Changchun (, ; ),
also romanized as Ch'angch'un, is the capital and largest city of
Jilin Province,
People's Republic of China. Lying in the center of the
Songliao Plain, Changchun is administered as a , comprising 7 districts, 1 county and 3 county-level cities. According to the 2020 census of China, Changchun had a total population of 9,066,906 under its jurisdiction. The city's metro area, comprising 5 districts and 1 development area, had a population of 5,019,477 in 2020, as the
Shuangyang
Shuangyang District () is one of seven districts of the prefecture-level city of Changchun, the capital of Jilin Province, Northeast China, forming part of the city's southeastern suburbs. Despite its name, it lies more than southeast of the urban ...
and
Jiutai districts are not urbanized yet.
It is one of the biggest cities in
Northeast China, along with
Shenyang
Shenyang (, ; ; Mandarin pronunciation: ), formerly known as Fengtian () or by its Manchu language, Manchu name Mukden, is a major China, Chinese sub-provincial city and the List of capitals in China#Province capitals, provincial capital of Lia ...
,
Dalian
Dalian () is a major sub-provincial port city in Liaoning province, People's Republic of China, and is Liaoning's second largest city (after the provincial capital Shenyang) and the third-most populous city of Northeast China. Located on the ...
and
Harbin
Harbin (; mnc, , v=Halbin; ) is a sub-provincial city and the provincial capital and the largest city of Heilongjiang province, People's Republic of China, as well as the second largest city by urban population after Shenyang and largest ...
.
The name of the city means "long spring" in
Chinese. Between 1932 and 1945, Changchun was renamed Xinjing () or Hsinking by the
Kwantung Army as it became the capital of the
Imperial Japanese
puppet state of
Manchukuo
Manchukuo, officially the State of Manchuria prior to 1934 and the Empire of (Great) Manchuria after 1934, was a puppet state of the Empire of Japan in Northeast China, Manchuria from 1932 until 1945. It was founded as a republic in 1932 afte ...
, occupying modern
Northeast China. After the
foundation of the
People's Republic of China in 1949, Changchun was established as the provincial capital of Jilin in 1954.
Known locally as China's "City of Automobiles",
Changchun is an important industrial base with a particular focus on the automotive sector.
[
] Because of its key role in the domestic automobile industry, Changchun was sometimes referred to as the "
Detroit of China."
Apart from this industrial aspect, Changchun is also one of four "National Garden Cities" awarded by the Ministry of Construction of P.R. China in 2001 due to its high
urban greening
In land-use planning, urban green space is open-space areas reserved for parks and other "green spaces", including plant life, water features -also referred to as blue spaces- and other kinds of natural environment. Most urban open spaces are ...
rate.
Changchun is also one of the top
40 cities in the world by scientific research as tracked by the
Nature Index according to the Nature Index 2020 Science Cities. The city is home to
several major universities, notably
Jilin University
Jilin University (JLU; ; often abbreviated JLU or ) is a leading national research university located in Changchun, China. It is under the direct jurisdiction of China's Ministry of Education. It is a Chinese Ministry of Education Class A Doub ...
and
Northeast Normal University, members of
China's prestigious universities in the
Double First Class University Plan.
History
Early history
Changchun was initially established on imperial decree as a small trading post and frontier village during the reign of the
Jiaqing Emperor in the
Qing dynasty. Trading activities mainly involved furs and other natural products during this period. In 1800, the Jiaqing Emperor selected a small village on the east bank of the
Yitong River
The Yitong River () is a river in Jilin Province. It is the mother river of Changchun, the capital of Jilin Province.
General
The Yitong River starts in Yitong Manchu Autonomous County, flows north through Changchun and Dehui cities, and flows ...
and named it "Changchun Ting".
At the end of the 18th century peasants from overpopulated provinces such as
Shandong
Shandong ( , ; ; alternately romanized as Shantung) is a coastal province of the People's Republic of China and is part of the East China region.
Shandong has played a major role in Chinese history since the beginning of Chinese civilizati ...
and
Hebei began to settle in the region. In 1889, the village was promoted into a city known as "Changchun Fu".
Railway era
In May 1898, Changchun got its first railway station, located in
Kuancheng, part of the railway from
Harbin
Harbin (; mnc, , v=Halbin; ) is a sub-provincial city and the provincial capital and the largest city of Heilongjiang province, People's Republic of China, as well as the second largest city by urban population after Shenyang and largest ...
to
L├╝shun (the southern branch of the
Chinese Eastern Railway), constructed by the
Russian Empire.

After Russia's loss of the southernmost section of this branch as a result of the
Russo-Japanese War of 1904ŌĆō1905, the Kuancheng station (Kuanchengtze, in contemporary spelling) became the last Russian station on this branch.
The next station just a short distance to the southŌĆöthe new "Japanese" Changchun stationŌĆöbecame the first station of the
South Manchuria Railway,
[
"Provisional Convention ... concerning the junction of the Japanese and Russian Railways in Manchuria" ŌĆō 13 June 1907.
] which now owned all the tracks running farther south, to
L├╝shun, which they re-gauged to the
standard gauge
A standard-gauge railway is a railway with a track gauge of . The standard gauge is also called Stephenson gauge (after George Stephenson), International gauge, UIC gauge, uniform gauge, normal gauge and European gauge in Europe, and SGR in Ea ...
(after a short period of using the narrow Japanese gauge during the war).
[
Luis Jackson, Industrial Commissioner of the Erie Railroad. "Rambles in Japan and China". I]
Railway and Locomotive Engineering
, vol. 26 (March 1913), pp. 91ŌĆō92
A special Russo-Japanese agreement of 1907 provided that
Russian gauge tracks would continue from the "Russian" Kuancheng Station to the "Japanese" Changchun Station, and vice versa, tracks on the "gauge adapted by the South Manchuria Railway" (i.e. the standard gauge) would continue from Changchun Station to Kuancheng Station.
[
An epidemic of pneumonic plague occurred in surrounding Manchuria from 1910 to 1911, known as the Manchurian plague. It was the worst-ever recorded outbreak of pneumonic plague which was spread through the Trans-Manchurian railway from the border trade port of Manzhouli. This turned out to be the beginning of the large pneumonic plague pandemic of Manchuria and Mongolia which ultimately claimed 60,000 victims.]
City planning and development from 1906 to 1931
 The Treaty of Portsmouth formally ended the Russo-Japanese War of 1904ŌĆō05 and saw the transfer and assignment to the Empire of Japan in 1906 the railway between Changchun and Port Arthur, and all its branches.
Having realized the strategic importance of Changchun's location with respect to Japan, China and Russia, the Japanese Government sent a group of planners and engineers to Changchun to determine the best site for a new railway station.
