Cambridge First Church on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Cambridge ( ) is a university city and the county town in


 Following the
Following the
The 28 Cities of Britain
" at Britannia. 2000. Evidence exists that the invading Anglo-Saxons had begun occupying the area by the end of the century. Their settlement – also on and around Castle Hill – became known as Grantebrycge. ("
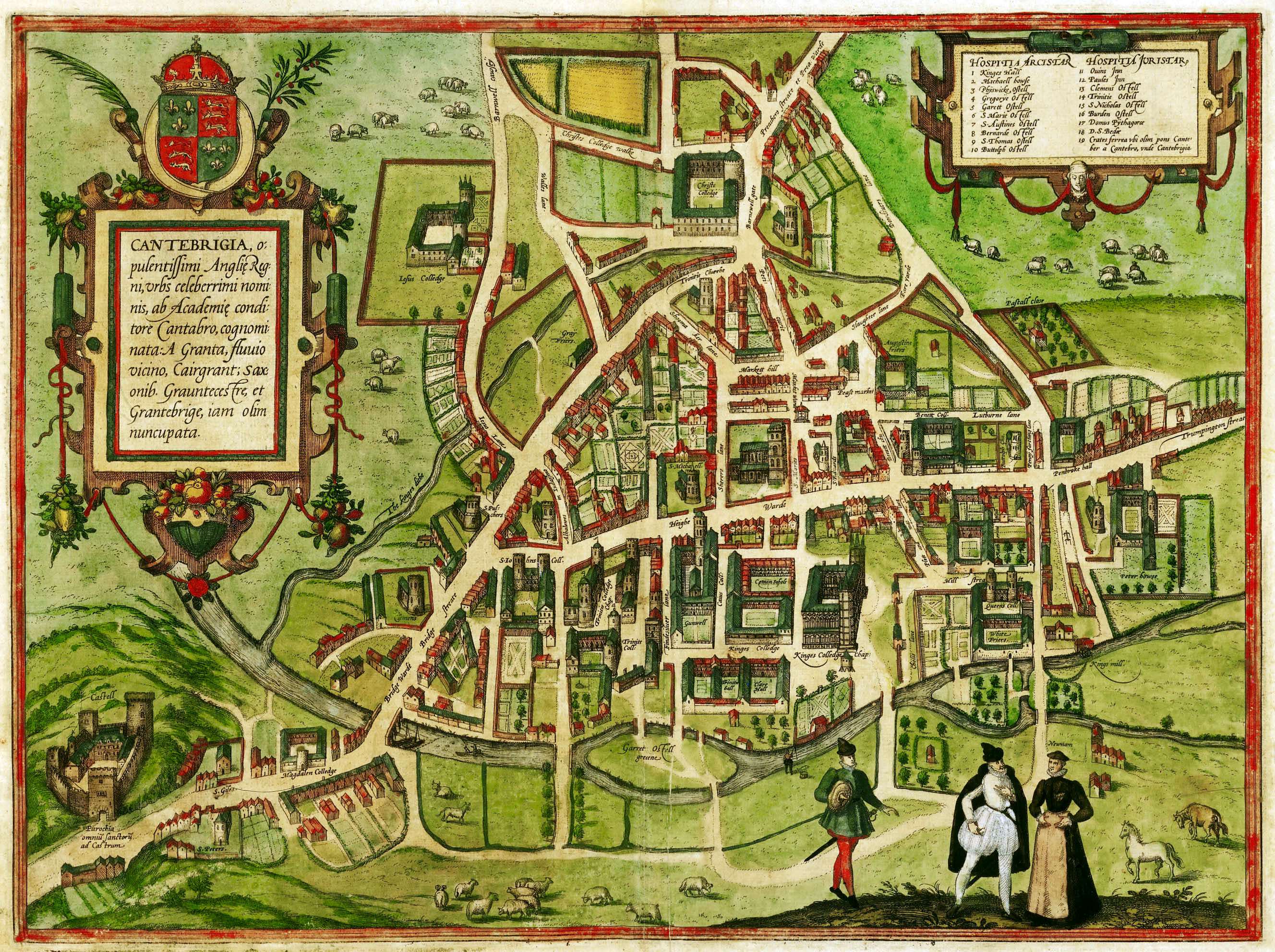 Following repeated outbreaks of pestilence throughout the 16th century, sanitation and fresh water were brought to Cambridge by the construction of
Following repeated outbreaks of pestilence throughout the 16th century, sanitation and fresh water were brought to Cambridge by the construction of
 Cambridge is a
Cambridge is a

 Cambridge is situated about north-by-east of London and 95 miles (152 kilometres) east of Birmingham. The city is located in an area of level and relatively low-lying terrain just south of the Fens, which varies between above mean sea level, above sea level. The town was thus historically surrounded by low-lying wetlands that have been drained as the town has expanded.
The underlying geology of Cambridge consists of gault clay and Chalk Group, Chalk Marl, known locally as Cambridge Greensand, partly overlaid by Gravel, terrace gravel. A layer of Phosphate nodule, phosphatic nodules (coprolites) under the marl was mined in the 19th century for fertiliser; this became a major industry in the county, and its profits yielded buildings such as the Cambridge Corn Exchange, Corn Exchange, Fulbourn Hospital, and St John's College, Cambridge#College Chapel, St. John's Chapel until the Quarries Act 1894 and competition from America ended production.
The River Cam flows through the city from the village of Grantchester, to the southwest. It is bordered by water meadows within the city such as Sheep's Green as well as residential development. Like most cities, modern-day Cambridge has many suburbs and areas of high-density housing. The city centre of Cambridge is mostly commercial, historic buildings, and large green areas such as Jesus Green, Parker's Piece and
Cambridge is situated about north-by-east of London and 95 miles (152 kilometres) east of Birmingham. The city is located in an area of level and relatively low-lying terrain just south of the Fens, which varies between above mean sea level, above sea level. The town was thus historically surrounded by low-lying wetlands that have been drained as the town has expanded.
The underlying geology of Cambridge consists of gault clay and Chalk Group, Chalk Marl, known locally as Cambridge Greensand, partly overlaid by Gravel, terrace gravel. A layer of Phosphate nodule, phosphatic nodules (coprolites) under the marl was mined in the 19th century for fertiliser; this became a major industry in the county, and its profits yielded buildings such as the Cambridge Corn Exchange, Corn Exchange, Fulbourn Hospital, and St John's College, Cambridge#College Chapel, St. John's Chapel until the Quarries Act 1894 and competition from America ended production.
The River Cam flows through the city from the village of Grantchester, to the southwest. It is bordered by water meadows within the city such as Sheep's Green as well as residential development. Like most cities, modern-day Cambridge has many suburbs and areas of high-density housing. The city centre of Cambridge is mostly commercial, historic buildings, and large green areas such as Jesus Green, Parker's Piece and
 At the 2011 Census, the population of the Cambridge contiguous built-up area (urban area) was 158,434, while that of the City Council area was 123,867.
In the United Kingdom Census 2001, 2001 Census held during University term, 89.44% of Cambridge residents identified themselves as white, compared with a national average of 92.12%. Within the university, 84% of undergraduates and 80% of post-graduates identified as white (including overseas students).
Cambridge has a much higher than average proportion of people in the highest paid professional, managerial or administrative jobs (32.6% vs. 23.5%)ONS 2001 Census (Approximated Social Grade – Workplace Population, Cambridge local authority) and a much lower than average proportion of manual workers (27.6% vs. 40.2%). In addition, 41.2% have a higher-level qualification (e.g. degree, Higher National Diploma, Master's or PhD), much higher than the national average proportion (19.7%).
Centre for Cities identified Cambridge as the UK's most unequal city in 2017 and 2018. Residents' income was the least evenly distributed of 57 British cities measured, with its top 6% earners accounting for 19% of its total income and the bottom 20% for only 2%, and a Gini coefficient of 0.460 in 2018.
At the 2011 Census, the population of the Cambridge contiguous built-up area (urban area) was 158,434, while that of the City Council area was 123,867.
In the United Kingdom Census 2001, 2001 Census held during University term, 89.44% of Cambridge residents identified themselves as white, compared with a national average of 92.12%. Within the university, 84% of undergraduates and 80% of post-graduates identified as white (including overseas students).
Cambridge has a much higher than average proportion of people in the highest paid professional, managerial or administrative jobs (32.6% vs. 23.5%)ONS 2001 Census (Approximated Social Grade – Workplace Population, Cambridge local authority) and a much lower than average proportion of manual workers (27.6% vs. 40.2%). In addition, 41.2% have a higher-level qualification (e.g. degree, Higher National Diploma, Master's or PhD), much higher than the national average proportion (19.7%).
Centre for Cities identified Cambridge as the UK's most unequal city in 2017 and 2018. Residents' income was the least evenly distributed of 57 British cities measured, with its top 6% earners accounting for 19% of its total income and the bottom 20% for only 2%, and a Gini coefficient of 0.460 in 2018.
 The town's river link to the surrounding agricultural land, and good road connections to London in the south meant Cambridge has historically served as an important regional trading post. King Henry I granted Cambridge a monopoly on river trade, privileging this area of the economy of Cambridge The town Market Hill, Cambridge, market provided for trade in a wide variety of goods and annual trading fairs such as Stourbridge Fair and Midsummer Fair were visited by merchants from across the country. The river was described in an account of 1748 as being "often so full of [merchant boats] that the navigation thereof is stopped for some time". For example, 2000 wikt:Special:Search/firkin, firkins of butter were brought up the river every Monday from the agricultural lands to the North East, particularity Norfolk, to be unloaded in the town for road transportation to London. Changing patterns of retail distribution and the advent of the railways led to a decline in Cambridge's importance as a market town.
Cambridge today has a diverse economy with strength in sectors such as research and development, software consultancy, high value engineering, creative industries, pharmaceuticals and tourism. Described as one of the "most beautiful cities in the world" by ''Forbes'' in 2010, with the view from The Backs being selected as one of the 10 greatest in England by National Trust for Places of Historic Interest or Natural Beauty, National Trust chair Simon Jenkins, tourism generates over £750 million for the city's economy.
Cambridge and its surrounds are sometimes referred to as
The town's river link to the surrounding agricultural land, and good road connections to London in the south meant Cambridge has historically served as an important regional trading post. King Henry I granted Cambridge a monopoly on river trade, privileging this area of the economy of Cambridge The town Market Hill, Cambridge, market provided for trade in a wide variety of goods and annual trading fairs such as Stourbridge Fair and Midsummer Fair were visited by merchants from across the country. The river was described in an account of 1748 as being "often so full of [merchant boats] that the navigation thereof is stopped for some time". For example, 2000 wikt:Special:Search/firkin, firkins of butter were brought up the river every Monday from the agricultural lands to the North East, particularity Norfolk, to be unloaded in the town for road transportation to London. Changing patterns of retail distribution and the advent of the railways led to a decline in Cambridge's importance as a market town.
Cambridge today has a diverse economy with strength in sectors such as research and development, software consultancy, high value engineering, creative industries, pharmaceuticals and tourism. Described as one of the "most beautiful cities in the world" by ''Forbes'' in 2010, with the view from The Backs being selected as one of the 10 greatest in England by National Trust for Places of Historic Interest or Natural Beauty, National Trust chair Simon Jenkins, tourism generates over £750 million for the city's economy.
