationa ...
, Ghorpade of
Mudhol
Mudhol is a city previously known as "'Muduvolalu"' in the Bagalkote District in the northern part of the South Indian state of Karnataka. It is about from the district headquarters of Bagalkot and from subdivision of Jamakhandi. It is famo ...
,
Nimbalkar
Nimbalkar is a Maratha clan, which derives its surname from the forest of Nimbalak in Phaltan taluka, Satara district, Maharashtra, India.
Some Nimbalkars served as head of the deshmukhs (''sardeshmukhs'' or ''sardars'') during the period of the ...
of
Phaltan
Phaltan () is a town, a tehsil, and a municipal council in the Satara district in the Indian state of Maharashtra. The town is about northeast of the city of Satara and about 110 km from Pune.
History
Phaltan was one of the non-salu ...
, Shirke, Mane and
Mohite
Mohite is a copper tin sulfide mineral with the chemical formula Cu2SnS3. It is colored greenish gray and leaves a gray streak (mineralogy), streak. It is Opacity (optics), opaque and has metallic Lustre (mineralogy), luster. Its crystal system is ...
also served Adilshahi of Bijapur, many with
Deshmukh
Deshmukh (IAST:Dēśamukh), is a historical title conferred to the rulers of a . It is used as a surname in certain regions of India, specifically in the states of Maharashtra, Karnataka, Telangana and Andhra Pradesh whose family received it as a ...
i rights. Shivaji adopted different strategies to subdue these powerful families such as forming marital alliances, dealing directly with village Patils to bypass the Deshmukhs, or subduing them by force.
Shahaji in his later years had an ambivalent attitude to his son, and disavowed his rebellious activities. He told the Bijapuris to do whatever they wanted with Shivaji. Shahaji died around 1664–1665 in a hunting accident.
Combat with Afzal Khan


The Bijapur sultanate was displeased at their losses to Shivaji's forces, which their vassal Shahaji disavowed. After a peace treaty with the Mughals, and the general acceptance of the young
Ali Adil Shah II
On the death of Mohammed Adil Shah, Sultan of Bijapur on 4 November 1656, Ali Adil Shah II, a youth of eighteen, succeeded to the throne of Bijapur through the efforts of the Prime Minister Khan Muhammad and the Queen, Badi Sahiba, sister o ...
as the sultan, the Bijapur government became more stable, and turned its attention towards Shivaji. In 1657 the sultan, or more likely his mother and regent, sent
Afzal Khan, a veteran general, to arrest Shivaji. Before engaging him, the Bijapuri forces desecrated the
Tulja Bhavani Temple
Tulja Bhavani Temple (Marathi: श्री क्षेत्र तुळजा भवानी देवस्थान) is a Hindu temple dedicated to goddess Bhavani (goddess Parvati), also referred to as Durga and Sati. It is located in ...
, holy to Shivaji's family, and the
Vithoba temple
The Vithoba Temple, officially known as Shri Vitthal-Rukmini Mandir ( mr, श्री विठ्ठल-रूक्मिणी मंदिर kn, ಶ್ರೀ ವಿಟ್ಟಲ-ರುಕ್ಮಿಣಿ ಗುಡಿ ), is a Hindu temple in ...
at
Pandharpur
Pandharpur (Pronunciation: əɳɖʱəɾpuːɾ is a well known pilgrimage town, on the banks of Candrabhagā River, near Solapur city in Solapur District, Maharashtra, India. Its administrative area is one of eleven tehsils in the District, ...
, a major pilgrimage site for the Hindus.
Pursued by Bijapuri forces, Shivaji retreated to
Pratapgad
Pratapgad is a mountain fort located in Satara district, in the Western Indian state of Maharashtra.The fort is situated 24 kilometres from the Mahabaleshwar hill station. The fort is now a popular tourist destination.
The fort's historical s ...
fort, where many of his colleagues pressed him to surrender.
The two forces found themselves at a stalemate, with Shivaji unable to break the siege, while Afzal Khan, having a powerful cavalry but lacking siege equipment, was unable to take the fort. After two months, Afzal Khan sent an envoy to Shivaji suggesting the two leaders meet in private outside the fort for negotiations.
The two met in a hut at the foothills of Pratapgad fort on 10 November 1659. The arrangements had dictated that each come armed only with a sword, and attended by one follower. Shivaji, suspecting Afzal Khan would arrest or attack him, wore armour beneath his clothes, concealed a ''
bagh nakh
The bagh nakh, vagh nakh, or vagh nakhya ( mr, वाघनख / वाघनख्या, bn, বাঘনখ, hi, बाघ नख, ur, باگھ نکھ, lit. tiger claw) is a "fist-load, claw-like" dagger, originating from the Indian subcontin ...
'' (metal "tiger claw") on his left arm, and had a dagger in his right hand. The precise transpirings are not recoverable to historical certainty and remains enmeshed with legends in Maratha sources; however, they agree upon the fact that the protagonists landed themselves in a physical struggle which would prove fatal for Khan. Khan's dagger failed to pierce Shivaji's armour, but Shivaji had him disemboweled; he then fired a cannon to signal his hidden troops to attack the Bijapuri army.
In the ensuing
Battle of Pratapgarh
The Battle of Pratapgad was a battle fought on 10 November 1659, at the fort of Pratapgad, near the town of Satara, Maharashtra, India, between the forces of the Marathas under Chhatrapati Shivaji and the Adilshahi troops under the Adilshahi ...
fought on 10 November 1659, Shivaji's forces decisively defeated the
Bijapur Sultanate
The Adil Shahi or Adilshahi, was a Shia,Salma Ahmed Farooqui, ''A Comprehensive History of Medieval India: From Twelfth to the Mid-Eighteenth Century'', (Dorling Kindersley Pvt Ltd., 2011), 174. and later Sunni Muslim,Muhammad Qasim Firishta's T ...
's forces. More than 3,000 soldiers of the Bijapur army were killed and one sardar of high rank, two sons of Afzal Khan and two Maratha chiefs were taken prisoner. After the victory, a grand review was held by Shivaji below Pratapgarh. The captured enemy, both officers and men, were set free and sent back to their homes with money, food and other gifts. Marathas were rewarded accordingly.
Siege of Panhala
Having defeated the Bijapuri forces sent against him, Shivaji's army marched towards the
Konkan
The Konkan ( kok, कोंकण) or Kokan () is a stretch of land by the western coast of India, running from Damaon in the north to Karwar in the south; with the Arabian Sea to the west and the Deccan plateau in the east. The hinterland ...
and
Kolhapur
Kolhapur () is a city on the banks of the Panchganga River in the southern part of the Indian state of Maharashtra. It is the administrative headquarter of the Kolhapur district. In, around 2 C.E. Kolapur's name was 'Kuntal'.
Kolhapur is kn ...
, seizing
Panhala fort, and defeating Bijapuri forces sent against them under
Rustam Zaman and Fazl Khan in 1659. In 1660, Adilshah sent his general Siddi Jauhar to attack Shivaji's southern border, in alliance with the Mughals who planned to attack from the north. At that time, Shivaji was encamped at Panhala fort with his forces. Siddi Jauhar's army besieged
Panhala
Panhala (Pronunciation: ənʱaːɭa is a city and a Hill station Municipal Council (3177 feet above sea level) 18 km northwest of Kolhapur, in Kolhapur district in the Indian state of Maharashtra. Panhala is the smallest city in Maharash ...
in mid-1660, cutting off supply routes to the fort. During the bombardment of Panhala, Siddi Jauhar purchased grenades from the English at
Rajapur to increase his efficacy, and also hired some English artillerymen to assist in his bombardment of the fort, conspicuously flying a flag used by the English. This perceived betrayal angered Shivaji, who in December would retaliate by plundering the English factory at Rajapur and capturing four of the factors, imprisoning them until mid-1663.
After months of siege, Shivaji negotiated with Siddi Jauhar and handed over the fort on 22 September 1660, withdrawing to Vishalgad;
Shivaji retook Panhala in 1673.
Battle of Pavan Khind
Shivaji escaped from Panhala by cover of night, and as he was pursued by the enemy cavalry, his Maratha sardar
Baji Prabhu Deshpande
Baji Prabhu Deshpande ( 1615–1660) was a commander of Chatrapati Shivaji Maharaj, the founder of the Maratha empire. Baji Prabhu is linked with an important rear guard battle enabling Chatrapati Shivaji Maharaj's escape from Panhala fort; he w ...
of Bandal
Deshmukh
Deshmukh (IAST:Dēśamukh), is a historical title conferred to the rulers of a . It is used as a surname in certain regions of India, specifically in the states of Maharashtra, Karnataka, Telangana and Andhra Pradesh whose family received it as a ...
, along with 300 soldiers, volunteered to fight to the death to hold back the enemy at Ghod Khind ("horse ravine") to give Shivaji and the rest of the army a chance to reach the safety of the
Vishalgad
Vishalgad (also called Vishalgarh, Khelna or Khilna) was a jagir during the Maratha Empire and then later part of the Deccan States Agency of the British Raj. It was governed by Deshastha Brahmins, who were feudatories of Kolhapur State.
Fort
...
fort.
In the ensuing
Battle of Pavan Khind
Battle of Pävankhind was a rearguard last stand that took place on 13 July 1660, at a mountain pass in the vicinity of fort Vishalgad, near the city of Kolhapur with the Maratha warrior Baji Prabhu Deshpande and Sambhu Singh Jadhav against Si ...
, the smaller Maratha force held back the larger enemy to buy time for Shivaji to escape. Baji Prabhu Deshpande was wounded but continued to fight until he heard the sound of cannon fire from Vishalgad,
signalling Shivaji had safely reached the fort, on the evening of 13 July 1660.
''Ghod Khind'' (''khind'' meaning "a narrow mountain pass") was later renamed ''Paavan Khind'' ("sacred pass") in honour of Bajiprabhu Deshpande, Shibosingh Jadhav, Fuloji, and all other soldiers who fought in there.
Conflict with the Mughals
Until 1657, Shivaji maintained peaceful relations with the Mughal Empire. Shivaji offered his assistance to
Aurangzeb
Muhi al-Din Muhammad (; – 3 March 1707), commonly known as ( fa, , lit=Ornament of the Throne) and by his regnal title Alamgir ( fa, , translit=ʿĀlamgīr, lit=Conqueror of the World), was the sixth emperor of the Mughal Empire, ruling ...
who then, was the Mughal
viceroy
A viceroy () is an official who reigns over a polity in the name of and as the representative of the monarch of the territory. The term derives from the Latin prefix ''vice-'', meaning "in the place of" and the French word ''roy'', meaning "k ...
of the Deccan and son of the Mughal emperor, in conquering Bijapur in return for formal recognition of his right to the Bijapuri forts and villages under his possession. Dissatisfied with the Mughal response, and receiving a better offer from Bijapur, he launched a raid into the Mughal Deccan. Shivaji's confrontations with the Mughals began in March 1657, when two of Shivaji's officers raided the Mughal territory near
Ahmednagar
Ahmednagar (), is a city located in the Ahmednagar district in the state of Maharashtra, India, about 120 km northeast of Pune and 114 km from Aurangabad. Ahmednagar takes its name from Ahmad Nizam Shah I, who founded the town in 1494 ...
