Campinas State University on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Campinas (, ''Plains'' or ''Meadows'') is a Brazilian municipality in São Paulo State, part of the country's Southeast Region. According to the 2020 estimate, the city's population is 1,213,792, making it the fourteenth most populous Brazilian city and the third most populous municipality in São Paulo state. The city's

 The city was founded on July 14, 1774, by Barreto Leme. It was initially a simple outpost on the way to Minas Gerais and Goiás serving the "
The city was founded on July 14, 1774, by Barreto Leme. It was initially a simple outpost on the way to Minas Gerais and Goiás serving the "
 The area of the city, according to the Brazilian Institute of Geography and Statistics, is ; of this is the urban area and remaining constitute greater Campinas. It is located at 22°54′21″S, 47°03′39″W and is at a distance of northwest of São Paulo. Its neighboring cities are Paulínia, Jaguariúna and Pedreira, north; Morungaba, Itatiba and Valinhos in the east; Itupeva, Indaiatuba and Monte Mor, south, and Hortolândia in the west.
The area of the city, according to the Brazilian Institute of Geography and Statistics, is ; of this is the urban area and remaining constitute greater Campinas. It is located at 22°54′21″S, 47°03′39″W and is at a distance of northwest of São Paulo. Its neighboring cities are Paulínia, Jaguariúna and Pedreira, north; Morungaba, Itatiba and Valinhos in the east; Itupeva, Indaiatuba and Monte Mor, south, and Hortolândia in the west.
 The city has a dry-winter tropical climate (''Aw'' type in the Köppen classification, with dry winters and hot months).
The lowest temperature recorded in the city was 3.0 °C on June 25, 1918. The highest temperature was 39.0 °C, observed on 17 November 1985. The highest cumulative rainfall recorded in 24 hours in the city between June 1988 and October 2008 was 143.4 mm there are also episodes of strong winds, with gusts exceeding 100 km / h, and training records were made in the city day May 4, 2001, and March 9, 2008.
The city has a dry-winter tropical climate (''Aw'' type in the Köppen classification, with dry winters and hot months).
The lowest temperature recorded in the city was 3.0 °C on June 25, 1918. The highest temperature was 39.0 °C, observed on 17 November 1985. The highest cumulative rainfall recorded in 24 hours in the city between June 1988 and October 2008 was 143.4 mm there are also episodes of strong winds, with gusts exceeding 100 km / h, and training records were made in the city day May 4, 2001, and March 9, 2008.


 According to the 2010
According to the 2010
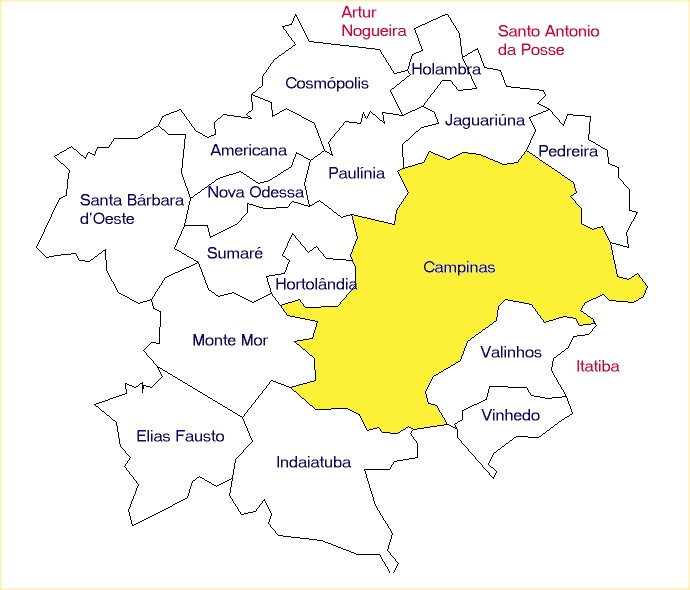
 , Campinas became an official metropolitan region (RMC — Região Metropolitana de Campinas), with 19 municipalities, with a total of 2.8 million inhabitants and a total land area of (data ), adjacent to the São Paulo metropolitan region (RMSP) and São José dos Campos (RMVale). The Campinas Metropolitan area also comprehends a gross domestic product (GDP) of R$70.7 billion (around U$42 billion).
* Americana
* Artur Nogueira
*
, Campinas became an official metropolitan region (RMC — Região Metropolitana de Campinas), with 19 municipalities, with a total of 2.8 million inhabitants and a total land area of (data ), adjacent to the São Paulo metropolitan region (RMSP) and São José dos Campos (RMVale). The Campinas Metropolitan area also comprehends a gross domestic product (GDP) of R$70.7 billion (around U$42 billion).
* Americana
* Artur Nogueira
*


 Campinas is the richest city in the metropolitan region of Campinas and the 10th richest city in Brazil, showing a gross domestic product (GDP) of 36.68 billion reais (2010), which represents almost 1% (0.998%) of all Brazilian GDP. Currently, the city concentrates 10% of industrial production of Brazil. The paper highlights the high-tech industries and metallurgical park, considered the capital of Silicon Valley Sterling.
The region hosts 17,677
Campinas is the richest city in the metropolitan region of Campinas and the 10th richest city in Brazil, showing a gross domestic product (GDP) of 36.68 billion reais (2010), which represents almost 1% (0.998%) of all Brazilian GDP. Currently, the city concentrates 10% of industrial production of Brazil. The paper highlights the high-tech industries and metallurgical park, considered the capital of Silicon Valley Sterling.
The region hosts 17,677
Daitan
The airline
Times Higher Education 2007 World University Rankings
the University of Campinas ( Unicamp) is the 177th best university in the world, and the 2nd best in Latin America (after the University of São Paulo in 176th place). Campinas also boasts the largest number of high-tech business incubators and industrial parks (a total of eight), such as the CIATEC I and II, Softex, TechnoPark, InCamp, Polis, TechTown, Industrial Park of Campinas, and others. The presence of one of the largest
 The responsible for the cultural sector of Campinas is the City Department of Culture, which aims to plan and implement the cultural policy of the municipality through the development of programs, projects, and activities aimed at cultural development.
The city has always been a cultural center in the State of São Paulo. This has increased greatly with the proliferation of universities. Campinas has three theater houses, a
The responsible for the cultural sector of Campinas is the City Department of Culture, which aims to plan and implement the cultural policy of the municipality through the development of programs, projects, and activities aimed at cultural development.
The city has always been a cultural center in the State of São Paulo. This has increased greatly with the proliferation of universities. Campinas has three theater houses, a
Hippie Fair.
 * the ''Castelo'' (Castle) Water Tower, which provides views over the downtown;
* the Historical Railway Society of Campinas, which maintains the Anhumas station, a set of steam
* the ''Castelo'' (Castle) Water Tower, which provides views over the downtown;
* the Historical Railway Society of Campinas, which maintains the Anhumas station, a set of steam
 Campinas is home to two football clubs nationally recognized: Associação Atlética Ponte Preta and Guarani Futebol Clube, who perform " Campineiro derby" match that is considered one of the most traditional of the state occurring since 1912. There is also Red Bull Brasil, which was created in November 2007 and lately has gained significant prominence. Women's football also has been outstanding, albeit amateur. In the story also revealed other clubs, such as Mogiana Sports Club, which was created on June 7, 1933, and came into bankruptcy in the 60s.
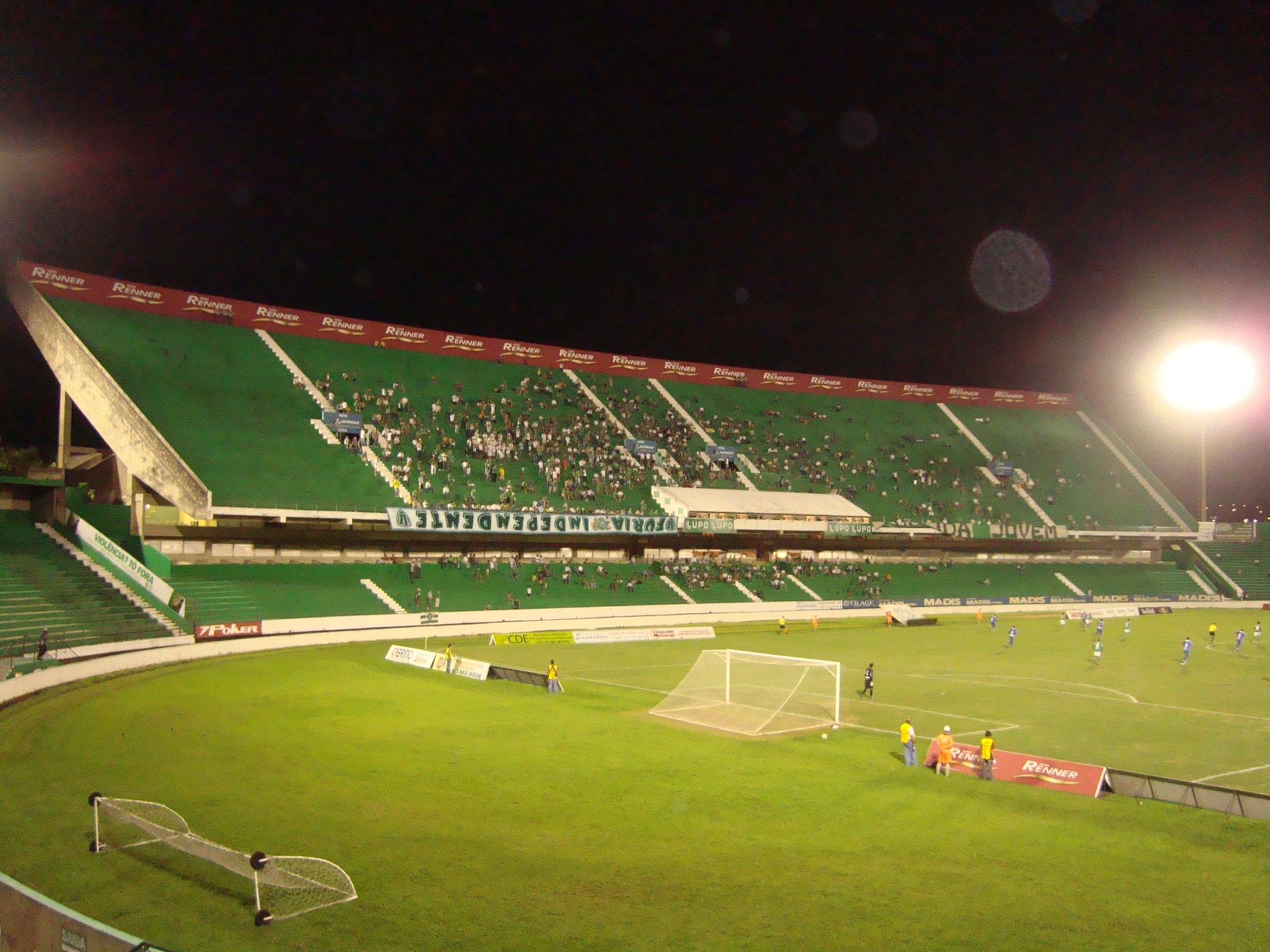
The city also has three major venues: Estádio Brinco de Ouro da Princesa, owned by Guarani, which opened in 1953 and today has a capacity of around 29,130 people, Sport and Recreation Centre in Campinas Dr. Horacio Antonio da Costa (Cerecamp Stadium or Mogiana Stadium), which belongs to the state of São Paulo and was opened in 1940, right by the Estádio Moisés Lucarelli, owned by Ponte Preta, which was built by its own supporters, and founded in 1948 and has the capacity to 19,728 visitors. It is popularly known as "Majestoso" (The Majestic One), for being the third-largest stadium in Brazil as the year of its foundation (1948), smaller only than
Campinas is home to two football clubs nationally recognized: Associação Atlética Ponte Preta and Guarani Futebol Clube, who perform " Campineiro derby" match that is considered one of the most traditional of the state occurring since 1912. There is also Red Bull Brasil, which was created in November 2007 and lately has gained significant prominence. Women's football also has been outstanding, albeit amateur. In the story also revealed other clubs, such as Mogiana Sports Club, which was created on June 7, 1933, and came into bankruptcy in the 60s.
