Casemate De Marckolsheim Sud on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Casemate de Marckolsheim Sud is a pre-
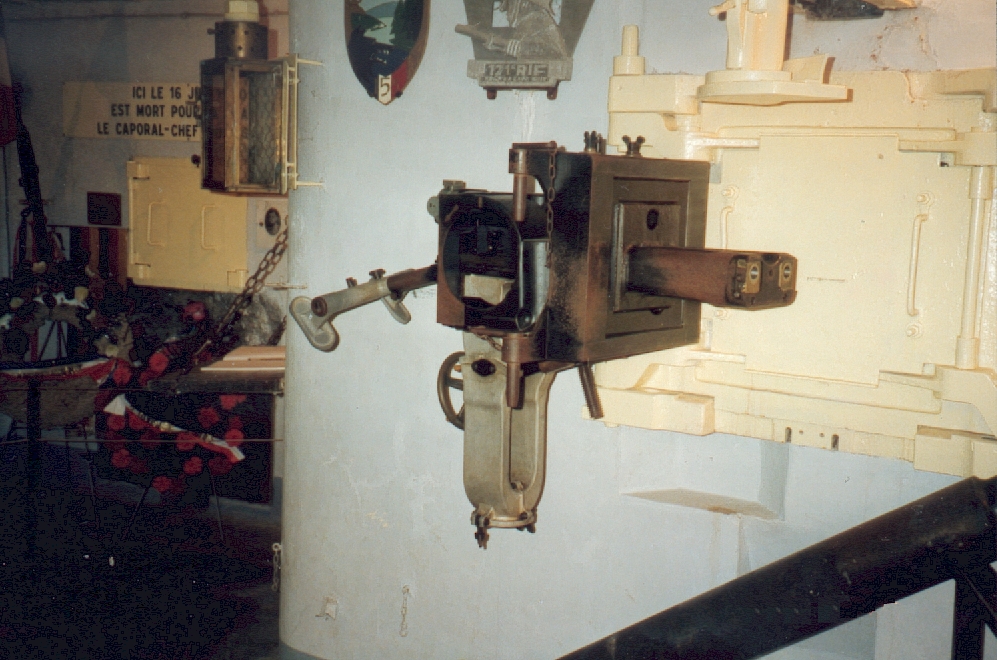 Marckolsheim Sud was commanded in 1940 by Lieutenant Marois of the French 42nd Fortress Infantry Regiment. On 15–17 June, the sector was attacked by German forces of the German 360th Infantry Regiment, 221st Infantry Division. Marckolsheim Sud and Nord put up particularly fierce resistance to German attack. The Germans brought up 8.8 cm guns, disabling one cloche, and called in
Marckolsheim Sud was commanded in 1940 by Lieutenant Marois of the French 42nd Fortress Infantry Regiment. On 15–17 June, the sector was attacked by German forces of the German 360th Infantry Regiment, 221st Infantry Division. Marckolsheim Sud and Nord put up particularly fierce resistance to German attack. The Germans brought up 8.8 cm guns, disabling one cloche, and called in
 Marckolsheim Sud was restored in 1972Kaufmann 2011, p. 181 and houses a museum, the ''Musée Mémorial de la Ligne Maginot du Rhin''.
Marckolsheim Sud was restored in 1972Kaufmann 2011, p. 181 and houses a museum, the ''Musée Mémorial de la Ligne Maginot du Rhin''.
Marckolsheim Museum
at Musées d'Alsace
at darkplaces.org
Casemate de Marckolsheim Sud
at fortiff.be {{DEFAULTSORT:Marckolsheim, Casemate De Fortified Sector of Colmar World War II museums in France
World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposin ...
fortified position near the Rhine
), Surselva, Graubünden, Switzerland
, source1_coordinates=
, source1_elevation =
, source2 = Rein Posteriur/Hinterrhein
, source2_location = Paradies Glacier, Graubünden, Switzerland
, source2_coordinates=
, so ...
river in eastern France. The casemate was part of an extension of the Maginot Line
The Maginot Line (french: Ligne Maginot, ), named after the French Minister of War André Maginot, is a line of concrete fortifications, obstacles and weapon installations built by France in the 1930s to deter invasion by Germany and force the ...
fortifications along France's border with Germany. As a unit of the Fortified Sector of Colmar
The Fortified Sector of Colmar (''Secteur Fortifié de Colmar'') was the French military organization that in 1940 controlled the section of the French frontier with Germany in the vicinity of Colmar. The fortifications were built as part of Franc ...
, the casemate was part of French defenses during the German assault of 15–18 June 1940, Operation ''Kleiner Bär''. It has been preserved and is part of a museum focusing on the Rhine section of the Maginot Line. The museum is located at the eastern edge of the town of Marckolsheim
Marckolsheim () is a commune in the Bas-Rhin department in Alsace in north-eastern France.
On the eastern edge of the town the Casemate de Marckolsheim Sud, a Maginot Line fortification left over from the Second World War, has been converted ...
.
