Etymology
 The Spaniards gave the name to the peninsula of Baja California and to Alta California, the latter region becoming the present-day state of California.
The name likely derived from the mythical island of California in the fictional story of Queen Calafia, as recorded in a 1510 work '' The Adventures of Esplandián'' by Garci Rodríguez de Montalvo. This work was the fifth in a popular Spanish chivalric romance series that began with '' Amadís de Gaula''. Queen Calafia's kingdom was said to be a remote land rich in gold and pearls, inhabited by beautiful Black women who wore gold armor and lived like
The Spaniards gave the name to the peninsula of Baja California and to Alta California, the latter region becoming the present-day state of California.
The name likely derived from the mythical island of California in the fictional story of Queen Calafia, as recorded in a 1510 work '' The Adventures of Esplandián'' by Garci Rodríguez de Montalvo. This work was the fifth in a popular Spanish chivalric romance series that began with '' Amadís de Gaula''. Queen Calafia's kingdom was said to be a remote land rich in gold and pearls, inhabited by beautiful Black women who wore gold armor and lived like History
First inhabitants
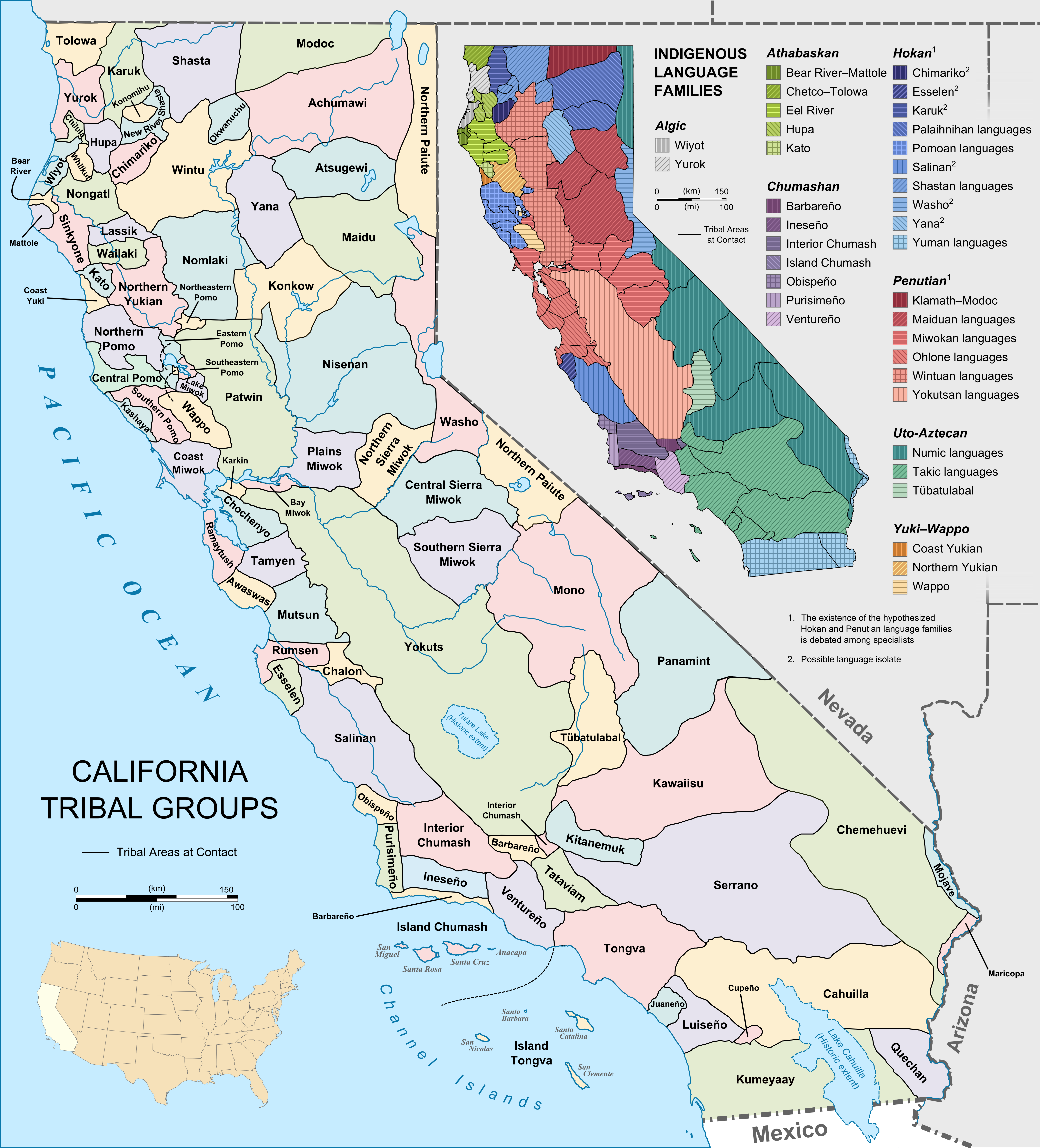
Settled by successive waves of arrivals during at least the last 13,000 years, California was one of the most culturally and linguistically diverse areas in pre-Columbian North America. Various estimates of the native population have ranged from 100,000 to 300,000. The indigenous peoples of California included more than 70 distinct ethnic groups, inhabiting environments from mountains and deserts to islands and redwood forests. These groups were also diverse in their political organization, with bands, tribes, villages, and on the resource-rich coasts, large chiefdoms, such as the Chumash, Pomo and Salinan. Trade, intermarriage and military alliances fostered social and economic relationships between many groups.Spanish period
The first Europeans to explore the coast of California were the members of a Spanish maritime expedition led by Portuguese captain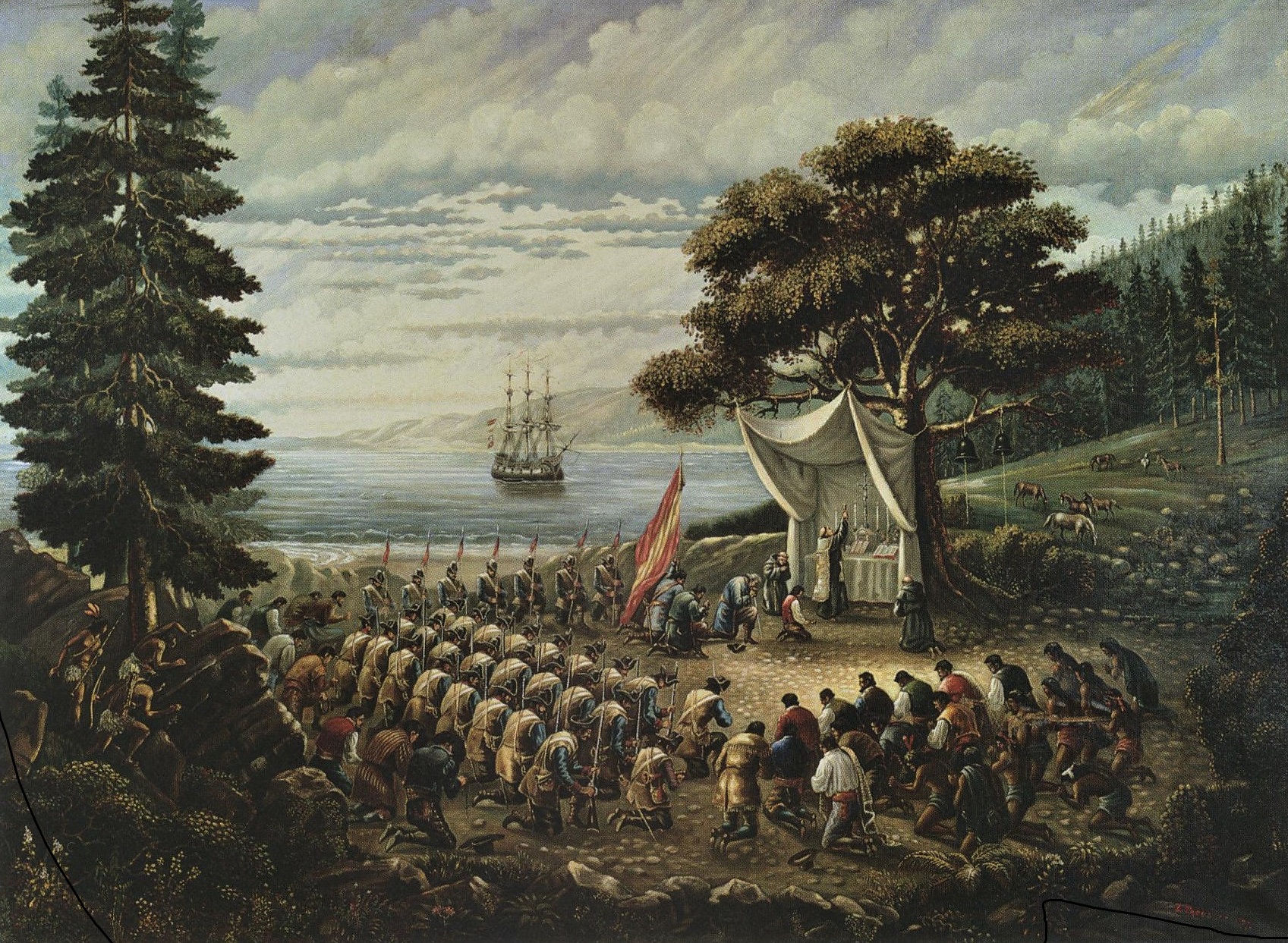 After the Portolà expedition, Spanish
After the Portolà expedition, Spanish  During this same period, sailors from the Russian Empire explored along the northern coast of California. In 1812, the Russian-American Company established a trading post and small fortification at Fort Ross on the
During this same period, sailors from the Russian Empire explored along the northern coast of California. In 1812, the Russian-American Company established a trading post and small fortification at Fort Ross on the Mexican period
 In 1821, the Mexican War of Independence gave the Mexican Empire (which included California) independence from Spain. For the next 25 years, Alta California remained a remote, sparsely populated, northwestern administrative district of the newly independent country of Mexico, which shortly after independence became a republic.
The
In 1821, the Mexican War of Independence gave the Mexican Empire (which included California) independence from Spain. For the next 25 years, Alta California remained a remote, sparsely populated, northwestern administrative district of the newly independent country of Mexico, which shortly after independence became a republic.
The U.S. Conquest and the California Republic
 In 1846, a group of American settlers in and around Sonoma rebelled against Mexican rule during the
In 1846, a group of American settlers in and around Sonoma rebelled against Mexican rule during the Early American period
 Following the Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo (February 2, 1848) that ended the war, the westernmost portion of the annexed Mexican territory of Alta California soon became the American state of California, and the remainder of the old territory was then subdivided into the new American Territories of Arizona, Nevada, Colorado and Utah. The even more lightly populated and arid lower region of old Baja California remained as a part of Mexico. In 1846, the total settler population of the western part of the old Alta California had been estimated to be no more than 8,000, plus about 100,000 Native Americans, down from about 300,000 before Hispanic settlement in 1769.
In 1848, only one week before the official American annexation of the area, gold was discovered in California, this being an event which was to forever alter both the state's demographics and its finances. Soon afterward, a massive influx of immigration into the area resulted, as prospectors and miners arrived by the thousands. The population burgeoned with United States citizens, Europeans, Chinese and other immigrants during the great
Following the Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo (February 2, 1848) that ended the war, the westernmost portion of the annexed Mexican territory of Alta California soon became the American state of California, and the remainder of the old territory was then subdivided into the new American Territories of Arizona, Nevada, Colorado and Utah. The even more lightly populated and arid lower region of old Baja California remained as a part of Mexico. In 1846, the total settler population of the western part of the old Alta California had been estimated to be no more than 8,000, plus about 100,000 Native Americans, down from about 300,000 before Hispanic settlement in 1769.