The city also has three major venues: Estádio Brinco de Ouro da Princesa, owned by Guarani, which opened in 1953 and today has a capacity of around 29,130 people, Sport and Recreation Centre in Campinas Dr. Horacio Antonio da Costa (Cerecamp Stadium or Mogiana Stadium), which belongs to the state of São Paulo and was opened in 1940, right by the Estádio Moisés Lucarelli, owned by Ponte Preta, which was built by its own supporters, and founded in 1948 and has the capacity to 19,728 visitors. It is popularly known as "Majestoso" (The Majestic One), for being the third-largest stadium in Brazil as the year of its foundation (1948), smaller only than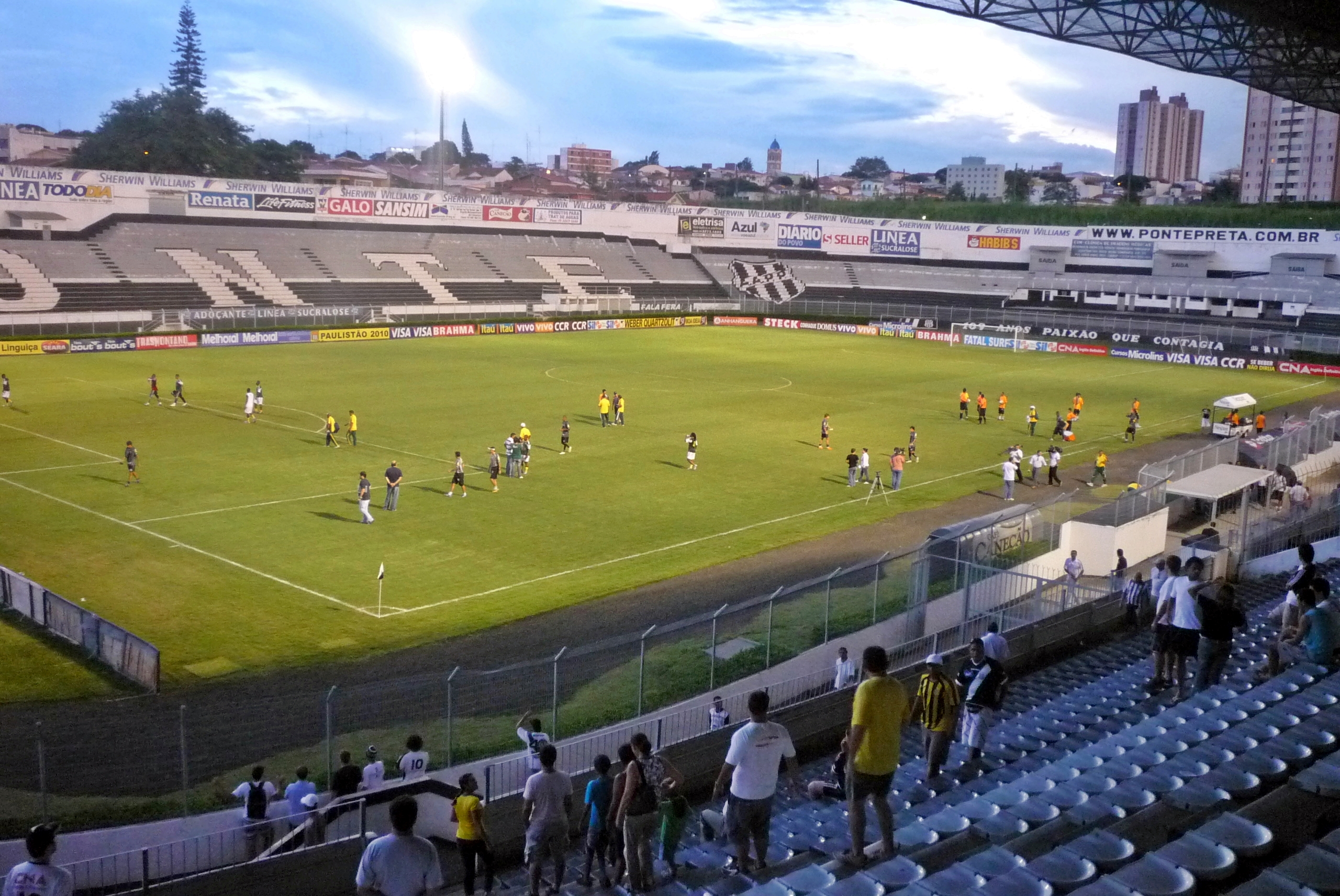  The city is still home to several sporting events in other modalities, such as Corrida Integração (Integration Race), which is held since 1983 by Pioneer Broadcasters Television (EPTV), being divided into two modes (a 5 km-dedicated to disabled people and wheelchair users, and another 10 km, for non-disabled people).
Campinas also has a tradition in the Open Games of the Interior, created in 1936, and competition involving various sports. Four times, hosted the competition (1939, 1945, 1960, and 1994), and ten times the city came out as the winner of the competition (1939, 1955, 1956, 1958, 1960, 1971, 1974, 1975, 1978, 1979), being the third city which has won the most competition.
In tennis, there is the Tennis Club of Campinas (CBT), which was created in 1913, offering, in addition to the blocks of the sport, swimming pools, courts for basketball and soccer, as well as rooms suitable for the practice of judo, gymnastics, and dance. Club de Regatas Campineiro and Swim (CCRN) also provides space for the practice of various types of Olympic sports.
The city is still home to several sporting events in other modalities, such as Corrida Integração (Integration Race), which is held since 1983 by Pioneer Broadcasters Television (EPTV), being divided into two modes (a 5 km-dedicated to disabled people and wheelchair users, and another 10 km, for non-disabled people).
Campinas also has a tradition in the Open Games of the Interior, created in 1936, and competition involving various sports. Four times, hosted the competition (1939, 1945, 1960, and 1994), and ten times the city came out as the winner of the competition (1939, 1955, 1956, 1958, 1960, 1971, 1974, 1975, 1978, 1979), being the third city which has won the most competition.
In tennis, there is the Tennis Club of Campinas (CBT), which was created in 1913, offering, in addition to the blocks of the sport, swimming pools, courts for basketball and soccer, as well as rooms suitable for the practice of judo, gymnastics, and dance. Club de Regatas Campineiro and Swim (CCRN) also provides space for the practice of various types of Olympic sports.






 Portuguese is the official national language, and thus the primary language taught in schools. But English and Spanish are part of the official high school curriculum.
Portuguese is the official national language, and thus the primary language taught in schools. But English and Spanish are part of the official high school curriculum.
INPG
* PUC-Campinas (
Fatec Campinas
Campinas
was the first city in Brazil, outside the capitals of Brazilian states, which received the transmission in digital signal for TV, by EPTV, an affiliate of Rede Globo, on October 3, 2008. It currently has the second TV station that also broadcasts the signal by TVB, now an affiliate of Rede Record, since February 2011 (before
Official home page
(in Portuguese).
EncontraCampinas - Find everything about Campinas
(in Portuguese)
The Seven Wonders of Campinas
(in Portuguese)
Other Campinas Tourist Spots
(in Portuguese) {{Authority control Populated places established in 1774 1774 establishments in South America
metropolitan area
A metropolitan area or metro is a region that consists of a densely populated urban agglomeration and its surrounding territories sharing industries, commercial areas, transport network, infrastructures and housing. A metro area usually com ...
, Metropolitan Region of Campinas, contains twenty municipalities with a total population of 3,656,363 people.
Etymology
Campinas means ''grass fields'' in Portuguese and refers to its characteristic landscape, which originally comprised large stretches of dense subtropical forests (mato grosso or thick woods in Portuguese), mainly along the many rivers, interspersed with gently rolling hills covered by low-lying vegetation. Campinas' official crest and flag has a picture of the mythical bird, the phoenix, because it was practically reborn after a devastating epidemic of yellow fever in the 1800s, which killed more than 25% of the city's inhabitants.History

 The city was founded on July 14, 1774, by Barreto Leme. It was initially a simple outpost on the way to Minas Gerais and Goiás serving the "
The city was founded on July 14, 1774, by Barreto Leme. It was initially a simple outpost on the way to Minas Gerais and Goiás serving the "Bandeirantes
The ''Bandeirantes'' (), literally "flag-carriers", were slavers, explorers, adventurers, and fortune hunters in early Colonial Brazil. They are largely responsible for Brazil's great expansion westward, far beyond the Tordesillas Line of 1494 ...
