Cepheid Inc on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Cepheid is an American molecular diagnostics company. Its systems automate traditional nucleic acid tests (tests for specific sequences of DNA or
 Cepheid owns the GeneXpert rapid molecular diagnostic system, its main product. The system was developed in the 1990s; the design remained substantially the same from the turn of the century to 2020. Similar tests have subsequently been developed by
Cepheid owns the GeneXpert rapid molecular diagnostic system, its main product. The system was developed in the 1990s; the design remained substantially the same from the turn of the century to 2020. Similar tests have subsequently been developed by
''Marsh's California Corporation Law''
4th ed., vol. 1 (New York: Aspen Publishers, 2004), 5–15 — 5–16.
RNA
Ribonucleic acid (RNA) is a polymeric molecule essential in various biological roles in coding, decoding, regulation and expression of genes. RNA and deoxyribonucleic acid ( DNA) are nucleic acids. Along with lipids, proteins, and carbohydra ...
). The tests can be used to identify and analyze pathogens and genetic disorders. Cepheid sells clinical tests for healthcare-associated infections, infectious diseases
An infection is the invasion of tissues by pathogens, their multiplication, and the reaction of host tissues to the infectious agent and the toxins they produce. An infectious disease, also known as a transmissible disease or communicable dise ...
, sexual health, oncology and genetics.
System
 Cepheid owns the GeneXpert rapid molecular diagnostic system, its main product. The system was developed in the 1990s; the design remained substantially the same from the turn of the century to 2020. Similar tests have subsequently been developed by
Cepheid owns the GeneXpert rapid molecular diagnostic system, its main product. The system was developed in the 1990s; the design remained substantially the same from the turn of the century to 2020. Similar tests have subsequently been developed by Abbott
Abbott may refer to:
People
*Abbott (surname)
*Abbott Handerson Thayer (1849–1921), American painter and naturalist
* Abbott and Costello, famous American vaudeville act
Places Argentina
* Abbott, Buenos Aires United States
* Abbott, Arkansas ...
and Roche.
The GeneXpert system identifies organisms from their DNA. It extracts genetic material from a sample and, in the case of RNA virus
An RNA virus is a virusother than a retrovirusthat has ribonucleic acid (RNA) as its genetic material. The nucleic acid is usually single-stranded RNA ( ssRNA) but it may be double-stranded (dsRNA). Notable human diseases caused by RNA viruses ...
es, it converts the RNA into DNA first. The GeneXpert test is basically an automated version of standard real-time PCR (polymerase chain reaction) amplification and detection.
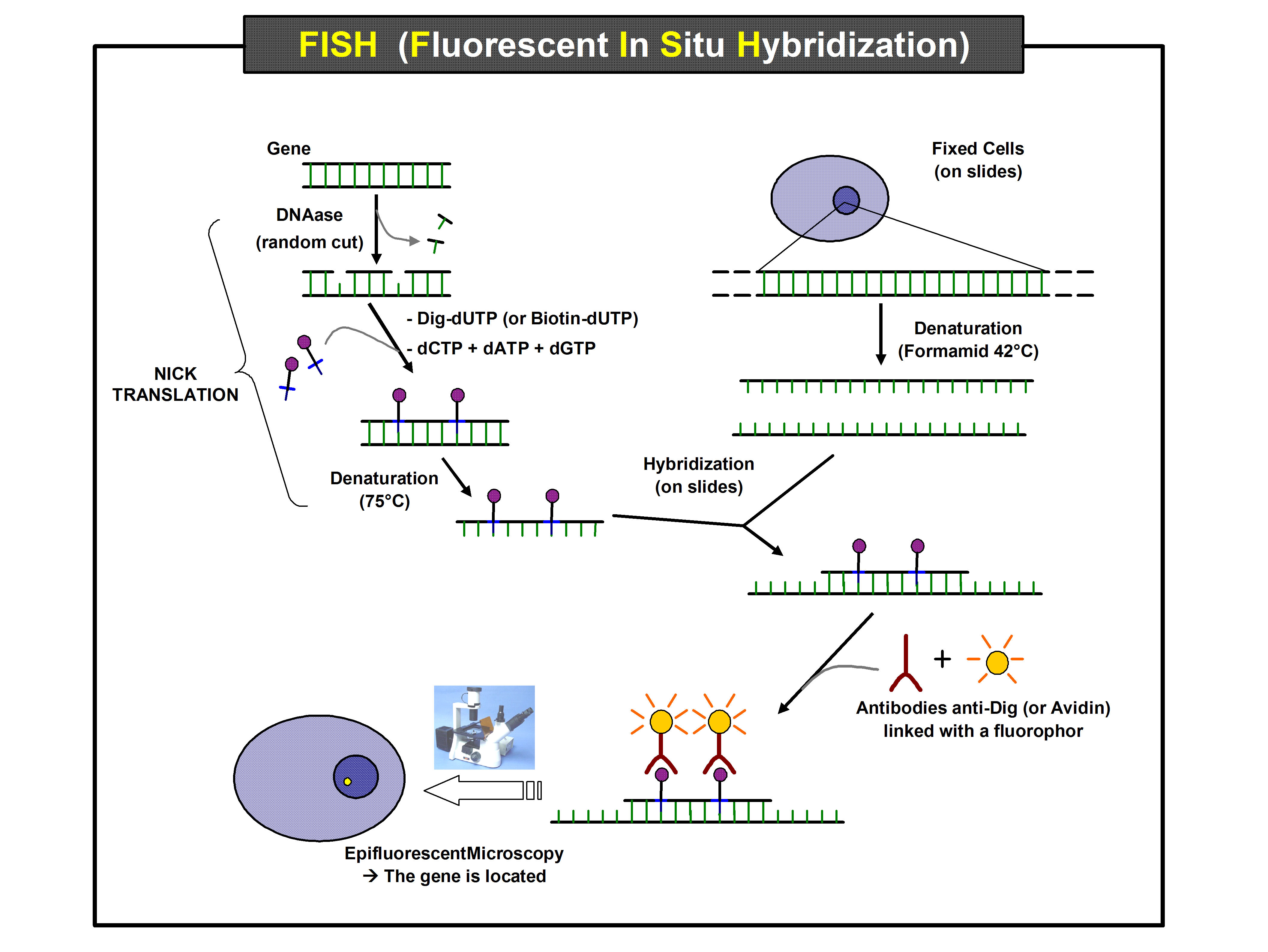
Each sample to be tested is added to a single-use GeneXpert cartridge, sold by Cepheid; after this, the tests are self-contained and fully-automated. The cartridge contains a series of injection-moulded plastic chambers, which hold the chemicals and the sample. To run the test, multiple cartridges are loaded into a desktop machine (also made by Cepheid, but reusable). The sample and chemicals are moved into the test chambers using microfluidics: there is a rotary valve in the center, and some small plungers; the plungers push the sample into the valve, the valve rotates to a new position, and the sample is then pulled out into a new chamber. The