Care Management Organization on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Health care or healthcare is the improvement of health via the prevention, diagnosis, treatment,
Health care or healthcare is the improvement of health via the prevention, diagnosis, treatment,
 The delivery of modern health care depends on groups of trained professionals and paraprofessionals coming together as
The delivery of modern health care depends on groups of trained professionals and paraprofessionals coming together as
''Employment and Training Administration: Health care''
. Retrieved June 24, 2011. This includes professionals in medicine, psychology,
''No Cookie-Cutter Response: Conceptualizing Primary Health Care.''
Retrieved 26 August 2014. Health care can be defined as either public or private.
 Secondary care includes acute care: necessary treatment for a short period of time for a brief but serious illness, injury, or other health condition. This care is often found in a
Secondary care includes acute care: necessary treatment for a short period of time for a brief but serious illness, injury, or other health condition. This care is often found in a
 Tertiary care is specialized consultative health care, usually for inpatients and on referral from a primary or secondary health professional, in a facility that has personnel and facilities for advanced medical investigation and treatment, such as a tertiary referral hospital.
Examples of tertiary care services are cancer management, neurosurgery, cardiac surgery, plastic surgery, treatment for severe burns, advanced
Tertiary care is specialized consultative health care, usually for inpatients and on referral from a primary or secondary health professional, in a facility that has personnel and facilities for advanced medical investigation and treatment, such as a tertiary referral hospital.
Examples of tertiary care services are cancer management, neurosurgery, cardiac surgery, plastic surgery, treatment for severe burns, advanced
School of Medicine.
Accessed 27 June 2011.
 Health care or healthcare is the improvement of health via the prevention, diagnosis, treatment,
Health care or healthcare is the improvement of health via the prevention, diagnosis, treatment, amelioration
Amelioration may refer to:
* Amelioration patterns, a software design pattern
* Amelioration Act 1798, a statute in the Leeward Islands regarding the treatment of slaves
* Rapid climatic amelioration, in geology, a major change from glacial to i ...
or cure
A cure is a substance or procedure that ends a medical condition, such as a medication, a surgical operation, a change in lifestyle or even a philosophical mindset that helps end a person's sufferings; or the state of being healed, or cured. The ...
of disease, illness, injury
An injury is any physiological damage to living tissue caused by immediate physical stress. An injury can occur intentionally or unintentionally and may be caused by blunt trauma, penetrating trauma, burning, toxic exposure, asphyxiation, o ...
, and other physical and mental impairments in people. Health care is delivered by health professional
A health professional, healthcare professional, or healthcare worker (sometimes abbreviated HCW) is a provider of health care treatment and advice based on formal training and experience. The field includes those who work as a nurse, physician (suc ...
s and allied health fields. Medicine, dentistry
Dentistry, also known as dental medicine and oral medicine, is the branch of medicine focused on the teeth, gums, and mouth. It consists of the study, diagnosis, prevention, management, and treatment of diseases, disorders, and conditions o ...
, pharmacy
Pharmacy is the science and practice of discovering, producing, preparing, dispensing, reviewing and monitoring medications, aiming to ensure the safe, effective, and affordable use of medicines. It is a miscellaneous science as it links heal ...
, midwifery, nursing, optometry
Optometry is a specialized health care profession that involves examining the eyes and related structures for defects or abnormalities. Optometrists are health care professionals who typically provide comprehensive primary eye care.
In the Uni ...
, audiology, psychology, occupational therapy
Occupational therapy (OT) is a global healthcare profession. It involves the use of assessment and intervention to develop, recover, or maintain the meaningful activities, or ''occupations'', of individuals, groups, or communities. The field of ...
, physical therapy
Physical therapy (PT), also known as physiotherapy, is one of the allied health professions. It is provided by physical therapists who promote, maintain, or restore health through physical examination, diagnosis, management, prognosis, patient ...
, athletic training
Athletic training is an allied health care profession recognized by the American Medical Association (AMA)"What is an Athletic Trainer?". The Board of Certification Website. 2003.
Athletic training is also recognized by the Health Resources Serv ...
