Cation Exchange Resin on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
An ion-exchange resin or ion-exchange polymer is a
 The resin can be recharged by washing it with a solution containing a high concentration of sodium ions (e.g. it has large amounts of
The resin can be recharged by washing it with a solution containing a high concentration of sodium ions (e.g. it has large amounts of
 Ion-exchange processes are used to separate and purify
Ion-exchange processes are used to separate and purify
A. A. Zagorodni, Ion Exchange Materials: Properties and Applications, Elsevier, Amsterdam, 2006.
* Alexandratos S D . Ion-Exchange Resins: A Retrospective from Industrial and Engineering Chemistry Research. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2009. * Catalyst system comprising an ion exchange resin and a dimethyl thiazolidine promoter, Hasyagar U K , Mahalingam R J , Kishan G, WO 2012. {{Authority control Polymers Water Synthetic resins Polyelectrolytes
resin
In polymer chemistry and materials science, resin is a solid or highly viscous substance of plant or synthetic origin that is typically convertible into polymers. Resins are usually mixtures of organic compounds. This article focuses on n ...
or polymer
A polymer (; Greek ''poly-'', "many" + '' -mer'', "part")
is a substance or material consisting of very large molecules called macromolecules, composed of many repeating subunits. Due to their broad spectrum of properties, both synthetic and ...
that acts as a medium for ion exchange
Ion exchange is a reversible interchange of one kind of ion present in an insoluble solid with another of like charge present in a solution surrounding the solid with the reaction being used especially for softening or making water demineralised, ...
. It is an insoluble
In chemistry, solubility is the ability of a substance, the solute, to form a solution with another substance, the solvent. Insolubility is the opposite property, the inability of the solute to form such a solution.
The extent of the solub ...
matrix (or support structure) normally in the form of small (0.25–1.43 mm radius) microbead
Microbeads are manufactured solid plastic particles of less than one millimeter in their largest dimension. They are most frequently made of polyethylene but can be of other petrochemical plastics such as polypropylene and polystyrene.
They are u ...
s, usually white or yellowish, fabricated from an organic polymer
A polymer (; Greek ''poly-'', "many" + '' -mer'', "part")
is a substance or material consisting of very large molecules called macromolecules, composed of many repeating subunits. Due to their broad spectrum of properties, both synthetic and ...
substrate. The beads are typically porous
Porosity or void fraction is a measure of the void (i.e. "empty") spaces in a material, and is a fraction of the volume of voids over the total volume, between 0 and 1, or as a percentage between 0% and 100%. Strictly speaking, some tests measure ...
, providing a large surface area
The surface area of a solid object is a measure of the total area that the surface of the object occupies. The mathematical definition of surface area in the presence of curved surfaces is considerably more involved than the definition of ...
on and inside them where the trapping of ions occurs along with the accompanying release of other ions, and thus the process is called ion exchange. There are multiple types of ion-exchange resin. Most commercial resins are made of polystyrene sulfonate.François Dardel and Thomas V. Arden "Ion Exchangers" in Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry, 2008, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim. .
Ion-exchange resins are widely used in different separation
Separation may refer to:
Films
* ''Separation'' (1967 film), a British feature film written by and starring Jane Arden and directed by Jack Bond
* ''La Séparation'', 1994 French film
* ''A Separation'', 2011 Iranian film
* ''Separation'' (20 ...
, purification, and decontamination processes. The most common examples are water softening and water purification
Water purification is the process of removing undesirable chemicals, biological contaminants, suspended solids, and gases from water. The goal is to produce water that is fit for specific purposes. Most water is purified and disinfected for hu ...
. In many cases ion-exchange resins were introduced in such processes as a more flexible alternative to the use of natural or artificial zeolite
Zeolites are microporous, crystalline aluminosilicate materials commonly used as commercial adsorbents and catalysts. They mainly consist of silicon, aluminium, oxygen, and have the general formula ・y where is either a metal ion or H+. These ...
s. Also, ion-exchange resins are highly effective in the biodiesel filtration process.