Cambridge and its surrounds are sometimes referred to as
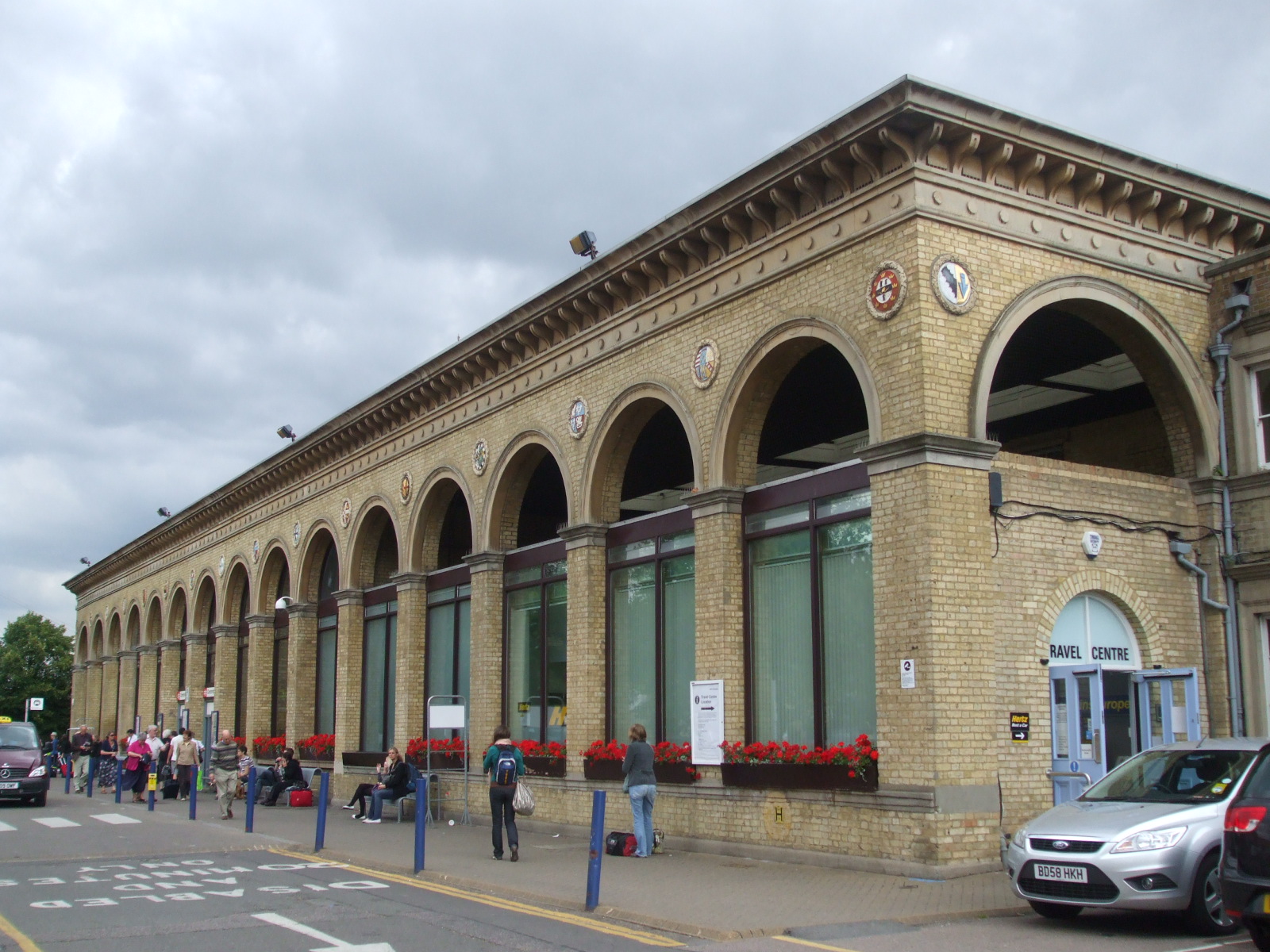
 Cambridge railway station was opened in 1845, initially linking to Bishopsgate railway station, Bishopsgate station in London, via Bishops Stortford. Further lines opened throughout the 19th century, including the Cambridge and St Ives branch line, the Stour Valley Railway, the Cambridge to Mildenhall railway, and the Varsity Line to Oxford. Cherryhinton railway station, Another station was opened in Cherry Hinton though, at the time, this was a separate village to Cambridge. Several of these lines were closed during the 1960s.
Today, Cambridge station has direct rail links to London with termini at (via the Cambridge Line and the East Coast Main Line), (on the West Anglia Main Line) and St Pancras railway station, St Pancras (on the Thameslink line). Commuter trains to King's Cross run every half-hour during peak hours, with a journey time of 53 minutes. Trains also run to and (via the Fen Line), (via the Breckland Line), , Birmingham New Street railway station, Birmingham, , , , Stansted Airport railway station, Stansted Airport, Brighton railway station, Brighton and Gatwick Airport railway station, Gatwick Airport railway stations.
A second railway station, Cambridge North railway station, Cambridge North, opened on 21 May 2017, having originally planned to open in March 2015. A third railway station, , near Addenbrooke's Hospital, has been proposed; it is expected to open in 2025.
Cambridge railway station was opened in 1845, initially linking to Bishopsgate railway station, Bishopsgate station in London, via Bishops Stortford. Further lines opened throughout the 19th century, including the Cambridge and St Ives branch line, the Stour Valley Railway, the Cambridge to Mildenhall railway, and the Varsity Line to Oxford. Cherryhinton railway station, Another station was opened in Cherry Hinton though, at the time, this was a separate village to Cambridge. Several of these lines were closed during the 1960s.
Today, Cambridge station has direct rail links to London with termini at (via the Cambridge Line and the East Coast Main Line), (on the West Anglia Main Line) and St Pancras railway station, St Pancras (on the Thameslink line). Commuter trains to King's Cross run every half-hour during peak hours, with a journey time of 53 minutes. Trains also run to and (via the Fen Line), (via the Breckland Line), , Birmingham New Street railway station, Birmingham, , , , Stansted Airport railway station, Stansted Airport, Brighton railway station, Brighton and Gatwick Airport railway station, Gatwick Airport railway stations.
A second railway station, Cambridge North railway station, Cambridge North, opened on 21 May 2017, having originally planned to open in March 2015. A third railway station, , near Addenbrooke's Hospital, has been proposed; it is expected to open in 2025.
 Cambridge's two universities, the collegiate
Cambridge's two universities, the collegiate
 Cambridge played a unique role in the invention of modern association football, football: the game's first set of rules were drawn up by members of the university in 1848. The Cambridge Rules were first played on Parker's Piece and had a 'defining influence on the 1863 The Football Association, Football Association rules' which again were first played on Parker's Piece.
The city is home to Cambridge United FC, who play at the Abbey Stadium. Formed in 1912, as Abbey United, they were elected to the Football League in 1970 and reached the Football League Second Division in 1978, although a serious decline in them in the mid-1980s saw them drop back down to the Football League Fourth Division and almost go out of business. Success returned to the club in the early 1990s when they won two successive promotions and reached the FA Cup quarter finals in both of those seasons and, in 1992, they came close to becoming the first English team to win three successive Football League promotions which would have taken them into the newly created FA Premier League; however, they were beaten in the play-offs and another decline set in. In 2005, they were relegated from the Football League and, for the second time in 20 years, narrowly avoided going out of business. After nine years of non-league football, they returned to the Football League in 2014 by winning the Conference National play-offs.
Cambridge United WFC is a women's only football club based in Cambridge. The team compete in the FA Women's National League South East. The club plays home games at St Neots Town F.C. and the Abbey Stadium.
Cambridge City FC of the Southern Football League Premier Division now play in the adjoining village of Histon and Impington, Histon. Formed in Cambridge in 1908, as Cambridge Town, the club were Southern Football League, Southern Premier League champions in 1962–63, the highest they have finished in the English football pyramid. After a legal dispute with their landlords, the club left their home ground in Cambridge in order to groundshare with fellow Southern League Premier club Histon FC in 2013-14 and intend to construct a new ground outside the city, in Sawston.
Cambridge played a unique role in the invention of modern association football, football: the game's first set of rules were drawn up by members of the university in 1848. The Cambridge Rules were first played on Parker's Piece and had a 'defining influence on the 1863 The Football Association, Football Association rules' which again were first played on Parker's Piece.
The city is home to Cambridge United FC, who play at the Abbey Stadium. Formed in 1912, as Abbey United, they were elected to the Football League in 1970 and reached the Football League Second Division in 1978, although a serious decline in them in the mid-1980s saw them drop back down to the Football League Fourth Division and almost go out of business. Success returned to the club in the early 1990s when they won two successive promotions and reached the FA Cup quarter finals in both of those seasons and, in 1992, they came close to becoming the first English team to win three successive Football League promotions which would have taken them into the newly created FA Premier League; however, they were beaten in the play-offs and another decline set in. In 2005, they were relegated from the Football League and, for the second time in 20 years, narrowly avoided going out of business. After nine years of non-league football, they returned to the Football League in 2014 by winning the Conference National play-offs.
Cambridge United WFC is a women's only football club based in Cambridge. The team compete in the FA Women's National League South East. The club plays home games at St Neots Town F.C. and the Abbey Stadium.
Cambridge City FC of the Southern Football League Premier Division now play in the adjoining village of Histon and Impington, Histon. Formed in Cambridge in 1908, as Cambridge Town, the club were Southern Football League, Southern Premier League champions in 1962–63, the highest they have finished in the English football pyramid. After a legal dispute with their landlords, the club left their home ground in Cambridge in order to groundshare with fellow Southern League Premier club Histon FC in 2013-14 and intend to construct a new ground outside the city, in Sawston.
 The River Cam, which runs through the city centre, is used for boating. The university and its colleges are well known for Rowing (sport), rowing and the Cambridgeshire Rowing Association, formed in 1868, organises competitive rowing on the river outside of the university. Rowing clubs based in the city include City of Cambridge Rowing Club, City of Cambridge RC, Cambridge '99 Rowing Club, Cambridge '99 RC, Cantabrigian Rowing Club, Cantabrigian RC and Rob Roy Boat Club, Rob Roy BC. Parts of the Cam are used for recreational punt (boat), punting, a type of boating in which the craft is propelled by pushing against the river bed with a quant pole.
Cambridge Swimming Club, Cambridge Dive team and City of Cambridge Water Polo Club are all based at Parkside Swimming Pool.
The River Cam, which runs through the city centre, is used for boating. The university and its colleges are well known for Rowing (sport), rowing and the Cambridgeshire Rowing Association, formed in 1868, organises competitive rowing on the river outside of the university. Rowing clubs based in the city include City of Cambridge Rowing Club, City of Cambridge RC, Cambridge '99 Rowing Club, Cambridge '99 RC, Cantabrigian Rowing Club, Cantabrigian RC and Rob Roy Boat Club, Rob Roy BC. Parts of the Cam are used for recreational punt (boat), punting, a type of boating in which the craft is propelled by pushing against the river bed with a quant pole.
Cambridge Swimming Club, Cambridge Dive team and City of Cambridge Water Polo Club are all based at Parkside Swimming Pool.



 Several fairs and festivals take place in Cambridge, mostly during the British summer. Midsummer Common, Midsummer Fair dates back to 1211, when it was granted a charter by John, King of England, King John. Today it exists primarily as an annual travelling funfair, funfair with the vestige of a market attached and is held over several days around or close to midsummers day. On the first Saturday in June Midsummer Common is the site for Strawberry Fair, a free music and children's fair, with various market stalls. For one week in May, on
Several fairs and festivals take place in Cambridge, mostly during the British summer. Midsummer Common, Midsummer Fair dates back to 1211, when it was granted a charter by John, King of England, King John. Today it exists primarily as an annual travelling funfair, funfair with the vestige of a market attached and is held over several days around or close to midsummers day. On the first Saturday in June Midsummer Common is the site for Strawberry Fair, a free music and children's fair, with various market stalls. For one week in May, on
 Cambridge is served by Cambridge University Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust, with several smaller medical centres in the city and a teaching hospital at Addenbrooke's Hospital, Addenbrooke's. Located on the
Cambridge is served by Cambridge University Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust, with several smaller medical centres in the city and a teaching hospital at Addenbrooke's Hospital, Addenbrooke's. Located on the
Cambridge City Council
Greater Cambridge Partnership
Cambridgeshire Association for Local History
Cambridgeshire Community Archives
Visit Cambridge
the official tourism website for Cambridge {{authority control Cambridge, Cities in the East of England County towns in England Non-metropolitan districts of Cambridgeshire Towns in Cambridgeshire Unparished areas in Cambridgeshire Boroughs in England
Cambridgeshire
Cambridgeshire (abbreviated Cambs.) is a county in the East of England, bordering Lincolnshire to the north, Norfolk to the north-east, Suffolk to the east, Essex and Hertfordshire to the south, and Bedfordshire and Northamptonshire to the ...
