Catalan () is a
Western Romance language
Western Romance languages are one of the two subdivisions of a proposed subdivision of the Romance languages based on the La Spezia–Rimini Line. They include the Iberian Romance languages, Ibero-Romance and Gallo-Romance languages, Gallo-Romanc ...
and is the official language of
Andorra
Andorra, officially the Principality of Andorra, is a Sovereignty, sovereign landlocked country on the Iberian Peninsula, in the eastern Pyrenees in Southwestern Europe, Andorra–France border, bordered by France to the north and Spain to A ...
, and the official language of three
autonomous communities
The autonomous communities () are the first-level administrative divisions of Spain, created in accordance with the Spanish Constitution of 1978, with the aim of guaranteeing limited autonomy to the nationalities and regions that make up Spa ...
in eastern
Spain
Spain, or the Kingdom of Spain, is a country in Southern Europe, Southern and Western Europe with territories in North Africa. Featuring the Punta de Tarifa, southernmost point of continental Europe, it is the largest country in Southern Eur ...
:
Catalonia
Catalonia is an autonomous community of Spain, designated as a ''nationalities and regions of Spain, nationality'' by its Statute of Autonomy of Catalonia of 2006, Statute of Autonomy. Most of its territory (except the Val d'Aran) is situate ...
, the
Balearic Islands
The Balearic Islands are an archipelago in the western Mediterranean Sea, near the eastern coast of the Iberian Peninsula. The archipelago forms a Provinces of Spain, province and Autonomous communities of Spain, autonomous community of Spain, ...
and the
Valencian Community
The Valencian Community is an Autonomous communities of Spain, autonomous community of Spain. It is the fourth most populous Spanish Autonomous communities of Spain, autonomous community after Andalusia, Catalonia and the Community of Madrid wit ...
, where it is called ''
Valencian Valencian can refer to:
* Something related to the Valencian Community ( Valencian Country) in Spain
* Something related to the city of Valencia
* Something related to the province of Valencia in Spain
* Something related to the old Kingdom of ...
'' (). It has semi-official status in the
Italian
Italian(s) may refer to:
* Anything of, from, or related to the people of Italy over the centuries
** Italians, a Romance ethnic group related to or simply a citizen of the Italian Republic or Italian Kingdom
** Italian language, a Romance languag ...
''
comune
A (; : , ) is an administrative division of Italy, roughly equivalent to a township or municipality. It is the third-level administrative division of Italy, after regions () and provinces (). The can also have the City status in Italy, titl ...
'' of
Alghero
Alghero (; ; ; ) is a city of about 45,000 inhabitants in the Italian province of Sassari in the north west of the island of Sardinia, next to the Mediterranean Sea. The city's name comes from ''Aleguerium'', which is a mediaeval Latin word m ...
, and it is spoken in the
Pyrénées-Orientales
Pyrénées-Orientales (; ; ; ), also known as Northern Catalonia, is a departments of France, department of the Regions of France, region of Occitania (administrative region), Occitania, Southern France, adjacent to the northern Spain, Spanish ...
department of
France
France, officially the French Republic, is a country located primarily in Western Europe. Overseas France, Its overseas regions and territories include French Guiana in South America, Saint Pierre and Miquelon in the Atlantic Ocean#North Atlan ...
and in two further areas in eastern Spain: the
eastern strip of
Aragon
Aragon ( , ; Spanish and ; ) is an autonomous communities of Spain, autonomous community in Spain, coextensive with the medieval Kingdom of Aragon. In northeastern Spain, the Aragonese autonomous community comprises three provinces of Spain, ...
and the
Carche
Carche ( ; ) is a mountainous, sparsely populated area in the Region of Murcia, Spain, lying between the municipalities of Jumilla and Yecla. The mountains reach an elevation of 1,371 metres at the ''Pico de la Madama'' and part of the region ...
area in the
Region of Murcia
The Region of Murcia (, ; ; ) is an Autonomous communities of Spain, autonomous community of Spain located in the southeastern part of the Iberian Peninsula, on the Mediterranean Sea, Mediterranean coast. The region is in area and had a popul ...
. The Catalan-speaking territories are often called the or "Països Catalans".
The language evolved from
Vulgar Latin
Vulgar Latin, also known as Colloquial, Popular, Spoken or Vernacular Latin, is the range of non-formal Register (sociolinguistics), registers of Latin spoken from the Crisis of the Roman Republic, Late Roman Republic onward. ''Vulgar Latin'' a ...
in the Middle Ages around the eastern
Pyrenees
The Pyrenees are a mountain range straddling the border of France and Spain. They extend nearly from their union with the Cantabrian Mountains to Cap de Creus on the Mediterranean coast, reaching a maximum elevation of at the peak of Aneto. ...
. It became the language of the
Principality of Catalonia
The Principality of Catalonia (; ; ; ) was a Middle Ages, medieval and early modern state (polity), state in the northeastern Iberian Peninsula. During most of its history it was in dynastic union with the Kingdom of Aragon, constituting together ...
and the kingdoms of
Valencia
Valencia ( , ), formally València (), is the capital of the Province of Valencia, province and Autonomous communities of Spain, autonomous community of Valencian Community, the same name in Spain. It is located on the banks of the Turia (r ...
and
Mallorca
Mallorca, or Majorca, is the largest of the Balearic Islands, which are part of Spain, and the List of islands in the Mediterranean#By area, seventh largest island in the Mediterranean Sea.
The capital of the island, Palma, Majorca, Palma, i ...
, being present throughout the Mediterranean. Replaced by Spanish as a language of government and literature in the 1700s, Nineteenth-century Spain saw a
Catalan literary revival, culminating in the early 1900s. With the end of
Franco dictatorship (1975) and its repressive measures against the language, Catalan entered in a relatively successful process of re-normalization between the 1980s and the 2000s. However, during the 2010s, it experienced signs of decline in social use,
diglossia
In linguistics, diglossia ( , ) is where two dialects or languages are used (in fairly strict compartmentalization) by a single language community. In addition to the community's everyday or vernacular language variety (labeled "L" or "low" v ...
and the re-growth of discrimination cases.
Etymology and pronunciation
The word ''Catalan'' is derived from the territorial name of
Catalonia
Catalonia is an autonomous community of Spain, designated as a ''nationalities and regions of Spain, nationality'' by its Statute of Autonomy of Catalonia of 2006, Statute of Autonomy. Most of its territory (except the Val d'Aran) is situate ...
, itself of disputed etymology. The main theory suggests that () derives from the name or ('Land of the
Goths
The Goths were a Germanic people who played a major role in the fall of the Western Roman Empire and the emergence of medieval Europe. They were first reported by Graeco-Roman authors in the 3rd century AD, living north of the Danube in what is ...
'), since the origins of the Catalan counts, lords and people were found in the
March of Gothia
Septimania is a historical region in modern-day southern France. It referred to the western part of the Roman province of ''Gallia Narbonensis'' that passed to the control of the Visigoths in 462, when Septimania was ceded to their king, Theodor ...
, whence ''Gothland'' > ''Gothlandia'' > ''Gothalania'' > ''Catalonia'' theoretically derived.
In English, the term referring to a person first appears in the mid 14th century as ''Catelaner'', followed in the 15th century as (from
Middle French
Middle French () is a historical division of the French language that covers the period from the mid-14th to the early 17th centuries. It is a period of transition during which:
* the French language became clearly distinguished from the other co ...
). It is attested a language name since at least 1652. The word ''Catalan'' can be pronounced in English as or .
The
endonym
An endonym (also known as autonym ) is a common, name for a group of people, individual person, geographical place, language, or dialect, meaning that it is used inside a particular group or linguistic community to identify or designate them ...
is pronounced in the Eastern Catalan dialects, and in the Western dialects. In the
Valencian Community
The Valencian Community is an Autonomous communities of Spain, autonomous community of Spain. It is the fourth most populous Spanish Autonomous communities of Spain, autonomous community after Andalusia, Catalonia and the Community of Madrid wit ...
and
Carche
Carche ( ; ) is a mountainous, sparsely populated area in the Region of Murcia, Spain, lying between the municipalities of Jumilla and Yecla. The mountains reach an elevation of 1,371 metres at the ''Pico de la Madama'' and part of the region ...
, the term is frequently used instead. Thus, the name "Valencian", although often employed for referring to the varieties specific to the Valencian Community and Carche, is also used by Valencians as a name for the language as a whole,
synonymous with "Catalan".
Both uses of the term have their respective entries in the dictionaries by the ''
Acadèmia Valenciana de la Llengua
The Acadèmia Valenciana de la Llengua ("Valencian Academy of the Language"), also known by the acronym
An acronym is a type of abbreviation consisting of a phrase whose only pronounced elements are the initial letters or initial sounds of ...
'' (AVL)
[The ''Valencian Normative Dictionary'' of the Valencian Academy of the Language states that Valencian is a "Romance language spoken in the Valencian Community, as well as in Catalonia, the Balearic Islands, the French department of the , the Principality of Andorra, the eastern flank of Aragon and the Sardinian town of Alghero (unique in Italy), where it receives the name of 'Catalan'".] and the ''
Institut d'Estudis Catalans
The Institute for Catalan Studies ( ), also known by the acronym and initialism, acronym IEC, is an academic institution which seeks to undertake research and study into "all elements of Catalan culture". It is based in Barcelona, Catalonia, Spai ...
'' (IEC).
[The ''Catalan Language Dictionary'' of the Institut d'Estudis Catalans states in the sixth definition of "Valencian" that, in the Valencian Community, it is equivalent to Catalan language.] (See also
status of Valencian below).
History
Middle Ages
By the 9th century, Catalan had evolved from
Vulgar Latin
Vulgar Latin, also known as Colloquial, Popular, Spoken or Vernacular Latin, is the range of non-formal Register (sociolinguistics), registers of Latin spoken from the Crisis of the Roman Republic, Late Roman Republic onward. ''Vulgar Latin'' a ...
on both sides of the eastern end of the
Pyrenees
The Pyrenees are a mountain range straddling the border of France and Spain. They extend nearly from their union with the Cantabrian Mountains to Cap de Creus on the Mediterranean coast, reaching a maximum elevation of at the peak of Aneto. ...
, as well as the territories of the Roman province of
Hispania Tarraconensis
Hispania Tarraconensis was one of three Roman provinces in Hispania. It encompassed much of the northern, eastern and central territories of modern Spain along with modern North Region, Portugal, northern Portugal. Southern Spain, the region now ...
to the south. From the 8th century onwards the Catalan counts extended their territory southwards and westwards at the expense of the
Muslims
Muslims () are people who adhere to Islam, a Monotheism, monotheistic religion belonging to the Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic tradition. They consider the Quran, the foundational religious text of Islam, to be the verbatim word of the God ...
, bringing their language with them. This process was given definitive impetus with the separation of the
County of Barcelona
The County of Barcelona (, ) was a polity in northeastern Iberian Peninsula, originally located in the southern frontier region of the Carolingian Empire. In the 10th century, the Counts of Barcelona progressively achieved independence from F ...
from the
Carolingian Empire
The Carolingian Empire (800–887) was a Franks, Frankish-dominated empire in Western and Central Europe during the Early Middle Ages. It was ruled by the Carolingian dynasty, which had ruled as List of Frankish kings, kings of the Franks since ...
in 988.
In the 11th century, documents written in
macaronic Latin begin to show Catalan elements, with texts written almost completely in Romance appearing by 1080. Old Catalan shared many features with
Gallo-Romance Gallo-Romance can refer to:
* Old Gallo-Romance, the Romance language spoken from around 600 to 900 AD.
* Gallo-Romance languages, a branch of the Romance language family, which includes in the narrowest sense the ''langues d'oïl'' and Franco-Prov ...
, diverging from
Old Occitan
Old Occitan (, ), also called Old Provençal, was the earliest form of the Occitano-Romance languages, as attested in writings dating from the 8th to the 14th centuries. Old Occitan generally includes Early and Old Occitan. Middle Occitan is some ...
between the 11th and 14th centuries.
During the 11th and 12th centuries the Catalan rulers expanded southward to the
Ebro river
The Ebro (Spanish and Basque ; , , ) is a river of the north and northeast of the Iberian Peninsula, in Spain. It rises in Cantabria and flows , almost entirely in an east-southeast direction. It flows into the Mediterranean Sea, forming a del ...
, and in the 13th century they conquered the lands that would become the Kingdoms of
Valencia
Valencia ( , ), formally València (), is the capital of the Province of Valencia, province and Autonomous communities of Spain, autonomous community of Valencian Community, the same name in Spain. It is located on the banks of the Turia (r ...
and the
Majorca
Mallorca, or Majorca, is the largest of the Balearic Islands, which are part of Spain, and the List of islands in the Mediterranean#By area, seventh largest island in the Mediterranean Sea.
The capital of the island, Palma, Majorca, Palma, i ...
. The city of
Alghero
Alghero (; ; ; ) is a city of about 45,000 inhabitants in the Italian province of Sassari in the north west of the island of Sardinia, next to the Mediterranean Sea. The city's name comes from ''Aleguerium'', which is a mediaeval Latin word m ...
in
Sardinia
Sardinia ( ; ; ) is the Mediterranean islands#By area, second-largest island in the Mediterranean Sea, after Sicily, and one of the Regions of Italy, twenty regions of Italy. It is located west of the Italian Peninsula, north of Tunisia an ...
was repopulated with Catalan speakers in the 14th century. The language also reached
Murcia
Murcia ( , , ) is a city in south-eastern Spain, the Capital (political), capital and most populous city of the autonomous community of the Region of Murcia, and the Ranked lists of Spanish municipalities#By population, seventh largest city i ...