Types of resins
Most typical ion-exchange resins are based on crosslinkedpolystyrene
Polystyrene (PS) is a synthetic polymer made from monomers of the aromatic hydrocarbon styrene. Polystyrene can be solid or foamed. General-purpose polystyrene is clear, hard, and brittle. It is an inexpensive resin per unit weight. It is ...
. The actual ion-exchanging sites are introduced after polymerisation. Additionally, in the case of polystyrene, crosslinking is introduced by copolymerisation of styrene and a few percent of divinylbenzene. Crosslinking decreases ion-exchange capacity of the resin and prolongs the time needed to accomplish the ion-exchange processes but improves the robustness of the resin. Particle size also influences the resin parameters; smaller particles have larger outer surface, but cause larger head loss
Hydraulic head or piezometric head is a specific measurement of liquid pressure above a vertical datum., 410 pages. See pp. 43–44., 650 pages. See p. 22.
It is usually measured as a liquid surface elevation, expressed in units of length, ...
in the column processes.
Besides being made as bead-shaped materials, ion-exchange resins are also produced as membranes. These ion-exchange membrane An ion-exchange membrane is a semi-permeable membrane that transports certain dissolved ions, while blocking other ions or neutral molecules.
Ion-exchange membranes are therefore electrically conductive. They are often used in desalination and ...
s, which are made of highly cross-linked ion-exchange resins that allow passage of ions, but not of water, are used for electrodialysis
Electrodialysis (ED) is used to transport salt ions from one solution through ion-exchange membranes to another solution under the influence of an applied electric potential difference. This is done in a configuration called an electrodialys ...
.
Four main types of ion-exchange resins differ in their functional group
In organic chemistry, a functional group is a substituent or moiety in a molecule that causes the molecule's characteristic chemical reactions. The same functional group will undergo the same or similar chemical reactions regardless of the res ...
s:
* strongly acidic, typically featuring sulfonic acid groups, e.g. sodium polystyrene sulfonate or polyAMPS,
* strongly basic, typically featuring quaternary amino
In chemistry, amines (, ) are compounds and functional groups that contain a basic nitrogen atom with a lone pair. Amines are formally derivatives of ammonia (), wherein one or more hydrogen atoms have been replaced by a substituent su ...
groups, for example, trimethylammonium
Trimethylamine (TMA) is an organic compound with the formula N(CH3)3. It is a colorless, hygroscopic, and flammable tertiary amine. It is a gas at room temperature but is usually sold as a 40% solution in water. (It is also sold in pressurized g ...
groups, e.g. polyAPTAC),
* weakly acidic, typically featuring carboxylic acid
In organic chemistry, a carboxylic acid is an organic acid that contains a carboxyl group () attached to an R-group. The general formula of a carboxylic acid is or , with R referring to the alkyl, alkenyl, aryl, or other group. Carboxyl ...
groups,
* weakly basic, typically featuring primary, secondary, and/or tertiary amino
In chemistry, amines (, ) are compounds and functional groups that contain a basic nitrogen atom with a lone pair. Amines are formally derivatives of ammonia (), wherein one or more hydrogen atoms have been replaced by a substituent su ...
groups, e.g. polyethylene amine.
Specialised ion-exchange resins are also known such as chelating resins (iminodiacetic acid
Iminodiacetic acid is the organic compound with the formula HN(CH2CO2H)2, often abbreviated to IDA. A white solid, the compound is a dicarboxylic acid amine (the nitrogen atom forms a secondary amino group, not an imino group as the name suggest ...
, thiourea
Thiourea () is an organosulfur compound with the formula and the structure . It is structurally similar to urea (), except that the oxygen atom is replaced by a sulfur atom (as implied by the '' thio-'' prefix); however, the properties of ur ...
-based resins, and many others).
Anion resins and cation resins are the two most common resins used in the ion-exchange process. While anion resins attract negatively charged ions, cation resins attract positively charged ions.