. This was followed by raids in
Junnar
Junnar (Marathi pronunciation: ͡ʒunːəɾ is a city in the Pune district of the Indian state of Maharashtra. The city has history dating back to the first millennium. The nearby fort of Shivneri was the birthplace of Maratha king Chatrapa ...
, with Shivaji carrying off 300,000 ''
hun
The Huns were a nomadic people who lived in Central Asia, the Caucasus, and Eastern Europe between the 4th and 6th century AD. According to European tradition, they were first reported living east of the Volga River, in an area that was part ...
'' in cash and 200 horses. Aurangzeb responded to the raids by sending Nasiri Khan, who defeated the forces of Shivaji at Ahmednagar. However, Aurangzeb's countermeasures against Shivaji were interrupted by the rainy season and his battle of succession with his brothers for the Mughal throne following the illness of the emperor
Shah Jahan
Shihab-ud-Din Muhammad Khurram (5 January 1592 – 22 January 1666), better known by his regnal name Shah Jahan I (; ), was the fifth emperor of the Mughal Empire, reigning from January 1628 until July 1658. Under his emperorship, the Mugha ...
.
Attacks on Shaista Khan and Surat

Upon the request of Badi Begum of Bijapur, Aurangzeb, now the Mughal emperor, sent his maternal uncle
Shaista Khan
Mirza Abu Talib (22 November 1600 – 1694), better known as Shaista Khan, was a general and the subahdar of Mughal Bengal. A maternal uncle to the emperor Aurangzeb, he acted as a key figure during his reign. Shaista Khan initially governed ...
, with an army numbering over 150,000 along with a powerful artillery division in January 1660 to attack Shivaji in conjunction with Bijapur's army led by Siddi Jauhar. Shaista Khan, with his better equipped and well provisioned army of 80,000 seized Pune. He also took the nearby fort of
Chakan, besieging it for a month and a half before breaching the walls. Shaista Khan pressed his advantage of having a larger, better provisioned and heavily armed Mughal army and made inroads into some of the Maratha territory, seizing the city of Pune and establishing his residence at Shivaji's palace of
Lal Mahal
The Lal Mahal (Red Palace) of Pune is one of the most famous monuments located in Pune, India, where Chhatrapati Shivaji Maharaj, founder of the Maratha Empire spent his childhood.
History
In the year 1630 AD, Shivaji Maharaj's Father Shahaji R ...
.
On the night of 5 April 1663, Shivaji led a daring night attack on Shaista Khan's camp. He, along with his 400 men, attacked Shaista Khan's mansion, broke into Khan's bedroom and wounded him. Khan lost three fingers. In the scuffle, Shaista Khan's son, several of his wives, servants and soldiers were killed. The Khan took refuge with the Mughal forces outside of Pune, and Aurangzeb punished him for this embarrassment with a transfer to
Bengal
Bengal ( ; bn, বাংলা/বঙ্গ, translit=Bānglā/Bôngô, ) is a geopolitical, cultural and historical region in South Asia, specifically in the eastern part of the Indian subcontinent at the apex of the Bay of Bengal, predom ...
.
In retaliation for Shaista Khan's attacks, and to replenish his now-depleted treasury, in 1664 Shivaji
sacked the port city of Surat, a wealthy Mughal trading centre. On 13
February 1665, he also conducted a
naval raid on the
Portuguese
Portuguese may refer to:
* anything of, from, or related to the country and nation of Portugal
** Portuguese cuisine, traditional foods
** Portuguese language, a Romance language
*** Portuguese dialects, variants of the Portuguese language
** Portu ...
held
Basrur
Basrur / Basroor is a village in Kundapura ''taluk'' in Udupi district of Karnataka. Historically Basrur was also called Barcelor, Barcelore, Barcalor, Basnur, Bares, Abu-Sarur and Barsellor.
History
Basrur, once called Vasupura, is a historic ...
in present day Karnataka, and gained a large booty.
Treaty of Purandar

The attacks on Shaista Khan and Surat enraged Aurangzeb. In response, he sent this
Rajput
Rajput (from Sanskrit ''raja-putra'' 'son of a king') is a large multi-component cluster of castes, kin bodies, and local groups, sharing social status and ideology of genealogical descent originating from the Indian subcontinent. The term Ra ...
general, Mirza Raja
Jai Singh I
Jai Singh I (15 July 1611 – 28 August 1667) was a senior general ("Mirza Raja") of the Mughal Empire and the Raja of the Kingdom of Amber (later called Jaipur). His predecessor was his grand uncle, Raja Bhau Singh.
Accession and early ca ...
with an army numbering around 15,000 to defeat Shivaji.
Throughout 1665, Jai Singh's forces pressed Shivaji, with their cavalry razing the countryside, and their siege forces investing Shivaji's forts. The Mughal commander succeeded in luring away several of Shivaji's key commanders, and many of his cavalrymen, into Mughal service. By mid-1665, with the fortress at Purandar besieged and near capture, Shivaji was forced to come to terms with Jai Singh.
In the
Treaty of Purandar, signed between Shivaji and Jai Singh on 11 June 1665, Shivaji agreed to give up 23 of his forts, keeping 12 for himself, and pay compensation of 400,000 gold
hun
The Huns were a nomadic people who lived in Central Asia, the Caucasus, and Eastern Europe between the 4th and 6th century AD. According to European tradition, they were first reported living east of the Volga River, in an area that was part ...
to the Mughals. Shivaji agreed to become a vassal of the Mughal empire, and to send his son Sambhaji, along with 5,000 horsemen, to fight for the Mughals in the Deccan as a ''
mansabdar
The Mansabdar was a military unit within the administrative system of the Mughal Empire introduced by Akbar. The word ''mansab'' is of Arabic origin meaning rank or position. The system determined the rank and status of a government official an ...
''.
Arrest in Agra and escape
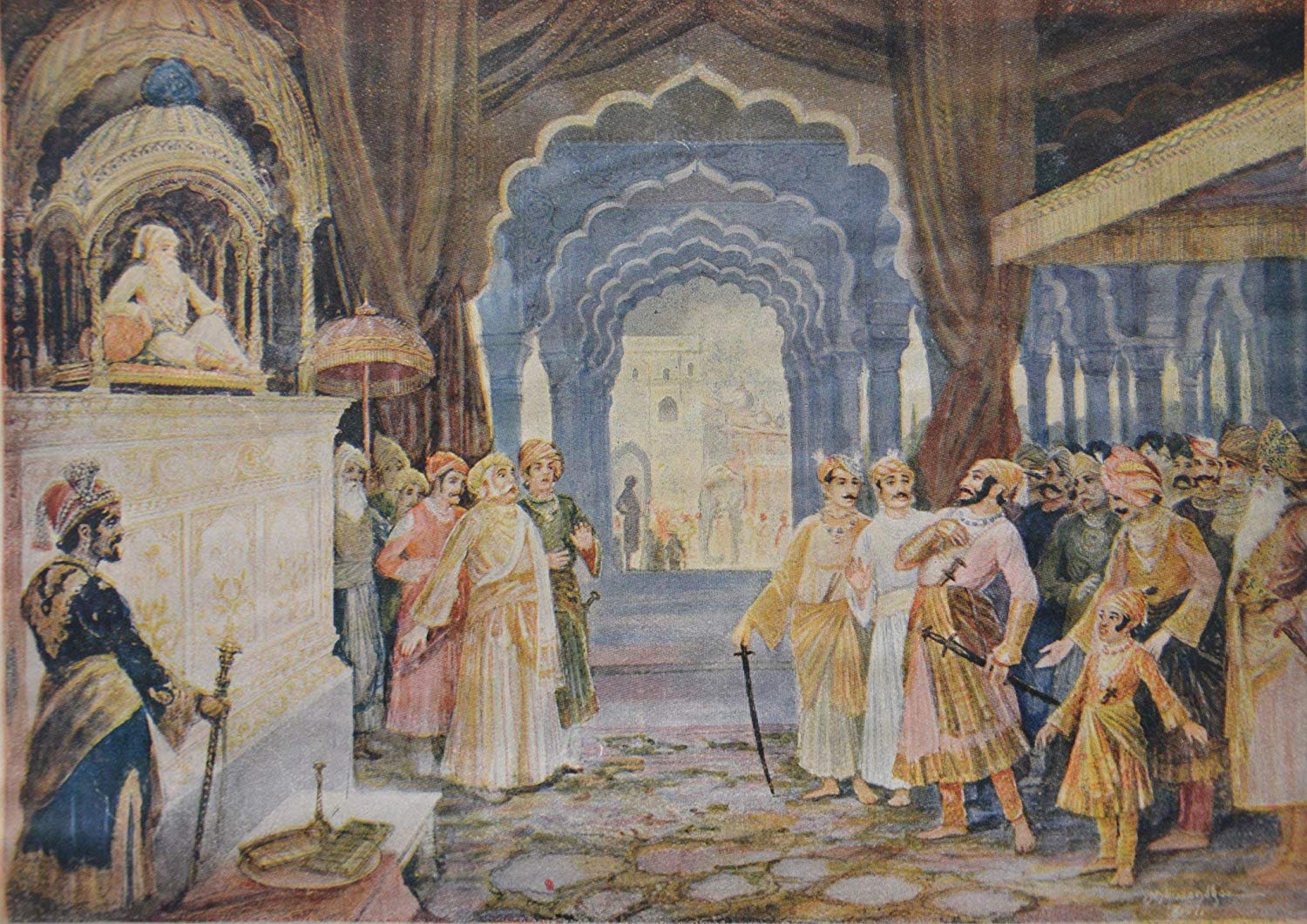
In 1666, Aurangzeb summoned Shivaji to
Agra
Agra (, ) is a city on the banks of the Yamuna river in the Indian state of Uttar Pradesh, about south-east of the national capital New Delhi and 330 km west of the state capital Lucknow. With a population of roughly 1.6 million, Agra is ...
(though some sources instead state Delhi), along with his nine-year-old son Sambhaji. Aurangzeb's planned to send Shivaji to
Kandahar
Kandahar (; Kandahār, , Qandahār) is a List of cities in Afghanistan, city in Afghanistan, located in the south of the country on the Arghandab River, at an elevation of . It is Afghanistan's second largest city after Kabul, with a population ...
, now in Afghanistan, to consolidate the Mughal empire's northwestern frontier. However, in the court, on 12 May 1666, Shivaji was made to stand alongside relatively low-ranking nobles, men he had already defeated in battle. Shivaji took offence and stormed out of court, and was promptly placed under house arrest. Ram Singh, son of Jai Singh, guaranteed custody of Shivaji and his son.
