Censuses In Bulgaria on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
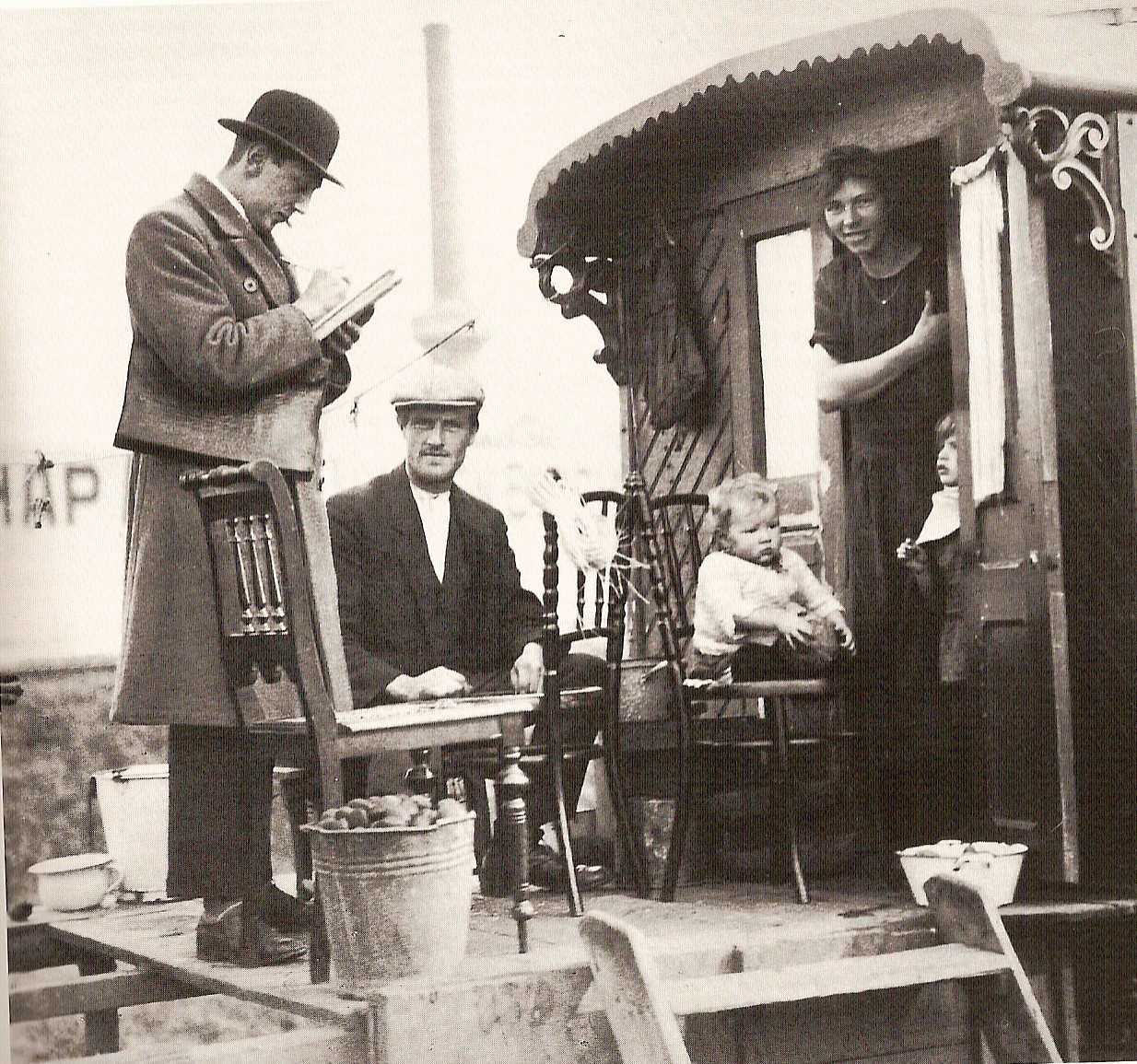 A census is the procedure of systematically acquiring, recording and calculating information about the members of a given population. This term is used mostly in connection with national population and housing censuses; other common censuses include censuses of agriculture, traditional culture, business, supplies, and traffic censuses. The United Nations (UN) defines the essential features of population and housing censuses as "individual enumeration, universality within a defined territory, simultaneity and defined periodicity", and recommends that population censuses be taken at least every ten years. UN recommendations also cover census topics to be collected, official definitions, classifications and other useful information to co-ordinate international practices.
The UN's Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO), in turn, defines the census of agriculture as "a statistical operation for collecting, processing and disseminating data on the structure of agriculture, covering the whole or a significant part of a country." "In a census of agriculture, data are collected at the holding level."
A census is the procedure of systematically acquiring, recording and calculating information about the members of a given population. This term is used mostly in connection with national population and housing censuses; other common censuses include censuses of agriculture, traditional culture, business, supplies, and traffic censuses. The United Nations (UN) defines the essential features of population and housing censuses as "individual enumeration, universality within a defined territory, simultaneity and defined periodicity", and recommends that population censuses be taken at least every ten years. UN recommendations also cover census topics to be collected, official definitions, classifications and other useful information to co-ordinate international practices.