, England
England is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. It shares land borders with Wales to its west and Scotland to its north. The Irish Sea lies northwest and the Celtic Sea to the southwest. It is separated from continental Europe b ...
. It is located on the River Cam approximately north of London. As of the 2021 United Kingdom census, the population of Cambridge was 145,700. Cambridge became an important trading centre during the Roman and Viking ages, and there is archaeological evidence of settlement in the area as early as the Bronze Age
The Bronze Age is a historic period, lasting approximately from 3300 BC to 1200 BC, characterized by the use of bronze, the presence of writing in some areas, and other early features of urban civilization. The Bronze Age is the second prin ...
. The first town charters were granted in the 12th century, although modern city status was not officially conferred until 1951.
The city is most famous as the home of the University of Cambridge
The University of Cambridge is a public collegiate research university in Cambridge, England. Founded in 1209 and granted a royal charter by Henry III in 1231, Cambridge is the world's third oldest surviving university and one of its most pr ...
, which was founded in 1209 and consistently ranks among the best universities in the world. The buildings of the university include King's College Chapel
King's College Chapel is the chapel of King's College, Cambridge, King's College in the University of Cambridge. It is considered one of the finest examples of late Perpendicular Gothic English architecture and features the world's largest fan ...
, Cavendish Laboratory, and the Cambridge University Library
Cambridge University Library is the main research library of the University of Cambridge. It is the largest of the over 100 libraries within the university. The Library is a major scholarly resource for the members of the University of Cambri ...
, one of the largest legal deposit libraries in the world. The city's skyline is dominated by several college buildings, along with the spire of the Our Lady and the English Martyrs Church
The Church of Our Lady of the Assumption and the English Martyrs, also known as the Church of Our Lady and the English Martyrs (OLEM), is an English Roman Catholic parish church located at the junction of Hills Road and Lensfield Road in southeas ...
, and the chimney of Addenbrooke's Hospital
Addenbrooke's Hospital is an internationally renowned large teaching hospital and research centre in Cambridge, England, with strong affiliations to the University of Cambridge. Addenbrooke's Hospital is based on the Cambridge Biomedical Camp ...
. Anglia Ruskin University
Anglia Ruskin University (ARU) is a public university in East Anglia, United Kingdom. Its origins are in the Cambridge School of Art, founded by William John Beamont in 1858. It became a university in 1992, and was renamed after John Ruskin in ...
, which evolved from the Cambridge School of Art and the Cambridgeshire College of Arts and Technology, also has its main campus in the city.
Cambridge is at the heart of the high-technology Silicon Fen
Silicon Fen (also known as the Cambridge Cluster) is the name given to the region around Cambridge, England, which is home to a large business cluster, cluster of high-tech businesses focusing on software, electronics and biotechnology, s ...
, which contains industries such as software
Software is a set of computer programs and associated software documentation, documentation and data (computing), data. This is in contrast to Computer hardware, hardware, from which the system is built and which actually performs the work.
...
and bioscience and many start-up companies born out of the university. Over 40 per cent of the workforce have a higher education qualification, more than twice the national average. The Cambridge Biomedical Campus
The Cambridge Biomedical Campus is the largest centre of medical research and health science in Europe. The site is located at the southern end of Hills Road in Cambridge, England.
Over 20,000 people work at the site, which is home to Cambridge ...
, one of the largest biomedical research clusters in the world includes the headquarters of AstraZeneca
AstraZeneca plc () is a British-Swedish multinational pharmaceutical and biotechnology company with its headquarters at the Cambridge Biomedical Campus in Cambridge, England. It has a portfolio of products for major diseases in areas includi ...
, a hotel, and the relocated Royal Papworth Hospital
Royal Papworth Hospital is a specialist heart and lung hospital, located on the Cambridge Biomedical Campus in Cambridgeshire, England. The Hospital is run by Royal Papworth Hospital NHS Foundation Trust.
The hospital is a world-leading cardiot ...
.
The first game of association football
Association football, more commonly known as football or soccer, is a team sport played between two teams of 11 players who primarily use their feet to propel the ball around a rectangular field called a pitch. The objective of the game is ...
took place at Parker's Piece. The Strawberry Fair music and arts festival and Midsummer Fair are held on Midsummer Common
Midsummer Common is an area of common land in Cambridge, England. It lies northeast of the city centre on the south bank of the River Cam.
The common borders the River Cam and houseboats are often moored on the common's bank. The boathouse ...
, and the annual Cambridge Beer Festival
The summer Cambridge Beer Festival is the longest-running CAMRA beer festival in the United Kingdom, having started in 1974. It is held at the end of May just before the Whitsuntide Bank Holiday. The winter beer festival is a smaller, indoor ev ...
takes place on Jesus Green
Jesus Green is a park in the north of central Cambridge, Cambridgeshire, England, north of Jesus College. Jesus Ditch runs along the southern edge Jesus Green. On the northern edge of Jesus Green is the River Cam, with Chesterton Road (th ...
. The city is adjacent to the M11 and A14 roads. Cambridge station
Cambridge railway station is the principal station serving the city of Cambridge in the east of England. It stands at the end of Station Road, south-east of the city centre. It is the northern terminus of the West Anglia Main Line, down th ...
is less than an hour from London King's Cross railway station.
History
Prehistory
Settlements have existed around the Cambridge area sinceprehistoric times
Prehistory, also known as pre-literary history, is the period of human history between the use of the first stone tools by hominins 3.3 million years ago and the beginning of recorded history with the invention of writing systems. The use of ...
. The earliest clear evidence of occupation is the remains of a year-old farmstead discovered at the site of Fitzwilliam College
Fitzwilliam College is a constituent college of the University of Cambridge.
The college traces its origins back to 1869 and the foundation of the Non-Collegiate Students Board, a venture intended to offer academically excellent students of all ...
. Archaeological evidence of occupation through the Iron Age
The Iron Age is the final epoch of the three-age division of the prehistory and protohistory of humanity. It was preceded by the Stone Age ( Paleolithic, Mesolithic, Neolithic) and the Bronze Age ( Chalcolithic). The concept has been mostl ...
is a settlement on Castle Hill from the 1st century BC, perhaps relating to wider cultural changes occurring in southeastern Britain linked to the arrival of the Belgae.
Roman
The principalRoman
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
*Rome, the capital city of Italy
*Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
*Roman people, the people of ancient Rome
*'' Epistle to the Romans'', shortened to ''Romans'', a lette ...
site is a small fort (') Duroliponte
Duroliponte or Durolipons was a small town in the Roman province of Britannia on the site of what is now the city of Cambridge.
The site of Roman Cambridge is located on Castle Hill, just northwest of the city centre. The fort ( la, castrum) was ...
on Castle Hill, just northwest of the city centre around the location of the earlier British
British may refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* British people, nationals or natives of the United Kingdom, British Overseas Territories, and Crown Dependencies.
** Britishness, the British identity and common culture
* British English, ...
village. The fort was bounded on two sides by the lines formed by the present Mount Pleasant, continuing across Huntingdon Road
Huntingdon Road is a major arterial road linking central Cambridge, England with Junction 14 of the M11 motorway and the A14 northwest from the city centre. The road is designated the A1307, follows the route of the Roman Via Devana, and is n ...
into Clare Street. The eastern side followed Magrath Avenue, with the southern side running near to Chesterton Lane and Kettle's Yard
Kettle's Yard is an art gallery and house in Cambridge, England. The director of the art gallery is Andrew Nairne. Both the house and gallery reopened in February 2018 after an expansion of the facilities.
Kettle's Yard galleries, shop and caf ...
before turning northwest at Honey Hill. It was constructed around AD 70 and converted to civilian use around 50 years later. Evidence of more widespread Roman settlement has been discovered including numerous farmsteads and a village in the Cambridge district of Newnham.
A Roman coffin for Etheldreda was found next to the Roman town, and taken back by river for her burial in Ely. (Bede)
Medieval


 Following the
Following the Roman withdrawal from Britain
The end of Roman rule in Britain was the transition from Roman Britain to post-Roman Britain. Roman rule ended in different parts of Britain at different times, and under different circumstances.
In 383, the usurper Magnus Maximus withdrew t ...
around 410, the location may have been abandoned by the Britons
British people or Britons, also known colloquially as Brits, are the citizens of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, the British Overseas Territories, and the Crown dependencies.: British nationality law governs mod ...
, although the site is usually identified as , Nennius (). Theodor Mommsen
Christian Matthias Theodor Mommsen (; 30 November 1817 – 1 November 1903) was a German classical scholar, historian, jurist, journalist, politician and archaeologist. He is widely regarded as one of the greatest classicists of the 19th centu ...
(). ''Historia Brittonum'', VI. Composed after AD 830. Hosted at Latin Wikisource. as listed among the 28 cities
A city is a human settlement of notable size.Goodall, B. (1987) ''The Penguin Dictionary of Human Geography''. London: Penguin.Kuper, A. and Kuper, J., eds (1996) ''The Social Science Encyclopedia''. 2nd edition. London: Routledge. It can be def ...
of Britain
Britain most often refers to:
* The United Kingdom, a sovereign state in Europe comprising the island of Great Britain, the north-eastern part of the island of Ireland and many smaller islands
* Great Britain, the largest island in the United King ...
in the ''History of the Britons
''The History of the Britons'' ( la, Historia Brittonum) is a purported history of the indigenous British ( Brittonic) people that was written around 828 and survives in numerous recensions that date from after the 11th century. The ''Historia Br ...
'' attributed to Nennius.Ford, David Nash.The 28 Cities of Britain
" at Britannia. 2000. Evidence exists that the invading Anglo-Saxons had begun occupying the area by the end of the century. Their settlement – also on and around Castle Hill – became known as Grantebrycge. ("
Granta
''Granta'' is a literary magazine and publisher in the United Kingdom whose mission centres on its "belief in the power and urgency of the story, both in fiction and non-fiction, and the story’s supreme ability to describe, illuminate and ma ...
-bridge"). (By Middle English
Middle English (abbreviated to ME) is a form of the English language that was spoken after the Norman conquest of 1066, until the late 15th century. The English language underwent distinct variations and developments following the Old English ...
, the settlement's name had changed to "Cambridge", deriving from the word 'Camboricum', meaning 'Passage' or 'ford' of stream in a town or settlement, and the lower stretches of the Granta
''Granta'' is a literary magazine and publisher in the United Kingdom whose mission centres on its "belief in the power and urgency of the story, both in fiction and non-fiction, and the story’s supreme ability to describe, illuminate and ma ...
changed their name to match.) Anglo-Saxon grave goods have been found in the area. During this period, Cambridge benefited from good trade links across the hard-to-travel fenlands. By the 7th century, the town was less significant and described by Bede as a "little ruined city" containing the burial site of Æthelthryth
Æthelthryth (or Æðelþryð or Æþelðryþe; 23 June 679 AD) was an East Anglian princess, a Fenland and Northumbrian queen and Abbess of Ely. She is an Anglo-Saxon saint, and is also known as Etheldreda or Audrey, especially in religious ...
(Etheldreda). Cambridge was on the border between the East
East or Orient is one of the four cardinal directions or points of the compass. It is the opposite direction from west and is the direction from which the Sun rises on the Earth.
Etymology
As in other languages, the word is formed from the fac ...
and Middle Anglian kingdoms and the settlement slowly expanded on both sides of the river.
The arrival of the Vikings
Vikings ; non, víkingr is the modern name given to seafaring people originally from Scandinavia (present-day Denmark, Norway and Sweden),
who from the late 8th to the late 11th centuries raided, pirated, traded and ...
was recorded in the '' Anglo-Saxon Chronicle'' in 875. Viking rule, the Danelaw
The Danelaw (, also known as the Danelagh; ang, Dena lagu; da, Danelagen) was the part of England in which the laws of the Danes held sway and dominated those of the Anglo-Saxons. The Danelaw contrasts with the West Saxon law and the Mercian ...