In 1848, only one week before the official American annexation of the area, gold was discovered in California, this being an event which was to forever alter both the state's demographics and its finances. Soon afterward, a massive influx of immigration into the area resulted, as prospectors and miners arrived by the thousands. The population burgeoned with United States citizens, Europeans, Chinese and other immigrants during the great California Genocide
Under earlier Spanish and Mexican rule, California's original native population had precipitously declined, above all, from Eurasian diseases to which the indigenous people of California had not yet developed a natural immunity. Under its new American administration, California's harsh governmental policies towards its own indigenous people did not improve. As in other American states, many of the native inhabitants were soon forcibly removed from their lands by incoming American settlers such as miners, ranchers, and farmers. Although California had entered the American union as a free state, the "loitering or orphaned Indians" were de facto enslaved by their new Anglo-American masters under the 1853 '' Act for the Government and Protection of Indians''. There were also massacres in which hundreds of indigenous people were killed. Between 1850 and 1860, the California state government paid around 1.5million dollars (some 250,000 of which was reimbursed by the federal government) to hire militias whose purpose was to protect settlers from the indigenous populations. In later decades, the native population was placed in reservations and rancherias, which were often small and isolated and without enough natural resources or funding from the government to sustain the populations living on them. As a result, the rise of California was a calamity for the native inhabitants. Several scholars and Native American activists, including Benjamin Madley and Ed Castillo, have described the actions of the California government as a genocide.1900–present
 In the twentieth century, thousands of Japanese people migrated to the US and California specifically to attempt to purchase and own land in the state. However, the state in 1913 passed the Alien Land Act, excluding Asian immigrants from owning land. During World War II, Japanese Americans in California were interned in concentration camps such as at Tule Lake and Manzanar. In 2020, California officially apologized for this internment.
Migration to California accelerated during the early 20th century with the completion of major transcontinental highways like the Lincoln Highway and
In the twentieth century, thousands of Japanese people migrated to the US and California specifically to attempt to purchase and own land in the state. However, the state in 1913 passed the Alien Land Act, excluding Asian immigrants from owning land. During World War II, Japanese Americans in California were interned in concentration camps such as at Tule Lake and Manzanar. In 2020, California officially apologized for this internment.
Migration to California accelerated during the early 20th century with the completion of major transcontinental highways like the Lincoln Highway and  Meanwhile, attracted to the mild Mediterranean climate, cheap land, and the state's wide variety of geography, filmmakers established the studio system in Hollywood in the 1920s. California manufactured 8.7 percent of total United States military armaments produced during World War II, ranking third (behind
Meanwhile, attracted to the mild Mediterranean climate, cheap land, and the state's wide variety of geography, filmmakers established the studio system in Hollywood in the 1920s. California manufactured 8.7 percent of total United States military armaments produced during World War II, ranking third (behind  During the 20th century, two great disasters happened in California. The
During the 20th century, two great disasters happened in California. The  In the twenty-first century, droughts and frequent wildfires attributed to climate change have occurred in the state. From 2011 to 2017, a 2011–2017 California drought, persistent drought was the worst in its recorded history. The 2018 wildfire season was the state's deadliest and most destructive, most notably Camp Fire (2018), Camp Fire.
Although air pollution problems have been reduced, health problems associated with pollution have continued. The brown haze that is known as "
In the twenty-first century, droughts and frequent wildfires attributed to climate change have occurred in the state. From 2011 to 2017, a 2011–2017 California drought, persistent drought was the worst in its recorded history. The 2018 wildfire season was the state's deadliest and most destructive, most notably Camp Fire (2018), Camp Fire.
Although air pollution problems have been reduced, health problems associated with pollution have continued. The brown haze that is known as "Geography
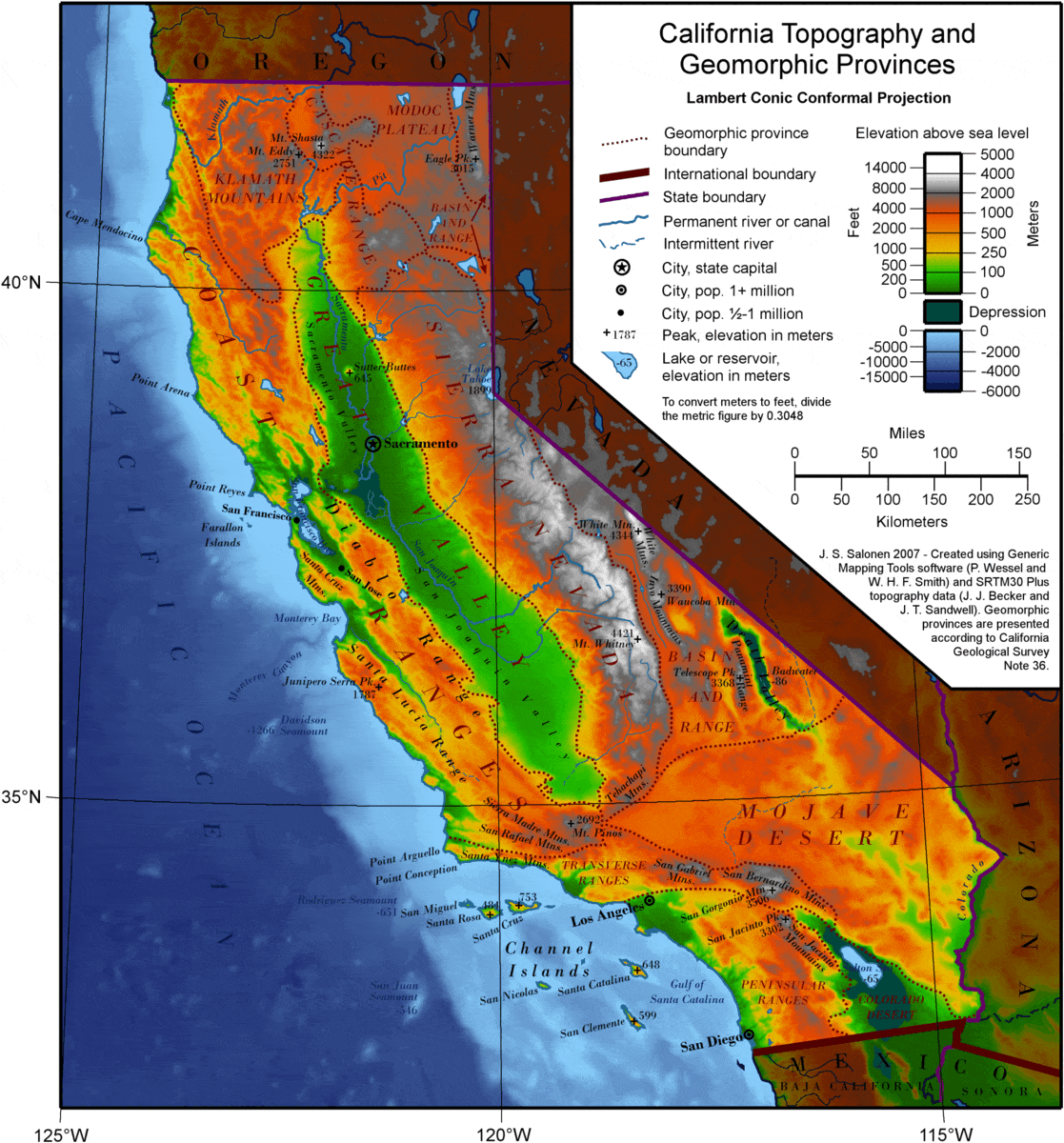 Covering an area of , California is the List of U.S. states by area, third-largest state in the United States in area, after Alaska and Texas. California is one of the most geographically diverse states in the union and is often geographically bisected into two regions, Southern California, comprising the ten southernmost counties, and Northern California, comprising the 48 northernmost counties. It is bordered by Oregon to the north, Nevada to the east and northeast, Arizona to the southeast, the Pacific Ocean to the west and shares an international border with the Mexico, Mexican state of Baja California to the south (with which it makes up part of The Californias region of North America, alongside Baja California Sur).
In the middle of the state lies the California Central Valley, bounded by the Sierra Nevada in the east, the Pacific Coast Ranges, coastal mountain ranges in the west, the Cascade Range to the north and by the Tehachapi Mountains in the south. The Central Valley is California's productive agricultural heartland.
Divided in two by the Sacramento-San Joaquin River Delta, the northern portion, the Sacramento Valley serves as the watershed of the Sacramento River, while the southern portion, the San Joaquin Valley is the watershed for the San Joaquin River. Both valleys derive their names from the rivers that flow through them. With dredging, the Sacramento and the San Joaquin Rivers have remained deep enough for several inland cities to be seaports.
Covering an area of , California is the List of U.S. states by area, third-largest state in the United States in area, after Alaska and Texas. California is one of the most geographically diverse states in the union and is often geographically bisected into two regions, Southern California, comprising the ten southernmost counties, and Northern California, comprising the 48 northernmost counties. It is bordered by Oregon to the north, Nevada to the east and northeast, Arizona to the southeast, the Pacific Ocean to the west and shares an international border with the Mexico, Mexican state of Baja California to the south (with which it makes up part of The Californias region of North America, alongside Baja California Sur).
In the middle of the state lies the California Central Valley, bounded by the Sierra Nevada in the east, the Pacific Coast Ranges, coastal mountain ranges in the west, the Cascade Range to the north and by the Tehachapi Mountains in the south. The Central Valley is California's productive agricultural heartland.
Divided in two by the Sacramento-San Joaquin River Delta, the northern portion, the Sacramento Valley serves as the watershed of the Sacramento River, while the southern portion, the San Joaquin Valley is the watershed for the San Joaquin River. Both valleys derive their names from the rivers that flow through them. With dredging, the Sacramento and the San Joaquin Rivers have remained deep enough for several inland cities to be seaports.


 The Tulare Lake was the largest freshwater lake west of the Mississippi River. A remnant of Pleistocene-era Lake Corcoran, Tulare Lake dried up by the early 20th century after its tributary rivers were diverted for agricultural irrigation and municipal water uses.
About 45 percent of the state's total surface area is covered by forests, and California's diversity of pine species is unmatched by any other state. California contains more forestland than any other state except Alaska. Many of the trees in the White Mountains (California), California White Mountains are the oldest in the world; an individual bristlecone pine is over 5,000 years old.
In the south is a large inland salt lake, the Salton Sea. The south-central desert is called the Mojave Desert, Mojave; to the northeast of the Mojave lies Death Valley, which contains the lowest and hottest place in North America, the Badwater Basin at . The horizontal distance from the bottom of Death Valley to the top of Mount Whitney is less than . Indeed, almost all of southeastern California is arid, hot desert, with routine extreme high temperatures during the summer. The southeastern border of California with Arizona is entirely formed by the Colorado River, from which the southern part of the state gets about half of its water.
A majority of California's cities are located in either the San Francisco Bay Area or the Sacramento metropolitan area in Northern California; or the Los Angeles metropolitan area, Los Angeles area, the Inland Empire, or the San Diego metropolitan area in Southern California. The Los Angeles Area, the Bay Area, and the San Diego metropolitan area are among several major metropolitan areas along the California coast.
As part of the Pacific Ring of Fire, Ring of Fire, California is subject to tsunamis, floods, droughts, Santa Ana winds, wildfires, landslides on steep terrain, and has several volcanoes. It has many List of earthquakes in California, earthquakes due to several faults running through the state, the largest being the San Andreas Fault. About 37,000 earthquakes are recorded each year, but most are too small to be felt.