Shivaji's position under house arrest was perilous, as Aurangzeb's court debated whether to kill him or continue to employ him. Jai Singh, having assured Shivaji of his personal safety, tried to influence Aurangzeb's decision.
Meanwhile, Shivaji hatched a plan to free himself. He sent most of his men back home and asked Ram Singh to withdraw his guarantees to the emperor for the safe custody of himself and his son and surrendered himself to Mughal forces.
Shivaji then pretended to be ill and began sending out large baskets packed with sweets to be given to the Brahmins and poor as penance. On 17 August 1666, by putting himself in one of the large baskets and his son Sambhaji in another, Shivaji escaped and left Agra.
Peace with the Mughals
After Shivaji's escape, hostilities with the Mughals ebbed, with Mughal sardar Jaswant Singh acting as an intermediary between Shivaji and Aurangzeb for new peace proposals. During the period between 1666 and 1668, Aurangzeb conferred the title of raja on Shivaji. Sambhaji was also restored as a
Mughal mansabdar with 5,000 horses. Shivaji at that time sent Sambhaji with general
Prataprao Gujar
Prataprao Gurjar (–24 February 1674) was the Senapati of Chatrapati Shivaji Maharaj's army. He was an aristocratic general who enjoyed the trust of the king and the loyalty of his troops. He defeated a large Mughal Army at the Battle of Sal ...
to serve with the Mughal viceroy in Aurangabad,
Prince Mu'azzam. Sambhaji was also granted territory in
Berar Berar may refer to:
*Vidarbha, the eastern region of Maharashtra Province, India, historically known as Berar
*Berar Sultanate (1490–1596), one of the Deccan sultanates
*Berar Subah (1596–1724), a Subah of the Mughal Empire
*Berar Province (1724 ...
for revenue collection.
Aurangzeb
Muhi al-Din Muhammad (; – 3 March 1707), commonly known as ( fa, , lit=Ornament of the Throne) and by his regnal title Alamgir ( fa, , translit=ʿĀlamgīr, lit=Conqueror of the World), was the sixth emperor of the Mughal Empire, ruling ...
also permitted Shivaji to attack the decaying
Adil Shahi
The Adil Shahi or Adilshahi, was a Shia,Salma Ahmed Farooqui, ''A Comprehensive History of Medieval India: From Twelfth to the Mid-Eighteenth Century'', (Dorling Kindersley Pvt Ltd., 2011), 174. and later Sunni Muslim,Muhammad Qasim Firishta's T ...
; the weakened Sultan
Ali Adil Shah II
On the death of Mohammed Adil Shah, Sultan of Bijapur on 4 November 1656, Ali Adil Shah II, a youth of eighteen, succeeded to the throne of Bijapur through the efforts of the Prime Minister Khan Muhammad and the Queen, Badi Sahiba, sister o ...
sued for peace and granted the rights of ''
sardeshmukhi
Chauth (from Sanskrit, meaning ''one fourth'') was a regular tax or tribute imposed from the early 18th century by the Maratha Empire in the Indian subcontinent. It was an annual tax nominally levied at 25% on revenue or produce, hence the name, on ...
'' and ''
chauth
Chauth (from Sanskrit, meaning ''one fourth'') was a regular tax or tribute imposed from the early 18th century by the Maratha Empire in the Indian subcontinent. It was an annual tax nominally levied at 25% on revenue or produce, hence the name, on ...
ai'' to Shivaji.
Reconquest
The peace between Shivaji and the Mughals lasted until 1670. At that time Aurangzeb became suspicious of the close ties between Shivaji and Mu'azzam, who he thought might usurp his throne, and may even have been receiving bribes from Shivaji.
Also at that time, Aurangzeb, occupied in fighting the Afghans, greatly reduced his army in the Deccan; many of the disbanded soldiers quickly joined Maratha service. The Mughals also took away the jagir of Berar from Shivaji to recover the money lent to him a few years earlier. In response, Shivaji launched an offensive against the Mughals and recovered a major portion of the territories surrendered to them in a span of four months.
Shivaji sacked Surat for second time in 1670; the English and Dutch factories were able to repel his attack, but he managed to sack the city itself, including plundering the goods of a Muslim prince from
Mawara-un-Nahr
Transoxiana or Transoxania (Land beyond the Oxus) is the Latin name for a region and civilization located in lower Central Asia roughly corresponding to modern-day eastern Uzbekistan, western Tajikistan, parts of southern Kazakhstan, parts of Tu ...
who was returning from
Mecca
Mecca (; officially Makkah al-Mukarramah, commonly shortened to Makkah ()) is a city and administrative center of the Mecca Province of Saudi Arabia, and the Holiest sites in Islam, holiest city in Islam. It is inland from Jeddah on the Red ...
. Angered by the renewed attacks, the Mughals resumed hostilities with the Marathas, sending a force under Daud Khan to intercept Shivaji on his return home from Surat, but were defeated in the Battle of Vani-Dindori near present-day
Nashik
Nashik (, Marathi: aːʃik, also called as Nasik ) is a city in the northern region of the Indian state of Maharashtra. Situated on the banks of river Godavari, Nashik is the third largest city in Maharashtra, after Mumbai and Pune. Nashik ...
.
In October 1670, Shivaji sent his forces to harass the English at Bombay; as they had refused to sell him war materiel, his forces blocked English woodcutting parties from leaving Bombay. In September 1671, Shivaji sent an ambassador to Bombay, again seeking materiel, this time for the fight against Danda-Rajpuri. The English had misgivings of the advantages Shivaji would gain from this conquest, but also did not want to lose any chance of receiving compensation for his looting their factories at Rajapur. The English sent Lieutenant Stephen Ustick to treat with Shivaji, but negotiations failed over the issue of the Rajapur indemnity. Numerous exchanges of envoys followed over the coming years, with some agreement as to the arms issues in 1674, but Shivaji was never to pay the Rajapur indemnity before his death, and the factory there dissolved at the end of 1682.
Battles of Umrani and Nesari
In 1674,
Prataprao Gujar
Prataprao Gurjar (–24 February 1674) was the Senapati of Chatrapati Shivaji Maharaj's army. He was an aristocratic general who enjoyed the trust of the king and the loyalty of his troops. He defeated a large Mughal Army at the Battle of Sal ...
, the commander-in-chief of the Maratha forces, was sent to push back the invading force led by the Bijapuri general, Bahlol Khan. Prataprao's forces defeated and captured the opposing general in the battle, after cutting-off their water supply by encircling a strategic lake, which prompted Bahlol Khan to sue for peace. In spite of Shivaji's specific warnings against doing so, Prataprao released Bahlol Khan, who started preparing for a fresh invasion.
Shivaji sent a displeased letter to Prataprao, refusing him audience until Bahlol Khan was re-captured. Upset by his commander's rebuke, Prataprao found Bahlol Khan and charged his position with only six other horsemen, leaving his main force behind. Prataprao was killed in combat; Shivaji was deeply grieved on hearing of Prataprao's death, and arranged for the marriage of his second son,
Rajaram, to Prataprao's daughter. Prataprao was succeeded by
Hambirrao Mohite
Hambirrao Mohite was the chief military commander of Chattrapati Shivaji's army. An able military general, he executed several campaigns for Chattrapati Shivaji Maharaj and later served under Chattrapati Sambhaji Maharaj.
Early life
Hambirra ...
, as the new ''sarnaubat'' (commander-in-chief of the Maratha forces).
Raigad Fort
Raigad is a hill fort situated in Mahad, Raigad district of Maharashtra, India. It is one of the strongest fortresses on the Deccan Plateau. It was previously known as Rairee or Rairy fort.
Many constructions and structures on Raigad were b ...
was newly built by
Hiroji Indulkar
Hiroji Indulkar was a great architect of 17th century during the reign of Maratha King Chhatrapati Shivaji Maharaj. He is credited with building Raigad, the second capital of the Maratha Empire and the sea fort Sindhudurg. He was also entrusted i ...
as a capital of nascent Maratha kingdom.
Coronation
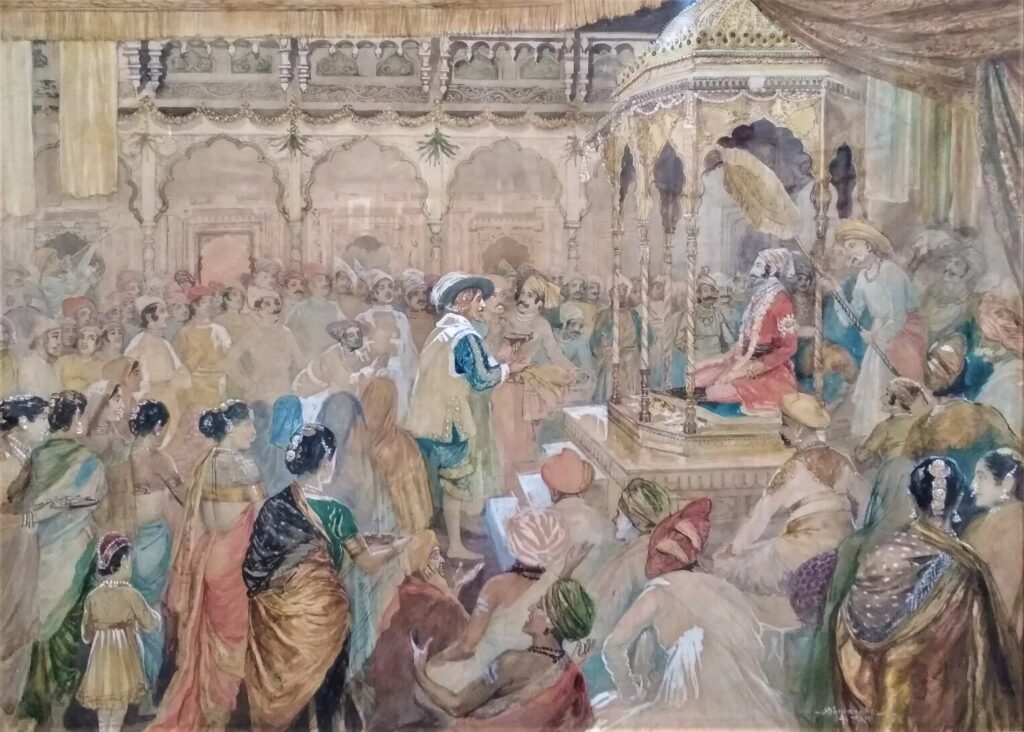

Shivaji had acquired extensive lands and wealth through his campaigns, but lacking a formal title, he was still technically a Mughal
zamindar
A zamindar ( Hindustani: Devanagari: , ; Persian: , ) in the Indian subcontinent was an autonomous or semiautonomous ruler of a province. The term itself came into use during the reign of Mughals and later the British had begun using it as a ...
or the son of a Bijapuri
jagirdar, with no legal basis to rule his de facto domain. A kingly title could address this and also prevent any challenges by other Maratha leaders, to whom he was technically equal. it would also provide the
Hindu Marathas with a fellow Hindu sovereign in a region otherwise ruled by Muslims.
