Central Estonia on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Between 57.3 and 59.5 latitude and 21.5 and 28.1 longitude, Estonia lies on the eastern coast of the Baltic Sea on the level northwestern part of the rising East European Platform. Estonia's continental mainland is bordered to the north by the
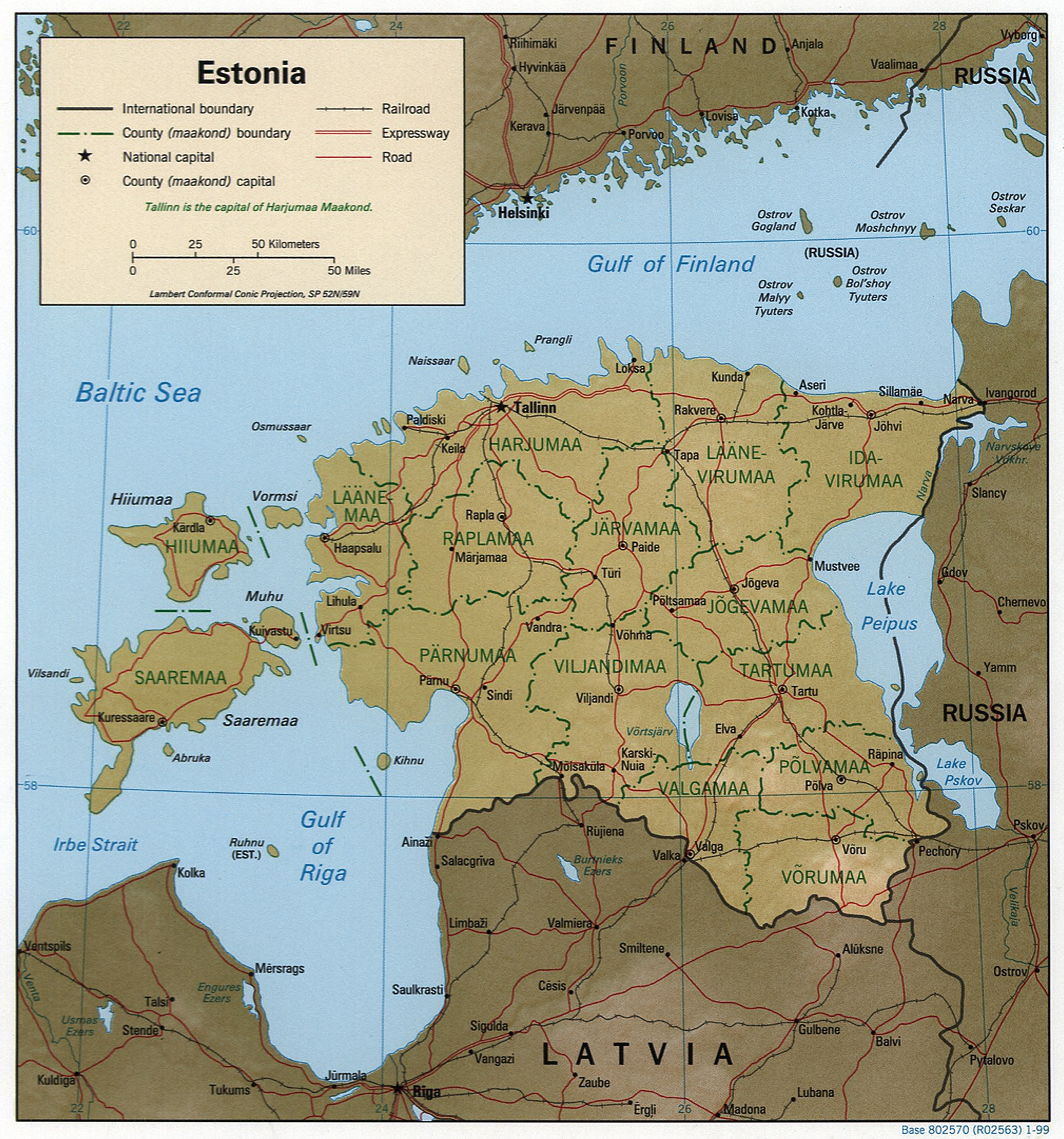 Estonia is a flat country covering . Estonia has a long, shallow coastline () along the Baltic Sea, with 1,520 islands dotting the shore. The two largest islands are Saaremaa (literally, island land), at , and Hiiumaa, at . The two islands are favorite Estonian vacation spots. The country's highest point,
Estonia is a flat country covering . Estonia has a long, shallow coastline () along the Baltic Sea, with 1,520 islands dotting the shore. The two largest islands are Saaremaa (literally, island land), at , and Hiiumaa, at . The two islands are favorite Estonian vacation spots. The country's highest point,
GBIF

 One of the most burdensome legacies of the 1944–1991 Soviet occupation of Estonia is widespread environmental pollution.Auer, M.R., Raukas, A. (2002). Determinants of environmental cleanup in Estonia. ''Environment and Planning C: Government and Policy'', 20: 679–698. The worst offender in this regard was the Soviet army. Across military installations covering more than of Estonian territory, the army dumped hundreds of thousands of tons of jet fuel into the ground, improperly disposed of toxic chemicals, and discarded outdated explosives and weapons in coastal and inland waters. In the 1990s, during the army's withdrawal from Estonia, extensive damage was done to discarded buildings and equipment. In October 1993, the Estonian Ministry of Environment issued a preliminary report summing up part of the degradation it had surveyed thus far. The report described the worst damage as having been done to Estonia's topsoil and underground water supply by the systematic dumping of jet fuel at six Soviet army air bases. At the air base near Tapa, site of the worst damage, officials estimated that of land were covered by a layer of fuel; of underground water were said to be contaminated. The water in the surrounding area was undrinkable, and was sometimes set fire by locals to provide heat during the winter. With Danish help, Estonian crews began cleaning up the site, although they estimated the likely cost to be as much as 4 million
