Canis Rufus on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The red wolf (''Canis rufus'') is a canine native to the
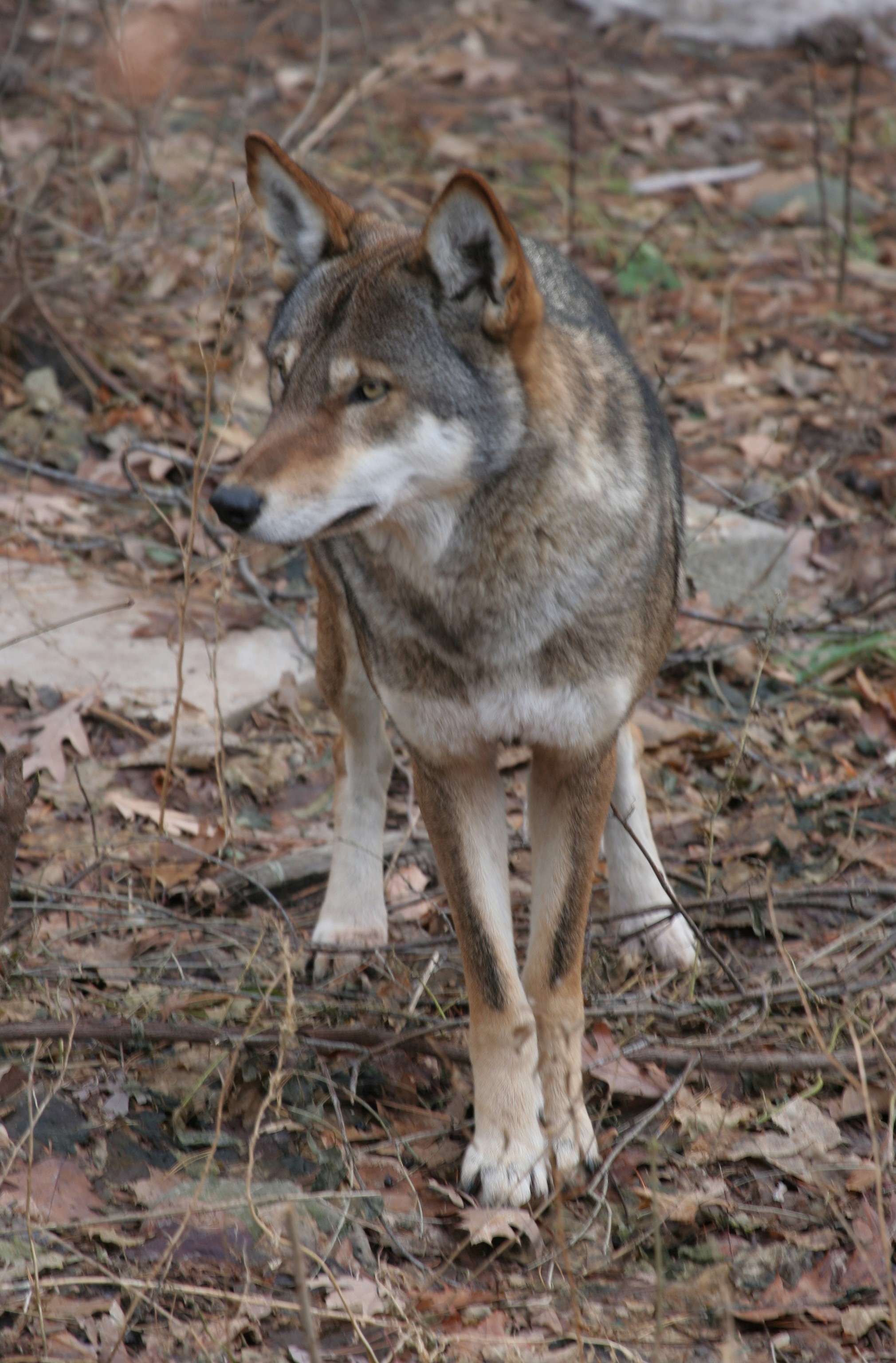 The red wolf's appearance is typical of the genus ''Canis'', and is generally intermediate in size between the coyote and gray wolf, though some specimens may overlap in size with small gray wolves. A study of ''Canis'' morphometrics conducted in eastern North Carolina reported that red wolves are morphometrically distinct from coyotes and hybrids. Adults measure 136–160 cm (53.5–63 in) in length, and weigh 23–39 kg (50-85 lbs). Its pelage is typically more reddish and sparsely furred than the coyote's and gray wolf's, though melanistic individuals do occur. Its fur is generally tawny to grayish in color, with light markings around the lips and eyes.Woodward, D. W. (1980),
The red wolf's appearance is typical of the genus ''Canis'', and is generally intermediate in size between the coyote and gray wolf, though some specimens may overlap in size with small gray wolves. A study of ''Canis'' morphometrics conducted in eastern North Carolina reported that red wolves are morphometrically distinct from coyotes and hybrids. Adults measure 136–160 cm (53.5–63 in) in length, and weigh 23–39 kg (50-85 lbs). Its pelage is typically more reddish and sparsely furred than the coyote's and gray wolf's, though melanistic individuals do occur. Its fur is generally tawny to grayish in color, with light markings around the lips and eyes.Woodward, D. W. (1980),
The Red Wolf
', FWS The red wolf has been compared by some authors to the
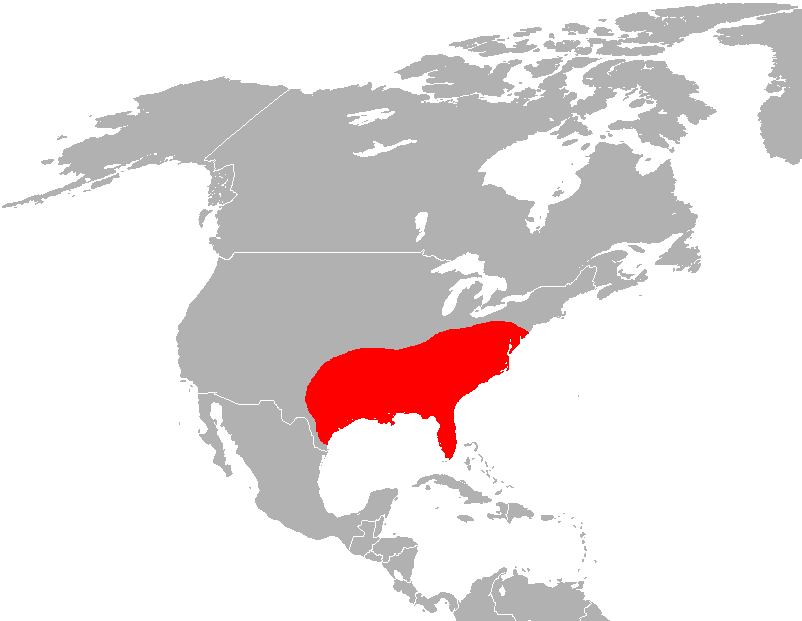 The originally recognized red wolf range extended throughout the
The originally recognized red wolf range extended throughout the
 In 1940 the biologist Stanley P. Young noted that the red wolf was still common in eastern Texas, where more than 800 had been caught in 1939 because of their attacks on livestock. He did not believe that they could be exterminated because of their habit of living concealed in thickets. In 1962 a study of skull morphology of wild ''Canis'' in the states of Arkansas, Louisiana, Oklahoma, and Texas indicated that the red wolf existed in only a few populations due to hybridization with the coyote. The explanation was that either the red wolf could not adapt to changes to its environment due to human land-use along with its accompanying influx of competing coyotes from the west, or that the red wolf was being hybridized out of existence by the coyote.
In 1940 the biologist Stanley P. Young noted that the red wolf was still common in eastern Texas, where more than 800 had been caught in 1939 because of their attacks on livestock. He did not believe that they could be exterminated because of their habit of living concealed in thickets. In 1962 a study of skull morphology of wild ''Canis'' in the states of Arkansas, Louisiana, Oklahoma, and Texas indicated that the red wolf existed in only a few populations due to hybridization with the coyote. The explanation was that either the red wolf could not adapt to changes to its environment due to human land-use along with its accompanying influx of competing coyotes from the west, or that the red wolf was being hybridized out of existence by the coyote.
 After the passage of the
After the passage of the
07-03-23RedWolfAlbanyGAChehaw.jpg, Showing color variation
Red Wolf Portrait - 6189163039.jpg, In winter
Red_Wolf.jpg, Color contrast
Adult Red Wolf.jpg, A red wolf in a breeding program. Fewer than 100 remain in the wild.
Red wolf with radio collar.jpg, With radio collar
The Wolves of North America (1944) Oklahoma Red Wolf.png, A captive red wolf from Oklahoma (1944)
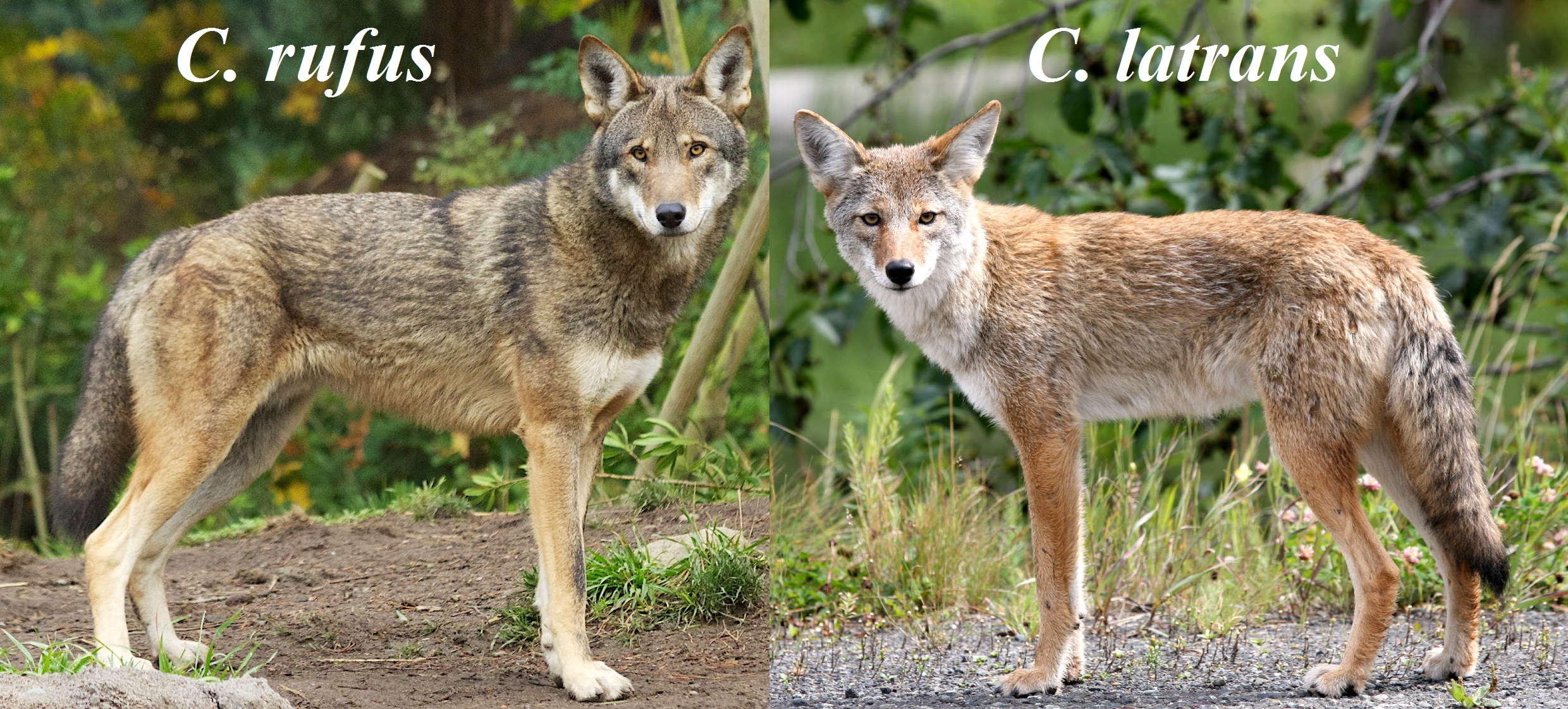 The taxonomic status of the red wolf is debated. It has been described as either a species with a distinct lineage, a recent hybrid of the gray wolf and the coyote, an ancient hybrid of the gray wolf and the coyote which warrants species status, or a distinct species that has undergone recent hybridization with the coyote.