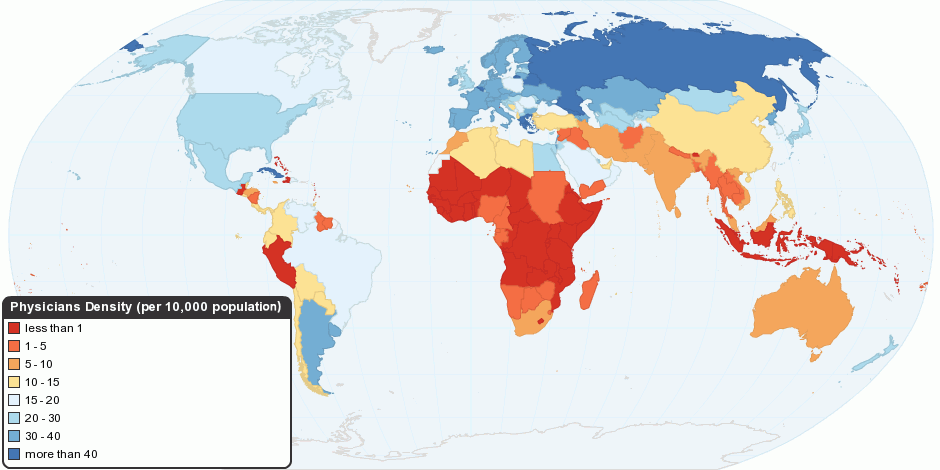
, and other health professions all constitute health care. It includes work done in providing primary care, secondary care, and tertiary care, as well as in public health.
Access to health care may vary across countries, communities, and individuals, influenced by social and economic conditions as well as health policies. Providing health care services means "the timely use of personal health services to achieve the best possible health outcomes". Factors to consider in terms of health care access include financial limitations (such as insurance coverage), geographical and logistical barriers (such as additional transportation costs and the possibility to take paid time off work to use such services), sociocultural
Sociocultural evolution, sociocultural evolutionism or social evolution are theories of sociobiology and cultural evolution that describe how societies and culture change over time. Whereas sociocultural development traces processes that tend t ...
expectations, and personal limitations (lack of ability to communicate with health care providers, poor health literacy
Health literacy is the ability to obtain, read, understand, and use healthcare information in order to make appropriate health decisions and follow instructions for treatment. There are multiple definitions of health literacy, in part, because heal ...
, low income). Limitations to health care services affects negatively the use of medical services, the efficacy of treatments, and overall outcome (well-being, mortality rates).
Health system
Health, according to the World Health Organization, is "a state of complete physical, mental and social well-being and not merely the absence of disease and infirmity".World Health Organization. (2006)''Constitution of the World Health Organiza ...
s are organizations established to meet the health needs of targeted populations. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), a well-functioning health care system requires a financing mechanism, a well-trained and adequately paid workforce, reliable information on which to base decisions and policies
Policy is a deliberate system of guidelines to guide decisions and achieve rational outcomes. A policy is a statement of intent and is implemented as a procedure or protocol. Policies are generally adopted by a governance body within an organ ...
, and well-maintained health facilities to deliver quality medicines and technologies.
An efficient health care system can contribute to a significant part of a country's economy, development, and industrialization
Industrialisation ( alternatively spelled industrialization) is the period of social and economic change that transforms a human group from an agrarian society into an industrial society. This involves an extensive re-organisation of an econo ...
. Health care is conventionally regarded as an important determinant in promoting the general physical
Physical may refer to:
*Physical examination
In a physical examination, medical examination, or clinical examination, a medical practitioner examines a patient for any possible medical signs or symptoms of a medical condition. It generally co ...
and mental health and well-being of people around the world. An example of this was the worldwide eradication of smallpox in 1980, declared by the WHO as the first disease in human history to be eliminated by deliberate health care interventions.
Delivery
 The delivery of modern health care depends on groups of trained professionals and paraprofessionals coming together as
The delivery of modern health care depends on groups of trained professionals and paraprofessionals coming together as interdisciplinary team
Interdisciplinarity or interdisciplinary studies involves the combination of multiple academic disciplines into one activity (e.g., a research project). It draws knowledge from several other fields like sociology, anthropology, psychology, ec ...
s.United States Department of Labor''Employment and Training Administration: Health care''
. Retrieved June 24, 2011. This includes professionals in medicine, psychology,
physiotherapy
Physical therapy (PT), also known as physiotherapy, is one of the allied health professions. It is provided by physical therapists who promote, maintain, or restore health through physical examination, diagnosis, management, prognosis, patient ...
, nursing, dentistry
Dentistry, also known as dental medicine and oral medicine, is the branch of medicine focused on the teeth, gums, and mouth. It consists of the study, diagnosis, prevention, management, and treatment of diseases, disorders, and conditions o ...