One of the most burdensome legacies of the 1944–1991 Soviet occupation of Estonia is widespread environmental pollution.Auer, M.R., Raukas, A. (2002). Determinants of environmental cleanup in Estonia. ''Environment and Planning C: Government and Policy'', 20: 679–698. The worst offender in this regard was the Soviet army. Across military installations covering more than of Estonian territory, the army dumped hundreds of thousands of tons of jet fuel into the ground, improperly disposed of toxic chemicals, and discarded outdated explosives and weapons in coastal and inland waters. In the 1990s, during the army's withdrawal from Estonia, extensive damage was done to discarded buildings and equipment. In October 1993, the Estonian Ministry of Environment issued a preliminary report summing up part of the degradation it had surveyed thus far. The report described the worst damage as having been done to Estonia's topsoil and underground water supply by the systematic dumping of jet fuel at six Soviet army air bases. At the air base near Tapa, site of the worst damage, officials estimated that of land were covered by a layer of fuel; of underground water were said to be contaminated. The water in the surrounding area was undrinkable, and was sometimes set fire by locals to provide heat during the winter. With Danish help, Estonian crews began cleaning up the site, although they estimated the likely cost to be as much as 4 million
''party to:'' Air Pollution, Air Pollution-Heavy Metals, Air Pollution-Nitrogen Oxides, Air Pollution-Persistent Organic Pollutants, Air Pollution-Sulphur 85, Air Pollution-Volatile Organic Compounds, Antarctic Treaty, Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-
 Area:
Area:
''total:''
''land:''
''water:''
''note:'' includes 1,520 islands in the Baltic Sea Land boundaries:
''total:''
''border countries:'' Latvia , Russia Coastline: Maritime claims:
''territorial sea:'' '' exclusive economic zone:'' limits as agreed to by Estonia, Finland, Latvia, Sweden, and Russia Elevation extremes:
''lowest point:'' Baltic Sea 0 m
''highest point:''
 Natural resources: oil shale (
Natural resources: oil shale (
Gulf of Finland
The Gulf of Finland ( fi, Suomenlahti; et, Soome laht; rus, Фи́нский зали́в, r=Finskiy zaliv, p=ˈfʲinskʲɪj zɐˈlʲif; sv, Finska viken) is the easternmost arm of the Baltic Sea. It extends between Finland to the north and E ...