" who were in search of precious minerals and Indian slaves
Slavery and enslavement are both the state and the condition of being a slave—someone forbidden to quit one's service for an enslaver, and who is treated by the enslaver as property. Slavery typically involves slaves being made to perf ...
. In the first half of the 19th century, Campinas became a growing population center, with many coffee, cotton and sugarcane
Sugarcane or sugar cane is a species of (often hybrid) tall, Perennial plant, perennial grass (in the genus ''Saccharum'', tribe Andropogoneae) that is used for sugar Sugar industry, production. The plants are 2–6 m (6–20 ft) tall with ...
farms.
The construction of a railway linking the city of São Paulo to Santos' seaport, in 1867, was very important for its growth. In the second half of the 19th century, with the abolition of slavery, farming and industrialization
Industrialisation ( alternatively spelled industrialization) is the period of social and economic change that transforms a human group from an agrarian society into an industrial society. This involves an extensive re-organisation of an econo ...
attracted many foreign immigrants to replace the lost manpower, mainly from Italy.
Coffee became an important export and the city became wealthy. In consequence, a large service sector was established to serve the growing population, and in the first decades of the 20th century, Campinas could already boast of an opera house, theaters, banks, movie theaters, radio stations, a philharmonic orchestra, two newspapers ('' Correio Popular'' and ''Diário do Povo
''Diário do Povo'' (Portuguese for ''People's Diary'') is a newspaper published in the city of Campinas, state of São Paulo, Brazil.
''Correio Popular'' is owned and managed by a larger communications holding company, ''Rede Anhangüera de ...
''), a good public education system (with the Escola Normal de Campinas and the Colégio Culto à Ciência), and hospitals, such as the Santa Casa de Misericórdia (a charity for poor people).
And the Casa de Saúde de Campinas (for the Italian community, formerly known as ''Circolo Italiani Uniti''), and the most important Brazilian research center in agricultural sciences, the Instituto Agronômico de Campinas
The Instituto Agronômico de Campinas () (Agronomical Institute of Campinas—IAC) is a research and development institution affiliated to the Agência Paulista de Tecnologia dos Agronegócios (São Paulo Agency of Agrobusiness Technology), of th ...
, which was founded by Emperor Pedro II. Finally, the construction of the first Brazilian highway in 1938, between Campinas and São Paulo, the Anhanguera Highway
The Rodovia Anhanguera (official designation SP-330) (In English: Anhanguera Highway) is a highway in the state of São Paulo, Brazil. It is one of the country's busiest transportation corridors. A 2005 survey conducted amongst Brazilian truck d ...
, was a turning point in the integration of Campinas into the rest of the state.
Campinas was the birthplace of opera composer Carlos Gomes (1836 — 1896) and of the President of the Republic Campos Salles
Campos may refer to:
Geography
* Campos (crater), a crater on Mars
* Campos, Spain, a municipality in Mallorca
* Campos Basin, a sedimentary basin offshore of Rio de Janeiro state, named after Campos
* Campos do Jordão, a municipality in the s ...
(1841 — 1913). It was home for 49 years to Hércules Florence, reputed as one of the early inventors of photography, photocopying
A photocopier (also called copier or copy machine, and formerly Xerox machine, the generic trademark) is a machine that makes copies of documents and other visual images onto paper or plastic film quickly and cheaply. Most modern photocopiers u ...
and the mimeograph.
Geography
 The area of the city, according to the Brazilian Institute of Geography and Statistics, is ; of this is the urban area and remaining constitute greater Campinas. It is located at 22°54′21″S, 47°03′39″W and is at a distance of northwest of São Paulo. Its neighboring cities are Paulínia, Jaguariúna and Pedreira, north; Morungaba, Itatiba and Valinhos in the east; Itupeva, Indaiatuba and Monte Mor, south, and Hortolândia in the west.
The area of the city, according to the Brazilian Institute of Geography and Statistics, is ; of this is the urban area and remaining constitute greater Campinas. It is located at 22°54′21″S, 47°03′39″W and is at a distance of northwest of São Paulo. Its neighboring cities are Paulínia, Jaguariúna and Pedreira, north; Morungaba, Itatiba and Valinhos in the east; Itupeva, Indaiatuba and Monte Mor, south, and Hortolândia in the west.
Ecology
Most of the original vegetation of the city was largely eliminated. Like 13 other municipalities in the metropolitan region of Campinas, the city is subject to someenvironmental stress
Stress, either physiological, biological or psychological, is an organism's response to a stressor such as an environmental condition. Stress is the body's method of reacting to a condition such as a threat, challenge or physical and psych ...
, and Campinas is considered one of the areas liable to flooding and silting; it now has less than 5% of vegetation cover in total area.
Trying to reverse this situation, several projects have been and are being conducted and planned, such as building corridors, and the regulation of the Management Plan of Environmental Preservation Area (APA) in Campinas. There are also several environmental projects to combat the destruction of riparian forests located along the banks of the Atibaia river
Atibaia (or ''Estância de Atibaia'') is a Brazilian municipality in the state of São Paulo, Brazil. The name is derived from an indigenous language called Tupi, and means "healthy water river". Its name has changed over time, from the primitive ...
, which has a high level of pollution. Today, Campinas houses the area of relevant ecological interest
An area of relevant ecological interest ( pt, Área de Relevante Interesse Ecológico, Arie) is a type of protected area of Brazil with unusual natural features and with little or no human occupation.
Definition
"Area of relevant ecological inte ...
(ARIE) Mata de Santa Genebra
Mata de Santa Genebra (Saint Geneva Forest) is an area of relevant ecological interest in the state of São Paulo, Brazil.
History
The area was originally part of the Fazenda Santa Genebra, a coffee plantation owned by Baron Geraldo de Resende, ...
, , established in 1985 by the city of Campinas' Fundação José Pedro de Oliveira and regulated by the Brazilian Environment and Renewable Natural Resources Institute ( IBAMA). This is the now second-largest urban forest of Brazil, behind only the Tijuca Forest
The Tijuca National Park () is an urban national park in the mountains of the city of Rio de Janeiro, Brazil. The park is part of the Atlantic Forest Biosphere Preserve, and is administered by the Chico Mendes Institute for Biodiversity Conservat ...
, in Rio de Janeiro.
The city also has smaller urban forest groves and reserve park
Reserve or reserves may refer to:
Places
* Reserve, Kansas, a US city
* Reserve, Louisiana, a census-designated place in St. John the Baptist Parish
* Reserve, Montana, a census-designated place in Sheridan County
* Reserve, New Mexico, a US vi ...
s, such as the Bosque dos Jequitibas (installed in 1881
Events
January–March
* January 1– 24 – Siege of Geok Tepe: Russian troops under General Mikhail Skobelev defeat the Turkomans.
* January 13 – War of the Pacific – Battle of San Juan and Chorrillos: The C ...
), the Bosque dos Italianos (transl. Italian's Grove), the Bosque dos Alemães (transl. German's Grove), Guarantã's Park, as well as the larger Parque Portugal (Taquaral Lagoon, transl. Park and Lagoon of Bamboos), "Dom Bosco" Ecological Park and Monsenhor "Emílio José Salim" Ecological Park.
Climate
 The city has a dry-winter tropical climate (''Aw'' type in the Köppen classification, with dry winters and hot months).
The lowest temperature recorded in the city was 3.0 °C on June 25, 1918. The highest temperature was 39.0 °C, observed on 17 November 1985. The highest cumulative rainfall recorded in 24 hours in the city between June 1988 and October 2008 was 143.4 mm there are also episodes of strong winds, with gusts exceeding 100 km / h, and training records were made in the city day May 4, 2001, and March 9, 2008.
The city has a dry-winter tropical climate (''Aw'' type in the Köppen classification, with dry winters and hot months).
The lowest temperature recorded in the city was 3.0 °C on June 25, 1918. The highest temperature was 39.0 °C, observed on 17 November 1985. The highest cumulative rainfall recorded in 24 hours in the city between June 1988 and October 2008 was 143.4 mm there are also episodes of strong winds, with gusts exceeding 100 km / h, and training records were made in the city day May 4, 2001, and March 9, 2008.
Demographics


 According to the 2010
According to the 2010 IBGE
The Brazilian Institute of Geography and Statistics ( pt, Instituto Brasileiro de Geografia e Estatística; IBGE) is the agency responsible for official collection of statistical, geographic, cartographic, geodetic and environmental information ...
Census, as of November 2010, Campinas had a population of 1,080,999 and a population density of 1358.6 (inhabitants / km ²). Infant mortality levels were at up to 1 year (per thousand): 14.05 and life expectancy in the city was 72.22 years. The fertility rate was at 1.78 children per woman. 96.01 of the populace could read.
* Human Development Index (HDI-M): 0.852 (high)
* HDI-M Income: 0.845 (high)
* HDI-M Longevity: 0.787
* HDI-M Education: 0.925 (very high)
(Source: DATA)
Ethnicity
Source: 2010 census:Composition
Source: 2010 Census Population (IBGE): 1,080,999Metropolitan region

 , Campinas became an official metropolitan region (RMC — Região Metropolitana de Campinas), with 19 municipalities, with a total of 2.8 million inhabitants and a total land area of (data ), adjacent to the São Paulo metropolitan region (RMSP) and São José dos Campos (RMVale). The Campinas Metropolitan area also comprehends a gross domestic product (GDP) of R$70.7 billion (around U$42 billion).
* Americana
* Artur Nogueira
*
, Campinas became an official metropolitan region (RMC — Região Metropolitana de Campinas), with 19 municipalities, with a total of 2.8 million inhabitants and a total land area of (data ), adjacent to the São Paulo metropolitan region (RMSP) and São José dos Campos (RMVale). The Campinas Metropolitan area also comprehends a gross domestic product (GDP) of R$70.7 billion (around U$42 billion).
* Americana
* Artur Nogueira
* Cosmópolis
Cosmópolis is a municipality in the state of São Paulo in Brazil. It is part of the Metropolitan Region of Campinas The Metropolitan Region of Campinas ( pt, Região Metropolitana de Campinas) is an administrative division of the state of São P ...