, which became Spanish-speaking in the 15th century.

In the
Low Middle Ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the 5th to the late 15th centuries, similarly to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire and t ...
, Catalan went through a golden age, reaching a peak of maturity and cultural richness. Examples include the work of Majorcan polymath
Ramon Llull
Ramon Llull (; ; – 1316), sometimes anglicized as ''Raymond Lully'', was a philosopher, theologian, poet, missionary, Christian apologist and former knight from the Kingdom of Majorca.
He invented a philosophical system known as the ''Art ...
(1232–1315), the Four Great Chronicles (13th–14th centuries), and the Valencian school of poetry culminating in
Ausiàs March
Ausiàs March (; 1400March 3, 1459) was a medieval Valencian poet and knight from Gandia, Valencia. He is considered one of the most important poets of the "Golden Century" (''Segle d'or'') of Catalan literature.
Biography
Not much is known of Ma ...
(1397–1459). By the 15th century, the city of
Valencia
Valencia ( , ), formally València (), is the capital of the Province of Valencia, province and Autonomous communities of Spain, autonomous community of Valencian Community, the same name in Spain. It is located on the banks of the Turia (r ...
had become the sociocultural center of the
Crown of Aragon
The Crown of Aragon (, ) ;, ; ; . was a composite monarchy ruled by one king, originated by the dynastic union of the Kingdom of Aragon and the County of Barcelona (later Principality of Catalonia) and ended as a consequence of the War of the Sp ...
, and Catalan was present all over the
Mediterranean
The Mediterranean Sea ( ) is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the east by the Levant in West Asia, on the north by Anatolia in West Asia and Southern ...
world. During this period, the Royal Chancery propagated a highly standardized language. Catalan was widely used as an official language in Sicily until the 15th century, and in Sardinia until the 17th. During this period, the language was what Costa Carreras terms "one of the 'great languages' of medieval Europe".
Martorell
Martorell () is a municipality, county, and city that forms part of the Baix Llobregat Comarques of Catalonia, comarca, in Catalonia, Spain, primarily known for its medieval Pont del Diable, Devil's bridge. It lies at the confluence of the Llobr ...
's novel of chivalry ''
Tirant lo Blanc
''Tirant lo Blanch'' (; modern spelling: ''Tirant lo Blanc''), in English ''Tirant the White'', is a chivalric romance written by the Valencian knight Joanot Martorell, finished posthumously by his friend Martí Joan de Galba and published in ...
'' (1490) shows a transition from Medieval to Renaissance values, something that can also be seen in
Metge's work. The first book produced with movable type in the
Iberian Peninsula
The Iberian Peninsula ( ), also known as Iberia, is a peninsula in south-western Europe. Mostly separated from the rest of the European landmass by the Pyrenees, it includes the territories of peninsular Spain and Continental Portugal, comprisin ...
was printed in Catalan.
Early modern era
Spain
With the union of the crowns of
Castille and
Aragon
Aragon ( , ; Spanish and ; ) is an autonomous communities of Spain, autonomous community in Spain, coextensive with the medieval Kingdom of Aragon. In northeastern Spain, the Aragonese autonomous community comprises three provinces of Spain, ...
in 1479, the Spanish kings ruled over different kingdoms, each with its own cultural, linguistic and political particularities, and they had to swear by the
laws
Law is a set of rules that are created and are law enforcement, enforceable by social or governmental institutions to regulate behavior, with its precise definition a matter of longstanding debate. It has been variously described as a Socia ...
of each territory before the respective
parliament
In modern politics and history, a parliament is a legislative body of government. Generally, a modern parliament has three functions: Representation (politics), representing the Election#Suffrage, electorate, making laws, and overseeing ...
s. But after the
War of the Spanish Succession
The War of the Spanish Succession was a European great power conflict fought between 1701 and 1714. The immediate cause was the death of the childless Charles II of Spain in November 1700, which led to a struggle for control of the Spanish E ...
, Spain became an
absolute monarchy under
Philip V, which led to the assimilation of the
Crown of Aragon
The Crown of Aragon (, ) ;, ; ; . was a composite monarchy ruled by one king, originated by the dynastic union of the Kingdom of Aragon and the County of Barcelona (later Principality of Catalonia) and ended as a consequence of the War of the Sp ...
by the
Crown of Castile
The Crown of Castile was a medieval polity in the Iberian Peninsula that formed in 1230 as a result of the third and definitive union of the crowns and, some decades later, the parliaments of the kingdoms of Kingdom of Castile, Castile and Kingd ...
through the
Nueva Planta decrees
The Nueva Planta decrees (, , ) were a number of decrees signed between 1707 and 1716 by Philip V of Spain, Philip V, the first House of Bourbon, Bourbon Monarchy of Spain, King of Spain, during and shortly after the end of the War of the Spani ...
, as a first step in the creation of the Spanish
nation-state
A nation state, or nation-state, is a political entity in which the state (a centralized political organization ruling over a population within a territory) and the nation (a community based on a common identity) are (broadly or ideally) con ...
; as in other contemporary European states, this meant the imposition of the political and cultural characteristics of the dominant groups. Since the political unification of 1714, Spanish assimilation policies towards national minorities have been a constant.
The process of assimilation began with secret instructions to the corregidores of the Catalan territory: they "will take the utmost care to introduce the Castilian language, for which purpose he will give the most temperate and disguised measures so that the effect is achieved, without the care being noticed".
From there, actions in the service of assimilation, discreet or aggressive, were continued, and reached to the last detail, such as, in 1799, the Royal Certificate forbidding anyone to "represent, sing and dance pieces that were not in Spanish".
The use of
Spanish
Spanish might refer to:
* Items from or related to Spain:
**Spaniards are a nation and ethnic group indigenous to Spain
**Spanish language, spoken in Spain and many countries in the Americas
**Spanish cuisine
**Spanish history
**Spanish culture
...
gradually became more prestigious and marked the start of the decline of Catalan. Starting in the 16th century, Catalan literature came under the influence of Spanish, and the nobles, part of the urban and literary classes became
bilingual
Multilingualism is the use of more than one language, either by an individual speaker or by a group of speakers. When the languages are just two, it is usually called bilingualism. It is believed that multilingual speakers outnumber monolin ...
.
France
With the
Treaty of the Pyrenees
The Treaty of the Pyrenees(; ; ) was signed on 7 November 1659 and ended the Franco-Spanish War that had begun in 1635.
Negotiations were conducted and the treaty was signed on Pheasant Island, situated in the middle of the Bidasoa River on ...
(1659),
Spain
Spain, or the Kingdom of Spain, is a country in Southern Europe, Southern and Western Europe with territories in North Africa. Featuring the Punta de Tarifa, southernmost point of continental Europe, it is the largest country in Southern Eur ...
ceded the
northern part of the Principality of Catalonia to
France
France, officially the French Republic, is a country located primarily in Western Europe. Overseas France, Its overseas regions and territories include French Guiana in South America, Saint Pierre and Miquelon in the Atlantic Ocean#North Atlan ...
, and soon thereafter the
local Catalan varieties came under the influence of
French, which in 1700 became the sole official language of the region.
Shortly after the
French Revolution (1789), the
French First Republic
In the history of France, the First Republic (), sometimes referred to in historiography as Revolutionary France, and officially the French Republic (), was founded on 21 September 1792 during the French Revolution. The First Republic lasted un ...
prohibited official use of, and enacted discriminating policies against, the regional languages of France, such as Catalan,
Alsatian,
Breton
Breton most often refers to:
*anything associated with Brittany, and generally
**Breton people
**Breton language, a Southwestern Brittonic Celtic language of the Indo-European language family, spoken in Brittany
** Breton (horse), a breed
**Gale ...
,
Occitan Occitan may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to the Occitania territory in parts of France, Italy, Monaco and Spain.
* Something of, from, or related to the Occitania administrative region of France.
* Occitan language, spoken in parts o ...
,
Flemish
Flemish may refer to:
* Flemish, adjective for Flanders, Belgium
* Flemish region, one of the three regions of Belgium
*Flemish Community, one of the three constitutionally defined language communities of Belgium
* Flemish dialects, a Dutch dialec ...
, and
Basque
Basque may refer to:
* Basques, an ethnic group of Spain and France
* Basque language, their language
Places
* Basque Country (greater region), the homeland of the Basque people with parts in both Spain and France
* Basque Country (autonomous co ...
.
France: 19th to 20th century
After the French colony of
Algeria
Algeria, officially the People's Democratic Republic of Algeria, is a country in the Maghreb region of North Africa. It is bordered to Algeria–Tunisia border, the northeast by Tunisia; to Algeria–Libya border, the east by Libya; to Alger ...
was established in 1830, many Catalan-speaking settlers moved there. People from the Spanish
province of Alicante
Alicante (, , ; ; ; officially: / ) is a province located in eastern Spain, in the southern part of the Valencian Community. It is the second most populated Valencian province, containing the second and third biggest cities in the Valencian Co ...
settled around
Oran
Oran () is a major coastal city located in the northwest of Algeria. It is considered the second most important city of Algeria, after the capital, Algiers, because of its population and commercial, industrial and cultural importance. It is w ...
, while those from
French Catalonia and
Menorca
Menorca or Minorca (from , later ''Minorica'') is one of the Balearic Islands located in the Mediterranean Sea belonging to Spain. Its name derives from its size, contrasting it with nearby Mallorca. Its capital is Maó, situated on the isl ...
migrated to
Algiers
Algiers is the capital city of Algeria as well as the capital of the Algiers Province; it extends over many Communes of Algeria, communes without having its own separate governing body. With 2,988,145 residents in 2008Census 14 April 2008: Offi ...
.
By 1911, there were around 100,000 speakers of ''
Patuet
Patuet (from the French language, French ) is the dialect of the Catalan language that was spoken in the Maghreb, mainly in Algeria, during the French Algeria, French administration. Mainly of Menorcan, Menorca, Southern Valencian, Alicante and ...
'', as their speech was called. After the Algerian declaration of independence in 1962, almost all the ''
Pied-Noir
The (; ; : ) are an ethno-cultural group of people of French and other European descent who were born in Algeria during the period of French colonial rule from 1830 to 1962. Many of them departed for mainland France during and after the ...
'' Catalan speakers fled to Northern Catalonia or Alicante.
The French government only recognizes French as an official language. Nevertheless, on 10 December 2007, the then
General Council of the Pyrénées-Orientales
A general officer is an officer of high rank in the armies, and in some nations' air and space forces, marines or naval infantry.
In some usages, the term "general officer" refers to a rank above colonel."general, adj. and n.". OED Online. Ma ...
officially recognized Catalan as one of the départment's languages
[ ] and seeks to further promote it in public life and education.
Spain: 18th to 20th century
In 1807, the Statistics Office of the French Ministry of the Interior asked the
prefects
Prefect (from the Latin ''praefectus'', substantive adjectival form of ''praeficere'': "put in front", meaning in charge) is a magisterial title of varying definition, but essentially refers to the leader of an administrative area.
A prefect' ...
for an official survey on the limits of the
French language
French ( or ) is a Romance languages, Romance language of the Indo-European languages, Indo-European family. Like all other Romance languages, it descended from the Vulgar Latin of the Roman Empire. French evolved from Northern Old Gallo-R ...
. The survey found that in
Roussillon
Roussillon ( , , ; , ; ) was a historical province of France that largely corresponded to the County of Roussillon and French Cerdagne, part of the County of Cerdagne of the former Principality of Catalonia. It is part of the region of ' ...
, almost only Catalan was spoken, and since Napoleon wanted to incorporate Catalonia into France, as happened in 1812, the
consul
Consul (abbrev. ''cos.''; Latin plural ''consules'') was the title of one of the two chief magistrates of the Roman Republic, and subsequently also an important title under the Roman Empire. The title was used in other European city-states thro ...
in
Barcelona
Barcelona ( ; ; ) is a city on the northeastern coast of Spain. It is the capital and largest city of the autonomous community of Catalonia, as well as the second-most populous municipality of Spain. With a population of 1.6 million within c ...
was also asked. He declared that Catalan "is taught in schools, it is printed and spoken, not only among the lower class, but also among people of first quality, also in social gatherings, as in visits and congresses", indicating that it was spoken everywhere "with the exception of the royal courts". He also indicated that Catalan was spoken "in the Kingdom of Valencia, in the islands of Mallorca, Menorca, Ibiza, Sardinia, Corsica and much of Sicily, in the Vall d "Aran and Cerdaña".
The defeat of the pro-Habsburg coalition in the
War of Spanish Succession
The War of the Spanish Succession was a European great power conflict fought between 1701 and 1714. The immediate cause was the death of the childless Charles II of Spain in November 1700, which led to a struggle for control of the Spanish ...
(1714) initiated a series of
laws
Law is a set of rules that are created and are law enforcement, enforceable by social or governmental institutions to regulate behavior, with its precise definition a matter of longstanding debate. It has been variously described as a Socia ...
which, among other centralizing measures, imposed the use of
Spanish
Spanish might refer to:
* Items from or related to Spain:
**Spaniards are a nation and ethnic group indigenous to Spain
**Spanish language, spoken in Spain and many countries in the Americas
**Spanish cuisine
**Spanish history
**Spanish culture
...
in legal documentation all over Spain. Because of this, use of the Catalan language declined into the 18th century.
However, the 19th century saw a Catalan literary revival (), which has continued up to the present day. This period starts with
Aribau's ''Ode to the Homeland'' (1833); followed in the second half of the 19th century, and the early 20th by the work of
Verdaguer (poetry),
Oller (realist novel), and
Guimerà
Guimerà () is a municipality and village in the Comarques of Catalonia, comarca of Urgell in the province of Lleida in Catalonia, Spain. The village, the only settlement in the municipality, is situated on the banks of the Corb (river), Corb rive ...