The naturalists
The taxonomic status of the red wolf is debated. It has been described as either a species with a distinct lineage, a recent hybrid of the gray wolf and the coyote, an ancient hybrid of the gray wolf and the coyote which warrants species status, or a distinct species that has undergone recent hybridization with the coyote.
The naturalists
 In 2000, a study looked at red wolves and eastern Canadian wolves. The study agreed that these two wolves readily hybridize with the coyote. The study used eight
In 2000, a study looked at red wolves and eastern Canadian wolves. The study agreed that these two wolves readily hybridize with the coyote. The study used eight
 In July 2016, a whole-genome DNA study proposed, based on the assumptions made, that all of the North American wolves and coyotes diverged from a common ancestor less than 6,000–117,000 years ago. The study also indicated that all North America wolves have a significant amount of coyote ancestry and all coyotes some degree of wolf ancestry, and that the red wolf and Great Lakes region wolf are highly admixed with different proportions of gray wolf and coyote ancestry. One test indicated a wolf/coyote divergence time of 51,000 years before present that matched other studies indicating that the extant wolf came into being around this time. Another test indicated that the red wolf diverged from the coyote between 55,000 and 117,000 years before present and the Great Lakes region wolf 32,000 years before present. Other tests and modelling showed various divergence ranges and the conclusion was a range of less than 6,000 and 117,000 years before present. The study found that coyote ancestry was highest in red wolves from the southeast of the United States and lowest among the Great Lakes region wolves.
The theory proposed was that this pattern matched the south-to-north disappearance of the wolf due to European colonization and its resulting loss of habitat. Bounties led to the extirpation of wolves initially in the southeast, and as the wolf population declined wolf-coyote admixture increased. Later, this process occurred in the Great Lakes region with the influx of coyotes replacing wolves, followed by the expansion of coyotes and their hybrids across the wider region. The red wolf may possess some genomic elements that were unique to gray wolf and coyote lineages from the American South. The proposed timing of the wolf/coyote divergence conflicts with the finding of a coyote-like specimen in strata dated to 1 million years before present, and red wolf fossil specimens dating back 10,000 years ago. The study concluded by stating that because of the extirpation of gray wolves in the American Southeast, "the reintroduced population of red wolves in eastern North Carolina is doomed to genetic swamping by coyotes without the extensive management of hybrids, as is currently practiced by the USFWS."
In September 2016, the USFWS announced a program of changes to the red wolf recovery program and "will begin implementing a series of actions based on the best and latest scientific information". The service will secure the captive population which is regarded as not sustainable, determine new sites for additional experimental wild populations, revise the application of the existing experimental population rule in North Carolina, and complete a comprehensive Species Status Assessment.
In 2017, a group of canid researchers challenged the recent finding that the red wolf and the eastern wolf were the result of recent coyote-wolf hybridization. The group highlight that no testing had been undertaken to ascertain the time period that hybridization had occurred and that, by the previous study's own figures, the hybridization could not have occurred recently but supports a much more ancient hybridization. The group found deficiencies in the previous study's selection of specimens and the findings drawn from the different techniques used. Therefore, the group argues that both the red wolf and the eastern wolf remain genetically distinct North American taxa. This was rebutted by the authors of the earlier study. Another study in late 2018 of wild canids in southwestern
In July 2016, a whole-genome DNA study proposed, based on the assumptions made, that all of the North American wolves and coyotes diverged from a common ancestor less than 6,000–117,000 years ago. The study also indicated that all North America wolves have a significant amount of coyote ancestry and all coyotes some degree of wolf ancestry, and that the red wolf and Great Lakes region wolf are highly admixed with different proportions of gray wolf and coyote ancestry. One test indicated a wolf/coyote divergence time of 51,000 years before present that matched other studies indicating that the extant wolf came into being around this time. Another test indicated that the red wolf diverged from the coyote between 55,000 and 117,000 years before present and the Great Lakes region wolf 32,000 years before present. Other tests and modelling showed various divergence ranges and the conclusion was a range of less than 6,000 and 117,000 years before present. The study found that coyote ancestry was highest in red wolves from the southeast of the United States and lowest among the Great Lakes region wolves.
The theory proposed was that this pattern matched the south-to-north disappearance of the wolf due to European colonization and its resulting loss of habitat. Bounties led to the extirpation of wolves initially in the southeast, and as the wolf population declined wolf-coyote admixture increased. Later, this process occurred in the Great Lakes region with the influx of coyotes replacing wolves, followed by the expansion of coyotes and their hybrids across the wider region. The red wolf may possess some genomic elements that were unique to gray wolf and coyote lineages from the American South. The proposed timing of the wolf/coyote divergence conflicts with the finding of a coyote-like specimen in strata dated to 1 million years before present, and red wolf fossil specimens dating back 10,000 years ago. The study concluded by stating that because of the extirpation of gray wolves in the American Southeast, "the reintroduced population of red wolves in eastern North Carolina is doomed to genetic swamping by coyotes without the extensive management of hybrids, as is currently practiced by the USFWS."
In September 2016, the USFWS announced a program of changes to the red wolf recovery program and "will begin implementing a series of actions based on the best and latest scientific information". The service will secure the captive population which is regarded as not sustainable, determine new sites for additional experimental wild populations, revise the application of the existing experimental population rule in North Carolina, and complete a comprehensive Species Status Assessment.
In 2017, a group of canid researchers challenged the recent finding that the red wolf and the eastern wolf were the result of recent coyote-wolf hybridization. The group highlight that no testing had been undertaken to ascertain the time period that hybridization had occurred and that, by the previous study's own figures, the hybridization could not have occurred recently but supports a much more ancient hybridization. The group found deficiencies in the previous study's selection of specimens and the findings drawn from the different techniques used. Therefore, the group argues that both the red wolf and the eastern wolf remain genetically distinct North American taxa. This was rebutted by the authors of the earlier study. Another study in late 2018 of wild canids in southwestern
Red wolf
U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service * * * * * {{Taxonbar, from=Q200442 Mammals described in 1851 Mammals of the United States Canid hybrids Controversial mammal taxa Wolves Wolves in the United States ESA endangered species Taxa named by John James Audubon Taxa named by John Bachman
southeastern United States
The Southeastern United States, also referred to as the American Southeast or simply the Southeast, is a geographical region of the United States. It is located broadly on the eastern portion of the southern United States and the southern por ...
. Its size is intermediate between the coyote
The coyote (''Canis latrans'') is a species of canis, canine native to North America. It is smaller than its close relative, the wolf, and slightly smaller than the closely related eastern wolf and red wolf. It fills much of the same ecologica ...
(''Canis latrans'') and gray wolf
The wolf (''Canis lupus''; : wolves), also known as the gray wolf or grey wolf, is a large canine native to Eurasia and North America. More than thirty subspecies of ''Canis lupus'' have been recognized, and gray wolves, as popularly ...
(''Canis lupus'').
The red wolf's taxonomic classification as being a separate species, a subspecies of the gray wolf ''Canis lupus rufus'', or a coywolf
Coywolf is an informal term for a canid hybrid descended from coyotes, eastern wolves, gray wolves and dogs. All members of the genus ''Canis'' are closely genetically related with 78 chromosomes and therefore can interbreed. One genetic study ...
(a genetic admixture
Genetic admixture occurs when previously diverged or isolated genetic lineages mix.⅝ Admixture results in the introduction of new genetic lineages into a population.
Examples
Climatic cycles facilitate genetic admixture in cold periods and gene ...
of wolf and coyote) has been contentious for nearly a century. Because of this, it is sometimes excluded from endangered species lists, despite its critically low numbers. Under the Endangered Species Act of 1973
The Endangered Species Act of 1973 (ESA or "The Act"; 16 U.S.C. § 1531 et seq.) is the primary law in the United States for protecting imperiled species. Designed to protect critically imperiled species from extinction as a "consequence of ec ...
, the U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service
The United States Fish and Wildlife Service (USFWS or FWS) is an agency within the United States Department of the Interior dedicated to the management of fish, wildlife, and natural habitats. The mission of the agency is "working with othe ...
currently recognizes the red wolf as an endangered species
An endangered species is a species that is very likely to become extinct in the near future, either worldwide or in a particular political jurisdiction. Endangered species may be at risk due to factors such as habitat loss, poaching and inv ...
and grants protected status. Since 1996, the IUCN
The International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN; officially International Union for Conservation of Nature and Natural Resources) is an international organization working in the field of nature conservation and sustainable use of natu ...
has listed the red wolf as a Critically Endangered species; however, it is not listed in the CITES Appendices of endangered species.
History
Red wolves were originally distributed throughout the southeastern and south-central United States from the Atlantic Ocean to central Texas, southeastern Oklahoma and southwestern Illinois in the west, and in the north from theOhio River Valley
The Ohio River is a long river in the United States. It is located at the boundary of the Midwestern and Southern United States, flowing southwesterly from western Pennsylvania to its mouth on the Mississippi River at the southern tip of Illinoi ...
, northern Pennsylvania
Pennsylvania (; ( Pennsylvania Dutch: )), officially the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania, is a state spanning the Mid-Atlantic, Northeastern, Appalachian, and Great Lakes regions of the United States. It borders Delaware to its southeast, ...
, southern New York
New York most commonly refers to:
* New York City, the most populous city in the United States, located in the state of New York
* New York (state), a state in the northeastern United States
New York may also refer to:
Film and television
* '' ...
, and extreme southern Ontario
Ontario ( ; ) is one of the thirteen provinces and territories of Canada.Ontario is located in the geographic eastern half of Canada, but it has historically and politically been considered to be part of Central Canada. Located in Central Ca ...
in Canada
Canada is a country in North America. Its ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, covering over , making it the world's second-largest country by tot ...
south to the Gulf of Mexico
The Gulf of Mexico ( es, Golfo de México) is an oceanic basin, ocean basin and a marginal sea of the Atlantic Ocean, largely surrounded by the North American continent. It is bounded on the northeast, north and northwest by the Gulf Coast of ...