* Engenheiro Coelho
Engenheiro Coelho is a municipality in the east of the State of São Paulo, Brazil. It is part of the Metropolitan Region of Campinas. The population is 21,249 (2020 est.) in an area of 109.94 km². It is located about from São Paulo and f ...
* Holambra
Holambra (from the words Holland-America-Brazil) is a municipality in the state of São Paulo in Brazil. It is part of the Metropolitan Region of Campinas. Holambra is the largest producer of flowers and ornamental plants in Latin America, also ho ...
* Hortolândia
Hortolândia is a Brazilian municipality in the interior of the state of São Paulo. It is part of the Metropolitan Region of Campinas and the Mesoregion and Microregion of Campinas. It is located northwest of the state capital, about 110 k ...
* Indaiatuba
* Itatiba
Itatiba is a municipality in the state of São Paulo in Brazil, approximately 80 km from the State Capital. It is part of the Metropolitan Region of Campinas. The population is 122,581 (2020 est.) in an area of 322.28 km². The average e ...
* Jaguariúna
* Monte Mor
Monte Mor is a municipality ''( município)'' in the state of São Paulo in Brazil. It is part of the Metropolitan Region of Campinas The Metropolitan Region of Campinas ( pt, Região Metropolitana de Campinas) is an administrative division of the ...
* Nova Odessa
Nova Odessa (lit., New Odessa) is a Brazilian municipality in the state of São Paulo. It is part of the Metropolitan Region of Campinas. The population is 60,956 (2020 est.) in an area of 73.79 km². Nova Odessa was founded on May 24, 1905, ...
* Paulínia
* Pedreira
* Santa Bárbara d'Oeste
* Santo Antônio de Posse
Santo Antônio de Posse is a municipality in the state of São Paulo in Brazil. It is part of the Metropolitan Region of Campinas The Metropolitan Region of Campinas ( pt, Região Metropolitana de Campinas) is an administrative division of the sta ...
* Sumaré
Sumaré is a city in the State of São Paulo, Brazil. It is part of the Metropolitan Region of Campinas. The population is 286,211 (2020 est.) in an area of 153.47 km2. The elevation is 583 m. Sumaré was founded in 1868, after being upgrade ...
* Valinhos
Valinhos () is a municipality (''município'') in the state of São Paulo, Brazil. It is the birthplace of Adoniran Barbosa. Valinhos is famous for its purple fig, the theme of its annual Fig Fest. It is part of the Metropolitan Region of Campina ...
* Vinhedo
Vinhedo is a municipality in the state of São Paulo in Brazil. It is part of the Metropolitan Region of Campinas. The population in 2020 was 80,111 and its area is . It has a population density of 777 inhabitants per square kilometer. The elevatio ...
The Campinas municipality is also the administrative center of the micro- and meso-regions of the same name. The micro-region includes the RMC (Metropolitan Region of Campinas) and the municipality of Elias Fausto
Elias Fausto is a municipality in the state of São Paulo in Brazil
Brazil ( pt, Brasil; ), officially the Federative Republic of Brazil (Portuguese: ), is the largest country in both South America and Latin America. At and with over 217 ...
; the meso-region also includes the following municipalities: Aguaí
Aguaí is a Brazilian municipality located in the eastern part of the state of São Paulo. The population is 36,648 (2020 est.) in an area of . The settlement ''Cascavel'' was established in 1887 near a railway station. In 1944, when it was separat ...
, Amparo, Águas da Prata
Águas da Prata is a Brazilian municipality in the state of São Paulo
São Paulo (, ; Portuguese for ' Saint Paul') is the most populous city in Brazil, and is the capital of the state of São Paulo, the most populous and wealthiest Brazil ...
, Águas de Lindóia Águas may refer to:
Places
* Dos Aguas, a municipality in the Valencian Community, Spain
* Aguas, municipality in Aragon, Spain
* Palace of the Marqués de Dos Aguas, a Rococo palace in Valencia, Spain
People
People with this surname include:
* J ...
, Caconde, Casa Branca, Divinolândia
Divinolândia is a municipality in the state of São Paulo in Brazil
Brazil ( pt, Brasil; ), officially the Federative Republic of Brazil (Portuguese: ), is the largest country in both South America and Latin America. At and with over 21 ...
, Espírito Santo do Pinhal
Espírito Santo do Pinhal (Portuguese meaning "Holy Spirit of Pinhal") is a municipality in the state of São Paulo in Brazil. The population in 2020 is 44,471 (IBGE 2020) and the area is 389 km². The elevation is 870 m.
Notable people
*S ...
, Estiva Gerbi
Estiva Gerbi is a municipality in the state of São Paulo in Brazil
Brazil ( pt, Brasil; ), officially the Federative Republic of Brazil (Portuguese: ), is the largest country in both South America and Latin America. At and with over 217 ...
, Itapira
Itapira is a municipality in the state of São Paulo in Brazil. The population is 75,234 (2020 est.) in an area of 518 km². The elevation is 643 m.
History
From the eighteenth century, there were already some residents in the region, whose ...
, Itobi, Lindóia, Mococa Mococa is a municipality in the state of São Paulo (state), São Paulo in Brazil. The population is 68,980 (2020 est.) in an area of 855 km². The elevation is 645 m.
The local government is made up of a mayor (in Brazil, '':pt:Prefeito, Pre ...
, Mogi Guaçu
Mogi Guaçu is a municipality in the state of São Paulo in Brazil. The population is 153,033 (2020 est.) in an area of . The city is at an average elevation of above sea level. Mogi Guaçu is a place name that probably originates from the Tupi ...
, Moji-Mirim
Mogi Mirim is a municipality located in the eastern part of São Paulo State, in Brazil. The population is 93,650 (2020 est.) in an area of 498 km². The elevation is 611 m.
Mogi Mirim is around 65 km from Campinas, the biggest city in ...
, Monte Alegre do Sul
Monte Alegre do Sul is a municipality in the state of São Paulo in Brazil
Brazil ( pt, Brasil; ), officially the Federative Republic of Brazil (Portuguese: ), is the largest country in both South America and Latin America. At and with ov ...
, Pedra Bela
Pedra Bela is a municipality in the state of São Paulo in Brazil
Brazil ( pt, Brasil; ), officially the Federative Republic of Brazil (Portuguese: ), is the largest country in both South America and Latin America. At and with over 217 mi ...
, Pinhalzinho, Pirassununga, Porto Ferreira
Porto Ferreira is a municipality in the state of São Paulo in Brazil. It is situated on the Mojiguaçu River at an altitude of 559 meters. The population is 56,504 (2020 est.) in an area of 244.9 km².
History
The valley where Porto Ferreir ...
, Santa Cruz das Palmeiras
Santa Cruz das Palmeiras is a municipality in the state of São Paulo in Brazil. The population is 34,737 (2020 est.) in an areaIt of 295 km². The elevation is 635 m. Description
Santa Cruz is located in the Mojiguaçu River basin and is 30& ...
, Santo Antônio do Jardim, São João da Boa Vista
São João da Boa Vista (; "Saint John of the Good View" in English) is a municipality in the state of São Paulo (state), São Paulo, Brazil. The population in 2020 was 91,771 and the area is . The elevation is .
The foundation history
The city ...
, São José do Rio Pardo
São José do Rio Pardo is a municipality in the state of São Paulo in Brazil. The population is 55,124 (2020 est.) in an area of 419 km2. The elevation is 676 m. It was founded by Colonel Antônio Marçal Nogueira de Barros in 1870. In the s ...
, São Sebastião da Grama
São Sebastião da Grama is a municipality in the state of São Paulo in Brazil
Brazil ( pt, Brasil; ), officially the Federative Republic of Brazil (Portuguese: ), is the largest country in both South America and Latin America. At and wi ...
, Serra Negra
Serra Negra is a municipality in the state of São Paulo, Brazil. It belongs to the meso-region of Campinas. Population (2020) was 29,452 inhabitants. Total area: 203,5 km2, demographic density: 112 inhabitants/km2
Location
The name of th ...
, Socorro, Tambaú
Tambaú is a municipality in the state of São Paulo in Brazil. The population is 23,232 (2020 est.) in an area of 562 km². The elevation is 698 m. Tambaú was famous for the annual sermons of Padre Donizetti.
References
Municipalities ...
, Tapiratiba
Tapiratiba is a municipality in the state of São Paulo in Brazil
Brazil ( pt, Brasil; ), officially the Federative Republic of Brazil (Portuguese: ), is the largest country in both South America and Latin America. At and with over 217 mi ...
, Vargem Grande do Sul and Vinhedo
Vinhedo is a municipality in the state of São Paulo in Brazil. It is part of the Metropolitan Region of Campinas. The population in 2020 was 80,111 and its area is . It has a population density of 777 inhabitants per square kilometer. The elevatio ...
.
Other cities which are geographically, historically or economically tied to the meso-region of Campinas could be mentioned: Araras, Atibaia
Atibaia (or ''Estância de Atibaia'') is a Brazilian municipality in the state of São Paulo, Brazil. The name is derived from an indigenous language called Tupi, and means "healthy water river". Its name has changed over time, from the primitive ...
, Bragança Paulista
Bragança Paulista is a municipality in the state of São Paulo in Brazil. The population is 170,533 (2020 est.) in an area of 512.6 km². The elevation is 817 m.
The city is famous for its traditional sausages, with several establishments c ...
, Capivari, Conchal
Conchal is a municipality in São Paulo
São Paulo (, ; Portuguese for 'Saint Paul') is the most populous city in Brazil, and is the capital of the state of São Paulo, the most populous and wealthiest Brazilian state, located in the country ...
, Iracemápolis
Iracemápolis is a municipality in the state of São Paulo in Brazil. The population is 24,614 (2020 est.) in an area of 115.1 km². The elevation is 608 m.
It is known as the birthplace of footballer Elano
Elano Blumer (born 14 June 198 ...
, Itu
The International Telecommunication Union is a specialized agency of the United Nations responsible for many matters related to information and communication technologies. It was established on 17 May 1865 as the International Telegraph Unio ...
, Itupeva
Itupeva is a municipality in the state of São Paulo in Brazil
Brazil ( pt, Brasil; ), officially the Federative Republic of Brazil (Portuguese: ), is the largest country in both South America and Latin America. At and with over 217 milli ...