Without the consent of the Chinese Government, Japan purchased or seized from local farmers the land on which the Changchun Railway Station was to be constructed as the centre of the South Manchuria Railway Affiliated Areas (SMRAA). In order to turn Changchun into the centre for extracting the agricultural and mineral resources of Manchuria, Japan developed a blueprint for Changchun and invested heavily in the construction of the city.
At the beginning of 1907, as the prelude to, and preparation for, the invasion and occupation of China, Japan initiated the planning programme of the SMRAA, which embodied distinctive colonial characteristics. The guiding ideology of the overall design was to build a high standard colonial city with sophisticated facilities, multiple functions and a large scale.
Accordingly, nearly ┬ź7 million on average was allocated on a year-by-year basis for urban planning and construction during the period 1907 to 1931.
The Treaty of Portsmouth formally ended the Russo-Japanese War of 1904ŌĆō05 and saw the transfer and assignment to the Empire of Japan in 1906 the railway between Changchun and Port Arthur, and all its branches.
Having realized the strategic importance of Changchun's location with respect to Japan, China and Russia, the Japanese Government sent a group of planners and engineers to Changchun to determine the best site for a new railway station.
Without the consent of the Chinese Government, Japan purchased or seized from local farmers the land on which the Changchun Railway Station was to be constructed as the centre of the South Manchuria Railway Affiliated Areas (SMRAA). In order to turn Changchun into the centre for extracting the agricultural and mineral resources of Manchuria, Japan developed a blueprint for Changchun and invested heavily in the construction of the city.
At the beginning of 1907, as the prelude to, and preparation for, the invasion and occupation of China, Japan initiated the planning programme of the SMRAA, which embodied distinctive colonial characteristics. The guiding ideology of the overall design was to build a high standard colonial city with sophisticated facilities, multiple functions and a large scale.
Accordingly, nearly ┬ź7 million on average was allocated on a year-by-year basis for urban planning and construction during the period 1907 to 1931.[Akira Koshizawa, Manchukuo Capital Planning (Jiangsu: Social Sciences Academic Press,2011), 26ŌĆō97]
The comprehensive plan was to ensure the comfort required by Japanese employees on Manchurian Railways, build up Changchun into a base for Japanese control of the whole Manchuria in order to provide an effective counterweight to Russia in this area of China.
The city's role as a rail hub was underlined in its planning and construction, the main design concepts of which read as follows: under conventional grid pattern terms, two geoplagiotropic boulevards were newly carved eastward and westward from the grand square of the new railway station. The two helped form two intersections with the gridded prototypes, which led to two circles of South and West. The two sub-civic centres served as axes on which eight radial roads were blazed that took the shape of a sectoral structure.
At that time, the radial circles and the design concept of urban roads were quite advanced and scientific. It activated to great extent the serious urban landscapes as well as clearly identifying the traditional gridded pattern.
With the new Changchun railway station as its centre, the urban plan divided the SMRAA into various specified areas: residential quarters 15%, commerce 33%, grain depot 19%, factories 12%, public entertainment 9%, and administrative organs (including a Japanese garrison) 12%.Japanese architecture
has been typified by wooden structures, elevated slightly off the ground, with tiled or thatched roofs. Sliding doors (''fusuma'') and other traditional partitions were used in place of walls, allowing the internal configuration of a space to ...
and culture had been widely applied to Manchukuo to highlight the special status of the Japanese puppet. Urban planning clearly stems from a culture, be it aggressive or creative. Changchun's planning and construction process serves as a good example.
Changchun expanded rapidly as the junction between of the Japanese-owned South Manchurian Railway and the Russian-owned Chinese Eastern Railway, remaining the break of gauge point between the Russian and standard gauges into the 1930s,
Manchukuo and World War II
On 10 March 1932 the capital of Manchukuo
Manchukuo, officially the State of Manchuria prior to 1934 and the Empire of (Great) Manchuria after 1934, was a puppet state of the Empire of Japan in Northeast China, Manchuria from 1932 until 1945. It was founded as a republic in 1932 afte ...
, a Japan-controlled puppet state in Manchuria, was established in Changchun.
Construction of Hsinking
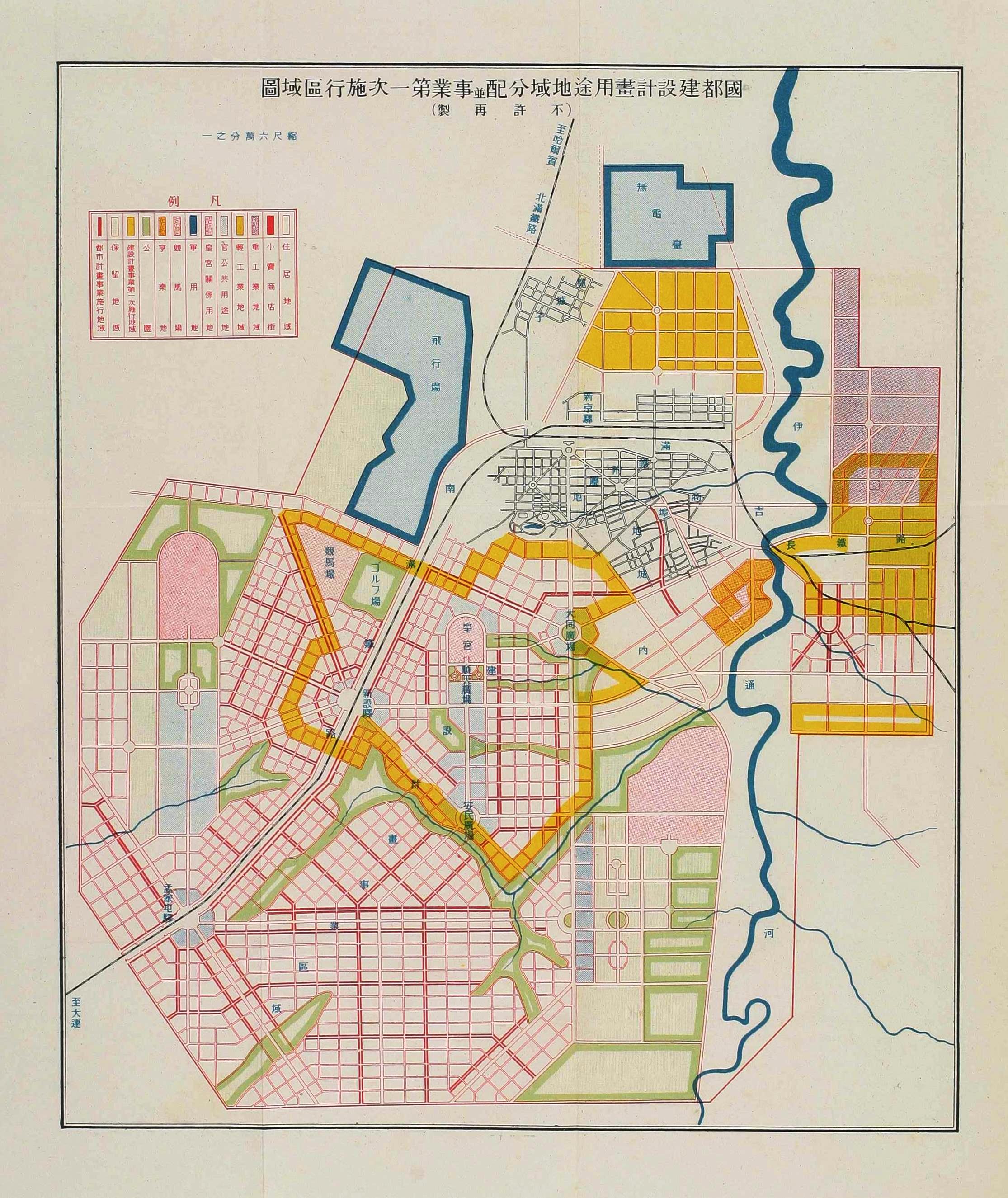 Hsinking was the only Direct-controlled municipality () in Manchukuo after
Hsinking was the only Direct-controlled municipality () in Manchukuo after Harbin
Harbin (; mnc, , v=Halbin; ) is a sub-provincial city and the provincial capital and the largest city of Heilongjiang province, People's Republic of China, as well as the second largest city by urban population after Shenyang and largest ...