, midwifery and allied health, along with many others such as public health practitioners, community health workers and assistive personnel, who systematically provide personal and population-based preventive, curative and rehabilitative care services.
While the definitions of the various types of health care vary depending on the different cultural, political, organizational, and disciplinary perspectives, there appears to be some consensus that primary care constitutes the first element of a continuing health care process and may also include the provision of secondary and tertiary levels of care.Thomas-MacLean R et al''No Cookie-Cutter Response: Conceptualizing Primary Health Care.''
Retrieved 26 August 2014. Health care can be defined as either public or private.
Primary care
Primary care refers to the work ofhealth professionals
A health professional, healthcare professional, or healthcare worker (sometimes abbreviated HCW) is a provider of health care treatment and advice based on formal training and experience. The field includes those who work as a nurse, physician (suc ...
who act as a first point of consultation for all patients within the health care system
Health, according to the World Health Organization, is "a state of complete physical, Mental health, mental and social well-being and not merely the absence of disease and infirmity".World Health Organization. (2006)''Constitution of the World H ...
. Such a professional would usually be a primary care physician, such as a general practitioner or family physician. Another professional would be a licensed independent practitioner such as a physiotherapist, or a non-physician primary care provider such as a physician assistant
A physician assistant or physician associate (PA) is a type of Mid-level practitioner, mid-level health care provider. In North America PAs may diagnose illnesses, develop and manage treatment plans, prescribe medications, and may serve as a pri ...
or nurse practitioner. Depending on the locality, health system organization the patient may see another health care professional first, such as a pharmacist
A pharmacist, also known as a chemist (Commonwealth English) or a druggist (North American and, archaically, Commonwealth English), is a healthcare professional who prepares, controls and distributes medicines and provides advice and instructi ...
or nurse. Depending on the nature of the health condition, patients may be referred for secondary or tertiary care.
Primary care is often used as the term for the health care services that play a role in the local community. It can be provided in different settings, such as Urgent care centers that provide same-day appointments or services on a walk-in basis.
Primary care involves the widest scope of health care, including all ages of patients, patients of all socioeconomic and geographic origins, patients seeking to maintain optimal health, and patients with all types of acute and chronic physical, mental
Mental may refer to:
* of or relating to the mind
Films
* ''Mental'' (2012 film), an Australian comedy-drama
* ''Mental'' (2016 film), a Bangladeshi romantic-action movie
* ''Mental'', a 2008 documentary by Kazuhiro Soda
* ''Mental'', a 2014 O ...
and social health issues, including multiple chronic diseases. Consequently, a primary care practitioner must possess a wide breadth of knowledge in many areas. Continuity is a key characteristic of primary care, as patients usually prefer to consult the same practitioner for routine check-ups and preventive care, health education, and every time they require an initial consultation about a new health problem. The International Classification of Primary Care (ICPC) is a standardized tool for understanding and analyzing information on interventions in primary care based on the reason for the patient's visit.
Common chronic illnesses usually treated in primary care may include, for example, hypertension
Hypertension (HTN or HT), also known as high blood pressure (HBP), is a long-term medical condition in which the blood pressure in the arteries is persistently elevated. High blood pressure usually does not cause symptoms. Long-term high bl ...
, diabetes, asthma, COPD, depression and anxiety, back pain, arthritis
Arthritis is a term often used to mean any disorder that affects joints. Symptoms generally include joint pain and stiffness. Other symptoms may include redness, warmth, swelling, and decreased range of motion of the affected joints. In som ...
or thyroid dysfunction. Primary care also includes many basic maternal and child health care services, such as family planning
Family planning is the consideration of the number of children a person wishes to have, including the choice to have no children, and the age at which they wish to have them. Things that may play a role on family planning decisions include marita ...
services and vaccinations. In the United States, the 2013 National Health Interview Survey found that skin disorders (42.7%), osteoarthritis and joint disorders (33.6%), back problems (23.9%), disorders of lipid metabolism (22.4%), and upper respiratory tract disease (22.1%, excluding asthma) were the most common reasons for accessing a physician.
In the United States, primary care physicians have begun to deliver primary care outside of the managed care (insurance-billing) system through direct primary care which is a subset of the more familiar concierge medicine
Concierge medicine, also known as retainer medicine, is a relationship between a patient and a primary care physician in which the patient pays an annual fee or retainer. This may or may not be in addition to other charges. In exchange for the reta ...