The UN's Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO), in turn, defines the census of agriculture as "a statistical operation for collecting, processing and disseminating data on the structure of agriculture, covering the whole or a significant part of a country." "In a census of agriculture, data are collected at the holding level."  Text was copied from this source, which is available under
Text was copied from this source, which is available under
Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 IGO (CC BY 3.0 IGO)
license. The word is of Latin origin: during the Roman Republic, the census was a list that kept track of all adult males fit for military service. The modern census is essential to international comparisons of any kind of statistics, and censuses collect data on many attributes of a population, not just how many people there are. Censuses typically began as the only method of collecting national demographic data and are now part of a larger system of different surveys. Although population estimates remain an important function of a census, including exactly the geographic distribution of the population or the agricultural population, statistics can be produced about combinations of attributes, e.g., education by age and sex in different regions. Current
 A census is often construed as the opposite of a sample as its intent is to count everyone in a population, rather than a fraction. However, population censuses do rely on a sampling frame to count the population. This is the only way to be sure that everyone has been included, as otherwise those not responding would not be followed up on and individuals could be missed. The fundamental premise of a census is that the population is not known, and a new estimate is to be made by the analysis of primary data. The use of a sampling frame is counterintuitive as it suggests that the population size is already known. However, a census is also used to collect attribute data on the individuals in the nation, not only to assess population size. This process of sampling marks the difference between a historical census, which was a house-to-house process or the product of an imperial decree, and the modern statistical project.
The sampling frame used by a census is almost always an address register. Thus, it is not known if there is anyone resident or how many people there are in each household. Depending on the mode of enumeration, a form is sent to the householder, an enumerator calls, or administrative records for the dwelling are accessed. As a preliminary to the dispatch of forms, census workers will check any address problems on the ground. While it may seem straightforward to use the postal service file for this purpose, this can be out of date and some dwellings may contain a number of independent households. A particular problem is what are termed "communal establishments", a category that includes student residences, religious orders, homes for the elderly, people in prisons etc. As these are not easily enumerated by a single householder, they are often treated differently and visited by special teams of census workers to ensure they are classified appropriately.
A census is often construed as the opposite of a sample as its intent is to count everyone in a population, rather than a fraction. However, population censuses do rely on a sampling frame to count the population. This is the only way to be sure that everyone has been included, as otherwise those not responding would not be followed up on and individuals could be missed. The fundamental premise of a census is that the population is not known, and a new estimate is to be made by the analysis of primary data. The use of a sampling frame is counterintuitive as it suggests that the population size is already known. However, a census is also used to collect attribute data on the individuals in the nation, not only to assess population size. This process of sampling marks the difference between a historical census, which was a house-to-house process or the product of an imperial decree, and the modern statistical project.
The sampling frame used by a census is almost always an address register. Thus, it is not known if there is anyone resident or how many people there are in each household. Depending on the mode of enumeration, a form is sent to the householder, an enumerator calls, or administrative records for the dwelling are accessed. As a preliminary to the dispatch of forms, census workers will check any address problems on the ground. While it may seem straightforward to use the postal service file for this purpose, this can be out of date and some dwellings may contain a number of independent households. A particular problem is what are termed "communal establishments", a category that includes student residences, religious orders, homes for the elderly, people in prisons etc. As these are not easily enumerated by a single householder, they are often treated differently and visited by special teams of census workers to ensure they are classified appropriately.
 Triple system enumeration has been proposed as an improvement as it would allow evaluation of the statistical dependence of pairs of sources. However, as the matching process is the most difficult aspect of census estimation this has never been implemented for a national enumeration. It would also be difficult to identify three different sources that were sufficiently different to make the triple system effort worthwhile. The DSE approach has another weakness in that it assumes there is no person counted twice (over count). In ''de facto'' residence definitions this would not be a problem but in ''de jure'' definitions individuals risk being recorded on more than one form leading to double counting. A particular problem here is students who often have a term time and family address.
Several countries have used a system known as short form/long form. This is a sampling strategy that randomly chooses a proportion of people to send a more detailed questionnaire to (the long form). Everyone receives the short form questions. This means more data are collected, but without imposing a burden on the whole population. This also reduces the burden on the statistical office. Indeed, in the UK until 2001 all residents were required to fill in the whole form but only a 10% sample were coded and analysed in detail. New technology means that all data are now scanned and processed. During the 2011 Canadian census there was controversy about the cessation of the mandatory long form census; the head of
Triple system enumeration has been proposed as an improvement as it would allow evaluation of the statistical dependence of pairs of sources. However, as the matching process is the most difficult aspect of census estimation this has never been implemented for a national enumeration. It would also be difficult to identify three different sources that were sufficiently different to make the triple system effort worthwhile. The DSE approach has another weakness in that it assumes there is no person counted twice (over count). In ''de facto'' residence definitions this would not be a problem but in ''de jure'' definitions individuals risk being recorded on more than one form leading to double counting. A particular problem here is students who often have a term time and family address.
Several countries have used a system known as short form/long form. This is a sampling strategy that randomly chooses a proportion of people to send a more detailed questionnaire to (the long form). Everyone receives the short form questions. This means more data are collected, but without imposing a burden on the whole population. This also reduces the burden on the statistical office. Indeed, in the UK until 2001 all residents were required to fill in the whole form but only a 10% sample were coded and analysed in detail. New technology means that all data are now scanned and processed. During the 2011 Canadian census there was controversy about the cessation of the mandatory long form census; the head of
19 ''Western State University Law Review'' 1
available a
HeinOnline
.
Effects of UK 'Jedi' hoax on 2001 UK census from ONS
*
Census of Ireland 1911
Online Historical Population Reports Project (OHPR)
PR as a function of census management: comparative analysis of fifteen census experiences
{{Authority control Population Survey methodology Sampling (statistics) Latin words and phrases
 A census is the procedure of systematically acquiring, recording and calculating information about the members of a given population. This term is used mostly in connection with national population and housing censuses; other common censuses include censuses of agriculture, traditional culture, business, supplies, and traffic censuses. The United Nations (UN) defines the essential features of population and housing censuses as "individual enumeration, universality within a defined territory, simultaneity and defined periodicity", and recommends that population censuses be taken at least every ten years. UN recommendations also cover census topics to be collected, official definitions, classifications and other useful information to co-ordinate international practices.