, had been imposed by 878 Their vigorous trading habits caused the town to grow rapidly. During this period the centre of the town shifted from Castle Hill on the left bank of the river to the area now known as the Quayside on the right bank. After the Viking period, the Saxons enjoyed a return to power, building churches such as St Bene't's Church
St Bene't's Church is a Church of England parish church in central Cambridge, England. Parts of the church, most notably the tower, are Anglo-Saxon, and it is the oldest church in Cambridgeshire as well as the oldest building in Cambridge.
Th ...
, wharves, merchant houses and a mint
MiNT is Now TOS (MiNT) is a free software alternative operating system kernel for the Atari ST system and its successors. It is a multi-tasking alternative to TOS and MagiC. Together with the free system components fVDI device drivers, XaA ...
, which produced coins with the town's name abbreviated to "Grant".
In 1068, two years after the Norman Conquest
The Norman Conquest (or the Conquest) was the 11th-century invasion and occupation of England by an army made up of thousands of Norman, Breton, Flemish, and French troops, all led by the Duke of Normandy, later styled William the Con ...
of England, William the Conqueror
William I; ang, WillelmI (Bates ''William the Conqueror'' p. 33– 9 September 1087), usually known as William the Conqueror and sometimes William the Bastard, was the first House of Normandy, Norman List of English monarchs#House of Norman ...
built a castle on Castle Hill, the motte
A motte-and-bailey castle is a European fortification with a wooden or stone keep situated on a raised area of ground called a motte, accompanied by a walled courtyard, or bailey, surrounded by a protective ditch and palisade. Relatively easy to ...
of which survives. Like the rest of the newly conquered kingdom, Cambridge fell under the control of the King and his deputies.
The first town charter was granted by Henry I Henry I may refer to:
876–1366
* Henry I the Fowler, King of Germany (876–936)
* Henry I, Duke of Bavaria (died 955)
* Henry I of Austria, Margrave of Austria (died 1018)
* Henry I of France (1008–1060)
* Henry I the Long, Margrave of the ...
between 1120 and 1131. It gave Cambridge monopoly of waterborne traffic and hithe tolls and recognised the borough
A borough is an administrative division in various English-speaking countries. In principle, the term ''borough'' designates a self-governing walled town, although in practice, official use of the term varies widely.
History
In the Middle A ...
court. The distinctive Round Church
A round church is a church construction with a completely circular plan. There are many Nordic round churches in Sweden and Denmark (notably the island of Bornholm); round churches were popular in Scandinavia in the 11th and early 12th centurie ...
dates from this period. In 1209, Cambridge University was founded by Oxford students fleeing from hostility. The oldest existing college, Peterhouse
Peterhouse is the oldest constituent college of the University of Cambridge in England, founded in 1284 by Hugh de Balsham, Bishop of Ely. Today, Peterhouse has 254 undergraduates, 116 full-time graduate students and 54 fellows. It is quite o ...
, was founded in 1284.
In 1349 Cambridge was affected by the Black Death. Few records survive but 16 of 40 scholars at King's Hall died. The town north of the river was severely affected being almost wiped out. Following further depopulation after a second national epidemic in 1361, a letter from the Bishop of Ely suggested that two parishes in Cambridge be merged as there were not enough people to fill even one church. With more than a third of English clergy dying in the Black Death, four new colleges were established at the university over the following years to train new clergymen, namely Gonville Hall
Gonville and Caius College, often referred to simply as Caius ( ), is a constituent college of the University of Cambridge in Cambridge, England. Founded in 1348, it is the fourth-oldest of the University of Cambridge's 31 colleges and one of th ...
, Trinity Hall, Corpus Christi and Clare.
In 1382 a revised town charter effects a "diminution of the liberties that the community had enjoyed", due to Cambridge's participation in the Peasants' Revolt
The Peasants' Revolt, also named Wat Tyler's Rebellion or the Great Rising, was a major uprising across large parts of England in 1381. The revolt had various causes, including the socio-economic and political tensions generated by the Blac ...
. The charter transfers supervision of baking and brewing, weights and measures, and forestalling and regrating, from the town to the university.
King's College Chapel
King's College Chapel is the chapel of King's College, Cambridge, King's College in the University of Cambridge. It is considered one of the finest examples of late Perpendicular Gothic English architecture and features the world's largest fan ...
, was begun in 1446 by King Henry VI. The chapel was built in phases by a succession of kings of England from 1446 to 1515, its history intertwined with the Wars of the Roses
The Wars of the Roses (1455–1487), known at the time and for more than a century after as the Civil Wars, were a series of civil wars fought over control of the English throne in the mid-to-late fifteenth century. These wars were fought bet ...
, and completed during the reign of King Henry VIII. The building would become synonymous with Cambridge, and currently is used in the logo for the Cambridge City Council
Cambridge City Council is a district council in the county of Cambridgeshire, which governs the City of Cambridge.
History
Cambridge was granted a Royal Charter by King John in 1207, which permitted the appointment of a mayor. The first recorde ...
.
Early modern
 Following repeated outbreaks of pestilence throughout the 16th century, sanitation and fresh water were brought to Cambridge by the construction of
Following repeated outbreaks of pestilence throughout the 16th century, sanitation and fresh water were brought to Cambridge by the construction of Hobson's Conduit
Hobson's Conduit, also called Hobson's Brook, is a watercourse that was built from 1610 to 1614 by Thomas Hobson and others to bring fresh water into the city of Cambridge, England from springs at Nine Wells, a Local Nature Reserve (), near the ...
in the early 1600s. Water was brought from Nine Wells, at the foot of the Gog Magog Hills
The Gog Magog Hills are a range of low chalk hills, extending for several miles to the southeast of Cambridge in England. The highest points are situated either side of the A1307 Babraham Road, and are marked on Ordnance Survey 1:25000 maps as ...
to the southeast of Cambridge, into the centre of the town.
Cambridge played a significant role in the early part of the English Civil War
The English Civil War (1642–1651) was a series of civil wars and political machinations between Parliamentarians (" Roundheads") and Royalists led by Charles I ("Cavaliers"), mainly over the manner of England's governance and issues of re ...
as it was the headquarters of the Eastern Counties Association, an organisation administering a regional East Anglian
East Anglia is an area in the East of England, often defined as including the counties of Norfolk, Suffolk and Cambridgeshire. The name derives from the Anglo-Saxon kingdom of the East Angles, a people whose name originated in Anglia, in ...
army, which became the mainstay of the Parliamentarian military effort before the formation of the New Model Army. In 1643 control of the town was given by Parliament to Oliver Cromwell
Oliver Cromwell (25 April 15993 September 1658) was an English politician and military officer who is widely regarded as one of the most important statesmen in English history. He came to prominence during the 1639 to 1651 Wars of the Three K ...
, who had been educated at Sidney Sussex College
Sidney Sussex College (referred to informally as "Sidney") is a constituent college of the University of Cambridge in England. The College was founded in 1596 under the terms of the will of Frances Sidney, Countess of Sussex (1531–1589), wife ...
in Cambridge. The town's castle was fortified and garrisoned with troops and some bridges were destroyed to aid its defence. Although Royalist
A royalist supports a particular monarch as head of state for a particular kingdom, or of a particular dynastic claim. In the abstract, this position is royalism. It is distinct from monarchism, which advocates a monarchical system of governm ...
forces came within of the town in 1644, the defences were never used, and the garrison was stood down the following year.
Early-industrial era
In the 19th century, in common with many other English towns, Cambridge expanded rapidly, due in part to increased life expectancy and improved agricultural production leading to increased trade in town markets. TheInclosure Acts
The Inclosure Acts, which use an archaic spelling of the word now usually spelt "enclosure", cover enclosure of open fields and common land in England and Wales, creating legal property rights to land previously held in common. Between 1604 and 1 ...
of 1801 and 1807 enabled the town to expand over surrounding open fields and in 1912 and again in 1935 its boundaries were extended to include Chesterton, Cherry Hinton, and Trumpington.
The railway came to Cambridge in 1845 after initial resistance, with the opening of the Great Eastern Railway's London to Norwich line. The station was outside the town centre following pressure from the university to restrict travel by undergraduates. With the arrival of the railway and associated employment came development of areas around the station, such as Romsey Town. The rail link to London stimulated heavier industries, such as the production of brick, cement and malt.
20th and 21st centuries
From the 1930s to the 1980s, the size of the city was increased by several largecouncil estate
Public housing in the United Kingdom, also known as council estates, council housing, or social housing, provided the majority of rented accommodation until 2011 when the number of households in private rental housing surpassed the number in so ...
s. The biggest impact has been on the area north of the river, which are now the estates of East Chesterton, King's Hedges
King's Hedges is an electoral ward in the north of the city of Cambridge, England.
History
The open land to the north of Cambridge that now comprises King's Hedges was known as ''Albrach'' from as early as the 13th century. In 1558 it was agree ...
, and Arbury
Arbury is a district and electoral ward of the city of Cambridge, England. The ward borders the following other wards (from North, proceeding clockwise): Histon, King's Hedges, West Chesterton, Market and Castle.
History
The area has been occu ...
where Archbishop Rowan Williams
Rowan Douglas Williams, Baron Williams of Oystermouth, (born 14 June 1950) is a Welsh Anglican bishop, theologian and poet. He was the 104th Archbishop of Canterbury, a position he held from December 2002 to December 2012. Previously the Bish ...
lived and worked as an assistant priest in the early 1980s.
During World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposing ...
, Cambridge was an important centre for defence of the east coast. The town became a military centre, with an R.A.F.
The Royal Air Force (RAF) is the United Kingdom's air and space force. It was formed towards the end of the First World War on 1 April 1918, becoming the first independent air force in the world, by regrouping the Royal Flying Corps (RFC) and ...
training centre and the regional headquarters for Norfolk, Suffolk, Essex, Cambridgeshire, Huntingdonshire
Huntingdonshire (; abbreviated Hunts) is a non-metropolitan district of Cambridgeshire and a historic county of England. The district council is based in Huntingdon. Other towns include St Ives, Godmanchester, St Neots and Ramsey. The popu ...
, Hertfordshire, and Bedfordshire
Bedfordshire (; abbreviated Beds) is a ceremonial county in the East of England. The county has been administered by three unitary authorities, Borough of Bedford, Central Bedfordshire and Borough of Luton, since Bedfordshire County Council ...
established during the conflict. The town itself escaped relatively lightly from German bombing raids, which were mainly targeted at the railway. 29 people were killed and no historic buildings were damaged. In 1944, a secret meeting of military leaders held in Trinity College laid the foundation for the allied invasion of Europe. During the war Cambridge served as an evacuation centre for over 7,000 people from London, as well as for parts of the University of London
The University of London (UoL; abbreviated as Lond or more rarely Londin in post-nominals) is a federal public research university located in London, England, United Kingdom. The university was established by royal charter in 1836 as a degree ...
.
Cambridge was granted its city charter
A city charter or town charter (generically, municipal charter) is a legal document ('' charter'') establishing a municipality such as a city or town. The concept developed in Europe during the Middle Ages.
Traditionally the granting of a charte ...
in 1951 in recognition of its history, administrative importance and economic success. Cambridge does not have a cathedral, traditionally a prerequisite for city status, instead falling within the Church of England Diocese of Ely. In 1962 Cambridge's first shopping arcade, Bradwell's Court, opened on Drummer Street, though this was demolished in 2006. Other shopping arcades followed at Lion Yard, which housed a relocated Central Library for the city, and the Grafton Centre
The Grafton centre is a covered shopping centre in the east of central Cambridge, England. It is one of the three main shopping centres in Cambridge, with Lion Yard and Grand Arcade in the city's centre.
The Centre dominates Fitzroy Street and Bu ...
which replaced Victorian housing stock which had fallen into disrepair in the Kite
A kite is a tethered heavier-than-air or lighter-than-air craft with wing surfaces that react against the air to create lift and drag forces. A kite consists of wings, tethers and anchors. Kites often have a bridle and tail to guide the fac ...
area of the city. This latter project was controversial at the time.