. Physicians in this model bill patients directly for services, either on a pre-paid monthly, quarterly, or annual basis, or bill for each service in the office. Examples of direct primary care practices include Foundation Health
Health Net, LLC, a subsidiary of Centene Corporation, is an American health care insurance provider. Health Net and its subsidiaries provide health plans for individuals, families, businesses and people with Medicare and Medicaid, as well as com ...
in Colorado and Qliance Qliance Medical Group was a direct primary care healthcare business based in Seattle
Seattle ( ) is a seaport city on the West Coast of the United States. It is the seat of King County, Washington. With a 2020 population of 737,015, it ...
in Washington.
In the context of global population aging, with increasing numbers of older adults at greater risk of chronic non-communicable diseases, rapidly increasing demand for primary care services is expected in both developed and developing countries. The World Health Organization attributes the provision of essential primary care as an integral component of an inclusive primary health care strategy.
Secondary care
 Secondary care includes acute care: necessary treatment for a short period of time for a brief but serious illness, injury, or other health condition. This care is often found in a
Secondary care includes acute care: necessary treatment for a short period of time for a brief but serious illness, injury, or other health condition. This care is often found in a hospital
A hospital is a health care institution providing patient treatment with specialized health science and auxiliary healthcare staff and medical equipment. The best-known type of hospital is the general hospital, which typically has an emerge ...
emergency department
An emergency department (ED), also known as an accident and emergency department (A&E), emergency room (ER), emergency ward (EW) or casualty department, is a medical treatment facility specializing in emergency medicine, the acute care of pati ...
. Secondary care also includes skilled attendance during childbirth, intensive care, and medical imaging
Medical imaging is the technique and process of imaging the interior of a body for clinical analysis and medical intervention, as well as visual representation of the function of some organs or tissues (physiology). Medical imaging seeks to rev ...
services.
The term "secondary care" is sometimes used synonymously with "hospital care". However, many secondary care providers, such as psychiatrists, clinical psychologists, occupational therapists, most dental specialties In the United States and Canada, there are twelve recognized dental specialties in which some dentists choose to train and practice, in addition to or instead of general dentistry. In the United Kingdom and Australia, there are thirteen.
To become ...
or physiotherapists, do not necessarily work in hospitals. Some primary care services are delivered within hospitals. Depending on the organization and policies of the national health system, patients may be required to see a primary care provider for a referral before they can access secondary care.
In countries that operate under a mixed market
A mixed economy is variously defined as an economic system blending elements of a market economy with elements of a planned economy, markets with state interventionism, or private enterprise with public enterprise. Common to all mixed econ ...
health care system, some physicians limit their practice to secondary care by requiring patients to see a primary care provider first. This restriction may be imposed under the terms of the payment agreements in private or group health insurance
Health insurance or medical insurance (also known as medical aid in South Africa) is a type of insurance that covers the whole or a part of the risk of a person incurring medical expenses. As with other types of insurance, risk is shared among ma ...
plans. In other cases, medical specialists
A medical specialty is a branch of medical practice that is focused on a defined group of patients, diseases, skills, or philosophy. Examples include those branches of medicine that deal exclusively with children ( paediatrics), cancer (oncology), ...
may see patients without a referral, and patients may decide whether self-referral is preferred.
In other countries patient self-referral to a medical specialist for secondary care is rare as prior referral from another physician (either a primary care physician or another specialist) is considered necessary, regardless of whether the funding is from private insurance schemes or national health insurance
National health insurance (NHI), sometimes called statutory health insurance (SHI), is a system of health insurance that insures a national population against the costs of health care. It may be administered by the public sector, the private sector ...
.
Allied health professionals, such as physical therapists
Physical therapy (PT), also known as physiotherapy, is one of the allied health professions. It is provided by physical therapists who promote, maintain, or restore health through physical examination, diagnosis, management, prognosis, patient ...
, respiratory therapists, occupational therapists, speech therapists, and dietitians, also generally work in secondary care, accessed through either patient self-referral or through physician referral.
Tertiary care
 Tertiary care is specialized consultative health care, usually for inpatients and on referral from a primary or secondary health professional, in a facility that has personnel and facilities for advanced medical investigation and treatment, such as a tertiary referral hospital.