The UN's Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO), in turn, defines the census of agriculture as "a statistical operation for collecting, processing and disseminating data on the structure of agriculture, covering the whole or a significant part of a country." "In a census of agriculture, data are collected at the holding level."
A census is the procedure of systematically acquiring, recording and calculating information about the members of a given population. This term is used mostly in connection with national population and housing censuses; other common censuses include censuses of agriculture, traditional culture, business, supplies, and traffic censuses. The United Nations (UN) defines the essential features of population and housing censuses as "individual enumeration, universality within a defined territory, simultaneity and defined periodicity", and recommends that population censuses be taken at least every ten years. UN recommendations also cover census topics to be collected, official definitions, classifications and other useful information to co-ordinate international practices.
The UN's Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO), in turn, defines the census of agriculture as "a statistical operation for collecting, processing and disseminating data on the structure of agriculture, covering the whole or a significant part of a country." "In a census of agriculture, data are collected at the holding level." Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 IGO (CC BY 3.0 IGO)
license. The word is of Latin origin: during the Roman Republic, the census was a list that kept track of all adult males fit for military service. The modern census is essential to international comparisons of any kind of statistics, and censuses collect data on many attributes of a population, not just how many people there are. Censuses typically began as the only method of collecting national demographic data and are now part of a larger system of different surveys. Although population estimates remain an important function of a census, including exactly the geographic distribution of the population or the agricultural population, statistics can be produced about combinations of attributes, e.g., education by age and sex in different regions. Current
administrative data Administrative data are collected by governments or other organizations for non-statistical reasons to provide overviews on registration, transactions, and record keeping. They evaluate part of the output of administrating a program. Border records, ...
systems allow for other approaches to enumeration with the same level of detail but raise concerns about privacy and the possibility of biasing estimates.
A census can be contrasted with sampling in which information is obtained only from a subset of a population; typically, main population estimates are updated by such intercensal estimates. Modern census data are commonly used for research, business marketing, and planning, and as a baseline for designing sample surveys by providing a sampling frame such as an address register. Census counts are necessary to adjust samples to be representative of a population by weighting them as is common in opinion polling. Similarly, stratification requires knowledge of the relative sizes of different population strata, which can be derived from census enumerations. In some countries, the census provides the official counts used to apportion the number of elected representatives to regions (sometimes controversially – e.g., ''Utah v. Evans
''Utah v. Evans'', 536 U.S. 452 (2002), was a United States Supreme Court case holding that the use of certain statistical techniques in the United States Census does not violate 13 USC §195 or the Census Clause of the Constitution.
In instance ...
''). In many cases, a carefully chosen random sample can provide more accurate information than attempts to get a population census.
Sampling
 A census is often construed as the opposite of a sample as its intent is to count everyone in a population, rather than a fraction. However, population censuses do rely on a sampling frame to count the population. This is the only way to be sure that everyone has been included, as otherwise those not responding would not be followed up on and individuals could be missed. The fundamental premise of a census is that the population is not known, and a new estimate is to be made by the analysis of primary data. The use of a sampling frame is counterintuitive as it suggests that the population size is already known. However, a census is also used to collect attribute data on the individuals in the nation, not only to assess population size. This process of sampling marks the difference between a historical census, which was a house-to-house process or the product of an imperial decree, and the modern statistical project.
The sampling frame used by a census is almost always an address register. Thus, it is not known if there is anyone resident or how many people there are in each household. Depending on the mode of enumeration, a form is sent to the householder, an enumerator calls, or administrative records for the dwelling are accessed. As a preliminary to the dispatch of forms, census workers will check any address problems on the ground. While it may seem straightforward to use the postal service file for this purpose, this can be out of date and some dwellings may contain a number of independent households. A particular problem is what are termed "communal establishments", a category that includes student residences, religious orders, homes for the elderly, people in prisons etc. As these are not easily enumerated by a single householder, they are often treated differently and visited by special teams of census workers to ensure they are classified appropriately.
A census is often construed as the opposite of a sample as its intent is to count everyone in a population, rather than a fraction. However, population censuses do rely on a sampling frame to count the population. This is the only way to be sure that everyone has been included, as otherwise those not responding would not be followed up on and individuals could be missed. The fundamental premise of a census is that the population is not known, and a new estimate is to be made by the analysis of primary data. The use of a sampling frame is counterintuitive as it suggests that the population size is already known. However, a census is also used to collect attribute data on the individuals in the nation, not only to assess population size. This process of sampling marks the difference between a historical census, which was a house-to-house process or the product of an imperial decree, and the modern statistical project.
The sampling frame used by a census is almost always an address register. Thus, it is not known if there is anyone resident or how many people there are in each household. Depending on the mode of enumeration, a form is sent to the householder, an enumerator calls, or administrative records for the dwelling are accessed. As a preliminary to the dispatch of forms, census workers will check any address problems on the ground. While it may seem straightforward to use the postal service file for this purpose, this can be out of date and some dwellings may contain a number of independent households. A particular problem is what are termed "communal establishments", a category that includes student residences, religious orders, homes for the elderly, people in prisons etc. As these are not easily enumerated by a single householder, they are often treated differently and visited by special teams of census workers to ensure they are classified appropriately.