The city gained its second University in 1992 when Anglia Polytechnic became Anglia Polytechnic University. Renamed Anglia Ruskin University
Anglia Ruskin University (ARU) is a public university in East Anglia, United Kingdom. Its origins are in the Cambridge School of Art, founded by William John Beamont in 1858. It became a university in 1992, and was renamed after John Ruskin in ...
in 2005, the institution has its origins in the Cambridge School of Art opened in 1858 by John Ruskin
John Ruskin (8 February 1819 20 January 1900) was an English writer, philosopher, art critic and polymath of the Victorian era. He wrote on subjects as varied as geology, architecture, myth, ornithology, literature, education, botany and pol ...
. The Open University
The Open University (OU) is a British public research university and the largest university in the United Kingdom by number of students. The majority of the OU's undergraduate students are based in the United Kingdom and principally study o ...
also has a presence in the city, with an office operating on Hills Road.
Governance
Local government
non-metropolitan district
Non-metropolitan districts, or colloquially "shire districts", are a type of Districts of England, local government district in England. As created, they are sub-divisions of non-metropolitan county, non-metropolitan counties (colloquially ''shi ...
– one of six districts within the county of Cambridgeshire – and is administered by Cambridge City Council
Cambridge City Council is a district council in the county of Cambridgeshire, which governs the City of Cambridge.
History
Cambridge was granted a Royal Charter by King John in 1207, which permitted the appointment of a mayor. The first recorde ...
. The district covers most of the city's urban area, although some suburbs extend into the surrounding South Cambridgeshire
South Cambridgeshire is a local government district of Cambridgeshire, England, with a population of 162,119 at the 2021 census. It was formed on 1 April 1974 by the merger of Chesterton Rural District and South Cambridgeshire Rural District. ...
district. The city council's headquarters are in the Guildhall
A guildhall, also known as a "guild hall" or "guild house", is a historical building originally used for tax collecting by municipalities or merchants in Great Britain and the Low Countries. These buildings commonly become town halls and in som ...
, a large building in the market square. Cambridge was granted a Royal Charter by King John in 1207, which permitted the appointment of a mayor, although the first recorded mayor, Harvey FitzEustace, served in 1213. City councillors now elect a mayor annually.
For electoral purposes the city is divided into 14 wards: Abbey, Arbury
Arbury is a district and electoral ward of the city of Cambridge, England. The ward borders the following other wards (from North, proceeding clockwise): Histon, King's Hedges, West Chesterton, Market and Castle.
History
The area has been occu ...
, Castle, Cherry Hinton
Cherry Hinton is a suburban area of the city of Cambridge, in Cambridgeshire, England. It is around southeast of Cambridge city centre.
History
The rectangular parish of Cherry Hinton occupies the western corner of Flendish hundred on the so ...
, Coleridge, East Chesterton, King's Hedges
King's Hedges is an electoral ward in the north of the city of Cambridge, England.
History
The open land to the north of Cambridge that now comprises King's Hedges was known as ''Albrach'' from as early as the 13th century. In 1558 it was agree ...
, Market, Newnham, Petersfield
Petersfield is a market town and civil parish in the East Hampshire district of Hampshire, England. It is north of Portsmouth. The town has its own railway station on the Portsmouth Direct line, the mainline rail link connecting Portsmouth a ...
, Queen Edith's, Romsey, Trumpington
Trumpington is a village and parish to the south of Cambridge, England. The village is an electoral ward of the City of Cambridge and a ward of South Cambridgeshire District Council. The 2011 Census recorded the ward's population as 8,034.
T ...
, and West Chesterton
West or Occident is one of the four cardinal directions or points of the compass. It is the opposite direction from east and is the direction in which the Sun sets on the Earth.
Etymology
The word "west" is a Germanic word passed into some ...
. At the 2019 election, Labour retained its majority.
Each of the 14 wards also elects councillors to Cambridgeshire County Council
Cambridgeshire County Council is the county council of Cambridgeshire, England. The council consists of 61 councillors, representing 59 electoral divisions. The council is based at New Shire Hall at Alconbury Weald, near Huntingdon. It is a me ...
, which is responsible for services including school education, social care and highways.
Since 2017, Cambridge has also been within the area of the Cambridgeshire and Peterborough Combined Authority
The Cambridgeshire and Peterborough Combined Authority is a combined authority covering the ceremonial county of Cambridgeshire in the East of England. The authority was established on 3 March 2017. The authority is led by the directly elected Mayo ...
, which is led by a directly elected Mayor. The city is represented on the authority by the leader of the City Council.
Westminster
Theparliamentary
A parliamentary system, or parliamentarian democracy, is a system of democratic governance of a state (or subordinate entity) where the executive derives its democratic legitimacy from its ability to command the support ("confidence") of the ...
constituency of Cambridge covers most of the city; Daniel Zeichner
Daniel Stephen Zeichner (born 9 November 1956) is a British politician who has served as the Member of Parliament (MP) for Cambridge since 2015. A member of the Labour Party, he defeated Liberal Democrat Julian Huppert before retaining his sea ...
(Labour
Labour or labor may refer to:
* Childbirth, the delivery of a baby
* Labour (human activity), or work
** Manual labour, physical work
** Wage labour, a socioeconomic relationship between a worker and an employer
** Organized labour and the labour ...
) has represented the seat since the 2015 general election. The seat was generally held by the Conservatives
Conservatism is a cultural, social, and political philosophy that seeks to promote and to preserve traditional institutions, practices, and values. The central tenets of conservatism may vary in relation to the culture and civilization in ...
until it was won by Labour in 1992, then taken by the Liberal Democrats in 2005 and 2010, before returning to Labour in 2015. A southern area of the city, Queen Edith's ward, falls within the South Cambridgeshire
South Cambridgeshire is a local government district of Cambridgeshire, England, with a population of 162,119 at the 2021 census. It was formed on 1 April 1974 by the merger of Chesterton Rural District and South Cambridgeshire Rural District. ...
constituency, whose MP is Anthony Browne (Conservative), first elected in 2019.
The University of Cambridge formerly had two seats in the House of Commons; Sir Isaac Newton
Sir Isaac Newton (25 December 1642 – 20 March 1726/27) was an English mathematician, physicist, astronomer, alchemist, theologian, and author (described in his time as a " natural philosopher"), widely recognised as one of the grea ...
was one of the most notable MPs. The Cambridge University constituency was abolished under 1948 legislation, and ceased at the dissolution of Parliament for the 1950 general election, along with the other university constituencies
A university constituency is a constituency, used in elections to a legislature, that represents the members of one or more universities rather than residents of a geographical area. These may or may not involve plural voting, in which voters a ...
.
Geography and environment

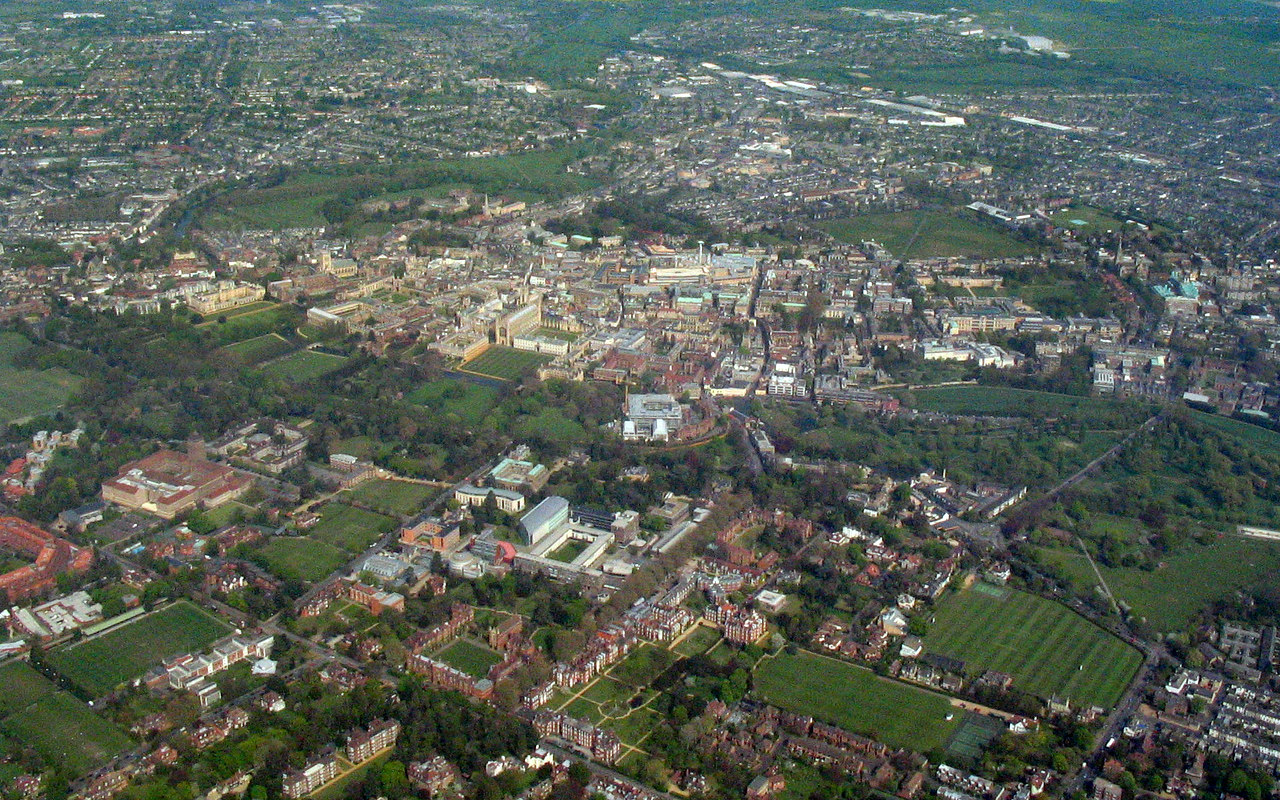
 Cambridge is situated about north-by-east of London and 95 miles (152 kilometres) east of Birmingham. The city is located in an area of level and relatively low-lying terrain just south of the Fens, which varies between above mean sea level, above sea level. The town was thus historically surrounded by low-lying wetlands that have been drained as the town has expanded.
The underlying geology of Cambridge consists of gault clay and Chalk Group, Chalk Marl, known locally as Cambridge Greensand, partly overlaid by Gravel, terrace gravel. A layer of Phosphate nodule, phosphatic nodules (coprolites) under the marl was mined in the 19th century for fertiliser; this became a major industry in the county, and its profits yielded buildings such as the Cambridge Corn Exchange, Corn Exchange, Fulbourn Hospital, and St John's College, Cambridge#College Chapel, St. John's Chapel until the Quarries Act 1894 and competition from America ended production.
The River Cam flows through the city from the village of Grantchester, to the southwest. It is bordered by water meadows within the city such as Sheep's Green as well as residential development. Like most cities, modern-day Cambridge has many suburbs and areas of high-density housing. The city centre of Cambridge is mostly commercial, historic buildings, and large green areas such as Jesus Green, Parker's Piece and
Cambridge is situated about north-by-east of London and 95 miles (152 kilometres) east of Birmingham. The city is located in an area of level and relatively low-lying terrain just south of the Fens, which varies between above mean sea level, above sea level. The town was thus historically surrounded by low-lying wetlands that have been drained as the town has expanded.
The underlying geology of Cambridge consists of gault clay and Chalk Group, Chalk Marl, known locally as Cambridge Greensand, partly overlaid by Gravel, terrace gravel. A layer of Phosphate nodule, phosphatic nodules (coprolites) under the marl was mined in the 19th century for fertiliser; this became a major industry in the county, and its profits yielded buildings such as the Cambridge Corn Exchange, Corn Exchange, Fulbourn Hospital, and St John's College, Cambridge#College Chapel, St. John's Chapel until the Quarries Act 1894 and competition from America ended production.
The River Cam flows through the city from the village of Grantchester, to the southwest. It is bordered by water meadows within the city such as Sheep's Green as well as residential development. Like most cities, modern-day Cambridge has many suburbs and areas of high-density housing. The city centre of Cambridge is mostly commercial, historic buildings, and large green areas such as Jesus Green, Parker's Piece and Midsummer Common
Midsummer Common is an area of common land in Cambridge, England. It lies northeast of the city centre on the south bank of the River Cam.
