Celiac plexus on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The celiac plexus, also known as the solar plexus because of its radiating nerve fibers, is a complex network of nerves located in the
 The celiac plexus includes a number of smaller plexuses:
Other plexuses that are derived from the celiac plexus:
The celiac plexus includes a number of smaller plexuses:
Other plexuses that are derived from the celiac plexus:
 A blunt injury to the celiac plexus normally resolves with rest and deep breathing.
A celiac plexus block by means of fluoroscopically guided injection is sometimes used to treat intractable pain from cancers such as
A blunt injury to the celiac plexus normally resolves with rest and deep breathing.
A celiac plexus block by means of fluoroscopically guided injection is sometimes used to treat intractable pain from cancers such as
The Solar Plexus: Abdominal Brain By Theron Q. Dumont
{{Authority control Nerve plexus Nerves of the torso Vagus nerve
abdomen
The abdomen (colloquially called the belly, tummy, midriff, tucky or stomach) is the part of the body between the thorax (chest) and pelvis, in humans and in other vertebrates. The abdomen is the front part of the abdominal segment of the torso. ...
, near where the celiac trunk
The celiac () artery (also spelled ''coeliac''), also known as the celiac trunk or truncus coeliacus, is the first major branch of the abdominal aorta. It is about 1.25 cm in length. Branching from the aorta at thoracic vertebra 12 (T12) i ...
, superior mesenteric artery
In human anatomy, the superior mesenteric artery (SMA) is an artery which arises from the anterior surface of the abdominal aorta, just inferior to the origin of the celiac trunk, and supplies blood to the intestine from the lower part of the ...
, and renal arteries
The renal arteries are paired arteries that supply the kidneys with blood. Each is directed across the crus of the diaphragm, so as to form nearly a right angle.
The renal arteries carry a large portion of total blood flow to the kidneys. Up to a ...
branch from the abdominal aorta
In human anatomy, the abdominal aorta is the largest artery in the abdominal cavity. As part of the aorta, it is a direct continuation of the descending aorta (of the thorax).
Structure
The abdominal aorta begins at the level of the thoracic d ...
. It is behind the stomach
The stomach is a muscular, hollow organ in the gastrointestinal tract of humans and many other animals, including several invertebrates. The stomach has a dilated structure and functions as a vital organ in the digestive system. The stomach i ...
and the omental bursa
The lesser sac, also known as the omental bursa, is a part of the peritoneal cavity that is formed by the lesser and greater omentum. Usually found in mammals, it is connected with the greater sac via the omental foramen or ''Foramen of Winsl ...
, and in front of the crura of the diaphragm, on the level of the first lumbar vertebra
The lumbar vertebrae are, in human anatomy, the five vertebrae between the rib cage and the pelvis. They are the largest segments of the vertebral column and are characterized by the absence of the foramen transversarium within the transverse p ...
.
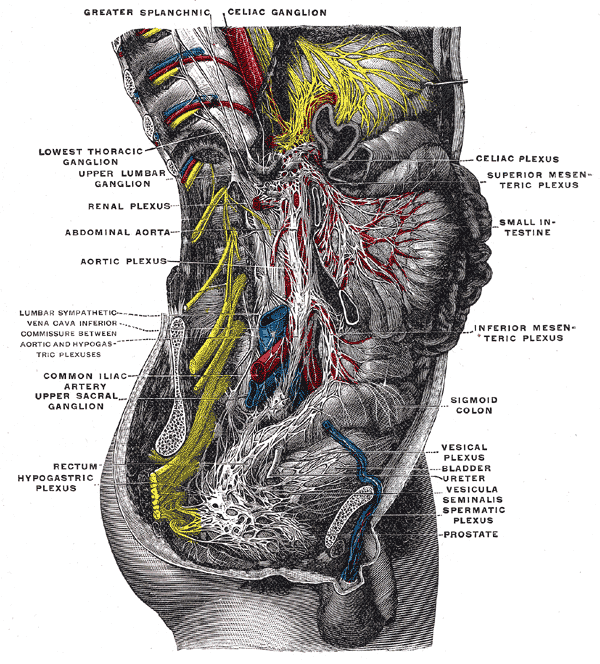
The plexus is formed in part by the greater and lesser splanchnic nerves
The splanchnic nerves are paired visceral nerves (nerves that contribute to the innervation of the viscera, innervation of the internal organs), carrying fibers of the autonomic nervous system (visceral efferent fibers) as well as sensory fibers fr ...
of both sides, and fibers from the anterior and posterior vagal trunks.