was incorporated into the jurisdiction of Binjiang Province
Binjiang Province (Chinese: µ┐▒µ▒¤ń£ü) was one of the provinces of Manchukuo. Binjiang was founded on December 1, 1934 and was dissolved in August 1945. Binjiang had a mix of Chinese, Korean, Japanese, and Russian people. Binjiang was created whe ...
. In March 1932, the Inspection Division of South Manchuria Railway started to draw up the Metropolitan Plan of Great Hsinking (). The Bureau of capital construction () which was directly under the control of State Council of Manchukuo was established to take complete responsibility of the formulation and the implementation of the plan.Kuniaki Koiso
was a Japanese general in the Imperial Japanese Army, Governor-General of Korea and Prime Minister of Japan from 1944 to 1945.
After Japan's defeat in World War II, he was convicted of war crimes and sentenced to life imprisonment.
Early lif ...
, the Chief of Staff of the Kwantung Army, and Yasuji Okamura, the Vice Chief-of-Staff, finalized the plan of a construction area. The Metropolitan Plan of Great Hsinking was influenced by the renovation plan of Paris in the 19th century, the garden city movement, and theories of American cities' planning and design in the 1920s. The city development plan included extensive tree planting. By 1934 Hsinking was known as ''the Forest Capital'' with Jingyuetan Park built, which is now China's largest Plantation and a AAAA-rated recreational area.
In accordance with the Metropolitan Plan of Great Hsinking, the area of publicly shared land (including the Imperial Palace, government offices, roads, parks and athletic grounds) in Hsinking was , whilst the area of residential, commercial and industrial developments was planned to be . However, Hsinking's population exceeded the prediction of 500,000 by 1940. In 1941, the Capital Construction Bureau modified the original plan, which expanded the urban area to . The new plan also focused on the construction of satellite towns around the city with a planning of land per capita.
Japanese chemical warfare agents
In 1936, the Imperial Japanese Army established Unit 100 to develop plague biological weapons, although the declared purpose of Unit 100 was to conduct research about diseases originating from animals. During the Second Sino-Japanese War (1937ŌĆō1945) and World War II the headquarters of Unit 100 ("Wakamatsu Unit") was located in downtown Hsinking, under command of veterinarian Yujiro Wakamatsu. This facility was involved in research of animal vaccines to protect Japanese resources, and, especially, biological-warfare. Diseases were tested for use against Soviet and Chinese horses and other livestock. In addition to these tests, Unit 100 ran a bacteria factory to produce the pathogens needed by other units. Biological sabotage testing was also handled at this facility: everything from poisons to chemical crop destruction.
Siege of Changchun
 On 20 August 1945 the city was captured by the Soviet Red Army and renamed Changchun.
On 20 August 1945 the city was captured by the Soviet Red Army and renamed Changchun.[LTC David M. Glantz]
"August Storm: The Soviet 1945 Strategic Offensive in Manchuria"
. Leavenworth Papers No. 7, Combat Studies Institute, February 1983, Fort Leavenworth Kansas. The Russians maintained a presence in the city during the Soviet occupation of Manchuria
The Soviet occupation of Manchuria took place after the Red Army invaded the Japanese puppet state of Manchukuo in August 1945; the occupation would continue until Soviet forces withdrew in May 1946.
History
On 11 February 1945, the Big Three ( ...
until 1946.
National Revolutionary Army
The National Revolutionary Army (NRA; ), sometimes shortened to Revolutionary Army () before 1928, and as National Army () after 1928, was the military arm of the Kuomintang (KMT, or the Chinese Nationalist Party) from 1925 until 1947 in China ...
forces under Zheng Dongguo occupied the city in 1946, but were unable to hold the countryside against Lin Biao's People's Liberation Army
The People's Liberation Army (PLA) is the principal military force of the People's Republic of China and the armed wing of the Chinese Communist Party (CCP). The PLA consists of five service branches: the Ground Force, Navy, Air Force, ...
forces during the Chinese Civil War. The city fell to the Chinese Communist Party in 1948 after the five-month Siege of Changchun, and the communist victory was a turning point which allowed an offensive to capture the remainder of Mainland China. Between 10 and 30 percent[China Is Wordless on Traumas of Communists' Rise]
, Andrew Jacobs, New York Times, 1 October 2009 of the civilian population starved to death under the siege; estimates range from 150,000[Chang, Jung; Halliday, Jon. 2006. ''Mao: The Unknown Story''. London: Vintage Books. p383.] the PRC government avoids all mention of the siege.
People's Republic
Renamed Changchun by the People's Republic of China government, it became the capital of Jilin in 1954. The Changchun Film Studio is also one of the remaining film studios of the era. Changchun Film Festival has become a unique gala for film industries since 1992.[FAW Group Steps up Global Expansion](_blank)
FAW Official Site, 27 March 2007 and production of the Jiefang CA-10 truck, based on the Soviet ZIS-150 started in 1956.[About FAW > Key Events](_blank)
FAW Official Site Soviet Union lent assistance during these early years, providing technical support, tooling, and production machinery.Eternal_Spring_(film)
''Eternal Spring'' () is a 2022 Canadian animated documentary film, directed by Jason Loftus and released in 2022.Patrick Mullen"Eternal Spring Review: Animating an Awakening" ''Point of View'', May 1, 2022. Based around the animation of Chinese ...
.
Changchun hosted the 2007 Winter Asian Games
The 6th Asian Winter Games () were held in Changchun, Jilin, China from January 28 to February 4, 2007. The Winter Games are a celebration of Winter sports in Asia. This was the second time that China hosted the Asian Winter Games; the first wa ...
.