The Tulare Lake was the largest freshwater lake west of the Mississippi River. A remnant of Pleistocene-era Lake Corcoran, Tulare Lake dried up by the early 20th century after its tributary rivers were diverted for agricultural irrigation and municipal water uses.
About 45 percent of the state's total surface area is covered by forests, and California's diversity of pine species is unmatched by any other state. California contains more forestland than any other state except Alaska. Many of the trees in the White Mountains (California), California White Mountains are the oldest in the world; an individual bristlecone pine is over 5,000 years old.
In the south is a large inland salt lake, the Salton Sea. The south-central desert is called the Mojave Desert, Mojave; to the northeast of the Mojave lies Death Valley, which contains the lowest and hottest place in North America, the Badwater Basin at . The horizontal distance from the bottom of Death Valley to the top of Mount Whitney is less than . Indeed, almost all of southeastern California is arid, hot desert, with routine extreme high temperatures during the summer. The southeastern border of California with Arizona is entirely formed by the Colorado River, from which the southern part of the state gets about half of its water.
A majority of California's cities are located in either the San Francisco Bay Area or the Sacramento metropolitan area in Northern California; or the Los Angeles metropolitan area, Los Angeles area, the Inland Empire, or the San Diego metropolitan area in Southern California. The Los Angeles Area, the Bay Area, and the San Diego metropolitan area are among several major metropolitan areas along the California coast.
As part of the Pacific Ring of Fire, Ring of Fire, California is subject to tsunamis, floods, droughts, Santa Ana winds, wildfires, landslides on steep terrain, and has several volcanoes. It has many List of earthquakes in California, earthquakes due to several faults running through the state, the largest being the San Andreas Fault. About 37,000 earthquakes are recorded each year, but most are too small to be felt.
Climate
 Although most of the state has a Mediterranean climate, due to the state's large size the climate ranges from Polar climate, polar to subtropical climate, subtropical. The cool California Current offshore often creates summer fog near the coast. Farther inland, there are colder winters and hotter summers. The maritime moderation results in the shoreline summertime temperatures of Los Angeles and San Francisco being the coolest of all major metropolitan areas of the United States and uniquely cool compared to areas on the same latitude in the interior and on the east coast of the North American continent. Even the San Diego shoreline bordering Mexico is cooler in summer than most areas in the contiguous United States. Just a few miles inland, summer temperature extremes are significantly higher, with downtown Los Angeles being several degrees Climate of the Los Angeles Basin, warmer than at the coast. The same microclimate phenomenon is seen in the San Francisco Bay Area#Climate, climate of the Bay Area, where areas sheltered from the ocean experience significantly hotter summers in contrast with nearby areas closer to the ocean.
Although most of the state has a Mediterranean climate, due to the state's large size the climate ranges from Polar climate, polar to subtropical climate, subtropical. The cool California Current offshore often creates summer fog near the coast. Farther inland, there are colder winters and hotter summers. The maritime moderation results in the shoreline summertime temperatures of Los Angeles and San Francisco being the coolest of all major metropolitan areas of the United States and uniquely cool compared to areas on the same latitude in the interior and on the east coast of the North American continent. Even the San Diego shoreline bordering Mexico is cooler in summer than most areas in the contiguous United States. Just a few miles inland, summer temperature extremes are significantly higher, with downtown Los Angeles being several degrees Climate of the Los Angeles Basin, warmer than at the coast. The same microclimate phenomenon is seen in the San Francisco Bay Area#Climate, climate of the Bay Area, where areas sheltered from the ocean experience significantly hotter summers in contrast with nearby areas closer to the ocean.
 Northern parts of the state have more rain than the south. California's mountain ranges also influence the climate: some of the rainiest parts of the state are west-facing mountain slopes. Northwestern California has a temperate climate, and the Central Valley has a Mediterranean climate but with greater temperature extremes than the coast. The high mountains, including the Sierra Nevada, have an alpine climate with snow in winter and mild to moderate heat in summer.
California's mountains produce rain shadows on the eastern side, creating extensive deserts. The higher elevation deserts of eastern California have hot summers and cold winters, while the low deserts east of the Southern California mountains have hot summers and nearly frostless mild winters. Death Valley, a desert with large expanses below sea level, is considered the hottest location in the world; the highest temperature in the world, (The 136.4°F (58°C), claimed by 'Aziziya, Libya, on September 13, 1922, has been officially deemed invalid by the World Meteorological Organization.) , was recorded there on July 10, 1913. The lowest temperature in California was on January 20, 1937, in Boca, California, Boca.
The table below lists average temperatures for January and August in a selection of places throughout the state; some highly populated and some not. This includes the relatively cool summers of the Humboldt Bay region around Eureka, California, Eureka, the extreme heat of Death Valley, and the mountain climate of Mammoth Lakes, California, Mammoth in the Sierra Nevada.
The wide range of climates leads to a high demand for water. Over time, Droughts in California, droughts and List of California wildfires, wildfires have been increasing Climate change in California, due to climate change and Water extraction, overextraction, becoming less seasonal and more year-round, further straining California's electricity supply and water security and having an impact on California business, industry, and agriculture.
Northern parts of the state have more rain than the south. California's mountain ranges also influence the climate: some of the rainiest parts of the state are west-facing mountain slopes. Northwestern California has a temperate climate, and the Central Valley has a Mediterranean climate but with greater temperature extremes than the coast. The high mountains, including the Sierra Nevada, have an alpine climate with snow in winter and mild to moderate heat in summer.
California's mountains produce rain shadows on the eastern side, creating extensive deserts. The higher elevation deserts of eastern California have hot summers and cold winters, while the low deserts east of the Southern California mountains have hot summers and nearly frostless mild winters. Death Valley, a desert with large expanses below sea level, is considered the hottest location in the world; the highest temperature in the world, (The 136.4°F (58°C), claimed by 'Aziziya, Libya, on September 13, 1922, has been officially deemed invalid by the World Meteorological Organization.) , was recorded there on July 10, 1913. The lowest temperature in California was on January 20, 1937, in Boca, California, Boca.
The table below lists average temperatures for January and August in a selection of places throughout the state; some highly populated and some not. This includes the relatively cool summers of the Humboldt Bay region around Eureka, California, Eureka, the extreme heat of Death Valley, and the mountain climate of Mammoth Lakes, California, Mammoth in the Sierra Nevada.
The wide range of climates leads to a high demand for water. Over time, Droughts in California, droughts and List of California wildfires, wildfires have been increasing Climate change in California, due to climate change and Water extraction, overextraction, becoming less seasonal and more year-round, further straining California's electricity supply and water security and having an impact on California business, industry, and agriculture.
Ecology
 California is one of the ecologically richest and most diverse parts of the world, and includes some of the most endangered ecological communities. California is part of the Nearctic realm and spans a number of terrestrial ecoregions.
California's large number of endemic (ecology), endemic species includes Relict (biology), relict species, which have died out elsewhere, such as the Catalina ironwood (''Lyonothamnus floribundus''). Many other endemics originated through differentiation or adaptive radiation, whereby multiple species develop from a common ancestor to take advantage of diverse ecological conditions such as the California lilac (''Ceanothus''). Many California endemics have become endangered, as urbanization, logging, overgrazing, and the introduction of exotic species have encroached on their habitat.
California is one of the ecologically richest and most diverse parts of the world, and includes some of the most endangered ecological communities. California is part of the Nearctic realm and spans a number of terrestrial ecoregions.
California's large number of endemic (ecology), endemic species includes Relict (biology), relict species, which have died out elsewhere, such as the Catalina ironwood (''Lyonothamnus floribundus''). Many other endemics originated through differentiation or adaptive radiation, whereby multiple species develop from a common ancestor to take advantage of diverse ecological conditions such as the California lilac (''Ceanothus''). Many California endemics have become endangered, as urbanization, logging, overgrazing, and the introduction of exotic species have encroached on their habitat.
Flora and fauna
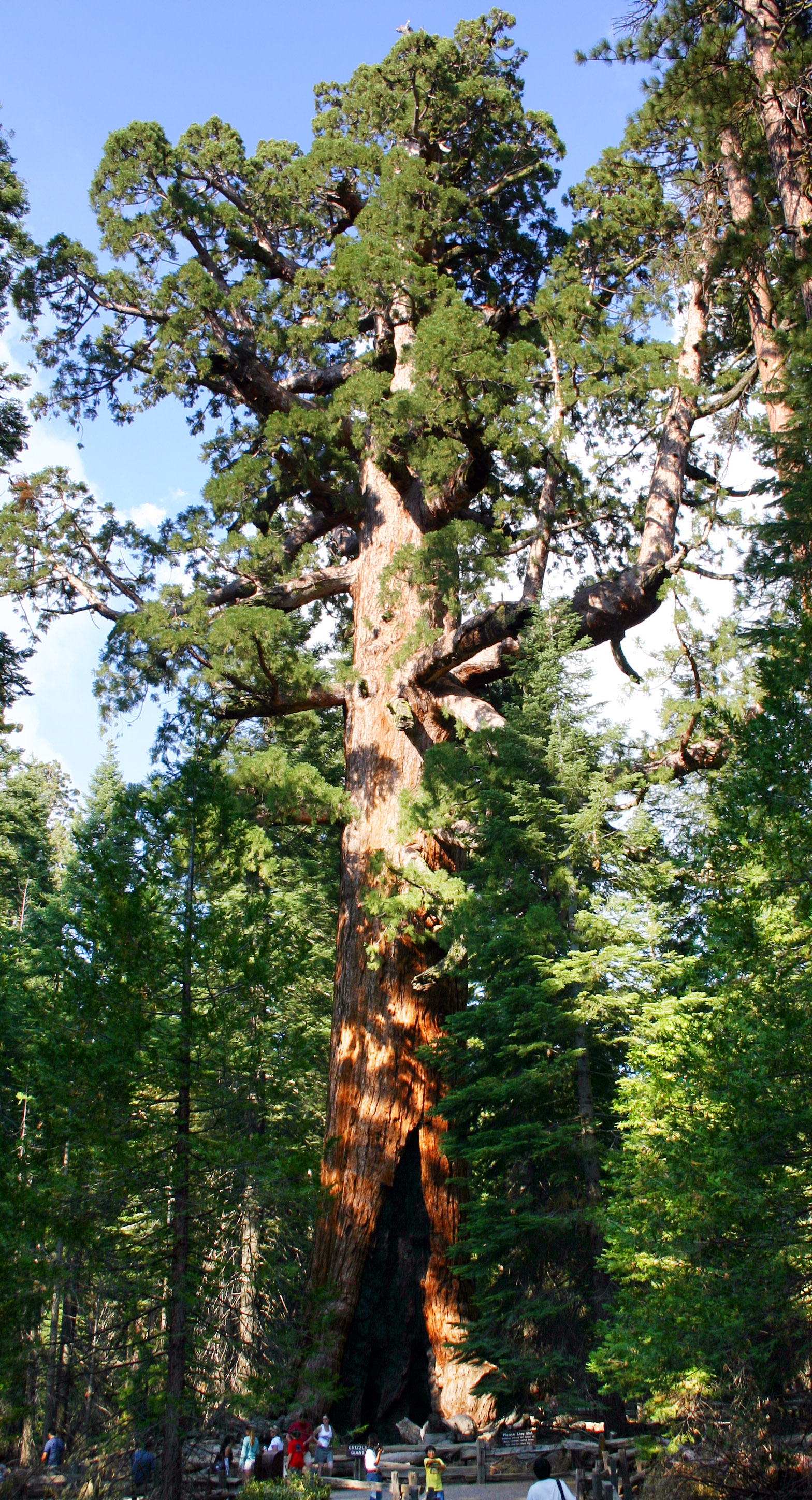 California boasts several superlatives in its collection of flora: the giant sequoia, largest trees, the coast redwood, tallest trees, and the pinus longaeva, oldest trees. California's native grasses are perennial plants, and there are close to hundred succulent species native to the state. After European contact, these were generally replaced by invasive species of European annual grasses; and, in modern times, California's hills turn a characteristic golden-brown in summer.