The common borders the River Cam and houseboats are often moored on the common's bank. The boathouse ...
. Many of the roads in the centre are pedestrianised.
Population growth has seen new housing developments in the 21st century, with estates such as the CB1 and Accordia schemes near the station, and developments such as Great Kneighton, formally known as Clay Farm, and Trumpington Meadows currently under construction in the south of the city. Other major developments currently being constructed in the city are Darwin Green (formerly National Institute of Agricultural Botany, NIAB), and University-led developments at West Cambridge and North West Cambridge Development, North West Cambridge, (Eddington, Cambridge, Eddington).
The entire city centre, as well as parts of Chesterton, Petersfield, West Cambridge, Newnham, and Abbey, are covered by an Air Quality Management Area, implemented to counter high levels of nitrogen dioxide in the atmosphere.
Climate
The city has an oceanic climate. (Köppen climate classification, Köppen: ''Cfb''). Cambridge has an official weather observing station, at the Cambridge University Botanic Garden, about south of the city centre. In addition, the Digital Technology Group of the university's Department of Computer Science and Technology, University of Cambridge, Department of Computer Science and Technology maintains a weather station on the West Cambridge, West Cambridge site, displaying current weather conditions online via web browsers or an mobile app, app, and also an archive dating back to 1995. The city, like most of the UK, has a oceanic climate, maritime climate highly influenced by the Gulf Stream. Located in the driest region of Britain, Cambridge's rainfall averages around per year, around half the national average, The driest recent year was in 2011 with of rain at the Botanic Garden and at the NIAB site. This is just below the semi-arid precipitation threshold for the area, which is 350mm of annual precipitation. Conversely, 2012 was the wettest year on record, with reported. Snowfall accumulations are usually small, in part because of Cambridge's low elevation, and low precipitation tendency during transitional snow events. Owing to its low-lying, inland, and easterly position within the British Isles, summer temperatures tend to be somewhat higher than areas further west, and often rival or even exceed those recorded in the London area. Cambridge also often records the annual highest national temperature in any given year – in July 2008 at NIAB and in August 2007 at the Botanic Garden are two recent examples. Other years include 1876, 1887, 1888, 1892, 1897, 1899 and 1900. The absolute maximum stands at recorded on 19 July 2022 at Cambridge University Botanic Garden. Before this date, Cambridge held the record for the United Kingdom weather records, all-time maximum temperature in the UK, after recording on 25 July 2019. Typically the temperature will reach or higher on over 25 days of the year over the 1981–2010 period, with the annual warmest day averaging over the same period. The absolute minimum temperature recorded at the Botanic Garden site was , recorded in February 1947, although a minimum of was recorded at the now defunct observatory site in December 1879. More recently the temperature fell to on 11 February 2012, on 22 January 2013 and on 20 December 2010. The average frequency of air frosts ranges from 42.8 days at the NIAB site, to 48.3 days at the Botanic Garden per year over the 1981–2010 period. Typically the coldest night of the year at the Botanic Garden will fall to . Such minimum temperatures and frost averages are typical for inland areas across much of southern and central England. Sunshine averages around 1,500 hours a year or around 35% of possible, a level typical of most locations in inland central England.Ecology
The city contains three Site of Special Scientific Interest, Sites of Special Scientific Interest (SSSIs), at Cherry Hinton East Pit, Cherry Hinton West Pit, and Travellers Pit, and ten Local nature reserve, Local Nature Reserves (LNRs): Sheep's Green and Coe Fen, Coldham's Common, Stourbridge Common, Nine Wells, Byron's Pool, West Pit, Paradise, Barnwell West, Barnwell East, and Logan's Meadow.Green belt
Cambridge is completely enclosed by Green belt (United Kingdom), green belt as a part of a wider environmental and planning policy first defined in 1965 and formalised in 1992. While some small tracts of green belt exist on the fringes of the city's boundary, much of the protection is in the surrounding South Cambridgeshire and nearby East Cambridgeshire districts, helping to maintain local green space, prevent further urban sprawl and unplanned expansion of the city, as well as protecting smaller outlying villages from further convergence with each other as well as the city.Demography
Historical population
Local census 1749 Census: Regional District 1801–1901 Civil Parish 1911–1961 District 1971–2011Ethnicity
Religion
Economy
 The town's river link to the surrounding agricultural land, and good road connections to London in the south meant Cambridge has historically served as an important regional trading post. King Henry I granted Cambridge a monopoly on river trade, privileging this area of the economy of Cambridge The town Market Hill, Cambridge, market provided for trade in a wide variety of goods and annual trading fairs such as Stourbridge Fair and Midsummer Fair were visited by merchants from across the country. The river was described in an account of 1748 as being "often so full of [merchant boats] that the navigation thereof is stopped for some time". For example, 2000 wikt:Special:Search/firkin, firkins of butter were brought up the river every Monday from the agricultural lands to the North East, particularity Norfolk, to be unloaded in the town for road transportation to London. Changing patterns of retail distribution and the advent of the railways led to a decline in Cambridge's importance as a market town.
Cambridge today has a diverse economy with strength in sectors such as research and development, software consultancy, high value engineering, creative industries, pharmaceuticals and tourism. Described as one of the "most beautiful cities in the world" by ''Forbes'' in 2010, with the view from The Backs being selected as one of the 10 greatest in England by National Trust for Places of Historic Interest or Natural Beauty, National Trust chair Simon Jenkins, tourism generates over £750 million for the city's economy.
Cambridge and its surrounds are sometimes referred to as
The town's river link to the surrounding agricultural land, and good road connections to London in the south meant Cambridge has historically served as an important regional trading post. King Henry I granted Cambridge a monopoly on river trade, privileging this area of the economy of Cambridge The town Market Hill, Cambridge, market provided for trade in a wide variety of goods and annual trading fairs such as Stourbridge Fair and Midsummer Fair were visited by merchants from across the country. The river was described in an account of 1748 as being "often so full of [merchant boats] that the navigation thereof is stopped for some time". For example, 2000 wikt:Special:Search/firkin, firkins of butter were brought up the river every Monday from the agricultural lands to the North East, particularity Norfolk, to be unloaded in the town for road transportation to London. Changing patterns of retail distribution and the advent of the railways led to a decline in Cambridge's importance as a market town.
Cambridge today has a diverse economy with strength in sectors such as research and development, software consultancy, high value engineering, creative industries, pharmaceuticals and tourism. Described as one of the "most beautiful cities in the world" by ''Forbes'' in 2010, with the view from The Backs being selected as one of the 10 greatest in England by National Trust for Places of Historic Interest or Natural Beauty, National Trust chair Simon Jenkins, tourism generates over £750 million for the city's economy.
Cambridge and its surrounds are sometimes referred to as Silicon Fen
Silicon Fen (also known as the Cambridge Cluster) is the name given to the region around Cambridge, England, which is home to a large business cluster, cluster of high-tech businesses focusing on software, electronics and biotechnology, s ...
, an allusion to Silicon Valley, because of the density of high-tech businesses and business incubator, technology incubators that have developed on science parks around the city. Many of these parks and buildings are owned or leased by university colleges, and the companies often have been spun out of the university. Cambridge Science Park, which is the largest commercial R&D centre in Europe, is owned by Trinity College, Cambridge, Trinity College; St John's College, Cambridge, St John's is the landlord of St John's Innovation Centre. Technology companies include Abcam plc, Abcam, CSR plc, CSR, ARM Limited, Cambridge Semiconductor Limited, CamSemi, Jagex and Sinclair Research Ltd, Sinclair. Microsoft has located its Microsoft Research UK offices in West Cambridge, separate from the main Microsoft UK campus in Reading, Berkshire, Reading, and also has an office on Station Road.
Cambridge was also the home of Pye Ltd, founded in 1898 by W. G. Pye, who worked in the Cavendish Laboratory; it began by supplying the university and later specialised in wireless telegraphy equipment, radios, televisions and also defence equipment. Pye Ltd evolved into several other companies including TETRA radio equipment manufacturer Sepura. Another major business is Marshall Aerospace located on the eastern edge of the city. The Cambridge Network keeps businesses in touch with each other.
Transport

Road
Due to its rapid growth in the 20th century, Cambridge has a congested road network. The M11 motorway from east London terminates to the north-west of the city where it joins the A14, a major freight route which connects the port of Felixstowe on the east coast with the English Midlands, Midlands. The A428 road, A428 connects the city with the A1 road (Great Britain), A1 at St Neots: the route continues westwards towards Oxford (as the A421 road, A421) via Bedford, Bedfordshire, Bedford and Milton Keynes. The A10 road (England), A10 connects the city to King's Lynn to the north via Ely, Cambridgeshire, Ely and is the historic route south to the City of London. , the Greater Cambridge Parternship is consulting on plans comprising: transforming the bus network; investing in other sustainable travel scheme; and creating a sustainable travel zone, which includes the introduction of a congestion charge.Cycling
As a university town lying on fairly flat ground and with traffic congestion, Cambridge has the highest level of cycle use in the UK. According to the 2001 census, 25% of residents travelled to work by bicycle. Furthermore, a survey in 2013 found that 47% of residents travel by bike at least once a week.Park and ride
Cambridge has five Park and Ride sites, all of which operate seven days a week and are aimed at encouraging motorists to park near the city's edge. Since 2011, the Cambridgeshire Guided Busway has carried bus services into the centre of Cambridge from St Ives, Cambridgeshire, St Ives, Huntingdon and other towns and villages along the routes, operated by Stagecoach in the Fens and Whippet (bus company), Whippet. The A service continues on to the railway station and Addenbrooke's Hospital, Addenbrookes, before terminating at a new Park and Ride inTrumpington
Trumpington is a village and parish to the south of Cambridge, England. The village is an electoral ward of the City of Cambridge and a ward of South Cambridgeshire District Council. The 2011 Census recorded the ward's population as 8,034.
T ...
. Since 2017, it has also linked to Cambridge North railway station.
Air
Although Cambridge has its own airport, Cambridge City Airport, it has no scheduled services and is used mainly by charter and training flights and by Marshall Aerospace for aircraft maintenance. London Stansted Airport, about south via the M11 or direct rail, offers a broad range of international destinations.Metro
In February 2020, consultations opened for a transport system known as the Cambridgeshire Autonomous Metro. It would have connected the historic city centre and the existing busway route with the mainline railway stations, Cambridge Science Park, and Haverhill, Suffolk, Haverhill. In May 2021 the newly elected mayor said he was focused instead on a "revamped bus network" but would not yet abandon the work done.Rail
Education
 Cambridge's two universities, the collegiate
Cambridge's two universities, the collegiate University of Cambridge
The University of Cambridge is a public collegiate research university in Cambridge, England. Founded in 1209 and granted a royal charter by Henry III in 1231, Cambridge is the world's third oldest surviving university and one of its most pr ...
and the local campus of Anglia Ruskin University
Anglia Ruskin University (ARU) is a public university in East Anglia, United Kingdom. Its origins are in the Cambridge School of Art, founded by William John Beamont in 1858. It became a university in 1992, and was renamed after John Ruskin in ...
, serve around 30,000 students, by some estimates. Cambridge University estimated its 2007/08 student population at 17,662, and Anglia Ruskin reports 24,000 students across its two campuses (one of which is outside Cambridge, in Chelmsford, Essex, Chelmsford) for the same period. ARU now (2019) has additional campuses in London and Peterborough. State provision in the further education sector includes Hills Road Sixth Form College, Long Road Sixth Form College, and Cambridge Regional College.
Both state and Independent school (UK), independent schools serve Cambridge pupils from nursery to secondary school age. State schools are administered by Cambridgeshire County Council, which maintains 251 schools in total, 35 of them in Cambridge city. Netherhall School, Chesterton Community College, the Parkside Federation (comprising Parkside Community College and Coleridge Community College), North Cambridge Academy and the Christian inter-denominational St Bede's Inter-Church School, St Bede's School provide comprehensive school, comprehensive secondary education. Many other pupils from the Cambridge area attend village colleges, an educational institution unique to Cambridgeshire, which serve as secondary schools during the day and adult education centres outside of school hours. Independent schools in the city include The Perse School, Stephen Perse Foundation, Sancton Wood School, St Mary's School, Cambridge, St Mary's School, Heritage School, Cambridge, Heritage School and The Leys School. The city has one University Technical College, university technical college, Cambridge Academy for Science and Technology, which opened in September 2014.