(drama). In the 19th century, the region of
Carche
Carche ( ; ) is a mountainous, sparsely populated area in the Region of Murcia, Spain, lying between the municipalities of Jumilla and Yecla. The mountains reach an elevation of 1,371 metres at the ''Pico de la Madama'' and part of the region ...
, in the
province of Murcia
The Region of Murcia (, ; ; ) is an autonomous community of Spain located in the southeastern part of the Iberian Peninsula, on the Mediterranean coast. The region is in area and had a population of 1,511,251 as at the start of 2020. About a ...
was repopulated with Valencian speakers. Catalan spelling was standardized in 1913 and the language became official during the
Second Spanish Republic
The Spanish Republic (), commonly known as the Second Spanish Republic (), was the form of democratic government in Spain from 1931 to 1939. The Republic was proclaimed on 14 April 1931 after the deposition of Alfonso XIII, King Alfonso XIII. ...
(1931–1939). The Second Spanish Republic saw a brief period of tolerance, with most restrictions against Catalan lifted. The
Generalitat
Generalitat (, literally in English 'Generality') is the name of two major medieval and early modern political institutions and their modern-day analogues in Kingdom of Spain. The ancient Principality of Catalonia and the Kingdom of Valencia we ...
(the autonomous government of Catalonia, established during the Republic in 1931) made a normal use of Catalan in its administration and put efforts to promote it at the social level, including in schools and the
University of Barcelona
The University of Barcelona (official name in ; UB), formerly also known as Central University of Barcelona (), is a public research university located in the city of Barcelona, Catalonia, Spain. It was established in 1450. With 76,000 students, ...
.
The Catalan language and culture were still vibrant during the
Spanish Civil War
The Spanish Civil War () was a military conflict fought from 1936 to 1939 between the Republican faction (Spanish Civil War), Republicans and the Nationalist faction (Spanish Civil War), Nationalists. Republicans were loyal to the Left-wing p ...
(1936–1939), but were crushed at an unprecedented level throughout the subsequent decades due to
Francoist dictatorship
Francoist Spain (), also known as the Francoist dictatorship (), or Nationalist Spain () was the period of Spanish history between 1936 and 1975, when Francisco Franco ruled Spain after the Spanish Civil War with the title . After his death i ...
(1939–1975), which abolished the official status of Catalan and imposed the use of Spanish in schools and in public administration in all of
Spain
Spain, or the Kingdom of Spain, is a country in Southern Europe, Southern and Western Europe with territories in North Africa. Featuring the Punta de Tarifa, southernmost point of continental Europe, it is the largest country in Southern Eur ...
, while banning the use of Catalan in them.
Between 1939 and 1943 newspapers and book printing in Catalan almost disappeared. Francisco Franco's desire for a homogeneous Spanish population resonated with some Catalans in favor of his regime, primarily members of the upper class, who began to reject the use of Catalan. Despite all of these hardships, Catalan continued to be used privately within households, and it was able to survive Franco's dictatorship. At the end of
World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
, however, some of the harsh measures began to be lifted and, while Spanish language remained the sole promoted one, limited number of Catalan literature began to be tolerated. Several prominent Catalan authors resisted the suppression through literature. Private initiative contests were created to reward works in Catalan, among them ''Joan Martorell'' prize (1947), ''Víctor Català'' prize (1953) ''Carles Riba'' award (1950), or the
Honor Award of Catalan Letters (1969). The first Catalan-language TV show was broadcast in 1964. At the same time, oppression of the Catalan language and identity was carried out in schools, through governmental bodies, and in religious centers.
In addition to the loss of prestige for Catalan and its prohibition in schools, migration during the 1950s into
Catalonia
Catalonia is an autonomous community of Spain, designated as a ''nationalities and regions of Spain, nationality'' by its Statute of Autonomy of Catalonia of 2006, Statute of Autonomy. Most of its territory (except the Val d'Aran) is situate ...
from other parts of Spain also contributed to the diminished use of the language. These migrants were often unaware of the existence of Catalan, and thus felt no need to learn or use it.
Catalonia
Catalonia is an autonomous community of Spain, designated as a ''nationalities and regions of Spain, nationality'' by its Statute of Autonomy of Catalonia of 2006, Statute of Autonomy. Most of its territory (except the Val d'Aran) is situate ...
was the economic powerhouse of Spain, so these migrations continued to occur from all corners of the country. Employment opportunities were reduced for those who were not
bilingual
Multilingualism is the use of more than one language, either by an individual speaker or by a group of speakers. When the languages are just two, it is usually called bilingualism. It is believed that multilingual speakers outnumber monolin ...
. Daily newspapers remained exclusively in Spanish until after Franco's death, when the first one in Catalan since the end of the Civil War,
Avui
''Avui'' (; ) was a Catalan-language daily newspaper, based in Barcelona, Catalonia. It was one of the city's newest papers, having been founded in 1976. The editorial line was Catalan nationalist.
History and profile
''Avui'' was first publi ...
, began to be published in 1976.
Present day
Since the
Spanish transition to democracy
The Spanish transition to democracy, known in Spain as (; ) or (), is a period of History of Spain, modern Spanish history encompassing the regime change that moved from the Francoist dictatorship to the consolidation of a parliamentary system ...
(1975–1982), Catalan has been institutionalized as an official language, language of education, and language of mass media; all of which have contributed to its increased prestige. In
Catalonia
Catalonia is an autonomous community of Spain, designated as a ''nationalities and regions of Spain, nationality'' by its Statute of Autonomy of Catalonia of 2006, Statute of Autonomy. Most of its territory (except the Val d'Aran) is situate ...
, there is an unparalleled large
bilingual
Multilingualism is the use of more than one language, either by an individual speaker or by a group of speakers. When the languages are just two, it is usually called bilingualism. It is believed that multilingual speakers outnumber monolin ...
European
non-state linguistic community. The teaching of Catalan is mandatory in all schools, but it is possible to use Spanish for studying in the public education system of Catalonia in two situations—if the teacher assigned to a class chooses to use Spanish, or during the learning process of one or more recently arrived immigrant students. There is also some intergenerational shift towards Catalan.
More recently, several Spanish political forces have tried to increase the use of Spanish in the Catalan educational system.
As a result, in May 2022 the Spanish Supreme Court urged the Catalan regional government to enforce a measure by which 25% of all lessons must be taught in Spanish.
According to the
Statistical Institute of Catalonia
The Statistical Institute of Catalonia (in Catalan: Institut d'Estadística de Catalunya, usually referred to by its acronym IDESCAT) is the official body responsible for collecting, processing, and disseminating statistics in the autonomous commu ...
, in 2013 the Catalan language is the second most commonly used in Catalonia, after
Spanish
Spanish might refer to:
* Items from or related to Spain:
**Spaniards are a nation and ethnic group indigenous to Spain
**Spanish language, spoken in Spain and many countries in the Americas
**Spanish cuisine
**Spanish history
**Spanish culture
...
, as a native or self-defining language: 7% of the population self-identifies with both Catalan and Spanish equally, 36.4% with Catalan and 47.5% only Spanish.
In 2003 the same studies concluded no language preference for self-identification within the population above 15 years old: 5% self-identified with both languages, 44.3% with Catalan and 47.5% with Spanish. To promote use of Catalan, the
Generalitat de Catalunya
The Generalitat de Catalunya (; ; ), or the Government of Catalonia, is the institutional system by which Catalonia is self-governed as an autonomous community of Spain. It is made up of the Parliament of Catalonia, the President of the Govern ...
(Catalonia's official Autonomous government) spends part of its annual budget on the promotion of the use of Catalan in Catalonia and in other territories, with entities such as (Consortium for Linguistic Normalization).
In
Andorra
Andorra, officially the Principality of Andorra, is a Sovereignty, sovereign landlocked country on the Iberian Peninsula, in the eastern Pyrenees in Southwestern Europe, Andorra–France border, bordered by France to the north and Spain to A ...
, Catalan has always been the sole official language. Since the promulgation of the
1993 constitution, several policies favoring Catalan have been enforced, such as Catalan medium education.
On the other hand, there are several
language shift
Language shift, also known as language transfer, language replacement or language assimilation, is the process whereby a speech community shifts to a different language, usually over an extended period of time. Often, languages that are perceived ...
processes currently taking place. In the
Northern Catalonia
Northern Catalonia, North Catalonia or French Catalonia is the Catalan language, Catalan-speaking and cultural territory ceded to France by Spain through the signing of the Treaty of the Pyrenees in 1659 in exchange for France's effective renu ...
area of France, Catalan has followed the same trend as the other minority languages of France, with most of its native speakers being 60 or older (as of 2004). Catalan is studied as a foreign language by 30% of the primary education students, and by 15% of the secondary. The cultural association promotes a network of community-run schools engaged in Catalan language immersion programs.
In
Alicante province
Alicante (, , ; ; ; officially: / ) is a province located in eastern Spain, in the southern part of the Valencian Community. It is the second most populated Valencian province, containing the second and third biggest cities in the Valencian Co ...
, Catalan is being replaced by
Spanish
Spanish might refer to:
* Items from or related to Spain:
**Spaniards are a nation and ethnic group indigenous to Spain
**Spanish language, spoken in Spain and many countries in the Americas
**Spanish cuisine
**Spanish history
**Spanish culture
...
and in
Alghero
Alghero (; ; ; ) is a city of about 45,000 inhabitants in the Italian province of Sassari in the north west of the island of Sardinia, next to the Mediterranean Sea. The city's name comes from ''Aleguerium'', which is a mediaeval Latin word m ...
by
Italian
Italian(s) may refer to:
* Anything of, from, or related to the people of Italy over the centuries
** Italians, a Romance ethnic group related to or simply a citizen of the Italian Republic or Italian Kingdom
** Italian language, a Romance languag ...
. There is also well ingrained
diglossia
In linguistics, diglossia ( , ) is where two dialects or languages are used (in fairly strict compartmentalization) by a single language community. In addition to the community's everyday or vernacular language variety (labeled "L" or "low" v ...
in the
Valencian Community
The Valencian Community is an Autonomous communities of Spain, autonomous community of Spain. It is the fourth most populous Spanish Autonomous communities of Spain, autonomous community after Andalusia, Catalonia and the Community of Madrid wit ...
,
Ibiza
Ibiza (; ; ; #Names and pronunciation, see below) or Iviza is a Spanish island in the Mediterranean Sea off the eastern coast of the Iberian Peninsula. It is 150 kilometres (93 miles) from the city of Valencia. It is the third largest of th ...
, and to a lesser extent, in the rest of the
Balearic islands
The Balearic Islands are an archipelago in the western Mediterranean Sea, near the eastern coast of the Iberian Peninsula. The archipelago forms a Provinces of Spain, province and Autonomous communities of Spain, autonomous community of Spain, ...
.
During the 20th century many Catalans emigrated or went into exile to
Venezuela
Venezuela, officially the Bolivarian Republic of Venezuela, is a country on the northern coast of South America, consisting of a continental landmass and many Federal Dependencies of Venezuela, islands and islets in the Caribbean Sea. It com ...
,
Mexico
Mexico, officially the United Mexican States, is a country in North America. It is the northernmost country in Latin America, and borders the United States to the north, and Guatemala and Belize to the southeast; while having maritime boundar ...
,
Cuba
Cuba, officially the Republic of Cuba, is an island country, comprising the island of Cuba (largest island), Isla de la Juventud, and List of islands of Cuba, 4,195 islands, islets and cays surrounding the main island. It is located where the ...
,
Argentina
Argentina, officially the Argentine Republic, is a country in the southern half of South America. It covers an area of , making it the List of South American countries by area, second-largest country in South America after Brazil, the fourt ...
, and other South American countries. They formed a large number of Catalan colonies that today continue to maintain the Catalan language. They also founded many Catalan casals (associations).
Classification and relationship with other Romance languages

One classification of Catalan is given by
Pèire Bèc:
*
Romance languages
The Romance languages, also known as the Latin or Neo-Latin languages, are the languages that are Language family, directly descended from Vulgar Latin. They are the only extant subgroup of the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-E ...
**
Italo-Western languages
Italo-Western is, in some classifications, the largest branch of the Romance languages. It comprises two of the branches of Romance languages: Italo-Dalmatian languages, Italo-Dalmatian and Western Romance languages, Western Romance. It excludes ...
***
Western Romance languages
Western Romance languages are one of the two subdivisions of a proposed subdivision of the Romance languages based on the La Spezia–Rimini Line. They include the Ibero-Romance and Gallo-Romance. Gallo-Italic may also be included. The subdivi ...
****
Gallo-Iberian languages
Western Romance languages are one of the two subdivisions of a proposed subdivision of the Romance languages based on the La Spezia–Rimini Line. They include the Ibero-Romance and Gallo-Romance. Gallo-Italic may also be included. The subdivisi ...
*****
Gallo-Romance languages
The Gallo-Romance branch of the Romance languages includes in the narrowest sense the ''langues d'oïl'' and Franco-Provençal. However, other definitions are far broader and variously encompass the Occitan or Occitano-Romance, Gallo-Italic o ...
******
Occitano-Romance languages
Occitano-Romance (; ; ) is a branch of the Romance language group that encompasses the Catalan/Valencian, Occitan languages and sometimes Aragonese, spoken in parts of southern France and northeastern Spain.
The classification of Occitano-Ro ...
