Central Vermont Railway on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
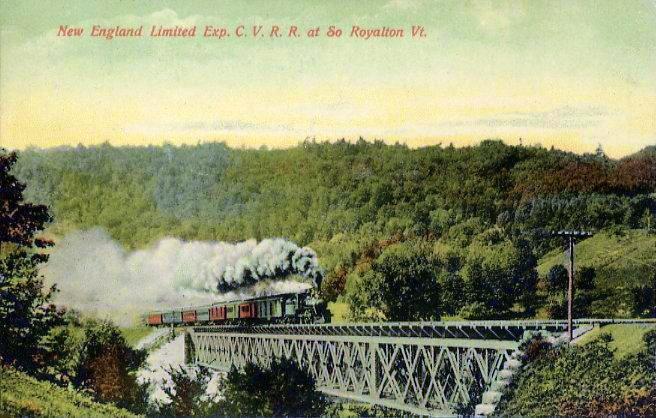
The Central Vermont Railway was a railroad that operated in the
 In 1889 the
In 1889 the
Central Vermont Railway Historical Society
* ttp://www.images.technomuses.ca/?en/stories/central_vermont/intro/page/1 Picturing the Past: The Central Vermont Railway - includes many railway photosbr>Mamacoke Company Portal to Central Vermont Railway Archives
* {{DEFAULTSORT:Central Vermont Railway Railway companies established in 1899 Railway companies disestablished in 1995 American companies established in 1899 American companies disestablished in 1995 Grand Trunk Railway subsidiaries Canadian National Railway subsidiaries Defunct Connecticut railroads Defunct Massachusetts railroads Defunct New Hampshire railroads Defunct Vermont railroads Defunct Quebec railways Former Class I railroads in the United States Standard gauge railways in the United States Predecessors of the Grand Trunk Railway Defunct New York (state) railroads Historic American Engineering Record in Vermont 1899 establishments in Vermont
U.S. state
In the United States, a state is a constituent political entity, of which there are 50. Bound together in a political union, each state holds governmental jurisdiction over a separate and defined geographic territory where it shares its sove ...
s of Connecticut
Connecticut () is the southernmost state in the New England region of the Northeastern United States. It is bordered by Rhode Island to the east, Massachusetts to the north, New York to the west, and Long Island Sound to the south. Its cap ...
, Massachusetts
Massachusetts (Massachusett language, Massachusett: ''Muhsachuweesut assachusett writing systems, məhswatʃəwiːsət'' English: , ), officially the Commonwealth of Massachusetts, is the most populous U.S. state, state in the New England ...
, New Hampshire
New Hampshire is a state in the New England region of the northeastern United States. It is bordered by Massachusetts to the south, Vermont to the west, Maine and the Gulf of Maine to the east, and the Canadian province of Quebec to the nor ...
, New York
New York most commonly refers to:
* New York City, the most populous city in the United States, located in the state of New York
* New York (state), a state in the northeastern United States
New York may also refer to:
Film and television
* '' ...
, and Vermont
Vermont () is a state in the northeast New England region of the United States. Vermont is bordered by the states of Massachusetts to the south, New Hampshire to the east, and New York to the west, and the Canadian province of Quebec to the ...
, as well as the Canadian province
Within the geographical areas of Canada, the ten provinces and three territories are sub-national administrative divisions under the jurisdiction of the Canadian Constitution. In the 1867 Canadian Confederation, three provinces of British Nort ...
of Quebec
Quebec ( ; )According to the Government of Canada, Canadian government, ''Québec'' (with the acute accent) is the official name in Canadian French and ''Quebec'' (without the accent) is the province's official name in Canadian English is ...
.
It connected Montreal
Montreal ( ; officially Montréal, ) is the second-most populous city in Canada and most populous city in the Canadian province of Quebec. Founded in 1642 as '' Ville-Marie'', or "City of Mary", it is named after Mount Royal, the triple- ...
, Quebec, with New London, Connecticut
New London is a seaport city and a port of entry on the northeast coast of the United States, located at the mouth of the Thames River in New London County, Connecticut. It was one of the world's three busiest whaling ports for several decades ...