The preparation for the proposed coronation began in 1673. However, some controversial problems delayed the coronation by almost a year. Controversy erupted amongst the Brahmins of Shivaji's court: they refused to crown Shivaji as a king because that status was reserved for those of the
kshatriya
Kshatriya ( hi, क्षत्रिय) (from Sanskrit ''kṣatra'', "rule, authority") is one of the four varna (social orders) of Hindu society, associated with warrior aristocracy. The Sanskrit term ''kṣatriyaḥ'' is used in the con ...
(warrior)
varna
Varna may refer to:
Places Europe
*Varna, Bulgaria, a city in Bulgaria
**Varna Province
**Varna Municipality
** Gulf of Varna
**Lake Varna
**Varna Necropolis
*Vahrn, or Varna, a municipality in Italy
*Varniai, a city in Lithuania
* Varna (Šaba ...
in Hindu society.
Shivaji was descended from a line of headmen of farming villages, and the Brahmins accordingly categorised him as being of the
shudra
Shudra or ''Shoodra'' (Sanskrit: ') is one of the four '' varnas'' of the Hindu caste system and social order in ancient India. Various sources translate it into English as a caste, or alternatively as a social class. Theoretically, class ser ...
(cultivator) varna.
They noted that Shivaji had never had a
sacred thread
''Upanayana'' ( sa, उपनयनम्, lit=initiation, translit=Upanāyanam) is a Hindus, Hindu educational sacrament, one of the traditional Samskara (rite of passage), saṃskāras or rites of passage that marked the acceptance of a student ...
ceremony, and did not wear the thread, which a kshatriya would. Shivaji summoned
Gaga Bhatt
Vishveshvara Bhatta (), popularly known as Gaga Bhatt (from ') was a 17th-century Brahmin scholar from Varanasi, best known for presiding over the coronation of the Maratha king, Chatrapati Shivaji Maharaj.
Life and career
Early life and ...
, a
pandit
A Pandit ( sa, पण्डित, paṇḍit; hi, पंडित; also spelled Pundit, pronounced ; abbreviated Pt.) is a man with specialised knowledge or a teacher of any field of knowledge whether it is shashtra (Holy Books) or shastra (Wea ...
of Varanasi, who stated that he had found a genealogy proving that Shivaji was descended from the
Sisodia
The Sisodia is an Indian Rajput dynasty belonging to the clan that ruled over the kingdom of Mewar in Rajasthan. The name of the clan is also transliterated as ''Sesodia'', ''Shishodia'', ''Sishodia'', ''Shishodya'', ''Sisodya'', ''Sisodiya'',
...
s, and thus indeed a kshatriya, albeit one in need of the ceremonies befitting his rank. To enforce this status, Shivaji was given a sacred thread ceremony, and remarried his spouses under the Vedic rites expected of a kshatriya.
However, following historical evidence, Shivaji's claim to Rajput, and specifically Sisodia ancestry may be interpreted as being anything from tenuous at best, to inventive in a more extreme reading.
On 28 May, Shivaji performed penance for not observing Kshatriya rites by his ancestors' and himself for so long. Then he was invested by Gaga Bhatt with the sacred thread. On insistence of other Brahmins, Gaga Bhatt dropped the Vedic chant and initiated Shivaji in a modified form of the life of the twice-born, instead of putting him on a par with the Brahmins. Next day, Shivaji made atonement for the sins, deliberate or accidental, committed in his own lifetime. He was weighed separately against seven metals including gold, silver and several other articles like fine linen, camphor, salt, sugar etc. All these metals and articles along with a lakh of hun were distributed among the Brahmins. But even this failed to satisfy the greed of the Brahmins. Two of the learned Brahmins pointed out that Shivaji, while conducting his raids, had burnt cities involving the death of Brahmins, cows, women and children and he could be cleansed of this sin for a price of Rs. 8,000, and Shivaji paid this amount. Total expenditure made for feeding the assemblage, general alms giving, throne and ornaments approached 1.5 million Rupees.
Shivaji was crowned king of the
Maratha Empire
The Maratha Empire, also referred to as the Maratha Confederacy, was an early modern Indian confederation that came to dominate much of the Indian subcontinent in the 18th century. Maratha rule formally began in 1674 with the coronation of Shi ...
(''Hindawi Swaraj'') in a lavish ceremony on 6 June 1674 at Raigad fort.
In the
Hindu calendar
The Hindu calendar, Panchanga () or Panjika is one of various lunisolar calendars that are traditionally used in the Indian subcontinent and Southeast Asia, with further regional variations for social and Hindu religious purposes. They adopt a s ...
it was on the 13th day (''trayodashi'') of the first fortnight of the month of ''
Jyeshtha
Jyeshtha or Jyēṣṭha ( sa, ज्येष्ठ; ne, जेठ ''jēṭ''; as, জেঠ ''zeth''; or, ଜ୍ୟେଷ୍ଠ ''Jyeṣṭha'') is a month of the Hindu calendar. In India's national civil calendar, Jyestha is the third mon ...
'' in the year 1596.
Gaga Bhatt officiated, pouring water from a gold vessel filled with the waters of the seven sacred rivers
Yamuna
The Yamuna (Hindustani language, Hindustani: ), also spelt Jumna, is the second-largest tributary river of the Ganges by discharge and the longest tributary in List of major rivers of India, India. Originating from the Yamunotri Glacier at a ...
,
Indus
The Indus ( ) is a transboundary river of Asia and a trans-Himalayan river of South and Central Asia. The river rises in mountain springs northeast of Mount Kailash in Western Tibet, flows northwest through the disputed region of Kashmir, ...
,
Ganges
The Ganges ( ) (in India: Ganga ( ); in Bangladesh: Padma ( )). "The Ganges Basin, known in India as the Ganga and in Bangladesh as the Padma, is an international river to which India, Bangladesh, Nepal and China are the riparian states." is ...
,
Godavari
The Godavari ( IAST: ''Godāvarī'' �od̪aːʋəɾiː is India's second longest river after the Ganga river and drains into the third largest basin in India, covering about 10% of India's total geographical area. Its source is in Trimbakesh ...
,
Narmada,
Krishna
Krishna (; sa, कृष्ण ) is a major deity in Hinduism. He is worshipped as the eighth avatar of Vishnu and also as the Supreme god in his own right. He is the god of protection, compassion, tenderness, and love; and is one ...
and
Kaveri
The Kaveri (also known as Cauvery, the anglicized name) is one of the major Indian rivers flowing through the states of Karnataka and Tamil Nadu. The Kaveri river rises at Talakaveri in the Brahmagiri range in the Western Ghats, Kodagu dis ...
over Shivaji's head, and chanted the Vedic coronation mantras. After the ablution, Shivaji bowed before Jijabai and touched her feet. Nearly fifty thousand people gathered at Raigad for the ceremonies. Shivaji was entitled ''Shakakarta'' ("founder of an era") and ''
Chhatrapati
Chhatrapati is a royal title from Sanskrit language.The word ‘Chhatrapati’ is a Sanskrit language compound word (tatpurusha in Sanskrit) of ''Chatra (umbrella), chhatra'' (''parasol'' or ''umbrella'') and ''pati'' (''master/lord/ruler''). Th ...
'' ("
sovereign
''Sovereign'' is a title which can be applied to the highest leader in various categories. The word is borrowed from Old French , which is ultimately derived from the Latin , meaning 'above'.
The roles of a sovereign vary from monarch, ruler or ...
"). He also took the title of ''
Haindava Dharmodhhaarak'' (protector of the Hindu faith)
and Kshatriya Kulavantas.
''
Kshatriya
Kshatriya ( hi, क्षत्रिय) (from Sanskrit ''kṣatra'', "rule, authority") is one of the four varna (social orders) of Hindu society, associated with warrior aristocracy. The Sanskrit term ''kṣatriyaḥ'' is used in the con ...
'' is one of the four
varnas of
Hinduism
Hinduism () is an Indian religion or '' dharma'', a religious and universal order or way of life by which followers abide. As a religion, it is the world's third-largest, with over 1.2–1.35 billion followers, or 15–16% of the global p ...
and means the 'head of the , or race'.
Shivaji's mother Jijabai died on 18 June 1674. The Marathas summoned Nischal Puri Goswami, a tantrik priest, who declared that the original coronation had been held under inauspicious stars, and a second coronation was needed. This second coronation on 24 September 1674 had a dual-use, mollifying those who still believed that Shivaji was not qualified for the Vedic rites of his first coronation, by performing a less-contestable additional ceremony.
Conquest of southern India
Beginning in 1674, the Marathas undertook an aggressive campaign, raiding
Khandesh
Khandesh is a geographic region in Central India, which includes parts of the northwestern portion of Maharashtra as well as Burhanpur District of Madhya Pradesh.
The use of Khandeshi Language (a.k.a. the Ahirani Language) is prevalent in ...
(October), capturing Bijapuri
Ponda (April 1675),
Karwar
Karwar is a seaside city, ''taluka'', and administrative headquarters of Uttara Kannada district lying at the mouth of the Kali river on the Kanara coast of Karnataka state, India.
Karwar is a popular tourist destination and with a city urba ...
(mid-year), and Kolhapur (July). In November, the Maratha navy skirmished with the
Siddi
The Siddi (), also known as the Sheedi, Sidi, or Siddhi, or Habshi are an ethnic group inhabiting India and Pakistan. They are primarily descended from the Bantu peoples of the Zanj coast in Southeast Africa and Ethiopia, most whom arrived to ...
s of
Janjira, but failed to dislodge them.
Having recovered from an illness, and taking advantage of a civil war that had broken out between the Deccanis and the Afghans at Bijapur, Shivaji raided
Athani in April 1676.
In the run-up to his expedition, Shivaji appealed to a sense of Deccani patriotism, that Southern India was a homeland that should be protected from outsiders.
His appeal was somewhat successful, and in 1677 Shivaji visited
Hyderabad
Hyderabad ( ; , ) is the capital and largest city of the Indian state of Telangana and the ''de jure'' capital of Andhra Pradesh. It occupies on the Deccan Plateau along the banks of the Musi River (India), Musi River, in the northern part ...
for a month and entered into a treaty with the
Qutubshah
The Qutb Shahi dynasty also called as Golconda Sultanate (Persian: ''Qutb Shāhiyān'' or ''Sultanat-e Golkonde'') was a Persianate Shia Islam dynasty of Turkoman origin that ruled the sultanate of Golkonda in southern India. After the coll ...
of the Golkonda sultanate, agreeing to reject his alliance with Bijapur and jointly oppose the Mughals. In 1677, Shivaji invaded Karnataka with 30,000 cavalry and 40,000 infantry, backed by Golkonda artillery and funding. Proceeding south, Shivaji seized the forts of
Vellore
Vellore (English: ), also spelt as Velur (), is a city and the administrative headquarters of Vellore district in the Indian state of Tamil Nadu. It is located on the banks of the Palar River in the northeastern part of Tamil Nadu and is separa ...
and
Gingee
Gingee, also known as Senji or Jinji and originally called Singapuri, is a panchayat town in Viluppuram district in the Indian state of Tamil Nadu. Gingee is located between three hills covering a perimeter of 3 km, and lies west of the Sa ...