Sport
Football
 Cambridge played a unique role in the invention of modern association football, football: the game's first set of rules were drawn up by members of the university in 1848. The Cambridge Rules were first played on Parker's Piece and had a 'defining influence on the 1863 The Football Association, Football Association rules' which again were first played on Parker's Piece.
The city is home to Cambridge United FC, who play at the Abbey Stadium. Formed in 1912, as Abbey United, they were elected to the Football League in 1970 and reached the Football League Second Division in 1978, although a serious decline in them in the mid-1980s saw them drop back down to the Football League Fourth Division and almost go out of business. Success returned to the club in the early 1990s when they won two successive promotions and reached the FA Cup quarter finals in both of those seasons and, in 1992, they came close to becoming the first English team to win three successive Football League promotions which would have taken them into the newly created FA Premier League; however, they were beaten in the play-offs and another decline set in. In 2005, they were relegated from the Football League and, for the second time in 20 years, narrowly avoided going out of business. After nine years of non-league football, they returned to the Football League in 2014 by winning the Conference National play-offs.
Cambridge United WFC is a women's only football club based in Cambridge. The team compete in the FA Women's National League South East. The club plays home games at St Neots Town F.C. and the Abbey Stadium.
Cambridge City FC of the Southern Football League Premier Division now play in the adjoining village of Histon and Impington, Histon. Formed in Cambridge in 1908, as Cambridge Town, the club were Southern Football League, Southern Premier League champions in 1962–63, the highest they have finished in the English football pyramid. After a legal dispute with their landlords, the club left their home ground in Cambridge in order to groundshare with fellow Southern League Premier club Histon FC in 2013-14 and intend to construct a new ground outside the city, in Sawston.
Cambridge played a unique role in the invention of modern association football, football: the game's first set of rules were drawn up by members of the university in 1848. The Cambridge Rules were first played on Parker's Piece and had a 'defining influence on the 1863 The Football Association, Football Association rules' which again were first played on Parker's Piece.
The city is home to Cambridge United FC, who play at the Abbey Stadium. Formed in 1912, as Abbey United, they were elected to the Football League in 1970 and reached the Football League Second Division in 1978, although a serious decline in them in the mid-1980s saw them drop back down to the Football League Fourth Division and almost go out of business. Success returned to the club in the early 1990s when they won two successive promotions and reached the FA Cup quarter finals in both of those seasons and, in 1992, they came close to becoming the first English team to win three successive Football League promotions which would have taken them into the newly created FA Premier League; however, they were beaten in the play-offs and another decline set in. In 2005, they were relegated from the Football League and, for the second time in 20 years, narrowly avoided going out of business. After nine years of non-league football, they returned to the Football League in 2014 by winning the Conference National play-offs.
Cambridge United WFC is a women's only football club based in Cambridge. The team compete in the FA Women's National League South East. The club plays home games at St Neots Town F.C. and the Abbey Stadium.
Cambridge City FC of the Southern Football League Premier Division now play in the adjoining village of Histon and Impington, Histon. Formed in Cambridge in 1908, as Cambridge Town, the club were Southern Football League, Southern Premier League champions in 1962–63, the highest they have finished in the English football pyramid. After a legal dispute with their landlords, the club left their home ground in Cambridge in order to groundshare with fellow Southern League Premier club Histon FC in 2013-14 and intend to construct a new ground outside the city, in Sawston.
Cricket
Parker's Piece was used for first-class cricket matches from 1817 to 1864. The University of Cambridge's cricket ground, Fenner's, is located in the city and is one of the home grounds for minor counties team Cambridgeshire CCC. The Cambridgeshire Cricket Association operates an amateur club cricket league with six adult divisions, including numerous clubs in the city, plus junior divisions. Most of the university colleges also operate their own teams, and there are several casual village cricket teams that play in the city suburbs.Rugby
The city is represented in both codes of Rugby football. Rugby union club Cambridge R.U.F.C. were founded in 1923 and play in National League 1 at their home ground, Grantchester Road, in the south-west corner of the city. Cambridge Lions represent the city in rugby league and are members of East Men's League, East Rugby League.Watersports
 The River Cam, which runs through the city centre, is used for boating. The university and its colleges are well known for Rowing (sport), rowing and the Cambridgeshire Rowing Association, formed in 1868, organises competitive rowing on the river outside of the university. Rowing clubs based in the city include City of Cambridge Rowing Club, City of Cambridge RC, Cambridge '99 Rowing Club, Cambridge '99 RC, Cantabrigian Rowing Club, Cantabrigian RC and Rob Roy Boat Club, Rob Roy BC. Parts of the Cam are used for recreational punt (boat), punting, a type of boating in which the craft is propelled by pushing against the river bed with a quant pole.
Cambridge Swimming Club, Cambridge Dive team and City of Cambridge Water Polo Club are all based at Parkside Swimming Pool.
The River Cam, which runs through the city centre, is used for boating. The university and its colleges are well known for Rowing (sport), rowing and the Cambridgeshire Rowing Association, formed in 1868, organises competitive rowing on the river outside of the university. Rowing clubs based in the city include City of Cambridge Rowing Club, City of Cambridge RC, Cambridge '99 Rowing Club, Cambridge '99 RC, Cantabrigian Rowing Club, Cantabrigian RC and Rob Roy Boat Club, Rob Roy BC. Parts of the Cam are used for recreational punt (boat), punting, a type of boating in which the craft is propelled by pushing against the river bed with a quant pole.
Cambridge Swimming Club, Cambridge Dive team and City of Cambridge Water Polo Club are all based at Parkside Swimming Pool.
Parkour/freerunning
Home and training ground to many influential traceurs, Cambridge is well known for its vibrant, and at times high-profile, parkour and freerunning scene.Other sports
Cambridge is home to two real tennis courts (out of about 50 in the world) at Cambridge University Real Tennis Club. Cambridgeshire Cats play American football at Coldham's Common. Cambridge Royals are members of the British Baseball Federation's Triple-A South Division. Cambridge has two cycling clubs: Team Cambridge and Cambridge Cycling Club. Cambridge & Coleridge Athletic Club is the city's track and field club, based at the University of Cambridge's Wilberforce Road track. Cambridge Handball Club compete in the men's England Handball National Super 8 League and the women's England Handball National Super 7 League. There are three field hockey clubs; Cambridge City Hockey Club, Cambridge South Hockey Club and Cambridge Nomads. The city is also represented in polo by Cambridge Polo Club, based in Barton, Cambridgeshire, Barton, just outside the city. The Romsey Town Rollerbillies play roller derby in Cambridge. Speedway in the United Kingdom, Speedway racing was formerly staged at a greyhound stadium in Coldhams Lane.Varsity sports
Cambridge is known for the sporting events between theUniversity of Cambridge
The University of Cambridge is a public collegiate research university in Cambridge, England. Founded in 1209 and granted a royal charter by Henry III in 1231, Cambridge is the world's third oldest surviving university and one of its most pr ...
and the University of Oxford, especially the rugby union The Varsity Match, Varsity Match and the Oxford and Cambridge Boat Race, Boat Race, though many of these do not take place within either Cambridge or Oxford.
Culture


Theatre
Cambridge's main traditional theatre is the Cambridge Arts Theatre, Arts Theatre, a venue with 666 seats in the town centre. The theatre often has touring shows, as well as those by local companies. The largest venue in the city to regular hold theatrical performances is the Cambridge Corn Exchange with a capacity of 1,800 standing or 1,200 seated. Housed within the city's 19th century former corn exchange building the venue was used for a variety of additional functions throughout the 20th century including Tea party (social gathering), tea parties, motor shows, sports matches and a music venue with temporary stage. The City Council renovated the building in the 1980s, turning it into a full-time arts venue, hosting theatre, dance and music performances. The newest theatre venue in Cambridge is the 220-seat J2, part of Cambridge Junction in Cambridge Leisure Park. The venue was opened in 2005 and hosts theatre, dance, live music and comedy The ADC Theatre is managed by the University of Cambridge, and typically has 3 shows a week during term time. It hosts the Cambridge University Footlights Dramatic Club which has produced many notable figures in British comedy. The Mumford Theatre is part ofAnglia Ruskin University
Anglia Ruskin University (ARU) is a public university in East Anglia, United Kingdom. Its origins are in the Cambridge School of Art, founded by William John Beamont in 1858. It became a university in 1992, and was renamed after John Ruskin in ...
, and hosts shows by both student and non-student groups. There are also a number of venues within the colleges.
Museums
Within the city there are several notable museums, some run by the University of Cambridge Museums consortium and others independent of it. The Fitzwilliam Museum is the city's largest, and is the lead museum of the University of Cambridge Museums. Founded in 1816 from the bequeathment and collections of Richard FitzWilliam, 7th Viscount FitzWilliam, Richard, Viscount FitzWilliam, the museum was originally located in the building of the Perse Grammar School in Free School Lane. After a brief housing in the University of Cambridge library, it moved to its current, purpose-built building on Trumpington Street in 1848. The museum has five departments: Antiquities; Applied Arts; Coins and Medals; Manuscripts and Printed Books; and Paintings, Drawings and Prints. Other members of the University of Cambridge Museums are the Museum of Archaeology and Anthropology, University of Cambridge, Museum of Archaeology and Anthropology, Scott Polar Research Institute, The Polar Museum, Sedgwick Museum of Earth Sciences, The Sedgwick Museum of Earth Sciences, Museum of Classical Archaeology, Cambridge, Museum of Classical Archaeology, Whipple Museum of the History of Science, The Whipple Museum of the History of Science, and the Cambridge University Museum of Zoology, University Museum of Zoology. The Museum of Cambridge, formerly known as the Cambridge & County Folk Museum, is a social history museum located in a former pub on Castle Street. The Centre for Computing History, a museum dedicated to the story of the Information age, moved to Cambridge from Haverhill, Suffolk, Haverhill in 2013. Housed in a former sewage pumping station, the Cambridge Museum of Technology has a collection of large exhibits related to the city's industrial heritage.Music
Popular music
Pink Floyd are the most notable band with roots in Cambridge. The band's former songwriter, guitarist and vocalist Syd Barrett was born and lived in the city, and he and another founding member, Roger Waters, went to school together at Cambridgeshire High School for Boys. David Gilmour, the guitarist who replaced Barrett, was also a Cambridge resident and attended the nearby Perse School. Bands that were formed in Cambridge include Clean Bandit, Henry Cow, The Movies (UK band), The Movies, Katrina and the Waves, The Soft Boys, Ezio (band), Ezio The Broken Family Band, Uncle Acid & the Deadbeats, and the pop-classical group the King's Singers, who were formed at the university. Solo artist Boo Hewerdine is from Cambridge, as are drum and bass artists (and brothers) Nu:Tone and Logistics (artist), Logistics. Singers Matthew Bellamy, of the rock band Muse (band), Muse, Tom Robinson, Olivia Newton-John and Charli XCX were born in the city. 2012 Mercury Prize winners Alt-J are based in Cambridge. Live music venues hosting popular music in the city include the Cambridge Corn Exchange, Cambridge Junction and the Portland Arms, as well as The Blue Moon.Classical music
Started in 1991, the annual Cambridge Music Festival takes place each November. The Cambridge Summer Music Festival takes place in July.Contemporary art
Cambridge containsKettle's Yard
Kettle's Yard is an art gallery and house in Cambridge, England. The director of the art gallery is Andrew Nairne. Both the house and gallery reopened in February 2018 after an expansion of the facilities.
Kettle's Yard galleries, shop and caf ...
gallery of modern and contemporary art and the Downing College, Cambridge#Heong Gallery, Heong Gallery which opened to the public in 2016 at Downing College, Cambridge, Downing College. Anglia Ruskin University operates the publicly accessible Ruskin Gallery within the Cambridge School of Art. Wysing Arts Centre, one of the leading research centres for the visual arts in Europe, is associated with the city, though is located several miles west of Cambridge. Artist-run organisations including Aid & Abet, Cambridge Art Salon, Changing Spaces and Motion Sickness also run exhibitions, events and artists' studios in the city, often in short-term or temporary spaces.