, using a route along the shores of Lake Champlain
, native_name_lang =
, image = Champlainmap.svg
, caption = Lake Champlain-River Richelieu watershed
, image_bathymetry =
, caption_bathymetry =
, location = New York/Vermont in the United States; and Quebec in Canada
, coords =
, type =
, ...
, through the Green Mountains
The Green Mountains are a mountain range in the U.S. state of Vermont. The range runs primarily south to north and extends approximately from the border with Massachusetts to the border with Quebec, Canada. The part of the same range that is i ...
and along the Connecticut River valley, as well as Montreal to Boston
Boston (), officially the City of Boston, is the capital city, state capital and List of municipalities in Massachusetts, most populous city of the Commonwealth (U.S. state), Commonwealth of Massachusetts, as well as the cultural and financ ...
, Massachusetts, through a connection with the Boston and Maine Railroad
The Boston and Maine Railroad was a U.S. Class I railroad in northern New England. Originally chartered in 1835, it became part of what was the Pan Am Railways network in 1983 (most of which was purchased by CSX in 2022).
At the end of 1970 ...
at White River Junction, Vermont
White River Junction is an unincorporated village and census-designated place (CDP) in the town of Hartford in Windsor County, Vermont, United States. The population was 2,528 at the 2020 census, up from 2,286 in 2010, making it the largest com ...
.
History
The Vermont Central Railroad was chartered October 31, 1843, to build a line across the center of Vermont, running from Burlington on Lake Champlain east to Montpelier, and then southeast and south to Windsor on the Connecticut River. Initial plans had the main line running through Montpelier. However, due to the difficulty of building through the Williamstown Gulf, a narrow valley south of Barre, Vermont, and to land interests of Charles Paine inNorthfield, Vermont
Northfield is a town in Washington County, Vermont, United States. The town lies in a valley within the Green Mountains and has been home to Norwich University since 1866. It contains the village of Northfield, where over half of the population ...
, a course to the west was selected, leaving the state capital to be served by a short branch line. Construction began on December 15, 1845, and the first section, from White River Junction west to Bethel
Bethel ( he, בֵּית אֵל, translit=Bēṯ 'Ēl, "House of El" or "House of God",Bleeker and Widegren, 1988, p. 257. also transliterated ''Beth El'', ''Beth-El'', ''Beit El''; el, Βαιθήλ; la, Bethel) was an ancient Israelite san ...
, opened on June 26, 1848. Subsequent sections opened to Roxbury Roxbury may refer to:
Places
;Canada
* Roxbury, Nova Scotia
* Roxbury, Prince Edward Island
;United States
* Roxbury, Connecticut
* Roxbury, Kansas
* Roxbury, Maine
* Roxbury, Boston, a municipality that was later integrated into the city of Bosto ...
on September 17, 1848, Northfield on October 10, 1848, Montpelier (including the branch from Montpelier Junction) on June 20, 1849, Middlesex
Middlesex (; abbreviation: Middx) is a historic county in southeast England. Its area is almost entirely within the wider urbanised area of London and mostly within the ceremonial county of Greater London, with small sections in neighbourin ...
on August 30, 1849, Waterbury
Waterbury is a city in the U.S. state of Connecticut on the Naugatuck River, southwest of Hartford and northeast of New York City. Waterbury is the second-largest city in New Haven County, Connecticut. According to the 2020 US Census, in 20 ...
on September 29, 1849, and the full distance to Burlington on December 31, 1849. The part along the Connecticut River from Hartford south to Windsor opened on February 13, 1849.
The Vermont and Canada Railroad was chartered October 31, 1845, as a continuation of the Vermont Central north and west to Rouses Point, New York
Rouses Point is a village in Clinton County, New York, United States, along the 45th parallel. The population was 2,209 at the 2010 census. The village is named after Jacques Rouse, a French Canadian soldier who fought alongside the Americans ...
, splitting at Essex Junction, Vermont
Essex Junction is a city in Chittenden County, Vermont, United States. As of the 2020 U.S. census, the population was 10,590. It was incorporated as a village on November 15, 1892. Essex Junction became Vermont’s 10th city on July 1, 2022.
...