Geography
 Changchun lies in the middle portion of the Northeast China Plain. Its municipality area is located at latitude 43┬░ 05ŌĆ▓ŌłÆ45┬░ 15ŌĆ▓ N and longitude 124┬░ 18ŌĆ▓ŌłÆ127┬░ 02' E. The total area of Changchun municipality is , including metro areas of , and a city proper area of . The city is situated at a moderate elevation, ranging from within its administrative region.
Changchun lies in the middle portion of the Northeast China Plain. Its municipality area is located at latitude 43┬░ 05ŌĆ▓ŌłÆ45┬░ 15ŌĆ▓ N and longitude 124┬░ 18ŌĆ▓ŌłÆ127┬░ 02' E. The total area of Changchun municipality is , including metro areas of , and a city proper area of . The city is situated at a moderate elevation, ranging from within its administrative region.
Climate
Changchun has a four-season, monsoon-influenced, humid continental climate ( K├Čppen ''Dwa''). Winters are long (lasting from November to March), cold, and windy, but dry, due to the influence of the Siberian anticyclone
The Siberian High (also Siberian Anticyclone; russian: ąÉąĘąĖą░čéčüą║ąĖą╣ ą░ąĮčéąĖčåąĖą║ą╗ąŠąĮ (''Aziatsky antitsiklon'')) is a massive collection of cold dry air that accumulates in the northeastern part of Eurasia from September until April. It ...
, with a January mean temperature of . Spring and autumn are somewhat short transitional periods, with some precipitation, but are usually dry and windy. Summers are hot and humid, with a prevailing southeasterly wind due to the East Asian monsoon; July averages . Snow is usually light during the winter, and annual rainfall is heavily concentrated from June to August. With monthly percent possible sunshine ranging from 47 percent in July to 66 percent in January and February, a typical year will see around 2,617 hours of sunshine, and a frost-free period of 140 to 150 days. Extreme temperatures have ranged from to .
Administrative divisions
 The sub-provincial city of Changchun has direct jurisdiction over 7
The sub-provincial city of Changchun has direct jurisdiction over 7 districts
A district is a type of administrative division that, in some countries, is managed by the local government. Across the world, areas known as "districts" vary greatly in size, spanning regions or counties, several municipalities, subdivisions o ...
, 3 county-level cities and 1 County:
Demographics
According to the '' Sixth China Census'', the total population of the City of Changchun reached 7.677 million in 2010.[
] The statistics in 2011 estimated the total population to be 7.59 million. The birth rate was 6.08 per thousand and the death rate was 5.51 per thousand. The urban area had a population of 3.53 million people. In 2010 the sex ratio of the city population was 102.10 males to 100 females.
Ethnic groups
As in most of Northeastern China the ethnic makeup of Changchun is predominantly Han nationality
The Han Chinese () or Han people (), are an East Asian ethnic group native to China. They constitute the world's largest ethnic group, making up about 18% of the global population and consisting of various subgroups speaking distinctive ...
(96.57 percent), with several other minority nationalities.
Culture
Dialect
The most commonly spoken dialect in Changchun is the Northeastern Mandarin, which is originated from the mix of several languages spoken by immigrants from Hebei and Shandong
Shandong ( , ; ; alternately romanized as Shantung) is a coastal province of the People's Republic of China and is part of the East China region.
Shandong has played a major role in Chinese history since the beginning of Chinese civilizati ...
. Then, after the PRC was established, the rapid economic growth in Changchun attracted a huge amount of immigrants from various places, so the northeastern dialect spoken in urban areas of Changchun is closer to the Mandarin Chinese than the in rural areas because the immigrants had a great impact on the northeastern dialect spoken in urban areas.
Religion
Changchun has five major religions: Buddhism, Taoism, Catholicism, Protestantism (locally called "Christianity"), and Islam. There are 396 government-approved places for religious activities and worship services.
Places of interest
Jilin Provincial Museum
The Jilin Provincial Museum () is a first-grade museum in Changchun, Jilin province, China, dedicated to history and art. It is a subordinate unit of the Jilin Province Department of Culture and Tourism.
History
The Jilin Provincial Museum was ...
, a national first-grade museum, is located in Changchun. The museum was moved to Changchun from Jilin City after the transfer of the provincial government seat.Nanguan District
Nanguan District () is one of seven districts of the prefecture-level city of Changchun, the capital of Jilin Province, Northeast China, and forms part of the urban core. It borders the districts of Kuancheng to the north, Erdao to the northe ...
near Jingyuetan Park.Manchukuo
Manchukuo, officially the State of Manchuria prior to 1934 and the Empire of (Great) Manchuria after 1934, was a puppet state of the Empire of Japan in Northeast China, Manchuria from 1932 until 1945. It was founded as a republic in 1932 afte ...
ministries which are Ministry of Public Safety, Ministry of Justice, Ministry of Economy, Ministry of Communications, Ministry of Agriculture, Ministry of Culture and Education, Ministry of Foreign Affairs, Ministry of Civil Affairs that has recently become a sightseeing highlight because of their unique combined Chinese, Japanese and Manchurian architecture.
Economy
Changchun achieved a gross domestic product (GDP) of RMB332.9 billion in 2010, representing a rise of 15.3 percent year on year. Primary industry output increased by 3.3 percent to RMB25.27 billion. Secondary industry output experienced an increase of 19.0 percent, reaching RMB171.99 billion, while the tertiary industry output increased 12.6 percent to RMB135.64 billion. The GDP per capita
Lists of countries by GDP per capita list the countries in the world by their gross domestic product (GDP) per capita. The lists may be based on nominal or purchasing power parity GDP. Gross national income (GNI) per capita accounts for inflows ...
of Changchun was ┬ź58,691 in 2012, which equates to $9338. The GDP of Changchun in 2012 was RMB445.66 billion and increased 12.0 percent compared with 2011. The primary industry grew 4.3 percent to RMB31.71 billion. Secondary industry increased by RMB229.19 billion, which is a rise of 13.1 percent year on year. Tertiary industry of Changchun in 2012 grew 11.8 percent and increased by RMB184.76 billion.[
]
 The city's leading industries are production of automobiles, agricultural product processing, biopharmaceuticals, photo electronics, construction materials, and the energy industry.
