Carpus and tarsus of land vertebrates on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Carpals and tarsals
The carpus ( * Three proximals. In the hand humans have all three. In the foot the middle proximal appears in 5-15% of people as an os trigonum and can be involved in foot pain.
* Centrale or os centrale, on the medial side. In humans and our closest relatives the African apes (
* Three proximals. In the hand humans have all three. In the foot the middle proximal appears in 5-15% of people as an os trigonum and can be involved in foot pain.
* Centrale or os centrale, on the medial side. In humans and our closest relatives the African apes (
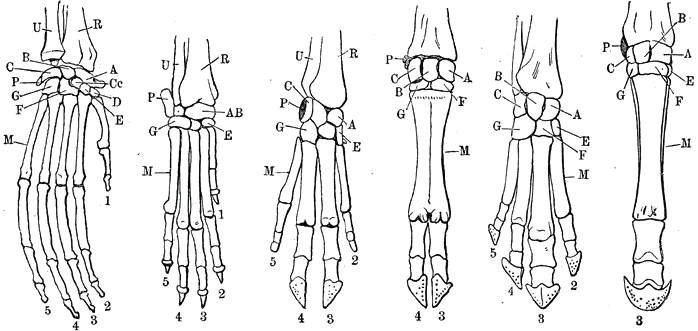 Abbreviations: A,
Abbreviations: A,  Frog four limbs and human foot compared.
Frog four limbs and human foot compared.
wrist
In human anatomy, the wrist is variously defined as (1) the Carpal bones, carpus or carpal bones, the complex of eight bones forming the proximal skeletal segment of the hand; "The wrist contains eight bones, roughly aligned in two rows, known ...
) and tarsus ( ankle) of land vertebrates
Vertebrates () comprise all animal taxa within the subphylum Vertebrata () ( chordates with backbones), including all mammals, birds, reptiles, amphibians, and fish. Vertebrates represent the overwhelming majority of the phylum Chordata, ...
primitively had three rows of carpal or tarsal bones. Often some of these have become lost or fused in evolution
Evolution is change in the heritable characteristics of biological populations over successive generations. These characteristics are the expressions of genes, which are passed on from parent to offspring during reproduction. Variation ...
.
 * Three proximals. In the hand humans have all three. In the foot the middle proximal appears in 5-15% of people as an os trigonum and can be involved in foot pain.
* Centrale or os centrale, on the medial side. In humans and our closest relatives the African apes (
* Three proximals. In the hand humans have all three. In the foot the middle proximal appears in 5-15% of people as an os trigonum and can be involved in foot pain.
* Centrale or os centrale, on the medial side. In humans and our closest relatives the African apes (chimpanzee
The chimpanzee (''Pan troglodytes''), also known as simply the chimp, is a species of great ape native to the forest and savannah of tropical Africa. It has four confirmed subspecies and a fifth proposed subspecies. When its close relative th ...
s and gorilla
Gorillas are herbivorous, predominantly ground-dwelling great apes that inhabit the tropical forests of equatorial Africa. The genus ''Gorilla'' is divided into two species: the eastern gorilla and the western gorilla, and either four or fi ...
s) it fuses to the scaphoid where it forms the articulation with the trapezoid bone; occasionally it stays separate. In Man's foot it is the navicular
The navicular bone is a small bone found in the feet of most mammals.
Human anatomy
The navicular bone in humans is one of the tarsal bones, found in the foot. Its name derives from the human bone's resemblance to a small boat, caused by th ...
. Some early land vertebrates had more than one (up to three) os centrale per hand or foot (plural "(ossa) centralia").
* Distals, one per finger / toe at the base of each metacarpal or metatarsal. In mammal
Mammals () are a group of vertebrate animals constituting the class Mammalia (), characterized by the presence of mammary glands which in females produce milk for feeding (nursing) their young, a neocortex (a region of the brain), fur or ...
s the 4th and 5th fuse. In the horse
The horse (''Equus ferus caballus'') is a domesticated, one-toed, hoofed mammal. It belongs to the taxonomic family Equidae and is one of two extant subspecies of ''Equus ferus''. The horse has evolved over the past 45 to 55 million y ...
the 1st is lost.