(east of Burlington) and running north via St. Albans and Swanton. A branch split at Swanton and ran north to the border with Canada
Canada is a country in North America. Its ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, covering over , making it the world's second-largest country by tota ...
. On August 24, 1849, the Vermont Central leased the Vermont and Canada, and it was completed in 1851. However, the Vermont Central defaulted on rental payments, and the Vermont and Canada returned to its original owners on June 28, 1852. The lease was later reinstated.
The Montreal and Vermont Junction Railway was chartered in 1860 and opened in the 1860s, extending the Vermont and Canada's branch from the international border north to St. Johns, Quebec
Saint-Jean-sur-Richelieu () is a city in eastern Montérégie in the Canadian province of Quebec, about southeast of Montreal. It is situated on the west bank of the Richelieu River at the northernmost navigable point of Lake Champlain. As of De ...
, on the Grand Trunk Railway
The Grand Trunk Railway (; french: Grand Tronc) was a railway system that operated in the Canadian provinces of Quebec and Ontario and in the American states of Connecticut, Maine, Michigan, Massachusetts, New Hampshire, and Vermont. The rai ...
's Montreal and Champlain Railroad
The Champlain and St. Lawrence Railroad (C&SL) was a historic railway in Lower Canada, the first Canadian public railway and one of the first railways built in British North America.
Origin
The C&SL was financed by Montreal entrepreneur and br ...
. From opening it was operated as an extension of the Vermont and Canada.
The Sullivan County Railroad continued south from Windsor to Bellows Falls, Vermont
Bellows Falls is an incorporated village located in the town of Rockingham in Windham County, Vermont, United States. The population was 2,747 at the 2020 census. Bellows Falls is home to the Green Mountain Railroad, a heritage railroad; the ...
, where it met the Cheshire Railroad
The Fitchburg Railroad is a former railroad company, which built a railroad line across northern Massachusetts, United States, leading to and through the Hoosac Tunnel. The Fitchburg was leased to the Boston and Maine Railroad in 1900. The main li ...
towards Boston
Boston (), officially the City of Boston, is the capital city, state capital and List of municipalities in Massachusetts, most populous city of the Commonwealth (U.S. state), Commonwealth of Massachusetts, as well as the cultural and financ ...
. At first it was operated by the Central Vermont, but later the Boston and Maine Railroad
The Boston and Maine Railroad was a U.S. Class I railroad in northern New England. Originally chartered in 1835, it became part of what was the Pan Am Railways network in 1983 (most of which was purchased by CSX in 2022).
At the end of 1970 ...
gained control of it, giving trackage rights
Railway companies can interact with and control others in many ways. These relationships can be complicated by bankruptcies.
Operating
Often, when a railroad first opens, it is only a short spur of a main line. The owner of the spur line may c ...
to the Central Vermont. Similarly, the Vermont Valley Railroad, running south from Bellows Falls to the New London Northern Railroad in Brattleboro, was originally owned by the Rutland Railroad
The Rutland Railroad was a railroad in the northeastern United States, located primarily in the state of Vermont but extending into the state of New York at both its northernmost and southernmost ends. After its closure in 1961, parts of the ...
and later by the B&M.
In 1867 the Vermont Central leased the Stanstead, Shefford and Chambly Railroad, running east from St. Johns to Waterloo, Quebec
Waterloo ( 2021 population 4,920) is a city in the Canadian province of Quebec. It is included in La Haute-Yamaska Regional County Municipality, in the administrative area of Estrie. Completely encircled by the township of Shefford, this reside ...
. The Waterloo and Magog Railway
Waterloo most commonly refers to:
* Battle of Waterloo, a battle on 18 June 1815 in which Napoleon met his final defeat
* Waterloo, Belgium, where the battle took place.
Waterloo may also refer to:
Other places
Antarctica
* King George Island ( ...
was later built as an extension from Waterloo south to Magog.
The Vermont Central leased the Ogdensburg and Lake Champlain Railroad
The Ogdensburg and Lake Champlain Railroad was founded in 1849 as the Northern Railroad running from Ogdensburg to Rouses Point, New York. The railroad was leased by rival Central Vermont Railroad for several decades, ending in 1896. It was pur ...
on March 1, 1870, extending its line from Rouses Point west to Ogdensburg, New York
Ogdensburg ( moh, Kaniatarahòn:tsi) is a city in St. Lawrence County, New York, United States. The population was 10,436 at the 2019 census. In the late 18th century, European-American settlers named the community after American land owner and d ...