The city's leading industries are production of automobiles, agricultural product processing, biopharmaceuticals, photo electronics, construction materials, and the energy industry.research and development
Research and development (R&D or R+D), known in Europe as research and technological development (RTD), is the set of innovative activities undertaken by corporations or governments in developing new services or products, and improving existi ...
centre in China, producing 9 percent of the country's automobiles in 2009. Changchun is home to China's biggest vehicle producer FAW (First Automotive Works
China FAW Group Corp., Ltd. (First Automobile Works) is a Chinese state-owned automobile manufacturer headquartered in Changchun, Jilin. ) Group, which manufactured the first Chinese truck in 1956 and car in 1958. The automaker's factories and associated housing and services occupy a substantial portion of the city's southwest end. Specific brands produced in Changchun include the Red Flag Red flag may refer to:
* Red flag (idiom), a metaphor for something signalling a problem
** Red flag warning, a term used by meteorologists
** Red flag (battle ensign), maritime flag signaling an intention to give battle with no quarter (fight to ...
luxury brand, as well as joint ventures with Audi, Volkswagen, and Toyota. In 2012, FAW sold 2.65 million units of auto. The sales revenue of FAW amounted to RMB 408.46 billion, representing a rise of 10.8% on year.passenger train
A passenger train is a train used to transport people along a railroad line. These trains may consist of unpowered passenger railroad cars (also known as coaches or carriages) hauled by one or more locomotives, or may be self-propelled; self pr ...
s, and 10 percent of tractors are produced in Changchun. Changchun Railway Vehicles, one of the main branches of China CNR Corporation, has a joint venture established with Bombardier Transportation
Bombardier Transportation was a Canadian-German rolling stock and rail transport manufacturer, headquartered in Berlin, Germany.
It was one of the world's largest companies in the rail vehicle and equipment manufacturing and servicing industry ...
to build Movia metro cars for the Guangzhou Metro and Shanghai Metro
The Shanghai Metro (; Shanghainese: ''Zaon6he5 Di6thiq7'') is a rapid transit system in Shanghai, operating urban and suburban transit services to 14 of its 16 municipal districts and to Kunshan, Jiangsu Province. Served as a part of Shangha ...
, and the Tianjin Metro.
Foreign direct investment
A foreign direct investment (FDI) is an investment in the form of a controlling ownership in a business in one country by an entity based in another country. It is thus distinguished from a foreign portfolio investment by a notion of direct co ...
in the city was US$3.68 billion in 2012, up 19.6% year on year.Celsius
The degree Celsius is the unit of temperature on the Celsius scale (originally known as the centigrade scale outside Sweden), one of two temperature scales used in the International System of Units (SI), the other being the Kelvin scale. The ...
, have Wi-Fi hubs and contain sleeper berths that fold into seats during the day.Shanghai Stock Exchange
The Shanghai Stock Exchange (SSE) is a stock exchange based in the city of Shanghai, China. It is one of the three stock exchanges operating independently in mainland China, the others being the Beijing Stock Exchange and the Shenzhen Stock Exc ...
in 1995. It has developed into a major conglomerate involved in a wide range of industries including property development
Real estate development, or property development, is a business process, encompassing activities that range from the renovation and re-lease of existing buildings to the purchase of raw land and the sale of developed land or parcels to others. R ...
, cement manufacturing, securities, coal mining
Coal mining is the process of extracting coal from the ground. Coal is valued for its energy content and since the 1880s has been widely used to generate electricity. Steel and cement industries use coal as a fuel for extraction of iron from ...
, pharmaceuticals
A medication (also called medicament, medicine, pharmaceutical drug, medicinal drug or simply drug) is a drug used to diagnose, cure, treat, or prevent disease. Drug therapy (pharmacotherapy) is an important part of the medical field and rel ...
and trading.
*Jilin Grain Group, a major processor of grains.
Development zones
Changchun Automotive Economic Trade and Development Zone
 Founded in 1993, the Changchun Automotive Trade Center was re-established as the Changchun Automotive Economic Trade and Development Zone in 1996. The development zone is situated in the southwest of the city and is adjacent to the China First Automobile Works Group Corporation and the Changchun Film ThemeCity. It covers a total area of approximately . Within the development zone lies an exhibition center and five specially demarcated industrial centers. Th
Founded in 1993, the Changchun Automotive Trade Center was re-established as the Changchun Automotive Economic Trade and Development Zone in 1996. The development zone is situated in the southwest of the city and is adjacent to the China First Automobile Works Group Corporation and the Changchun Film ThemeCity. It covers a total area of approximately . Within the development zone lies an exhibition center and five specially demarcated industrial centers. Th
Changchun Automobile Wholesale Center
began operations in 1994 and is the largest auto-vehicle and spare parts wholesale center in China. The other centers include a resale center for used auto-vehicles, a specialized center for industrial/commercial vehicles, and a tire wholesale center.
Changchun High Technology Development Zone
The zone is one of the first 27 state-level advanced technology development zones and is situated in the southern part of the city, covering a total area of . There are 18 full-time universities and colleges, 39 state and provincial-level scientific research institutions, and 11 key national laboratories. The zone is mainly focusing on developing five main industries, namely bio-engineering, automobile engineering, new material fabrication, photo-electricity, and information technology.
Changchun Economic and Technological Development Zone
Established in April 1993, the zone enjoys all the preferential policies stipulated for economic and technological development zones of coastal open cities.
Infrastructure
Changchun is a very compact city, planned by the Japanese with a layout of open avenues and public squares. The city is developing its layout in a long-term bid to alleviate pressure on limited land, aid economic development, and absorb a rising population. According to a draft plan up until 2020, the downtown area will expand southwards to form a new city center around Changchun World Sculpture Park, Weixing Square and their outskirts, and the new development zone.
Railways
 Changchun has three passenger rail stations, most trains only stop at the central Changchun railway station (), where there are multiple daily departures to other northeast cities such as Jilin City,
Changchun has three passenger rail stations, most trains only stop at the central Changchun railway station (), where there are multiple daily departures to other northeast cities such as Jilin City, Harbin
Harbin (; mnc, , v=Halbin; ) is a sub-provincial city and the provincial capital and the largest city of Heilongjiang province, People's Republic of China, as well as the second largest city by urban population after Shenyang and largest ...
, Shenyang
Shenyang (, ; ; Mandarin pronunciation: ), formerly known as Fengtian () or by its Manchu language, Manchu name Mukden, is a major China, Chinese sub-provincial city and the List of capitals in China#Province capitals, provincial capital of Lia ...
, and Dalian
Dalian () is a major sub-provincial port city in Liaoning province, People's Republic of China, and is Liaoning's second largest city (after the provincial capital Shenyang) and the third-most populous city of Northeast China. Located on the ...
, as well as other major cities throughout the country such as Beijing, Shanghai and Guangzhou. The HarbinŌĆōDalian high-speed railway which runs through three provinces in northeastern China, has a stop in Changchun. The new Changchun West railway station
Changchunxi West railway station is a railway station on the HarbinŌĆōDalian section of the BeijingŌĆōHarbin High-Speed Railway, and the ChangchunŌĆōJilin Intercity Railway. It is in the western part of Changchun, Jilin province, China.
See ...
, situated in the western end of urbanized area, is the station for the high-speed trains of the HarbinŌĆōDalian high-speed railway.
Public transport
Changchun Rail Transit is an urban rail transit service of Changchun. Its first line was opened on 30 October 2002, making Changchun the fifth metropolitan city in China to open rail transit.