******* Catalan language
However, the ascription of Catalan to the
Occitano-Romance branch of
Gallo-Romance languages
The Gallo-Romance branch of the Romance languages includes in the narrowest sense the ''langues d'oïl'' and Franco-Provençal. However, other definitions are far broader and variously encompass the Occitan or Occitano-Romance, Gallo-Italic o ...
is not shared by all linguists and philologists, particularly among Spanish ones, such as
Ramón Menéndez Pidal
Ramón Menéndez Pidal (; 13 March 1869 – 14 November 1968) was a Spanish philologist and historian."Ramon Menendez Pidal", ''Almanac of Famous People'' (2011) ''Biography in Context'', Gale, Detroit He worked extensively on the history of t ...
.
Catalan bears varying degrees of similarity to the linguistic varieties subsumed under the cover term ''
Occitan language
Occitan (; ), also known by its native speakers as (; ), sometimes also referred to as Provençal, is a Romance language spoken in Southern France, Monaco, Italy's Occitan Valleys, as well as Spain's Val d'Aran in Catalonia; collectively, ...
'' (see also
differences between Occitan and Catalan and
Gallo-Romance languages
The Gallo-Romance branch of the Romance languages includes in the narrowest sense the ''langues d'oïl'' and Franco-Provençal. However, other definitions are far broader and variously encompass the Occitan or Occitano-Romance, Gallo-Italic o ...
). Thus, as it should be expected from closely related languages, Catalan today shares many traits with other Romance languages.
Relationship with other Romance languages
Some include Catalan in Occitan, as the
linguistic distance
Linguistic distance is the measure of how different one language (or dialect) is from another. Although they lack a uniform approach to quantifying linguistic distance between languages, linguists apply the concept to a variety of linguistic co ...
between this language and some Occitan dialects (such as the
Gascon dialect
Gascon ( , , ) is the vernacular Romance variety spoken mainly in the region of Gascony, France. It is often considered a variety of larger Occitan macrolanguage, although some authors consider it a separate language due to hindered mutual ...
) is similar to the distance among different Occitan dialects. Catalan was considered a dialect of Occitan until the end of the 19th century and still today remains its closest relative.
Catalan shares many traits with the other neighboring
Romance languages
The Romance languages, also known as the Latin or Neo-Latin languages, are the languages that are Language family, directly descended from Vulgar Latin. They are the only extant subgroup of the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-E ...
(Occitan, French,
Italian
Italian(s) may refer to:
* Anything of, from, or related to the people of Italy over the centuries
** Italians, a Romance ethnic group related to or simply a citizen of the Italian Republic or Italian Kingdom
** Italian language, a Romance languag ...
,
Sardinian as well as Spanish and Portuguese among others). However, despite being spoken mostly on the
Iberian Peninsula
The Iberian Peninsula ( ), also known as Iberia, is a peninsula in south-western Europe. Mostly separated from the rest of the European landmass by the Pyrenees, it includes the territories of peninsular Spain and Continental Portugal, comprisin ...
, Catalan has marked differences with the
Iberian Romance
The Iberian Romance, Ibero-Romance or sometimes Iberian languages Iberian languages is also used as a more inclusive term for all languages spoken on the Iberian Peninsula, which in antiquity included the non-Indo-European Iberian language. are ...
group (
Spanish
Spanish might refer to:
* Items from or related to Spain:
**Spaniards are a nation and ethnic group indigenous to Spain
**Spanish language, spoken in Spain and many countries in the Americas
**Spanish cuisine
**Spanish history
**Spanish culture
...
and
Portuguese) in terms of
pronunciation
Pronunciation is the way in which a word or a language is spoken. To
This may refer to generally agreed-upon sequences of sounds used in speaking a given word or all language in a specific dialect—"correct" or "standard" pronunciation—or si ...
, grammar, and especially vocabulary; it shows instead its closest affinity with languages native to France and northern Italy, particularly
Occitan Occitan may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to the Occitania territory in parts of France, Italy, Monaco and Spain.
* Something of, from, or related to the Occitania administrative region of France.
* Occitan language, spoken in parts o ...
and to a lesser extent
Gallo-Romance Gallo-Romance can refer to:
* Old Gallo-Romance, the Romance language spoken from around 600 to 900 AD.
* Gallo-Romance languages, a branch of the Romance language family, which includes in the narrowest sense the ''langues d'oïl'' and Franco-Prov ...
(
Franco-Provençal
Franco-Provençal (also Francoprovençal, Patois or Arpitan) is a Gallo-Romance languages, Gallo-Romance language that originated and is spoken in eastern France, western Switzerland, and northwestern Italy.
Franco-Provençal has several di ...
,
French,
Gallo-Italian).
According to
Ethnologue
''Ethnologue: Languages of the World'' is an annual reference publication in print and online that provides statistics and other information on the living languages of the world. It is the world's most comprehensive catalogue of languages. It w ...
, the lexical similarity between Catalan and other Romance languages is: 87% with Italian; 85% with Portuguese and Spanish; 76% with
Ladin and
Romansh; 75% with Sardinian; and 73% with Romanian.
During much of its history, and especially during the
Francoist dictatorship
Francoist Spain (), also known as the Francoist dictatorship (), or Nationalist Spain () was the period of Spanish history between 1936 and 1975, when Francisco Franco ruled Spain after the Spanish Civil War with the title . After his death i ...
(1939–1975), the Catalan language was ridiculed as a mere dialect of
Spanish
Spanish might refer to:
* Items from or related to Spain:
**Spaniards are a nation and ethnic group indigenous to Spain
**Spanish language, spoken in Spain and many countries in the Americas
**Spanish cuisine
**Spanish history
**Spanish culture
...
. This view, based on political and ideological considerations, has no linguistic validity. Spanish and Catalan have important differences in their sound systems, lexicon, and grammatical features, placing the language in features closer to
Occitan Occitan may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to the Occitania territory in parts of France, Italy, Monaco and Spain.
* Something of, from, or related to the Occitania administrative region of France.
* Occitan language, spoken in parts o ...
(and
French).
There is evidence that, at least from the 2nd century AD, the vocabulary and phonology of Roman
Tarraconensis
Hispania Tarraconensis was one of three Roman provinces in Hispania. It encompassed much of the northern, eastern and central territories of modern Spain along with modern northern Portugal. Southern Spain, the region now called Andalusia, was t ...
was different from the rest of Roman Hispania. Differentiation arose generally because Spanish,
Asturian, and Galician-Portuguese share certain peripheral archaisms (Spanish , Asturian and Portuguese vs. Catalan , Occitan "to boil") and innovatory regionalisms (Spanish , Asturian vs. Catalan , Occitan "bullock"), while Catalan has a shared history with the Western Romance innovative core, especially Occitan.
Like all Romance languages, Catalan has a handful of native words which are unique to it, or rare elsewhere. These include:
* verbs: 'to fasten; transfix' > 'to compose, write up', > 'to combine, conjugate', > 'to wake; awaken', 'to thicken; crowd together' > 'to save, keep', > 'to miss, yearn, pine for', 'to investigate, track' > Old Catalan ''enagar'' 'to incite, induce', > Old Catalan ''ujar'' 'to exhaust, fatigue', > 'to appease, mollify', > 'to reject, refuse';
* nouns: > 'pomace', > 'reedmace', > 'catarrh', > 'snowdrift', > 'ardor, passion', > 'brake', > 'avalanche', > 'edge, border', 'sawfish' > ''pestriu'' > 'thresher shark, smooth hound; ray', 'live coal' > 'spark', > ''tardaó'' > 'autumn'.
The
Gothic superstrate produced different outcomes in Spanish and Catalan. For example, Catalan "mud" and "to roast", of Germanic origin, contrast with Spanish and , of Latin origin; whereas Catalan "spinning wheel" and "temple", of Latin origin, contrast with Spanish and , of Germanic origin.
The same happens with
Arabic
Arabic (, , or , ) is a Central Semitic languages, Central Semitic language of the Afroasiatic languages, Afroasiatic language family spoken primarily in the Arab world. The International Organization for Standardization (ISO) assigns lang ...
loanwords. Thus, Catalan "large earthenware jar" and "tile", of Arabic origin, contrast with Spanish and , of Latin origin; whereas Catalan "oil" and "olive", of Latin origin, contrast with Spanish and . However, the Arabic element is generally much more prevalent in Spanish.
Situated between two large linguistic blocks (Iberian Romance and Gallo-Romance), Catalan has many unique lexical choices, such as "to miss somebody", "to calm somebody down", and "reject".
Geographic distribution
Catalan-speaking territories
Traditionally Catalan-speaking territories are sometimes called the (Catalan Countries), a denomination based on cultural affinity and common heritage, that has also had a subsequent political interpretation but no official status. Various interpretations of the term may include some or all of these regions.
Number of speakers
The number of people known to be fluent in Catalan varies depending on the sources used. A 2004 study did not count the total number of speakers, but estimated a total of 9–9.5 million by matching the percentage of speakers to the population of each area where Catalan is spoken. The web site of the
Generalitat de Catalunya
The Generalitat de Catalunya (; ; ), or the Government of Catalonia, is the institutional system by which Catalonia is self-governed as an autonomous community of Spain. It is made up of the Parliament of Catalonia, the President of the Govern ...
estimated that as of 2004 there were 9,118,882 speakers of Catalan. These figures only reflect potential speakers; today it is the native language of only 35.6% of the Catalan population.
[Población según lengua habitual. Datos comparados 2003–2008. Cataluña. Año 2008](_blank)
, Encuesta de Usos Lingüísticos de la población (2003 y 2008), Instituto de Estadística de Cataluña According to ''
Ethnologue
''Ethnologue: Languages of the World'' is an annual reference publication in print and online that provides statistics and other information on the living languages of the world. It is the world's most comprehensive catalogue of languages. It w ...
'', Catalan had 4.1 million
native speakers
A first language (L1), native language, native tongue, or mother tongue is the first language a person has been exposed to from birth or within the critical period. In some countries, the term ''native language'' or ''mother tongue'' refers ...
and 5.1 million
second-language speakers in 2021.
According to a 2011 study the total number of Catalan speakers was over 9.8 million, with 5.9 million residing in Catalonia. More than half of them spoke Catalan as a second language, with native speakers being about 4.4 million of those (more than 2.8 in Catalonia). Very few Catalan
monoglot
Monoglottism (Greek μόνος ''monos'', "alone, solitary", + γλῶττα , "tongue, language") or, more commonly, monolingualism or unilingualism, is the condition of being able to speak only a single language, as opposed to multilingualism. ...
s exist; virtually all of the Catalan speakers in Spain are
bilingual
Multilingualism is the use of more than one language, either by an individual speaker or by a group of speakers. When the languages are just two, it is usually called bilingualism. It is believed that multilingual speakers outnumber monolin ...
speakers of Catalan and Spanish, with 99.7% of Catalan speakers in Catalonia able to speak Spanish and 99.9% able to understand it.
In
Roussillon
Roussillon ( , , ; , ; ) was a historical province of France that largely corresponded to the County of Roussillon and French Cerdagne, part of the County of Cerdagne of the former Principality of Catalonia. It is part of the region of ' ...
, only a minority of French Catalans speak Catalan nowadays, with French being the majority language for the inhabitants after a continued process of
language shift
Language shift, also known as language transfer, language replacement or language assimilation, is the process whereby a speech community shifts to a different language, usually over an extended period of time. Often, languages that are perceived ...
. According to a 2019 survey by the Catalan government, 31.5% of the inhabitants of Catalonia predominantly spoke Catalan at home whereas 52.7% spoke Spanish, 2.8% both Catalan and Spanish and 10.8% other languages.
Spanish
Spanish might refer to:
* Items from or related to Spain:
**Spaniards are a nation and ethnic group indigenous to Spain
**Spanish language, spoken in Spain and many countries in the Americas
**Spanish cuisine
**Spanish history
**Spanish culture
...
was the most spoken language in Barcelona (according to the linguistic census held by the Government of Catalonia in 2013) and it is understood almost universally. According to 2013 census, Catalan was also very commonly spoken in the city of 1,501,262: it was understood by 95% of the population, while 72.3% over the age of two could speak it (1,137,816), 79% could read it (1,246.555), and 53% could write it (835,080). The share of Barcelona residents who could speak it (72.3%) was lower than that of the overall Catalan population, of whom 81.2% over the age of 15 spoke the language. Knowledge of Catalan has increased significantly in recent decades thanks to a
language immersion
Language immersion, or simply immersion, is a technique used in Bilingual education, bilingual language education in which two languages are used for instruction in a variety of topics, including maths, science, or social studies. The languages ...
educational system. An important social characteristic of the Catalan language is that all the areas where it is spoken are bilingual in practice: together with French in Roussillon, with Italian in Alghero, with Spanish and French in Andorra, and with Spanish in the rest of the territories.
:1. The number of people who understand Catalan includes those who can speak it.
:2. Figures relate to all self-declared capable speakers, not just native speakers.
Level of knowledge
(% of the population 15 years old and older).
Social use
(% of the population 15 years old and older).
Native language
To calculate the absolute number the figures have been proportioned to the whole population regardless of the age, rounded to the nearest 500.
Phonology
Catalan phonology varies by dialect. Notable features include:
* Marked contrast of the vowel pairs and , as in other
Western Romance
Western Romance languages are one of the two subdivisions of a proposed subdivision of the Romance languages based on the La Spezia–Rimini Line. They include the Ibero-Romance and Gallo-Romance. Gallo-Italic may also be included. The subdivi ...
languages, other than
Spanish
Spanish might refer to:
* Items from or related to Spain:
**Spaniards are a nation and ethnic group indigenous to Spain
**Spanish language, spoken in Spain and many countries in the Americas
**Spanish cuisine
**Spanish history
**Spanish culture
...