;
the latter would later serve as a capital of the Marathas during the reign of his son
Rajaram I
Rajaram Bhosle I (Pronunciation: �aːd͡ʒaɾaːm – 3 March 1700) was the third ''Chhatrapati'' of Maratha Empire, who ruled from 1689 to his death in 1700. He was the second son of the Shivaji, the founder of the empire and younger half- ...
.
Shivaji intended to reconcile with his half-brother
Venkoji (Ekoji I), Shahaji's son by his second wife, Tukabai (née
Mohite
Mohite is a copper tin sulfide mineral with the chemical formula Cu2SnS3. It is colored greenish gray and leaves a gray streak (mineralogy), streak. It is Opacity (optics), opaque and has metallic Lustre (mineralogy), luster. Its crystal system is ...
), who ruled Thanjavur (Tanjore) after Shahaji. The initially promising negotiations were unsuccessful, so whilst returning to Raigad, Shivaji defeated his half-brother's army on 26 November 1677 and seized most of his possessions in the
Mysore
Mysore (), officially Mysuru (), is a city in the southern part of the state of Karnataka, India. Mysore city is geographically located between 12° 18′ 26″ north latitude and 76° 38′ 59″ east longitude. It is located at an altitude of ...
plateau. Venkoji's wife Dipa Bai, whom Shivaji deeply respected, took up new negotiations with Shivaji and also convinced her husband to distance himself from Muslim advisors. In the end, Shivaji consented to turn over to her and her female descendants many of the properties he had seized, with Venkoji consenting to a number of conditions for the proper administration of the territories and maintenance of
Shahji's memorial (''samadhi'').
Death and succession

The question of Shivaji's heir-apparent was complicated. Shivaji confined his son to
Panhala
Panhala (Pronunciation: ənʱaːɭa is a city and a Hill station Municipal Council (3177 feet above sea level) 18 km northwest of Kolhapur, in Kolhapur district in the Indian state of Maharashtra. Panhala is the smallest city in Maharash ...
in 1678, only to have the prince escape with his wife and defect to the
Mughals
The Mughal Empire was an early-modern empire that controlled much of South Asia between the 16th and 19th centuries. Quote: "Although the first two Timurid emperors and many of their noblemen were recent migrants to the subcontinent, the d ...
for a year. Sambhaji then returned home, unrepentant, and was again confined to Panhala.
Shivaji died around 3–5 April 1680 at the age of 50, on the eve of
Hanuman Jayanti
Hanuman Jayanti () is a Hindu festival that celebrates the birth of the Hindu deity, and one of the protagonists of the Ramayana, Hanuman. In most states of India, the festival is observed on the full-moon day of the Hindu month of Chaitra ...
. The cause of Shivaji's death is disputed. British records states that Shivaji died of bloody flux being sick for 12 days. In a contemporary work in Portuguese, the Biblioteca Nacional de Lisboa, the recorded cause of death of Shivaji is anthrax.
However, Krishnaji Anant Sabhasad, author of
Sabhasad Bakhar
''Shri-Shiva-Prabhuche-Charitra'' (IAST: ''Śrī-Śiva-Prabhuce-Caritra''), better known as ''Sabhasad Bakhar'', is a Marathi language biography of Shivaji, the founder of the Maratha Empire. It was written by Krishnaji Anant Sabhasad at Jinji, a ...
, the biography of Shivaji has mentioned fever as the cause of death of Shivaji.
Putalabai
Putalabai Bhosale was the third queen of the Maratha king Shivaji. She was from Palkar Family and married Shivaji in 1653. Putalabai was the oldest of the surviving wives of Shivaji, and had no children. She committed Sati after the death of Shi ...
, the childless eldest of the surviving wives of Shivaji committed ''
sati
Sati or SATI may refer to:
Entertainment
* ''Sati'' (film), a 1989 Bengali film by Aparna Sen and starring Shabana Azmi
* ''Sati'' (novel), a 1990 novel by Christopher Pike
*Sati (singer) (born 1976), Lithuanian singer
*Sati, a character in ''Th ...
'' by jumping into his funeral pyre. Another surviving spouse, Sakwarbai, was not allowed to follow suit because she had a young daughter. There were also allegations, though doubted by later scholars, that his second wife
Soyarabai
Soyarabai Bhosale (née Mohite) (died 1681) was one of the eight wives of Shivaji, the founder of Maratha empire in western India. She was mother of Shivaji's second son, Rajaram. She was the younger sister of Maratha army chief Hambirrao Mohi ...
had poisoned him in order to put her 10-year-old son
Rajaram on the throne.
After Shivaji's death,
Soyarabai
Soyarabai Bhosale (née Mohite) (died 1681) was one of the eight wives of Shivaji, the founder of Maratha empire in western India. She was mother of Shivaji's second son, Rajaram. She was the younger sister of Maratha army chief Hambirrao Mohi ...
made plans with various ministers of the administration to crown her son
Rajaram rather than her stepson
Sambhaji
Sambhaji Bhosale (14 May 1657 – 11 March 1689) was the second Chhatrapati of the Maratha Empire, ruling from 1681 to 1689. He was the eldest son of Shivaji, the founder of the Maratha Empire. Sambhaji's rule was largely shaped by the ongoing ...
. On 21 April 1680, ten-year-old Rajaram was installed on the throne. However, Sambhaji took possession of
Raigad Fort
Raigad is a hill fort situated in Mahad, Raigad district of Maharashtra, India. It is one of the strongest fortresses on the Deccan Plateau. It was previously known as Rairee or Rairy fort.
Many constructions and structures on Raigad were b ...
after killing the commander, and on 18 June acquired control of Raigad, and formally ascended the throne on 20 July. Rajaram, his wife
Janki Bai, and mother
Soyrabai were imprisoned, and Soyrabai executed on charges of conspiracy that October.
Governance
Ashta Pradhan Mandal
The Council of Eight Ministers, or
Ashta Pradhan
Ashta Pradhan (literally, ''Modern council of ministers'') was a system
/topic/Ashta-Pradhan, title = Ashta Pradhan | Marathi council The council is credited with having implemented good governance practices in the Maratha heartland, as well ...
Mandal, was an administrative and advisory council set up by Shivaji.
[.] It consisted of eight ministers who regularly advised Shivaji on political and administrative matters. The eight ministers were as follows:
Except the Panditrao and Nyayadhis all other ministers held military commands, their civil duties often being performed by deputies.
Promotion of Marathi and Sanskrit
In his court, Shivaji replaced Persian, the common courtly language in the region, with Marathi, and emphasised Hindu political and courtly traditions. Shivaji's reign stimulated the deployment of Marathi as a tool of systematic description and understanding. Shivaji's royal seal was in Sanskrit. Shivaji commissioned one of his officials to make a comprehensive lexicon to replace Persian and
Arabic
Arabic (, ' ; , ' or ) is a Semitic languages, Semitic language spoken primarily across the Arab world.Semitic languages: an international handbook / edited by Stefan Weninger; in collaboration with Geoffrey Khan, Michael P. Streck, Janet C ...
terms with their Sanskrit equivalents. This led to production of ‘Rājavyavahārakośa’, the thesaurus of state usage in 1677.
Religious policy
Shivaji is known for his liberal and tolerant religious policies. While Hindus were relieved to practice their religion freely under a Hindu ruler, Shivaji not only allowed Muslims to practice without harassment, but supported their ministries with endowments. When
Aurangzeb
Muhi al-Din Muhammad (; – 3 March 1707), commonly known as ( fa, , lit=Ornament of the Throne) and by his regnal title Alamgir ( fa, , translit=ʿĀlamgīr, lit=Conqueror of the World), was the sixth emperor of the Mughal Empire, ruling ...
imposed the
Jizya
Jizya ( ar, جِزْيَة / ) is a per capita yearly taxation historically levied in the form of financial charge on dhimmis, that is, permanent Kafir, non-Muslim subjects of a state governed by Sharia, Islamic law. The jizya tax has been unde ...
tax on non-Muslims on 3 April 1679, Shivaji wrote a strict letter to
Aurangzeb
Muhi al-Din Muhammad (; – 3 March 1707), commonly known as ( fa, , lit=Ornament of the Throne) and by his regnal title Alamgir ( fa, , translit=ʿĀlamgīr, lit=Conqueror of the World), was the sixth emperor of the Mughal Empire, ruling ...
criticising his tax policy. He wrote:
Noting that Shivaji had stemmed the spread of the neighbouring Muslim states, his contemporary, the poet
Kavi Bhushan
Kavi Bhushan (c. 1613–1715) was an Indian poet in the courts of the Bundeli king Chhatrasal and the Maratha king Chhatrapati Shivaji Maharaj. He mainly wrote in Brajbhasha interspersed with words from Sanskrit, Arabic and Persian languages. H ...
stated:
However, Gijs Kruijtzer, in his book Xenophobia in Seventeenth-Century India argues that the roots of modern communalism (the antagonism between “communities” of Hindus and Muslims) first appeared in the decade 1677–1687, in the interplay between Shivaji and the Mughal emperor Aurangzeb (though Shivaji died in 1680). During the sack of Surat in 1664, Shivaji was approached by Ambrose, a Capuchin Monastery, Capuchin monk who asked him to spare the city's Christians. Shivaji left the Christians untouched, saying "the Frankish Padrys are good men."
Shivaji was not attempting to create a universal Hindu rule. He was tolerant to different religions and believed in syncretism. He urged Aurangzeb to act like Akbar in according respect to Hindu beliefs and places. Shivaji had little trouble forming alliances with the surrounding Muslim nations even against Hindu powers. He also did not join forces with other Hindu powers, such as the Rajputs, to fight the Mughals. In his own army, Muslim leaders appear quite early. The first Pathan unit was formed in 1656. His naval admiral, Darya Sarang, was a Muslim.
Ramdas

Shivaji was a contemporary of Samarth Ramdas. Historian Stewart N. Gordon, Stewart Gordon concludes about their relationship:
Seal

Seals were means to confer authenticity on official documents. Shahaji and Jijabai had Persian seals. But Shivaji, right from beginning, used Sanskrit for his seal.
The seal proclaims: "This seal of Shiva, son of Shah, shines forth for the welfare of the people and is meant to command increasing respect from the universe like the first phase of the moon."