Till November 2018, there are 5 lines in Changchun, including Line 1, Line 2, Line 3, Line 4, and Line 8. Changchun railway covers about 100.17 kilometers.
Till September 2019, there are 4 lines of Changchun Rail Transit under construction, including Line 6 and Line 9, as well as Line 2 West Extension and Line 3 East Extension. By 2025, the Changchun rail transit line network will consist of 10 lines with a total length of 341.62 kilometers.
In September 2019, the average daily passenger volume of Changchun Rail Transit reached 680,400 person, and the maximum daily passenger volume of its line network was 830,500 person on 13 November 2019. The total estimated passenger volume in 2019 is about 168 million person.
Road network
Changchun is linked to the national highway network through the Beijing ŌĆō Harbin Expressway (G1), the Ulanhot ŌĆō Changchun ŌĆō Jilin ŌĆō Hunchun Expressway (G12), the Changchun ŌĆō Shenzhen Expressway (G25), the Changchun ŌĆō Changbaishan Expressway (S1) and the busiest section in the province, the ChangchunŌĆōJilin North Highway. This section connects the two biggest cities in Jilin and is the trunk line for the social and economic communication of the two cities.
Air
Changchun Longjia International Airport is located north-east of Changchun urban area. The airport's construction began in 1998, and was intended to replace the older Changchun Dafangshen Airport, which was built in 1941. The airport opened for passenger service on 27 August 2005. The operation of the airport is shared by both Changchun and nearby Jilin City. The airport has scheduled flights to major cities including Beijing, Shanghai, Guangzhou, Shenzhen, Chengdu and 68 other cities. There are also scheduled international flights between Changchun and overseas cities such as Bangkok, Osaka, Khabarovsk
Khabarovsk ( rus, ąźą░ą▒ačĆąŠą▓čüą║, a=ąźą░ą▒ą░čĆąŠą▓čüą║.ogg, r=Hab├Īrovsk, p=x╔É╦łbar╔Öfsk) is the largest types of inhabited localities in Russia, city and the administrative centre of Khabarovsk Krai, Russia,Law #109 located from the China ...
,
Singapore, Tokyo and Vladivostok.
Military
Changchun is headquarters of the 16th Group Army
The 78th Group Army (), is a military formation of the Chinese People's Liberation Army Ground Forces (PLAGF). The 78th Group Army is one of twelve total group armies of the PLAGF, the largest echelon of ground forces in the People's Republic of ...
of the People's Liberation Army
The People's Liberation Army (PLA) is the principal military force of the People's Republic of China and the armed wing of the Chinese Communist Party (CCP). The PLA consists of five service branches: the Ground Force, Navy, Air Force, ...
, one of the four group armies that comprise the Northern Theater Command responsible for defending China's northeastern borders with Russia, Mongolia and North Korea.
Education
Universities and colleges
 Changchun has 27 regular institutions of full-time tertiary education with a total enrollment of approximate 160,000 students. Jilin University and Northeast Normal University are two key universities in China.
Changchun has 27 regular institutions of full-time tertiary education with a total enrollment of approximate 160,000 students. Jilin University and Northeast Normal University are two key universities in China.Jilin University
Jilin University (JLU; ; often abbreviated JLU or ) is a leading national research university located in Changchun, China. It is under the direct jurisdiction of China's Ministry of Education. It is a Chinese Ministry of Education Class A Doub ...
* Jilin University of Finance and Economics
* Jilin Agricultural University
* Northeast Normal University
* Jilin Engineering Normal University
* Changchun Institute of Technology
Middle schools
* High School Attached to Northeast Normal University
* Affiliated Middle School to Jilin University
* No.72 Middle School of Changchun
* Second experimental school of Jilin Province
* No.11 High School of Changchun
* Changchun No.6 middle school
* Changchun Foreign Languages School
Primary and secondary schools
International schools include:
* Changchun American International School
* Deutsche Internationale Schule Changchun
* St John's College Changchun
Sports and stadiums
 As a major Chinese city, Changchun is home to many professional sports teams:
* Jilin Northeast Tigers (Basketball), is a competitive team which has long been one of the major clubs fighting in China top-level league, CBA.
*
As a major Chinese city, Changchun is home to many professional sports teams:
* Jilin Northeast Tigers (Basketball), is a competitive team which has long been one of the major clubs fighting in China top-level league, CBA.
* Changchun Yatai
Changchun Yatai Football Club () is a professional Chinese football club that currently participates in the Chinese Super League under licence from the Chinese Football Association (CFA). The team is based in Changchun, Jilin and their home stadi ...
, who have played home soccer matches at the Development Area Stadium since 2009. In 2007 they won the Chinese Super League.
There are two major multi-purpose stadiums in Changchun, including Changchun City Stadium
Changchun Stadium (), also known as Nanling Stadium, is a multi-purpose stadium in Changchun, Jilin, China. It is predominantly used for football matches. The stadium holds 38,500. It is currently the home of Changchun Yatai of the Chinese Super ...
and Development Area Stadium.
* Changchun Wuhuan Gymnasium, the main venue of the 2007 Asian Winter Games
The 6th Asian Winter Games () were held in Changchun, Jilin, China from January 28 to February 4, 2007. The Winter Games are a celebration of Winter sports in Asia. This was the second time that China hosted the Asian Winter Games; the first wa ...
.
* It has an indoor speed skating arena, Jilin Provincial Speed Skating Rink, as one of five in China.
Jinlin Tseng Tou are a professional ice hockey team based in the city, and compete in the Russian-based Supreme Hockey League.
Film
* Changchun Film Group Corporation
* Changchun Film Festival
* Locale of The Farewell
People
* , 2010 Nobel Prize winner in chemistry, was born in Japan Imperial-era Hsinking
* Liu Xiaobo
Liu Xiaobo (; 28 December 1955 ŌĆō 13 July 2017) was a Chinese writer, literary critic, human rights activist, philosopher and Nobel Peace Prize laureate who called for political reforms and was involved in campaigns to end communist one-par ...
(), 2010 Nobel Peace Prize winner, was born in Changchun
* Song Zirui (King)
A song is a musical composition intended to be performed by the human voice. This is often done at distinct and fixed pitches (melodies) using patterns of sound and silence. Songs contain various forms, such as those including the repetition ...
(), The King, was born in Changchun
Twin towns and sister cities
* Nuuk, Sermersooq, Greenland
* Sendai
is the capital Cities of Japan, city of Miyagi Prefecture, the largest city in the T┼Źhoku region. , the city had a population of 1,091,407 in 525,828 households, and is one of Japan's 20 Cities designated by government ordinance of Japan, desig ...