. The red wolf was nearly driven to extinction by the mid-1900s due to aggressive predator-control programs, habitat destruction, and extensive hybridization with coyotes. By the late 1960s, it occurred in small numbers in the Gulf Coast
The Gulf Coast of the United States, also known as the Gulf South, is the coastline along the Southern United States where they meet the Gulf of Mexico. The coastal states that have a shoreline on the Gulf of Mexico are Texas, Louisiana, Mississ ...
of western Louisiana
Louisiana , group=pronunciation (French: ''La Louisiane'') is a state in the Deep South and South Central regions of the United States. It is the 20th-smallest by area and the 25th most populous of the 50 U.S. states. Louisiana is borde ...
and eastern Texas
Texas (, ; Spanish language, Spanish: ''Texas'', ''Tejas'') is a state in the South Central United States, South Central region of the United States. At 268,596 square miles (695,662 km2), and with more than 29.1 million residents in 2 ...
.
Fourteen of these survivors were selected to be the founders of a captive-bred population, which was established in the Point Defiance Zoo and Aquarium
Point Defiance Zoo & Aquarium (PDZA) is the only combined zoo and aquarium in the Pacific Northwest, located in Tacoma, Washington, US, owned by Metro Parks Tacoma. Situated on in Tacoma's Point Defiance Park, the zoo and aquarium are home to ov ...
between 1974 and 1980. After a successful experimental relocation to Bulls Island off the coast of South Carolina
)''Animis opibusque parati'' ( for, , Latin, Prepared in mind and resources, links=no)
, anthem = " Carolina";" South Carolina On My Mind"
, Former = Province of South Carolina
, seat = Columbia
, LargestCity = Charleston
, LargestMetro = ...
in 1978, the red wolf was declared extinct in the wild
A species that is extinct in the wild (EW) is one that has been categorized by the International Union for Conservation of Nature as known only by living members kept in captivity or as a naturalized population outside its historic range due ...
in 1980 to proceed with restoration efforts. In 1987, the captive animals were released into the Alligator River National Wildlife Refuge
The Alligator River National Wildlife Refuge is a National Wildlife Refuge located in eastern North Carolina along the Atlantic Coast. It was established on March 14, 1984, to preserve and protect a unique wetland habitat type—the pocosin—a ...
on the Albemarle Peninsula in North Carolina
North Carolina () is a state in the Southeastern region of the United States. The state is the 28th largest and 9th-most populous of the United States. It is bordered by Virginia to the north, the Atlantic Ocean to the east, Georgia and So ...
, with a second release, since reversed, taking place two years later in the Great Smoky Mountains National Park
Great Smoky Mountains National Park is an American national park in the southeastern United States, with parts in North Carolina and Tennessee. The park straddles the ridgeline of the Great Smoky Mountains, part of the Blue Ridge Mountains, whi ...
. Of 63 red wolves released from 1987 to 1994, the population rose to as many as 100–120 individuals in 2012, but due to the lack of regulation enforcement by the US Fish and Wildlife Service
The United States Fish and Wildlife Service (USFWS or FWS) is an agency within the United States Department of the Interior dedicated to the management of fish, wildlife, and natural habitats. The mission of the agency is "working with othe ...
, the population has declined to 40 individuals in 2018, about 14 in 2019 and 8 as of October 2021.
Description and behavior
 The red wolf's appearance is typical of the genus ''Canis'', and is generally intermediate in size between the coyote and gray wolf, though some specimens may overlap in size with small gray wolves. A study of ''Canis'' morphometrics conducted in eastern North Carolina reported that red wolves are morphometrically distinct from coyotes and hybrids. Adults measure 136–160 cm (53.5–63 in) in length, and weigh 23–39 kg (50-85 lbs). Its pelage is typically more reddish and sparsely furred than the coyote's and gray wolf's, though melanistic individuals do occur. Its fur is generally tawny to grayish in color, with light markings around the lips and eyes.Woodward, D. W. (1980),
The red wolf's appearance is typical of the genus ''Canis'', and is generally intermediate in size between the coyote and gray wolf, though some specimens may overlap in size with small gray wolves. A study of ''Canis'' morphometrics conducted in eastern North Carolina reported that red wolves are morphometrically distinct from coyotes and hybrids. Adults measure 136–160 cm (53.5–63 in) in length, and weigh 23–39 kg (50-85 lbs). Its pelage is typically more reddish and sparsely furred than the coyote's and gray wolf's, though melanistic individuals do occur. Its fur is generally tawny to grayish in color, with light markings around the lips and eyes.Woodward, D. W. (1980), The Red Wolf
', FWS The red wolf has been compared by some authors to the
greyhound
The English Greyhound, or simply the Greyhound, is a breed of dog, a sighthound which has been bred for coursing, greyhound racing and hunting. Since the rise in large-scale adoption of retired racing Greyhounds, the breed has seen a resurge ...
in general form, owing to its relatively long and slender limbs. The ears are also proportionately larger than the coyote's and gray wolf's. The skull is typically narrow, with a long and slender rostrum
Rostrum may refer to:
* Any kind of a platform for a speaker:
**dais
**pulpit
* Rostrum (anatomy), a beak, or anatomical structure resembling a beak, as in the mouthparts of many sucking insects
* Rostrum (ship), a form of bow on naval ships
* Ros ...
, a small braincase and a well developed sagittal crest
A sagittal crest is a ridge of bone running lengthwise along the midline of the top of the skull (at the sagittal suture) of many mammalian and reptilian skulls, among others. The presence of this ridge of bone indicates that there are exceptiona ...
. Its cerebellum
The cerebellum (Latin for "little brain") is a major feature of the hindbrain of all vertebrates. Although usually smaller than the cerebrum, in some animals such as the mormyrid fishes it may be as large as or even larger. In humans, the cerebel ...
is unlike that of other ''Canis'' species, being closer in form to that of canids of the ''Vulpes
'' Vulpes '' is a genus of the sub-family Caninae. The members of this genus are colloquially referred to as true foxes, meaning they form a proper clade. The word "fox" occurs in the common names of all species of the genus, but also appears ...
'' and ''Urocyon
''Urocyon'' (Greek: "tailed dog") is a genus of Canidae which includes the gray fox (''Urocyon cinereoargenteus'') and the island fox (''Urocyon littoralis''). These two fox species are found in the Western Hemisphere. Whole genome sequencing i ...
'' genera
Genus ( plural genera ) is a taxonomic rank used in the biological classification of living and fossil organisms as well as viruses. In the hierarchy of biological classification, genus comes above species and below family. In binomial nomenclat ...
, thus indicating that the red wolf is one of the more plesiomorphic
In phylogenetics, a plesiomorphy ("near form") and symplesiomorphy are synonyms for an ancestral character shared by all members of a clade, which does not distinguish the clade from other clades.
Plesiomorphy, symplesiomorphy, apomorphy, and ...
members of its genus.
The red wolf is more sociable than the coyote, but less so than the gray wolf. It mates in January–February, with an average of 6-7 pups being born in March, April, and May. It is monogamous, with both parents participating in the rearing of young. Denning sites include hollow tree trunks, along stream banks and the abandoned earths of other animals. By the age of six weeks, the pups distance themselves from the den, and reach full size at the age of one year, becoming sexually mature
Sexual maturity is the capability of an organism to reproduce. In humans it might be considered synonymous with adulthood, but here puberty is the name for the process of biological sexual maturation, while adulthood is based on cultural definitio ...
two years later.
Using long-term data on red wolf individuals of known pedigree, it was found that inbreeding
Inbreeding is the production of offspring from the mating or breeding of individuals or organisms that are closely related genetically. By analogy, the term is used in human reproduction, but more commonly refers to the genetic disorders and o ...
among first-degree relatives was rare. A likely mechanism for avoidance of inbreeding is independent dispersal trajectories from the natal pack. Many of the young wolves spend time alone or in small non-breeding packs composed of unrelated individuals. The union of two unrelated individuals in a new home range is the predominant pattern of breeding pair formation. Inbreeding is avoided because it results in progeny with reduced fitness (inbreeding depression
Inbreeding depression is the reduced biological fitness which has the potential to result from inbreeding (the breeding of related individuals). Biological fitness refers to an organism's ability to survive and perpetuate its genetic material. In ...
) that is predominantly caused by the homozygous
Zygosity (the noun, zygote, is from the Greek "yoked," from "yoke") () is the degree to which both copies of a chromosome or gene have the same genetic sequence. In other words, it is the degree of similarity of the alleles in an organism.
Mo ...
expression of recessive deleterious alleles.
Prior to its extinction in the wild, the red wolf's diet consisted of rabbits, rodents, and nutria
The nutria (''Myocastor coypus''), also known as the coypu, is a large, herbivorous, semiaquatic rodent.
Classified for a long time as the only member of the family Myocastoridae, ''Myocastor'' is now included within Echimyidae, the family of t ...
(an introduced species). In contrast, the red wolves from the restored population rely on white-tailed deer
The white-tailed deer (''Odocoileus virginianus''), also known as the whitetail or Virginia deer, is a medium-sized deer native to North America, Central America, and South America as far south as Peru and Bolivia. It has also been introduced t ...
, raccoon
The raccoon ( or , ''Procyon lotor''), sometimes called the common raccoon to distinguish it from other species, is a mammal native to North America. It is the largest of the procyonid family, having a body length of , and a body weight of ...
, nutria and rabbits. White-tailed deer were largely absent from the last wild refuge of red wolves on the Gulf Coast between Texas and Louisiana (where specimens were trapped from the last wild population for captive breeding), which likely accounts for the discrepancy in their dietary habits listed here. Historical accounts of wolves in the southeast by early explorers such as William Hilton, who sailed along the Cape Fear River in what is now North Carolina in 1644, also note that they ate deer.
Range and habitat
 The originally recognized red wolf range extended throughout the
The originally recognized red wolf range extended throughout the southeastern United States
The Southeastern United States, also referred to as the American Southeast or simply the Southeast, is a geographical region of the United States. It is located broadly on the eastern portion of the southern United States and the southern por ...
from the Atlantic and Gulf Coasts, north to the Ohio River Valley and central Pennsylvania, and west to Central Texas
Central Texas is a region in the U.S. state of Texas surrounding Austin and roughly bordered by San Saba to Bryan and San Marcos to Hillsboro. Central Texas overlaps with and includes part of the Texas Hill Country and corresponds to a ph ...
and southeastern Missouri. Research into paleontological, archaeological and historical specimens of red wolves by Ronald Nowak expanded their known range to include land south of the Saint Lawrence River in Canada, along the eastern seaboard, and west to Missouri and mid-Illinois, terminating in the southern latitudes of Central Texas.
