Camp Nong Pladuk on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Camp Nong Pladuk (also: ''Nompuradokku'') was a Japanese prisoner of war transit camp during
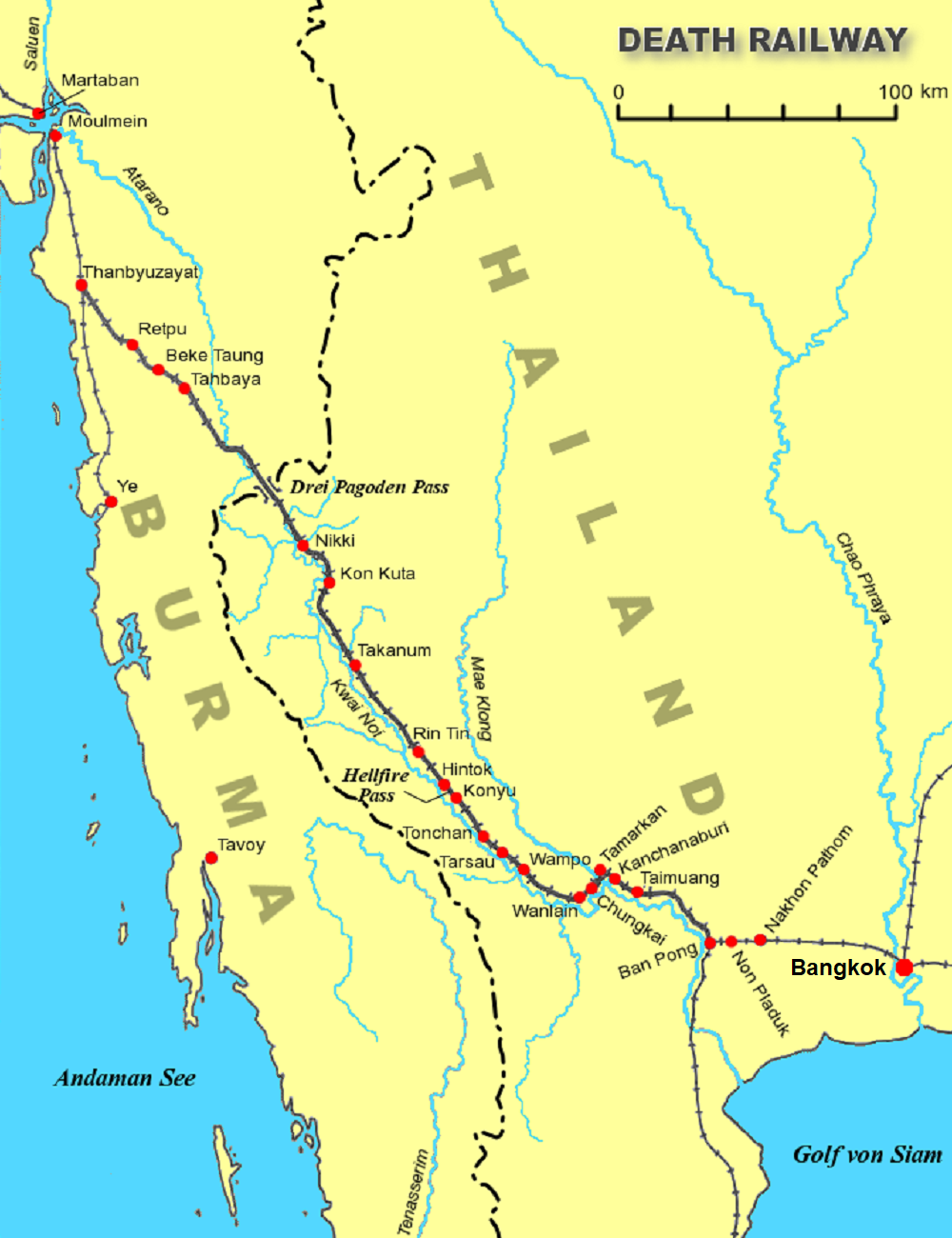 Camp Nong Pladuk was initially used as a transit camp from where the prisoners were transported or had to walk to work camps along the Burma Railway. Later Nong Pladuk was also used a revalidation camp. The work camps were numbered according to the distance in kilometres from Nong Pladuk.
During World War II, at least 23,289 British, 12,329 Dutch, 4,708 Australian, 482 American, and 7,030 undetermined soldiers passed through the camp. Of the 61,811 prisoners deployed on both sides of the railway line, 12,619 died. Of the estimated 177,700 civilian forced laborers deployed, 85,400 died.
In December 1943, a second camp was constructed at Nong Pladuk. The British, Australian and American prisoners were housed in Camp I while Camp II was used for the Dutch prisoners. The proximity to a large
Camp Nong Pladuk was initially used as a transit camp from where the prisoners were transported or had to walk to work camps along the Burma Railway. Later Nong Pladuk was also used a revalidation camp. The work camps were numbered according to the distance in kilometres from Nong Pladuk.