(part of the Baltic Sea) across from Finland, to the east by Lake Peipus and Russia, and to the south by Latvia
Latvia ( or ; lv, Latvija ; ltg, Latveja; liv, Leţmō), officially the Republic of Latvia ( lv, Latvijas Republika, links=no, ltg, Latvejas Republika, links=no, liv, Leţmō Vabāmō, links=no), is a country in the Baltic region of ...
. Besides the part of the European continent, Estonian territory also includes the larger islands of Saaremaa and Hiiumaa, and over 2,200 other islands and islets in the Baltic Sea, off the western and northern shores of the country's mainland.
Average elevation in Estonia reaches .
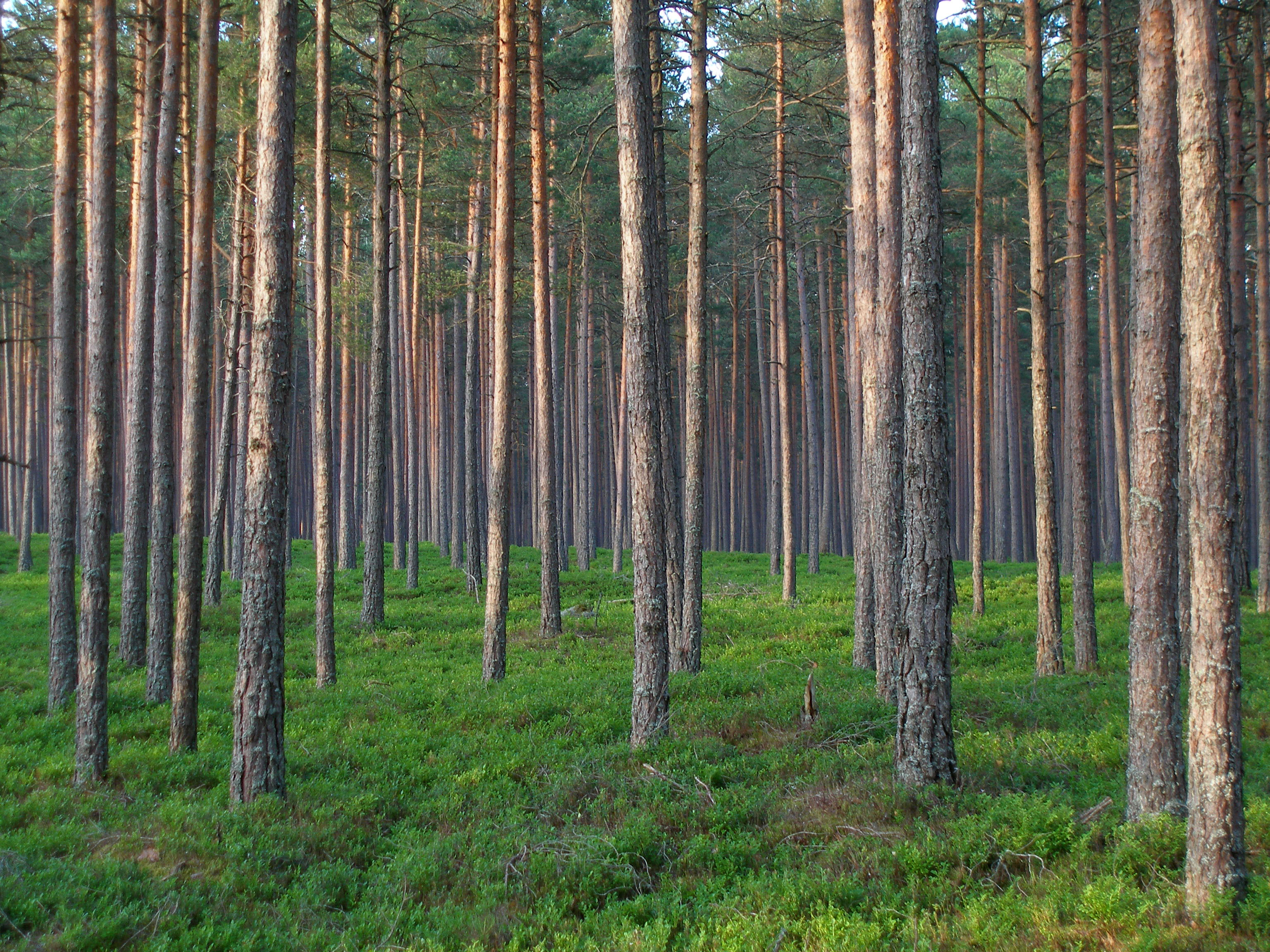
The climate is maritime, wet, with moderate winters and cool summers. Oil shale and limestone deposits, along with forests which cover 47% of the land, play key economic roles in this generally resource-poor country. Estonia boasts over 1,500 lakes, numerous bog
A bog or bogland is a wetland that accumulates peat as a deposit of dead plant materials often mosses, typically sphagnum moss. It is one of the four main types of wetlands. Other names for bogs include mire, mosses, quagmire, and muskeg; a ...