, Jarinu, Jundiai, Limeira, Louveira
Louveira is a municipality in the state of São Paulo in Brazil
Brazil ( pt, Brasil; ), officially the Federative Republic of Brazil (Portuguese: ), is the largest country in both South America and Latin America. At and with over 217 mil ...
, Mombuca
Mombuca is a municipality in the state of São Paulo in Brazil
Brazil ( pt, Brasil; ), officially the Federative Republic of Brazil (Portuguese: ), is the largest country in both South America and Latin America. At and with over 217 milli ...
, Morungaba
Morungaba is a municipality in the state of São Paulo in Brazil. It is part of the Metropolitan Region of Campinas The Metropolitan Region of Campinas ( pt, Região Metropolitana de Campinas) is an administrative division of the state of São Paul ...
, Piracicaba, Rafard, Rio das Pedras, Salto and Tuiuti.
Economy


 Campinas is the richest city in the metropolitan region of Campinas and the 10th richest city in Brazil, showing a gross domestic product (GDP) of 36.68 billion reais (2010), which represents almost 1% (0.998%) of all Brazilian GDP. Currently, the city concentrates 10% of industrial production of Brazil. The paper highlights the high-tech industries and metallurgical park, considered the capital of Silicon Valley Sterling.
The region hosts 17,677
Campinas is the richest city in the metropolitan region of Campinas and the 10th richest city in Brazil, showing a gross domestic product (GDP) of 36.68 billion reais (2010), which represents almost 1% (0.998%) of all Brazilian GDP. Currently, the city concentrates 10% of industrial production of Brazil. The paper highlights the high-tech industries and metallurgical park, considered the capital of Silicon Valley Sterling.
The region hosts 17,677 industries
Industry may refer to:
Economics
* Industry (economics), a generally categorized branch of economic activity
* Industry (manufacturing), a specific branch of economic activity, typically in factories with machinery
* The wider industrial secto ...
, the second largest number in the State of São Paulo.
The petrochemical complex is centered in the Southeastern section, a few miles from Campinas, near the refinery of Petrobras Planalto Paulista (Replan), the largest in Brazil one of the largest in Latin America, and has companies like Dupont
DuPont de Nemours, Inc., commonly shortened to DuPont, is an American multinational chemical company first formed in 1802 by French-American chemist and industrialist Éleuthère Irénée du Pont de Nemours. The company played a major role in ...
, Chevron, Shell, Exxon
ExxonMobil Corporation (commonly shortened to Exxon) is an American multinational oil and gas corporation headquartered in Irving, Texas. It is the largest direct descendant of John D. Rockefeller's Standard Oil, and was formed on November 30, ...
, Group Ipiranga, Eucatex, Rhodia, and others. It is the hub of companies and Blue Trip. The largest companies have a global turnover of more than $80 billion, larger than many Latin American countries.
The city has several shopping malls, two of the largest being Iguatemi Campinas and Shopping Parque Dom Pedro. Campinas has, within its metropolitan area, the largest cargo airport for import/export, Viracopos International Airport, a significant entity in the international transport of cargo.
Campinas' main economic activities are agriculture (mainly coffee, sugarcane
Sugarcane or sugar cane is a species of (often hybrid) tall, Perennial plant, perennial grass (in the genus ''Saccharum'', tribe Andropogoneae) that is used for sugar Sugar industry, production. The plants are 2–6 m (6–20 ft) tall with ...
, and cotton), industry (textiles
Textile is an umbrella term that includes various fiber-based materials, including fibers, yarns, filaments, threads, different fabric types, etc. At first, the word "textiles" only referred to woven fabrics. However, weaving is not the ...
, motorcycles, cars, machinery
A machine is a physical system using power to apply forces and control movement to perform an action. The term is commonly applied to artificial devices, such as those employing engines or motors, but also to natural biological macromolecule ...
, agricultural equipment
Agricultural machinery relates to the mechanical structures and devices used in farming or other agriculture. There are many types of such equipment, from hand tools and power tools to tractors and the countless kinds of farm implements that they ...
, food and beverages, chemical and petrochemical, pharmaceuticals
A medication (also called medicament, medicine, pharmaceutical drug, medicinal drug or simply drug) is a drug used to diagnose, cure, treat, or prevent disease. Drug therapy (pharmacotherapy) is an important part of the medical field and rel ...
, paper and cellulose, telecommunications, computers
A computer is a machine that can be programmed to carry out sequences of arithmetic or logical operations (computation) automatically. Modern digital electronic computers can perform generic sets of operations known as programs. These programs ...
and electronics, etc.), commerce and services.
The Campinas Metropolitan Region is home to many national and international high-tech industries and IT companies, including IBM, Dell
Dell is an American based technology company. It develops, sells, repairs, and supports computers and related products and services. Dell is owned by its parent company, Dell Technologies.
Dell sells personal computers (PCs), servers, data ...
, Motorola, NXP
NXP Semiconductors N.V. (NXP) is a Dutch semiconductor designer and manufacturer with headquarters in Eindhoven, Netherlands. The company employs approximately 31,000 people in more than 30 countries. NXP reported revenue of $11.06 billion in 2 ...
, Lucent, Nortel, Compaq, Celestica, Samsung, Alcatel, Bosch, 3M, Texas Instruments, CI&T anDaitan
The airline
TRIP Linhas Aéreas
TRIP Linhas Aéreas S/A (formerly Transporte Aéreo Regional do Interior Paulista) was a domestic regional airline based in Belo Horizonte, Minas Gerais, Brazil.
According to the National Civil Aviation Agency of Brazil (ANAC) between January an ...
is headquartered in Campinas. The Viracopos airport is also the operational hub of Azul Airlines
Azul Linhas Aéreas Brasileiras S/A (''Azul Brazilian Airlines''; or simply Azul) is a Brazilian carrier based in Barueri, a suburb of São Paulo. The company's business model is to stimulate demand by providing frequent and affordable air serv ...
.
The automotive industry is also heavily represented: General Motors
The General Motors Company (GM) is an American Multinational corporation, multinational Automotive industry, automotive manufacturing company headquartered in Detroit, Michigan, United States. It is the largest automaker in the United States and ...
, Mercedes-Benz, Honda, Magneti Marelli, Eaton Corporation
Eaton Corporation plc is an American-Irish multinational power management company with 2021 sales of $19.63 billion, founded in the United States with global headquarters in Dublin, Ireland, and a secondary administrative center in Beachwood, ...
, Tenneco, Toyota and many others are present. It also has a sizable pharmaceutical industry sector, with companies like Medley Farma, EMS Farma, Altana, Merck Sharp and Dohme, Cristália
Cristália is a Brazilian municipality located in the north of the state of Minas Gerais. In 2020 the population was 5,982 in a total area of 841 km2. The elevation is 728 meters. It became a municipality in 1962.
Location and Distances
...
, Valeo
Valeo is a French global automotive supplier headquartered in France, listed on the Paris Stock Exchange ( CAC-40 Index). It supplies a wide range of products to automakers and the aftermarket. The Group employs 113,600 people in 33 countries wo ...
, etc.
In addition the region is home to many research centers and universities, such as the Brazilian Synchrotron Light Laboratory, Brazilian Nanotechnology National Laboratory
Brazilian commonly refers to:
* Something of, from or relating to Brazil
* Brazilian Portuguese, the dialect of the Portuguese language used mostly in Brazil
* Brazilians, the people (citizens) of Brazil, or of Brazilian descent
Brazilian may also ...
, National Laboratory of Science and Technology of Bioethanol
National may refer to:
Common uses
* Nation or country
** Nationality – a ''national'' is a person who is subject to a nation, regardless of whether the person has full rights as a citizen
Places in the United States
* National, Maryland, ce ...
, Brazilian Biosciences National Laboratory
Brazilian commonly refers to:
* Something of, from or relating to Brazil
* Brazilian Portuguese, the dialect of the Portuguese language used mostly in Brazil
* Brazilians, the people (citizens) of Brazil, or of Brazilian descent
Brazilian may also ...
, Centro de Pesquisa e Desenvolvimento em Telecomunicações
CPQD is a Research and Development Center in Telecommunications and one of the largest Latin American R&D centers in Telecommunications and IT. Located in Campinas, São Paulo, Brazil, CPQD has operated as a contractor for institutions and enterp ...
(CPqD), CenPRA, Embrapa
The Brazilian Agricultural Research Corporation (Embrapa - pt, Empresa Brasileira de Pesquisa Agropecuária) is a state-owned research corporation affiliated with the Brazilian Ministry of Agriculture. Since its inception on April 26, 1973, it ha ...
, Unicamp, Facamp and Puccamp
The Pontifical Catholic University of Campinas ( pt, Pontifícia Universidade Católica de Campinas, PUC-Campinas; ) is a private and non-profit Catholic university, located in Campinas, the second largest city in the State of São Paulo. The univ ...
. According to thTimes Higher Education 2007 World University Rankings
the University of Campinas ( Unicamp) is the 177th best university in the world, and the 2nd best in Latin America (after the University of São Paulo in 176th place). Campinas also boasts the largest number of high-tech business incubators and industrial parks (a total of eight), such as the CIATEC I and II, Softex, TechnoPark, InCamp, Polis, TechTown, Industrial Park of Campinas, and others. The presence of one of the largest
oil refineries
An oil refinery or petroleum refinery is an industrial process plant where petroleum (crude oil) is transformed and refined into useful products such as gasoline (petrol), diesel fuel, asphalt base, fuel oils, heating oil, kerosene, liquefie ...
in Latin America ( of crude per day), operated by Petrobras
Petróleo Brasileiro S.A., better known by the portmanteau Petrobras (), is a state owned enterprise, state-owned Brazilian multinational corporation in the petroleum industry headquartered in Rio de Janeiro, Brazil. The company's name transla ...
in the neighboring county of Paulínia, has attracted many petrochemical companies to the Campinas area, including DuPont
DuPont de Nemours, Inc., commonly shortened to DuPont, is an American multinational chemical company first formed in 1802 by French-American chemist and industrialist Éleuthère Irénée du Pont de Nemours. The company played a major role in ...
, Rhone-Poulenc, and Royal Dutch Shell.
The Brazilian Pró-Álcool Program was developed in Campinas: a whole industry based on the use of ethanol as a combustible for motor vehicles, going from a new sucrose
Sucrose, a disaccharide, is a sugar composed of glucose and fructose subunits. It is produced naturally in plants and is the main constituent of white sugar. It has the molecular formula .