Residence definitions
Individuals are normally counted within households, and information is typically collected about the household structure and the housing. For this reason, international documents refer to censuses of population and housing. Normally the census response is made by a household, indicating details of individuals resident there. An important aspect of census enumerations is determining which individuals can be counted and which cannot be counted. Broadly, three definitions can be used: ''de facto'' residence; ''de jure'' residence; and permanent residence. This is important in considering individuals who have multiple or temporary addresses. Every person should be identified uniquely as resident in one place; but the place where they happen to be onCensus Day
A census is the procedure of systematically acquiring, recording and calculating information about the members of a given population. This term is used mostly in connection with national population and housing censuses; other common censuses incl ...
, their ''de facto'' residence, may not be the best place to count them. Where an individual uses services may be more useful, and this is at their usual residence. An individual may be recorded at a "permanent" address, which might be a family home for students or long-term migrants.
A precise definition of residence is needed, to decide whether visitors to a country should be included in the population count. This is becoming more important as students travel abroad for education for a period of several years. Other groups causing problems of enumeration are new-born babies, refugees, people away on holiday, people moving home around census day, and people without a fixed address.
People with second homes because they are working in another part of the country or have a holiday cottage are difficult to fix at a particular address; this sometimes causes double counting or houses being mistakenly identified as vacant. Another problem is where people use a different address at different times e.g. students living at their place of education in term time but returning to a family home during vacations, or children whose parents have separated who effectively have two family homes. Census enumeration has always been based on finding people where they live, as there is no systematic alternative: any list used to find people is likely to be derived from census activities in the first place. Recent UN guidelines provide recommendations on enumerating such complex households.
In the census of agriculture, data is collected at the agricultural holding unit. An agricultural holding is an economic unit of agricultural production under single management comprising all livestock kept and all land used wholly or partly for agricultural production purposes, without regard to title, legal form, or size. Single management may be exercised by an individual or household, jointly by two or more individuals or households, by a clan or tribe, or by a juridical person such as a corporation, cooperative or government agency. The holding's land may consist of one or more parcels, located in one or more separate areas or in one or more territorial or administrative divisions, providing the parcels share the same production means, such as labour, farm buildings, machinery or draught animals.
Enumeration strategies
Historical censuses used crude enumeration assuming absolute accuracy. Modern approaches take into account the problems of overcount and undercount, and the coherence of census enumerations with other official sources of data. This reflects a realist approach to measurement, acknowledging that under any definition of residence there is a true value of the population but this can never be measured with complete accuracy. An important aspect of the census process is to evaluate the quality of the data. Many countries use a post-enumeration survey to adjust the raw census counts. This works in a similar manner to capture-recapture estimation for animal populations. Among census experts this method is called dual system enumeration (DSE). A sample of households are visited by interviewers who record the details of the household as at census day. These data are then matched to census records, and the number of people missed can be estimated by considering the numbers of people who are included in one count but not the other. This allows adjustments to the count for non-response, varying between differentdemographic
Demography () is the statistical study of populations, especially human beings.
Demographic analysis examines and measures the dimensions and dynamics of populations; it can cover whole societies or groups defined by criteria such as edu ...
groups. An explanation using a fishing analogy can be found in "Trout, Catfish and Roach..." which won an award from the Royal Statistical Society for excellence in official statistics
Official statistics are statistics published by government agencies or other public bodies such as international organizations as a public good. They provide quantitative or qualitative information on all major areas of citizens' lives, such as e ...
in 2011.
 Triple system enumeration has been proposed as an improvement as it would allow evaluation of the statistical dependence of pairs of sources. However, as the matching process is the most difficult aspect of census estimation this has never been implemented for a national enumeration. It would also be difficult to identify three different sources that were sufficiently different to make the triple system effort worthwhile. The DSE approach has another weakness in that it assumes there is no person counted twice (over count). In ''de facto'' residence definitions this would not be a problem but in ''de jure'' definitions individuals risk being recorded on more than one form leading to double counting. A particular problem here is students who often have a term time and family address.
Several countries have used a system known as short form/long form. This is a sampling strategy that randomly chooses a proportion of people to send a more detailed questionnaire to (the long form). Everyone receives the short form questions. This means more data are collected, but without imposing a burden on the whole population. This also reduces the burden on the statistical office. Indeed, in the UK until 2001 all residents were required to fill in the whole form but only a 10% sample were coded and analysed in detail. New technology means that all data are now scanned and processed. During the 2011 Canadian census there was controversy about the cessation of the mandatory long form census; the head of
Triple system enumeration has been proposed as an improvement as it would allow evaluation of the statistical dependence of pairs of sources. However, as the matching process is the most difficult aspect of census estimation this has never been implemented for a national enumeration. It would also be difficult to identify three different sources that were sufficiently different to make the triple system effort worthwhile. The DSE approach has another weakness in that it assumes there is no person counted twice (over count). In ''de facto'' residence definitions this would not be a problem but in ''de jure'' definitions individuals risk being recorded on more than one form leading to double counting. A particular problem here is students who often have a term time and family address.
Several countries have used a system known as short form/long form. This is a sampling strategy that randomly chooses a proportion of people to send a more detailed questionnaire to (the long form). Everyone receives the short form questions. This means more data are collected, but without imposing a burden on the whole population. This also reduces the burden on the statistical office. Indeed, in the UK until 2001 all residents were required to fill in the whole form but only a 10% sample were coded and analysed in detail. New technology means that all data are now scanned and processed. During the 2011 Canadian census there was controversy about the cessation of the mandatory long form census; the head of Statistics Canada
Statistics Canada (StatCan; french: Statistique Canada), formed in 1971, is the agency of the Government of Canada commissioned with producing statistics to help better understand Canada, its population, resources, economy, society, and cultur ...