Anion resins
Anion resins may be either strongly or weakly basic. Strongly basic anion resins maintain their negative charge across a wide pH range, whereas weakly basic anion resins are neutralized at higher pH levels. Wikibooks:Proteomics/Protein Separations - Chromatography/Ion exchange#Anion Exchangers. Weakly basic resins do not maintain their charge at a high pH because they undergo deprotonation. They do, however, offer excellent mechanical and chemical stability. This, combined with a high rate of ion exchange, make weakly base anion resins well suited for the organic salts. For anion resins, regeneration typically involves treatment of the resin with a strongly basic solution, e.g. aqueous sodium hydroxide. During regeneration, the regenerant chemical is passed through the resin, and trapped negative ions are flushed out, renewing the resin exchange capacity.Cation-exchange resin
Formula: R−H acidic The cation exchange method removes the hardness of water but induces acidity in it, which is further removed in the next stage of treatment of water by passing this acidic water through an anion exchange process. Reaction: :R−H + M+ = R−M + H+.Anion-exchange resin
Formula: –NR4+OH− Often these arestyrene
Styrene () is an organic compound with the chemical formula C6H5CH=CH2. This derivative of benzene is a colorless oily liquid, although aged samples can appear yellowish. The compound evaporates easily and has a sweet smell, although high concen ...
– divinylbenzene copolymer
In polymer chemistry, a copolymer is a polymer derived from more than one species of monomer. The polymerization of monomers into copolymers is called copolymerization. Copolymers obtained from the copolymerization of two monomer species are some ...
resins that have quaternary ammonium cation
In chemistry, quaternary ammonium cations, also known as quats, are positively charged polyatomic ions of the structure , R being an alkyl group or an aryl group. Unlike the ammonium ion () and the primary, secondary, or tertiary ammonium cat ...
s as an integral part of the resin matrix.
Reaction:
: –NR4+OH− + HCl = –NR4+Cl− + H2O.
Anion-exchange chromatography
Anion-exchange chromatography is a process that separates substances based on their charges using an ion-exchange resin containing positively charged groups, such as diethyl-aminoethyl groups (DEAE). In solution, the resin is coated with positive ...
makes use of this principle to extract and purify materials from mixtures or solutions.
Uses
Water softening
In this application, Ion-exchange resins are used to replace themagnesium
Magnesium is a chemical element with the symbol Mg and atomic number 12. It is a shiny gray metal having a low density, low melting point and high chemical reactivity. Like the other alkaline earth metals (group 2 of the periodic ...
and calcium
Calcium is a chemical element with the symbol Ca and atomic number 20. As an alkaline earth metal, calcium is a reactive metal that forms a dark oxide-nitride layer when exposed to air. Its physical and chemical properties are most similar t ...
ions found in hard water
Hard water is water that has high mineral content (in contrast with "soft water"). Hard water is formed when water percolates through deposits of limestone, chalk or gypsum, which are largely made up of calcium and magnesium carbonates, bicarbo ...
with sodium
Sodium is a chemical element with the symbol Na (from Latin ''natrium'') and atomic number 11. It is a soft, silvery-white, highly reactive metal. Sodium is an alkali metal, being in group 1 of the periodic table. Its only stable ...