Shivaji's mode of warfare
Shivaji maintained a small but effective standing army. The core of Shivaji's army consisted of peasants of the Maratha and Kunbi castes. Shivaji was aware of the limitations of his army. He realised that conventional warfare methods were inadequate to confront the big, well-trained cavalry of the Mughals which was equipped with field artillery. As a result, Shivaji adopted Guerrilla warfare, guerilla tactics which became known as 'Ganimi Kawa'. Shivaji was a master of guerrilla warfare. His strategies consistently perplexed and defeated armies sent against him. He realized that the most vulnerable point of the large, slow-moving armies of the time was supply. He utilised knowledge of the local terrain and the superior mobility of his light cavalry to cut off supplies to the enemy. Shivaji refused to confront in pitched battles. Instead, he lured the enemies in difficult hills and jungles of his own choosing, catching them at a disadvantage and routing them.
Shivaji didn't stick to a particular tactic but used several methods to undermine his enemies as required by circumstances, like sudden raids, sweeps and ambushes and use of psychological pressure.
Shivaji was contemptuously called a "Mountain Rat" by
Aurangzeb
Muhi al-Din Muhammad (; – 3 March 1707), commonly known as ( fa, , lit=Ornament of the Throne) and by his regnal title Alamgir ( fa, , translit=ʿĀlamgīr, lit=Conqueror of the World), was the sixth emperor of the Mughal Empire, ruling ...
and his generals because of his guerilla tactics of attacking enemy forces and then retreating into his mountain forts.
Military
Shivaji demonstrated great skill in creating his military organisation, which lasted until the demise of the Maratha Empire. His strategy rested on leveraging his ground forces, naval forces, and series of forts across his territory. The Maval infantry served as the core of his ground forces (reinforced with Telangi musketeers from Karnataka), supported by Maratha cavalry. His artillery was relatively underdeveloped and reliant on European suppliers, further inclining him to a very mobile form of warfare.
Hill forts
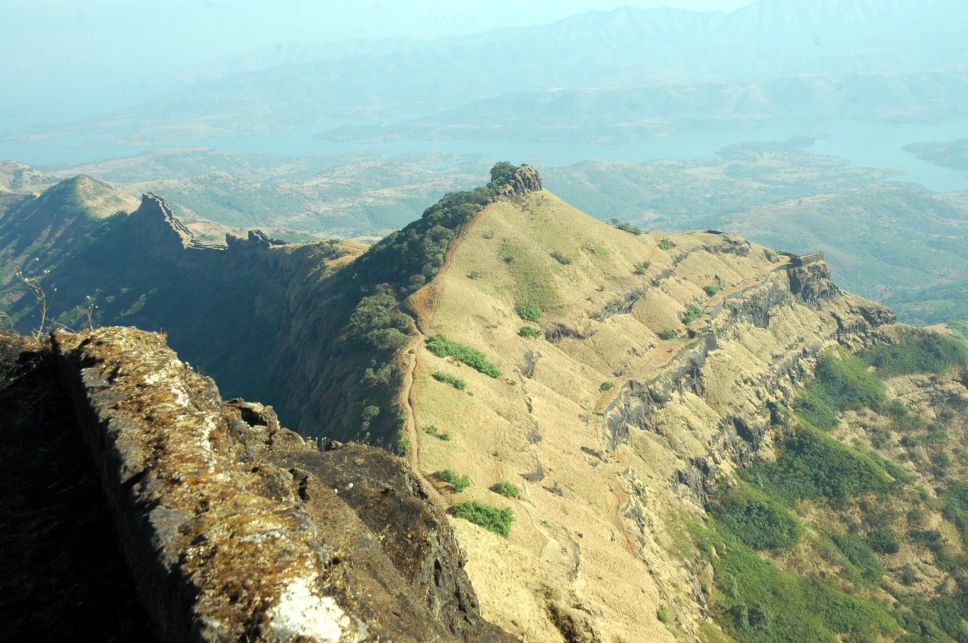

Hill forts played a key role in Shivaji's strategy. He captured important forts at Murambdev (Rajgad), Torna Fort, Torna, Kondhana (Sinhagad) and Purandar fort, Purandar. He also rebuilt or repaired many forts in advantageous locations. In addition, Shivaji built a number of forts; the number "111" is reported in some accounts, but it is likely the actual number "did not exceed 18."
The historian Jadunath Sarkar assessed that Shivaji owned some 240–280 forts at the time of his death. Each was placed under three officers of equal status, lest a single traitor be bribed or tempted to deliver it to the enemy. The officers acted jointly and provided mutual checks and balance.
Navy
Aware of the need for naval power to maintain control along the Konkan coast, Shivaji began to build his navy in 1657 or 1659, with the purchase of twenty galivats from the Portuguese shipyards of Vasai, Bassein.
Marathi chronicles state that at its height his fleet counted some 400 warships, though contemporary English chronicles counter that the number never exceeded 160. Kanhoji Angre was the chief of Maratha Navy.
With the Marathas being accustomed to a land-based military, Shivaji widened his search for qualified crews for his ships, taking on lower-caste Hindus of the coast who were long familiar with naval operations (the famed "Malabar pirates") as well as Muslim mercenaries. Noting the power of the Portuguese navy, Shivaji hired a number of Portuguese sailors and Goan Christian converts, and made Rui Leitao Viegas commander of his fleet. Viegas was later to defect back to the Portuguese, taking 300 sailors with him.
Shivaji fortified his coastline by seizing coastal forts and refurbishing them, and built his first marine fort at Sindhudurg Fort, Sindhudurg, which was to become the headquarters of the Maratha navy.
The navy itself was a brown-water navy, coastal navy, focused on travel and combat in the littoral areas, and not intended to go far out to sea.
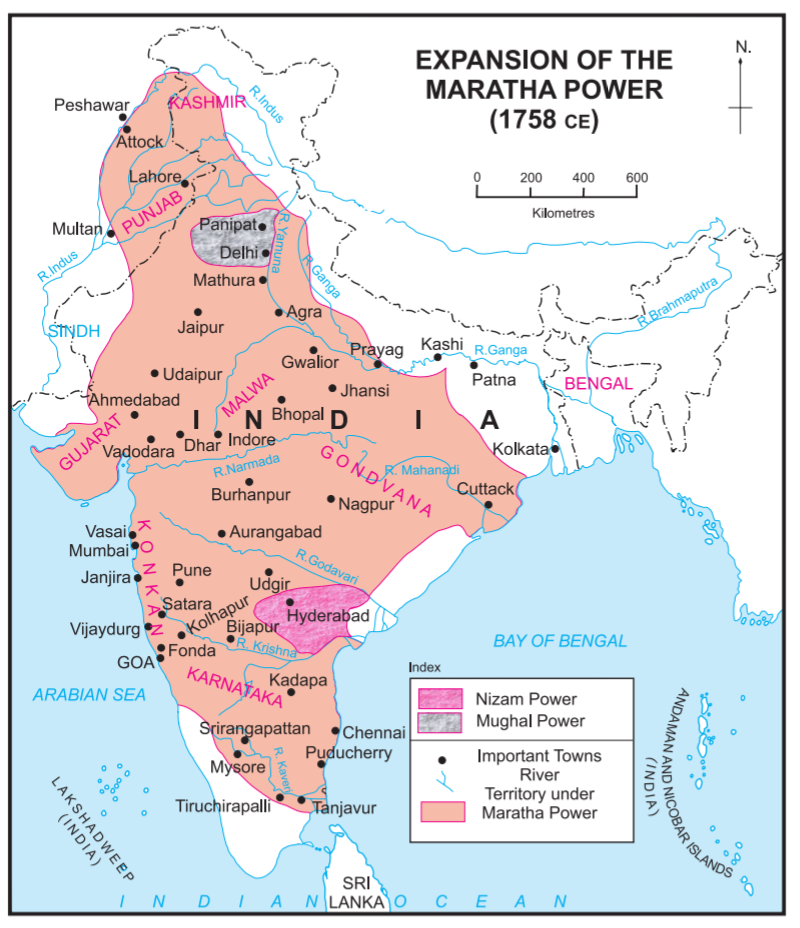
Expansion of Maratha Empire after Shivaji
Shivaji left behind a state always at odds with the Mughals. Soon after his death, in 1681, Aurangzeb launched an offensive in the South to capture territories held by the Marathas, the Bijapur-based Adilshahi and Qutb Shahi dynasty, Qutb Shahi of Golkonda respectively. He was successful in obliterating the Sultanates but could not subdue the Marathas after spending 27 years in the Deccan. The period saw the capture, torture, and execution of Sambhaji in 1689, and the Marathas offering strong resistance under the leadership of Sambhaji's successor,
Rajaram and then Rajaram's widow Tarabai. Territories changed hands repeatedly between the Mughals and the Marathas; the conflict ended in Mughal–Maratha Wars, defeat for the Mughals in 1707.
Chattrapati Shahu, Shahu, a grandson of Shivaji and son of
Sambhaji
Sambhaji Bhosale (14 May 1657 – 11 March 1689) was the second Chhatrapati of the Maratha Empire, ruling from 1681 to 1689. He was the eldest son of Shivaji, the founder of the Maratha Empire. Sambhaji's rule was largely shaped by the ongoing ...
, was kept prisoner by
Aurangzeb
Muhi al-Din Muhammad (; – 3 March 1707), commonly known as ( fa, , lit=Ornament of the Throne) and by his regnal title Alamgir ( fa, , translit=ʿĀlamgīr, lit=Conqueror of the World), was the sixth emperor of the Mughal Empire, ruling ...
during the 27-year period conflict. After the latter's death, his successor released Shahu. After a brief power struggle over succession with his aunt Tarabai, Shahu ruled the Maratha Empire from 1707 to 1749. Early in his reign, he appointed Balaji Vishwanath and later his descendants, as Peshwas (prime ministers) of the Maratha Empire. The empire expanded greatly under the leadership of Balaji's son, Peshwa Bajirao I and grandson, Peshwa Balaji Bajirao. At its peak, the Maratha empire stretched from Tamil Nadu in the south, to Maratha conquest of North-west India, Peshawar (modern-day Khyber Pakhtunkhwa) in the north, and Expeditions in Bengal, Bengal, in the east. In 1761, the Maratha army lost the Third Battle of Panipat to Ahmed Shah Abdali of the Afghan Durrani Empire, which halted their imperial expansion in northwestern India. Ten years after Panipat, Maratha Resurrection, Marathas regained influence in North India during the rule of Madhavrao Peshwa.
In a bid to effectively manage the large empire, Shahu and the Peshwas gave semi-autonomy to the strongest of the knights, creating the Maratha Confederacy. They became known as Gaekwads of Vadodara, Baroda, the Holkars of Indore and Malwa, the Scindias of Gwalior and Bhonsales of Nagpur kingdom, Nagpur. In 1775, the East India Company intervened in a succession struggle in Pune, which became the First Anglo-Maratha War. The Marathas remained the pre-eminent power in India until their defeat by the British in the Second Anglo-Maratha War, Second and Third Anglo-Maratha War, Third Anglo-Maratha wars (1805–1818), which left the company the dominant power in most of India.
