cervical margins on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 The cervical margins of teeth are the surfaces where the crown and root meet, and is also referred to as the tooth's neck or cervical line.
The cervical margins of teeth are the surfaces where the crown and root meet, and is also referred to as the tooth's neck or cervical line.
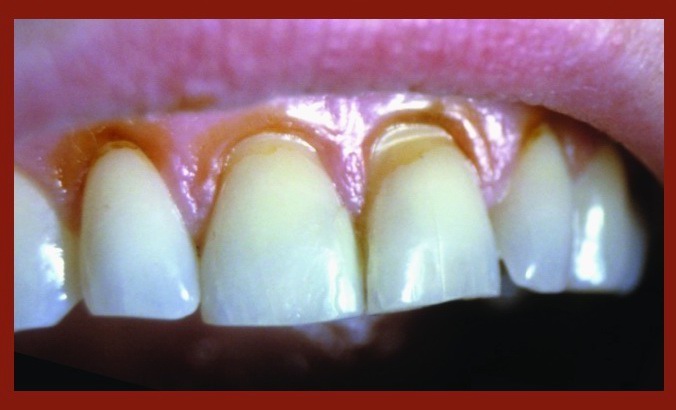 * Abfraction: Caused by occlusal forces leading to microfractures in the enamel and dentin
* Abrasion: Mechanical wear due to habits like aggressive tooth brushing
* Erosion: Chemical dissolution from acidic foods, beverages, or gastric reflux
* Abfraction: Caused by occlusal forces leading to microfractures in the enamel and dentin
* Abrasion: Mechanical wear due to habits like aggressive tooth brushing
* Erosion: Chemical dissolution from acidic foods, beverages, or gastric reflux
 The cervical margins of teeth are the surfaces where the crown and root meet, and is also referred to as the tooth's neck or cervical line.
The cervical margins of teeth are the surfaces where the crown and root meet, and is also referred to as the tooth's neck or cervical line.
Anatomy
The cervical margin, also known as the cervical line or neck of the tooth, represents the boundary between the enamel covering the crown and the cementum covering the root. The cementum typically overlaps the enamel, although in some cases, it may meet edge-to-edge. The cervical region includes the residual tooth structure between the gingival margin and the bone crest, encompassing the supragingival tooth area (STA) and gingival sulcus.Periodontal consideration
Biological width
The biological width is a crucial factor in maintaining periodontal health. It refers to the soft tissue dimensions coronal to the alveolar bone, consisting of junctional epithelium and supracrestal connective tissue attachment. However, by violating the biological width during restorative procedures can lead to periodontal breakdown, inflammation, gingival recession, and bone loss. Gargiulo et al. (1961) established that the biological width is approximately 2.04 mm, composed of epithelial and connective tissue components.Importance
Subgingival crown margins can contribute to gingivitis and periodontitis, leading to attachment loss, and improperly placed restoration margins and ill-fitting restorations violate the biological width, impacting periodontal health. Key considerations for subgingival margins include: proper contouring in the gingival third, polishing and rounding of the margin, ensuring an adequate zone of attached gingiva, avoiding biological width violation, regular maintenance and patient compliance to prevent periodontal issues.Relationship with Cemento-enamel junction
The curvature of the CEJ varies and is influenced by the height of the contact area and the crown’s buccolingual diameter. Proximal cervical curvatures are more pronounced on mesial surfaces, with central incisors exhibiting the most significant curvature, progressively decreasing toward posterior teeth . However, relationship between CEJ and cervical margin is often suggested as age related factor, as there could be extra gingiva covering the anatomical crown in a 10 - year old child, meanwhile old adults with periodontal disease can reveal their CEJ due to gingival recession. Despite this, gingival margin and CEJ are still consistently on the same or almost same location on a healthy adult. There are three possible relationships at the CEJ: Cementum overlaps enamel (65% of cases), cementum and enamel meet end-to-end (25%), dentin is exposed due to a gap between enamel and cementum (10%) and these variations can occur around different areas of the same tooth.Histology
Histologically, the cervical margin area can be appreciated by thegingiva
The gums or gingiva (: gingivae) consist of the mucosal tissue that lies over the mandible and maxilla inside the mouth. Gum health and disease can have an effect on general health.