Figure to the right shows locations of rare accessory bones of the foot (presence variable from person to person):
1=Os cuneometatarsale I plantare, 2=os uncinatum, 3=os sesamoideum tibialis posterior, 4=os sesamoideum peroneum, 5=os cuboideum secundarium, 6=os trochleare calcanei, 7=os in sinus tarsi, 8=os sustentaculum tali, 9=os talocalcaneale posterius, 10=os aponeurosis plantaris, 11=os subcalcaneum, 12=os sesamoideum tibialis anterior, 13=os cuneometatarsale I tibiale, 14=os intermetatarsale I, 15=os cuneometatarsale II dorsale, 16=os paracuneiforme, 17=os cuneonaviculare, 18=os intercuneiforme, 19=os intermetatarsale IV, 20=/os talonaviculare, 21=os vesalianum pedis, 22=os tibiale externum, 23=os talotibiale dorsale, 24=os supratalare, 25=os calcaneus secundarius, 26=os subtibiale, 27=os subfibulare, 28=os retinaculi, 29=os calcaneus accessorius, 30=os trigonum, 31=os supracalcaneum, 32=os tendinis calcanei.
Comparative vertebrate anatomy
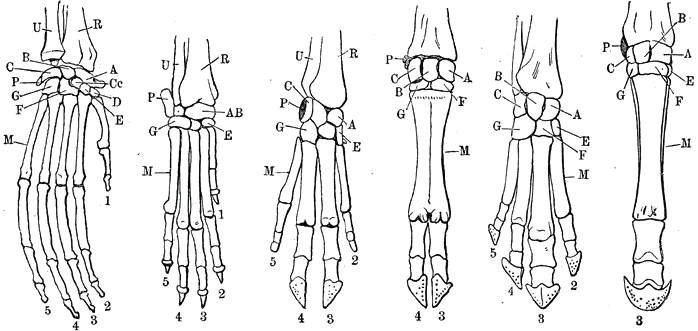 Abbreviations: A,
Abbreviations: A, Scaphoid bone
The scaphoid bone is one of the carpal bones of the wrist. It is situated between the hand and forearm on the thumb side of the wrist (also called the lateral or radial side). It forms the radial border of the carpal tunnel. The scaphoid bone is ...
; B, Lunate bone
The lunate bone (semilunar bone) is a carpal bone in the human hand. It is distinguished by its deep concavity and crescentic outline. It is situated in the center of the proximal row carpal bones, which lie between the ulna and radius and the han ...
; C, Triquetrum; D, Trapezium; E, Trapezoid; F, Capitatum; G, Hamatum;
P, Pisiform
The pisiform bone ( or ), also spelled pisiforme (from the Latin ''pisifomis'', pea-shaped), is a small knobbly, sesamoid bone that is found in the wrist. It forms the ulnar border of the carpal tunnel.
Structure
The pisiform is a sesamoid bone, ...
; Cc, Central carpal; M, Metacarpal; (A-G, Cc, P are Carpals).
1-5, thumb and digits two to five. R, Radius
In classical geometry, a radius ( : radii) of a circle or sphere is any of the line segments from its center to its perimeter, and in more modern usage, it is also their length. The name comes from the latin ''radius'', meaning ray but also the ...
; U, Ulna
The ulna (''pl''. ulnae or ulnas) is a long bone found in the forearm that stretches from the elbow to the smallest finger, and when in anatomical position, is found on the medial side of the forearm. That is, the ulna is on the same side of t ...
.
From the classic German encyclopedia Meyers Konversations-Lexikon 1888.
 Frog four limbs and human foot compared.
Frog four limbs and human foot compared.
See also
* Tetrapod limbsReferences
Skeletal system {{Anatomy-stub