Legacy

Shivaji was well known for his strong religious and warrior code of ethics and exemplary character. He was recognized as a national hero during the Indian Independence Movement.
While some accounts of Shivaji state that he was greatly influenced by the Brahmin guru Samarth Ramdas, others have said that Ramdas' role has been overemphasised by later Brahmin commentators to enhance their position.
Early depictions
Shivaji was admired for his heroic exploits and clever stratagems in the contemporary accounts of English, French, Dutch, Portuguese and Italian writers. Contemporary English writers compared him with Alexander the Great, Alexander, Hannibal and Julius Caesar. The French traveller Francois Bernier wrote in his ''Travels in Mughal India'':
I forgot to mention that during pillage of Sourate, Seva-Gy, the Holy Seva-Gi! respected the habitation of the Reverend Father Ambrose, the Order of Friars Minor Capuchin, Capuchin missionary. 'The Frankish Padres are good men', he said 'and shall not be attacked.' He spared also the house of a deceased Delale or Gentile broker, of the Dutch, because assured that he had been very charitable while alive.
Mughal Empire, Mughal depictions of Shivaji were largely negative, referring to him simply as "Shiva" without the honorific "-ji". One Mughal writer in the early 1700s described Shivaji's death as ().
Reimagining

In the mid-19th century, Marathi social reformer Jyotirao Phule wrote his interpretation of the Shivaji legend, portraying him as a hero of the shudras and Dalits. Phule sought to use the Shivaji legends to undermine the Brahmins he accused of hijacking the narrative, and uplift the lower classes; his 1869 ballad-form story of Shivaji was met with great hostility by the Brahmin-dominated media.
At the end of the 19th century, Shivaji's memory was leveraged by the non-Brahmin intellectuals of Bombay, who identified as his descendants and through him claimed the kshatriya varna. While some Brahmins rebutted this identity, defining them as of the lower shudra varna, other Brahmins recognised the Marathas' utility to the Indian independence movement, and endorsed this kshatriya legacy and the significance of Shivaji.
In 1895, Indian nationalist leader Lokmanya Tilak organised what was to be an annual festival to mark the birthday of Shivaji. He portrayed Shivaji as the "opponent of the oppressor", with possible negative implications concerning the colonial government.
Tilak denied any suggestion that his festival was anti-Muslim or disloyal to the government, but simply a celebration of a hero. These celebrations prompted a British commentator in 1906 to note: "Cannot the annals of the Hindu race point to a single hero whom even the tongue of slander will not dare call a chief of dacoits...?"
One of the first commentators to reappraise the critical British view of Shivaji was M. G. Ranade, whose ''Rise of the Maratha Power'' (1900) declared Shivaji's achievements as the beginning of modern nation-building. Ranade criticised earlier British portrayals of Shivaji's state as "a freebooting Power, which thrived by plunder and adventure, and succeeded only because it was the most cunning and adventurous ... This is a very common feeling with the readers, who derive their knowledge of these events solely from the works of English historians."
In 1919, Jadunath Sarkar, Sarkar published the seminal ''Shivaji and His Times'', hailed as the most authoritative biography of the king since James Grant Duff's 1826 ''A History of the Mahrattas''. A respected scholar, Sarkar was able to read primary sources in Persian, Marathi, and Arabic, but was challenged for his criticism of the "chauvinism" of Marathi historians' views of Shivaji.
Likewise, though supporters cheered his depiction of the killing of
Afzal Khan as justified, they decried Sarkar's terming as "murder" the killing of the Hindus, Hindu raja Chandrao More and his clan.
Inspiration


As political tensions rose in India in the early 20th century, some Indian leaders came to re-work their earlier stances on Shivaji's role. Jawaharlal Nehru had in 1934 noted "Some of the Shivaji's deeds, like the treacherous killing of the Bijapur general, lower him greatly in our estimation." Following a public outcry from Pune intellectuals, Indian National Congress, Congress leader T. R. Deogirikar noted that Nehru had admitted he was wrong regarding Shivaji, and now endorsed Shivaji as a great nationalist.
In 1966, the Shiv Sena () political party was formed to promote the interests of Marathi speaking people in the face of migration to Maharashtra from other parts of India, and the accompanying loss of power for locals. His image adorns literature, propaganda and icons of the party.
In modern times, Shivaji is considered as a national hero in India, especially in the state of Maharashtra, where he remains an important figure in the state's history. Stories of his life form an integral part of the upbringing and identity of the Marathi people. Shivaji is upheld by regional political parties and also by the Maratha caste dominated Indian National Congress, Congress party's offshoots in Maharashtra, such as the Indian National Congress (organisation), Indira Congress and the Nationalist Congress Party.
In the late 20th century, Babasaheb Purandare became one of the most significant author in portraying Shivaji in his writings, leading him to be declared in 1964 as the ''Shiv-Shahir'' (). However, Purandare, a Brahmin, was also accused of overemphasising the influence of Brahmin gurus on Shivaji, and his Maharashtra Bhushan award ceremony in 2015 was protested by those claiming he had defamed Shivaji.
Controversy
In 1993, the ''The Illustrated Weekly of India, Illustrated Weekly'' published an article suggesting that Shivaji was not opposed to Muslims ''per se'', and that his style of governance was influenced by that of the Mughal Empire. Congress Party members called for legal actions against the publisher and writer, Marathi newspapers accused them of "imperial prejudice" and Shiv Sena called for the writer's public flogging. Maharashtra brought legal action against the publisher under regulations prohibiting enmity between religious and cultural groups, but a High Court found the ''Illustrated Weekly'' had operated within the bounds of freedom of expression.
In 2003, American academic James W. Laine published his book ''Shivaji: Hindu King in Islamic India'' to, what Ananya Vajpeyi terms, a regime of "cultural policing by militant Marathas".
As a result of this publication, the Bhandarkar Oriental Research Institute in Pune where Laine had researched was attacked by the Sambhaji Brigade. Laine was even threatened to be arrested
and the book was banned in Maharashtra in January 2004, but the ban was lifted by the Bombay High Court in 2007, and in July 2010 the Supreme Court of India upheld the lifting of the ban. This lifting was followed by public demonstrations against the author and the decision of the Supreme Court.
Commemorations

Commemorations of Shivaji are found throughout India, most notably in Maharashtra. Shivaji's statues and monuments are found almost in every town and city in Maharashtra as well as in different places across India. Other commemorations include the Indian Navy's station INS Shivaji, numerous postage stamps, and the Chhatrapati Shivaji International Airport, main airport and Chhatrapati Shivaji Maharaj Terminus, railway headquarters in Mumbai. In Maharashtra, there has been a long tradition of children building a replica fort with toy soldiers and other figures during the festival of Diwali in memory of Shivaji.
A proposal to build a giant memorial called Shiv Smarak was approved in 2016 to be located near Mumbai on a small island in the Arabian Sea. It will be 210 meters tall, making it the List of tallest statues, world's largest statue when completed in possibly 2021.
In March 2022 a statue made of gunmetal was inaugurated in Pune.
Sources
Notes
References
Bibliography
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
Further reading
*
*
*
*
External links
*
*
{{Authority control
Shivaji,
1630 births
1680 deaths
17th-century Indian monarchs
Marathi people
Indian warriors
Indian Hindus
Hindu nationalists
Hindu monarchs
People of the Maratha Empire
Infectious disease deaths in India
Age controversies
Founding monarchs
Legendary Indian people
 Shivaji was born in the hill-fort of
Shivaji was born in the hill-fort of 
 The Bijapur sultanate was displeased at their losses to Shivaji's forces, which their vassal Shahaji disavowed. After a peace treaty with the Mughals, and the general acceptance of the young
The Bijapur sultanate was displeased at their losses to Shivaji's forces, which their vassal Shahaji disavowed. After a peace treaty with the Mughals, and the general acceptance of the young  Upon the request of Badi Begum of Bijapur, Aurangzeb, now the Mughal emperor, sent his maternal uncle
Upon the request of Badi Begum of Bijapur, Aurangzeb, now the Mughal emperor, sent his maternal uncle  The attacks on Shaista Khan and Surat enraged Aurangzeb. In response, he sent this
The attacks on Shaista Khan and Surat enraged Aurangzeb. In response, he sent this  In 1666, Aurangzeb summoned Shivaji to
In 1666, Aurangzeb summoned Shivaji to  Shivaji had acquired extensive lands and wealth through his campaigns, but lacking a formal title, he was still technically a Mughal
Shivaji had acquired extensive lands and wealth through his campaigns, but lacking a formal title, he was still technically a Mughal  Shivaji was a contemporary of Samarth Ramdas. Historian Stewart N. Gordon, Stewart Gordon concludes about their relationship:
Shivaji was a contemporary of Samarth Ramdas. Historian Stewart N. Gordon, Stewart Gordon concludes about their relationship:
 Seals were means to confer authenticity on official documents. Shahaji and Jijabai had Persian seals. But Shivaji, right from beginning, used Sanskrit for his seal. The seal proclaims: "This seal of Shiva, son of Shah, shines forth for the welfare of the people and is meant to command increasing respect from the universe like the first phase of the moon."
Seals were means to confer authenticity on official documents. Shahaji and Jijabai had Persian seals. But Shivaji, right from beginning, used Sanskrit for his seal. The seal proclaims: "This seal of Shiva, son of Shah, shines forth for the welfare of the people and is meant to command increasing respect from the universe like the first phase of the moon."
 Hill forts played a key role in Shivaji's strategy. He captured important forts at Murambdev (Rajgad), Torna Fort, Torna, Kondhana (Sinhagad) and Purandar fort, Purandar. He also rebuilt or repaired many forts in advantageous locations. In addition, Shivaji built a number of forts; the number "111" is reported in some accounts, but it is likely the actual number "did not exceed 18." The historian Jadunath Sarkar assessed that Shivaji owned some 240–280 forts at the time of his death. Each was placed under three officers of equal status, lest a single traitor be bribed or tempted to deliver it to the enemy. The officers acted jointly and provided mutual checks and balance.
Hill forts played a key role in Shivaji's strategy. He captured important forts at Murambdev (Rajgad), Torna Fort, Torna, Kondhana (Sinhagad) and Purandar fort, Purandar. He also rebuilt or repaired many forts in advantageous locations. In addition, Shivaji built a number of forts; the number "111" is reported in some accounts, but it is likely the actual number "did not exceed 18." The historian Jadunath Sarkar assessed that Shivaji owned some 240–280 forts at the time of his death. Each was placed under three officers of equal status, lest a single traitor be bribed or tempted to deliver it to the enemy. The officers acted jointly and provided mutual checks and balance.