machine provides the temperature cycling needed for the PCR (much like a programmable oven). This makes many copies of DNA matching the sample (amplification). Finally, the presences or absence of the pathogen is detected using FISH probes. These are short sections of DNA which have been made to attach to a fluorescent molecule. If the DNA from the sample matches the DNA of the FISH probes, the two bind, and the sample fluoresces. An optical system detects the glow, or its absence. A test for a new disease can be made by simply swapping in a FISH probe that matches the sequence of the new disease.
Tests
Tests for which a GeneXpert cartridge is sold (not exhaustive):History
The key engineering innovations underlying GeneXpert technologies, as well as early versions of the product and field testing, were done at theLawrence Livermore National Laboratory
Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) is a federal research facility in Livermore, California, United States. The lab was originally established as the University of California Radiation Laboratory, Livermore Branch in 1952 in response ...
at the University of California. It was funded by the microelectromechanical systems (MEMS) program of the DARPA and the U.S. Army, as well as through LLNL’s internal budget.
Cepheid was founded in 1995 and mainly funded by the US military until the 2001 anthrax attacks
The 2001 anthrax attacks, also known as Amerithrax (a portmanteau of "America" and "anthrax", from its FBI case name), occurred in the United States over the course of several weeks beginning on September 18, 2001, one week after the September 11 ...
.
During the 2001 anthrax attacks
The 2001 anthrax attacks, also known as Amerithrax (a portmanteau of "America" and "anthrax", from its FBI case name), occurred in the United States over the course of several weeks beginning on September 18, 2001, one week after the September 11 ...
, U.S. federal agencies contracted with Cepheid to track the anthrax. In 2003, the company put a temporary hold on some healthcare development to work with defense contractor, Northrop Grumman, on a U.S. federal government contract to install anthrax detection systems at US Post Office sites nationwide.
Cepheid won the 2006 Industrial Design Excellence Awards for its product, Reagent Bead Dispenser.
The first clinical application for the GeneXpert System was introduced in 2006 with the U.S. FDA clearance of XpertGBS, a rapid molecular diagnostic test for Group B Streptococcus
''Streptococcus agalactiae'' (also known as group B streptococcus or GBS) is a gram-positive coccus (round bacterium) with a tendency to form chains (as reflected by the genus name '' Streptococcus''). It is a beta- hemolytic, catalase-negative ...
in expectant women. That same year, XpertGBS was categorized by the FDA as "Moderate Complexity" under the Clinical Laboratory Improvement Amendments (CLIA). It was the first amplified molecular diagnostic test using real-time PCR to receive this categorization. This allowed the test to be performed by the over 27,000 institutions registered for CLIA Moderate Complexity in addition to the approximately 7,000 institutions registered for High Complexity tests.
In 2012, Cepheid won a contract with the U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs for its MRSA reagent test kits.
As of March 31, 2014, Cepheid markets 14 U.S. FDA-cleared clinical in vitro diagnostic (IVD) tests in the U.S. and 16 IVD tests internationally and has placed 6,012 GeneXpert systems globally.