Given their wide historical distribution, red wolves probably used a large suite of habitat types at one time. The last naturally occurring population used coastal prairie marshes, swamps, and agricultural fields used to grow rice and cotton. However, this environment probably does not typify preferred red wolf habitat. Some evidence shows the species was found in highest numbers in the once extensive bottom-land river forests and swamps of the southeastern United States. Red wolves reintroduced into northeastern North Carolina have used habitat types ranging from agricultural lands to forest/wetland mosaics characterized by an overstory of pine and an understory of evergreen shrubs. This suggests that red wolves are habitat generalists and can thrive in most settings where prey populations are adequate and persecution by humans is slight.
Extirpation in the wild
 In 1940 the biologist Stanley P. Young noted that the red wolf was still common in eastern Texas, where more than 800 had been caught in 1939 because of their attacks on livestock. He did not believe that they could be exterminated because of their habit of living concealed in thickets. In 1962 a study of skull morphology of wild ''Canis'' in the states of Arkansas, Louisiana, Oklahoma, and Texas indicated that the red wolf existed in only a few populations due to hybridization with the coyote. The explanation was that either the red wolf could not adapt to changes to its environment due to human land-use along with its accompanying influx of competing coyotes from the west, or that the red wolf was being hybridized out of existence by the coyote.
In 1940 the biologist Stanley P. Young noted that the red wolf was still common in eastern Texas, where more than 800 had been caught in 1939 because of their attacks on livestock. He did not believe that they could be exterminated because of their habit of living concealed in thickets. In 1962 a study of skull morphology of wild ''Canis'' in the states of Arkansas, Louisiana, Oklahoma, and Texas indicated that the red wolf existed in only a few populations due to hybridization with the coyote. The explanation was that either the red wolf could not adapt to changes to its environment due to human land-use along with its accompanying influx of competing coyotes from the west, or that the red wolf was being hybridized out of existence by the coyote.
Reintroduced habitat
Since 1987, red wolves have been released into northeastern North Carolina, where they roam 1.7 million acres. These lands span five counties (Dare, Hyde, Tyrrell, Washington, and Beaufort) and include three national wildlife refuges, a U.S. Air Force bombing range, and private land. The red wolf recovery program is unique for a large carnivore reintroduction in that more than half of the land used for reintroduction lies on private property. Approximately are federal and state lands, and are private lands. Beginning in 1991, red wolves were also released into the Great Smoky Mountains National Park in eastern Tennessee. However, due to exposure to environmental disease (parvovirus), parasites, and competition (with coyotes as well as intraspecific aggression), the red wolf was unable to successfully establish a wild population in the park. Low prey density was also a problem, forcing the wolves to leave the park boundaries in pursuit of food in lower elevations. In 1998, the FWS took away the remaining red wolves in the Great Smoky Mountains National Park, relocating them to Alligator River National Wildlife Refuge in eastern North Carolina. Other red wolves have been released on the coastal islands in Florida, Mississippi, and South Carolina as part of the captive breeding management plan. St. Vincent Island in Florida is currently the only active island propagation site.Captive breeding and reintroduction
 After the passage of the
After the passage of the Endangered Species Act of 1973
The Endangered Species Act of 1973 (ESA or "The Act"; 16 U.S.C. § 1531 et seq.) is the primary law in the United States for protecting imperiled species. Designed to protect critically imperiled species from extinction as a "consequence of ec ...
, formal efforts backed by the U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service began to save the red wolf from extinction, when a captive-breeding program was established at the Point Defiance Zoological Gardens, Tacoma, Washington. Four hundred animals were captured from southwestern Louisiana and southeastern Texas from 1973 to 1980 by the USFWS.
Measurements, vocalization analyses, and skull X-rays were used to distinguish red wolves from coyotes and red wolf × coyote hybrids. Of the 400 canids captured, only 43 were believed to be red wolves and sent to the breeding facility. The first litters were produced in captivity in May 1977. Some of the pups were determined to be hybrids, and they and their parents were removed from the program. Of the original 43 animals, only 17 were considered pure red wolves and since three were unable to breed, 14 became the breeding stock for the captive-breeding program. These 14 were so closely related that they had the genetic effect of being only eight individuals.
In 1996, the red wolf was listed by the International Union for Conservation of Nature
The International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN; officially International Union for Conservation of Nature and Natural Resources) is an international organization working in the field of nature conservation and sustainable use of natu ...
as a critically endangered species.
20th century releases
;1976 release in Cape Romain NWR :In December 1976, two wolves were released ontoCape Romain National Wildlife Refuge
The Cape Romain National Wildlife Refuge is a 66,287 acre (267 km²) National Wildlife Refuge in southeastern South Carolina near Awendaw, South Carolina. The refuge lands and waters encompass water impoundments, creeks and bays, eme ...
's Bulls Island in South Carolina with the intent of testing and honing reintroduction methods. They were not released with the intent of beginning a permanent population on the island. The first experimental translocation lasted for 11 days, during which a mated pair of red wolves was monitored day and night with remote telemetry. A second experimental translocation was tried in 1978 with a different mated pair, and they were allowed to remain on the island for close to nine months. After that, a larger project was executed in 1987 to reintroduce a permanent population of red wolves back to the wild in the Alligator River National Wildlife Refuge
The Alligator River National Wildlife Refuge is a National Wildlife Refuge located in eastern North Carolina along the Atlantic Coast. It was established on March 14, 1984, to preserve and protect a unique wetland habitat type—the pocosin—a ...
(ARNWR) on the eastern coast of North Carolina
North Carolina () is a state in the Southeastern region of the United States. The state is the 28th largest and 9th-most populous of the United States. It is bordered by Virginia to the north, the Atlantic Ocean to the east, Georgia and So ...
. Also in 1987, Bulls Island became the first island breeding site. Pups were raised on the island and relocated to North Carolina until 2005.
;1986 release in Alligator River NWR
:In September 1987, four male-female pairs of red wolves were released in the Alligator River National Wildlife Refuge, in northeastern North Carolina, and designated as an experimental population. Since then, the experimental population has grown and the recovery area expanded to include four national wildlife refuges, a Department of Defense bombing range, state-owned lands, and private lands, encompassing about .
;1989 release on Horn Island, Mississippi
:In 1989, the second island propagation project was initiated with release of a population on Horn Island off the Mississippi coast. This population was removed in 1998 because of a likelihood of encounters with humans. The third island propagation project introduced a population on St. Vincent Island, Florida, offshore between Cape San Blas
Cape San Blas is part of a peninsula in Gulf County, Florida, extending westward from the mainland of Florida, separating St. Joseph Bay to the north from the Gulf of Mexico to the south. It is fifty-nine miles southeast of Panama City. The St. ...
and Apalachicola, Florida
Apalachicola ( ) is a city and the county seat of Franklin County, Florida, United States, on the shore of Apalachicola Bay, an inlet of the Gulf of Mexico. The population was 2,231 at the 2010 census.
History
The Apalachicola people, after ...
, in 1990, and in 1997, the fourth island propagation program introduced a population to Cape St. George Island
Cape St. George Island (also known as Little St. George Island) is an uninhabited barrier island situated on Florida's North Gulf Coast, south-southeast of St. Vincent Island, west of St. George Island and 8–10 miles south-southwest of the t ...
, Florida, south of Apalachicola.
;1991 release in the Great Smoky Mountains
:In 1991, two pairs were reintroduced into the Great Smoky Mountains National Park
Great Smoky Mountains National Park is an American national park in the southeastern United States, with parts in North Carolina and Tennessee. The park straddles the ridgeline of the Great Smoky Mountains, part of the Blue Ridge Mountains, whi ...
, where the last known red wolf was killed in 1905. Despite some early success, the wolves were relocated to eastern North Carolina in 1998, ending the effort to reintroduce the species to the park.
21st century status
Over 30 facilities participate in the red wolfSpecies Survival Plan
The American Species Survival Plan or SSP program was developed in 1981 by the (American) Association of Zoos and Aquariums to help ensure the survival of selected species in zoos and aquariums, most of which are threatened or endangered in the wi ...
and oversee the breeding and reintroduction of over 150 wolves.
In 2007, the USFWS estimated that 300 red wolves remained in the world, with 207 of those in captivity. By late 2020, the number of wild individuals had shrunk to only about 7 radio-collared and a dozen uncollared individuals, with no wild pups born since 2018. This decline has been linked to shooting and poisoning of wolves by landowners, and suspended conservation efforts by the USFWS.
A 2019 analysis by the Center for Biological Diversity
The Center for Biological Diversity is a nonprofit membership organization known for its work protecting endangered species through legal action, scientific petitions, creative media and grassroots activism. It was founded in 1989 by Kieran Suckl ...
of available habitat throughout the red wolf's former range found that over 20,000 square miles of public land
In all modern states, a portion of land is held by central or local governments. This is called public land, state land, or Crown land (Australia, and Canada). The system of tenure of public land, and the terminology used, varies between countrie ...
across 5 sites had viable habitat for red wolves to be reintroduced to in the future. These sites were chosen based on prey levels, isolation from coyotes and human development, and connectivity with other sites. These sites include: the Apalachicola and Osceola
Osceola (1804 – January 30, 1838, Asi-yahola in Muscogee language, Creek), named Billy Powell at birth in Alabama, became an influential leader of the Seminole people in Florida. His mother was Muscogee, and his great-grandfather was a S ...
National Forests along with the Okefenokee National Wildlife Refuge
The Okefenokee National Wildlife Refuge is a 402,000‑acre (1,627 km2) National Wildlife Refuge located in Charlton, Ware, and Clinch Counties of Georgia, and Baker County in Florida, United States. The refuge is administered from offic ...
and nearby protected lands; numerous national parks and national forests in the Appalachian Mountains
The Appalachian Mountains, often called the Appalachians, (french: Appalaches), are a system of mountains in eastern to northeastern North America. The Appalachians first formed roughly 480 million years ago during the Ordovician Period. They ...
including the Monongahela, George Washington & Jefferson, Cherokee
The Cherokee (; chr, ᎠᏂᏴᏫᏯᎢ, translit=Aniyvwiyaʔi or Anigiduwagi, or chr, ᏣᎳᎩ, links=no, translit=Tsalagi) are one of the indigenous peoples of the Southeastern Woodlands of the United States. Prior to the 18th century, t ...
, Pisgah, Nantahala, Chattahoochee
The Chattahoochee River forms the southern half of the Alabama and Georgia (U.S. state), Georgia border, as well as a portion of the Florida - Georgia border. It is a tributary of the Apalachicola River, a relatively short river formed by the con ...
, and Talladega National Forests along with Shenandoah National Park
Shenandoah National Park (often ) is an American national park that encompasses part of the Blue Ridge Mountains in the Commonwealth of Virginia. The park is long and narrow, with the Shenandoah River and its broad valley to the west, and the ...
and the lower elevations of Great Smoky Mountains National Park
Great Smoky Mountains National Park is an American national park in the southeastern United States, with parts in North Carolina and Tennessee. The park straddles the ridgeline of the Great Smoky Mountains, part of the Blue Ridge Mountains, whi ...
; Croatoan National Forest and Hofmann Forest on the North Carolina
North Carolina () is a state in the Southeastern region of the United States. The state is the 28th largest and 9th-most populous of the United States. It is bordered by Virginia to the north, the Atlantic Ocean to the east, Georgia and So ...
coast, and the Ozark
The Ozarks, also known as the Ozark Mountains, Ozark Highlands or Ozark Plateau, is a physiographic region in the U.S. states of Missouri, Arkansas, Oklahoma and the extreme southeastern corner of Kansas. The Ozarks cover a significant portio ...