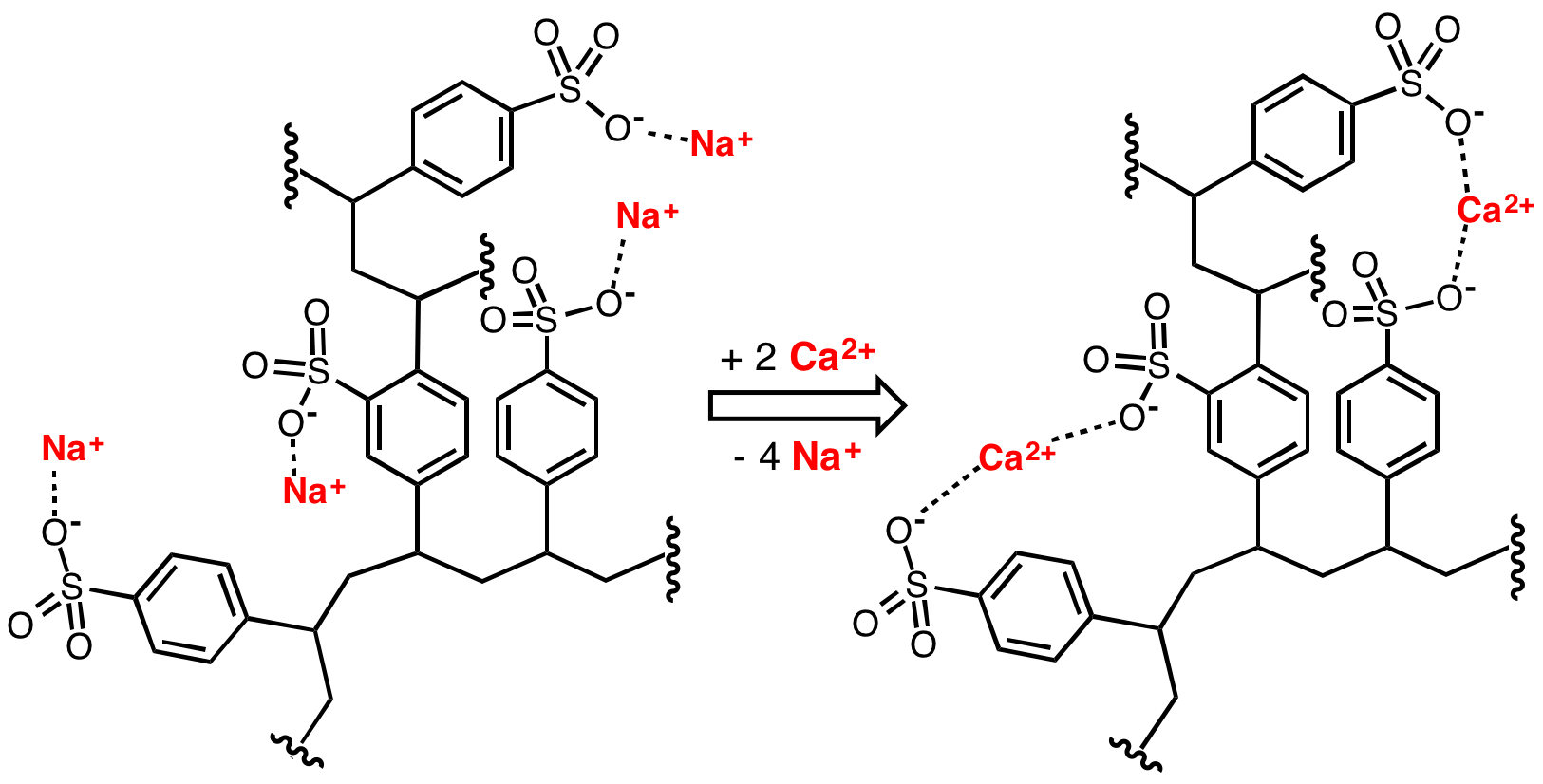
ions. When the resin is fresh, it contains sodium ions at its active sites. When in contact with a solution containing magnesium and calcium ions (but a low concentration of sodium ions), the magnesium and calcium ions preferentially migrate out of solution to the active sites on the resin, being replaced in solution by sodium ions. This process reaches equilibrium with a much lower concentration of magnesium and calcium ions in solution than was started with.
 The resin can be recharged by washing it with a solution containing a high concentration of sodium ions (e.g. it has large amounts of
The resin can be recharged by washing it with a solution containing a high concentration of sodium ions (e.g. it has large amounts of common salt
Salt is a mineral composed primarily of sodium chloride (NaCl), a chemical compound belonging to the larger class of Salt (chemistry), salts; salt in the form of a natural crystallinity, crystalline mineral is known as rock salt or halite. ...
(NaCl) dissolved in it). The calcium and magnesium ions migrate from the resin, being replaced by sodium ions from the solution until a new equilibrium is reached. The salt is used to recharge an ion-exchange resin, which itself is used to soften the water.