. On January 1, 1871, the Vermont Central leased the Rutland Railroad
The Rutland Railroad was a railroad in the northeastern United States, located primarily in the state of Vermont but extending into the state of New York at both its northernmost and southernmost ends. After its closure in 1961, parts of the ...
system, giving it routes from Burlington to Bellows Falls, Vermont
Bellows Falls is an incorporated village located in the town of Rockingham in Windham County, Vermont, United States. The population was 2,747 at the 2020 census. Bellows Falls is home to the Green Mountain Railroad, a heritage railroad; the ...
, and Chatham, New York
Chatham is a town in Columbia County, New York, United States. The population was 4,104 at the 2020 census, down from the 2010 census.
The town has a village also called Chatham on its southern town line. The town is at the northern border of ...
. The New London Northern Railroad was leased on December 1, 1871. On November 2, 1872, the name was changed to the Central Vermont Railroad.
Though chartered as an independent entity in 1867, control of the Missisquoi Railroad was gained shortly thereafter, and it was formally leased in July 1873, providing a branch from St. Albans northeast to Richford, Vermont
Richford is a town in Franklin County, Vermont, United States, located along the Canada–United States border. The population was 2,346 at the 2020 census.
Richford is the birthplace of R. G. LeTourneau, an industrialist who founded LeTournea ...
. It was operated until November 15, 1877, when the Connecticut and Passumpsic Rivers Railroad took it over. The company was reorganized in December 1886 as the Missisquoi Valley Railway, and was once again leased to the Central Vermont.
The Montpelier and White River Railroad Montpelier or Montpellier may refer to:
Locations Australia
* Montpelier (Queensland), a hill in the suburb of Bowen Hills, Brisbane
Canada
* Montpellier, Quebec
France
* Montpellier, a city in southern France
** The University of Montpellier
...
opened in 1876 and was leased to the Central Vermont, running from the end of the Montpelier Branch south to and beyond Barre.
The Consolidated Railway was formed on June 30, 1884, to consolidate the Central Vermont and Vermont and Canada and to settle litigation between the two companies. A new Central Vermont Railroad was formed on July 1, 1884 to take over from the Consolidated Railway.
 In 1889 the
In 1889 the Burlington and Lamoille Railroad
The Central Vermont Railway was a railroad that operated in the U.S. states of Connecticut, Massachusetts, New Hampshire, New York, and Vermont, as well as the Canadian province of Quebec.
It connected Montreal, Quebec, with New London, ...
was reorganized as the Burlington and Lamoille Valley Railroad and leased by the Central Vermont. This provided a branch from Essex Junction
Essex Junction is a city in Chittenden County, Vermont, United States. As of the 2020 U.S. census, the population was 10,590. It was incorporated as a village on November 15, 1892. Essex Junction became Vermont’s 10th city on July 1, 2022.
A ...
to the Lamoille Valley Railroad at Cambridge Junction in Cambridge, Vermont, and a quickly-abandoned redundant line from Essex Junction west to Burlington. This second connection crossed the Winooski River
The Winooski River (formerly the Onion River) is a tributary of Lake Champlain, approximately long, in the northern half of Vermont. Although not Vermont's longest river, it is one of the state's most significant, forming a major valley way from ...
near Essex Junction and connected to the Rutland Railroad
The Rutland Railroad was a railroad in the northeastern United States, located primarily in the state of Vermont but extending into the state of New York at both its northernmost and southernmost ends. After its closure in 1961, parts of the ...
at the south end of Burlington near the present-day terminus of I-189
Interstate 189 (I-189) is an auxiliary Interstate Highway in Chittenden County, Vermont. The spur extends for from I-89 exit 13 in South Burlington to US Route 7 (US 7) at the Burlington
Burlington may refer to:
Places Ca ...
.