.
* Lack of
diphthongization
In historical linguistics, vowel breaking, vowel fracture, or diphthongization is the sound change of a monophthong into a diphthong or triphthong.
Types
Vowel breaking may be unconditioned or conditioned. It may be triggered by the presence of ...
of
Latin
Latin ( or ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally spoken by the Latins (Italic tribe), Latins in Latium (now known as Lazio), the lower Tiber area aroun ...
short , , as in
Galician and
Portuguese, but unlike French, Spanish, or Italian.
* Abundance of diphthongs containing , as in Galician and Portuguese.
In contrast to other Romance languages, Catalan has many
monosyllabic
In linguistics, a monosyllable is a word or utterance of only one syllable. It is most commonly studied in the fields of phonology and morphology. The word has originated from the Greek language
Greek (, ; , ) is an Indo-European languages, Ind ...
words, and these may end in a wide variety of consonants, including some
consonant cluster
In linguistics, a consonant cluster, consonant sequence or consonant compound is a group of consonants which have no intervening vowel. In English, for example, the groups and are consonant clusters in the word ''splits''. In the education fie ...
s. Additionally, Catalan has
final obstruent devoicing
Final-obstruent devoicing or terminal devoicing is a systematic phonological process occurring in languages such as Catalan, German, Dutch, Quebec French, Breton, Russian, Polish, Lithuanian, Turkish, and Wolof. In such languages, voiced ...
, which gives rise to an abundance of such couplets as ("male friend") vs. ("female friend").
Central Catalan
Central Catalan () is an Eastern Catalan dialect spoken in the whole province of Barcelona, the eastern half of the province of Tarragona and most of the province of Girona, except for its northern part, where a transition to Northern Catalan ...
pronunciation is considered to be standard for the language. The descriptions below are mostly representative of this variety. For the differences in pronunciation between the different dialects, see the section on
pronunciation of dialects in this article.
Vowels

Catalan has inherited the typical vowel system of
Vulgar Latin
Vulgar Latin, also known as Colloquial, Popular, Spoken or Vernacular Latin, is the range of non-formal Register (sociolinguistics), registers of Latin spoken from the Crisis of the Roman Republic, Late Roman Republic onward. ''Vulgar Latin'' a ...
, with seven stressed phonemes: , a common feature in
Western Romance
Western Romance languages are one of the two subdivisions of a proposed subdivision of the Romance languages based on the La Spezia–Rimini Line. They include the Ibero-Romance and Gallo-Romance. Gallo-Italic may also be included. The subdivi ...
, with the exception of
Spanish
Spanish might refer to:
* Items from or related to Spain:
**Spaniards are a nation and ethnic group indigenous to Spain
**Spanish language, spoken in Spain and many countries in the Americas
**Spanish cuisine
**Spanish history
**Spanish culture
...
.
Balearic also has instances of stressed . Dialects differ in the different degrees of
vowel reduction
In phonetics, vowel reduction is any of various changes in the acoustic ''quality'' of vowels as a result of changes in stress, sonority, duration, loudness, articulation, or position in the word (e.g. for the Muscogee language), and which ar ...
, and the incidence of the pair .
In
Central Catalan
Central Catalan () is an Eastern Catalan dialect spoken in the whole province of Barcelona, the eastern half of the province of Tarragona and most of the province of Girona, except for its northern part, where a transition to Northern Catalan ...
, unstressed vowels reduce to three: ; ; remains distinct. The other dialects have different vowel reduction processes (see the section
pronunciation of dialects in this article).
Consonants
The consonant system of Catalan is rather conservative.
* has a
velarized
Velarization merican spelling/small> or velarisation ritish spelling/sup> is a secondary articulation of consonants by which the back of the tongue is raised toward the velum during the articulation of the consonant.
In the International Pho ...
allophone in
syllable coda
A syllable is a basic unit of organization within a sequence of speech sounds, such as within a word, typically defined by linguists as a ''nucleus'' (most often a vowel) with optional sounds before or after that nucleus (''margins'', which are ...
position in most dialects. However, is velarized irrespective of position in Eastern dialects such as Majorcan and standard Eastern Catalan.
* occurs in Balearic,
Algherese,
standard Valencian
Valencian () or the Valencian language () is the official, historical and traditional name used in the Valencian Community to refer to the Romance language also known as Catalan, and some areas in southern Catalonia. It has
merged
Mergers and acquisitions (M&A) are business transactions in which the ownership of a company, business organization, or one of their operating units is transferred to or consolidated with another entity. They may happen through direct absorpt ...
with elsewhere.
* The velar nasal /ŋ/ is an allophone of /n/ before /g/ or /k/. However, it has become phonemic in Central dialects that delete the final element of word-final consonant clusters, resulting in minimal pairs such as ''fan''
�fan(“they do”) and ''fang''
�faŋ(“mud”, pronounced
�faŋkin other dialects).
* In Valencian, the fricative
�(and
ʒ appears only as a voiced allophone of /ʃ/ (and /jʃ/) before vowels and voiced consonants; e.g. peix al forn
�pejʒ al ˈfoɾn('oven fish'). The /ʒ/ phoneme in other Catalan dialects is pronounced /dʒ/ in standard Valencian.
* Voiced obstruents undergo
final-obstruent devoicing
Final-obstruent devoicing or terminal devoicing is a systematic phonological process occurring in languages such as Catalan, German, Dutch, Quebec French, Breton, Russian, Polish, Lithuanian, Turkish, and Wolof. In such languages, voic ...
: .
* Voiced stops become
lenited
In linguistics, lenition is a sound change that alters consonants, making them "weaker" in some way. The word ''lenition'' itself means "softening" or "weakening" (from Latin 'weak'). Lenition can happen both synchronically (within a language ...
to approximants in syllable onsets, after continuants: > , > , > . Exceptions include after
lateral consonant
A lateral is a consonant in which the airstream proceeds along one or both of the sides of the tongue, but it is blocked by the tongue from going through the middle of the mouth. An example of a lateral consonant is the English ''L'', as in ''L ...
s, and after . In coda position, these sounds are realized as stops, except in some Valencian dialects where they are lenited.
* There is some confusion in the literature about the precise phonetic characteristics of , , , . Some sources describe them as "postalveolar". Others as "back alveolo-palatal", implying that the characters would be more accurate. However, in all literature only the characters for
palato-alveolar
Postalveolar (post-alveolar) consonants are consonants articulated with the tongue near or touching the ''back'' of the alveolar ridge. Articulation is farther back in the mouth than the alveolar consonants, which are at the ridge itself, but n ...
affricates and fricatives are used, even when the same sources use for other languages such as Polish and Chinese.
* The distribution of the two rhotics and closely parallels
that of Spanish. Between vowels, the two contrast, but they are otherwise in complementary distribution: in the onset of the first syllable in a word, appears unless preceded by a consonant. Dialects vary in regards to rhotics in the coda with Western Catalan generally featuring and Central Catalan dialects featuring a weakly trilled unless it precedes a vowel-initial word in the same
prosodic unit
In linguistics, a prosodic unit is a segment of speech that occurs with specific prosodic properties. These properties can be those of stress, intonation (a single pitch and rhythm contour), or tonal patterns.
Prosodic units occur at a hie ...
, in which case appears.
* In careful speech, , , may be
geminated
In phonetics and phonology, gemination (; from Latin 'doubling', itself from '' gemini'' 'twins'), or consonant lengthening, is an articulation of a consonant for a longer period of time than that of a singleton consonant. It is distinct from ...
. Geminated may also occur. Some analyze intervocalic as the result of gemination of a single rhotic phoneme. This is similar to the common analysis of Spanish and
Portuguese rhotics.
Phonological evolution

Catalan shares features with neighboring Romance languages (
Occitan Occitan may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to the Occitania territory in parts of France, Italy, Monaco and Spain.
* Something of, from, or related to the Occitania administrative region of France.
* Occitan language, spoken in parts o ...
,
Italian
Italian(s) may refer to:
* Anything of, from, or related to the people of Italy over the centuries
** Italians, a Romance ethnic group related to or simply a citizen of the Italian Republic or Italian Kingdom
** Italian language, a Romance languag ...
,
Sardinian,
French,
Spanish
Spanish might refer to:
* Items from or related to Spain:
**Spaniards are a nation and ethnic group indigenous to Spain
**Spanish language, spoken in Spain and many countries in the Americas
**Spanish cuisine
**Spanish history
**Spanish culture
...
).
* Marked contrast of the vowel pairs and , as in other
Western Romance
Western Romance languages are one of the two subdivisions of a proposed subdivision of the Romance languages based on the La Spezia–Rimini Line. They include the Ibero-Romance and Gallo-Romance. Gallo-Italic may also be included. The subdivi ...
languages, except Spanish and Sardinian.
* Lenition of voiced stops as in Galician and Spanish.
* Lack of
diphthongization
In historical linguistics, vowel breaking, vowel fracture, or diphthongization is the sound change of a monophthong into a diphthong or triphthong.
Types
Vowel breaking may be unconditioned or conditioned. It may be triggered by the presence of ...
of
Latin
Latin ( or ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally spoken by the Latins (Italic tribe), Latins in Latium (now known as Lazio), the lower Tiber area aroun ...
short , , as in
Galician, Sardinian and Portuguese, and unlike French, Spanish and Italian.
* Abundance of diphthongs containing , as in Galician and Portuguese.
* Abundance of and occurring at the end of words, as for instance ("wet") and ("year"), unlike Spanish, Portuguese or Italian.
In contrast with other Romance languages, Catalan has many
monosyllabic
In linguistics, a monosyllable is a word or utterance of only one syllable. It is most commonly studied in the fields of phonology and morphology. The word has originated from the Greek language
Greek (, ; , ) is an Indo-European languages, Ind ...
words; and those ending in a wide variety of consonants and some
consonant cluster
In linguistics, a consonant cluster, consonant sequence or consonant compound is a group of consonants which have no intervening vowel. In English, for example, the groups and are consonant clusters in the word ''splits''. In the education fie ...
s. Also, Catalan has
final obstruent devoicing
Final-obstruent devoicing or terminal devoicing is a systematic phonological process occurring in languages such as Catalan, German, Dutch, Quebec French, Breton, Russian, Polish, Lithuanian, Turkish, and Wolof. In such languages, voiced ...
, thus featuring many couplets like ('male friend') vs. ('female friend').
Sociolinguistics
Catalan
sociolinguistics
Sociolinguistics is the descriptive, scientific study of how language is shaped by, and used differently within, any given society. The field largely looks at how a language changes between distinct social groups, as well as how it varies unde ...
studies the situation of Catalan in the world and the different varieties that this language presents. It is a subdiscipline of Catalan
philology
Philology () is the study of language in Oral tradition, oral and writing, written historical sources. It is the intersection of textual criticism, literary criticism, history, and linguistics with strong ties to etymology. Philology is also de ...
and other affine studies and has as an objective to analyze the relation between the Catalan language, the speakers and the close reality (including the one of other languages in contact).
Preferential subjects of study
*
Dialect
A dialect is a Variety (linguistics), variety of language spoken by a particular group of people. This may include dominant and standard language, standardized varieties as well as Vernacular language, vernacular, unwritten, or non-standardize ...
s of Catalan
* Variations of Catalan by class, gender, profession, age and level of studies
* Process of
linguistic normalization
Linguistics is the scientific study of language. The areas of linguistic analysis are syntax (rules governing the structure of sentences), semantics (meaning), morphology (structure of words), phonetics (speech sounds and equivalent gestures i ...
* Relations between Catalan and
Spanish
Spanish might refer to:
* Items from or related to Spain:
**Spaniards are a nation and ethnic group indigenous to Spain
**Spanish language, spoken in Spain and many countries in the Americas
**Spanish cuisine
**Spanish history
**Spanish culture
...
or
French
* Perception on the language of Catalan speakers and non-speakers
* Presence of Catalan in several fields: tagging, public function, media, professional sectors
Dialects
Overview
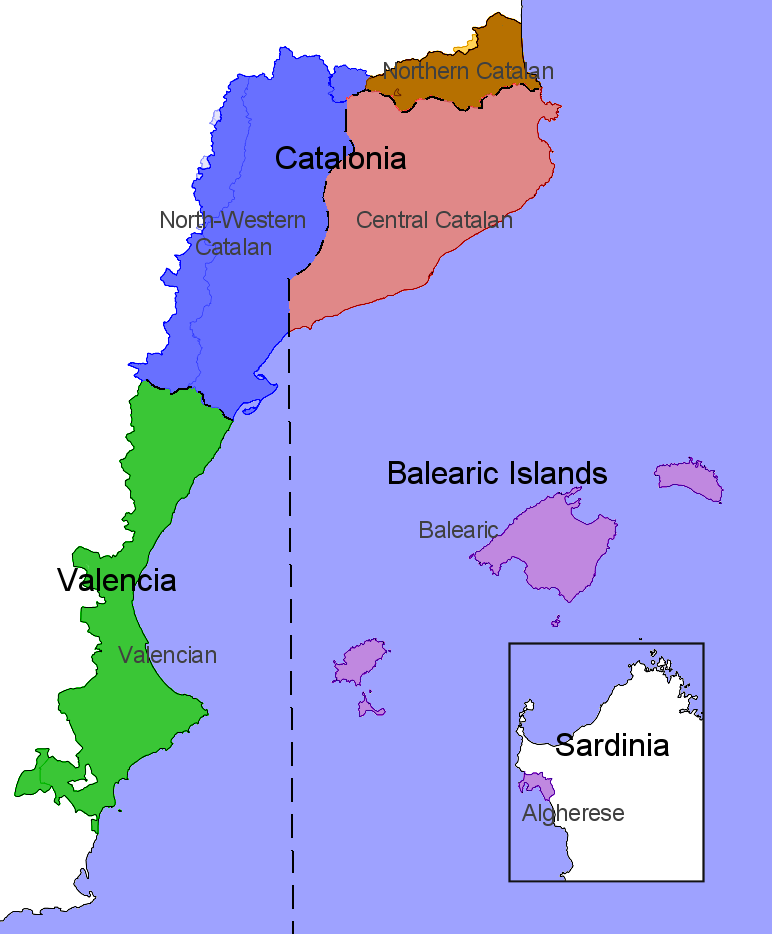
The dialects of the Catalan language feature a relative uniformity, especially when compared to other Romance languages; both in terms of
vocabulary
A vocabulary (also known as a lexicon) is a set of words, typically the set in a language or the set known to an individual. The word ''vocabulary'' originated from the Latin , meaning "a word, name". It forms an essential component of languag ...