Because California has the greatest diversity of climate and terrain, the state has six life zones which are the lower Sonoran Desert; upper Sonoran (foothill regions and some coastal lands), transition (coastal areas and moist northeastern counties); and the Canadian, Hudsonian, and Arctic Zones, comprising the state's highest elevations.
Plant life in the dry climate of the lower Sonoran zone contains a diversity of native cactus, mesquite, and paloverde. The Yucca brevifolia, Joshua tree is found in the Mojave Desert. Flowering plants include the dwarf desert poppy and a variety of aster (genus), asters. Fremont cottonwood and valley oak thrive in the Central Valley. The upper Sonoran zone includes the chaparral belt, characterized by forests of small shrubs, stunted trees, and herbaceous plants. ''Nemophila'', Lamiaceae, mint, ''Phacelia'', ''viola (plant), Viola'', and the California poppy (''Eschscholzia californica'', the state flower) also flourish in this zone, along with the lupine, more species of which occur here than anywhere else in the world.
California boasts several superlatives in its collection of flora: the giant sequoia, largest trees, the coast redwood, tallest trees, and the pinus longaeva, oldest trees. California's native grasses are perennial plants, and there are close to hundred succulent species native to the state. After European contact, these were generally replaced by invasive species of European annual grasses; and, in modern times, California's hills turn a characteristic golden-brown in summer.
Because California has the greatest diversity of climate and terrain, the state has six life zones which are the lower Sonoran Desert; upper Sonoran (foothill regions and some coastal lands), transition (coastal areas and moist northeastern counties); and the Canadian, Hudsonian, and Arctic Zones, comprising the state's highest elevations.
Plant life in the dry climate of the lower Sonoran zone contains a diversity of native cactus, mesquite, and paloverde. The Yucca brevifolia, Joshua tree is found in the Mojave Desert. Flowering plants include the dwarf desert poppy and a variety of aster (genus), asters. Fremont cottonwood and valley oak thrive in the Central Valley. The upper Sonoran zone includes the chaparral belt, characterized by forests of small shrubs, stunted trees, and herbaceous plants. ''Nemophila'', Lamiaceae, mint, ''Phacelia'', ''viola (plant), Viola'', and the California poppy (''Eschscholzia californica'', the state flower) also flourish in this zone, along with the lupine, more species of which occur here than anywhere else in the world.
 The transition zone includes most of California's forests with the redwood (''Sequoia sempervirens'') and the "big tree" or giant sequoia (''Sequoiadendron giganteum''), among the oldest living things on earth (some are said to have lived at least 4,000 years). Tanbark oak, California laurel, sugar pine, Arbutus, madrona, Acer macrophyllum, broad-leaved maple, and Douglas-fir also grow here. Forest floors are covered with Polystichum, swordfern, alumnroot, barrenwort, and trillium, and there are thickets of huckleberry, azalea, elder, and wild currant. Characteristic wild flowers include varieties of mariposa, tulip, and Lilium columbianum, tiger and Lilium pardalinum, leopard lilies.
The high elevations of the Canadian zone allow the Jeffrey pine, red fir, and lodgepole pine to thrive. Brushy areas are abundant with dwarf manzanita and ceanothus; the unique Calvatia sculpta, Sierra puffball is also found here. Right below the timberline, in the Hudsonian zone, the whitebark, foxtail, and silver pines grow. At about , begins the Arctic zone, a treeless region whose flora include a number of wildflowers, including Primula suffrutescens, Sierra primrose, Aquilegia flavescens, yellow columbine, Ranunculus, alpine buttercup, and Dodecatheon alpinum, alpine shooting star.
Common plants that have been introduced to the state include the eucalyptus, acacia, Schinus, pepper tree, geranium, and Scotch broom. The species that are federally classified as endangered are the Erysimum capitatum, Contra Costa wallflower, Oenothera deltoides subsp. howellii, Antioch Dunes evening primrose, Tuctoria mucronata, Solano grass, Delphinium variegatum, San Clemente Island larkspur, Cordylanthus maritimus, salt marsh bird's beak, Arabis blepharophylla, McDonald's rock-cress, and Dudleya traskiae, Santa Barbara Island liveforever. , 85 plant species were listed as threatened or endangered.
The transition zone includes most of California's forests with the redwood (''Sequoia sempervirens'') and the "big tree" or giant sequoia (''Sequoiadendron giganteum''), among the oldest living things on earth (some are said to have lived at least 4,000 years). Tanbark oak, California laurel, sugar pine, Arbutus, madrona, Acer macrophyllum, broad-leaved maple, and Douglas-fir also grow here. Forest floors are covered with Polystichum, swordfern, alumnroot, barrenwort, and trillium, and there are thickets of huckleberry, azalea, elder, and wild currant. Characteristic wild flowers include varieties of mariposa, tulip, and Lilium columbianum, tiger and Lilium pardalinum, leopard lilies.
The high elevations of the Canadian zone allow the Jeffrey pine, red fir, and lodgepole pine to thrive. Brushy areas are abundant with dwarf manzanita and ceanothus; the unique Calvatia sculpta, Sierra puffball is also found here. Right below the timberline, in the Hudsonian zone, the whitebark, foxtail, and silver pines grow. At about , begins the Arctic zone, a treeless region whose flora include a number of wildflowers, including Primula suffrutescens, Sierra primrose, Aquilegia flavescens, yellow columbine, Ranunculus, alpine buttercup, and Dodecatheon alpinum, alpine shooting star.
Common plants that have been introduced to the state include the eucalyptus, acacia, Schinus, pepper tree, geranium, and Scotch broom. The species that are federally classified as endangered are the Erysimum capitatum, Contra Costa wallflower, Oenothera deltoides subsp. howellii, Antioch Dunes evening primrose, Tuctoria mucronata, Solano grass, Delphinium variegatum, San Clemente Island larkspur, Cordylanthus maritimus, salt marsh bird's beak, Arabis blepharophylla, McDonald's rock-cress, and Dudleya traskiae, Santa Barbara Island liveforever. , 85 plant species were listed as threatened or endangered.
 In the deserts of the lower Sonoran zone, the mammals include the jackrabbit, kangaroo rat, squirrel, and opossum. Common birds include the owl, roadrunner, cactus wren, and various species of hawk. The area's reptilian life include the Crotalus cerastes, sidewinder viper, desert tortoise, and horned toad. The upper Sonoran zone boasts mammals such as the Pronghorn, antelope, Dusky-footed woodrat, brown-footed woodrat, and ring-tailed cat. Birds unique to this zone are the California thrasher, Psaltriparus minimus, bushtit, and California condor.
In the transition zone, there are Colombian black-tailed deer, American black bear, black bears, gray foxes, cougars, bobcats, and Roosevelt elk. Reptiles such as the garter snakes and rattlesnakes inhabit the zone. In addition, amphibians such as the Proteidae, water puppy and Batrachoseps attenuatus, redwood salamander are common too. Birds such as the kingfisher, chickadee, towhee, and hummingbird thrive here as well.
The Canadian zone mammals include the mountain weasel, snowshoe hare, and several species of chipmunks. Conspicuous birds include the Steller's jay, blue-fronted jay, mountain chickadee, hermit thrush, American dipper, and Townsend's solitaire. As one ascends into the Hudsonian zone, birds become scarcer. While the gray-crowned rosy finch is the only bird native to the high Arctic region, other bird species such as Anna's hummingbird and Clark's nutcracker. Principal mammals found in this region include the Sierra coney, white-tailed jackrabbit, and the bighorn sheep. , the bighorn sheep was listed as endangered by the U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service. The fauna found throughout several zones are the mule deer, coyote, mountain lion, northern flicker, and several species of hawk and sparrow.
In the deserts of the lower Sonoran zone, the mammals include the jackrabbit, kangaroo rat, squirrel, and opossum. Common birds include the owl, roadrunner, cactus wren, and various species of hawk. The area's reptilian life include the Crotalus cerastes, sidewinder viper, desert tortoise, and horned toad. The upper Sonoran zone boasts mammals such as the Pronghorn, antelope, Dusky-footed woodrat, brown-footed woodrat, and ring-tailed cat. Birds unique to this zone are the California thrasher, Psaltriparus minimus, bushtit, and California condor.
In the transition zone, there are Colombian black-tailed deer, American black bear, black bears, gray foxes, cougars, bobcats, and Roosevelt elk. Reptiles such as the garter snakes and rattlesnakes inhabit the zone. In addition, amphibians such as the Proteidae, water puppy and Batrachoseps attenuatus, redwood salamander are common too. Birds such as the kingfisher, chickadee, towhee, and hummingbird thrive here as well.
The Canadian zone mammals include the mountain weasel, snowshoe hare, and several species of chipmunks. Conspicuous birds include the Steller's jay, blue-fronted jay, mountain chickadee, hermit thrush, American dipper, and Townsend's solitaire. As one ascends into the Hudsonian zone, birds become scarcer. While the gray-crowned rosy finch is the only bird native to the high Arctic region, other bird species such as Anna's hummingbird and Clark's nutcracker. Principal mammals found in this region include the Sierra coney, white-tailed jackrabbit, and the bighorn sheep. , the bighorn sheep was listed as endangered by the U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service. The fauna found throughout several zones are the mule deer, coyote, mountain lion, northern flicker, and several species of hawk and sparrow.
 Aquatic life in California thrives, from the state's mountain lakes and streams to the rocky Pacific coastline. Numerous trout species are found, among them Rainbow trout, rainbow, Golden trout, golden, and Cutthroat trout, cutthroat. Migratory species of salmon are common as well. Deep-sea life forms include White seabass, sea bass, yellowfin tuna, barracuda, and several types of whale. Native to the cliffs of northern California are seals, sea lions, and many types of shorebirds, including migratory species.
, 118 California animals were on the federal endangered list; 181 plants were listed as endangered or threatened. Endangered animals include the Vulpes macrotis, San Joaquin kitfox, Aplodontia rufa nigra, Point Arena mountain beaver, Pacific pocket mouse, salt marsh harvest mouse, Morro Bay kangaroo rat (and five other species of kangaroo rat), California vole#Subspecies, Amargosa vole, California least tern, California condor, loggerhead shrike, Bell's sparrow, San Clemente sage sparrow, San Francisco garter snake, five species of salamander, three species of chub, and two species of pupfish. Eleven butterflies are also endangered and two that are threatened are on the federal list. Among threatened animals are the coastal California gnatcatcher, Paiute cutthroat trout, Sea otter#Subspecies, southern sea otter, and northern spotted owl. California has a total of of National Wildlife Refuges. , 123 California animals were listed as either endangered or threatened on the US Fish & Wildlife Service, federal list. Also, , 178 species of California plants were listed either as endangered or threatened on this federal list.
Aquatic life in California thrives, from the state's mountain lakes and streams to the rocky Pacific coastline. Numerous trout species are found, among them Rainbow trout, rainbow, Golden trout, golden, and Cutthroat trout, cutthroat. Migratory species of salmon are common as well. Deep-sea life forms include White seabass, sea bass, yellowfin tuna, barracuda, and several types of whale. Native to the cliffs of northern California are seals, sea lions, and many types of shorebirds, including migratory species.