Water purification
In this application, ion-exchange resins are used to removepoison
Poison is a chemical substance that has a detrimental effect to life. The term is used in a wide range of scientific fields and industries, where it is often specifically defined. It may also be applied colloquially or figuratively, with a broa ...
ous (e.g. copper
Copper is a chemical element with the symbol Cu (from la, cuprum) and atomic number 29. It is a soft, malleable, and ductile metal with very high thermal and electrical conductivity. A freshly exposed surface of pure copper has a pinkish ...
) and hazardous metal (e.g. lead
Lead is a chemical element with the Symbol (chemistry), symbol Pb (from the Latin ) and atomic number 82. It is a heavy metals, heavy metal that is density, denser than most common materials. Lead is Mohs scale of mineral hardness#Intermediate ...
or cadmium
Cadmium is a chemical element with the symbol Cd and atomic number 48. This soft, silvery-white metal is chemically similar to the two other stable metals in group 12, zinc and mercury. Like zinc, it demonstrates oxidation state +2 in most of ...
) ions from solution, replacing them with more innocuous ions, such as sodium
Sodium is a chemical element with the symbol Na (from Latin ''natrium'') and atomic number 11. It is a soft, silvery-white, highly reactive metal. Sodium is an alkali metal, being in group 1 of the periodic table. Its only stable ...
and potassium
Potassium is the chemical element with the symbol K (from Neo-Latin '' kalium'') and atomic number19. Potassium is a silvery-white metal that is soft enough to be cut with a knife with little force. Potassium metal reacts rapidly with atmosp ...
.
Few ion-exchange resins remove chlorine
Chlorine is a chemical element with the symbol Cl and atomic number 17. The second-lightest of the halogens, it appears between fluorine and bromine in the periodic table and its properties are mostly intermediate between them. Chlorine is ...
or organic contaminants from water – this is usually done by using an activated charcoal
"Activated" is a song by English singer Cher Lloyd. It was released on 22 July 2016 through Vixen Records. The song was made available to stream exclusively on ''Rolling Stone'' a day before to release (on 21 July 2016).
Background
In an inter ...
filter mixed in with the resin. There are some ion-exchange resins that do remove organic ions, such as MIEX (magnetic ion-exchange) resins. Domestic water purification resin is not usually recharged – the resin is discarded when it can no longer be used.
Water of highest purity is required for electronics, scientific experiments, production of superconductors, and nuclear industry, among others. Such water is produced using ion-exchange processes or combinations of membrane and ion-exchange methods.
Ion exchange in metal separation
 Ion-exchange processes are used to separate and purify
Ion-exchange processes are used to separate and purify metal
A metal (from Greek μέταλλον ''métallon'', "mine, quarry, metal") is a material that, when freshly prepared, polished, or fractured, shows a lustrous appearance, and conducts electricity and heat relatively well. Metals are typi ...
s, including separating uranium
Uranium is a chemical element with the symbol U and atomic number 92. It is a silvery-grey metal in the actinide series of the periodic table. A uranium atom has 92 protons and 92 electrons, of which 6 are valence electrons. Uranium is weakly ...
from plutonium
Plutonium is a radioactive chemical element with the symbol Pu and atomic number 94. It is an actinide metal of silvery-gray appearance that tarnishes when exposed to air, and forms a dull coating when oxidized. The element normally exhib ...
and other actinide
The actinide () or actinoid () series encompasses the 15 metallic chemical elements with atomic numbers from 89 to 103, actinium through lawrencium. The actinide series derives its name from the first element in the series, actinium. The inf ...
s, including thorium
Thorium is a weakly radioactive metallic chemical element with the symbol Th and atomic number 90. Thorium is silvery and tarnishes black when it is exposed to air, forming thorium dioxide; it is moderately soft and malleable and has a high ...
; and lanthanum, neodymium
Neodymium is a chemical element with the symbol Nd and atomic number 60. It is the fourth member of the lanthanide series and is considered to be one of the rare-earth metals. It is a hard, slightly malleable, silvery metal that quickly tarnishes ...
, ytterbium
Ytterbium is a chemical element with the symbol Yb and atomic number 70. It is a metal, the fourteenth and penultimate element in the lanthanide series, which is the basis of the relative stability of its +2 oxidation state. However, like the othe ...