The celiac plexus proper consists of the celiac ganglia
The celiac ganglia or coeliac ganglia are two large irregularly shaped masses of nerve tissue in the upper abdomen. Part of the sympathetic subdivision of the autonomic nervous system (ANS), the two celiac ganglia are the largest ganglia in t ...
with a network of interconnecting fibers. The aorticorenal ganglia
The aorticorenal ganglion is composed of the superior mesenteric, renal, and inferior mesenteric ganglia. This is distinct from the celiac ganglia. However, they are part of the preaortic ganglia.
Sympathetic input to the gut comes from the s ...
are often considered to be part of the celiac ganglia, and thus, part of the plexus.
Structure
 The celiac plexus includes a number of smaller plexuses:
Other plexuses that are derived from the celiac plexus:
The celiac plexus includes a number of smaller plexuses:
Other plexuses that are derived from the celiac plexus:
Terminology
The celiac plexus is often popularly referred to as the solar plexus. In the context of sparring or injury, a strike to the region of the stomach around the celiac plexus is commonly called a blow "to the solar plexus". In this case it is not the celiac plexus itself being referred to, but rather the region around it. A blow to this region may cause the diaphragm to spasm, resulting in difficulty in breathing—a sensation commonly known as "getting the wind knocked out of you
Getting the wind knocked out of you is an idiom that refers to the difficulty of breathing and temporary paralysis of the diaphragm caused by reflex diaphragmatic spasm when sudden force is applied to the upper central region of the abdomen and ...
". It may also affect the celiac plexus itself, which can cause great pain and interfere with the functioning of the viscera
In biology, an organ is a collection of tissues joined in a structural unit to serve a common function. In the hierarchy of life, an organ lies between tissue and an organ system. Tissues are formed from same type cells to act together in a ...
.
Clinical significance
 A blunt injury to the celiac plexus normally resolves with rest and deep breathing.
A celiac plexus block by means of fluoroscopically guided injection is sometimes used to treat intractable pain from cancers such as
A blunt injury to the celiac plexus normally resolves with rest and deep breathing.
A celiac plexus block by means of fluoroscopically guided injection is sometimes used to treat intractable pain from cancers such as pancreatic cancer
Pancreatic cancer arises when cell (biology), cells in the pancreas, a glandular organ behind the stomach, begin to multiply out of control and form a Neoplasm, mass. These cancerous cells have the malignant, ability to invade other parts of t ...
. Such a block may be performed by pain management specialists and radiologists, with CT scans for guidance.
Intractable pain related to chronic pancreatitis may be an indication for celiac plexus ablation.
See also
*Cardiac plexus
The cardiac plexus is a plexus of nerves situated at the base of the heart that innervates the heart.
Structure
The cardiac plexus is divided into a superficial part, which lies in the concavity of the aortic arch, and a deep part, between the ao ...
* Celiac ganglia
The celiac ganglia or coeliac ganglia are two large irregularly shaped masses of nerve tissue in the upper abdomen. Part of the sympathetic subdivision of the autonomic nervous system (ANS), the two celiac ganglia are the largest ganglia in t ...
* Superior hypogastric plexus
The superior hypogastric plexus (in older texts, hypogastric plexus or presacral nerve) is a plexus of nerves situated on the vertebral bodies anterior to the bifurcation of the abdominal aorta.
Structure
From the plexus, sympathetic fibers are ca ...
*Manipura
Manipura ( sa, मणिपूर, IAST: ) is the third primary chakra according to Vedic tradition.
Description
Location
Located above the navel, Manipura translates from Sanskrit as "city of jewels" alternatively translated as "resplendent ...
References
External links
* - "Posterior Abdominal Wall: The Celiac Plexus" *The Solar Plexus: Abdominal Brain By Theron Q. Dumont
{{Authority control Nerve plexus Nerves of the torso Vagus nerve