Festivals and events

 Several fairs and festivals take place in Cambridge, mostly during the British summer. Midsummer Common, Midsummer Fair dates back to 1211, when it was granted a charter by John, King of England, King John. Today it exists primarily as an annual travelling funfair, funfair with the vestige of a market attached and is held over several days around or close to midsummers day. On the first Saturday in June Midsummer Common is the site for Strawberry Fair, a free music and children's fair, with various market stalls. For one week in May, on
Several fairs and festivals take place in Cambridge, mostly during the British summer. Midsummer Common, Midsummer Fair dates back to 1211, when it was granted a charter by John, King of England, King John. Today it exists primarily as an annual travelling funfair, funfair with the vestige of a market attached and is held over several days around or close to midsummers day. On the first Saturday in June Midsummer Common is the site for Strawberry Fair, a free music and children's fair, with various market stalls. For one week in May, on Jesus Green
Jesus Green is a park in the north of central Cambridge, Cambridgeshire, England, north of Jesus College. Jesus Ditch runs along the southern edge Jesus Green. On the northern edge of Jesus Green is the River Cam, with Chesterton Road (th ...
, the annual Cambridge Beer Festival
The summer Cambridge Beer Festival is the longest-running CAMRA beer festival in the United Kingdom, having started in 1974. It is held at the end of May just before the Whitsuntide Bank Holiday. The winter beer festival is a smaller, indoor ev ...
has been held since 1974.
Cambridge Folk Festival is held annually in the grounds of Cherry Hinton Hall. The festival has been organised by the city council since its inception in 1964. The Cambridge Summer Music Festival is an annual festival of classical music, held in the university's colleges and chapels. The Cambridge Shakespeare Festival is an eight-week season of open-air performances of the works of William Shakespeare, held in the gardens of various colleges of the university. Started in 1977, the Cambridge Film Festival was held annually in July, moving to September in 2008 to avoid a clash with the rescheduled Edinburgh Film Festival.
The Cambridge Science Festival, typically held annually in March, is the United Kingdom's largest free science festival. The Cambridge Literary Festival, which focusses on contemporary literary fiction and non-fiction, is held bi-annually in April and November. Between 1975 and 1985 the Cambridge Poetry Festival was held biannually. Other festivals include the annual Mill Road Winter Fair, held the first Saturday of December, the E-luminate Festival, which took place every February from 2013 to 2018, and The Big Weekend, a city outdoor event organised by the City Council every July.
Three Cambridge Free Festivals held in 1969, 1970, and 1971 that featured artists including David Bowie, King Crimson, Roy Harper (singer), Roy Harper, Spontaneous Combustion (English band), Spontaneous Combustion, UFO (band), UFO and others are believed by the festival organiser to have been the first free multiple-day rock music festivals held in the UK.
Literature and film
The city has been the setting for all or part of several novels, including Douglas Adams' ''Dirk Gently's Holistic Detective Agency'', Rose Macaulay's ''They Were Defeated'', Kate Atkinson (writer), Kate Atkinson's ''Case Histories'', Rebecca Stott's ''Ghostwalk'' and Robert Harris (novelist), Robert Harris' ''Enigma'', while Susanna Gregory wrote a series of novels set in 14th century Cambridge. Gwen Raverat, the granddaughter of Charles Darwin, talked about her late Victorian Cambridge childhood in her memoir ''Period Piece (book), Period Piece'', and ''The Night Climbers of Cambridge'' is a book written by Noel Symington under the pseudonym "Whipplesnaith" about nocturnal climbing on the colleges and town buildings of Cambridge in the 1930s. Fictionalised versions of Cambridge appear in Philippa Pearce's ''Tom's Midnight Garden'' and ''Minnow on the Say'', the city renamed as Castleford, and as the home of Tom Sharpe's fictional college in ''Porterhouse Blue''. ITV (TV network), ITV TV series Grantchester (TV series), ''Granchester'' was partly filmed in Cambridge.Television
News and television programmes are broadcast from the BBC East studio in Cambridge that is home to BBC Look East (West) which covers the city,Cambridgeshire
Cambridgeshire (abbreviated Cambs.) is a county in the East of England, bordering Lincolnshire to the north, Norfolk to the north-east, Suffolk to the east, Essex and Hertfordshire to the south, and Bedfordshire and Northamptonshire to the ...
, Northamptonshire, Bedfordshire
Bedfordshire (; abbreviated Beds) is a ceremonial county in the East of England. The county has been administered by three unitary authorities, Borough of Bedford, Central Bedfordshire and Borough of Luton, since Bedfordshire County Council ...
, Milton Keynes (Buckinghamshire) and parts of Hertfordshire. ITV Anglia is another TV news which broadcasts from Norwich.
Public services
Cambridge Biomedical Campus
The Cambridge Biomedical Campus is the largest centre of medical research and health science in Europe. The site is located at the southern end of Hills Road in Cambridge, England.
Over 20,000 people work at the site, which is home to Cambridge ...
, Addenbrooke's is one of the largest hospitals in the United Kingdom and is a designated regional trauma centre.
The East of England Ambulance Service covers the city and has an ambulance station on Hills Road. The smaller Brookfields Hospital stands on Mill Road. Cambridgeshire Constabulary provides the city's policing; the main police station is at Parkside, Cambridge, Parkside, adjacent to the city's fire station, operated by Cambridgeshire Fire and Rescue Service.
Cambridge Water Company supplies water services to the city, while Anglian Water provides sewerage services. For the supply of electricity, Cambridge is part of the East of England region, for which the distribution network operator is UK Power Networks. The city has no power stations, though a five-metre wind turbine, part of a Cambridge Regional College development, can be seen in King's Hedges
King's Hedges is an electoral ward in the north of the city of Cambridge, England.
History
The open land to the north of Cambridge that now comprises King's Hedges was known as ''Albrach'' from as early as the 13th century. In 1558 it was agree ...
. The Cambridge Electric Supply Company had provided the city with electricity since the early twentieth century from Cambridge power station. Upon Nationalization, nationalisation of the electricity industry in 1948 ownership passed to the British Electricity Authority and later to the Central Electricity Generating Board. Electricity connections to the National Grid (Great Britain), national grid rendered the small 7.26 Watt, megawatt (MW) coal fired power station redundant. It closed in 1965 and was subsequently demolished; in its final year of operation it delivered 2771 Kilowatt hour, MWh of electricity to the city.
Following the Public Libraries Act 1850 the city's first public library, located on Jesus Lane, was opened in 1855. It was moved to the Guildhall in 1862, and is now located in the Grand Arcade (Cambridge), Grand Arcade shopping centre. The library was reopened in September 2009, after having been closed for refurbishment for 33 months, more than twice as long as was forecast when the library closed for redevelopment in January 2007. As of 2018 the city contains six public libraries, run by the County Council.
The Cambridge City Cemetery is located to the north of Newmarket Road, Cambridge, Newmarket Road.
Religion
Cambridge has a List of churches in Cambridge, number of churches, some of which form a significant part of the city's architectural landscape. Like the rest of Cambridgeshire it is part of the Anglican Diocese of Ely. St Mary the Great with St Michael, Cambridge, Great St Mary's Church has the status of "University Church". Many of the university colleges contain chapels that hold services according to the rites and ceremonies of the Church of England, while the chapel of St Edmund's College, Cambridge, St Edmund's College is Roman Catholic. The city also has a number of Cambridge Theological Federation, theological colleges training clergy for ordination into a number of denominations, with affiliations to both the University of Cambridge andAnglia Ruskin University
Anglia Ruskin University (ARU) is a public university in East Anglia, United Kingdom. Its origins are in the Cambridge School of Art, founded by William John Beamont in 1858. It became a university in 1992, and was renamed after John Ruskin in ...
.
Cambridge is in the Roman Catholic Diocese of East Anglia and is served by the large Gothic Revival Our Lady and the English Martyrs Church
The Church of Our Lady of the Assumption and the English Martyrs, also known as the Church of Our Lady and the English Martyrs (OLEM), is an English Roman Catholic parish church located at the junction of Hills Road and Lensfield Road in southeas ...
at the junction of Hills Road and Lensfield Road, St Laurence's Church, Cambridge, St Laurence's on Milton Road, St Vincent De Paul Church on Ditton Lane and by the church of St Philip Howard, in Cherry Hinton Road.
There is a Moscow Patriarchate, Russian Orthodox church under the Russian Orthodox Diocese of Sourozh, Diocese of Sourozh who worship at the chapel of Westcott House, Cambridge, Westcott House, the Greek Orthodox Church holds services at the purpose-built St Athanasios church under the Archdiocese of Thyateira and Great Britain, while the Romanian Orthodox Church share St Giles' Church, Cambridge, St Giles' with the Church of England.
There are two Methodism, Methodist churches in the city. Wesley Methodist Church, Cambridge, Wesley Methodist Church was built in 1913, and is located next to
Christ's Pieces. The Castle Street Methodist Church is the oldest of the two, having been built in 1823, and was formerly a Primitive Methodist Church, Primitive Methodist church.
There are three Quaker Meetings in Cambridge, located on Jesus Lane, Hartington Grove, and a Meeting called "Oast House" that meets in Pembroke College, Cambridge, Pembroke College.
An Orthodox Judaism, Orthodox synagogue and Jewish student centre is located on Thompson's Lane, operated jointly by the Cambridge Traditional Jewish Congregation and the Cambridge University Jewish Society, which is affiliated to the Union of Jewish Students. The Beth Shalom Reform Judaism, Reform synagogue which previously met at a local school, opened a purpose-built synagogue in 2015. There is also a student-led egalitarian minyan which holds services on Friday evenings.
Cambridge Central Mosque is the main place of worship for Cambridge's community of around 4,000 Muslims. Opened in 2019, it is described as Europe's first eco-friendly mosque and is the first purpose-built mosque within the city. The Abu Bakr Jamia Islamic Centre on Mawson Road and the Omar Faruque Mosque and Cultural Centre in Kings Hedges are additional places of Muslim worship.
Cambridge Buddhist Centre, which belongs to Triratna Buddhist Community, was opened in the former Theatre Royal, Barnwell, Cambridge, Barnwell Theatre on Newmarket Road in 1998. There are also several local Buddhist meditation groups from various Buddhist including Samatha Trust and Buddha Mettā Society.
A Hinduism, Hindu shrine was opened in 2010 at the Bharat Bhavan Indian cultural centre off Mill Road, Cambridge, Mill Road.
A Sikhism, Sikh community has met in the city since 1982, and a Gurdwara was opened in Arbury
Arbury is a district and electoral ward of the city of Cambridge, England. The ward borders the following other wards (from North, proceeding clockwise): Histon, King's Hedges, West Chesterton, Market and Castle.
History
The area has been occu ...
in 2013.
Twinned cities
Cambridge is Twin towns and sister cities, twinned with two cities. Like Cambridge, both have universities and are also similar in population; Heidelberg, Germany since 1965, and Szeged, Hungary since 1987.Panoramic gallery
See also
* List of bridges in Cambridge * List of churches in Cambridge * Cambridgeshire Archives and Local Studies * :Buildings and structures in Cambridge * :Organisations based in Cambridge * :People from CambridgeExplanatory notes
References
Further reading
* * Tim Rawle, Rawle, Tim (author and photographer), John Adamson (publisher), John Adamson (editor). ''Cambridge (book), Cambridge'' (new ed. with foreword by William Bortrick). Cambridge: The Oxbridge Portfolio (2016), 204 pp.External links
Cambridge City Council
Greater Cambridge Partnership
Cambridgeshire Association for Local History
Cambridgeshire Community Archives
Visit Cambridge
the official tourism website for Cambridge {{authority control Cambridge, Cities in the East of England County towns in England Non-metropolitan districts of Cambridgeshire Towns in Cambridgeshire Unparished areas in Cambridgeshire Boroughs in England