Centrocytes on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 A centrocyte generally refers to a
A centrocyte generally refers to a
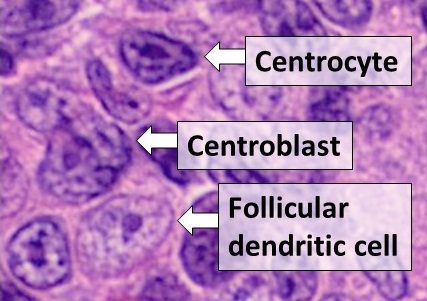 The dark zone of germinal centers contain proliferating centroblasts. Once these centroblasts are stimulated, they no longer divide, and proceed to move to the light zone of germinal centers. In the light zone, T follicular helper cells mediate centrocyte selection through CD40L and provide them with pro-survival signals. The centrocytes to compete for T follicular helper cell and dendritic cell help, allowing for selectivity towards centrocytes that bind to antigen with higher affinity. Centrocytes with high affinity are allowed to exit the germinal center as memory B cells or long-lived
The dark zone of germinal centers contain proliferating centroblasts. Once these centroblasts are stimulated, they no longer divide, and proceed to move to the light zone of germinal centers. In the light zone, T follicular helper cells mediate centrocyte selection through CD40L and provide them with pro-survival signals. The centrocytes to compete for T follicular helper cell and dendritic cell help, allowing for selectivity towards centrocytes that bind to antigen with higher affinity. Centrocytes with high affinity are allowed to exit the germinal center as memory B cells or long-lived
 A centrocyte generally refers to a
A centrocyte generally refers to a B cell
B cells, also known as B lymphocytes, are a type of white blood cell of the lymphocyte subtype. They function in the humoral immunity component of the adaptive immune system. B cells produce antibody molecules which may be either secreted or ...
with a cleaved nucleus, as may appear in e.g. follicular lymphoma.Table 12-8 in: 8th edition. Centrocytes are B cells that are found in the light zones of germinal centers. Centrocytes are the non-dividing progeny of Centroblasts, and although they are relatively similar in size, centrocytes lack distinct nucleoli and are more irregularly shaped than centroblasts Centrocytes also express the cell-surface hypermutated B-cell receptor following AID activation. This hypermutated B-cell receptor allows centrocytes to compete for binding of the antigen, internalize it, and then express the processed peptides through their MHC class II receptor. Centrocyte can also refer to a cell with a protoplasm that contains single and double granules of varying size stainable with hematoxylin, as seen in lesions of lichen planus, or a nondividing, activated B cell that expresses membrane immunoglobulin.
Development
 The dark zone of germinal centers contain proliferating centroblasts. Once these centroblasts are stimulated, they no longer divide, and proceed to move to the light zone of germinal centers. In the light zone, T follicular helper cells mediate centrocyte selection through CD40L and provide them with pro-survival signals. The centrocytes to compete for T follicular helper cell and dendritic cell help, allowing for selectivity towards centrocytes that bind to antigen with higher affinity. Centrocytes with high affinity are allowed to exit the germinal center as memory B cells or long-lived
The dark zone of germinal centers contain proliferating centroblasts. Once these centroblasts are stimulated, they no longer divide, and proceed to move to the light zone of germinal centers. In the light zone, T follicular helper cells mediate centrocyte selection through CD40L and provide them with pro-survival signals. The centrocytes to compete for T follicular helper cell and dendritic cell help, allowing for selectivity towards centrocytes that bind to antigen with higher affinity. Centrocytes with high affinity are allowed to exit the germinal center as memory B cells or long-lived plasma cell
Plasma cells, also called plasma B cells or effector B cells, are white blood cells that originate in the lymphoid organs as B lymphocytes and secrete large quantities of proteins called antibodies in response to being presented specific substan ...
s, while other selected centrocytes are allowed to reenter the cell cycle by T cells. The remaining centrocytes undergo apoptosis or return to the centroblast pool for further somatic hypermutation. Centrocytes that do not recognize antigen properly due to an altered B cell receptor will undergo apoptosis.
References
Lymphocytes {{Lymphatic-stub