, Ouatchita, and Mark Twain
Samuel Langhorne Clemens (November 30, 1835 – April 21, 1910), known by his pen name Mark Twain, was an American writer, humorist, entrepreneur, publisher, and lecturer. He was praised as the "greatest humorist the United States has p ...
National Forests in the central United States
The Central United States is sometimes conceived as between the Eastern and Western as part of a three-region model, roughly coincident with the U.S. Census' definition of the Midwestern United States plus the western and central portions of ...
.
In late 2018, two canids that are largely coyote were found on Galveston Island
Galveston Island ( ) is a barrier island on the Texas Gulf Coast in the United States, about southeast of Houston. The entire island, with the exception of Jamaica Beach, is within the city limits of the City of Galveston in Galveston County.
T ...
, Texas with red wolf alleles
An allele (, ; ; modern formation from Greek ἄλλος ''állos'', "other") is a variation of the same sequence of nucleotides at the same place on a long DNA molecule, as described in leading textbooks on genetics and evolution.
::"The chro ...
(gene expressions) left from a ghost population A ghost population is a population that has been inferred through using statistical techniques.
Population studies
In 2004, it was proposed that maximum likelihood or Bayesian approaches that estimate the migration rates and population sizes using ...
of red wolves. Since these alleles are from a different population from the red wolves in the North Carolina captive breeding program, there has been a proposal to selectively cross-breed the Galveston Island coyotes into the captive red wolf population. Another study published around the same time analyzing canid scat and hair samples in southwestern Louisiana found genetic evidence of red wolf ancestry in about 55% of sampled canids, with one such individual having between 78 and 100% red wolf ancestry, suggesting the possibility of more red wolf genes in the wild that may not be present in the captive population.
From 2015 to 2019, there were no red wolves released into the wild. But in March 2020, the FWS released a new breeding pair of red wolves, including a young male red wolf from St. Vincent Island, Florida into the Alligator River National Wildlife Refuge. The pair were unsuccessful at producing a litter of pups in the wild. On March 1, 2021, two male red wolves from Florida were paired with two female wild red wolves from eastern North Carolina and released into the wild. One of the male wolves was killed by a car shortly after being released into the wild. On April 30 and May 1, four adult red wolves were released into the wild and four red wolf pups were fostered by a wild female red wolf. In addition to the eight released wolves, the total number of red wolves living in the wild amount to nearly thirty wild individuals, including a dozen other wolves not wearing radio collars.
A study published in 2020 reported camera traps recorded "the presence of a large canid possessing wolf-like characters" in northeast Texas and later hair samples and tracks from the area indicated the presence of red wolves.Ladine, Troy A. (2020). "The Red Wolf (''Canis rufus'') in East Texas". ''The Southwestern Naturalist''. 65 (1): 52-56.
By fall of 2021, a total of six red wolves had been killed, including the four adults that had been released in the spring. Three of the released adults had been killed in vehicle collisions, two had died from unknown cases, and the fourth released adult had been shot by a landowner who feared the wolf was attempting to get his chickens. These losses dropped the number of wolves in the wild down to about 20 wild individuals. In the winter of 2021-2022, the Fish and Wildlife Services selected nine captive adult red wolves to be released into the wild. A family of five red wolves were released into the Pocosin Lakes National Wildlife Refuge, while two new breeding pairs of adult wolves were released into the Alligator River National Wildlife Refuge. The release of these new wolves brought the number of wild red wolves in eastern North Carolina up to less than 30 wild individuals.
On April 22, 2022, one of the breeding pairs of adult red wolves produced a litter of six wolf pups, four females and two males. This new litter of red wolf pups became the first litter born in the wild since 2018.
Coyote × re-introduced red wolf issues
Interbreeding with the coyote has been recognized as a threat affecting the restoration of red wolves. Currently, adaptive management efforts are making progress in reducing the threat of coyotes to the red wolf population in northeastern North Carolina. Other threats, such as habitat fragmentation, disease, and human-caused mortality, are of concern in the restoration of red wolves. Efforts to reduce the threats are presently being explored. By 1999, introgression of coyote genes was recognized as the single greatest threat to wild red wolf recovery and anadaptive management
Adaptive management, also known as adaptive resource management or adaptive environmental assessment and management, is a structured, iterative process of robust decision making in the face of uncertainty, with an aim to reducing uncertainty over ...
plan which included coyote sterilization has been successful, with coyote genes being reduced by 2015 to < 4% of the wild red wolf population.
Since the 2014 programmatic review, the USFWS ceased implementing the red wolf adaptive management plan that was responsible for preventing red wolf hybridization with coyotes and allowed the release of captive-born red wolves into the wild population. Since then, the wild population has decreased from 100 to 115 red wolves to less than 30. Despite the controversy over the red wolf's status as a unique taxon as well as the USFWS' apparent disinterest towards wolf conservation in the wild, the vast majority of public comments (including NC residents) submitted to the USFWS in 2017 over their new wolf management plan were in favor of the original wild conservation plan.
A 2016 genetic study of canid scats found that despite high coyote density inside the Red Wolf Experimental Population Area (RWEPA), hybridization occurs rarely (4% are hybrids).
Contested killing of re-introduced red wolves
High wolf mortality related to anthropogenic causes appeared to be the main factor limiting wolf dispersal westward from the RWEPA. High anthropogenic wolf mortality similarly limits expansion of eastern wolves outside of protected areas in south-eastern Canada. In 2012, theSouthern Environmental Law Center
Southern Environmental Law Center (SELC) is the largest 501(c)(3) organization, 501(c)(3) environmental nonprofit organization in the Southern region, with more than 80 attorneys and 75 staff members working at the local, state, and federal level ...
filed a lawsuit against the North Carolina Wildlife Resources Commission
The North Carolina Wildlife Resources Commission is a state government agency created by the North Carolina General Assembly, General Assembly in 1947 to Wildlife management, conserve and sustain North Carolina's fish and wildlife resources through ...
for jeopardizing the existence of the wild red wolf population by allowing nighttime hunting of coyotes in the five-county restoration area in eastern North Carolina. A 2014 court-approved settlement agreement was reached that banned nighttime hunting of coyotes and requires permitting and reporting coyote hunting. In response to the settlement, the North Carolina Wildlife Resources Commission adopted a resolution requesting the USFWS to remove all wild red wolves from private lands, terminate recovery efforts, and declare red wolves extinct in the wild. This resolution came in the wake of a 2014 programmatic review of the red wolf conservation program conducted by The Wildlife Management Institute. The Wildlife Management Institute indicated the reintroduction of the red wolf was an incredible achievement. The report indicated that red wolves could be released and survive in the wild, but that illegal killing of red wolves threatens the long-term persistence of the population. The report stated that the USFWS needed to update its red wolf recovery plan, thoroughly evaluate its strategy for preventing coyote hybridization and increase its public outreach.
In 2014, the USFWS issued the first take permit for a red wolf to a private landowner. Since then, the USFWS issued several other take permits to landowners in the five-county restoration area. During June 2015, a landowner shot and killed a female red wolf after being authorized a take permit, causing a public outcry. In response, the Southern Environmental Law Center filed a lawsuit against the USFWS for violating the Endangered Species Act.
By 2016, the red wolf population of North Carolina had declined to 45-60 wolves. The largest cause of this decline was gunshot.
In June 2018, the USFWS announced a proposal that would limit the wolves' safe range to only Alligator River National Wildlife Refuge, where only about 35 wolves remain, thus allowing hunting on private land. In November 2018, Chief Judge Terrence W. Boyle found that the USFWS had violated its congressional mandate to protect the red wolf, and ruled that USFWS had no power to give landowners the right to shoot them.
Relationship to humans
Since beforeEuropean colonization of the Americas
During the Age of Discovery, a large scale European colonization of the Americas took place between about 1492 and 1800. Although the Norse had explored and colonized areas of the North Atlantic, colonizing Greenland and creating a short ter ...
, the red wolf has featured prominently in Cherokee spiritual beliefs
Cherokee spiritual beliefs are held in common among the Cherokee people – Native American peoples who are indigenous to the Southeastern Woodlands, and today live primarily in communities in North Carolina (the Eastern Band of Cherokee Indians ...
, where it is known as ''wa'ya'' (ᏩᏯ), and is said to be the companion of Kana'ti - the hunter and father of the '' Aniwaya'' or Wolf Clan. Traditionally, Cherokee people generally avoid killing red wolves, as such an act is believed to bring about the vengeance of the killed animals' pack-mates.
Gallery
Taxonomy
 The taxonomic status of the red wolf is debated. It has been described as either a species with a distinct lineage, a recent hybrid of the gray wolf and the coyote, an ancient hybrid of the gray wolf and the coyote which warrants species status, or a distinct species that has undergone recent hybridization with the coyote.
The naturalists
The taxonomic status of the red wolf is debated. It has been described as either a species with a distinct lineage, a recent hybrid of the gray wolf and the coyote, an ancient hybrid of the gray wolf and the coyote which warrants species status, or a distinct species that has undergone recent hybridization with the coyote.
The naturalists John James Audubon
John James Audubon (born Jean-Jacques Rabin; April 26, 1785 – January 27, 1851) was an American self-trained artist, naturalist, and ornithologist. His combined interests in art and ornithology turned into a plan to make a complete pictoria ...
and John Bachman
John Bachman (February 4, 1790 – February 24, 1874) was an American Lutheran minister, social activist and naturalist who collaborated with John James Audubon to produce ''Viviparous Quadrupeds of North America'' and whose writings, particul ...
were the first to suggest that the wolves of the southern United States were different from wolves in its other regions. In 1851 they recorded the "Black American Wolf" as ''C. l.'' var. ''ater'' that existed in Florida, South Carolina, North Carolina, Kentucky, southern Indiana, southern Missouri, Louisiana, and northern Texas. They also recorded the "Red Texan Wolf" as ''C. l.'' var. ''rufus'' that existed from northern Arkansas, through Texas, and into Mexico. In 1912 the zoologist Gerrit Smith Miller Jr. noted that the designation ''ater'' was unavailable and recorded these wolves as ''C. l. floridanus''.
In 1937, the zoologist Edward Alphonso Goldman
Edward Alphonso Goldman (July 7, 1873 – September 2, 1946) was an American zoologist and botanist. He worked extensively in Mexico with Edward William Nelson and described and revised many groups of mammals.
He was born Edward Alphonso Goltman i ...
proposed a new species of wolf ''Canis rufus''. Three subspecies
In biological classification, subspecies is a rank below species, used for populations that live in different areas and vary in size, shape, or other physical characteristics (morphology), but that can successfully interbreed. Not all species ...
of red wolf were originally recognized by Goldman, with two of these subspecies now being extinct. The Florida black wolf (''Canis rufus floridanus'') (Maine to Florida) has been extinct since 1908 and the Mississippi Valley red wolf (''Canis rufus gregoryi'') (south-central United States) was declared extinct by 1980. By the 1970s, the Texas red wolf (''Canis rufus rufus'') existed only in the coastal prairies and marshes of extreme southeastern Texas and southwestern Louisiana. These were removed from the wild to form a captive breeding program and reintroduced into eastern North Carolina in 1987.