For human consumption, sucrose is extracted and refined ...
-rich sugarcane
Sugarcane or sugar cane is a species of (often hybrid) tall, Perennial plant, perennial grass (in the genus ''Saccharum'', tribe Andropogoneae) that is used for sugar Sugar industry, production. The plants are 2–6 m (6–20 ft) tall with ...
, to alcohol refineries, a huge distribution system, and, most recently, an internal combustion engine capable of using either gasoline or ethanol.
Other examples of Campinas-bred technologies are fiber optics
An optical fiber, or optical fibre in Commonwealth English, is a flexible, transparent fiber made by drawing glass (silica) or plastic to a diameter slightly thicker than that of a human hair. Optical fibers are used most often as a means to ...
, lasers for telecommunications and medical applications, integrated circuit
An integrated circuit or monolithic integrated circuit (also referred to as an IC, a chip, or a microchip) is a set of electronic circuits on one small flat piece (or "chip") of semiconductor material, usually silicon. Large numbers of tiny ...
s design and fabrication, satellite environmental monitoring of natural resources, software for agriculture, digital telephone switches, deep-water oil exploration platforms and technologies, biomedical equipment, medical software, genetic engineering
Genetic engineering, also called genetic modification or genetic manipulation, is the modification and manipulation of an organism's genes using technology. It is a set of technologies used to change the genetic makeup of cells, including t ...
and recombinant DNA technologies for food production and pharmaceutics, and food engineering. Because of this, Campinas has been called the Brazilian Silicon Valley.
Socio-economic conditions
Despite Campinas' position of wealth and social and economic opportunity vis-a-vis the rest of the country, the average per capita income of little more than US$17,700 per year clearly indicates that there are problems. If re-evaluated in terms of PPP (Purchasing Power Parity
Purchasing power parity (PPP) is the measurement of prices in different countries that uses the prices of specific goods to compare the absolute purchasing power of the countries' currency, currencies. PPP is effectively the ratio of the price of ...
), Campinas' average income looks better (roughly US$12,300 per year).
Culture
 The responsible for the cultural sector of Campinas is the City Department of Culture, which aims to plan and implement the cultural policy of the municipality through the development of programs, projects, and activities aimed at cultural development.
The city has always been a cultural center in the State of São Paulo. This has increased greatly with the proliferation of universities. Campinas has three theater houses, a
The responsible for the cultural sector of Campinas is the City Department of Culture, which aims to plan and implement the cultural policy of the municipality through the development of programs, projects, and activities aimed at cultural development.
The city has always been a cultural center in the State of São Paulo. This has increased greatly with the proliferation of universities. Campinas has three theater houses, a symphony orchestra
An orchestra (; ) is a large instrumental ensemble typical of classical music, which combines instruments from different families.
There are typically four main sections of instruments:
* bowed string instruments, such as the violin, viola, ce ...
, (considered one of the three best of the country), now under Principal Conductor Parcival Módolo and Karl Martin
Johann Karl Ludwig Martin (24 November 1851, Jever (Ostfriesland) – 14 November 1942, Leiden) was a German geologist. He was professor in geology at Leiden University from 1877 to 1922. From 1880 to 1922 he also was director of the Geological Mu ...
, classical music ensembles, choral groups, 43 movie screens and over a dozen cinemas, dozens of libraries (including a municipal library), art galleries, museums, etc.
Tourism and recreation
Tourist attractions include: * the Bosque dos Jequitibás, an urban preserved wooded area reminiscent of the original rain forest that covered the region in the past: it has a small zoo with local fauna and a natural history museum * the cathedral, which was built in the 19th century; its interior is entirely made of jacaranda wood sculptures and works. It was made using a technique called "taipa de pilão" using clay and rocks – it is one of the largest buildings in the world using this construction technique; * the Central Market, with typical stall stands full of the fresh products of the region * the old Central Railway Station, now converted to a cultural center; * ''Centro de Convivência'', a cultural complex of theater, an open arena for concerts and spectacles, and a plaza where Campinas Symphony Orchestra often plays to the public, during on Sundays this place receive many art exhibitors known by most people aHippie Fair.

 * the ''Castelo'' (Castle) Water Tower, which provides views over the downtown;
* the Historical Railway Society of Campinas, which maintains the Anhumas station, a set of steam
* the ''Castelo'' (Castle) Water Tower, which provides views over the downtown;
* the Historical Railway Society of Campinas, which maintains the Anhumas station, a set of steam locomotive
A locomotive or engine is a rail transport vehicle that provides the Power (physics), motive power for a train. If a locomotive is capable of carrying a payload, it is usually rather referred to as a multiple unit, Motor coach (rail), motor ...
s and full carriages and which promotes regular trips along a picturesque region dotted with old coffee farms;
* the Lagoa do Taquaral
Parque Portugal, also known as Lagoa do Taquaral (), is an urban public park in the city of Campinas, São Paulo, Brazil. It has been set around a beautiful lagoon and adjacent wooded park, and is a large municipal entertainment and sports park, wi ...
Park, a much-beloved urban lagoon and adjacent wooded park, includes: a planetarium
A planetarium ( planetariums or ''planetaria'') is a theatre built primarily for presenting educational and entertaining shows about astronomy and the night sky, or for training in celestial navigation.
A dominant feature of most planetarium ...
, a science museum, an indoor sports stadium and swimming pool, kart racing (now deactivated) and model airplane areas, an open concert auditorium, a floating caravel replica, an electric tramway (streetcar line), pedalos, plus facilities for several types of sports, including a long track for running and walking;
Campinas' readers of the '' Correio Popular'' newspaper and the Cosmo Website voted in July 2007 for the "Seven Wonders of Campinas".
The mountain region around Campinas has better travel and stay opportunities, such as in the spa cities of Serra Negra
Serra Negra is a municipality in the state of São Paulo, Brazil. It belongs to the meso-region of Campinas. Population (2020) was 29,452 inhabitants. Total area: 203,5 km2, demographic density: 112 inhabitants/km2
Location
The name of th ...
and Águas de Lindóia Águas may refer to:
Places
* Dos Aguas, a municipality in the Valencian Community, Spain
* Aguas, municipality in Aragon, Spain
* Palace of the Marqués de Dos Aguas, a Rococo palace in Valencia, Spain
People
People with this surname include:
* J ...
; and in Holambra
Holambra (from the words Holland-America-Brazil) is a municipality in the state of São Paulo in Brazil. It is part of the Metropolitan Region of Campinas. Holambra is the largest producer of flowers and ornamental plants in Latin America, also ho ...
, a rural region which was populated by immigrants from the Netherlands, with an annual flower festival and typical buildings and restaurants.
Seven Wonders of Campinas
The ''Seven Wonders of Campinas'' is a list of the most popular tourism spots in the city of Campinas, as voted for by the readers of '' Correio Popular'' newspaper and the Cosmo On-Line web portal. They are:Culture Station
The old train station of Companhia Paulista Railways, a symbol of the city of Campinas and of the development of the State of São Paulo, changed its name, was restored and converted into an important center forrecreation
Recreation is an activity of leisure, leisure being discretionary time. The "need to do something for recreation" is an essential element of human biology and psychology. Recreational activities are often done for enjoyment, amusement, or pleasur ...
and culture for the entire population. Workshops, concerts and other cultural activities are held throughout the year.
Metropolitan Cathedral
The construction of the Cathedral began in October 1807 and extended for more than seventy years until its inauguration in December 1883. The entire structure was made of compressed clay, a construction technique of old tradition in São Paulo. The internal decoration is made of dark jacaranda wood, The four bells in the main tower are a century old.Parque Portugal
Aimed at leisure and sports, the " Bamboo Grove Lagoon" brings together a wide variety of recreational and cultural resources, such as paddleboats, an exact replica of the caravel ship that brought Pedro Álvares Cabral to discover Brazil,picnic
A picnic is a meal taken outdoors ( ''al fresco'') as part of an excursion, especially in scenic surroundings, such as a park, lakeside, or other place affording an interesting view, or else in conjunction with a public event such as preceding ...
groves, bird nurseries; an area with fitness equipment, playground
A playground, playpark, or play area is a place designed to provide an environment for children that facilitates play, typically outdoors. While a playground is usually designed for children, some are designed for other age groups, or people ...
s, snack bar, restrooms and a scenic electric tramway that is operated by restored historic tramcars once used for regular transportation in Campinas.
Jockey Club Building
Inaugurated in 1925, this building held the headquarters of theJockey Club
The Jockey Club is the largest commercial horse racing organisation in the United Kingdom. It owns 15 of Britain's famous racecourses, including Aintree, Cheltenham, Epsom Downs and both the Rowley Mile and July Course in Newmarket, amo ...
of Campinas. The building has a classic facade and interior inspired by French palace
French (french: français(e), link=no) may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to France
** French language, which originated in France, and its various dialects and accents
** French people, a nation and ethnic group identified with France ...
s of the late 18th century.
Old Market
Located in the central region of Campinas, the Municipal Market, better known as "Mercadão", was inaugurated on April 12, 1908, by Mayor Orosimbo Maia. The work of architectRamos de Azevedo
Francisco de Paula Ramos de Azevedo (8 December 1851 — 13 June 1928) was a Brazilian architect, known for designing various buildings and landmarks in São Paulo, such as the Teatro Municipal, the Mercado Municipal and the Pinacoteca. He was o ...
, is still working today, with its colorful stalls full of fresh produce from the fields.
Army Cadets School
The project, in Spanish colonial style, was designed and conducted by the architect Ernani Do Val Penteado and inaugurated on January 23, 1959. Since 1961 theEscola Preparatória de Cadetes do Exército
The Escola Preparatória de Cadetes do Exército - EsPCEx (Brazilian Army Preparatory School of Cadets) is a coeducational one-year military school in Campinas, São Paulo, Brazil. EsPCEx started construction in 1944, but due to budget constrain ...
(Preparatory School of the Brazilian Army) of Campinas has become the legitimate custodian of the traditions of the preparatory education of the Brazilian Army. Its one-year course has university level and prepares the future cadets of the Academia Militar das Agulhas Negras.