, Munir Sheikh, resigned upon the federal government's decision to do so.
The use of alternative enumeration strategies is increasing but these are not as simple as many people assume and are only used in developed countries. The Netherlands has been most advanced in adopting a census using administrative data Administrative data are collected by governments or other organizations for non-statistical reasons to provide overviews on registration, transactions, and record keeping. They evaluate part of the output of administrating a program. Border records, ...
. This allows a simulated census to be conducted by linking several different administrative databases at an agreed time. Data can be matched, and an overall enumeration established allowing for discrepancies between different data sources. A validation survey is still conducted in a similar way to the post enumeration survey employed in a traditional census.
Other countries that have a population register use this as a basis for all the census statistics needed by users. This is most common among Nordic countries, but requires many distinct registers to be combined, including population, housing, employment and education. These registers are then combined and brought up to the standard of a statistical register by comparing the data in different sources and ensuring the quality is sufficient for official statistics to be produced.
A recent innovation is the French instigation of a rolling census programme with different regions enumerated each year, so that the whole country is completely enumerated every 5 to 10 years. In Europe, in connection with the 2010 census round, many countries adopted alternative census methodologies, often based on the combination of data from registers, surveys and other sources.
Technology
Censuses have evolved in their use of technology: censuses in 2010 used many new types of computing. In Brazil, handheld devices were used by enumerators to locate residences on the ground. In many countries, census returns could be made via the Internet as well as in paper form. DSE is facilitated by computer matching techniques that can be automated, such as propensity score matching. In the UK, all census formats are scanned and stored electronically before being destroyed, replacing the need for physical archives. The record linking to perform an administrative census would not be possible without large databases being stored on computer systems. There are sometimes problems in introducing new technology. The US census had been intended to use handheld computers, but cost escalated, and this was abandoned, with the contract being sold to Brazil. Online response has some advantages, but one of the functions of the census is to make sure everyone is counted accurately. A system that allowed people to enter their address without verification would be open to abuse. Therefore, households have to be verified on the ground, typically by an enumerator visit or post out. Paper forms are still necessary for those without access to the internet. It is also possible that the hidden nature of an administrative census means that users are not engaged with the importance of contributing their data to official statistics. Alternatively, population estimations may be carried out remotely withgeographic information system
A geographic information system (GIS) is a type of database containing Geographic data and information, geographic data (that is, descriptions of phenomena for which location is relevant), combined with Geographic information system software, sof ...
(GIS) and remote sensing technologies.
Development
According to the United Nations Population Fund (UNFPA), "The information generated by a population and housing census – numbers of people, their distribution, their living conditions and other key data – is critical for development." This is because this type of data is essential for policymakers so that they know where to invest. Unfortunately, many countries have outdated or inaccurate data about their populations and thus have difficulty in addressing the needs of the population. The UNFPA said:"The unique advantage of the census is that it represents the entire statistical universe, down to the smallest geographical units, of a country or region. Planners need this information for all kinds of development work, including: assessing demographic trends; analysing socio-economic conditions; designing evidence-based poverty-reduction strategies; monitoring and evaluating the effectiveness of policies; and tracking progress toward national and internationally agreed development goals."In addition to making policymakers aware of population issues, the census is also an important tool for identifying forms of social, demographic or economic exclusions, such as inequalities relating to race, ethics, and religion as well as disadvantaged groups such as those with disabilities and the poor. An accurate census can empower local communities by providing them with the necessary information to participate in local decision-making and ensuring they are represented. The importance of the census of agriculture for development is that it gives a snapshot of the structure of the agricultural sector in a country and, when compared with previous censuses, provides an opportunity to identify trends and structural transformations of the sector, and points towards areas for policy intervention. Census data are used as a benchmark for current statistics and their value is increased when they are employed together with other data sources.
Uses of census data
Early censuses in the 19th and 20th centuries collected paper documents which had to be collated by hand, so the statistical information obtained was quite basic. The government that owned the data could publish statistics on the state of the nation. The results were used to measure changes in the population and apportion representation. Population estimates could be compared to those of other countries. By the beginning of the 20th century, censuses were recording households and some indications of their employment. In some countries, census archives are released for public examination after many decades, allowing genealogists to track the ancestry of interested people. Archives provide a substantial historical record which may challenge established views. Information such as job titles and arrangements for the destitute and sick may also shed light on the historical structure of society. Political considerations influence the census in many countries. In Canada in 2010 for example, the government under the leadership of Stephen Harper abolished the mandatory long-form census. This abolition was a response to protests from some Canadians who resented the personal questions. The long-form census was reinstated by the Justin Trudeau government in 2016.Census data and research
As governments assumed responsibility for schooling and welfare, large government research departments made extensive use of census data. Population projections could be made, to help plan for provision in local government and regions. Central government could also use census data to allocate funding. Even in the mid 20th century, census data was only directly accessible to large government departments. However, computers meant that tabulations could be used directly by university researchers, large businesses and local government offices. They could use the detail of the data to answer new questions and add to local and specialist knowledge. Nowadays, census data are published in a wide variety of formats to be accessible to business, all levels of government, media, students and teachers, charities, and any citizen who is interested; researchers in particular have an interest in the role of Census Field Officers (CFO) and their assistants. Data can be represented visually or analysed in complex statistical models, to show the difference between certain areas, or to understand the association between different personal characteristics. Census data offer a unique insight into small areas and small demographic groups which sample data would be unable to capture with precision. In the census of agriculture, users need census data to: # support and contribute to evidence-based agricultural planning and policy-making. The census information is essential, for example, to monitor the performance of a policy or programme designed for crop diversification or to address food security issues; # provide data to facilitate research, investment and business decisions both in the public and private sector; # contribute to monitoring environmental changes and evaluating the impact of agricultural practices on the environment such as tillage practices, crop rotation or sources of greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions; # provide relevant data on work inputs and main work activities, as well as on the labour force in the agriculture sector; # provide an important information base for monitoring some key indicators of the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), in particular those goals related to food security in agricultural holdings, the role of women in agricultural activities and rural poverty; # provide baseline data both at the national and small administrative and geographical levels for formulating, monitoring and evaluating programmes and projects interventions; # provide essential information onsubsistence agriculture
Subsistence agriculture occurs when farmers grow food crops to meet the needs of themselves and their families on smallholdings. Subsistence agriculturalists target farm output for survival and for mostly local requirements, with little or no su ...