The Montreal and Province Line Railway was formed in 1896 as a reorganization of the Montreal, Portland and Boston Railroad. Originally planned as a branch of the Portland and Ogdensburg Railroad to Montreal
Montreal ( ; officially Montréal, ) is the second-most populous city in Canada and most populous city in the Canadian province of Quebec. Founded in 1642 as '' Ville-Marie'', or "City of Mary", it is named after Mount Royal, the triple- ...
, and operated by the Connecticut and Passumpsic Rivers Railroad, it was taken over by the Central Vermont upon reorganization. The main line ran from the Grand Trunk Railway
The Grand Trunk Railway (; french: Grand Tronc) was a railway system that operated in the Canadian provinces of Quebec and Ontario and in the American states of Connecticut, Maine, Michigan, Massachusetts, New Hampshire, and Vermont. The rai ...
's Montreal and Champlain Railroad
The Champlain and St. Lawrence Railroad (C&SL) was a historic railway in Lower Canada, the first Canadian public railway and one of the first railways built in British North America.
Origin
The C&SL was financed by Montreal entrepreneur and br ...
at Saint-Lambert, across the St. Lawrence River from Montreal, southeast to Farnham on the Stanstead, Shefford and Chambly Railroad, with an extension continuing southeast to Frelighsburg. A branch went east from Marieville to St. Cesaire.
In 1896 the Central Vermont entered receivership
In law, receivership is a situation in which an institution or enterprise is held by a receiver—a person "placed in the custodial responsibility for the property of others, including tangible and intangible assets and rights"—especially in c ...
, and the Rutland Railroad
The Rutland Railroad was a railroad in the northeastern United States, located primarily in the state of Vermont but extending into the state of New York at both its northernmost and southernmost ends. After its closure in 1961, parts of the ...
was separated. The Grand Trunk Railway bought the bankrupt company on March 20. The Ogdensburg and Lake Champlain Railroad
The Ogdensburg and Lake Champlain Railroad was founded in 1849 as the Northern Railroad running from Ogdensburg to Rouses Point, New York. The railroad was leased by rival Central Vermont Railroad for several decades, ending in 1896. It was pur ...
lease ended in 1898, and that company was leased by the Rutland in 1901. The Central Vermont Railroad was sold at foreclosure
Foreclosure is a legal process in which a lender attempts to recover the balance of a loan from a borrower who has stopped making payments to the lender by forcing the sale of the asset used as the collateral for the loan.
Formally, a mort ...
on March 21, 1899, and was reorganized as the Central Vermont Railway on May 1. During this process, on April 15, 1899, it purchased the Missisquoi Valley Railroad outright.
On July 12, 1920, the entire Grand Trunk system was placed under the control of a "Board of Management" by the federal Department of Railways and Canals in Canada
Canada is a country in North America. Its ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, covering over , making it the world's second-largest country by tota ...
after several years of financial difficulties. After several years of legal battles by Grand Trunk shareholders, intent on preventing the federal government from nationalizing
Nationalization (nationalisation in British English) is the process of transforming privately-owned assets into public assets by bringing them under the public ownership of a national government or state. Nationalization usually refers to priv ...
the company, the company was nationalized on January 20, 1923, and fully merged into the Crown corporation
A state-owned enterprise (SOE) is a government entity which is established or nationalised by the ''national government'' or ''provincial government'' by an executive order or an act of legislation in order to earn profit for the governmen ...
Canadian National Railway
The Canadian National Railway Company (french: Compagnie des chemins de fer nationaux du Canada) is a Canadian Class I railroad, Class I freight railway headquartered in Montreal, Quebec, which serves Canada and the Midwestern United States, M ...
.
CN and NECR: 1923-present
On December 12, 1927, the Central Vermont Railway enteredreceivership
In law, receivership is a situation in which an institution or enterprise is held by a receiver—a person "placed in the custodial responsibility for the property of others, including tangible and intangible assets and rights"—especially in c ...
again, and was reorganized January 31, 1930, to form a new company of the same name.
While the Central Vermont was no longer independent, it kept much of its corporate identity and was run as a separate railroad from the rest of the CN system. As the grip of the Great Depression eased, the railroad became a relatively successful arm of the CN network until the postwar period. It moved a wide range of freight from general merchandise and furniture to milk and agricultural products.