, 118 California animals were on the federal endangered list; 181 plants were listed as endangered or threatened. Endangered animals include the Vulpes macrotis, San Joaquin kitfox, Aplodontia rufa nigra, Point Arena mountain beaver, Pacific pocket mouse, salt marsh harvest mouse, Morro Bay kangaroo rat (and five other species of kangaroo rat), California vole#Subspecies, Amargosa vole, California least tern, California condor, loggerhead shrike, Bell's sparrow, San Clemente sage sparrow, San Francisco garter snake, five species of salamander, three species of chub, and two species of pupfish. Eleven butterflies are also endangered and two that are threatened are on the federal list. Among threatened animals are the coastal California gnatcatcher, Paiute cutthroat trout, Sea otter#Subspecies, southern sea otter, and northern spotted owl. California has a total of of National Wildlife Refuges. , 123 California animals were listed as either endangered or threatened on the US Fish & Wildlife Service, federal list. Also, , 178 species of California plants were listed either as endangered or threatened on this federal list.
Rivers
 The most prominent river system within California is formed by the Sacramento River and San Joaquin River, which are fed mostly by snowmelt from the west slope of the Sierra Nevada, and respectively drain the north and south halves of the Central Valley. The two rivers join in the Sacramento–San Joaquin River Delta, flowing into the Pacific Ocean through San Francisco Bay. Many major tributaries feed into the Sacramento–San Joaquin system, including the Pit River, Feather River and Tuolumne River.
The Klamath River, Klamath and Trinity River (California), Trinity Rivers drain a large area in far northwestern California. The Eel River (California), Eel River and Salinas River (California), Salinas River each drain portions of the California coast, north and south of San Francisco Bay, respectively. The Mojave River is the primary watercourse in the Mojave Desert, and the Santa Ana River drains much of the Transverse Ranges as it bisects Southern California. The Colorado River forms the state's southeast border with Arizona.
Most of California's major rivers are dammed as part of two massive water projects: the Central Valley Project, providing water for agriculture in the Central Valley, and the California State Water Project diverting water from Northern to Southern California. The state's coasts, rivers, and other bodies of water are regulated by the California Coastal Commission.
The most prominent river system within California is formed by the Sacramento River and San Joaquin River, which are fed mostly by snowmelt from the west slope of the Sierra Nevada, and respectively drain the north and south halves of the Central Valley. The two rivers join in the Sacramento–San Joaquin River Delta, flowing into the Pacific Ocean through San Francisco Bay. Many major tributaries feed into the Sacramento–San Joaquin system, including the Pit River, Feather River and Tuolumne River.
The Klamath River, Klamath and Trinity River (California), Trinity Rivers drain a large area in far northwestern California. The Eel River (California), Eel River and Salinas River (California), Salinas River each drain portions of the California coast, north and south of San Francisco Bay, respectively. The Mojave River is the primary watercourse in the Mojave Desert, and the Santa Ana River drains much of the Transverse Ranges as it bisects Southern California. The Colorado River forms the state's southeast border with Arizona.
Most of California's major rivers are dammed as part of two massive water projects: the Central Valley Project, providing water for agriculture in the Central Valley, and the California State Water Project diverting water from Northern to Southern California. The state's coasts, rivers, and other bodies of water are regulated by the California Coastal Commission.
Regions
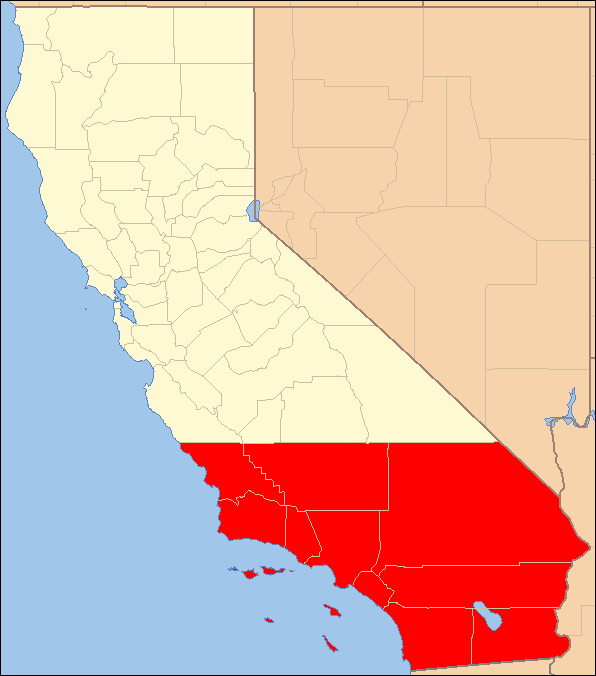 California is traditionally separated into Northern California and Southern California, divided by a straight border which runs across the state, separating the northern 48 counties from the southern 10 counties. Despite the persistence of the northern-southern divide, California is more precisely divided into many regions, multiple of which stretch across the northern-southern divide.
; Major divisions
* Northern California
* Southern California
; Regions
California is traditionally separated into Northern California and Southern California, divided by a straight border which runs across the state, separating the northern 48 counties from the southern 10 counties. Despite the persistence of the northern-southern divide, California is more precisely divided into many regions, multiple of which stretch across the northern-southern divide.
; Major divisions
* Northern California
* Southern California
; Regions
Cities and towns
The state has 482 Municipal corporation, incorporated cities and towns, of which 460 are cities and 22 are towns. Under California law, the terms "city" and "town" are explicitly interchangeable; the name of an incorporated municipality in the state can either be "City of (Name)" or "Town of (Name)". Sacramento became California's first incorporated city on February 27, 1850. San Jose, San Diego, andDemographics
Population
One out of every eight Americans live in California. The United States Census Bureau reported that the population of California was 39,538,223 on 2020 United States census, April 1, 2020, a 6.13% increase since the 2010 United States census. The estimated population as of 2022 is 39.22 million. For over a century (1900–2020), California experienced an explosion in population growth, adding an average of more than 300,000 people per year. California's rate of growth began to slow by the 1990s, although it continued to experience population growth in the first two decades of the 21st century. The state experienced population declines in 2020 and 2021, attributable to declining birth rates, COVID-19 pandemic deaths, and less internal migration from other states to California. The Greater Los Angeles Area is the 2nd-largest metropolitan area in the United States, after the New York metropolitan area, while Los Angeles, with nearly half the population of New York City, is the second-largest city in the United States. Conversely, San Francisco, with nearly one-quarter the population density of Manhattan, is the most densely populated city in California and one of the most densely populated cities in the United States. Also, Los Angeles County has held the title of most populous United States county for decades, and it alone is more populous than 42 U.S. states. Including Los Angeles, four of the List of United States cities by population, top 20 most populous cities in the U.S. are in California: Los Angeles (2nd), San Diego (8th), San Jose (10th), and San Francisco (17th). The center of population of California is located four miles west-southwest of the city of Shafter, California, Shafter, Kern County, California, Kern County.
As of 2019, California ranked List of U.S. states and territories by life expectancy, second among states by life expectancy (after Hawaii), with a life expectancy of 78.4 years.
Starting in the year 2010, for the first time since the
The Greater Los Angeles Area is the 2nd-largest metropolitan area in the United States, after the New York metropolitan area, while Los Angeles, with nearly half the population of New York City, is the second-largest city in the United States. Conversely, San Francisco, with nearly one-quarter the population density of Manhattan, is the most densely populated city in California and one of the most densely populated cities in the United States. Also, Los Angeles County has held the title of most populous United States county for decades, and it alone is more populous than 42 U.S. states. Including Los Angeles, four of the List of United States cities by population, top 20 most populous cities in the U.S. are in California: Los Angeles (2nd), San Diego (8th), San Jose (10th), and San Francisco (17th). The center of population of California is located four miles west-southwest of the city of Shafter, California, Shafter, Kern County, California, Kern County.
As of 2019, California ranked List of U.S. states and territories by life expectancy, second among states by life expectancy (after Hawaii), with a life expectancy of 78.4 years.
Starting in the year 2010, for the first time since the ''Bloomberg BusinessWeek'', May 3, 2012. Despite these recent trends, Illegal immigration to the United States, illegal Alien (law), aliens constituted an estimated 7.3 percent of the state's population, the third highest percentage of any state in the Illegal immigrant population of the United States, country,Behind Nevada and Arizona totaling nearly 2.6million. In particular, illegal immigrants tended to be concentrated in Los Angeles County, California, Los Angeles, Monterey County, California, Monterey, San Benito County, California, San Benito, Imperial County, California, Imperial, and Napa County, California, Napa Counties—the latter four of which have significant agricultural industries that depend on manual labor. More than half of illegal immigrants originate from Mexico. The state of California and some California cities, including Los Angeles, Oakland and San Francisco, have adopted Sanctuary city, sanctuary policies.
Race and ethnicity
 According to the United States Census Bureau in 2018 the population self-identified as (alone or in combination):2018 U.S. Census QuickFacts
According to the United States Census Bureau in 2018 the population self-identified as (alone or in combination):2018 U.S. Census QuickFactsUnited States Census Bureau, 2018. 72.1% White American, White (including Hispanic White Americans, Hispanic White Americans, Whites), 36.8% non-Hispanic whites, 15.3% Asian American, Asian, 6.5% Black or African American, 1.6% Native American and Alaska Native, 0.5% Native Hawaiian or Pacific Islander American, Pacific Islander, and 3.9% Multiracial American, two or more races. By ethnicity, in 2018 the population was 60.7% non-Hispanic (of any race) and 39.3% Hispanics and Latinos in California, Hispanic or Latino (of any race). Hispanics are the largest single ethnic group in California. Non-Hispanic whites constituted 36.8% of the state's population. ''
Languages
American English, English serves as California's de jure and de facto official language. In 2010, the Modern Language Association of America estimated that 57.02% (19,429,309) of California residents age5 and older spoke only English language, English at home, while 42.98% spoke another language at home. According to the 2007 American Community Survey, 73% of people who speak a language other than English at home are able to speak English "well" or "very well," while 9.8% of them could not speak English at all. Like most U.S. states (32 out of 50), California law enshrines English as its official language, and has done so since the passage of List of California ballot propositions 1980–1989#November 4, 1986, Proposition 63 by California voters in 1986. Various government agencies do, and are often required to, furnish documents in the various languages needed to reach their intended audiences. In total, 16 languages other than English were spoken as primary languages at home by more than 100,000 persons, more than any other state in the nation. New York State, in second place, had nine languages other than English spoken by more than 100,000 persons. The most common language spoken besides English was Spanish language, Spanish, spoken by 28.46% (9,696,638) of the population. With Asia contributing most of California's new immigrants, California had the highest concentration nationwide of Vietnamese language, Vietnamese and Chinese language, Chinese speakers, the second highest concentration of Korean language, Korean, and the third highest concentration of Tagalog language, Tagalog speakers. California has historically been one of the most linguistically diverse areas in the world, with more than 70 indigenous languages derived from 64 root languages in six language families. A survey conducted between 2007 and 2009 identified 23 different indigenous languages among California farmworkers. All of California's indigenous languages are endangered language, endangered, although there are now efforts toward language revitalization.The following are a list of the indigenous languages: Root languages of California: Athabaskan Family: Hupa, Mattole, Lassik, Wailaki, Sinkyone, Cahto, Tolowa, Nongatl, Wiyot, Chilula; Hokan Family: Pomo, Shasta, Karok, Chimiriko; Algonquian Family: Whilkut, Yurok; Yukian Family: Wappo; Penutian Family: Modok, Wintu, Nomlaki, Konkow, Maidu, Patwin, Nisenan, Miwok, Coast Miwok, Lake Miwok, Ohlone, Northern Valley Yokuts, Southern Valley Yokuts, Foothill Yokuts; Hokan Family: Esselen, Salinan, Chumash, Ipai, Tipai, Yuma, Halchichoma, Mohave; Uto-Aztecan Family: Mono Paiute, Monache, Owens Valley Paiute, Tubatulabal, Panamint Shoshone, Kawaisu, Kitanemuk, Tataviam, Gabrielino, Juaneno, Luiseno, Cuipeno, Cahuilla, Serrano, Chemehuevi As a result of the state's increasing diversity and migration from other areas across the country and around the globe, linguists began noticing a noteworthy set of emerging characteristics of spoken American English in California since the late 20th century. This variety, known as California English, has a vowel shift and several other phonological processes that are different from varieties of American English used in other regions of the United States.Religion
 The largest religious denominations by number of adherents as a percentage of California's population in 2014 were the Catholic Church with 28 percent, Evangelical Protestants with 20 percent, and Mainline Protestants with 10 percent. Together, all kinds of Protestants accounted for 32 percent. Those unaffiliated with any religion represented 27 percent of the population. The breakdown of other religions is 1% Muslim, 2% Hindu and 2% Buddhist. This is a change from 2008, when the population identified their religion with the Catholic Church with 31 percent; Evangelical Protestants with 18 percent; and Mainline Protestants with 14 percent. In 2008, those unaffiliated with any religion represented 21 percent of the population. The breakdown of other religions in 2008 was 0.5% Muslim, 1% Hindu and 2% Buddhist. The ''American Jewish Year Book'' placed the total American Jews, Jewish population of California at about 1,194,190 in 2006. According to the Association of Religion Data Archives (ARDA) the largest denominations by adherents in 2010 were the Catholic Church with 10,233,334; The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints with 763,818; and the Southern Baptist Convention with 489,953.