Examples of tertiary care services are cancer management, neurosurgery, cardiac surgery, plastic surgery, treatment for severe burns, advanced
Tertiary care is specialized consultative health care, usually for inpatients and on referral from a primary or secondary health professional, in a facility that has personnel and facilities for advanced medical investigation and treatment, such as a tertiary referral hospital.
Examples of tertiary care services are cancer management, neurosurgery, cardiac surgery, plastic surgery, treatment for severe burns, advanced neonatology
Neonatology is a subspecialty of pediatrics that consists of the medical care of newborn infants, especially the ill or premature newborn. It is a hospital-based specialty, and is usually practised in neonatal intensive care units (NICUs). The ...
services, palliative, and other complex medical and surgical interventions.Emory UniversitySchool of Medicine.
Accessed 27 June 2011.
Quaternary care
The term quaternary care is sometimes used as an extension of tertiary care in reference to advanced levels of medicine which are highly specialized and not widely accessed.Experimental medicine
An experimental drug is a medicinal product (a drug or vaccine) that has not yet received approval from governmental regulatory authorities for routine use in human or veterinary medicine. A medicinal product may be approved for use in one disea ...
and some types of uncommon diagnostic or surgical procedures are considered quaternary care. These services are usually only offered in a limited number of regional or national health care centers.
Home and community care
Many types of health care interventions are delivered outside of health facilities. They include many interventions of public health interest, such asfood safety
Food safety (or food hygiene) is used as a scientific method/discipline describing handling, preparation, and storage of food in ways that prevent food-borne illness. The occurrence of two or more cases of a similar illness resulting from t ...
surveillance, distribution of condom
A condom is a sheath-shaped barrier device used during sexual intercourse to reduce the probability of pregnancy or a sexually transmitted infection (STI). There are both male and female condoms. With proper use—and use at every act of in ...
s and needle-exchange programs for the prevention of transmissible diseases.
They also include the services of professionals in residential and community settings in support of self-care, home care Homecare (also spelled as home care) is health care or supportive care provided by a professional caregiver in the individual home where the patient or client is living, as opposed to care provided in group accommodations like clinics or nursing ho ...
, long-term care, assisted living, treatment for substance use disorder
Substance use disorder (SUD) is the persistent use of drugs (including alcohol) despite substantial harm and adverse consequences as a result of their use. Substance use disorders are characterized by an array of mental/emotional, physical, and ...
s among other types of health and social care services.
Community rehabilitation
Rehabilitation or Rehab may refer to:
Health
* Rehabilitation (neuropsychology), therapy to regain or improve neurocognitive function that has been lost or diminished
* Rehabilitation (wildlife), treatment of injured wildlife so they can be retur ...
services can assist with mobility and independence after the loss of limbs or loss of function. This can include prostheses, orthotics, or wheelchairs.
Many countries, especially in the west, are dealing with aging populations, so one of the priorities of the health care system is to help seniors live full, independent lives in the comfort of their own homes. There is an entire section of health care geared to providing seniors with help in day-to-day activities at home such as transportation to and from doctor's appointments along with many other activities that are essential for their health and well-being. Although they provide home care for older adults in cooperation, family members and care workers may harbor diverging attitudes and values towards their joint efforts. This state of affairs presents a challenge for the design of ICT (information and communication technology) for home care.
Because statistics show that over 80 million Americans have taken time off of their primary employment to care for a loved one, many countries have begun offering programs such as the Consumer Directed Personal Assistant Program to allow family members to take care of their loved ones without giving up their entire income.
With obesity in children rapidly becoming a major concern, health services often set up programs in schools aimed at educating children about nutritional eating habits, making physical education a requirement and teaching young adolescents to have a positive self-image.
Ratings
Health care ratings
Health care ratings are ratings or evaluations of health care. In the United States they have been an increasingly used tool to try to drive accountability among health care providers and in the context of classic supply/demand view of Health econo ...
are ratings or evaluations of health care used to evaluate the process of care and health care structures and/or outcomes of health care services. This information is translated into report cards that are generated by quality organizations, nonprofit, consumer groups and media. This evaluation of quality is based on measures of:
* hospital quality
* health plan quality
* physician quality
* quality for other health professionals
* of patient experience
Related sectors
Health care extends beyond the delivery of services to patients, encompassing many related sectors, and is set within a bigger picture of financing and governance structures.Health system
A health system, also sometimes referred to as health care system or healthcare system, is the organization of people, institutions, and resources that deliver health care services to populations in need.Healthcare industry
Thehealthcare industry
The healthcare industry (also called the medical industry or health economy) is an aggregation and integration of sectors within the economic system that provides goods and services to treat patients with curative, preventive, rehabilitative, a ...