, samarium, lutetium, from each other and the other lanthanide
The lanthanide () or lanthanoid () series of chemical elements comprises the 15 metallic chemical elements with atomic numbers 57–71, from lanthanum through lutetium. These elements, along with the chemically similar elements scandium and y ...
s. There are two series of rare-earth metals, the lanthanides and the actinides. Members of each family have very similar chemical and physical properties. Ion exchange was for many years the only practical way to separate the rare earths in large quantities. This application was developed in the 1940s by Frank Spedding
Frank Harold Spedding (22 October 1902 – 15 December 1984) was a Canadian American chemist. He was a renowned expert on rare earth elements, and on extraction of metals from minerals. The uranium extraction process helped make it possible f ...
. Subsequently, solvent extraction has mostly supplanted use of ion-exchange resins except for the highest-purity products.
A very important case is the PUREX
PUREX (plutonium uranium reduction extraction) is a chemistry, chemical method used to purify fuel for nuclear reactors or nuclear weapons. PUREX is the ''de facto'' standard aqueous nuclear reprocessing method for the recovery of uranium and p ...
process (plutonium-uranium extraction process), which is used to separate the plutonium
Plutonium is a radioactive chemical element with the symbol Pu and atomic number 94. It is an actinide metal of silvery-gray appearance that tarnishes when exposed to air, and forms a dull coating when oxidized. The element normally exhib ...
and the uranium
Uranium is a chemical element with the symbol U and atomic number 92. It is a silvery-grey metal in the actinide series of the periodic table. A uranium atom has 92 protons and 92 electrons, of which 6 are valence electrons. Uranium is weakly ...
from the spent fuel products from a nuclear reactor
A nuclear reactor is a device used to initiate and control a fission nuclear chain reaction or nuclear fusion reactions. Nuclear reactors are used at nuclear power plants for electricity generation and in nuclear marine propulsion. Heat from nu ...
, and to be able to dispose of the waste products. Then, the plutonium and uranium are available for making nuclear-energy materials, such as new reactor fuel and nuclear weapon
A nuclear weapon is an explosive device that derives its destructive force from nuclear reactions, either fission (fission bomb) or a combination of fission and fusion reactions ( thermonuclear bomb), producing a nuclear explosion. Both bom ...
s.
Ion-exchange beads are also an essential component in in-situ leach uranium mining. In-situ recovery involves the extraction of uranium-bearing water (grading as low as 0.05% U3O8) through boreholes. The extracted uranium solution is then filtered through the resin beads. Through an ion-exchange process, the resin beads attract uranium from the solution. Uranium-loaded resins are then transported to a processing plant, where U3O8 is separated from the resin beads, and yellowcake
Yellowcake (also called urania) is a type of uranium concentrate powder obtained from leach solutions, in an intermediate step in the processing of uranium ores. It is a step in the processing of uranium after it has been mined but before f ...
is produced. The resin beads can then be returned to the ion-exchange facility, where they are reused.
The ion-exchange process is also used to separate other sets of very similar chemical elements, such as zirconium
Zirconium is a chemical element with the symbol Zr and atomic number 40. The name ''zirconium'' is taken from the name of the mineral zircon, the most important source of zirconium. The word is related to Persian '' zargun'' (zircon; ''zar-gun'' ...
and hafnium
Hafnium is a chemical element with the symbol Hf and atomic number 72. A lustrous, silvery gray, tetravalent transition metal, hafnium chemically resembles zirconium and is found in many zirconium minerals. Its existence was predicted by D ...
, which incidentally is also very important for the nuclear industry. Zirconium is practically transparent to free neutrons, used in building reactors, but hafnium is a very strong absorber of neutrons, used in reactor control rod
Control rods are used in nuclear reactors to control the rate of fission of the nuclear fuel – uranium or plutonium. Their compositions include chemical elements such as boron, cadmium, silver, hafnium, or indium, that are capable of absorbing ...
s.