The first priests to come to California were Catholic missionaries from Spain. Catholics founded California missions, 21 missions along the California coast, as well as the cities of Los Angeles and San Francisco. California continues to have a large Catholic population due to the large numbers of Mexicans and Central Americans living within its borders. California has twelve dioceses and two archdioceses, the Archdiocese of Los Angeles and the Archdiocese of San Francisco, the former being the largest archdiocese in the United States.
A Pew Research Center survey revealed that California is somewhat less religious than the rest of the states: 62 percent of Californians say they are "absolutely certain" of their belief in God, while in the nation 71 percent say so. The survey also revealed 48 percent of Californians say religion is "very important", compared to 56 percent nationally.
The largest religious denominations by number of adherents as a percentage of California's population in 2014 were the Catholic Church with 28 percent, Evangelical Protestants with 20 percent, and Mainline Protestants with 10 percent. Together, all kinds of Protestants accounted for 32 percent. Those unaffiliated with any religion represented 27 percent of the population. The breakdown of other religions is 1% Muslim, 2% Hindu and 2% Buddhist. This is a change from 2008, when the population identified their religion with the Catholic Church with 31 percent; Evangelical Protestants with 18 percent; and Mainline Protestants with 14 percent. In 2008, those unaffiliated with any religion represented 21 percent of the population. The breakdown of other religions in 2008 was 0.5% Muslim, 1% Hindu and 2% Buddhist. The ''American Jewish Year Book'' placed the total American Jews, Jewish population of California at about 1,194,190 in 2006. According to the Association of Religion Data Archives (ARDA) the largest denominations by adherents in 2010 were the Catholic Church with 10,233,334; The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints with 763,818; and the Southern Baptist Convention with 489,953.
The first priests to come to California were Catholic missionaries from Spain. Catholics founded California missions, 21 missions along the California coast, as well as the cities of Los Angeles and San Francisco. California continues to have a large Catholic population due to the large numbers of Mexicans and Central Americans living within its borders. California has twelve dioceses and two archdioceses, the Archdiocese of Los Angeles and the Archdiocese of San Francisco, the former being the largest archdiocese in the United States.
A Pew Research Center survey revealed that California is somewhat less religious than the rest of the states: 62 percent of Californians say they are "absolutely certain" of their belief in God, while in the nation 71 percent say so. The survey also revealed 48 percent of Californians say religion is "very important", compared to 56 percent nationally.
Culture
 The culture of California is a Western culture and most clearly has its modern roots in the culture of the United States, but also, historically, many Hispanic
The culture of California is a Western culture and most clearly has its modern roots in the culture of the United States, but also, historically, many Hispanic Media and entertainment
 Hollywood, Los Angeles, Hollywood and the rest of the Los Angeles area is a major global center for entertainment, with the cinema in the United States, U.S. film industry's Major film studio, "Big Five" major film studios (Columbia Pictures, Columbia, Walt Disney Pictures, Disney, Paramount Pictures, Paramount, Universal Pictures, Universal, and Warner Bros.) being based in or around the area.
The four major American television broadcast networks (American Broadcasting Company, ABC, CBS, Fox Broadcasting Company, Fox and NBC) all have production facilities and offices in the state. All four, plus the two major Spanish-language networks (Telemundo and Univision) each have at least two Owned-and-operated television stations in the United States, owned-and-operated TV stations in California, one in Los Angeles and one in the San Francisco Bay Area.
The San Francisco Bay Area is home to several prominent internet media and social media companies, including three of the Big Tech, "Big Five" technology companies (Apple Inc., Apple, Facebook, and Google) as well as other services such as Netflix, Pandora Radio, Twitter, Yahoo!, and YouTube.
Hollywood, Los Angeles, Hollywood and the rest of the Los Angeles area is a major global center for entertainment, with the cinema in the United States, U.S. film industry's Major film studio, "Big Five" major film studios (Columbia Pictures, Columbia, Walt Disney Pictures, Disney, Paramount Pictures, Paramount, Universal Pictures, Universal, and Warner Bros.) being based in or around the area.
The four major American television broadcast networks (American Broadcasting Company, ABC, CBS, Fox Broadcasting Company, Fox and NBC) all have production facilities and offices in the state. All four, plus the two major Spanish-language networks (Telemundo and Univision) each have at least two Owned-and-operated television stations in the United States, owned-and-operated TV stations in California, one in Los Angeles and one in the San Francisco Bay Area.
The San Francisco Bay Area is home to several prominent internet media and social media companies, including three of the Big Tech, "Big Five" technology companies (Apple Inc., Apple, Facebook, and Google) as well as other services such as Netflix, Pandora Radio, Twitter, Yahoo!, and YouTube.
Sports
California has nineteen major professional sports leagues in the United States and Canada, major professional sports league franchises, far more than any other state. The San Francisco Bay Area has six major league teams spread in its three major cities: San Francisco, San Jose, and Oakland, while the Greater Los Angeles Area is home to ten major league franchises. San Diego and Sacramento each have one major league team. The NFL Super Bowl has been hosted in California 12 times at five different stadiums: Los Angeles Memorial Coliseum, the Rose Bowl, Stanford Stadium, Levi's Stadium, and San Diego's Qualcomm Stadium. A thirteenth, Super Bowl LVI, was held at Sofi Stadium in Inglewood, California, Inglewood on February 13, 2022. California has long had many respected collegiate sports programs. California is home to the oldest college bowl game, the annual Rose Bowl Game, Rose Bowl, among others. California is the only U.S. state to have hosted both the Summer Olympic Games, Summer and Winter Olympic Games, Winter Olympics. The 1932 Summer Olympics, 1932 and 1984 Summer Olympics, 1984 summer games were held in Los Angeles. Squaw Valley Ski Resort in the Lake Tahoe region hosted the 1960 Winter Olympics. Los Angeles will host the 2028 Summer Olympics, marking the fourth time that California will have hosted the Olympic Games. Multiple games during the 1994 FIFA World Cup took place in California, with the Rose Bowl Stadium, Rose Bowl hosting eight matches (including the 1994 FIFA World Cup Final, final), while Stanford Stadium hosted six matches.Education
California has the most school students in the country, with over 6.2 million in the 2005–06 school year, giving California more students in school than 36 states have in total population and one of the highest projected enrollments in the country. Public Secondary education in the United States, secondary education consists of High school (North America), high schools that teach elective courses in trades, languages, and liberal arts with tracks for gifted, college-bound and industrial arts students. California's public educational system is supported by a California Proposition 98 (1988), unique constitutional amendment that requires a minimum annual funding level for grades K–12 and community colleges that grows with the economy and student enrollment figures.
In 2016, California's K–12 public school per-pupil spending was ranked 22nd in the nation ($11,500 per student vs. $11,800 for the U.S. average).
For 2012, California's K–12 public schools ranked 48th in the number of employees per student, at 0.102 (the U.S. average was 0.137), while paying the 7th most per employee, $49,000 (the U.S. average was $39,000).
A 2007 study concluded that California's public school system was "broken" in that it suffered from overregulation.
Public Secondary education in the United States, secondary education consists of High school (North America), high schools that teach elective courses in trades, languages, and liberal arts with tracks for gifted, college-bound and industrial arts students. California's public educational system is supported by a California Proposition 98 (1988), unique constitutional amendment that requires a minimum annual funding level for grades K–12 and community colleges that grows with the economy and student enrollment figures.
In 2016, California's K–12 public school per-pupil spending was ranked 22nd in the nation ($11,500 per student vs. $11,800 for the U.S. average).
For 2012, California's K–12 public schools ranked 48th in the number of employees per student, at 0.102 (the U.S. average was 0.137), while paying the 7th most per employee, $49,000 (the U.S. average was $39,000).
A 2007 study concluded that California's public school system was "broken" in that it suffered from overregulation.
Higher education
California public postsecondary education is organized into three separate systems: * The state's Public university, public research university State university system, system is the University of California (UC). As of fall 2011, the University of California had a combined student body of 234,464 students. There are ten UC campuses. Nine are general campuses offering both undergraduate and graduate programs which culminate in the award of bachelor's degrees, master's degrees, and doctorates. There is one specialized campus, UC San Francisco, which is entirely dedicated to graduate education in health care, and is home to the UCSF Medical Center, the highest ranked hospital in California. The system was originally intended to accept the top one-eighth of California high school students, but several of the campuses have become even more selective.Powell, Farran. "California Students Face Competition for College Options". ''U.S. News & World Report''. N.p., February 6, 2017. Web. May 7, 2017. The UC system historically held exclusive authority to award the doctorate, but this has since changed and CSU now has limited statutory authorization to award a handful of types of doctoral degrees independently of UC. * The California State University (CSU) system has almost 430,000 students. The CSU (which takes the definite article in its abbreviated form, while UC does not) was originally intended to accept the top one-third of California high school students, but several of the campuses have become much more selective. The CSU was originally authorized to award only bachelor's and master's degrees, and could award the doctorate only as part of joint programs with UC or private universities. Since then, CSU has been granted the authority to independently award several doctoral degrees (in specific academic fields that do not intrude upon UC's traditional jurisdiction). * The California Community Colleges system provides lower-division coursework culminating in the associate degree, as well as basic skills and workforce training culminating in various kinds of certificates. (Fifteen California community colleges now award four-year bachelor's degrees in disciplines which are in high demand in their geographical area.) It is the largest network of higher education in the U.S., composed of 112 colleges serving a student population of over 2.6million. California is also home to such notable private universities asEconomy
 California's economy ranks among the largest in the world. , the gross state product (GSP) was $3.31000000000000 (number), trillion ($85,500 per capita), the largest in the United States. California is responsible for one seventh of the nation's gross domestic product (GDP). , California's nominal GDP is larger than all but four countries (the Economy of the United States, United States, Economy of China, China, Economy of Japan, Japan, and Economy of Germany, Germany). In terms of purchasing power parity (PPP), it is larger than all but eight countries (the United States, China, Economy of India, India, Japan, Germany, Economy of Russia, Russia, Economy of Brazil, Brazil, and Economy of Indonesia, Indonesia). California's economy is larger than Economy of Africa, Africa and Economy of Australia, Australia and is almost as large as Economy of South America, South America. The state recorded total, non-farm employment of 16,677,800 among 966,224 employer establishments ().