, there are over 23 000 GeneXpert machines globally, 7000 - 10,000 of them in Africa, Latin America and South-East Asia, with over a hundred in some African countries, due to long-term investment in tuberculosis-testing infrastructure by The Global Fund
The Global Fund to Fight AIDS, Tuberculosis and Malaria (or simply the Global Fund) is an international financing and partnership organization that aims to "attract, leverage and invest additional resources to end the epidemics of HIV/AIDS, t ...
, among others.
During the COVID-19 pandemic, Cepheid announced a partnership with Sherlock Biosciences
Sherlock Biosciences is a biotechnology company based in Cambridge, Massachusetts developing diagnostic tests using CRISPR-Cas13. The company was founded in 2019 by Feng Zhang, Jim Collins, Omar Abudayyeh, and Jonathan Gootenberg of the Broad Inst ...
in February 2020 to begin development of a CRISPR
CRISPR () (an acronym for clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats) is a family of DNA sequences found in the genomes of prokaryotic organisms such as bacteria and archaea. These sequences are derived from DNA fragments of bacte ...
-based diagnostic test for the SARS-CoV-2 (then called "2019-nCov") virus, to run on the same machines as Cepheid's 20-year-old GeneXpert tests, as there were machines already installed in hospitals. In March 2020, the company announced a rapid diagnostic test for SARS-CoV-2; the U.S. FDA granted an emergency use authorization for the test. The diagnostic is designed to run on any of the (over 23,000) existing Cepheid GeneXpert machines worldwide, with the standard 45 minute detection time.
Pricing controversy
There has been controversy around Cepheid's test-cartridge pricing. Cepheid announced that they would charge US$19.80 per COVID-19 test in developing countries (prices are higher in middle-income countries; for instance, GeneXpert TB tests cost $55-$82 per cartridge in Indonesia). Doctors without borders stated that that price was not affordable in countries where people live on less than two dollars a day. They estimated that the cost to Cepheid of providing the test is as low as $3, and called the offered price profiteering, asking that Cepheid make a more moderate profit by selling the tests for US$5 each. The Treatment Action Group (TAG) seconded this request, saying that the development of the tests, and their purchase and global deployment, has been done with public funds, while the owners of Cepeid (Danaher Corporation) made profits of $3 billion in 2019. They requested the same price reduction for all the tests using the same technique, including HIV, tuberculosis, andHepatitis C
Hepatitis C is an infectious disease caused by the hepatitis C virus (HCV) that primarily affects the liver; it is a type of viral hepatitis. During the initial infection people often have mild or no symptoms. Occasionally a fever, dark urine, a ...
, as the costs are similar regardless of the disease (see above). They pointed out that the cartridges for testing for COVID-19 were twice the price of nearly-identical cartridges for tuberculosis, . The International Union Against Tuberculosis and Lung Disease also gave public support. Some dozens of organizations worldwide had joined the “Time for $5” campaign .
Corporate status
Cepheid was founded in March 1996 by Thomas Gutshall, Bill McMillan, Dr. Kurt Petersen, Dr. Greg Kovacs, Steven Young and Dr. Allen Northrup. The company went public in 2000. The initial public offering was June 21, 2000 at US$6 per share. Cepheid stock was listed on theNasdaq
The Nasdaq Stock Market () (National Association of Securities Dealers Automated Quotations Stock Market) is an American stock exchange based in New York City. It is the most active stock trading venue in the US by volume, and ranked second ...
under the ticker symbol CPHD until it was acquired by Danaher in 2016.
The company's first CEO was Tom Gutshall, who held the position from 1996 to 2002. In April 2002, John L. Bishop was appointed CEO.
In August 2016, the company had a market capitalization
Market capitalization, sometimes referred to as market cap, is the total value of a publicly traded company's outstanding common shares owned by stockholders.
Market capitalization is equal to the market price per common share multiplied by t ...
of US$2.66 billion.
In late 2016, Danaher Corp. bought Cepheid for US$4 billion, citing a large base of already-installed test instruments, and a wide menu of tests that fit in them.
Cepheid is headquartered in Sunnyvale, California
Sunnyvale () is a city located in the Santa Clara Valley in northwest Santa Clara County in the U.S. state of California.
Sunnyvale lies along the historic El Camino Real and Highway 101 and is bordered by portions of San Jose to the nort ...
.
See also
* GeneXpert MTB/RIF (the tuberculosis test) * Nucleic acid test (the technique automated by Cepheid)Notes
* The legal name of the company is the single word Cepheid, with no indicator of corporate status in its name. This is legal in California.See Harold Marsh, Jr., R. Roy Finkle, Larry W. Sonsini, and Ann Yvonne Walker''Marsh's California Corporation Law''
4th ed., vol. 1 (New York: Aspen Publishers, 2004), 5–15 — 5–16.
References
{{reflist, 24em Companies established in 1996 2000 initial public offerings Companies formerly listed on the Nasdaq Companies associated with the COVID-19 pandemic 1996 establishments in the United States 1996 establishments in California