Catalysis
Ion exchange resins are used inorganic synthesis
Organic synthesis is a special branch of chemical synthesis and is concerned with the intentional construction of organic compounds. Organic molecules are often more complex than inorganic compounds, and their synthesis has developed into one o ...
, e.g. for esterification
In chemistry, an ester is a compound derived from an oxoacid (organic or inorganic) in which at least one hydroxyl group () is replaced by an alkoxy group (), as in the substitution reaction of a carboxylic acid and an alcohol. Glyceride ...
and hydrolysis
Hydrolysis (; ) is any chemical reaction in which a molecule of water breaks one or more chemical bonds. The term is used broadly for substitution, elimination, and solvation reactions in which water is the nucleophile.
Biological hydrolysis ...
. Being high surface area and insoluble, they are suitable for vapor-phase and liquid-phase reactions. Examples can be found where basic (OH−-form) of ion exchange resins are used to neutralize of ammonium salts and convert quaternary ammonium halides to hydroxides. Acidic (H+-form) ion exchange resins have been used as solid acid catalysts for scission of ether protecting groups. and for rearrangement reactions.
Juice purification
Ion-exchange resins are used in the manufacture of fruit juices such as orange and cranberry juice, where they are used to remove bitter-tasting components and so improve the flavor. This allows tart or poorer-tasting fruit sources to be used for juice production.Sugar manufacturing
Ion-exchange resins are used in the manufacturing of sugar from various sources. They are used to help convert one type of sugar into another type of sugar, and to decolorize and purify sugar syrups.Pharmaceuticals
Ion-exchange resins are used in the manufacturing of pharmaceuticals, not only for catalyzing certain reactions, but also for isolating and purifying pharmaceuticalactive ingredient
An active ingredient is any ingredient that provides biologically active or other direct effect in the diagnosis, cure, mitigation, treatment, or prevention of disease or to affect the structure or any function of the body of humans or animals. The ...
s.
Three ion-exchange resins, sodium polystyrene sulfonate, colestipol, and cholestyramine, are used as active ingredient
An active ingredient is any ingredient that provides biologically active or other direct effect in the diagnosis, cure, mitigation, treatment, or prevention of disease or to affect the structure or any function of the body of humans or animals. The ...
s. Sodium polystyrene sulfonate is a strongly acidic ion-exchange resin and is used to treat hyperkalemia
Hyperkalemia is an elevated level of potassium (K+) in the blood. Normal potassium levels are between 3.5 and 5.0 mmol/L (3.5 and 5.0 mEq/L) with levels above 5.5mmol/L defined as hyperkalemia. Typically hyperkalemia does not cause symptoms. Occa ...
. Colestipol is a weakly basic ion-exchange resin and is used to treat hypercholesterolemia
Hypercholesterolemia, also called high cholesterol, is the presence of high levels of cholesterol in the blood. It is a form of hyperlipidemia (high levels of lipids in the blood), hyperlipoproteinemia (high levels of lipoproteins in the bloo ...
. Cholestyramine is a strongly basic ion-exchange resin and is also used to treat hypercholesterolemia
Hypercholesterolemia, also called high cholesterol, is the presence of high levels of cholesterol in the blood. It is a form of hyperlipidemia (high levels of lipids in the blood), hyperlipoproteinemia (high levels of lipoproteins in the bloo ...
. Colestipol and cholestyramine are known as bile acid sequestrant The bile acid sequestrants are a group of resins used to bind certain components of bile in the gastrointestinal tract. They disrupt the enterohepatic circulation of bile acids by combining with bile constituents and preventing their reabsorption ...
s.
Ion-exchange resins are also used as excipients in pharmaceutical formulations such as tablets, capsules, gums, and suspensions. In these uses the ion-exchange resin can have several different functions, including taste-masking, extended release, tablet disintegration, increased bioavailability
In pharmacology, bioavailability is a subcategory of absorption and is the fraction (%) of an administered drug that reaches the systemic circulation.
By definition, when a medication is administered intravenously, its bioavailability is 100%. ...
, and improving the chemical stability of the active ingredient
An active ingredient is any ingredient that provides biologically active or other direct effect in the diagnosis, cure, mitigation, treatment, or prevention of disease or to affect the structure or any function of the body of humans or animals. The ...
s.