Structure
The gums are part of the soft tissue lining of the ...
histology surrounding the curvature, or cemento-enamel junction that aligns on the same location on a healthy tooth individual. However, due to pathological reasons such as gingival recession
Gingival recession, also known as gum recession and receding gums, is the exposure in the roots of the teeth caused by a loss of gum tissue or retraction of the gingival margin from the crown of the teeth.periodontitis
Periodontal disease, also known as gum disease, is a set of inflammatory conditions affecting the tissues surrounding the teeth. In its early stage, called gingivitis, the gums become swollen and red and may bleed. It is considered the main c ...
, the gingival margin may get located below CEJ, hence histologically it is difficult to have a precise sample to study on.
Diseases of cervical margin area
Due to the cervical margin area being extremely close to the cervical part of tooth, the diseases related are usually overlapping with other diseases that could happen in the area.Carious lesions
Caries
Tooth decay, also known as caries,The word 'caries' is a mass noun, and is not a plural of 'carie'.'' is the breakdown of teeth due to acids produced by bacteria. The resulting cavities may be a number of different colors, from yellow to black ...
occurring at the cervical region of the tooth are often linked to carious cervical lesions (CCLs), which are commonly found in patients with poor oral hygiene or exposed root surfaces due to improper brushing technique.
Non Cervical carious lesions (NCCL)
 * Abfraction: Caused by occlusal forces leading to microfractures in the enamel and dentin
* Abrasion: Mechanical wear due to habits like aggressive tooth brushing
* Erosion: Chemical dissolution from acidic foods, beverages, or gastric reflux
* Abfraction: Caused by occlusal forces leading to microfractures in the enamel and dentin
* Abrasion: Mechanical wear due to habits like aggressive tooth brushing
* Erosion: Chemical dissolution from acidic foods, beverages, or gastric reflux
Common treatments
Non-Carious Cervical Lesion (NCCL) Management
Composite restorations commonly restore lost tooth structure, andGlass Ionomer Cement
A glass ionomer cement (GIC) is a dental restorative material used in dentistry as a filling material and luting cement, including for orthodontic bracket attachment. Glass-ionomer cements are based on the reaction of silicate glass-powder (c ...
commonly used too due to difficulty in moisture control
Deep Margin Elevation (DME)
As proposed by Diestschi and Spreafico, this technique involves coronally repositioning sub-gingival margins using composite resin. It aids in dental dam isolation, impression-taking, restoration placement, and finishing. It is a conservative alternative to crown lengthening, which requires the removal of bone and gingival tissue. Moreover, DME improves bonding strength and marginal integrity, especially in cases where indirect restorations are planned. The Immediate Dentin Sealing (IDS) technique, often performed alongside DME, enhances bond strength, reduces marginal leakage, and minimizes post-operative sensitivityClinical relevance
Endodontics
In endodontics, gaining access to the pulp chamber is an essential step to complete procedures such asRoot Canal Treatment
Root canal treatment (also known as endodontic therapy, endodontic treatment, or root canal therapy) is a treatment sequence for the infected pulp of a tooth that is intended to result in the elimination of infection and the protection of t ...
or Pulpotomy
Pulpotomy is a minimally invasive procedure performed in children on a primary tooth with extensive Tooth decay, caries but without evidence of root pathology. The Minimally invasive procedure, minimally invasive, Endodontics, endodontic techniqu ...
. According to the Law of Centrality in Endodontics, the pulp chamber of the tooth is located at the level of the cementoenamel junction.
The cervical margin area is extremely critical in determining the success of few restorations in dentistry, such as crowns and bridges
A bridge is a structure built to span a physical obstacle (such as a body of water, valley, road, or railway) without blocking the path underneath. It is constructed for the purpose of providing passage over the obstacle, which is usually somet ...
. A ''good preparation'' around the cervical margin area, or the tooth structure near the cervical margin ensures the preparation is able to provide marginal integrity for accurate fit of the crown, reduced overhang between crown and cement to prevent bacteria or plaque accumulation. and providing resistance to occlusal forces to prevent fracture of the restorative material.
References
{{Reflist Dental anatomy