The five largest sectors of employment in California are trade, transportation, and utilities; government; professional and business services; education and health services; and leisure and hospitality. In output, the five largest sectors are financial services, followed by trade, transportation, and utilities; education and health services; government; and manufacturing. California has an California unemployment statistics, unemployment rate of 3.9% .
California's economy ranks among the largest in the world. , the gross state product (GSP) was $3.31000000000000 (number), trillion ($85,500 per capita), the largest in the United States. California is responsible for one seventh of the nation's gross domestic product (GDP). , California's nominal GDP is larger than all but four countries (the Economy of the United States, United States, Economy of China, China, Economy of Japan, Japan, and Economy of Germany, Germany). In terms of purchasing power parity (PPP), it is larger than all but eight countries (the United States, China, Economy of India, India, Japan, Germany, Economy of Russia, Russia, Economy of Brazil, Brazil, and Economy of Indonesia, Indonesia). California's economy is larger than Economy of Africa, Africa and Economy of Australia, Australia and is almost as large as Economy of South America, South America. The state recorded total, non-farm employment of 16,677,800 among 966,224 employer establishments ().
The five largest sectors of employment in California are trade, transportation, and utilities; government; professional and business services; education and health services; and leisure and hospitality. In output, the five largest sectors are financial services, followed by trade, transportation, and utilities; education and health services; government; and manufacturing. California has an California unemployment statistics, unemployment rate of 3.9% .
 California's economy is dependent on trade and international related commerce accounts for about one-quarter of the state's economy. In 2008, California exported $144billion worth of goods, up from $134billion in 2007 and $127billion in 2006.
Computers and electronic products are California's top export, accounting for 42 percent of all the state's exports in 2008.
Agriculture is an important sector in California's economy. Farming-related sales more than quadrupled over the past three decades, from $7.3billion in 1974 to nearly $31billion in 2004. This increase has occurred despite a 15 percent decline in acreage devoted to farming during the period, and water supply suffering from chronic instability. Factors contributing to the growth in sales-per-acre include more intensive use of active farmlands and technological improvements in crop production. In 2008, California's 81,500 farms and ranches generated $36.2billion products revenue. In 2011, that number grew to $43.5billion products revenue. The Agriculture sector accounts for two percent of the state's GDP and employs around three percent of its total workforce. According to the United States Department of Agriculture, USDA in 2011, the three largest California agricultural products by value were milk and cream, shelled almonds, and grapes.
California's economy is dependent on trade and international related commerce accounts for about one-quarter of the state's economy. In 2008, California exported $144billion worth of goods, up from $134billion in 2007 and $127billion in 2006.
Computers and electronic products are California's top export, accounting for 42 percent of all the state's exports in 2008.
Agriculture is an important sector in California's economy. Farming-related sales more than quadrupled over the past three decades, from $7.3billion in 1974 to nearly $31billion in 2004. This increase has occurred despite a 15 percent decline in acreage devoted to farming during the period, and water supply suffering from chronic instability. Factors contributing to the growth in sales-per-acre include more intensive use of active farmlands and technological improvements in crop production. In 2008, California's 81,500 farms and ranches generated $36.2billion products revenue. In 2011, that number grew to $43.5billion products revenue. The Agriculture sector accounts for two percent of the state's GDP and employs around three percent of its total workforce. According to the United States Department of Agriculture, USDA in 2011, the three largest California agricultural products by value were milk and cream, shelled almonds, and grapes.
 List of U.S. states by GDP per capita, Per capita GDP in 2007 was $38,956, ranking eleventh in the nation. California locations by per capita income, Per capita income varies widely by geographic region and profession. The Central Valley is the most impoverished, with migrant worker, migrant farm workers making less than minimum wage. According to a 2005 report by the Congressional Research Service, the San Joaquin Valley was characterized as one of the most economically depressed regions in the United States, on par with the region of Appalachia. Using the supplemental poverty measure, California has a Poverty in the United States, poverty rate of 23.5%, the highest of any state in the country. However, using the official measure the poverty rate was only 13.3% as of 2017. Many coastal cities include some of the wealthiest per-capita areas in the United States. The high-technology sectors in Northern California, specifically Silicon Valley, in Santa Clara County, California, Santa Clara and San Mateo County, California, San Mateo counties, have emerged from the economic downturn caused by the dot-com bubble, dot-com bust.
In 2019, there were 1,042,027 millionaire households in the state, more than any other state in the nation. In 2010, California residents were ranked first among the states with the best average credit score of 754.
List of U.S. states by GDP per capita, Per capita GDP in 2007 was $38,956, ranking eleventh in the nation. California locations by per capita income, Per capita income varies widely by geographic region and profession. The Central Valley is the most impoverished, with migrant worker, migrant farm workers making less than minimum wage. According to a 2005 report by the Congressional Research Service, the San Joaquin Valley was characterized as one of the most economically depressed regions in the United States, on par with the region of Appalachia. Using the supplemental poverty measure, California has a Poverty in the United States, poverty rate of 23.5%, the highest of any state in the country. However, using the official measure the poverty rate was only 13.3% as of 2017. Many coastal cities include some of the wealthiest per-capita areas in the United States. The high-technology sectors in Northern California, specifically Silicon Valley, in Santa Clara County, California, Santa Clara and San Mateo County, California, San Mateo counties, have emerged from the economic downturn caused by the dot-com bubble, dot-com bust.
In 2019, there were 1,042,027 millionaire households in the state, more than any other state in the nation. In 2010, California residents were ranked first among the states with the best average credit score of 754.
State finances
Infrastructure
Energy
 Because it is the most populous state in the United States, California is one of the country's largest users of energy. However, because of its high energy rates, conservation mandates, mild weather in the largest population centers and strong environmental movement, its ''per capita'' energy use is one of the smallest of any state in the United States. Due to the high electricity demand, California imports more electricity than any other state, primarily hydroelectric power from states in the Pacific Northwest (via Path 15 and Path 66) and coal- and natural gas-fired production from the desert Southwest via Path 46.
The state's crude oil and natural gas deposits are located in the Central Valley and along the coast, including the large Midway-Sunset Oil Field. Natural gas-fired power plants typically account for more than one-half of state electricity generation.
Because it is the most populous state in the United States, California is one of the country's largest users of energy. However, because of its high energy rates, conservation mandates, mild weather in the largest population centers and strong environmental movement, its ''per capita'' energy use is one of the smallest of any state in the United States. Due to the high electricity demand, California imports more electricity than any other state, primarily hydroelectric power from states in the Pacific Northwest (via Path 15 and Path 66) and coal- and natural gas-fired production from the desert Southwest via Path 46.
The state's crude oil and natural gas deposits are located in the Central Valley and along the coast, including the large Midway-Sunset Oil Field. Natural gas-fired power plants typically account for more than one-half of state electricity generation.
 As a result of the state's strong environmental movement, California has some of the most aggressive renewable energy goals in the United States, with a target for California to obtain a third of its electricity from renewables by 2020. Currently, several solar power plants such as the Solar Energy Generating Systems facility are located in the Mojave Desert. Wind power in California, California's wind farms include Altamont Pass Wind Farm, Altamont Pass, San Gorgonio Pass Wind Farm, San Gorgonio Pass, and Tehachapi Pass Wind Farm, Tehachapi Pass. The Tehachapi area is also where the Tehachapi Energy Storage Project is located. Several dams across the state provide Hydroelectricity, hydro-electric power. It would be possible to convert the total supply to 100% renewable energy, including heating, cooling and mobility, by 2050.
California is also home to two major nuclear power plants: Diablo Canyon Power Plant, Diablo Canyon and San Onofre Nuclear Generating Station, San Onofre, the latter having been shut down in 2013. More than 1,700tons of radioactive waste are stored at San Onofre, which sits in an area where there is a record of past tsunamis. Voters banned the approval of new nuclear power plants since the late 1970s because of concerns over High-level radioactive waste management, radioactive waste disposal. In addition, several cities such as Oakland, Berkeley, California, Berkeley and Davis, California, Davis have declared themselves as nuclear-free zones.
As a result of the state's strong environmental movement, California has some of the most aggressive renewable energy goals in the United States, with a target for California to obtain a third of its electricity from renewables by 2020. Currently, several solar power plants such as the Solar Energy Generating Systems facility are located in the Mojave Desert. Wind power in California, California's wind farms include Altamont Pass Wind Farm, Altamont Pass, San Gorgonio Pass Wind Farm, San Gorgonio Pass, and Tehachapi Pass Wind Farm, Tehachapi Pass. The Tehachapi area is also where the Tehachapi Energy Storage Project is located. Several dams across the state provide Hydroelectricity, hydro-electric power. It would be possible to convert the total supply to 100% renewable energy, including heating, cooling and mobility, by 2050.
California is also home to two major nuclear power plants: Diablo Canyon Power Plant, Diablo Canyon and San Onofre Nuclear Generating Station, San Onofre, the latter having been shut down in 2013. More than 1,700tons of radioactive waste are stored at San Onofre, which sits in an area where there is a record of past tsunamis. Voters banned the approval of new nuclear power plants since the late 1970s because of concerns over High-level radioactive waste management, radioactive waste disposal. In addition, several cities such as Oakland, Berkeley, California, Berkeley and Davis, California, Davis have declared themselves as nuclear-free zones.
Transportation
 California's vast terrain is connected by an extensive system of controlled-access highways ('freeways'), limited-access roads ('expressways'), and highways. California is known for its car culture, giving California's cities a reputation for severe traffic congestion. Construction and maintenance of state roads and statewide transportation planning are primarily the responsibility of the California Department of Transportation, nicknamed "Caltrans". The rapidly growing population of the state is straining all of its transportation networks, and California has some of the worst roads in the United States. The Reason Foundation's 19th Annual Report on the Performance of State Highway Systems ranked California's highways the third-worst of any state, with Alaska second, and Rhode Island first.
California's vast terrain is connected by an extensive system of controlled-access highways ('freeways'), limited-access roads ('expressways'), and highways. California is known for its car culture, giving California's cities a reputation for severe traffic congestion. Construction and maintenance of state roads and statewide transportation planning are primarily the responsibility of the California Department of Transportation, nicknamed "Caltrans". The rapidly growing population of the state is straining all of its transportation networks, and California has some of the worst roads in the United States. The Reason Foundation's 19th Annual Report on the Performance of State Highway Systems ranked California's highways the third-worst of any state, with Alaska second, and Rhode Island first.
 The state has been a pioneer in road construction. One of the state's more visible landmarks, the Golden Gate Bridge, was the List of longest suspension bridge spans, longest suspension bridge main span in the world at between 1937 (when it opened) and 1964. With its orange paint and panoramic views of the bay, this highway bridge is a popular tourist attraction and also accommodates pedestrians and bicyclists. The San Francisco–Oakland Bay Bridge (often abbreviated the "Bay Bridge"), completed in 1936, transports about 280,000 vehicles per day on two-decks. Its two sections meet at Yerba Buena Island through the world's largest diameter transportation bore tunnel, at wide by high. The Arroyo Seco Parkway, connecting Los Angeles and Pasadena, California, Pasadena, opened in 1940 as the first freeway in the Western United States. It was later extended south to the Four Level Interchange in downtown Los Angeles, regarded as the first stack interchange ever built.