and for the estimation of the non-observed economy, which plays an important role in the compilation of the national accounts and the economic accounts for agriculture.
Privacy and data stewardship
Although the census provides useful statistical information about a population, the availability of this information could sometimes lead to abuses, political or otherwise, by the linking of individuals' identities to anonymous census data. This is particularly important when individuals' census responses are made available inmicrodata Microdata can mean:
* Microdata (statistics), a statistical term for individual response data in surveys and censuses
* Microdata (HTML), a specification for semantic markup in HTML
* Microdata Corporation
Microdata Corporation was an American ...
form, but even aggregate-level data can result in privacy breaches when dealing with small areas and/or rare subpopulations.
For instance, when reporting data from a large city, it might be appropriate to give the average income for black males aged between 50 and 60. However, doing this for a town that only has two black males in this age group would be a breach of privacy because either of those persons, knowing his own income and the reported average, could determine the other man's income.
Typically, census data are processed to obscure such individual information. Some agencies do this by intentionally introducing small statistical errors to prevent the identification of individuals in marginal populations; others swap variables for similar respondents. Whatever is done to reduce the privacy risk, new improved electronic analysis of data can threaten to reveal sensitive individual information. This is known as statistical disclosure control.
Another possibility is to present survey results by means of statistical models in the form of a multivariate distribution mixture. The statistical information in the form of conditional distributions (histogram
A histogram is an approximate representation of the distribution of numerical data. The term was first introduced by Karl Pearson. To construct a histogram, the first step is to " bin" (or "bucket") the range of values—that is, divide the ent ...
s) can be derived interactively from the estimated mixture model without any further access to the original database. As the final product does not contain any protected microdata, the model-based interactive software can be distributed without any confidentiality concerns.
Another method is simply to release no data at all, except very large scale data directly to the central government. Differing release strategies of governments have led to an international project ( IPUMS) to co-ordinate access to microdata and corresponding metadata. Such projects such as SDMX also promote standardising metadata, so that best use can be made of the minimal data available.
History of censuses
Egypt
Censuses in Egypt first appeared in the late Middle Kingdom and developed in theNew Kingdom
New is an adjective referring to something recently made, discovered, or created.
New or NEW may refer to:
Music
* New, singer of K-pop group The Boyz
Albums and EPs
* ''New'' (album), by Paul McCartney, 2013
* ''New'' (EP), by Regurgitator, ...
Pharaoh Amasis, according to Herodotus, required every Egyptian to declare annually to the nomarch, "whence he gained his living". Under the Ptolemies
The Ptolemaic dynasty (; grc, Πτολεμαῖοι, ''Ptolemaioi''), sometimes referred to as the Lagid dynasty (Λαγίδαι, ''Lagidae;'' after Ptolemy I's father, Lagus), was a Macedonian Greek royal dynasty which ruled the Ptolemaic K ...
and the Romans several censuses were conducted in Egypt by government officials
Ancient Greece
There are several accounts of ancient Greek city states carrying out censuses.Israel
Censuses are mentioned in the Bible. God commands aper capita tax
A poll tax, also known as head tax or capitation, is a tax levied as a fixed sum on every liable individual (typically every adult), without reference to income or resources.
Head taxes were important sources of revenue for many governments fr ...
to be paid with the census for the upkeep of the Tabernacle. The Book of Numbers is named after the counting of the Israelite population according to the house of the Fathers after the exodus from Egypt. A second census was taken while the Israelites were camped in the " plains of Moab".
King David performed a census that produced disastrous results. His son, King Solomon
Solomon (; , ),, ; ar, سُلَيْمَان, ', , ; el, Σολομών, ; la, Salomon also called Jedidiah (Hebrew language, Hebrew: , Modern Hebrew, Modern: , Tiberian Hebrew, Tiberian: ''Yăḏīḏăyāh'', "beloved of Yahweh, Yah"), ...
, had all of the foreigners in Israel counted.
When the Romans took over Judea in AD6, the legate Publius Sulpicius Quirinius organised a census for tax purposes. The Gospel of Luke links the birth of Jesus either to this event, or to an otherwise unknown census conducted prior to Quirinius' tenure.
China
One of the world's earliest preserved censuses was held in China in AD2 during the Han dynasty, and is still considered by scholars to be quite accurate.Twitchett, D., Loewe, M., and Fairbank, J.K. ''Cambridge History of China: The Ch'in and Han Empires 221 B.C.–A.D. 220''. Cambridge University Press (1986), p. 240. The population was registered as having 57,671,400 individuals in 12,366,470 households but on this occasion only taxable families had been taken into account - indicating the income and the number of soldiers who could be mobilized. Another census was held in AD144.India
The oldest recorded census in India is thought to have occurred around 330BC during the reign of EmperorChandragupta Maurya
Chandragupta Maurya (350-295 BCE) was a ruler in Ancient India who expanded a geographically-extensive kingdom based in Magadha and founded the Maurya dynasty. He reigned from 320 BCE to 298 BCE. The Maurya kingdom expanded to become an empi ...
under the leadership of Chanakya and Ashoka.