incorporates several sectors that are dedicated to providing health care services and products. As a basic framework for defining the sector, the United Nations' International Standard Industrial Classification categorizes health care as generally consisting of hospital activities, medical and dental practice activities, and "other human health activities." The last class involves activities of, or under the supervision of, nurses, midwives, physiotherapists, scientific or diagnostic laboratories, pathology clinics, residential health facilities, patient advocates or other allied health professions
Allied health professions are health care professions distinct from optometry, dentistry, nursing, medicine, and pharmacy. They provide a range of diagnostic, technical, therapeutic, and support services in connection with health care.
Definitio ...
.
In addition, according to industry and market classifications, such as the Global Industry Classification Standard and the Industry Classification Benchmark, health care includes many categories of medical equipment, instruments and services including biotechnology, diagnostic laboratories and substances, drug manufacturing and delivery.
For example, pharmaceuticals and other medical devices are the leading high technology exports of Europe and the United States. The United States dominates the biopharmaceutical field, accounting for three-quarters of the world's biotechnology revenues.
Health care research
The quantity and quality of many health care interventions are improved through the results of science, such as advanced through the medical model of health which focuses on the eradication of illness through diagnosis and effective treatment. Many important advances have been made through health research,biomedical research
Medical research (or biomedical research), also known as experimental medicine, encompasses a wide array of research, extending from "basic research" (also called ''bench science'' or ''bench research''), – involving fundamental scientif ...
and pharmaceutical research
Pharmacy is the science and practice of discovering, producing, preparing, dispensing, reviewing and monitoring medications, aiming to ensure the safe, effective, and affordable use of medicines. It is a miscellaneous science as it links heal ...
, which form the basis for evidence-based medicine
Evidence-based medicine (EBM) is "the conscientious, explicit and judicious use of current best evidence in making decisions about the care of individual patients". The aim of EBM is to integrate the experience of the clinician, the values of t ...
and evidence-based practice in health care delivery. Health care research frequently engages directly with patients, and as such issues for whom to engage and how to engage with them become important to consider when seeking to actively include them in studies. While single best practice does not exist, the results of a systematic review on patient engagement suggest that research methods for patient selection need to account for both patient availability and willingness to engage.
Health services research can lead to greater efficiency and equitable delivery of health care interventions, as advanced through the social model of health and disability, which emphasizes the societal changes that can be made to make populations healthier. Results from health services research often form the basis of evidence-based policy
Evidence-based policy is an idea in public policy proposing that policy decisions should be based on, or informed by, rigorously established objective evidence. The implied contrast is with policymaking based on ideology, 'common sense,' anecd ...
in health care systems. Health services research is also aided by initiatives in the field of artificial intelligence for the development of systems of health assessment that are clinically useful, timely, sensitive to change, culturally sensitive, low-burden, low-cost, built into standard procedures, and involve the patient.
Health care financing
There are generally five primary methods of fundinghealth care systems
Health, according to the World Health Organization, is "a state of complete physical, mental and social well-being and not merely the absence of disease and infirmity".World Health Organization. (2006)''Constitution of the World Health Organiza ...
:
# General taxation to the state, county or municipality
# Social health insurance
# Voluntary or private health insurance
Health insurance or medical insurance (also known as medical aid in South Africa) is a type of insurance that covers the whole or a part of the risk of a person incurring medical expenses. As with other types of insurance, risk is shared among ma ...
# Out-of-pocket payments
# Donations to health charities
A charitable organization or charity is an organization whose primary objectives are philanthropy and social well-being (e.g. educational, religious or other activities serving the public interest or common good).
The legal definition of a cha ...
In most countries, there is a mix of all five models, but this varies across countries and over time within countries. Aside from financing mechanisms, an important question should always be how much to spend on health care. For the purposes of comparison, this is often expressed as the percentage of GDP spent on health care. In OECD countries for every extra $1000 spent on health care, life expectancy falls by 0.4 years. A similar correlation is seen from the analysis carried out each year by Bloomberg. Clearly this kind of analysis is flawed in that life expectancy is only one measure of a health system's performance, but equally, the notion that more funding is better is not supported.