,
semantics
Semantics is the study of linguistic Meaning (philosophy), meaning. It examines what meaning is, how words get their meaning, and how the meaning of a complex expression depends on its parts. Part of this process involves the distinction betwee ...
,
syntax
In linguistics, syntax ( ) is the study of how words and morphemes combine to form larger units such as phrases and sentences. Central concerns of syntax include word order, grammatical relations, hierarchical sentence structure (constituenc ...
,
morphology
Morphology, from the Greek and meaning "study of shape", may refer to:
Disciplines
*Morphology (archaeology), study of the shapes or forms of artifacts
*Morphology (astronomy), study of the shape of astronomical objects such as nebulae, galaxies, ...
, and
phonology
Phonology (formerly also phonemics or phonematics: "phonemics ''n.'' 'obsolescent''1. Any procedure for identifying the phonemes of a language from a corpus of data. 2. (formerly also phonematics) A former synonym for phonology, often pre ...
. Mutual intelligibility between dialects is very high, estimates ranging from 90% to 95%.
The only exception is the isolated idiosyncratic
Algherese dialect
Algherese or Alguerese (endonym and exonym, autonym: ) is the Variety (linguistics), variety of Catalan language, Catalan spoken in the city of Alghero ( in Catalan), in the northwest of Sardinia, Italy.
The dialect has its roots in 1372, w ...
.
Catalan is split in two major dialectal blocks: Eastern and Western. The main difference lies in the treatment of unstressed and ; which have merged to in Eastern dialects, but which remain distinct as and in Western dialects. There are a few other differences in pronunciation, verbal morphology, and vocabulary.
Western Catalan comprises the two dialects of
North-Western Catalan and
Valencian Valencian can refer to:
* Something related to the Valencian Community ( Valencian Country) in Spain
* Something related to the city of Valencia
* Something related to the province of Valencia in Spain
* Something related to the old Kingdom of ...
; the Eastern block comprises four dialects:
Central Catalan
Central Catalan () is an Eastern Catalan dialect spoken in the whole province of Barcelona, the eastern half of the province of Tarragona and most of the province of Girona, except for its northern part, where a transition to Northern Catalan ...
,
Balearic,
Roussillonese, and
Algherese. Each dialect can be further subdivided in several subdialects. The terms "Catalan" and "
Valencian Valencian can refer to:
* Something related to the Valencian Community ( Valencian Country) in Spain
* Something related to the city of Valencia
* Something related to the province of Valencia in Spain
* Something related to the old Kingdom of ...
" (respectively used in
Catalonia
Catalonia is an autonomous community of Spain, designated as a ''nationalities and regions of Spain, nationality'' by its Statute of Autonomy of Catalonia of 2006, Statute of Autonomy. Most of its territory (except the Val d'Aran) is situate ...
and the
Valencian Community
The Valencian Community is an Autonomous communities of Spain, autonomous community of Spain. It is the fourth most populous Spanish Autonomous communities of Spain, autonomous community after Andalusia, Catalonia and the Community of Madrid wit ...
) refer to two varieties of the same language.
There are two institutions regulating the two standard varieties, the
Institute of Catalan Studies
The Institute for Catalan Studies ( ), also known by the acronym IEC, is an academic institution which seeks to undertake research and study into "all elements of Catalan culture". It is based in Barcelona, Catalonia, Spain.
IEC
The IEC is known ...
in Catalonia and the
Valencian Academy of the Language in the Valencian Community.
Central Catalan is considered the standard pronunciation of the language and has the largest number of speakers. It is spoken in the densely populated regions of the
Barcelona province, the eastern half of the province of Tarragona, and most of the province of Girona.
Catalan has an inflectional grammar. Nouns have two
genders
Gender is the range of social, psychological, cultural, and behavioral aspects of being a man (or boy), woman (or girl), or third gender. Although gender often corresponds to sex, a transgender person may identify with a gender other than the ...
(masculine, feminine), and two
numbers
A number is a mathematical object used to count, measure, and label. The most basic examples are the natural numbers 1, 2, 3, 4, and so forth. Numbers can be represented in language with number words. More universally, individual numbers can ...
(singular, plural). Pronouns additionally can have a neuter gender, and some are also inflected for
case
Case or CASE may refer to:
Instances
* Instantiation (disambiguation), a realization of a concept, theme, or design
* Special case, an instance that differs in a certain way from others of the type
Containers
* Case (goods), a package of relate ...
and
politeness
Politeness is the practical application of good manners or etiquette so as not to offend others and to put them at ease. It is a culturally defined phenomenon, and therefore what is considered polite in one culture can sometimes be quite rude or ...
, and can be combined in very complex ways. Verbs are split in several paradigms and are inflected for
person
A person (: people or persons, depending on context) is a being who has certain capacities or attributes such as reason, morality, consciousness or self-consciousness, and being a part of a culturally established form of social relations suc ...
,
number
A number is a mathematical object used to count, measure, and label. The most basic examples are the natural numbers 1, 2, 3, 4, and so forth. Numbers can be represented in language with number words. More universally, individual numbers can ...
,
tense,
aspect,
mood, and
gender
Gender is the range of social, psychological, cultural, and behavioral aspects of being a man (or boy), woman (or girl), or third gender. Although gender often corresponds to sex, a transgender person may identify with a gender other tha ...
. In terms of pronunciation, Catalan has many words ending in a wide variety of consonants and some consonant clusters, in contrast with many other Romance languages.
Pronunciation
Vowels
Catalan has inherited the typical vowel system of
Vulgar Latin
Vulgar Latin, also known as Colloquial, Popular, Spoken or Vernacular Latin, is the range of non-formal Register (sociolinguistics), registers of Latin spoken from the Crisis of the Roman Republic, Late Roman Republic onward. ''Vulgar Latin'' a ...
, with seven stressed phonemes: , a common feature in
Western Romance
Western Romance languages are one of the two subdivisions of a proposed subdivision of the Romance languages based on the La Spezia–Rimini Line. They include the Ibero-Romance and Gallo-Romance. Gallo-Italic may also be included. The subdivi ...
, except
Spanish
Spanish might refer to:
* Items from or related to Spain:
**Spaniards are a nation and ethnic group indigenous to Spain
**Spanish language, spoken in Spain and many countries in the Americas
**Spanish cuisine
**Spanish history
**Spanish culture
...
.
Balearic has also instances of stressed . Dialects differ in the different degrees of
vowel reduction
In phonetics, vowel reduction is any of various changes in the acoustic ''quality'' of vowels as a result of changes in stress, sonority, duration, loudness, articulation, or position in the word (e.g. for the Muscogee language), and which ar ...
, and the incidence of the pair .
In
Eastern Catalan
The Catalan dialects (and restrictively also, Valencian dialects) feature a relative uniformity, especially when compared to other Romance languages; both in terms of vocabulary, semantics, syntax, morphology, and phonology. Mutual intelligibi ...
(except Majorcan), unstressed vowels reduce to three: ; ; remains distinct. There are a few instances of unreduced , in some words.
Algherese has lowered to .
In Majorcan, unstressed vowels reduce to four: follow the Eastern Catalan reduction pattern; however reduce to , with remaining distinct, as in Western Catalan.
In
Western Catalan
The Catalan dialects (and restrictively also, Valencian dialects) feature a relative uniformity, especially when compared to other Romance languages; both in terms of vocabulary, semantics, syntax, morphology, and phonology. Mutual intelligibil ...
, unstressed vowels reduce to five: ; ; remain distinct. This reduction pattern, inherited from
Proto-Romance
Proto-Romance is the result of applying the comparative method to reconstruct the latest common ancestor of the Romance languages. To what extent, if any, such a reconstruction reflects a real ''état de langue'' is controversial. The closest real ...
, is also found in
Italian
Italian(s) may refer to:
* Anything of, from, or related to the people of Italy over the centuries
** Italians, a Romance ethnic group related to or simply a citizen of the Italian Republic or Italian Kingdom
** Italian language, a Romance languag ...
and
Portuguese. Some Western dialects present further reduction or vowel harmony in some cases.
Central, Western, and Balearic differ in the lexical incidence of stressed and . Usually, words with in Central Catalan correspond to in Balearic and in Western Catalan. Words with in Balearic almost always have in Central and Western Catalan as well. As a result, Central Catalan has a much higher incidence of .
Consonants
Catalan dialects are characterized by
final-obstruent devoicing
Final-obstruent devoicing or terminal devoicing is a systematic phonological process occurring in languages such as Catalan, German, Dutch, Quebec French, Breton, Russian, Polish, Lithuanian, Turkish, and Wolof. In such languages, voic ...
,
lenition
In linguistics, lenition is a sound change that alters consonants, making them "weaker" in some way. The word ''lenition'' itself means "softening" or "weakening" (from Latin 'weak'). Lenition can happen both synchronically (within a language ...
and
voicing assimilation
In phonology, voicing (or sonorization) is a sound change where a voiceless consonant becomes voiced due to the influence of its phonological environment; shift in the opposite direction is referred to as devoicing or surdization. Most commonly ...
. Additionally, many dialects contrast two
rhotics
In phonetics, rhotic consonants, or "R-like" sounds, are liquid consonants that are traditionally represented orthographically by symbols derived from the Greek letter rho (Ρ and ρ), including , in the Latin script and , in the Cyrillic ...
() and two
laterals ().
Most Catalan dialects are also renowned by the usage of ''
dark l
The voiced dental, alveolar, and postalveolar lateral approximants are a type of consonantal sound used in many spoken languages. The symbol in the International Phonetic Alphabet that represents dental, alveolar, and postalveolar lateral ...
'' (i.e.
velarization
Velarization merican spelling/small> or velarisation ritish spelling/sup> is a secondary articulation of consonants by which the back of the tongue is raised toward the velum during the articulation of the consonant.
In the International Ph ...
of → ), which is especially noticeable in syllable
final
Final, Finals or The Final may refer to:
*Final examination or finals, a test given at the end of a course of study or training
*Final (competition), the last or championship round of a sporting competition, match, game, or other contest which d ...
position, in comparison to neighbouring languages, such as Spanish, Italian and French (that lack this pronunciation).
There is dialectal variation in regard to:
* The pronunciation and distribution of
sibilant
Sibilants (from 'hissing') are fricative and affricate consonants of higher amplitude and pitch, made by directing a stream of air with the tongue towards the teeth. Examples of sibilants are the consonants at the beginning of the English w ...
s (with different results according to
voicing and
affrication
An affricate is a consonant that begins as a stop and releases as a fricative, generally with the same place of articulation (most often coronal). It is often difficult to decide if a stop and fricative form a single phoneme or a consonant pai ...
vs.
deaffrication).
** While, arguably there are seven to eight sibilants in Standard Catalan and Standard Valencian, dialects like Central Valencian and Ribagorçan only have three or four.
* The usage of the voiced labiodental fricative phoneme .
* The pronunciation or not of
yod () in the digraph .
* The
elision
In linguistics, an elision or deletion is the omission of one or more sounds (such as a vowel, a consonant, or a whole syllable) in a word or phrase. However, these terms are also used to refer more narrowly to cases where two words are run to ...
and pronunciation of final
rhotics
In phonetics, rhotic consonants, or "R-like" sounds, are liquid consonants that are traditionally represented orthographically by symbols derived from the Greek letter rho (Ρ and ρ), including , in the Latin script and , in the Cyrillic ...
(either or ).
* The
delateralization
Delateralization is a replacement of a lateral consonant by a central consonant.
Yeísmo (Romance languages)
Arguably, the best known example of this sound change is yeísmo, which occurs in many Spanish and some Galician dialects.
In accent ...
of the palatal lateral approximant ().
* The alternation of
lenition
In linguistics, lenition is a sound change that alters consonants, making them "weaker" in some way. The word ''lenition'' itself means "softening" or "weakening" (from Latin 'weak'). Lenition can happen both synchronically (within a language ...
vs.
fortition
In articulatory phonetics, fortition, also known as strengthening, is a consonantal change that increases the degree of stricture. It is the opposite of the more common lenition. For example, a fricative or an approximant may become a stop (i ...
(such as in 'village, people' → vs. vs. vs. vs. ).
Morphology
Western Catalan: In verbs, the ending for 1st-person present indicative is in verbs of the 1st conjugation and -∅ in verbs of the 2nd and 3rd conjugations in most of the Valencian Community, or in all verb conjugations in the Northern Valencian Community and Western Catalonia.
E.g. , , (Valencian); , , (North-Western Catalan).
Eastern Catalan: In verbs, the ending for 1st-person present indicative is , , or -∅ in all conjugations.
E.g. (Central), (Balearic), and (Northern), all meaning ('I speak').
Western Catalan: In verbs, the inchoative endings are /, , , /.