s, and 3,794 kilometers of coastline marked by numerous bays, straits, and inlets.
Geographic features
 Estonia is a flat country covering . Estonia has a long, shallow coastline () along the Baltic Sea, with 1,520 islands dotting the shore. The two largest islands are Saaremaa (literally, island land), at , and Hiiumaa, at . The two islands are favorite Estonian vacation spots. The country's highest point,
Estonia is a flat country covering . Estonia has a long, shallow coastline () along the Baltic Sea, with 1,520 islands dotting the shore. The two largest islands are Saaremaa (literally, island land), at , and Hiiumaa, at . The two islands are favorite Estonian vacation spots. The country's highest point, Suur Munamägi
Suur Munamägi (; translation "Great Egg Mountain") is the highest peak in Estonia (and the Baltic states), reaching above sea level. It is located near the village of Haanja, in Võru County in the south-eastern corner of Estonia, close to t ...
(Egg Mountain), is in the hilly southeast and reaches above sea level. Estonia is covered by about of forest. Arable land amounts to about . Meadows cover about , and pastureland covers about . There are more than 1,400 natural and artificial lakes in Estonia. The largest of them, Lake Peipus (), forms much of the border between Estonia and Russia. Located in central Estonia, Võrtsjärv
Lake Võrtsjärv (; german: Wirzsee) is a lake in southern Estonia with an area of 270 km² (104 mi²).
It is the second largest lake in Estonia (behind Lake Peipus), and the largest lake situated entirely within Estonia. The shallow ...
is the second-largest lake (). The Narva and Emajõgi are among the most important of the country's many rivers.
A small, recent cluster of meteorite craters, the largest of which is called Kaali are found on the Estonian island of Saaremaa. The impact may have been witnessed by the Iron Age inhabitants of the area.
Estonia has a temperate climate, with four seasons of near-equal length. Average temperatures range from on the Baltic islands to inland in July, the warmest month, and from on the Baltic islands to inland in February, the coldest month. Precipitation averages per year and is heaviest in late summer.
Estonia's land border with Latvia runs ; the Russian border runs . From 1920 to 1945, Estonia's border with Russia, set by the 1920 Tartu Peace Treaty, extended beyond the Narva river in the northeast and beyond the town of Petseri in the southeast. This territory, amounting to some , was transferred to Soviet Russia at the end of World War II.
Fauna
There live 65 different species of mammals in the Estonian forests. There are an estimated 700 brown bears, over 150 wolves, 400 lynxes, 14,000–16,000 beavers, 3,400 wild boars, 10,000–11,000 moose and 120,000–130,000 deer. There are also red deer and other wild animals.AnimaliaGBIF
Flora

Environmental issues
EEK
Eek or EEK may refer to:
People
* Karl Morten Eek (born 1988), Norwegian footballer
* Maria Magdalena Eek (1733–1800), Finnish pastry chef
Places
* Eek, Alaska
* Eek Airport, Alaska
* Eek River, Alaska
Other uses
* Estonian kroon, a form ...
. The Ministry of Environment assigned a monetary cost of more than 10 billion EEK to the damage to the country's topsoil and water supply. However, the ministry was able to allocate only 5 million EEK in 1993 for cleanup operations.