Concept and design
Marckolsheim Sud's numerical designator was 35/3, referring to its place in the third, or "village" line of fortifications, about back from the river bank. It was built in the mid-1930s by the ''Commission d'Organisation des Régions Fortifiées (CORF)'', which was responsible for the major fortifications of the Maginot Line.Mary, Tome 3, p. 146 Unlike other portions of the Maginot Line, the Rhine defenses were not interconnected, consisting of individual casemates or blockhouses a few hundred meters apart, arranged to fire along the length of the defended frontier. The Marckolsheim Sud casemate is a double casemate, designed to fire laterally in either direction along the front, supporting its neighbors to the north and south. The position was armed with two twin heavy machine guns, type JM and, two 47mm anti-tank gun/JM combinations, one of each firing laterally. The faces of these firing positions were defended by two automatic rifle embrasures. A further automatic rifle position defended the casemate's entrance. On top of the fort, two cupolas or cloches were situated to fire in all directions, with aJM cloche
The JM cloche is an element of the Maginot Line. It is a non-retractable non-rotating cupola of steel alloy like GFM cloches, but are armed with twin heavy machine guns, as opposed to the lighter automatic rifles associated with the GFM. There are ...
mounted centrally and a GFM automatic rifle cloche to one side. The Marckolsheim Sud casemate, and its companion, Marckolsheim Nord, were not typical of the sector, being somewhat larger than most, with two cloches rather than the usual single GFM cloche. The design category was "SBFM special."=Mary, Tome 2, p. 14
1940
:''SeeFortified Sector of Colmar
The Fortified Sector of Colmar (''Secteur Fortifié de Colmar'') was the French military organization that in 1940 controlled the section of the French frontier with Germany in the vicinity of Colmar. The fortifications were built as part of Franc ...
for a broader discussion of the Colmar sector of the French defenses.''
 Marckolsheim Sud was commanded in 1940 by Lieutenant Marois of the French 42nd Fortress Infantry Regiment. On 15–17 June, the sector was attacked by German forces of the German 360th Infantry Regiment, 221st Infantry Division. Marckolsheim Sud and Nord put up particularly fierce resistance to German attack. The Germans brought up 8.8 cm guns, disabling one cloche, and called in
Marckolsheim Sud was commanded in 1940 by Lieutenant Marois of the French 42nd Fortress Infantry Regiment. On 15–17 June, the sector was attacked by German forces of the German 360th Infantry Regiment, 221st Infantry Division. Marckolsheim Sud and Nord put up particularly fierce resistance to German attack. The Germans brought up 8.8 cm guns, disabling one cloche, and called in Stuka
The Junkers Ju 87 or Stuka (from ''Sturzkampfflugzeug'', "dive bomber") was a German dive bomber and ground-attack aircraft. Designed by Hermann Pohlmann, it first flew in 1935. The Ju 87 made its combat debut in 1937 with the Luftwaffe's Cond ...
attacks, which buried the other in debris from bomb blasts. Without the means to defend itself in all directions, and with German assault teams throwing explosives into the casemate openings, the garrison was forced to surrender on the 17th.Romanych, pp. 88–90
Museum
 Marckolsheim Sud was restored in 1972Kaufmann 2011, p. 181 and houses a museum, the ''Musée Mémorial de la Ligne Maginot du Rhin''.
Marckolsheim Sud was restored in 1972Kaufmann 2011, p. 181 and houses a museum, the ''Musée Mémorial de la Ligne Maginot du Rhin''.
References
Bibliography
*Allcorn, William. ''The Maginot Line 1928-45.'' Oxford: Osprey Publishing, 2003. *Degon, André; Zylberyng, Didier, "La Ligne Maginot: Guide des Forts à Visiter," Editions Ouest-France, 2014. *Kaufmann, J.E. and Kaufmann, H.W. ''Fortress France: The Maginot Line and French Defenses in World War II'', Stackpole Books, 2006. *Kaufmann, J.E., Kaufmann, H.W., Jancovič-Potočnik, A. and Lang, P. ''The Maginot Line: History and Guide'', Pen and Sword, 2011. *Mary, Jean-Yves; Hohnadel, Alain; Sicard, Jacques. ''Hommes et Ouvrages de la Ligne Maginot, Tome 1.'' Paris, Histoire & Collections, 2001. *Mary, Jean-Yves; Hohnadel, Alain; Sicard, Jacques. ''Hommes et Ouvrages de la Ligne Maginot, Tome 2.'' Paris, Histoire & Collections, 2003. *Mary, Jean-Yves; Hohnadel, Alain; Sicard, Jacques. ''Hommes et Ouvrages de la Ligne Maginot, Tome 3.'' Paris, Histoire & Collections, 2003. *Mary, Jean-Yves; Hohnadel, Alain; Sicard, Jacques. ''Hommes et Ouvrages de la Ligne Maginot, Tome 5.'' Paris, Histoire & Collections, 2009.External links
Marckolsheim Museum
at Musées d'Alsace
at darkplaces.org
Casemate de Marckolsheim Sud
at fortiff.be {{DEFAULTSORT:Marckolsheim, Casemate De Fortified Sector of Colmar World War II museums in France