Eastern Catalan: In verbs, the inchoative endings are , , , .
Western Catalan: In nouns and adjectives, maintenance of of medieval plurals in
proparoxytone
In linguistics, a proparoxytone (, ) is a word with stress on the antepenultimate (third to last) syllable, such as the English language, English words "cinema" and "operational". Related concepts are paroxytone (stress on the penultimate syllable) ...
words.
E.g. 'men', 'youth'.
Eastern Catalan: In nouns and adjectives, loss of of medieval plurals in proparoxytone words.
E.g. 'men', 'youth' (Ibicencan, however, follows the model of Western Catalan in this case).
Vocabulary
Despite its relative lexical unity, the two dialectal blocks of Catalan (Eastern and Western) show some differences in word choices. Any lexical divergence within any of the two groups can be explained as an archaism. Also, usually
Central Catalan
Central Catalan () is an Eastern Catalan dialect spoken in the whole province of Barcelona, the eastern half of the province of Tarragona and most of the province of Girona, except for its northern part, where a transition to Northern Catalan ...
acts as an innovative element.
Standards
Standard Catalan, virtually accepted by all speakers, is mostly based on Eastern Catalan, which is the most widely used dialect. Nevertheless, the standards of the Valencian Community and the Balearics admit alternative forms, mostly traditional ones, which are not current in eastern Catalonia.
The most notable difference between both standards is some tonic accentuation, for instance: (IEC) – (AVL). Nevertheless, AVL's standard keeps the grave accent , while pronouncing it as rather than , in some words such as: ('what'), or . Other divergences include the use of (AVL) in some words instead of like in / ('almond'), / ('back'), the use of elided demonstratives ( 'this', 'that') in the same level as reinforced ones () or the use of many verbal forms common in Valencian, and some of these common in the rest of Western Catalan too, such as subjunctive mood or inchoative conjugation in at the same level as or the priority use of morpheme in 1st person singular in present indicative ( verbs): instead of ('I buy').
In the Balearic Islands, IEC's standard is used but adapted for the Balearic dialect by the
University of the Balearic Islands
The University of the Balearic Islands (, UIB; ) is a Balearic Islands, Balearic Spain, Spanish university, founded in 1978 and located in Palma de Mallorca, Palma on the island of Majorca. The university is funded by the autonomous Government o ...
's philological section. In this way, for instance, IEC says it is correct writing as much as ('we sing'), but the university says that the priority form in the Balearic Islands must be in all fields. Another feature of the Balearic standard is the non-ending in the 1st person singular present indicative: ('I buy'), ('I fear'), ('I sleep').
In Alghero, the IEC has adapted its standard to the
Algherese dialect. In this standard one can find, among other features: the definite article instead of , special possessive pronouns and determinants ('mine'), ('his/her'), ('yours'), and so on, the use of in the imperfect tense in all conjugations: , , ; the use of many archaic words, usual words in Algherese: instead of ('less'), instead of ('someone'), instead of ('which'), and so on; and the adaptation of
weak pronouns. In 1999, Catalan (
Algherese dialect
Algherese or Alguerese (endonym and exonym, autonym: ) is the Variety (linguistics), variety of Catalan language, Catalan spoken in the city of Alghero ( in Catalan), in the northwest of Sardinia, Italy.
The dialect has its roots in 1372, w ...
) was among the twelve minority languages officially recognized as Italy's "
historical linguistic minorities" by the Italian State under Law No. 482/1999.
In 2011, the
Aragon
Aragon ( , ; Spanish and ; ) is an autonomous communities of Spain, autonomous community in Spain, coextensive with the medieval Kingdom of Aragon. In northeastern Spain, the Aragonese autonomous community comprises three provinces of Spain, ...
ese government passed a decree approving the statutes of a new language regulator of Catalan in
La Franja
La Franja (; "The Strip"; ) is the area of Catalan-speaking territories of eastern Aragon bordering Catalonia, in Spain. It literally means ''"the strip"'' and can also more properly be called (Aragonese Strip), (Western Strip) or (Eastern St ...
(the so-called Catalan-speaking areas of Aragon) as originally provided for by Law 10/2009. The new entity, designated as , shall allow a facultative education in Catalan and a standardization of the Catalan language in
La Franja
La Franja (; "The Strip"; ) is the area of Catalan-speaking territories of eastern Aragon bordering Catalonia, in Spain. It literally means ''"the strip"'' and can also more properly be called (Aragonese Strip), (Western Strip) or (Eastern St ...
.
Status of Valencian
Valencian is classified as a
Western
Western may refer to:
Places
*Western, Nebraska, a village in the US
*Western, New York, a town in the US
*Western Creek, Tasmania, a locality in Australia
*Western Junction, Tasmania, a locality in Australia
*Western world, countries that id ...
dialect, along with the
North-Western varieties spoken in Western Catalonia (provinces of
Lleida
Lleida (, ; ; '' see below'') is a city in the west of Catalonia, Spain. It is the capital and largest town in Segrià county, the Ponent region and the province of Lleida. Geographically, it is located in the Catalan Central Depression. It ...
and the western half of
Tarragona
Tarragona (, ; ) is a coastal city and municipality in Catalonia (Spain). It is the capital and largest town of Tarragonès county, the Camp de Tarragona region and the province of Tarragona. Geographically, it is located on the Costa Daurada ar ...
). Central Catalan has 90% to 95% inherent intelligibility for speakers of Valencian.
Linguists, including Valencian scholars, deal with Catalan and Valencian as the same language. The official regulating body of the language of the Valencian Community, the
Valencian Academy of Language (''Acadèmia Valenciana de la Llengua'', AVL) declares the linguistic unity between Valencian and Catalan varieties.
The AVL, created by the Valencian parliament, is in charge of dictating the official rules governing the use of Valencian, and its standard is based on the Norms of Castelló (''
Normes de Castelló
Normes de Castelló (, "Norms of Castelló"), also known as Normes del 32 (), are elementary orthographic guidelines that follow Pompeu Fabra's Catalan language norms for its Valencian variety. They were signed in 1932 in Castelló de la Plana ...
''). Currently, everyone who writes in Valencian uses this standard, except the Royal Academy of Valencian Culture (''Real Acadèmia de Cultura Valenciana'', RACV), which uses an independent standard for Valencian.
Despite the position of the official organizations, an opinion poll carried out between 2001 and 2004 showed that the majority of the Valencian people consider Valencian different from Catalan. This position is promoted by people who do not use Valencian regularly. Furthermore, the data indicates that younger generations educated in Valencian are much less likely to hold these views. A minority of Valencian scholars active in fields other than linguistics defends the position of the Royal Academy of Valencian Culture (''Real Acadèmia de Cultura Valenciana'', RACV), which uses for Valencian a standard independent from Catalan.
This clash of opinions has sparked much controversy. For example, during the drafting of the
European Constitution
The Treaty establishing a Constitution for Europe (TCE; commonly referred to as the European Constitution or as the Constitutional Treaty) was an unratified international treaty intended to create a consolidated constitution for the European ...
in 2004, the Spanish government supplied the
EU with translations of the text into
Basque
Basque may refer to:
* Basques, an ethnic group of Spain and France
* Basque language, their language
Places
* Basque Country (greater region), the homeland of the Basque people with parts in both Spain and France
* Basque Country (autonomous co ...
,
Galician, Catalan, and Valencian, but the latter two were identical.
Vocabulary
Word choices
Despite its relative lexical unity, the two dialectal blocks of Catalan (Eastern and Western) show some differences in word choices. Any lexical divergence within any of the two groups can be explained as an archaism. Also, usually
Central Catalan
Central Catalan () is an Eastern Catalan dialect spoken in the whole province of Barcelona, the eastern half of the province of Tarragona and most of the province of Girona, except for its northern part, where a transition to Northern Catalan ...
acts as an innovative element.
Literary Catalan allows the use of words from different dialects, except those of very restricted use. However, from the 19th century onwards, there has been a tendency towards favoring words of Northern dialects to the detriment of others.
Latin and Greek loanwords
Like other languages, Catalan has a large list of loanwords from Greek and Latin. This process started very early, and one can find such examples in
Ramon Llull
Ramon Llull (; ; – 1316), sometimes anglicized as ''Raymond Lully'', was a philosopher, theologian, poet, missionary, Christian apologist and former knight from the Kingdom of Majorca.
He invented a philosophical system known as the ''Art ...
's work. In the 14th and 15th centuries Catalan had a far greater number of Greco-Latin loanwords than other Romance languages, as is attested for example in
Roís de Corella's writings. The incorporation of learned, or "bookish" words from its own ancestor language,
Latin
Latin ( or ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally spoken by the Latins (Italic tribe), Latins in Latium (now known as Lazio), the lower Tiber area aroun ...
, into Catalan is arguably another form of lexical borrowing through the influence of
written language
A written language is the representation of a language by means of writing. This involves the use of visual symbols, known as graphemes, to represent linguistic units such as phonemes, syllables, morphemes, or words. However, written language is ...
and the liturgical language of the Church. Throughout the Middle Ages and into the early modern period, most literate Catalan speakers were also literate in Latin; and thus they easily adopted Latin words into their writing—and eventually speech—in Catalan.
Word formation
The process of
morphological derivation
Morphological derivation, in linguistics, is the process of forming a new word from an existing word, often by adding a prefix or suffix, such as For example, ''unhappy'' and ''happiness'' derive from the root word ''happy.''
It is differentia ...
in Catalan follows the same principles as the other
Romance languages
The Romance languages, also known as the Latin or Neo-Latin languages, are the languages that are Language family, directly descended from Vulgar Latin. They are the only extant subgroup of the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-E ...
, where
inflection
In linguistic Morphology (linguistics), morphology, inflection (less commonly, inflexion) is a process of word formation in which a word is modified to express different grammatical category, grammatical categories such as grammatical tense, ...
is common. Many times, several affixes are appended to a preexisting lexeme, and some sound alternations can occur, for example ("electrical") vs. .
Prefixes
A prefix is an affix which is placed before the stem of a word. Particularly in the study of languages, a prefix is also called a preformative, because it alters the form of the word to which it is affixed.
Prefixes, like other affixes, can b ...
are usually appended to verbs, as in ("foresee").
There is greater regularity in the process of
word-compounding
In linguistics, a compound is a lexeme (less precisely, a word or sign) that consists of more than one stem. Compounding, composition or nominal composition is the process of word formation that creates compound lexemes. Compounding occurs when two ...
, where one can find compounded words formed much like those in English.
Writing system

Catalan uses the
Latin script
The Latin script, also known as the Roman script, is a writing system based on the letters of the classical Latin alphabet, derived from a form of the Greek alphabet which was in use in the ancient Greek city of Cumae in Magna Graecia. The Gree ...
, with some added symbols and digraphs. The
Catalan orthography
The Catalan and Valencian orthographies encompass the spelling and punctuation of standard Catalan (set by the IEC) and Valencian (set by the AVL). There are also several adapted variants to the peculiarities of local dialects of Insular C ...
is systematic and largely phonologically based. Standardization of Catalan was among the topics discussed during the First International Congress of the Catalan Language, held in Barcelona October 1906. Subsequently, the Philological Section of the ''Institut d'Estudis Catalans'' (IEC, founded in 1911) published the ''Normes ortogràfiques'' in 1913 under the direction of
Antoni Maria Alcover
Father Antoni Maria Alcover i Sureda, also known (in Catalan) as ''Mossèn Alcover'' (; 2 February 1862 in Santa Cirga, Manacor – 8 January 1932 in Palma) was a modernist Majorcan writer, who wrote on a wide range of subjects including the Cat ...
and
Pompeu Fabra
Pompeu Fabra i Poch (; Gràcia, Barcelona, 20 February 1868 – Prada de Conflent, 25 December 1948) was a Catalan engineer and grammarian. He was the main author of the normative reform of contemporary Catalan language, and is the namesa ...
. In 1932, Valencian writers and intellectuals gathered in
Castelló de la Plana to make a formal adoption of the so-called ''
Normes de Castelló
Normes de Castelló (, "Norms of Castelló"), also known as Normes del 32 (), are elementary orthographic guidelines that follow Pompeu Fabra's Catalan language norms for its Valencian variety. They were signed in 1932 in Castelló de la Plana ...
'', a set of guidelines following Pompeu Fabra's Catalan language norms.
Grammar
The grammar of Catalan is similar to other
Romance languages
The Romance languages, also known as the Latin or Neo-Latin languages, are the languages that are Language family, directly descended from Vulgar Latin. They are the only extant subgroup of the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-E ...
. Features include:
* Use of
definite
In linguistics, definiteness is a semantic feature of noun phrases that distinguishes between referents or senses that are identifiable in a given context (definite noun phrases) and those that are not (indefinite noun phrases). The prototypical ...
and
indefinite article
In grammar, an article is any member of a class of dedicated words that are used with noun phrases to mark the identifiability of the referents of the noun phrases. The category of articles constitutes a part of speech.
In English, both "the ...
s.
*
Noun
In grammar, a noun is a word that represents a concrete or abstract thing, like living creatures, places, actions, qualities, states of existence, and ideas. A noun may serve as an Object (grammar), object or Subject (grammar), subject within a p ...
s,
adjective
An adjective (abbreviations, abbreviated ) is a word that describes or defines a noun or noun phrase. Its semantic role is to change information given by the noun.
Traditionally, adjectives are considered one of the main part of speech, parts of ...
s,
pronoun
In linguistics and grammar, a pronoun (Interlinear gloss, glossed ) is a word or a group of words that one may substitute for a noun or noun phrase.