In 1967, the zoologists Barbara Lawrence
Barbara Jo Lawrence (February 24, 1930 – November 13, 2013) was an American model, actress, and real estate agent.
Early years
Born to Morris and Bernice ( Eaton) Lawrence in Carnegie, Oklahoma, Barbara Jo moved with her mother to Kansas C ...
and William H. Bossert believed that the case for classifying ''C. rufus'' as a species was based too heavily on the small red wolves of central Texas, from where it was known that there existed hybridization with the coyote. They said that if an adequate number of specimens had been included from Florida, then the separation of ''C. rufus'' from ''C. lupus'' would have been unlikely. The taxonomic reference ''Catalogue of Life
The Catalogue of Life is an online database that provides an index of known species of animals, plants, fungi, and microorganisms. It was created in 2001 as a partnership between the global Species 2000 and the American Integrated Taxonomic Info ...
'' classifies the red wolf as a subspecies of ''Canis lupus''. The mammalogist W. Christopher Wozencraft, writing in ''Mammal Species of the World
''Mammal Species of the World: A Taxonomic and Geographic Reference'' is a standard reference work in mammalogy giving descriptions and bibliographic data for the known species of mammals. It is now in its third edition, published in late 2005, ...
'' (2005), regards the red wolf as a hybrid of the gray wolf and the coyote, but due to its uncertain status compromised by recognizing it as a subspecies of the gray wolf ''Canis lupus rufus''.
In 2021, the American Society of Mammalogists
The American Society of Mammalogists (ASM) was founded in 1919. Its primary purpose is to encourage the study of mammals, and professions studying them. There are over 4,500 members of this society, and they are primarily professional scientists ...
considered the red wolf as its own species (''Canis rufus'').
Taxonomic debate
When European settlers first arrived to North America, the coyote's range was limited to the western half of the continent. They existed in the arid areas and across the open plains, including the prairie regions of the midwestern states. Early explorers found some in Indiana and Wisconsin. From the mid-1800s onward, coyotes began expanding beyond their original range. The taxonomic debate regarding North American wolves can be summarised as follows:Fossil evidence
Thepaleontologist
Paleontology (), also spelled palaeontology or palæontology, is the scientific study of life that existed prior to, and sometimes including, the start of the Holocene epoch (roughly 11,700 years before present). It includes the study of fossi ...
Ronald M. Nowak notes that the oldest fossil remains of the red wolf are 10,000 years old and were found in Florida near Melbourne
Melbourne ( ; Boonwurrung/Woiwurrung: ''Narrm'' or ''Naarm'') is the capital and most populous city of the Australian state of Victoria, and the second-most populous city in both Australia and Oceania. Its name generally refers to a met ...
, Brevard County
Brevard County ( ) is a county located in the east central portion of the U.S. state of Florida. As of the 2020 census, the population was 606,612, making it the 10th-most populated county in Florida. The official county seat is located in T ...
, Withlacoochee River, Citrus County
Citrus County is a county located on the west central coast of the U.S. state of Florida. As of the 2020 census, the population was 153,843. Its county seat is Inverness, and its largest community is Homosassa Springs.
Citrus County compris ...
, and Devil's Den Cave
Devil's Den is formed by a karst window, in which the roof over a subterranean river has collapsed, exposing the water to the open surface, near Williston, Florida. It is privately owned, and operated as a SCUBA diving training and recreational fa ...
, Levy County
Levy County is a county located on the Gulf coast and in the northern part of the U.S. state of Florida. As of the 2020 census, the population was 42,915. Its county seat is Bronson.
History
Levy County was created in 1845, after the Seminol ...
. He notes that there are only a few, but questionable, fossil remains of the gray wolf found in the southeastern states. He proposes that following the extinction of the dire wolf
The dire wolf (''Aenocyon dirus'' ) is an extinct canine. It is one of the most famous prehistoric carnivores in North America, along with its extinct competitor ''Smilodon''. The dire wolf lived in the Americas and eastern Asia during the Lat ...
, the coyote appears to have been displaced from the southeastern US by the red wolf until the last century, when the extirpation of wolves allowed the coyote to expand its range. He also proposes that the ancestor of all North American and Eurasian wolves was '' C. mosbachensis'', which lived in the Middle Pleistocene
The Chibanian, widely known by its previous designation of Middle Pleistocene, is an age in the international geologic timescale or a stage in chronostratigraphy, being a division of the Pleistocene Epoch within the ongoing Quaternary Period. The ...
700,000–300,000 years ago.
''C. mosbachensis'' was a wolf that once lived across Eurasia before going extinct. It was smaller than most North American wolf populations and smaller than ''C. rufus'', and has been described as being similar in size to the small Indian wolf
The Indian wolf (''Canis lupus pallipes'') is a subspecies of gray wolf that ranges from Southwest Asia to the Indian Subcontinent. It is intermediate in size between the Himalayan wolf and the Arabian wolf, and lacks the former's luxuriant wint ...
, ''Canis lupus pallipes''. He further proposes that ''C. mosbachensis'' invaded North America where it became isolated by the later glaciation and there gave rise to ''C. rufus''. In Eurasia, ''C. mosbachensis'' evolved into ''C. lupus'', which later invaded North America.
The paleontologist
Paleontology (), also spelled palaeontology or palæontology, is the scientific study of life that existed prior to, and sometimes including, the start of the Holocene epoch (roughly 11,700 years before present). It includes the study of fossi ...
and expert on the genus ''Canis'' natural history, Xiaoming Wang, looked at red wolf fossil material but could not state if it was, or was not, a separate species. He said that Nowak had put together more morphometric
Morphometrics (from Greek μορϕή ''morphe'', "shape, form", and -μετρία ''metria'', "measurement") or morphometry refers to the quantitative analysis of ''form'', a concept that encompasses size and shape. Morphometric analyses are co ...
data on red wolves than anybody else, but Nowak's statistical analysis of the data revealed a red wolf that is difficult to deal with. Wang proposes that studies of ancient DNA
Ancient DNA (aDNA) is DNA isolated from ancient specimens. Due to degradation processes (including cross-linking, deamination and fragmentation) ancient DNA is more degraded in comparison with contemporary genetic material. Even under the bes ...
taken from fossils might help settle the debate.
Morphological evidence
In 1771, the English naturalistMark Catesby
Mark Catesby (24 March 1683 – 23 December 1749) was an English naturalist who studied the flora and fauna of the New World. Between 1729 and 1747 Catesby published his ''Natural History of Carolina, Florida and the Bahama Islands'', the fi ...
referred to Florida and the Carolinas when he wrote that "The Wolves in America are like those of Europe, in shape and colour, but are somewhat smaller." They were described as being more timid and less voracious. In 1791 the American naturalist William Bartram
William Bartram (April 20, 1739 – July 22, 1823) was an American botanist, ornithologist, natural historian and explorer. Bartram was the author of an acclaimed book, now known by the shortened title ''Bartram's Travels'', which chronicled ...
wrote in his book '' Travels'' about a wolf which he had encountered in Florida that was larger than a dog, but was black in contrast to the larger yellow-brown wolves of Pennsylvania and Canada. In 1851 the naturalists John James Audubon
John James Audubon (born Jean-Jacques Rabin; April 26, 1785 – January 27, 1851) was an American self-trained artist, naturalist, and ornithologist. His combined interests in art and ornithology turned into a plan to make a complete pictoria ...
and John Bachman
John Bachman (February 4, 1790 – February 24, 1874) was an American Lutheran minister, social activist and naturalist who collaborated with John James Audubon to produce ''Viviparous Quadrupeds of North America'' and whose writings, particul ...
described the "Red Texan Wolf" in detail. They noted that it could be found in Florida and other southeastern states, but it differed from other North American wolves and named it ''Canis lupus rufus''. It was described as being more fox-like than the gray wolf, but retaining the same "sneaking, cowardly, yet ferocious disposition".
In 1905, the mammalogist Vernon Bailey referred to the "Texan Red Wolf" with the first use of the name ''Canis rufus''. In 1937 the zoologist Edward Goldman undertook a morphological study of southeastern wolf specimens. He noted that their skulls and dentition differed from those of gray wolves and closely approached those of coyotes. He identified the specimens as all belonging to the one species which he referred to as ''Canis rufus''. Goldman then examined a large number of southeastern wolf specimens and identified three subspecies, noting that their colors ranged from black, gray, and cinnamon-buff.
It is difficult to distinguish the red wolf from a red wolf × coyote hybrid. During the 1960s, two studies of the skull morphology of wild ''Canis'' in the southeastern states found them to belong to the red wolf, the coyote, or many variations in between. The conclusion was that there has been recent massive hybridization with the coyote. In contrast, another 1960s study of ''Canis'' morphology concluded that the red wolf, eastern wolf, and domestic dog were closer to the gray wolf than the coyote, while still remaining clearly distinctive from each other. The study regarded these 3 canines as subspecies of the gray wolf. However, the study noted that "red wolf" specimens taken from the edge of their range which they shared with the coyote could not be attributed to any one species because the cranial variation was very wide. The study proposed further research to ascertain if hybridization had occurred.
In 1971, a study of the skulls of ''C. rufus'', ''C. lupus'' and ''C. latrans'' indicated that ''C. rufus'' was distinguishable by being in size and shape midway between the gray wolf and the coyote. A re-examination of museum canine skulls collected from central Texas between 1915 and 1918 showed variations spanning from ''C. rufus'' through to ''C. latrans''. The study proposes that by 1930 due to human habitat modification, the red wolf had disappeared from this region and had been replaced by a hybrid swarm
A hybrid swarm is a population of hybrids that has survived beyond the initial hybrid generation, with interbreeding between hybrid individuals and backcrossing with its parent types. Such population are highly variable, with the genetic and phe ...
. By 1969, this hybrid swarm was moving eastwards into eastern Texas and Louisiana.
In the late 19th century, sheep farmers in Kerr County, Texas
Kerr County is a county located on the Edwards Plateau in the U.S. state of Texas. As of the 2020 census, its population was 52,598. Its county seat is Kerrville. The county was named by Joshua D. Brown for his fellow Kentucky native, James ...
, stated that the coyotes in the region were larger than normal coyotes, and they believed that they were a gray wolf and coyote cross. In 1970, the wolf mammalogist L. David Mech
Lucyan David Mech (; born January 18, 1937), also known as Dave Mech, is an American biologist specializing in the study of wolves. He is a senior research scientist for the U.S. Geological Survey and an adjunct professor at the University of Min ...
proposed that the red wolf was a hybrid of the gray wolf and coyote. However, a 1971 study compared the cerebellum
The cerebellum (Latin for "little brain") is a major feature of the hindbrain of all vertebrates. Although usually smaller than the cerebrum, in some animals such as the mormyrid fishes it may be as large as or even larger. In humans, the cerebel ...
within the brain of six ''Canis'' species and found that the cerebellum of the red wolf indicated a distinct species, was closest to that of the gray wolf, but in contrast indicated some characteristics that were more primitive than those found in any of the other ''Canis'' species. In 2014, a three-dimensional morphometrics
Morphometrics (from Greek μορϕή ''morphe'', "shape, form", and -μετρία ''metria'', "measurement") or morphometry refers to the quantitative analysis of ''form'', a concept that encompasses size and shape. Morphometric analyses are co ...
study of ''Canis'' species accepted only six red wolf specimens for analysis from those on offer, due to the impact of hybridization on the others.