In a 1992 government report to the United Nations Conference on the Environment and Development, Estonia detailed other major environmental concerns. For instance, for several consecutive years Estonia had led the world in the production of sulfur dioxide per capita. Nearly 75% of Estonia's air pollution was reported to come from two oil shale-based thermal power stations operating near Narva. The mining of oil shale in northeastern Estonia has also left large mounds of limestone tailings dotting the region. Near the town of Sillamäe, site of a former uranium enrichment plant, about 1,200 tons of uranium and about 750 tons of thorium had been dumped into a reservoir on the shore of the Gulf of Finland. This was said to have caused severe health problems among area residents. In the coastal town of Paldiski, the removal of waste left by Soviet army nuclear reactors was also a major concern. The combined cost of environmental cleanup at both towns was put at more than EEK3.5 billion.
Natural hazards: flooding occurs frequently in the spring in certain areas
Environment – current issues: air polluted with sulfur dioxide from oil-shale burning power plants in northeast; however, the amounts of pollutants emitted to the air have fallen dramatically and the pollution load of wastewater at purification plants has decreased substantially due to improved technology and environmental monitoring; Estonia has more than 1,400 natural and manmade lakes, the smaller of which in agricultural areas need to be monitored; coastal seawater is polluted in certain locations.
Environment – international agreements:''party to:'' Air Pollution, Air Pollution-Heavy Metals, Air Pollution-Nitrogen Oxides, Air Pollution-Persistent Organic Pollutants, Air Pollution-Sulphur 85, Air Pollution-Volatile Organic Compounds, Antarctic Treaty, Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-
Kyoto Protocol
The Kyoto Protocol was an international treaty which extended the 1992 United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC) that commits state parties to reduce greenhouse gas emissions, based on the scientific consensus that (part ...
, Climate Change-Paris Agreement
The Paris Agreement (french: Accord de Paris), often referred to as the Paris Accords or the Paris Climate Accords, is an international treaty on climate change. Adopted in 2015, the agreement covers climate change mitigation, Climate change a ...
, Comprehensive Nuclear Test Ban, Desertification, Endangered Species, Environmental Modification, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Marine Dumping-London Protocol, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution, Tropical Timber 2006, Wetlands, Whaling
Area and boundaries
 Area:
Area:''total:''
''land:''
''water:''
''note:'' includes 1,520 islands in the Baltic Sea Land boundaries:
''total:''
''border countries:'' Latvia , Russia Coastline: Maritime claims:
''territorial sea:'' '' exclusive economic zone:'' limits as agreed to by Estonia, Finland, Latvia, Sweden, and Russia Elevation extremes:
''lowest point:'' Baltic Sea 0 m
''highest point:''
Suur Munamägi
Suur Munamägi (; translation "Great Egg Mountain") is the highest peak in Estonia (and the Baltic states), reaching above sea level. It is located near the village of Haanja, in Võru County in the south-eastern corner of Estonia, close to t ...
Geographical (landscape) areas
*Northern Estonia (roughly equivalent to ''Põhja-Eesti maastikuvaldkond'' ( :et), which includes the capital city Tallinn) *Southern Estonia *Western Estonia *Eastern EstoniaResources and land use
 Natural resources: oil shale (
Natural resources: oil shale (kukersite
Kukersite is a light-brown marine type oil shale of Ordovician age. It is found in the Baltic Oil Shale Basin in Estonia and North-West Russia. It is of the lowest Upper Ordovician formation, formed some 460 million years ago. It was nam ...
), peat, rare earth elements, phosphorite
Phosphorite, phosphate rock or rock phosphate is a non-detrital sedimentary rock that contains high amounts of phosphate minerals. The phosphate content of phosphorite (or grade of phosphate rock) varies greatly, from 4% to 20% phosphorus pentoxi ...
, clay, limestone, sand, dolomite, arable land, sea mud
Land use (2018 est.):
* agricultural land: 22.2% (14% arable land, 0.1% permanent crops, 7.2% permanent pasture)
* forest: 52.1%
* other: 25.7%
Irrigated land:
Total renewable water resources: (2017 est.)
See also
* Extreme points of Estonia *Climate of Estonia
Estonia lies in the northern part of the temperate climate zone and in the transition zone between maritime and continental climate. Because Estonia (and all of Northern Europe) is continuously warmed by maritime air influenced by the heat con ...
References
{{DEFAULTSORT:Geography Of Estonia