During the 1950s, diesels from CN began to appear on the Central Vermont, with the last steam locomotive ending service in 1957. The 1960s were an especially-rough period due to declining traffic, rising costs, and falling revenues.
Under the Grand Trunk and later the Canadian National
The Canadian National Railway Company (french: Compagnie des chemins de fer nationaux du Canada) is a Canadian Class I freight railway headquartered in Montreal, Quebec, which serves Canada and the Midwestern and Southern United States.
CN ...
, the Central Vermont system saw many of its unprofitable branch lines abandoned. The CN continued to operate the CV as a modestly successful system; however, in the process leading up to the privatization
Privatization (also privatisation in British English) can mean several different things, most commonly referring to moving something from the public sector into the private sector. It is also sometimes used as a synonym for deregulation when ...
of the CN, which took place on November 28, 1995, several non-core routes were identified for sale, one of then being the CV.
On February 3, 1995, the CN sold the CV mainline from New London, Connecticut
New London is a seaport city and a port of entry on the northeast coast of the United States, located at the mouth of the Thames River in New London County, Connecticut. It was one of the world's three busiest whaling ports for several decades ...
, to East Alburg, Vermont
East Alburgh (also known as East Alburg and Alburg Junction) is a populated place in Grand Isle County in the U.S. state of Vermont
Vermont () is a state in the northeast New England region of the United States. Vermont is bordered by the ...
, to shortline operating company RailTex, which renamed the property the New England Central Railroad
The New England Central Railroad is a regional railroad in the New England region of the United States. It began operations in 1995, as the successor of the Central Vermont Railway (CV). The company was originally a subsidiary of holding com ...
. RailTex was merged into RailAmerica
RailAmerica, Inc., based in Jacksonville, Florida, was a holding company of a number of short-line railroads and regional railroads in the United States and Canada.
In 2007, RailAmerica was acquired by Fortress Investment Group. Before that, it ...
in 2000. Genesee & Wyoming
Genesee & Wyoming Inc. (G&W) is an American short line railroad holding company, that owns or maintains an interest in 122 railroads in the United States, Canada, Belgium, Netherlands, Poland, United Kingdom and formerly Australia. It operates ...
acquired RailAmerica at the end of 2012. Operations have continued as before.
Divisions and branches

Richford Branch
This line was formed as the Missisquoi Railroad, then became the Missisquoi Valley Railroad, and then the Missisquoi Valley Division, before gaining its final name. Operations continued on the entire length until 1984, when a derailment on the bridge spanning theMissisquoi River