Selective polymeric chelators have been proposed for maintenance therapy
Maintenance therapy is a medical therapy that is designed to help a primary treatment succeed. For example, maintenance chemotherapy may be given to people who have a cancer in remission in an attempt to prevent a relapse. This form of treatment ...
of some pathologies, where chronic ion accumulation occurs, such as Wilson disease (where copper
Copper is a chemical element with the symbol Cu (from la, cuprum) and atomic number 29. It is a soft, malleable, and ductile metal with very high thermal and electrical conductivity. A freshly exposed surface of pure copper has a pinkish ...
accumulation occurs) or hereditary hemochromatosis (iron overload
Iron overload or hemochromatosis (also spelled ''haemochromatosis'' in British English) indicates increased total accumulation of iron in the body from any cause and resulting organ damage. The most important causes are hereditary haemochromatos ...
, where iron
Iron () is a chemical element with symbol Fe (from la, ferrum) and atomic number 26. It is a metal that belongs to the first transition series and group 8 of the periodic table. It is, by mass, the most common element on Earth, right in ...
accumulation occurs) These polymers or particles have a negligible or null systemic biological availability and they are designed to form stable complexes with Fe2+ and Fe3+ in the GIT and thus limiting the uptake of these ions and their long-term accumulation. Although this method has only a limited efficacy, unlike small-molecular chelators (deferasirox
Deferasirox, sold under the brand name Exjade & Asunra (in injectable form) & Oleptiss (Tablet formulation) both by Novartis among others, is an oral iron chelator. Its main use is to reduce chronic iron overload in patients who are receiving l ...
, deferiprone, or deferoxamine), such an approach may have only minor side effects
In medicine, a side effect is an effect, whether therapeutic or adverse, that is secondary to the one intended; although the term is predominantly employed to describe adverse effects, it can also apply to beneficial, but unintended, consequence ...
in sub-chronic studies. Interestingly, the simultaneous chelation of Fe2+ and Fe3+ increases the treatment efficacy.
CO2 Capture from Ambient Air
Anion exchange resins readily absorb CO2 when dry and release it again when exposed to moisture. This makes them one of the most promising materials for direct carbon capture from ambient air, or direct air capture, since the moisture swing replaces the more energy-intensive temperature swing or pressure swing used with other sorbents. A prototype demonstrating this process has been developed byKlaus Lackner
Klaus S. Lackner is the Founding Director of the Center for Negative Carbon Emissions (CNCE) and a professor in School of Sustainable Engineering and the Built Environment at Arizona State University
Arizona State University (Arizona State ...
at the Center for Negative Carbon Emissions
The Center for Negative Carbon Emissions (CNCE) is led by Director Matthew Green, and was founded by Klaus S. Lackner in the School of Sustainable Engineering and the Built Environment (SSEBE) at Arizona State University
Arizona State Univer ...
.
See also
*Polyelectrolyte
Polyelectrolytes are polymers whose repeating units bear an electrolyte group. Polycations and polyanions are polyelectrolytes. These groups dissociate in aqueous solutions (water), making the polymers charged. Polyelectrolyte properties are th ...
* Water softening
Notes
Further reading
* * * Ion Exchangers (K. Dorfner, ed.), Walter de Gruyter, Berlin, 1991. * C. E. Harland, Ion exchange: Theory and Practice, The Royal Society of Chemistry, Cambridge, 1994. * Ion exchange (D. Muraviev, V. Gorshkov, A. Warshawsky), M. Dekker, New York, 2000.A. A. Zagorodni, Ion Exchange Materials: Properties and Applications, Elsevier, Amsterdam, 2006.
* Alexandratos S D . Ion-Exchange Resins: A Retrospective from Industrial and Engineering Chemistry Research. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2009. * Catalyst system comprising an ion exchange resin and a dimethyl thiazolidine promoter, Hasyagar U K , Mahalingam R J , Kishan G, WO 2012. {{Authority control Polymers Water Synthetic resins Polyelectrolytes