Castle Tower
This water tower was built between 1936 and 1940 in the highest altitude point inside the urban area, 735 meters above sea level. From its gazebo on the top, one can enjoy a wide panorama view of the city.Other tourist spots
A number of other attractions were voted in the poll:Sports
Pacaembu
Pacaembu () is a municipality in the state of São Paulo in Brazil
Brazil ( pt, Brasil; ), officially the Federative Republic of Brazil (Portuguese: ), is the largest country in both South America and Latin America. At and with over 217 ...
, in São Paulo and São Januário
SAO or Sao may refer to:
Places
* Sao civilisation, in Middle Africa from 6th century BC to 16th century AD
* Sao, a town in Boussé Department, Burkina Faso
* Saco Transportation Center (station code SAO), a train station in Saco, Maine, U. ...
, in Rio de Janeiro. The city is still home to several sporting events in other modalities, such as Corrida Integração (Integration Race), which is held since 1983 by Pioneer Broadcasters Television (EPTV), being divided into two modes (a 5 km-dedicated to disabled people and wheelchair users, and another 10 km, for non-disabled people).
Campinas also has a tradition in the Open Games of the Interior, created in 1936, and competition involving various sports. Four times, hosted the competition (1939, 1945, 1960, and 1994), and ten times the city came out as the winner of the competition (1939, 1955, 1956, 1958, 1960, 1971, 1974, 1975, 1978, 1979), being the third city which has won the most competition.
In tennis, there is the Tennis Club of Campinas (CBT), which was created in 1913, offering, in addition to the blocks of the sport, swimming pools, courts for basketball and soccer, as well as rooms suitable for the practice of judo, gymnastics, and dance. Club de Regatas Campineiro and Swim (CCRN) also provides space for the practice of various types of Olympic sports.
The city is still home to several sporting events in other modalities, such as Corrida Integração (Integration Race), which is held since 1983 by Pioneer Broadcasters Television (EPTV), being divided into two modes (a 5 km-dedicated to disabled people and wheelchair users, and another 10 km, for non-disabled people).
Campinas also has a tradition in the Open Games of the Interior, created in 1936, and competition involving various sports. Four times, hosted the competition (1939, 1945, 1960, and 1994), and ten times the city came out as the winner of the competition (1939, 1955, 1956, 1958, 1960, 1971, 1974, 1975, 1978, 1979), being the third city which has won the most competition.
In tennis, there is the Tennis Club of Campinas (CBT), which was created in 1913, offering, in addition to the blocks of the sport, swimming pools, courts for basketball and soccer, as well as rooms suitable for the practice of judo, gymnastics, and dance. Club de Regatas Campineiro and Swim (CCRN) also provides space for the practice of various types of Olympic sports.
Government
The municipality is subdivided into one main district and four subdistricts, Joaquim Egídio,Sousas Sousas () is one of the six districts in the city of Campinas, in the state of São Paulo
São Paulo (, ; Portuguese for ' Saint Paul') is the most populous city in Brazil, and is the capital of the state of São Paulo, the most populous and ...
, Barão Geraldo and Nova Aparecida. There are also 14 regional administrations.
The Secretariat of International Cooperation (SMCI) was created on April 28, 1994. It is one of the 18 Secretariats of the City Hall of Campinas and it is currently located in that building.
Its main goals are:
* the attraction and facilitation for the arrival of new investments to the city;
* the expansion of the companies activities that are already established in the city;
* the perpetuation of the relations between the city, its international community, and partners, such as the Sister-Cities.
The Secretariat also acts as a supporter to other secretariats in the City Hall, often through: the identification of national and foreign potentials investors; keeping systematic contacts with executives in Brazil and abroad, Embassies, Chambers of Commerces and relevant International Organizations; presenting Campinas to the cities and interested investors.
Mayors
* Orozimbo Maia – 1904, 1908–1910, 1926–1930 *Ruy Hellmeister Novais
Ruy Hellmeister Novais was a Brazilian politician from Campinas, who was twice elected mayor
In many countries, a mayor is the highest-ranking official in a municipal government such as that of a city or a town. Worldwide, there is a wide ...
– 1956–1959, 1964–1969
* Orestes Quércia
Orestes Quércia () (18 August 1938 – 24 December 2010) was a Brazilian politician. He was the 28th governor of São Paulo State.
Quércia moved with his family from Pedregulho to the city of Campinas, where he graduated in journalism. He was ...
– 1969–1972
* Lauro Péricles Gonçalves; 1973–1976
* Francisco Amaral; 1977–1982, 1997–2001
* José Roberto Magalhães Teixeira
José Roberto Magalhães Teixeira was a Brazilian politician, twice mayor of the municipality of Campinas, in the state of São Paulo.
Born in Andradas, state of Minas Gerais, on 18 June 1937, he moved to Campinas in 1957, in order to study den ...
– 1983–1988, 1993–1996 (died of hepatic cancer while in office)
* Jacó Bittar – 1989–1992
* Antonio da Costa Santos
Antonio is a masculine given name of Etruscan origin deriving from the root name Antonius. It is a common name among Romance language-speaking populations as well as the Balkans and Lusophone Africa. It has been among the top 400 most popular male ...
(''Toninho'') – 2001 (murdered while in office)
* Izalene Tiene
Izalene Tiene (born 20 March 1943) is a Brazilian social worker and politician, affiliated to the Brazilian Worker's Party (PT).
In 2000 she was elected vice-Mayor of Campinas
Campinas (, ''Plains'' or ''Meadows'') is a Brazilian municipalit ...
– 2001–2005
* Hélio de Oliveira Santos
Hélio de Oliveira Santos (born September 7, 1950, Corumbá, Mato Grosso do Sul) is a physician, graduated in the Medical School of the State University of Campinas and specialized in pediatrics, federal representative, and was the mayor of the m ...
(''Dr. Hélio'') – 2005–2011 (deposed)
* Demétrio Vilagra – 2011(removed)
* Pedro Serafim Júnior – 2011
* Demétrio Vilagra – 2011 (deposed)
* Pedro Serafim Júnior – 2011–2012 (interim)
* Jonas Donizette – 2013–2020
* Dário Saadi – 2021–present
Infrastructure




Transportation
Campinas is a major transportation and telecommunications hub for the State of São Paulo, as it is located on the major motorways that connect thecapital
Capital may refer to:
Common uses
* Capital city, a municipality of primary status
** List of national capital cities
* Capital letter, an upper-case letter Economics and social sciences
* Capital (economics), the durable produced goods used f ...
to the Northwest and Northern parts of the State. The city is served by the Campinas Beltway (''Anel Viário'') and the following main motorways:
* Rodovia Anhangüera
The Rodovia Anhanguera (official designation SP-330) (In English: Anhanguera Highway) is a highway in the state of São Paulo, Brazil. It is one of the country's busiest transportation corridors. A 2005 survey conducted amongst Brazilian truck d ...
* Rodovia dos Bandeirantes
The Rodovia Bandeirantes (official designation SP-348) is a highway in the state of São Paulo, Brazil.
Once the traffic capacity of the Anhangüera Highway was exceeded in the 1960s, the state government decided to build another highway, with ...
* Rodovia Santos Dumont
Rodovia Santos Dumont (officially designated SP-075) is a highway in the state of São Paulo, Brazil.
It runs in a north–south direction and interconnects the cities of Campinas, Indaiatuba, Salto, Itu and Sorocaba, crossing with two other m ...
* Rodovia Dom Pedro I
Rodovia Dom Pedro I (official designation SP-065) is a highway in the state of São Paulo, Brazil.
One of the most modern and scenic highways in the country, it interconnects the Anhangüera and the Presidente Dutra highways, serving the major ...
* Rodovia Adhemar de Barros
Rodovia Adhemar de Barros (official designation SP-340) is a highway in the state of São Paulo, Brazil. It is 170 km long.
The highway follows very closely a south–north direction, departing from the city of Campinas, then passing by Jagu ...
* Rodovia Professor Zeferino Vaz
* Rodovia Jornalista Francisco Aguirre Proença
Rodovia Jornalista Francisco Aguirre Proença (SP-101) is a state highway in the State of São Paulo which connects the cities of Campinas, Hortolândia, Monte Mor, Elias Fausto and Capivari. Its first 25 kilometers are double-laned, the rest i ...
All these motorways are built according to the highest international standards (see highway system of São Paulo The highway system of São Paulo is the largest statewide road transportation system in Brazil, with 34,650 km. It consists of a hugely interconnected network of municipal (11,600 km), state (22,000 km) and federal (1,050 km) roa ...
). The Anel Viário José Magalhães Teixeira
The Independent Greeks - National Patriotic Alliance ( el, Ανεξάρτητοι Έλληνες (ΑΝΕΛ), ''Anexartitoi Ellines'', ANEL) is a national-conservative political party in Greece.
The party was the junior coalition partner to the ...
(SP-038) around the city currently interconnects the Anhangüera and Dom Pedro I motorways.
The main airport of the city is Viracopos International Airport, located from Downtown Campinas and from the city of São Paulo. The airport is the second largest cargo terminal in Brazil. It is one of the fastest-growing airports in the country, and since it was turned over to the private sector in 2012, a number of improvements and innovations have been implemented through the Viracopos Brazil Airports concession.
A second facility, Campo dos Amarais Airport located from downtown Campinas, is dedicated to general aviation.
Campinas public transportation statistics
The average amount of time people spend commuting with public transit in Campinas, for example to and from work, on a weekday is 77 min. 21% of public transit riders, ride for more than 2 hours every day. The average amount of time people wait at a stop or station for public transit is 23 min, while 52% of riders wait for over 20 minutes on average every day. The average distance people usually ride in a single trip with public transit is 7.9 km, while 16% travel for over 12 km in a single direction.Education

 Portuguese is the official national language, and thus the primary language taught in schools. But English and Spanish are part of the official high school curriculum.
Portuguese is the official national language, and thus the primary language taught in schools. But English and Spanish are part of the official high school curriculum.
Universities and colleges
* Unicamp ( Universidade Estadual de Campinas); * IFSP ( Instituto Federal de São Paulo); * INPG Business School (Instituto Nacional de Pós-Graduação)INPG
* PUC-Campinas (
Pontifícia Universidade Católica de Campinas
The Pontifical Catholic University of Campinas ( pt, Pontifícia Universidade Católica de Campinas, PUC-Campinas; ) is a private and non-profit Catholic university, located in Campinas, the second largest city in the State of São Paulo. The univ ...