DNA studies
Different DNA studies may give conflicting results because of the specimens selected, the technology used, and the assumptions made by the researchers.Phylogenetic trees
A phylogenetic tree (also phylogeny or evolutionary tree Felsenstein J. (2004). ''Inferring Phylogenies'' Sinauer Associates: Sunderland, MA.) is a branching diagram or a tree showing the evolutionary relationships among various biological spec ...
compiled using different genetic markers A genetic marker is a gene or DNA sequence with a known location on a chromosome that can be used to identify individuals or species. It can be described as a variation (which may arise due to mutation or alteration in the genomic loci) that can be ...
have given conflicting results on the relationship between the wolf, dog and coyote. One study based on SNPs
In genetics, a single-nucleotide polymorphism (SNP ; plural SNPs ) is a germline substitution of a single nucleotide at a specific position in the genome. Although certain definitions require the substitution to be present in a sufficiently larg ...
(a single mutation
In biology, a mutation is an alteration in the nucleic acid sequence of the genome of an organism, virus, or extrachromosomal DNA. Viral genomes contain either DNA or RNA. Mutations result from errors during DNA or viral replication, mi ...
), and another based on nuclear gene
A nuclear gene is a gene whose physical DNA nucleotide sequence is located in the cell nucleus of a eukaryote. The term is used to distinguish nuclear genes from genes found in mitochondria or chloroplasts. The vast majority of genes in eukaryote ...
sequences (taken from the cell nucleus
The cell nucleus (pl. nuclei; from Latin or , meaning ''kernel'' or ''seed'') is a membrane-bound organelle found in eukaryotic cells. Eukaryotic cells usually have a single nucleus, but a few cell types, such as mammalian red blood cells, h ...
), showed dogs clustering with coyotes and separate from wolves. Another study based on SNPS showed wolves clustering with coyotes and separate from dogs. Other studies based on a number of markers show the more widely accepted result of wolves clustering with dogs separate from coyotes. These results demonstrate that caution is needed when interpreting the results provided by genetic markers.
Genetic marker evidence
In 1980, a study usedgel electrophoresis
Gel electrophoresis is a method for separation and analysis of biomacromolecules ( DNA, RNA, proteins, etc.) and their fragments, based on their size and charge. It is used in clinical chemistry to separate proteins by charge or size (IEF ...
to look at fragments of DNA taken from dogs, coyotes, and wolves from the red wolf's core range. The study found that a unique allele
An allele (, ; ; modern formation from Greek ἄλλος ''állos'', "other") is a variation of the same sequence of nucleotides at the same place on a long DNA molecule, as described in leading textbooks on genetics and evolution.
::"The chro ...
(expression of a gene
In biology, the word gene (from , ; "...Wilhelm Johannsen coined the word gene to describe the Mendelian units of heredity..." meaning ''generation'' or ''birth'' or ''gender'') can have several different meanings. The Mendelian gene is a ba ...
) associated with Lactate dehydrogenase
Lactate dehydrogenase (LDH or LD) is an enzyme found in nearly all living cells. LDH catalyzes the conversion of lactate to pyruvate and back, as it converts NAD+ to NADH and back. A dehydrogenase is an enzyme that transfers a hydride from on ...
could be found in red wolves, but not dogs and coyotes. The study suggests that this allele survives in the red wolf. The study did not compare gray wolves for the existence of this allele.
Mitochondrial DNA
Mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA or mDNA) is the DNA located in mitochondria, cellular organelles within eukaryotic cells that convert chemical energy from food into a form that cells can use, such as adenosine triphosphate (ATP). Mitochondrial D ...
(mDNA) passes along the maternal line and can date back thousands of years. In 1991, a study of red wolf mDNA indicates that red wolf genotypes
The genotype of an organism is its complete set of genetic material. Genotype can also be used to refer to the alleles or variants an individual carries in a particular gene or genetic location. The number of alleles an individual can have in a ...
match those known to belong to the gray wolf or the coyote. The study concluded that the red wolf is either a wolf × coyote hybrid or a species that has hybridized with the wolf and coyote across its entire range. The study proposed that the red wolf is a southeastern occurring subspecies of the gray wolf that has undergone hybridization due to an expanding coyote population; however, being unique and threatened that it should remain protected. This conclusion led to debate for the remainder of the decade.
microsatellites
A microsatellite is a tract of repetitive DNA in which certain DNA motifs (ranging in length from one to six or more base pairs) are repeated, typically 5–50 times. Microsatellites occur at thousands of locations within an organism's genome. ...
(genetic markers taken from across the genome
In the fields of molecular biology and genetics, a genome is all the genetic information of an organism. It consists of nucleotide sequences of DNA (or RNA in RNA viruses). The nuclear genome includes protein-coding genes and non-coding ge ...
of a specimen). The phylogenetic tree produced from the genetic sequences showed red wolves and eastern Canadian wolves clustering together. These then clustered next closer with the coyote and away from the gray wolf. A further analysis using mDNA sequences indicated the presence of coyote in both of these two wolves, and that these two wolves had diverged from the coyote 150,000–300,000 years ago. No gray wolf sequences were detected in the samples. The study proposes that these findings are inconsistent with the two wolves being subspecies of the gray wolf, that red wolves and eastern Canadian wolves evolved in North America after having diverged from the coyote, and therefore they are more likely to hybridize with coyotes.
In 2009, a study of eastern Canadian wolves using microsatellites, mDNA, and the paternally-inherited yDNA
The Y chromosome is one of two sex chromosomes (allosomes) in therian mammals, including humans, and many other animals. The other is the X chromosome. Y is normally the sex-determining chromosome in many species, since it is the presence or abs ...
markers found that the eastern Canadian wolf was a unique ecotype
In evolutionary ecology, an ecotype,Greek: ''οίκος'' = home and ''τύπος'' = type, coined by Göte Turesson in 1922 sometimes called ecospecies, describes a genetically distinct geographic variety, population, or race within a species, ...
of the gray wolf that had undergone recent hybridization with other gray wolves and coyotes. It could find no evidence to support the findings of the earlier 2000 study regarding the eastern Canadian wolf. The study did not include the red wolf.
In 2011, a study compared the genetic sequences of 48,000 single nucleotide polymorphisms
In genetics, a single-nucleotide polymorphism (SNP ; plural SNPs ) is a germline substitution of a single nucleotide at a specific position in the genome. Although certain definitions require the substitution to be present in a sufficiently larg ...
(mutations
In biology, a mutation is an alteration in the nucleic acid sequence of the genome of an organism, virus, or extrachromosomal DNA. Viral genomes contain either DNA or RNA. Mutations result from errors during DNA or viral replication, mi ...
) taken from the genomes of canids from around the world. The comparison indicated that the red wolf was about 76% coyote and 24% gray wolf with hybridization having occurred 287–430 years ago. The eastern wolf was 58% gray wolf and 42% coyote with hybridization having occurred 546–963 years ago. The study rejected the theory of a common ancestry for the red and eastern wolves. However the next year, a study reviewed a subset of the 2011 study's Single-nucleotide polymorphism
In genetics, a single-nucleotide polymorphism (SNP ; plural SNPs ) is a germline substitution of a single nucleotide at a specific position in the genome. Although certain definitions require the substitution to be present in a sufficiently lar ...
(SNP) data and proposed that its methodology had skewed the results and that the red and eastern wolves are not hybrids but are in fact the same species separate from the gray wolf. The 2012 study proposed that there are three true ''Canis'' species in North America - the gray wolf, the western coyote, and the red wolf / eastern wolf, with the eastern wolf represented by the Algonquin wolf, with the Great Lakes wolf being a hybrid of the eastern wolf and the gray wolf, and the eastern coyote being a hybrid of the western coyote and the eastern (Algonquin) wolf.
Also in 2011, a scientific literature review
A literature review is an overview of the previously published works on a topic. The term can refer to a full scholarly paper or a section of a scholarly work such as a book, or an article. Either way, a literature review is supposed to provid ...
was undertaken to help assess the taxonomy of North American wolves. One of the findings proposed was that the eastern wolf is supported as a separate species by morphological and genetic data. Genetic data supports a close relationship between the eastern and red wolves, but not close enough to support these as one species. It was "likely" that these were the separate descendants of a common ancestor shared with coyotes. This review was published in 2012. In 2014, the National Center for Ecological Analysis and Synthesis The National Center for Ecological Analysis and Synthesis (NCEAS) is a research center at the University of California, Santa Barbara, in Santa Barbara, California, Santa Barbara, California. Better known by its acronym, NCEAS (pronounced “n-seas� ...
was invited by the United States Fish and Wildlife Service
The United States Fish and Wildlife Service (USFWS or FWS) is an agency within the United States Department of the Interior dedicated to the management of fish, wildlife, and natural habitats. The mission of the agency is "working with othe ...
to provide an independent review of its proposed rule relating to gray wolves. The center's panel findings were that the proposed rule was heavily dependent upon the analysis contained in a scientific literature review conducted in 2011 (Chambers ''et al''.), that this work was not universally accepted, that the issue was "not settled", and that the rule does not represent the "best available science".
In early 2016, an mDNA analysis of three ancient (300–1,900 years old) wolf-like samples from the southeastern United States found that they grouped with the coyote clade, although their teeth were wolf-like. The study proposed that the specimens were either coyotes and this would mean that coyotes had occupied this region continuously rather than intermittently, a North American evolved red wolf lineage related to coyotes, or an ancient coyote–wolf hybrid. Ancient hybridization between wolves and coyotes would likely have been due to natural events or early human activities, not landscape changes associated with European colonization because of the age of these samples. Coyote–wolf hybrids may have occupied the southeastern United States for a long time, filling an important niche as a large predator.
Whole-genome evidence
 In July 2016, a whole-genome DNA study proposed, based on the assumptions made, that all of the North American wolves and coyotes diverged from a common ancestor less than 6,000–117,000 years ago. The study also indicated that all North America wolves have a significant amount of coyote ancestry and all coyotes some degree of wolf ancestry, and that the red wolf and Great Lakes region wolf are highly admixed with different proportions of gray wolf and coyote ancestry. One test indicated a wolf/coyote divergence time of 51,000 years before present that matched other studies indicating that the extant wolf came into being around this time. Another test indicated that the red wolf diverged from the coyote between 55,000 and 117,000 years before present and the Great Lakes region wolf 32,000 years before present. Other tests and modelling showed various divergence ranges and the conclusion was a range of less than 6,000 and 117,000 years before present. The study found that coyote ancestry was highest in red wolves from the southeast of the United States and lowest among the Great Lakes region wolves.
