Central-Northern Latian on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
{{short description, Central Italian dialect
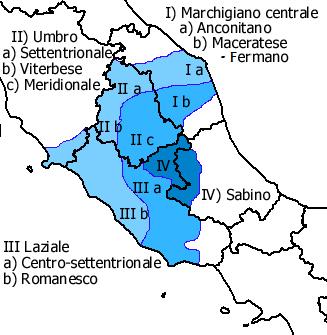 The Central-Northern Latian dialect (''Laziale centro-settentrionale'') is an Italian dialect belonging to the Central Italian dialects, of which it represents the southern offshoot.
The Central-Northern Latian dialect (''Laziale centro-settentrionale'') is an Italian dialect belonging to the Central Italian dialects, of which it represents the southern offshoot.
 The Central-Northern Latian dialect (''Laziale centro-settentrionale'') is an Italian dialect belonging to the Central Italian dialects, of which it represents the southern offshoot.
The Central-Northern Latian dialect (''Laziale centro-settentrionale'') is an Italian dialect belonging to the Central Italian dialects, of which it represents the southern offshoot.
Territory
It is spoken in theLazio
it, Laziale
, population_note =
, population_blank1_title =
, population_blank1 =
, demographics_type1 =
, demographics1_footnotes =
, demographics1_title1 =
, demographics1_info1 =
, demographics1_title2 ...
(Latium) region, and in particular in the northern areas of the Province of Frosinone
The Province of Frosinone ( it, Provincia di Frosinone) is a province in the Lazio region of Italy, with 91 ''comuni'' (singular: ''comune''; see Comuni of the Province of Frosinone). Its capital is the city of Frosinone. It has an area of ...
(whose variants are often improperly defined as the Ciociaro dialect or more anciently Campanino), in the central-northern areas of the Province of Latina and in most of the Metropolitan city of Rome with the exception, however, of the city of Rome, where the Romanesco dialect is widespread and which differs widely from the rest of the Latian dialects.
Features
Phonetics
The central-northern Lazio is characterized, like the other Central Italian dialects and theTuscan dialect
Tuscan ( it, dialetto toscano ; it, vernacolo, label=locally) is a set of Italo-Dalmatian varieties of Romance mainly spoken in Tuscany, Italy.
Standard Italian is based on Tuscan, specifically on its Florentine dialect, and it became the lan ...
(but unlike the neighboring Southern Latian dialect and most of the other Italian dialects), by the presence of seven vowels, also typical of standard Italian.
The Judeo-Roman dialect
The Judaic-Roman dialect can be inserted within the Central-Northern Latian dialect, having diverged considerably from the Romanesco dialect after the establishment of theghetto
A ghetto, often called ''the'' ghetto, is a part of a city in which members of a minority group live, especially as a result of political, social, legal, environmental or economic pressure. Ghettos are often known for being more impoverished t ...
in 1555 and therefore not undergoing the influence of the Tuscan as strongly as the dialect of the capital.On this dialect, see: Migliau Bice, Il dialetto giudaico-romanesco, in: Migliau Bice e Procaccia Micaela, ''Lazio: Itinerari ebraici. I luoghi, la storia, l’arte'', Marsilio, Venezia, 1997 The dialect is now used for literary and theatrical works.
References
Further bibliography
* C. Vignoli, ''Vernacolo e canti di Amaseno'', I dialetti di Roma e del Lazio, I, Società Filologica Romana, Roma, 1920See also
* Southern Latian dialect Dialects of Italian