In 2011, the health care industry
The healthcare industry (also called the medical industry or health economy) is an aggregation and integration of sectors within the economic system that provides goods and services to treat patients with curative, preventive, rehabilitative, a ...
consumed an average of 9.3 percent of the GDP or US$
The United States dollar (symbol: $; code: USD; also abbreviated US$ or U.S. Dollar, to distinguish it from other dollar-denominated currencies; referred to as the dollar, U.S. dollar, American dollar, or colloquially buck) is the official ...
3,322 ( PPP-adjusted) per capita across the 34 members of OECD countries. The US (17.7%, or US$ PPP 8,508), the Netherlands (11.9%, 5,099), France (11.6%, 4,118), Germany (11.3%, 4,495), Canada (11.2%, 5669), and Switzerland
). Swiss law does not designate a ''capital'' as such, but the federal parliament and government are installed in Bern, while other federal institutions, such as the federal courts, are in other cities (Bellinzona, Lausanne, Luzern, Neuchâtel ...
(11%, 5,634) were the top spenders, however life expectancy in total population at birth was highest in Switzerland (82.8 years), Japan
Japan ( ja, 日本, or , and formally , ''Nihonkoku'') is an island country in East Asia. It is situated in the northwest Pacific Ocean, and is bordered on the west by the Sea of Japan, while extending from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north ...
and Italy (82.7), Spain and Iceland (82.4), France (82.2) and Australia
Australia, officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a Sovereign state, sovereign country comprising the mainland of the Australia (continent), Australian continent, the island of Tasmania, and numerous List of islands of Australia, sma ...
(82.0), while OECD's average exceeds 80 years for the first time ever in 2011: 80.1 years, a gain of 10 years since 1970. The US (78.7 years) ranges only on place 26 among the 34 OECD member countries, but has the highest costs by far. All OECD countries have achieved universal (or almost universal) health coverage, except the US and Mexico. (see also international comparisons.)
In the United States, where around 18% of GDP is spent on health care, the Commonwealth Fund analysis of spend and quality shows a clear correlation between worse quality and higher spending.
Administration and regulation
The management and administration of health care is vital to the delivery of health care services. In particular, the practice of health professionals and the operation of health care institutions is typically regulated by national or state/provincial authorities through appropriate regulatory bodies for purposes ofquality assurance
Quality assurance (QA) is the term used in both manufacturing and service industries to describe the systematic efforts taken to ensure that the product(s) delivered to customer(s) meet with the contractual and other agreed upon performance, design ...
. Most countries have credentialing staff in regulatory boards or health department
A health department or health ministry is a part of government which focuses on issues related to the general health of the citizenry. Subnational entities, such as states, counties and cities, often also operate a health department of their ow ...
s who document the certification or licensing of health workers and their work history.
Health information technology
Health information technology (HIT) is "the application of information processing involving both computer hardware and software that deals with the storage, retrieval, sharing, and use of health care information, data, and knowledge for communication and decision making." Health information technology components: *Electronic Health Record
An electronic health record (EHR) is the systematized collection of patient and population electronically stored health information in a digital format. These records can be shared across different health care settings. Records are shared throu ...
(EHR) - An EHR contains a patient's comprehensive medical history, and may include records from multiple providers.
* Electronic Medical Record (EMR) - An EMR contains the standard medical and clinical data gathered in one's provider's office.
* Personal Health Record (PHR) - A PHR is a patient's medical history that is maintained privately, for personal use.
* Medical Practice Management software (MPM) - is designed to streamline the day-to-day tasks of operating a medical facility. Also known as practice management software or practice management system (PMS).
* Health Information Exchange (HIE) - Health Information Exchange allows health care professionals and patients to appropriately access and securely share a patient's vital medical information electronically.
See also
* :Health care by country * Healthcare system /Health professionals
A health professional, healthcare professional, or healthcare worker (sometimes abbreviated HCW) is a provider of health care treatment and advice based on formal training and experience. The field includes those who work as a nurse, physician (suc ...
* Health equity
* Health policy
Health policy can be defined as the "decisions, plans, and actions that are undertaken to achieve specific healthcare goals within a society".World Health Organization''Health Policy'' accessed 22 March 2011(Web archive)/ref> According to the ...
* Tobacco control laws
* Universal health care
By country:
References
External links
* * {{DEFAULTSORT:Health Care Primary care Public services *