, Miyagi, Japan
* Ulsan, Yeongnam, South Korea
* Flint, Michigan, United States
* Little Rock, Arkansas, United States
* Windsor, Ontario, Canada
* Ulan-Ude, Buryatia, Russia
* Minsk, Belarus
* Chongjin, North Hamgyong, North Korea
* Birmingham, West Midlands, United Kingdom
* Wolfsburg, Lower Saxony, Germany
* ┼Įilina, Slovakia
* Novi Sad, Vojvodina, Serbia
* Masterton
Masterton ( mi, Whakaoriori), a large town in the Greater Wellington Region of New Zealand, operates as the seat of the Masterton District (a territorial authority or local-government district). It is the largest town in the Wairarapa, a r ...
, Wellington Region, New Zealand
See also
* List of twin towns and sister cities in China
* Changchun smog
A dense wave of smog began in Northeast China, especially in major cities including Harbin, Changchun and Shenyang, as well as the surrounding Heilongjiang, Jilin, and Liaoning provinces on 20 October 2013. Unseasonably warm temperatures with ver ...
* Changchun Confucius Temple
* :People from Changchun
References
Citations
Sources
Changchun (China)ŌĆöBritannica Online Encyclopedia
External links
*
Changchun Government website
Changchun Foreign Affairs Information Portal
{{Authority control
Cities in Jilin
Provincial capitals in China
Capitals of former nations
Planned cities in China
 After Russia's loss of the southernmost section of this branch as a result of the Russo-Japanese War of 1904ŌĆō1905, the Kuancheng station (Kuanchengtze, in contemporary spelling) became the last Russian station on this branch. The next station just a short distance to the southŌĆöthe new "Japanese" Changchun stationŌĆöbecame the first station of the South Manchuria Railway,
"Provisional Convention ... concerning the junction of the Japanese and Russian Railways in Manchuria" ŌĆō 13 June 1907.
which now owned all the tracks running farther south, to L├╝shun, which they re-gauged to the
After Russia's loss of the southernmost section of this branch as a result of the Russo-Japanese War of 1904ŌĆō1905, the Kuancheng station (Kuanchengtze, in contemporary spelling) became the last Russian station on this branch. The next station just a short distance to the southŌĆöthe new "Japanese" Changchun stationŌĆöbecame the first station of the South Manchuria Railway,
"Provisional Convention ... concerning the junction of the Japanese and Russian Railways in Manchuria" ŌĆō 13 June 1907.
which now owned all the tracks running farther south, to L├╝shun, which they re-gauged to the  The Treaty of Portsmouth formally ended the Russo-Japanese War of 1904ŌĆō05 and saw the transfer and assignment to the Empire of Japan in 1906 the railway between Changchun and Port Arthur, and all its branches.
Having realized the strategic importance of Changchun's location with respect to Japan, China and Russia, the Japanese Government sent a group of planners and engineers to Changchun to determine the best site for a new railway station.
Without the consent of the Chinese Government, Japan purchased or seized from local farmers the land on which the Changchun Railway Station was to be constructed as the centre of the South Manchuria Railway Affiliated Areas (SMRAA). In order to turn Changchun into the centre for extracting the agricultural and mineral resources of Manchuria, Japan developed a blueprint for Changchun and invested heavily in the construction of the city.
At the beginning of 1907, as the prelude to, and preparation for, the invasion and occupation of China, Japan initiated the planning programme of the SMRAA, which embodied distinctive colonial characteristics. The guiding ideology of the overall design was to build a high standard colonial city with sophisticated facilities, multiple functions and a large scale.
Accordingly, nearly ┬ź7 million on average was allocated on a year-by-year basis for urban planning and construction during the period 1907 to 1931.Akira Koshizawa, Manchukuo Capital Planning (Jiangsu: Social Sciences Academic Press,2011), 26ŌĆō97
The comprehensive plan was to ensure the comfort required by Japanese employees on Manchurian Railways, build up Changchun into a base for Japanese control of the whole Manchuria in order to provide an effective counterweight to Russia in this area of China.
The city's role as a rail hub was underlined in its planning and construction, the main design concepts of which read as follows: under conventional grid pattern terms, two geoplagiotropic boulevards were newly carved eastward and westward from the grand square of the new railway station. The two helped form two intersections with the gridded prototypes, which led to two circles of South and West. The two sub-civic centres served as axes on which eight radial roads were blazed that took the shape of a sectoral structure.
At that time, the radial circles and the design concept of urban roads were quite advanced and scientific. It activated to great extent the serious urban landscapes as well as clearly identifying the traditional gridded pattern.
With the new Changchun railway station as its centre, the urban plan divided the SMRAA into various specified areas: residential quarters 15%, commerce 33%, grain depot 19%, factories 12%, public entertainment 9%, and administrative organs (including a Japanese garrison) 12%. Each block provided the railway station with supporting and systematic services dependent on its own functions.
In the meantime, a comprehensive system of judiciary and military police was established which was totally independent of China. That accounted for the widespread nature of military facilities within the urban construction area of , such as the railway garrison, the gendarmerie and the police department, with its 18 local police stations.
Perceiving Changchun as a ''tabula rasa'' upon which to construct new and sweeping conceptions of the built environment, the Japanese used the city as a practical laboratory to create two distinct and idealized urban milieus, each appropriate to a particular era. From 1906 to 1931, Changchun served as a key railway town through which the Japanese orchestrated an informal empire. Between 1932 and 1945, the city became home to a grandiose new Asian capital. Yet, while the fa├¦ades in the city and later the capital contrasted markedly, along with the attitudes of the state they upheld, the shifting styles of planning and architecture consistently attempted to represent Japanese rule as progressive, beneficent, and modern.
The development of Changchun, in addition to being driven by the railway system, suggested an important period of the Northeast modern architectural culture, reflecting Japanese urban design endeavours and revealing that county's ambition to invade and occupy China.
The Treaty of Portsmouth formally ended the Russo-Japanese War of 1904ŌĆō05 and saw the transfer and assignment to the Empire of Japan in 1906 the railway between Changchun and Port Arthur, and all its branches.
Having realized the strategic importance of Changchun's location with respect to Japan, China and Russia, the Japanese Government sent a group of planners and engineers to Changchun to determine the best site for a new railway station.
Without the consent of the Chinese Government, Japan purchased or seized from local farmers the land on which the Changchun Railway Station was to be constructed as the centre of the South Manchuria Railway Affiliated Areas (SMRAA). In order to turn Changchun into the centre for extracting the agricultural and mineral resources of Manchuria, Japan developed a blueprint for Changchun and invested heavily in the construction of the city.
At the beginning of 1907, as the prelude to, and preparation for, the invasion and occupation of China, Japan initiated the planning programme of the SMRAA, which embodied distinctive colonial characteristics. The guiding ideology of the overall design was to build a high standard colonial city with sophisticated facilities, multiple functions and a large scale.
Accordingly, nearly ┬ź7 million on average was allocated on a year-by-year basis for urban planning and construction during the period 1907 to 1931.Akira Koshizawa, Manchukuo Capital Planning (Jiangsu: Social Sciences Academic Press,2011), 26ŌĆō97
The comprehensive plan was to ensure the comfort required by Japanese employees on Manchurian Railways, build up Changchun into a base for Japanese control of the whole Manchuria in order to provide an effective counterweight to Russia in this area of China.