Rome
The English term is taken directly from the Latin ''census'', from ' ("to estimate"). The census played a crucial role in the administration of the Roman government, as it was used to determine the class a citizen belonged to for both military and tax purposes. Beginning in the middle republic, it was usually carried out every five years. It provided a register of citizens and their property from which their duties and privileges could be listed. It is said to have been instituted by the Roman king Servius Tullius in the at which time the number of arms-bearing citizens was supposedly counted at around 80,000. The 6AD " census of Quirinius" undertaken following the imposition of direct Roman rule in Judea was partially responsible for the development of the Zealot movement and several failed rebellions against Rome that ended in theDiaspora
A diaspora ( ) is a population that is scattered across regions which are separate from its geographic place of origin. Historically, the word was used first in reference to the dispersion of Greeks in the Hellenic world, and later Jews after ...
. The 15-year indiction cycle established by Diocletian
Diocletian (; la, Gaius Aurelius Valerius Diocletianus, grc, Διοκλητιανός, Diokletianós; c. 242/245 – 311/312), nicknamed ''Iovius'', was Roman emperor from 284 until his abdication in 305. He was born Gaius Valerius Diocles ...
in AD297 was based on quindecennial censuses and formed the basis for dating in late antiquity and under the Byzantine Empire.
Rashidun and Umayyad Caliphates
In the Middle Ages, the Caliphate began conducting regular censuses soon after its formation, beginning with the one ordered by the secondRashidun
, image = تخطيط كلمة الخلفاء الراشدون.png
, caption = Calligraphic representation of Rashidun Caliphs
, birth_place = Mecca, Hejaz, Arabia present-day Saudi Arabia
, known_for = Companions of t ...
caliph, Umar.
Medieval Europe
The Domesday Book was undertaken in AD1086 by William I of England so that he could properly tax the land he had recently conquered. In 1183, a census was taken of thecrusade
The Crusades were a series of religious wars initiated, supported, and sometimes directed by the Latin Church in the medieval period. The best known of these Crusades are those to the Holy Land in the period between 1095 and 1291 that were i ...
r Kingdom of Jerusalem, to ascertain the number of men and amount of money that could possibly be raised against an invasion by Saladin, sultan of Egypt and Syria
Syria ( ar, سُورِيَا or سُورِيَة, translit=Sūriyā), officially the Syrian Arab Republic ( ar, الجمهورية العربية السورية, al-Jumhūrīyah al-ʻArabīyah as-Sūrīyah), is a Western Asian country loc ...
.
1328 : First national census of France (''L'État des paroisses et des feux'') mostly for fiscal purposes. It estimated the French population at 16 to 17 million.
Inca Empire
In the 15th century, the Inca Empire had a unique way to record census information. The Incas did not have any written language but recorded information collected during censuses and other numeric information as well as non-numeric data on quipus, strings from llama or alpaca hair or cotton cords with numeric and other values encoded by knots in a base-10 positional system.Spanish Empire
On May 25, 1577,King Philip II of Spain
Philip II) in Spain, while in Kingdom of Portugal, Portugal and his Italian kingdoms he ruled as Philip I ( pt, Filipe I). (21 May 152713 September 1598), also known as Philip the Prudent ( es, Felipe el Prudente), was King of Spain from 1556, K ...
ordered by royal cédula the preparation of a general description of Spain's holdings in the Indies. Instructions and a questionnaire, issued in 1577 by the Office of the Cronista Mayor, were distributed to local officials in the Viceroyalties of New Spain and Peru to direct the gathering of information. The questionnaire, composed of fifty items, was designed to elicit basic information about the nature of the land and the life of its peoples. The replies, known as "", were written between 1579 and 1585 and were returned to the Cronista Mayor in Spain by the Council of the Indies.
World population estimates
The earliest estimate of the world population was made by Giovanni Battista Riccioli in 1661; the next byJohann Peter Süssmilch Johann Peter Süßmilch or Süssmilch (September 3, 1707 in Zehlendorf – March 22, 1767 in Berlin) was a German Protestant pastor, statistician and demographer.
Education and career
Süßmilch studied medicine and theology at Jena and Hal ...
in 1741, revised in 1762; the third by Karl Friedrich Wilhelm Dieterici
Karl Friedrich Wilhelm Dieterici (23 August 1790 – 30 July 1859) was a German political economist.
Biography
Dieterici was born and died in Berlin. He was an engineer-geographer in Blücher's army from 1813 to 1815, was engaged in the Minis ...
in 1859.
