Carbonyl Allylation on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
In 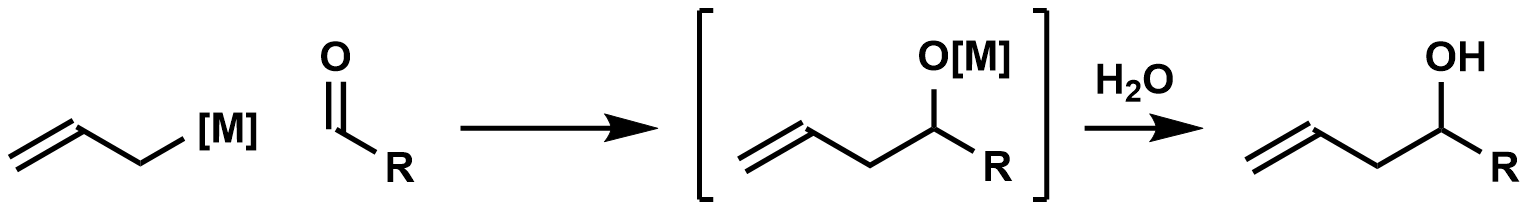
 As illustrated by the Keck allylation, catalytic enantioselective additions of achiral allylmetal reagents to carbonyl compounds also are possible by
As illustrated by the Keck allylation, catalytic enantioselective additions of achiral allylmetal reagents to carbonyl compounds also are possible by 

organic chemistry
Organic chemistry is a subdiscipline within chemistry involving the scientific study of the structure, properties, and reactions of organic compounds and organic materials, i.e., matter in its various forms that contain carbon atoms.Clayden, ...
, carbonyl allylation describes methods for adding an allyl anion to an aldehyde or ketone to produce a homoallylic alcohol. The carbonyl allylation was first reported in 1876 by Alexander Zaitsev Alexander Zaytsev may refer to:
*Alexander Zaytsev (artist), Alexander Dmitryevich Zaytsev (1903–1982), Russian painter and art educator
*Alexander Zaytsev (pilot), Alexander Andreyevich Zaytsev (1911–1965), Soviet aircraft pilot and Hero of the ...
and employed an allylzinc reagent.