During World War II, at least 23,289 British, 12,329 Dutch, 4,708 Australian, 482 American, and 7,030 undetermined soldiers passed through the camp. Of the 61,811 prisoners deployed on both sides of the railway line, 12,619 died. Of the estimated 177,700 civilian forced laborers deployed, 85,400 died.
In December 1943, a second camp was constructed at Nong Pladuk. The British, Australian and American prisoners were housed in Camp I while Camp II was used for the Dutch prisoners. The proximity to a large
World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposin ...
. It was located about five kilometres from the main railway station of Ban Pong near a junction station ''Junction station'' usually refers to a railway station situated on or close to a junction where lines to several destinations diverge. The usual minimum is three incoming lines. At a station with platforms running from left to right, the minimum ...
on the Southern Line to Bangkok
Bangkok, officially known in Thai language, Thai as Krung Thep Maha Nakhon and colloquially as Krung Thep, is the capital and most populous city of Thailand. The city occupies in the Chao Phraya River delta in central Thailand and has an estima ...
. Nong Pladuk served as the starting point of the Burma Railroad. Numerous British, Dutch, and allied troops passed through Nong Pladuk to construct the railroad. Nowadays, it serves as a rail road maintenance and repair facility.
History
In 1939, plans had been developed by theEmpire of Japan
The also known as the Japanese Empire or Imperial Japan, was a historical nation-state and great power that existed from the Meiji Restoration in 1868 until the enactment of the post-World War II 1947 constitution and subsequent fo ...
to construct a rail road connecting Thailand
Thailand ( ), historically known as Siam () and officially the Kingdom of Thailand, is a country in Southeast Asia, located at the centre of the Indochinese Peninsula, spanning , with a population of almost 70 million. The country is bo ...
with Burma
Myanmar, ; UK pronunciations: US pronunciations incl. . Note: Wikipedia's IPA conventions require indicating /r/ even in British English although only some British English speakers pronounce r at the end of syllables. As John Wells explai ...
. Nong Pladuk was chosen as the starting point, because it was the location of rail yard on the Southern Line to Bangkok. A camp was constructed to the north of the railway.
On 23 June 1942, the first 600 British prisoners arrived from the First Mainland Party lead by Major R.S. Sykes of the 18th Infantry Division. The first groups were tasked to clear the forest, built the shelters, and a Japanese workshop.
The barracks were made of wood with bamboo matting, and contained 200 to 300 prisoners each. There were originally six huts, a cook house with Chinese, British and Dutch canteens, a bamboo church, Japanese quarters and a guardroom. The camp was originally built to house 2,000 prisoners, but was gradually enlarged for 8,000 prisoners. On 16 September 1942, railway construction started at both ends of the planned line.
 Camp Nong Pladuk was initially used as a transit camp from where the prisoners were transported or had to walk to work camps along the Burma Railway. Later Nong Pladuk was also used a revalidation camp. The work camps were numbered according to the distance in kilometres from Nong Pladuk.
During World War II, at least 23,289 British, 12,329 Dutch, 4,708 Australian, 482 American, and 7,030 undetermined soldiers passed through the camp. Of the 61,811 prisoners deployed on both sides of the railway line, 12,619 died. Of the estimated 177,700 civilian forced laborers deployed, 85,400 died.
In December 1943, a second camp was constructed at Nong Pladuk. The British, Australian and American prisoners were housed in Camp I while Camp II was used for the Dutch prisoners. The proximity to a large
Camp Nong Pladuk was initially used as a transit camp from where the prisoners were transported or had to walk to work camps along the Burma Railway. Later Nong Pladuk was also used a revalidation camp. The work camps were numbered according to the distance in kilometres from Nong Pladuk.
During World War II, at least 23,289 British, 12,329 Dutch, 4,708 Australian, 482 American, and 7,030 undetermined soldiers passed through the camp. Of the 61,811 prisoners deployed on both sides of the railway line, 12,619 died. Of the estimated 177,700 civilian forced laborers deployed, 85,400 died.
In December 1943, a second camp was constructed at Nong Pladuk. The British, Australian and American prisoners were housed in Camp I while Camp II was used for the Dutch prisoners. The proximity to a large rail yard
A rail yard, railway yard, railroad yard (US) or simply yard, is a series of tracks in a rail network for storing, sorting, or loading and unloading rail vehicles and locomotives. Yards have many tracks in parallel for keeping rolling stock or u ...
implied it was a target for allied bombers. On 6 September 1944, the camp was hit by five bombs resulting in 92 deaths and 70 wounded. The camp closed on 22 February 1945. Nowadays, the camp is used as a rail road maintenance and repair facility.
There were two large cemeteries to the north-east of the camp. After the war, the bodies were re-buried at the Chungkai and the Kanchanaburi War Cemeteries except for the Americans who were repatriated back to the United States.
References
{{Reflist Japanese prisoner of war and internment camps Military history of Thailand during World War II Buildings and structures in Ratchaburi province World War II prisoner of war camps Burma Railway