Pronouns have traditionally been regarded as one of the part of speech, parts of speech, but so ...
s, and
articles
Article often refers to:
* Article (grammar), a grammatical element used to indicate definiteness or indefiniteness
* Article (publishing), a piece of nonfictional prose that is an independent part of a publication
Article(s) may also refer to:
...
are
inflected
In linguistic Morphology (linguistics), morphology, inflection (less commonly, inflexion) is a process of word formation in which a word is modified to express different grammatical category, grammatical categories such as grammatical tense, ...
for
gender
Gender is the range of social, psychological, cultural, and behavioral aspects of being a man (or boy), woman (or girl), or third gender. Although gender often corresponds to sex, a transgender person may identify with a gender other tha ...
(masculine and feminine), and
number
A number is a mathematical object used to count, measure, and label. The most basic examples are the natural numbers 1, 2, 3, 4, and so forth. Numbers can be represented in language with number words. More universally, individual numbers can ...
(singular and plural). There is no
case
Case or CASE may refer to:
Instances
* Instantiation (disambiguation), a realization of a concept, theme, or design
* Special case, an instance that differs in a certain way from others of the type
Containers
* Case (goods), a package of relate ...
inflexion, except in pronouns.
*
Verb
A verb is a word that generally conveys an action (''bring'', ''read'', ''walk'', ''run'', ''learn''), an occurrence (''happen'', ''become''), or a state of being (''be'', ''exist'', ''stand''). In the usual description of English, the basic f ...
s are highly inflected for
person
A person (: people or persons, depending on context) is a being who has certain capacities or attributes such as reason, morality, consciousness or self-consciousness, and being a part of a culturally established form of social relations suc ...
,
number
A number is a mathematical object used to count, measure, and label. The most basic examples are the natural numbers 1, 2, 3, 4, and so forth. Numbers can be represented in language with number words. More universally, individual numbers can ...
,
tense,
aspect, and
mood (including a
subjunctive
The subjunctive (also known as the conjunctive in some languages) is a grammatical mood, a feature of an utterance that indicates the speaker's attitude toward it. Subjunctive forms of verbs are typically used to express various states of unrealit ...
).
* There are no
modal auxiliaries.
* Word order is freer than in English.
Gender and number inflection
In
gender inflection
In linguistics, a grammatical gender system is a specific form of a noun class system, where nouns are assigned to gender categories that are often not related to the real-world qualities of the entities denoted by those nouns. In languages wit ...
, the most notable feature is (compared to
Portuguese,
Spanish
Spanish might refer to:
* Items from or related to Spain:
**Spaniards are a nation and ethnic group indigenous to Spain
**Spanish language, spoken in Spain and many countries in the Americas
**Spanish cuisine
**Spanish history
**Spanish culture
...
or
Italian
Italian(s) may refer to:
* Anything of, from, or related to the people of Italy over the centuries
** Italians, a Romance ethnic group related to or simply a citizen of the Italian Republic or Italian Kingdom
** Italian language, a Romance languag ...
), the loss of the typical
masculine
Masculinity (also called manhood or manliness) is a set of attributes, behaviors, and roles generally associated with men and boys. Masculinity can be theoretically understood as socially constructed, and there is also evidence that some beh ...
suffix
In linguistics, a suffix is an affix which is placed after the stem of a word. Common examples are case endings, which indicate the grammatical case of nouns and adjectives, and verb endings, which form the conjugation of verbs. Suffixes can ca ...
. Thus, the alternance of /, has been replaced by ''ø''/. There are only a few exceptions, such as / ("scarce"). Many not completely predictable morphological alternations may occur, such as:
* Affrication: / ("insane") vs. / ("ugly")
* Loss of : / ("flat") vs. / ("second")
*
Final obstruent devoicing
Final-obstruent devoicing or terminal devoicing is a systematic phonological process occurring in languages such as Catalan, German, Dutch, Quebec French, Breton, Russian, Polish, Lithuanian, Turkish, and Wolof. In such languages, voiced ...
: / ("felt") vs. / ("said")
Catalan has few
suppletive
In linguistics and etymology, suppletion is traditionally understood as the use of one word as the inflection, inflected form of another word when the two words are not cognate. For those learning a language, suppletive forms will be seen as "irre ...
couplets, like Italian and Spanish, and unlike French. Thus, Catalan has / ("boy"/"girl") and / ("cock"/"hen"), whereas French has / and /.
There is a tendency to abandon traditionally gender-invariable adjectives in favor of marked ones, something prevalent in
Occitan Occitan may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to the Occitania territory in parts of France, Italy, Monaco and Spain.
* Something of, from, or related to the Occitania administrative region of France.
* Occitan language, spoken in parts o ...
and French. Thus, one can find / ("boiling") in contrast with traditional /.
As in the other Western Romance languages, the main plural expression is the suffix , which may create morphological alternations similar to the ones found in gender inflection, albeit more rarely. The most important one is the addition of before certain consonant groups, a
phonetic
Phonetics is a branch of linguistics that studies how humans produce and perceive sounds or, in the case of sign languages, the equivalent aspects of sign. Linguists who specialize in studying the physical properties of speech are phoneticians ...
phenomenon that does not affect feminine forms: / ("the pulse"/"the pulses") vs. / ("the dust"/"the dusts").
Determiners
The inflection of determinatives is complex, specially because of the high number of elisions, but is similar to the neighboring languages. Catalan has more contractions of preposition + article than
Spanish
Spanish might refer to:
* Items from or related to Spain:
**Spaniards are a nation and ethnic group indigenous to Spain
**Spanish language, spoken in Spain and many countries in the Americas
**Spanish cuisine
**Spanish history
**Spanish culture
...
, such as ("of + the
lural), but not as many as
Italian
Italian(s) may refer to:
* Anything of, from, or related to the people of Italy over the centuries
** Italians, a Romance ethnic group related to or simply a citizen of the Italian Republic or Italian Kingdom
** Italian language, a Romance languag ...
(which has , , , etc.).
Central Catalan has abandoned almost completely unstressed possessives (, etc.) in favor of constructions of article + stressed forms (, etc.), a feature shared with Italian.
Personal pronouns
The morphology of Catalan personal pronouns is complex, especially in unstressed forms, which are numerous (13 distinct forms, compared to 11 in Spanish or 9 in Italian). Features include the gender-neutral and the great degree of freedom when combining different unstressed pronouns (65 combinations).
Catalan pronouns exhibit
T–V distinction
The T–V distinction is the contextual use of different pronouns that exists in some languages and serves to convey formality or familiarity. Its name comes from the Latin pronouns '' tu'' and '' vos''. The distinction takes a number of forms ...
, like all other Romance languages (and most European languages, but not Modern English). This feature implies the use of a different set of second person pronouns for formality.
This flexibility allows Catalan to use
extraposition
Extraposition is a mechanism of syntax that alters word order in such a manner that a relatively "heavy" constituent appears to the right of its canonical position. Extraposing a constituent results in a discontinuity and in this regard, it i ...
extensively, much more than French or Spanish. Thus, Catalan can have ("they recommended me to him"), whereas in French one must say , and Spanish . This allows the placement of almost any nominal term as a sentence
topic, without having to use so often the
passive voice
A passive voice construction is a grammatical voice construction that is found in many languages. In a clause with passive voice, the grammatical subject expresses the ''theme'' or ''patient'' of the main verb – that is, the person or thing ...
(as in French or English), or identifying the
direct object
In linguistics, an object is any of several types of arguments. In subject-prominent, nominative-accusative languages such as English, a transitive verb typically distinguishes between its subject and any of its objects, which can include but ...
with a
preposition
Adpositions are a part of speech, class of words used to express spatial or temporal relations (''in, under, towards, behind, ago'', etc.) or mark various thematic relations, semantic roles (''of, for''). The most common adpositions are prepositi ...
(as in Spanish).
Verbs
Like all the Romance languages, Catalan verbal inflection is more complex than the nominal.
Suffixation
In linguistics, a suffix is an affix which is placed after the stem of a word. Common examples are case endings, which indicate the grammatical case of nouns and adjectives, and verb endings, which form the conjugation of verbs. Suffixes can carr ...
is omnipresent, whereas morphological alternations play a secondary role. Vowel alternances are active, as well as infixation and suppletion. However, these are not as productive as in Spanish, and are mostly restricted to irregular verbs.
The Catalan verbal system is basically common to all Western Romance, except that most dialects have replaced the synthetic indicative perfect with a periphrastic form of ("to go") + infinitive.
Catalan verbs are traditionally divided into three conjugations, with vowel themes , , , the last two being split into two subtypes. However, this division is mostly theoretical. Only the first conjugation is nowadays productive (with about 3500 common verbs), whereas the third (the subtype of , with about 700 common verbs) is semiproductive. The verbs of the second conjugation are fewer than 100, and it is not possible to create new ones, except by compounding.
Syntax
The grammar of Catalan follows the general pattern of Western Romance languages. The primary
word order
In linguistics, word order (also known as linear order) is the order of the syntactic constituents of a language. Word order typology studies it from a cross-linguistic perspective, and examines how languages employ different orders. Correlatio ...
is subject–verb–object. However, word order is very flexible. Commonly, verb-subject constructions are used to achieve a semantic effect. The sentence "The train has arrived" could be translated as or . Both sentences mean "the train has arrived", but the former puts a focus on the train, while the latter puts a focus on the arrival. This subtle distinction is described as "what you might say while waiting in the station" versus "what you might say on the train".
Catalan names
In Spain, every person officially has two surnames, one of which is the father's first surname and the other is the mother's first surname. The law contemplates the possibility of joining both surnames with the Catalan conjunction ''i'' ("and").
[article 19.1 of Law 1/1998 stipulates that "the citizens of Catalonia have the right to use the proper regulation of their Catalan names and surnames and to introduce the conjunction between surnames"]
Sample text
Selected text from Manuel de Pedrolo's 1970 novel ("A love affair outside the city").
See also
;Organizations
* ''
Institut d'Estudis Catalans
The Institute for Catalan Studies ( ), also known by the acronym and initialism, acronym IEC, is an academic institution which seeks to undertake research and study into "all elements of Catalan culture". It is based in Barcelona, Catalonia, Spai ...
'' (Catalan Studies Institute)
* ''
Acadèmia Valenciana de la Llengua
The Acadèmia Valenciana de la Llengua ("Valencian Academy of the Language"), also known by the acronym
An acronym is a type of abbreviation consisting of a phrase whose only pronounced elements are the initial letters or initial sounds of ...
'' (Valencian Academy of the Language)
* Òmnium Cultural
* Plataforma per la Llengua
;Scholars
* Marina Abràmova
* Germà Colón
* Dominique de Courcelles
* Martí de Riquer
* Arthur Terry
* Lawrence Venuti
;Other
* Languages of Catalonia
** Linguistic features of Spanish as spoken by Catalan speakers
* Languages of France
* Languages of Italy
* Languages of Spain
*
Normes de Castelló
Normes de Castelló (, "Norms of Castelló"), also known as Normes del 32 (), are elementary orthographic guidelines that follow Pompeu Fabra's Catalan language norms for its Valencian variety. They were signed in 1932 in Castelló de la Plana ...
*
Pompeu Fabra
Pompeu Fabra i Poch (; Gràcia, Barcelona, 20 February 1868 – Prada de Conflent, 25 December 1948) was a Catalan engineer and grammarian. He was the main author of the normative reform of contemporary Catalan language, and is the namesa ...
Notes
References
Works cited
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
External links
Institutions
''Consorci per a la Normalització Lingüística''''Institut d'Estudis Catalans'' (IEC)''Acadèmia Valenciana de la Llengua'' (AVL)
About the Catalan/Valencian language
''Gramàtica de la Llengua Catalana''(Catalan grammar), from the ''Institut d'Estudis Catalans''
''Gramàtica Normativa Valenciana''(Valencian grammar). , from the ''Acadèmia Valenciana de la Llengua''
''Apunts de llengua'' learning program by À Punt
llengua.gencat.cat by the Government of Catalonia
verbs.cat(Catalan verb conjugations with online trainers)
LEXDIALGRAM(online portal of 19th-century dialectal lexicographical and grammatical works of Catalan hosted by the University of Barcelona)
Monolingual dictionaries
DIEC2 from the ''Institut d'Estudis Catalans''
''Diccionari Normatiu Valencià'' (DNV) from the ''Acadèmia Valenciana de la Llengua''
''Gran Diccionari de la Llengua Catalana'' , from Enciclopèdia Catalana
''Diccionari Català-Valencià-Balear''d'Alcover i Moll. , from the ''Institut d'Estudis Catalans''
''Diccionari Invers de la Llengua Catalana''(Dictionary of Catalan words spelled backward)
trobat.com(online Valencian dictionary)
Bilingual and multilingual dictionaries
''Diccionari de la Llengua Catalana Multilingüe'' (Catalan ↔ English, French, German and Spanish), from Enciclopèdia Catalana
Automated translation systems
Traductorautomated, online translations of text and web pages (Catalan ↔ English, French and Spanish), from gencat.cat by the Government of Catalonia
Learning resources
Catalan Swadesh list of basic vocabulary words from Wiktionary'
Swadesh-list appendix
Catalan-language online encyclopedia
''Enciclopèdia Catalana''
{{Authority control
Catalan language,
Subject–verb–object languages
Stress-timed languages
Occitano-Romance languages
 Catalan shares features with neighboring Romance languages (
Catalan shares features with neighboring Romance languages ( The dialects of the Catalan language feature a relative uniformity, especially when compared to other Romance languages; both in terms of
The dialects of the Catalan language feature a relative uniformity, especially when compared to other Romance languages; both in terms of  Catalan uses the
Catalan uses the