Enantioselective versions
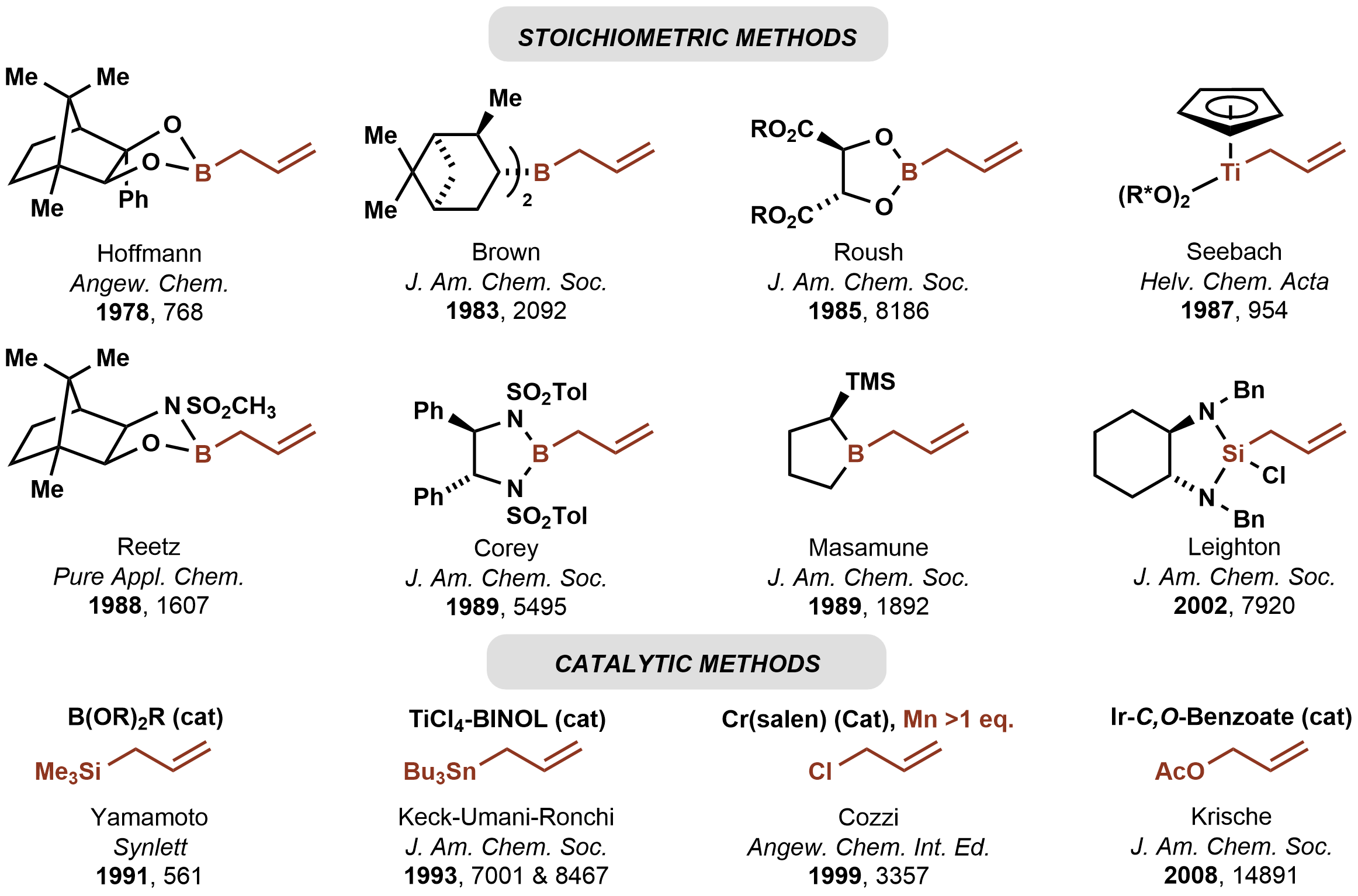
In 1978, Hoffmann reported the first asymmetric carbonyl allylation using achiral
Chirality is a property of asymmetry important in several branches of science. The word ''chirality'' is derived from the Greek (''kheir''), "hand", a familiar chiral object.
An object or a system is ''chiral'' if it is distinguishable from i ...
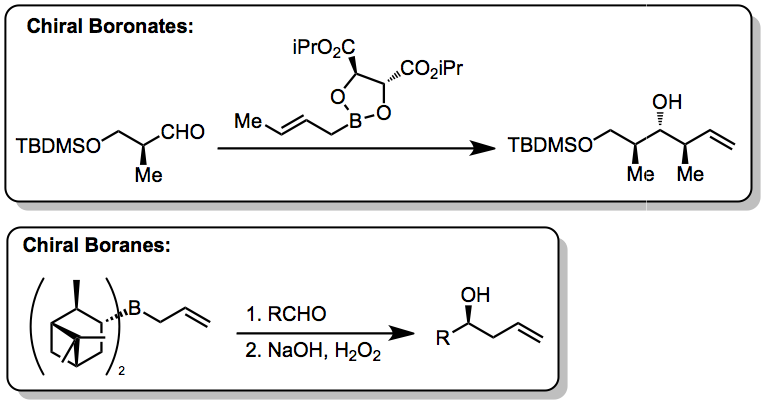
allylmetal reagent, an allylborane derived from camphor. Such methods utilize preformed allyl metal reagents. The approach is well developed using allyl boranesDenmark, S. E.; Almstead, N. G. In ''Modern Carbonyl Chemistry''; Otera, J., Ed.; Wiley-VCH: Weinheim, 2000; Chapter 10.
''(13)'' As illustrated by the Keck allylation, catalytic enantioselective additions of achiral allylmetal reagents to carbonyl compounds also are possible by
As illustrated by the Keck allylation, catalytic enantioselective additions of achiral allylmetal reagents to carbonyl compounds also are possible by organostannane addition Organostannane addition reactions comprise the nucleophilic addition of an allyl-, allenyl-, or propargylstannane to an aldehyde, imine, or, in rare cases, a ketone. The reaction is widely used for carbonyl allylation.
Organostannane addition to ...
s.
Allylic boronate and -borane reagents have also been developed for enantioselective addition to carbonyls—in this class of reactions, the allylic boron reagent confers stereochemical control
''(13)''
Catalysis
In 1991, Yamamoto disclosed the first catalytic enantioselective method for carbonyl allylation, which employed a chiral boron Lewis acid-catalyst in combination with allyltrimethylsilane. Numerous other catalytic enantioselective methods for carbonyl allylation followed. Catalytic variants of the Nozaki-Hiyama-Kishi reaction represent an alternative method for asymmetric carbonyl allylation, but stoichiometric metallic reductants are required. Whereas the aforementioned asymmetric carbonyl allylations rely on preformed allylmetal reagents, the Krische allylation exploitsallyl acetate
Allyl acetate is an organic compound with formula C3H5OC(O)CH3. This colourless liquid is a precursor to especially allyl alcohol, which is a useful industrial intermediate. It is the acetate ester of allyl alcohol.
Preparation
Allyl acetate i ...
for enantioselective carbonyl allylation. Selected methods for asymmetric carbonyl allylation are summarized below.

Use in total synthesis
Carbonyl allylation has been employed in the synthesis ofpolyketide
Polyketides are a class of natural products derived from a precursor molecule consisting of a chain of alternating ketone (or reduced forms of a ketone) and methylene groups: (-CO-CH2-). First studied in the early 20th century, discovery, biosynth ...
natural products and other oxygenated molecules with a contiguous array of stereocenters. For example, allylstannanation of a threose-derived aldehyde affords the macrolide
The Macrolides are a class of natural products that consist of a large macrocyclic lactone ring to which one or more deoxy sugars, usually cladinose and desosamine, may be attached. The lactone rings are usually 14-, 15-, or 16-membered. Ma ...
antascomicin B, which structurally resembles FK506 and rapamycin
Sirolimus, also known as rapamycin and sold under the brand name Rapamune among others, is a macrolide compound that is used to coat coronary stents, prevent organ transplant rejection, treat a rare lung disease called lymphangioleiomyomatosi ...
, and is a potent binder of FKBP12. The Krische allylation was used to prepare the polyketide (+)-SCH 351448, a macrodiolide ionophore bearing 14 stereogenic centers.

Older primary literature
* * * * * * *References