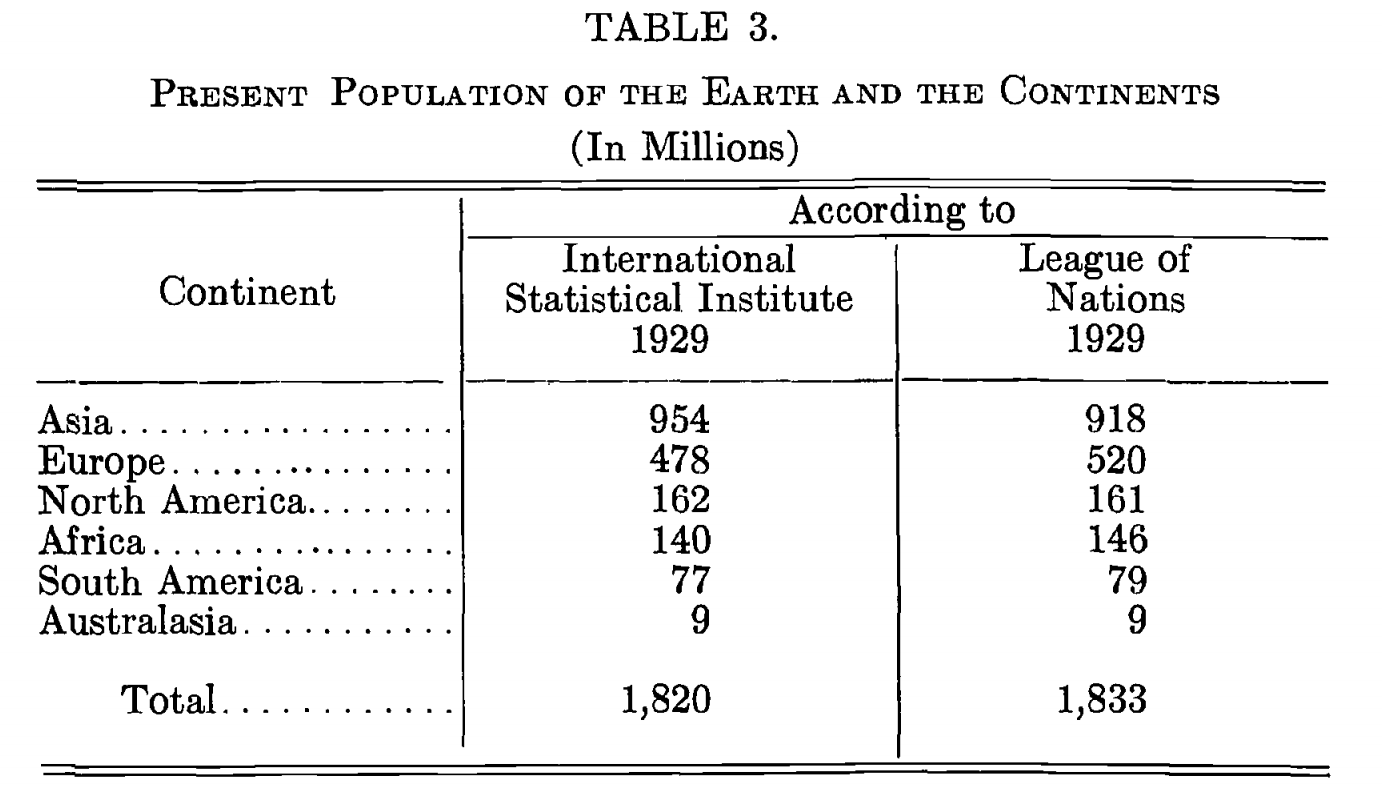
In 1931, Walter Willcox published a table in his book, ''International Migrations: Volume II Interpretations'', that estimated the 1929 world population to be roughly 1.8 billion.

Impact of COVID-19 on census
Impact
The UNFPA predicts that the COVID-19 pandemic will threaten the successful conduct of censuses of population and housing in many countries through delays, interruptions that compromise quality, or complete cancellation of census projects. Domestic and donor financing for census may be diverted to address COVID-19 leaving census without crucial funds. Several countries have already taken decisions to postpone the census, with many others yet to announce the way forward. In some countries this is already happening. The pandemic has also affected the planning and implementation of censuses of agriculture in all world regions. The extent of the impact has varied according to the stages at which the censuses are, ranging from planning (i.e. staffing, procurement, preparation of frames, questionnaires), fieldwork (field training and enumeration) or data processing/analysis stages. The census of agriculture's reference period is the agricultural year. Thus, a delay in any census activity may be critical and can result in a full year postponement of the enumeration if the agricultural season is missed. Some publications have discussed the impact of COVID-19 on national censuses of agriculture.Adaptation
The United Nations Population Fund (UNFPA) has requested a global effort to assure that even where census is delayed, census planning and preparations are not cancelled, but continue in order to assure that implementation can proceed safely when the pandemic is under control. While new census methods, including online, register-based, and hybrid approaches are being used across the world, these demand extensive planning and preconditions that cannot be created at short notice. The continuing low supply of personal protective equipment to protect against COVID-19 has immediate implications for conducting census in communities at risk of transmission. The UNFPA Procurement Office is partnering with other agencies to explore newsupply chains
In commerce, a supply chain is a network of facilities that procure raw materials, transform them into intermediate goods and then final products to customers through a distribution system. It refers to the network of organizations, people, activ ...
and resources.
Modern implementation
See also
* List of national and international statistical services * * * *Sources
Notes
References
* Alterman, Hyman, (1969). ''Counting People: The Census in History''. Harcourt, Brace & Company. * Behrisch, Lars. (2016) "Statistics and Politics in the 18th Century." ''Historical Social Research/Historische Sozialforschung'' (2016): 238–57. * Bielenstein, Hans, (1978). "Wang Mang, the restoration of the Han dynasty, and Later Han." In ''The Cambridge History of China'', vol. 1, eds. Denis Twitchett and John K. Fairbank, pp. 223–90, Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. * Krüger, Stephen, (Fall 1991). "The Decennial Census"19 ''Western State University Law Review'' 1
available a
HeinOnline
.
Effects of UK 'Jedi' hoax on 2001 UK census from ONS
*
External links
*Census of Ireland 1911
Online Historical Population Reports Project (OHPR)
PR as a function of census management: comparative analysis of fifteen census experiences
{{Authority control Population Survey methodology Sampling (statistics) Latin words and phrases