The city's role as a rail hub was underlined in its planning and construction, the main design concepts of which read as follows: under conventional grid pattern terms, two geoplagiotropic boulevards were newly carved eastward and westward from the grand square of the new railway station. The two helped form two intersections with the gridded prototypes, which led to two circles of South and West. The two sub-civic centres served as axes on which eight radial roads were blazed that took the shape of a sectoral structure.
At that time, the radial circles and the design concept of urban roads were quite advanced and scientific. It activated to great extent the serious urban landscapes as well as clearly identifying the traditional gridded pattern.
With the new Changchun railway station as its centre, the urban plan divided the SMRAA into various specified areas: residential quarters 15%, commerce 33%, grain depot 19%, factories 12%, public entertainment 9%, and administrative organs (including a Japanese garrison) 12%. Each block provided the railway station with supporting and systematic services dependent on its own functions.
In the meantime, a comprehensive system of judiciary and military police was established which was totally independent of China. That accounted for the widespread nature of military facilities within the urban construction area of , such as the railway garrison, the gendarmerie and the police department, with its 18 local police stations.
Perceiving Changchun as a ''tabula rasa'' upon which to construct new and sweeping conceptions of the built environment, the Japanese used the city as a practical laboratory to create two distinct and idealized urban milieus, each appropriate to a particular era. From 1906 to 1931, Changchun served as a key railway town through which the Japanese orchestrated an informal empire. Between 1932 and 1945, the city became home to a grandiose new Asian capital. Yet, while the fa├¦ades in the city and later the capital contrasted markedly, along with the attitudes of the state they upheld, the shifting styles of planning and architecture consistently attempted to represent Japanese rule as progressive, beneficent, and modern.
The development of Changchun, in addition to being driven by the railway system, suggested an important period of the Northeast modern architectural culture, reflecting Japanese urban design endeavours and revealing that county's ambition to invade and occupy China.  Hsinking was the only Direct-controlled municipality () in Manchukuo after
Hsinking was the only Direct-controlled municipality () in Manchukuo after  On 20 August 1945 the city was captured by the Soviet Red Army and renamed Changchun.LTC David M. Glantz
On 20 August 1945 the city was captured by the Soviet Red Army and renamed Changchun.LTC David M. Glantz Changchun lies in the middle portion of the Northeast China Plain. Its municipality area is located at latitude 43┬░ 05ŌĆ▓ŌłÆ45┬░ 15ŌĆ▓ N and longitude 124┬░ 18ŌĆ▓ŌłÆ127┬░ 02' E. The total area of Changchun municipality is , including metro areas of , and a city proper area of . The city is situated at a moderate elevation, ranging from within its administrative region. In the eastern portion of the city, there lies a small area of low mountains, with the Laodaodong Mountain, which has an altitude of 711 meters, being the highest. The city is also situated at the crisscross point of the third eastŌĆōwestward "Europe-Asia Continental Bridge". Changchun prefecture is dotted with 222 rivers and lakes. The Yitong River, a small tributary of the Songhua River, runs through the city proper.
Changchun lies in the middle portion of the Northeast China Plain. Its municipality area is located at latitude 43┬░ 05ŌĆ▓ŌłÆ45┬░ 15ŌĆ▓ N and longitude 124┬░ 18ŌĆ▓ŌłÆ127┬░ 02' E. The total area of Changchun municipality is , including metro areas of , and a city proper area of . The city is situated at a moderate elevation, ranging from within its administrative region. In the eastern portion of the city, there lies a small area of low mountains, with the Laodaodong Mountain, which has an altitude of 711 meters, being the highest. The city is also situated at the crisscross point of the third eastŌĆōwestward "Europe-Asia Continental Bridge". Changchun prefecture is dotted with 222 rivers and lakes. The Yitong River, a small tributary of the Songhua River, runs through the city proper.
 The sub-provincial city of Changchun has direct jurisdiction over 7
The sub-provincial city of Changchun has direct jurisdiction over 7  The city's leading industries are production of automobiles, agricultural product processing, biopharmaceuticals, photo electronics, construction materials, and the energy industry. Changchun is the largest automobile manufacturing,
The city's leading industries are production of automobiles, agricultural product processing, biopharmaceuticals, photo electronics, construction materials, and the energy industry. Changchun is the largest automobile manufacturing,  Founded in 1993, the Changchun Automotive Trade Center was re-established as the Changchun Automotive Economic Trade and Development Zone in 1996. The development zone is situated in the southwest of the city and is adjacent to the China First Automobile Works Group Corporation and the Changchun Film ThemeCity. It covers a total area of approximately . Within the development zone lies an exhibition center and five specially demarcated industrial centers. Th
Founded in 1993, the Changchun Automotive Trade Center was re-established as the Changchun Automotive Economic Trade and Development Zone in 1996. The development zone is situated in the southwest of the city and is adjacent to the China First Automobile Works Group Corporation and the Changchun Film ThemeCity. It covers a total area of approximately . Within the development zone lies an exhibition center and five specially demarcated industrial centers. Th Changchun has three passenger rail stations, most trains only stop at the central Changchun railway station (), where there are multiple daily departures to other northeast cities such as Jilin City,
Changchun has three passenger rail stations, most trains only stop at the central Changchun railway station (), where there are multiple daily departures to other northeast cities such as Jilin City,  Changchun has 27 regular institutions of full-time tertiary education with a total enrollment of approximate 160,000 students. Jilin University and Northeast Normal University are two key universities in China. Jilin University is also one of the largest universities in China, with more than 60,000 students.
* Changchun Normal University
* Changchun University
* Changchun University of Science and Technology
* Changchun University of Chinese Medicine
* Jilin College of the Arts
* Jilin Huaqiao Foreign Languages Institute, a private college offering bachelor study programs in foreign languages, international trade management and didactics
*
Changchun has 27 regular institutions of full-time tertiary education with a total enrollment of approximate 160,000 students. Jilin University and Northeast Normal University are two key universities in China. Jilin University is also one of the largest universities in China, with more than 60,000 students.
* Changchun Normal University
* Changchun University
* Changchun University of Science and Technology
* Changchun University of Chinese Medicine
* Jilin College of the Arts
* Jilin Huaqiao Foreign Languages Institute, a private college offering bachelor study programs in foreign languages, international trade management and didactics
*  As a major Chinese city, Changchun is home to many professional sports teams:
* Jilin Northeast Tigers (Basketball), is a competitive team which has long been one of the major clubs fighting in China top-level league, CBA.
*
As a major Chinese city, Changchun is home to many professional sports teams:
* Jilin Northeast Tigers (Basketball), is a competitive team which has long been one of the major clubs fighting in China top-level league, CBA.
*