The theory proposed was that this pattern matched the south-to-north disappearance of the wolf due to European colonization and its resulting loss of habitat. Bounties led to the extirpation of wolves initially in the southeast, and as the wolf population declined wolf-coyote admixture increased. Later, this process occurred in the Great Lakes region with the influx of coyotes replacing wolves, followed by the expansion of coyotes and their hybrids across the wider region. The red wolf may possess some genomic elements that were unique to gray wolf and coyote lineages from the American South. The proposed timing of the wolf/coyote divergence conflicts with the finding of a coyote-like specimen in strata dated to 1 million years before present, and red wolf fossil specimens dating back 10,000 years ago. The study concluded by stating that because of the extirpation of gray wolves in the American Southeast, "the reintroduced population of red wolves in eastern North Carolina is doomed to genetic swamping by coyotes without the extensive management of hybrids, as is currently practiced by the USFWS."
In September 2016, the USFWS announced a program of changes to the red wolf recovery program and "will begin implementing a series of actions based on the best and latest scientific information". The service will secure the captive population which is regarded as not sustainable, determine new sites for additional experimental wild populations, revise the application of the existing experimental population rule in North Carolina, and complete a comprehensive Species Status Assessment.
In 2017, a group of canid researchers challenged the recent finding that the red wolf and the eastern wolf were the result of recent coyote-wolf hybridization. The group highlight that no testing had been undertaken to ascertain the time period that hybridization had occurred and that, by the previous study's own figures, the hybridization could not have occurred recently but supports a much more ancient hybridization. The group found deficiencies in the previous study's selection of specimens and the findings drawn from the different techniques used. Therefore, the group argues that both the red wolf and the eastern wolf remain genetically distinct North American taxa. This was rebutted by the authors of the earlier study. Another study in late 2018 of wild canids in southwestern
In July 2016, a whole-genome DNA study proposed, based on the assumptions made, that all of the North American wolves and coyotes diverged from a common ancestor less than 6,000–117,000 years ago. The study also indicated that all North America wolves have a significant amount of coyote ancestry and all coyotes some degree of wolf ancestry, and that the red wolf and Great Lakes region wolf are highly admixed with different proportions of gray wolf and coyote ancestry. One test indicated a wolf/coyote divergence time of 51,000 years before present that matched other studies indicating that the extant wolf came into being around this time. Another test indicated that the red wolf diverged from the coyote between 55,000 and 117,000 years before present and the Great Lakes region wolf 32,000 years before present. Other tests and modelling showed various divergence ranges and the conclusion was a range of less than 6,000 and 117,000 years before present. The study found that coyote ancestry was highest in red wolves from the southeast of the United States and lowest among the Great Lakes region wolves.
The theory proposed was that this pattern matched the south-to-north disappearance of the wolf due to European colonization and its resulting loss of habitat. Bounties led to the extirpation of wolves initially in the southeast, and as the wolf population declined wolf-coyote admixture increased. Later, this process occurred in the Great Lakes region with the influx of coyotes replacing wolves, followed by the expansion of coyotes and their hybrids across the wider region. The red wolf may possess some genomic elements that were unique to gray wolf and coyote lineages from the American South. The proposed timing of the wolf/coyote divergence conflicts with the finding of a coyote-like specimen in strata dated to 1 million years before present, and red wolf fossil specimens dating back 10,000 years ago. The study concluded by stating that because of the extirpation of gray wolves in the American Southeast, "the reintroduced population of red wolves in eastern North Carolina is doomed to genetic swamping by coyotes without the extensive management of hybrids, as is currently practiced by the USFWS."
In September 2016, the USFWS announced a program of changes to the red wolf recovery program and "will begin implementing a series of actions based on the best and latest scientific information". The service will secure the captive population which is regarded as not sustainable, determine new sites for additional experimental wild populations, revise the application of the existing experimental population rule in North Carolina, and complete a comprehensive Species Status Assessment.
In 2017, a group of canid researchers challenged the recent finding that the red wolf and the eastern wolf were the result of recent coyote-wolf hybridization. The group highlight that no testing had been undertaken to ascertain the time period that hybridization had occurred and that, by the previous study's own figures, the hybridization could not have occurred recently but supports a much more ancient hybridization. The group found deficiencies in the previous study's selection of specimens and the findings drawn from the different techniques used. Therefore, the group argues that both the red wolf and the eastern wolf remain genetically distinct North American taxa. This was rebutted by the authors of the earlier study. Another study in late 2018 of wild canids in southwestern Louisiana
Louisiana , group=pronunciation (French: ''La Louisiane'') is a state in the Deep South and South Central regions of the United States. It is the 20th-smallest by area and the 25th most populous of the 50 U.S. states. Louisiana is borde ...
also supported the red wolf as a separate species, citing distinct red wolf DNA within hybrid canids.
In 2019, a literature review
A literature review is an overview of the previously published works on a topic. The term can refer to a full scholarly paper or a section of a scholarly work such as a book, or an article. Either way, a literature review is supposed to provid ...
of the previous studies was undertaken by the National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine
The National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine (also known as NASEM or the National Academies) are the collective scientific national academy of the United States. The name is used interchangeably in two senses: (1) as an umbrell ...
. The position of the National Academies is that the historical red wolf forms a valid taxonomic species, the modern red wolf is distinct from wolves and coyotes, and modern red wolves trace some of their ancestry to historic red wolves. The species ''Canis rufus'' is supported for the modern red wolf, unless genomic evidence from historical red wolf specimens changes this assessment, due to a lack of continuity between the historic and the modern red wolves.
Wolf genome
Genetic studies relating to wolves or dogs have inferred phylogenetic relationships based on the only reference genome available, that of the Boxer dog. In 2017, the first reference genome of the wolf ''Canis lupus lupus'' was mapped to aid future research. In 2018, a study looked at the genomic structure and admixture of North American wolves, wolf-like canids, and coyotes using specimens from across their entire range that mapped the largest dataset of nuclear genome sequences against the wolf reference genome. The study supports the findings of previous studies that North American gray wolves and wolf-like canids were the result of complex gray wolf and coyote mixing. A polar wolf from Greenland and a coyote from Mexico represented the purest specimens. The coyotes from Alaska, California, Alabama, and Quebec show almost no wolf ancestry. Coyotes from Missouri, Illinois, and Florida exhibit 5–10% wolf ancestry. There was 40%:60% wolf to coyote ancestry in red wolves, 60%:40% in Eastern timber wolves, and 75%:25% in the Great Lakes wolves. There was 10% coyote ancestry in Mexican wolves and Atlantic Coast wolves, 5% in Pacific Coast and Yellowstone wolves, and less than 3% in Canadian archipelago wolves. The study shows that the genomic ancestry of red, eastern timber and Great Lakes wolves were the result of admixture between modern gray wolves and modern coyotes. This was then followed by development into local populations. Individuals within each group showed consistent levels of coyote to wolf inheritance, indicating that this was the result of relatively ancient admixture. The eastern timber wolf (Algonquin Provincial Park
Algonquin Provincial Park is a provincial park located between Georgian Bay and the Ottawa River in Ontario, Canada, mostly within the Unorganized South Part of Nipissing District. Established in 1893, it is the oldest provincial park in Cana ...
) is genetically closely related to the Great Lakes wolf (Minnesota, Isle Royale National Park). If a third canid had been involved in the admixture of the North American wolf-like canids, then its genetic signature would have been found in coyotes and wolves, which it has not.
Gray wolves suffered a species-wide population bottleneck
A population bottleneck or genetic bottleneck is a sharp reduction in the size of a population due to environmental events such as famines, earthquakes, floods, fires, disease, and droughts; or human activities such as specicide, widespread violen ...
(reduction) approximately 25,000 YBP during the Last Glacial Maximum. This was followed by a single population of modern wolves expanding out of a Beringia refuge to repopulate the wolf's former range, replacing the remaining Late Pleistocene wolf populations across Eurasia and North America as they did so. This implies that if the coyote and red wolf were derived from this invasion, their histories date only tens of thousands and not hundreds of thousands of years ago, which is consistent with other studies.
The Endangered Species Act provides protection to endangered species, but does not provide protection for endangered admixed individuals, even if these serve as reservoirs for extinct genetic variation. Researchers on both sides of the red wolf debate argue that admixed canids warrant full protection under this Act.
Separate species that can be strengthened from hybrids
In 2020, a study conducted DNA sequencing ofcanines
Canine may refer to:
Zoology and anatomy
* a dog-like Canid animal in the subfamily Caninae
** ''Canis'', a genus including dogs, wolves, coyotes, and jackals
** Dog, the domestic dog
* Canine tooth, in mammalian oral anatomy
People with the surn ...
across southeastern US to detect those with any red wolf ancestry. The study found that red wolf ancestry exists in the coyote populations of southwestern Louisiana and southeastern Texas, but also newly detected in North Carolina. The red wolf ancestry of these populations possess unique red wolf alleles not found in the current captive red wolf population. The study proposes that the expanding coyotes admixed with red wolves to gain genetic material that was suited to the southeastern environment and would aid their adaptation to it, and that surviving red wolves admixed with coyotes because the red wolves were suffering from inbreeding.
In 2021, a study conducted DNA sequencing of canines across the remnant red wolf hybrid zone of southwestern Louisiana and southeastern Texas. The study found red wolf ancestry in the coyote genomes which increases up to 60% in a westward gradient. This was due to introgression from the remnant red wolf population over the past 100 years. The study proposes that coyotes expanded into the gulf
A gulf is a large inlet from the ocean into the landmass, typically with a narrower opening than a bay, but that is not observable in all geographic areas so named. The term gulf was traditionally used for large highly-indented navigable bodie ...
region and admixed with red wolves prior to the red wolf going extinct in the wild due to loss of habitat and persecution. In the past two decades the hybrid region has expanded. The study presented the genetic evidence that the red wolf is a separate species, based on the structure of one of the loci of its X-chromosome
The X chromosome is one of the two sex-determining chromosomes (allosomes) in many organisms, including mammals (the other is the Y chromosome), and is found in both males and females. It is a part of the XY sex-determination system and XO sex- ...
which is accepted as a marker for distinct species. As such, the study suggested that the introgressed red wolf ancestry could be de-introgressed back as a basis for breeding further red wolves from the hybrids.
Pre-dates the coyote in North America
In 2021, a study of mitochondrial genomes sourced from specimens dated before the 20th century revealed that red wolves could be found across North America. With the arrival of the gray wolf between 80,000–60,000 years ago, the red wolf's range shrank to the eastern forests and California, and the coyote replaced the red wolf mid-continent between 60,000–30,000 years ago. The coyote expanded into California at the beginning of theHolocene
The Holocene ( ) is the current geological epoch. It began approximately 11,650 cal years Before Present (), after the Last Glacial Period, which concluded with the Holocene glacial retreat. The Holocene and the preceding Pleistocene togethe ...
era 12,000–10,000 years ago and admixed with the red wolf, phenotypically replacing them. The study proposes that the red wolf may pre-date the coyote in North America.
Explanatory footnotes
References
Further reading
* * * * * *External links
Red wolf
U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service * * * * * {{Taxonbar, from=Q200442 Mammals described in 1851 Mammals of the United States Canid hybrids Controversial mammal taxa Wolves Wolves in the United States ESA endangered species Taxa named by John James Audubon Taxa named by John Bachman