);
* UNIP (Universidade Paulista);
* FACAMP (Faculdades de Campinas);
* METROCAMP (Faculdade Integrada Metropolitana de Campinas);
* IPEP (Faculdades Integradas IPEP);
* UNISAL (Centro Universitário Salesiano de São Paulo);
* USF (Universidade São Francisco
The Universidade São Francisco (USF; en, University of San Francisco) is a small university in Brazil, founded in 1976 by Franciscan priests.
It has campuses in four cities in the State of São Paulo: Bragança Paulista, Itatiba, Campinas, and ...
);
* ESAMC (Escola Superior de Administração, Marketing e Comunicação);
* Universidade Mackenzie
Mackenzie Presbyterian University (Portuguese: ''Universidade Presbiteriana Mackenzie'') is a private university in São Paulo, Brazil.
The Mackenzie Presbyterian University is an institution of higher learning that has strong tradition and history ...
;
* FAC (Faculdades Comunitárias de Campinas);
* Faculdades Fleming;
* Faculdade de Odontologia São Leopoldo Mandic.
Fatec Campinas
Technical schools
* ETE Bento Quirino (Escola Técnica Estadual Bento Quirino) * ETEC (Escola Técnica de Campinas) * ETECAP (Escola Técnica Estadual Conselheiro Antonio Prado) * POLI Bentinho (Colégio Politécnico Bento Quirino) * COTUCA (Colégio Técnico da Universidade de Campinas) *SENAI
:For the Malaysian town with the same name, see Senai.''
Serviço Nacional de Aprendizagem Industrial (SENAI), Portuguese language for ''National Service for Industrial Training'' is a network of profitable secondary level professional schools es ...
(Serviço Nacional de Aprendizagem Industrial)
* IFSP ( Instituto Federal de São Paulo)
Media
Three daily newspapers are published in Campinas, all owned by media companyRede Anhangüera de Comunicação
Rede is an archaic word meaning, among other things, " counsel" and "advice". It is cognate with Dutch "raad", Luxembourgish "Rot", Common Scandinavian "råd", Icelandic "ráð" and German "Rat".
Rede may refer to:
People
* Edward Rede (by 14 ...
: Correio Popular, Diário do Povo
''Diário do Povo'' (Portuguese for ''People's Diary'') is a newspaper published in the city of Campinas, state of São Paulo, Brazil.
''Correio Popular'' is owned and managed by a larger communications holding company, ''Rede Anhangüera de ...
and Notícia Já
''Notícia Já'' is a popular daily newspaper in the city of Campinas, state of São Paulo (state), São Paulo, Brazil. It was founded in 2007, and has a tabloid (newspaper format), tabloid format.
Currently it has an audited circulation of 60,000 ...
(a tabloid). Several other local newspapers with weekly or monthly circulation are also published. Several magazines are also published in Campinas, the largest one being ''Metrópole'', which circulates on Sundays as a supplement to ''Correio Popular''.
The city has also a large number of radio stations as well as several local TV stations, including ''TV Universidades'' and ''Fenix TV'' (both not-for-profit), distributed by Net Campinas, the local cable distributor.Campinas
was the first city in Brazil, outside the capitals of Brazilian states, which received the transmission in digital signal for TV, by EPTV, an affiliate of Rede Globo, on October 3, 2008. It currently has the second TV station that also broadcasts the signal by TVB, now an affiliate of Rede Record, since February 2011 (before
SBT
sbt is an open-source build tool for Scala and Java projects, similar to Apache's Maven and Gradle.
Its main features are:
*Native support for compiling Scala code and integrating with many Scala test frameworks
*Continuous compilation, t ...
, when it began on May 8, 2010).
Notable people
*Campos Sales
Manoel Ferraz de Campos Salles (; 15 February 1841 – 28 June 1913) was a Brazilian lawyer, coffee farmer, and politician who served as the fourth president of Brazil. He was born in the city of Campinas, São Paulo. He graduated as a law ...
(politician, fourth president of Brazil)
* Carlos Gomes (opera composer)
* Nelsinho Baptista (footballer)
* Olavo de Carvalho (philosopher and writer)
* Daniel Dias
Daniel de Faria Dias (born 24 May 1988) is a Brazilian Paralympic swimmer. Having learnt to swim in 2004 after being inspired by Clodoaldo Silva at the 2004 Summer Paralympics, he entered his first international competition two years later winni ...
(paralympic swimmer)
* Lovefoxxx
Luísa Hanae Matsushita (born February 25, 1984), known by her stage name Lovefoxxx, is the lead singer of the Brazilian indie band Cansei de Ser Sexy (CSS).
Early life and career
Lovefoxxx was born in Campinas, Brazil. She is of Portuguese, G ...
(singer)
* Rubem Alves (philosopher and writer)
* Marcelo Damy (physicist)
* Gilberto de Nucci Gilberto De Nucci (born 18 March 1958, Campinas) is a noted Brazilian physician, scientist and university professor in the field of pharmacology.
Education
He was born in Campinas, state of São Paulo (state), São Paulo, Brazil. His father was a w ...
(physician and biomedical researcher)
* Renato M.E. Sabbatini
Renato Marcos Endrizzi Sabbatini (born 20 February 1947, Campinas) is a retired professor at the Department of Biomedical Engineering and at the State University of Campinas Institute of Biology. He received a B.Sc. in Biomedical Sciences from ...
(biomedical scientist and writer)
* Regina Duarte (actress)
* Hércules Florence (inventor)
* Luís Fabiano (footballer)
* Carlos Roberto Martins
Carlos Wizard Martins (born 1956) is a Brazilian entrepreneur and founder of Grupo Multi, a company that offers franchises for English courses. Grupo Multi was bought out by Pearson in 2013.
Biography
He was born in Curitiba, Paraná, Brazil ...
(entrepreneur)
* Crodowaldo Pavan (biologist and scientist)
* José Aristodemo Pinotti (physician, former dean of UNICAMP)
* Zeferino Vaz
Zeferino Vaz (May 27, 1908 – February 19, 1981) led the construction, establishment and development of the Unicamp university, in the interior of the State of São Paulo, Brazil in the 1960s and 1970s. The main campus is named after Zeferin ...
(physician, former dean of UNICAMP)
* Hilda Hilst (writer)
* Oliver Minatel
Oliver Thomal Minatel (born 29 August 1992), known as Oliver, is a Brazilian former professional footballer.
Career
Youth
After spending five years at his home club Guarani, Mintatel joined the esteemed academy of Paulínia in 2007 where he wo ...
(footballer)
* José Pancetti
Giuseppe "José" Pancetti (June 18, 1902 – February 10, 1958) was a Brazilian modernist Painting, painter.
Biography
Born in Campinas into a family of immigrants from Tuscany, Italy, he lived in Campinas until he was 10 years old, when his f ...
(painter)
* Sandy Leah
Sandy Leah Lima (, born 28 January 1983), known mononymously as Sandy, is a Brazilian singer-songwriter and actress. Born and raised in Campinas, Sandy began her career in 1989 when she formed with her brother, musician Junior Lima, the vocal du ...
(singer)
* Fabinho (footballer)
Twin towns – sister cities
Campinas is twinned with: * Asunción, Paraguay (1973) * Auroville, India (2004) * Cabinda, Angola (2009) *Cascais
Cascais () is a town and municipality in the Lisbon District of Portugal, located on the Portuguese Riviera. The municipality has a total of 214,158 inhabitants in an area of 97.40 km2. Cascais is an important tourism in Portugal, tourist de ...
, Portugal (2012)
* Concepción, Chile (1979)
* Córdoba, Argentina (1993)
* Cotorro (Havana), Cuba (2009)
* Daloa
Daloa is a city in western Ivory Coast. It is the seat of both the Sassandra-Marahoué District and the Haut-Sassandra Region. It is also the seat of and a sub-prefectures of Ivory Coast, sub-prefecture of Daloa Department. Daloa is also a Commune ...
, Ivory Coast (1982)
* Durban, South Africa (2009)
* Fuzhou
Fuzhou (; , Fuzhounese: Hokchew, ''Hók-ciŭ''), alternately romanized as Foochow, is the capital and one of the largest cities in Fujian province, China. Along with the many counties of Ningde, those of Fuzhou are considered to constitute t ...
, China (1996)
* Gifu
is a city located in the south-central portion of Gifu Prefecture, Japan, and serves as the prefectural capital. The city has played an important role in Japan's history because of its location in the middle of the country. During the Sengoku ...
, Japan (1982)
* Indianapolis
Indianapolis (), colloquially known as Indy, is the state capital and most populous city of the U.S. state of Indiana and the seat of Marion County. According to the U.S. Census Bureau, the consolidated population of Indianapolis and Marion ...
, United States (2009)
* Jericho
Jericho ( ; ar, أريحا ; he, יְרִיחוֹ ) is a Palestinian city in the West Bank. It is located in the Jordan Valley, with the Jordan River to the east and Jerusalem to the west. It is the administrative seat of the Jericho Gove ...
, Palestine (2003)
* Malito, Italy (2006)
* San Diego, United States (1995)
* Viseu, Portugal (2012)
* Zaragoza, Spain (2013)
Cooperative agreements
Campinas signed Cooperation Protocol with: * Fundão, Portugal (2012)Domestic cooperation
Campinas cooperates with: * Belém, Pará (2003) * Blumenau, Santa Catarina (1983) *Camanducaia
Camanducaia is the southernmost municipality in Minas Gerais, Brazil
Brazil ( pt, Brasil; ), officially the Federative Republic of Brazil (Portuguese: ), is the largest country in both South America and Latin America. At and with over 217 ...
, Minas Gerais (2010)
* Peruíbe
Peruíbe is a municipality in the state of São Paulo in Brazil. It is part of the Metropolitan Region of Baixada Santista. The population is 69,001 (2020 est.) in an area of . Peruíbe is located to the southwest of the city of São Paulo and wes ...
, São Paulo (2007)
* Salinas, Minas Gerais (2012)
* Ubatuba, São Paulo (2007)
References
External links
Official home page
(in Portuguese).
EncontraCampinas - Find everything about Campinas
(in Portuguese)
The Seven Wonders of Campinas
(in Portuguese)
Other Campinas Tourist Spots
(in Portuguese) {{Authority control Populated places established in 1774 1774 establishments in South America