 Shivaji left behind a state always at odds with the Mughals. Soon after his death, in 1681, Aurangzeb launched an offensive in the South to capture territories held by the Marathas, the Bijapur-based Adilshahi and Qutb Shahi dynasty, Qutb Shahi of Golkonda respectively. He was successful in obliterating the Sultanates but could not subdue the Marathas after spending 27 years in the Deccan. The period saw the capture, torture, and execution of Sambhaji in 1689, and the Marathas offering strong resistance under the leadership of Sambhaji's successor, Rajaram and then Rajaram's widow Tarabai. Territories changed hands repeatedly between the Mughals and the Marathas; the conflict ended in Mughal–Maratha Wars, defeat for the Mughals in 1707.
Chattrapati Shahu, Shahu, a grandson of Shivaji and son of
Shivaji left behind a state always at odds with the Mughals. Soon after his death, in 1681, Aurangzeb launched an offensive in the South to capture territories held by the Marathas, the Bijapur-based Adilshahi and Qutb Shahi dynasty, Qutb Shahi of Golkonda respectively. He was successful in obliterating the Sultanates but could not subdue the Marathas after spending 27 years in the Deccan. The period saw the capture, torture, and execution of Sambhaji in 1689, and the Marathas offering strong resistance under the leadership of Sambhaji's successor, Rajaram and then Rajaram's widow Tarabai. Territories changed hands repeatedly between the Mughals and the Marathas; the conflict ended in Mughal–Maratha Wars, defeat for the Mughals in 1707.
Chattrapati Shahu, Shahu, a grandson of Shivaji and son of  Shivaji was well known for his strong religious and warrior code of ethics and exemplary character. He was recognized as a national hero during the Indian Independence Movement. While some accounts of Shivaji state that he was greatly influenced by the Brahmin guru Samarth Ramdas, others have said that Ramdas' role has been overemphasised by later Brahmin commentators to enhance their position.
Shivaji was well known for his strong religious and warrior code of ethics and exemplary character. He was recognized as a national hero during the Indian Independence Movement. While some accounts of Shivaji state that he was greatly influenced by the Brahmin guru Samarth Ramdas, others have said that Ramdas' role has been overemphasised by later Brahmin commentators to enhance their position.
 In the mid-19th century, Marathi social reformer Jyotirao Phule wrote his interpretation of the Shivaji legend, portraying him as a hero of the shudras and Dalits. Phule sought to use the Shivaji legends to undermine the Brahmins he accused of hijacking the narrative, and uplift the lower classes; his 1869 ballad-form story of Shivaji was met with great hostility by the Brahmin-dominated media. At the end of the 19th century, Shivaji's memory was leveraged by the non-Brahmin intellectuals of Bombay, who identified as his descendants and through him claimed the kshatriya varna. While some Brahmins rebutted this identity, defining them as of the lower shudra varna, other Brahmins recognised the Marathas' utility to the Indian independence movement, and endorsed this kshatriya legacy and the significance of Shivaji.
In 1895, Indian nationalist leader Lokmanya Tilak organised what was to be an annual festival to mark the birthday of Shivaji. He portrayed Shivaji as the "opponent of the oppressor", with possible negative implications concerning the colonial government. Tilak denied any suggestion that his festival was anti-Muslim or disloyal to the government, but simply a celebration of a hero. These celebrations prompted a British commentator in 1906 to note: "Cannot the annals of the Hindu race point to a single hero whom even the tongue of slander will not dare call a chief of dacoits...?"
One of the first commentators to reappraise the critical British view of Shivaji was M. G. Ranade, whose ''Rise of the Maratha Power'' (1900) declared Shivaji's achievements as the beginning of modern nation-building. Ranade criticised earlier British portrayals of Shivaji's state as "a freebooting Power, which thrived by plunder and adventure, and succeeded only because it was the most cunning and adventurous ... This is a very common feeling with the readers, who derive their knowledge of these events solely from the works of English historians."
In 1919, Jadunath Sarkar, Sarkar published the seminal ''Shivaji and His Times'', hailed as the most authoritative biography of the king since James Grant Duff's 1826 ''A History of the Mahrattas''. A respected scholar, Sarkar was able to read primary sources in Persian, Marathi, and Arabic, but was challenged for his criticism of the "chauvinism" of Marathi historians' views of Shivaji. Likewise, though supporters cheered his depiction of the killing of Afzal Khan as justified, they decried Sarkar's terming as "murder" the killing of the Hindus, Hindu raja Chandrao More and his clan.
In the mid-19th century, Marathi social reformer Jyotirao Phule wrote his interpretation of the Shivaji legend, portraying him as a hero of the shudras and Dalits. Phule sought to use the Shivaji legends to undermine the Brahmins he accused of hijacking the narrative, and uplift the lower classes; his 1869 ballad-form story of Shivaji was met with great hostility by the Brahmin-dominated media. At the end of the 19th century, Shivaji's memory was leveraged by the non-Brahmin intellectuals of Bombay, who identified as his descendants and through him claimed the kshatriya varna. While some Brahmins rebutted this identity, defining them as of the lower shudra varna, other Brahmins recognised the Marathas' utility to the Indian independence movement, and endorsed this kshatriya legacy and the significance of Shivaji.
In 1895, Indian nationalist leader Lokmanya Tilak organised what was to be an annual festival to mark the birthday of Shivaji. He portrayed Shivaji as the "opponent of the oppressor", with possible negative implications concerning the colonial government. Tilak denied any suggestion that his festival was anti-Muslim or disloyal to the government, but simply a celebration of a hero. These celebrations prompted a British commentator in 1906 to note: "Cannot the annals of the Hindu race point to a single hero whom even the tongue of slander will not dare call a chief of dacoits...?"
One of the first commentators to reappraise the critical British view of Shivaji was M. G. Ranade, whose ''Rise of the Maratha Power'' (1900) declared Shivaji's achievements as the beginning of modern nation-building. Ranade criticised earlier British portrayals of Shivaji's state as "a freebooting Power, which thrived by plunder and adventure, and succeeded only because it was the most cunning and adventurous ... This is a very common feeling with the readers, who derive their knowledge of these events solely from the works of English historians."
In 1919, Jadunath Sarkar, Sarkar published the seminal ''Shivaji and His Times'', hailed as the most authoritative biography of the king since James Grant Duff's 1826 ''A History of the Mahrattas''. A respected scholar, Sarkar was able to read primary sources in Persian, Marathi, and Arabic, but was challenged for his criticism of the "chauvinism" of Marathi historians' views of Shivaji. Likewise, though supporters cheered his depiction of the killing of Afzal Khan as justified, they decried Sarkar's terming as "murder" the killing of the Hindus, Hindu raja Chandrao More and his clan.

 As political tensions rose in India in the early 20th century, some Indian leaders came to re-work their earlier stances on Shivaji's role. Jawaharlal Nehru had in 1934 noted "Some of the Shivaji's deeds, like the treacherous killing of the Bijapur general, lower him greatly in our estimation." Following a public outcry from Pune intellectuals, Indian National Congress, Congress leader T. R. Deogirikar noted that Nehru had admitted he was wrong regarding Shivaji, and now endorsed Shivaji as a great nationalist.
In 1966, the Shiv Sena () political party was formed to promote the interests of Marathi speaking people in the face of migration to Maharashtra from other parts of India, and the accompanying loss of power for locals. His image adorns literature, propaganda and icons of the party.
In modern times, Shivaji is considered as a national hero in India, especially in the state of Maharashtra, where he remains an important figure in the state's history. Stories of his life form an integral part of the upbringing and identity of the Marathi people. Shivaji is upheld by regional political parties and also by the Maratha caste dominated Indian National Congress, Congress party's offshoots in Maharashtra, such as the Indian National Congress (organisation), Indira Congress and the Nationalist Congress Party.
In the late 20th century, Babasaheb Purandare became one of the most significant author in portraying Shivaji in his writings, leading him to be declared in 1964 as the ''Shiv-Shahir'' (). However, Purandare, a Brahmin, was also accused of overemphasising the influence of Brahmin gurus on Shivaji, and his Maharashtra Bhushan award ceremony in 2015 was protested by those claiming he had defamed Shivaji.
As political tensions rose in India in the early 20th century, some Indian leaders came to re-work their earlier stances on Shivaji's role. Jawaharlal Nehru had in 1934 noted "Some of the Shivaji's deeds, like the treacherous killing of the Bijapur general, lower him greatly in our estimation." Following a public outcry from Pune intellectuals, Indian National Congress, Congress leader T. R. Deogirikar noted that Nehru had admitted he was wrong regarding Shivaji, and now endorsed Shivaji as a great nationalist.
In 1966, the Shiv Sena () political party was formed to promote the interests of Marathi speaking people in the face of migration to Maharashtra from other parts of India, and the accompanying loss of power for locals. His image adorns literature, propaganda and icons of the party.
In modern times, Shivaji is considered as a national hero in India, especially in the state of Maharashtra, where he remains an important figure in the state's history. Stories of his life form an integral part of the upbringing and identity of the Marathi people. Shivaji is upheld by regional political parties and also by the Maratha caste dominated Indian National Congress, Congress party's offshoots in Maharashtra, such as the Indian National Congress (organisation), Indira Congress and the Nationalist Congress Party.
In the late 20th century, Babasaheb Purandare became one of the most significant author in portraying Shivaji in his writings, leading him to be declared in 1964 as the ''Shiv-Shahir'' (). However, Purandare, a Brahmin, was also accused of overemphasising the influence of Brahmin gurus on Shivaji, and his Maharashtra Bhushan award ceremony in 2015 was protested by those claiming he had defamed Shivaji.
 Commemorations of Shivaji are found throughout India, most notably in Maharashtra. Shivaji's statues and monuments are found almost in every town and city in Maharashtra as well as in different places across India. Other commemorations include the Indian Navy's station INS Shivaji, numerous postage stamps, and the Chhatrapati Shivaji International Airport, main airport and Chhatrapati Shivaji Maharaj Terminus, railway headquarters in Mumbai. In Maharashtra, there has been a long tradition of children building a replica fort with toy soldiers and other figures during the festival of Diwali in memory of Shivaji.
A proposal to build a giant memorial called Shiv Smarak was approved in 2016 to be located near Mumbai on a small island in the Arabian Sea. It will be 210 meters tall, making it the List of tallest statues, world's largest statue when completed in possibly 2021.
In March 2022 a statue made of gunmetal was inaugurated in Pune.
Commemorations of Shivaji are found throughout India, most notably in Maharashtra. Shivaji's statues and monuments are found almost in every town and city in Maharashtra as well as in different places across India. Other commemorations include the Indian Navy's station INS Shivaji, numerous postage stamps, and the Chhatrapati Shivaji International Airport, main airport and Chhatrapati Shivaji Maharaj Terminus, railway headquarters in Mumbai. In Maharashtra, there has been a long tradition of children building a replica fort with toy soldiers and other figures during the festival of Diwali in memory of Shivaji.
A proposal to build a giant memorial called Shiv Smarak was approved in 2016 to be located near Mumbai on a small island in the Arabian Sea. It will be 210 meters tall, making it the List of tallest statues, world's largest statue when completed in possibly 2021.
In March 2022 a statue made of gunmetal was inaugurated in Pune.