The Missisquoi River is a transboundary river of the east shore of Lake Champlain (via Missisquoi Bay), approximately long, in northern Vermont in the United States and southern Quebec in Canada.
It drains a rural area of the northern Green Mount ...
near Sheldon, Vermont, forced the dismantlement of one of three spans. Operations continued on the east end, while the Lamoille Valley Railroad operated on the isolated west end of the line to Richford occasionally after 1989. In 1990 the tracks from St. Albans to the bridge were pulled up.
The following stops were made on the branch from west to east:
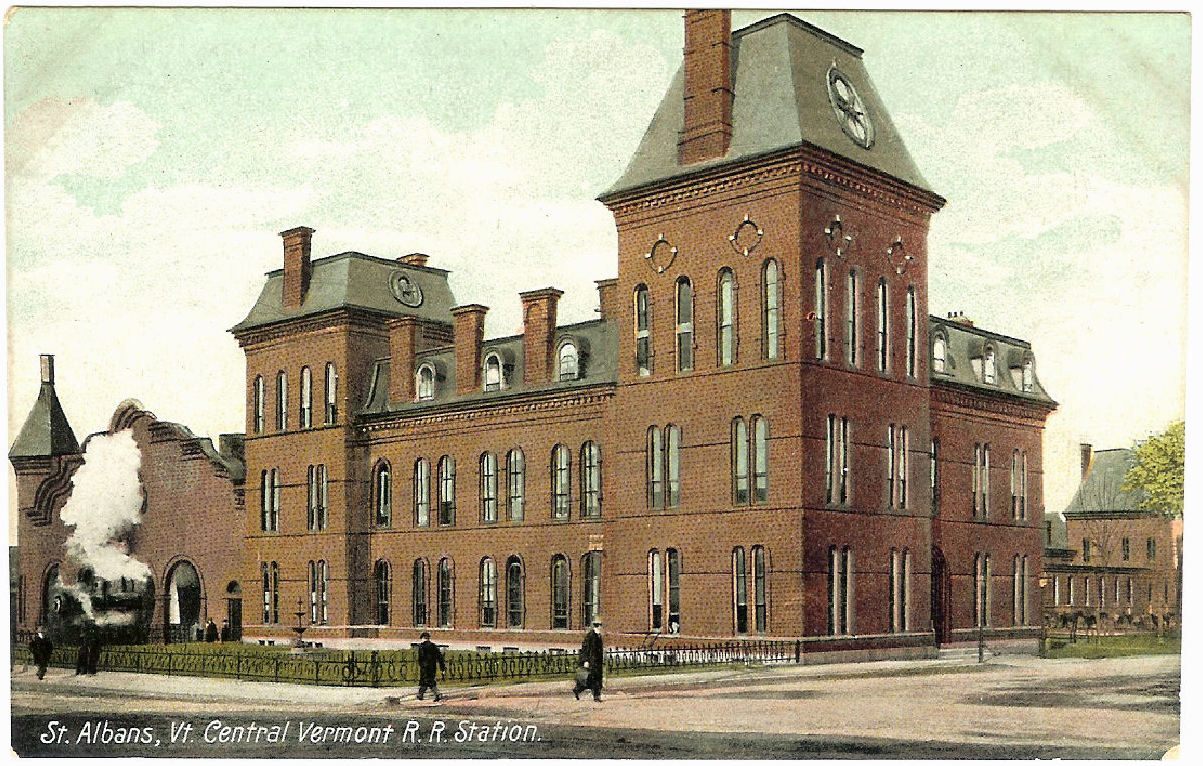
* Saint Albans, Vermont (interchange with the Central Vermont Railway)
* Green's Corners, Vermont
* Sheldon Springs, Vermont
* Sheldon, Vermont (interchange with the Missisquoi Pulp and Paper Company)
* North Sheldon, Vermont
* Sheldon Junction, Vermont (interchange with the Saint Johnsbury and Lake Champlain Railroad
The St. Johnsbury and Lamoille County Railroad (StJ&LC) was a railroad located in northern Vermont. It provided service to rural parts of the state for over a century, until track deterioration and flood damage made the line unusable and uneconom ...
)
* East Frankin, Vermont
* Enosburg Falls, Vermont
Enosburg Falls is a village in the town of Enosburgh in Franklin County, Vermont, in the United States. The population was 1,356 at the 2020 census.
Geography
The village is located in the northwest corner of the town of Enosburgh along the Mi ...
* North Enosburg, Vermont
* East Berkshire, Vermont
* Richford, Vermont
Richford is a town in Franklin County, Vermont, United States, located along the Canada–United States border. The population was 2,346 at the 2020 census.
Richford is the birthplace of R. G. LeTourneau, an industrialist who founded LeTournea ...
(interchange with the Canadian Pacific Railway
The Canadian Pacific Railway (french: Chemin de fer Canadien Pacifique) , also known simply as CPR or Canadian Pacific and formerly as CP Rail (1968–1996), is a Canadian Class I railway incorporated in 1881. The railway is owned by Canad ...
)
References
External links
Central Vermont Railway Historical Society
* ttp://www.images.technomuses.ca/?en/stories/central_vermont/intro/page/1 Picturing the Past: The Central Vermont Railway - includes many railway photosbr>Mamacoke Company Portal to Central Vermont Railway Archives
* {{DEFAULTSORT:Central Vermont Railway Railway companies established in 1899 Railway companies disestablished in 1995 American companies established in 1899 American companies disestablished in 1995 Grand Trunk Railway subsidiaries Canadian National Railway subsidiaries Defunct Connecticut railroads Defunct Massachusetts railroads Defunct New Hampshire railroads Defunct Vermont railroads Defunct Quebec railways Former Class I railroads in the United States Standard gauge railways in the United States Predecessors of the Grand Trunk Railway Defunct New York (state) railroads Historic American Engineering Record in Vermont 1899 establishments in Vermont