Los Angeles International Airport (LAX), World's busiest airports by passenger traffic, the 4th busiest airport in the world in 2018, and San Francisco International Airport (SFO), World's busiest airports by passenger traffic, the 25th busiest airport in the world in 2018, are major hubs for trans-Pacific and transcontinental traffic. There are about a dozen important commercial airports and many more general aviation List of airports in California, airports throughout the state.
The state has been a pioneer in road construction. One of the state's more visible landmarks, the Golden Gate Bridge, was the List of longest suspension bridge spans, longest suspension bridge main span in the world at between 1937 (when it opened) and 1964. With its orange paint and panoramic views of the bay, this highway bridge is a popular tourist attraction and also accommodates pedestrians and bicyclists. The San Francisco–Oakland Bay Bridge (often abbreviated the "Bay Bridge"), completed in 1936, transports about 280,000 vehicles per day on two-decks. Its two sections meet at Yerba Buena Island through the world's largest diameter transportation bore tunnel, at wide by high. The Arroyo Seco Parkway, connecting Los Angeles and Pasadena, California, Pasadena, opened in 1940 as the first freeway in the Western United States. It was later extended south to the Four Level Interchange in downtown Los Angeles, regarded as the first stack interchange ever built.
Los Angeles International Airport (LAX), World's busiest airports by passenger traffic, the 4th busiest airport in the world in 2018, and San Francisco International Airport (SFO), World's busiest airports by passenger traffic, the 25th busiest airport in the world in 2018, are major hubs for trans-Pacific and transcontinental traffic. There are about a dozen important commercial airports and many more general aviation List of airports in California, airports throughout the state.
 California also has several major seaports. The Port of Los Angeles and the Port of Long Beach in Southern California are the largest and second-largest seaports in the U.S., respectively, by volume of container cargo handled; as of 2018, collectively they handle 31.9% of all Twenty-foot equivalent unit, TEUs in the United States.Patrick Burnson
California also has several major seaports. The Port of Los Angeles and the Port of Long Beach in Southern California are the largest and second-largest seaports in the U.S., respectively, by volume of container cargo handled; as of 2018, collectively they handle 31.9% of all Twenty-foot equivalent unit, TEUs in the United States.Patrick BurnsonTop 30 U.S. Ports 2019: Trade tensions determine where cargo goes next
''Logistics Management'' (May 10, 2019). The Port of Oakland and Port of Hueneme are the 10th and 26th largest seaports in the U.S., respectively, by number of TEUs handled. The California Highway Patrol is the largest statewide police agency in the United States in employment with more than 10,000 employees. They are responsible for providing any police-sanctioned service to anyone on California's state-maintained highways and on state property. By the end of 2021, 30,610,058 people in California held a California Department of Motor Vehicles-issued driver's licenses or Identity documents in the United States, state identification card, and there were 36,229,205 Vehicle registration, registered vehicles, including 25,643,076 automobiles, 853,368 motorcycles, 8,981,787 trucks and trailers, and 121,716 miscellaneous vehicles (including historical vehicles and farm equipment).
 Inter-city rail travel is provided by Amtrak California; the three routes, the ''Capitol Corridor'', ''Pacific Surfliner'', and ''San Joaquin (train), San Joaquin'', are funded by Caltrans. These services are the busiest intercity rail lines in the United States outside the Northeast Corridor and ridership is continuing to set records. The routes are becoming increasingly popular over flying, especially on the LAX-SFO route. Integrated Rapid transit, subway and light rail networks are found in Los Angeles (LACMTA, Metro Rail) and San Francisco (San Francisco Municipal Railway, MUNI Metro). Light rail systems are also found in San Jose (Santa Clara VTA Light-rail, VTA), San Diego (San Diego Trolley), Sacramento (Sacramento RT Light Rail, RT Light Rail), and Northern San Diego County (Sprinter (San Diego), Sprinter). Furthermore, commuter rail networks serve the San Francisco Bay Area (Altamont Corridor Express, ACE, Bay Area Rapid Transit, BART, Caltrain, Sonoma–Marin Area Rail Transit, SMART), Greater Los Angeles (Metrolink (Southern California), Metrolink), and San Diego County (Coaster (San Diego), Coaster).
The California High-Speed Rail Authority was created in 1996 by the state to implement an extensive rail system. Construction was approved by the voters during the November 2008 general election, with the first phase of construction estimated to cost $64.2billion.
Nearly all counties operate bus lines, and many cities operate their own city bus lines as well. Intercity bus travel is provided by Greyhound Lines, Greyhound, Megabus (North America), Megabus, and Amtrak Thruway Motorcoach.
Inter-city rail travel is provided by Amtrak California; the three routes, the ''Capitol Corridor'', ''Pacific Surfliner'', and ''San Joaquin (train), San Joaquin'', are funded by Caltrans. These services are the busiest intercity rail lines in the United States outside the Northeast Corridor and ridership is continuing to set records. The routes are becoming increasingly popular over flying, especially on the LAX-SFO route. Integrated Rapid transit, subway and light rail networks are found in Los Angeles (LACMTA, Metro Rail) and San Francisco (San Francisco Municipal Railway, MUNI Metro). Light rail systems are also found in San Jose (Santa Clara VTA Light-rail, VTA), San Diego (San Diego Trolley), Sacramento (Sacramento RT Light Rail, RT Light Rail), and Northern San Diego County (Sprinter (San Diego), Sprinter). Furthermore, commuter rail networks serve the San Francisco Bay Area (Altamont Corridor Express, ACE, Bay Area Rapid Transit, BART, Caltrain, Sonoma–Marin Area Rail Transit, SMART), Greater Los Angeles (Metrolink (Southern California), Metrolink), and San Diego County (Coaster (San Diego), Coaster).
The California High-Speed Rail Authority was created in 1996 by the state to implement an extensive rail system. Construction was approved by the voters during the November 2008 general election, with the first phase of construction estimated to cost $64.2billion.
Nearly all counties operate bus lines, and many cities operate their own city bus lines as well. Intercity bus travel is provided by Greyhound Lines, Greyhound, Megabus (North America), Megabus, and Amtrak Thruway Motorcoach.
Water
 California's interconnected water system is the world's largest, managing over of water per year, centered on six main systems of aqueducts and infrastructure projects. Water use and conservation in California is a politically divisive issue, as the state experiences periodic droughts and has to balance the demands of its large agricultural and urban sectors, especially in the arid southern portion of the state. The state's widespread redistribution of water also invites the frequent scorn of environmentalists.
The California Water Wars, a conflict between Los Angeles and the Owens Valley over water rights, is one of the most well-known examples of the struggle to secure adequate water supplies. Former California Governor Arnold Schwarzenegger said: "We've been in crisis for quite some time because we're now 38million people and not anymore 18million people like we were in the late 60s. So it developed into a battle between environmentalists and farmers and between the south and the north and between rural and urban. And everyone has been fighting for the last four decades about water."
California's interconnected water system is the world's largest, managing over of water per year, centered on six main systems of aqueducts and infrastructure projects. Water use and conservation in California is a politically divisive issue, as the state experiences periodic droughts and has to balance the demands of its large agricultural and urban sectors, especially in the arid southern portion of the state. The state's widespread redistribution of water also invites the frequent scorn of environmentalists.
The California Water Wars, a conflict between Los Angeles and the Owens Valley over water rights, is one of the most well-known examples of the struggle to secure adequate water supplies. Former California Governor Arnold Schwarzenegger said: "We've been in crisis for quite some time because we're now 38million people and not anymore 18million people like we were in the late 60s. So it developed into a battle between environmentalists and farmers and between the south and the north and between rural and urban. And everyone has been fighting for the last four decades about water."
Government and politics

State government
The capital city of California is Sacramento. The state is organized into three separation of powers, branches of government—the executive branch consisting of the Governor of California, governor and the other independently elected constitutional officers; the legislative branch consisting of the California State Assembly, Assembly and California State Senate, Senate; and the judicial branch consisting of the Supreme Court of California and lower courts. The state also allows California ballot proposition, ballot propositions: direct participation of the electorate by initiative, referendum, recall election, recall, and ratification. Before the passage of California Proposition 14 (2010), California allowed each political party to choose whether to have a closed primary or a primary where only party members and independent (politics), independents vote. After June 8, 2010, when Proposition 14 was approved, excepting only the United States president and county central committee offices, all candidates in the primary elections are listed on the ballot with their preferred party affiliation, but they are not the official nominee of that party. At the primary election, the two candidates with the top votes will advance to the general election regardless of party affiliation. If at a special primary election, one candidate receives more than 50% of all the votes cast, they are elected to fill the vacancy and no special general election will be held.Judicial branch
 California's legal system is explicitly based upon English common law but carries many features from Spanish Civil law (legal system), civil law, such as community property. California's prison population grew from 25,000 in 1980 to over 170,000 in 2007. Capital punishment in California, Capital punishment is a legal form of punishment and the state has the largest "Death Row" population in the country (though Oklahoma and Texas are far more active in carrying out executions). California has performed List of people executed in California, 13 executions since 1976, with the last being in 2006.
California's judiciary system is the largest in the United States with a total of 1,600 judges (the federal system has only about 840). At the apex is the seven-member Supreme Court of California, while the California Courts of Appeal serve as the primary appellate courts and the California Superior Courts serve as the primary trial courts. Justices of the Supreme Court and Courts of Appeal are appointed by the governor, but are subject to retention by the electorate every 12 years.
The administration of the state's court system is controlled by the Judicial Council of California, Judicial Council, composed of the chief justice of the California Supreme Court, 14 judicial officers, four representatives from the State Bar of California, and one member from each house of the state legislature.
In fiscal year 2020–21, the state judiciary's 2,000 judicial officers and 18,000 judicial branch employees processed approximately 4.4 million cases.
California's legal system is explicitly based upon English common law but carries many features from Spanish Civil law (legal system), civil law, such as community property. California's prison population grew from 25,000 in 1980 to over 170,000 in 2007. Capital punishment in California, Capital punishment is a legal form of punishment and the state has the largest "Death Row" population in the country (though Oklahoma and Texas are far more active in carrying out executions). California has performed List of people executed in California, 13 executions since 1976, with the last being in 2006.
California's judiciary system is the largest in the United States with a total of 1,600 judges (the federal system has only about 840). At the apex is the seven-member Supreme Court of California, while the California Courts of Appeal serve as the primary appellate courts and the California Superior Courts serve as the primary trial courts. Justices of the Supreme Court and Courts of Appeal are appointed by the governor, but are subject to retention by the electorate every 12 years.
The administration of the state's court system is controlled by the Judicial Council of California, Judicial Council, composed of the chief justice of the California Supreme Court, 14 judicial officers, four representatives from the State Bar of California, and one member from each house of the state legislature.
In fiscal year 2020–21, the state judiciary's 2,000 judicial officers and 18,000 judicial branch employees processed approximately 4.4 million cases.
Executive branch
 The California executive branch consists of the governor and seven other elected constitutional officers: Lieutenant Governor of California, lieutenant governor, California Attorney General, attorney general, Secretary of State of California, secretary of state, California State Controller, state controller, California State Treasurer, state treasurer, California Insurance Commissioner, insurance commissioner, and California State Superintendent of Public Instruction, state superintendent of public instruction. They serve four-year terms and may be re-elected only once.
The California executive branch consists of the governor and seven other elected constitutional officers: Lieutenant Governor of California, lieutenant governor, California Attorney General, attorney general, Secretary of State of California, secretary of state, California State Controller, state controller, California State Treasurer, state treasurer, California Insurance Commissioner, insurance commissioner, and California State Superintendent of Public Instruction, state superintendent of public instruction. They serve four-year terms and may be re-elected only once.
Legislative branch
The California State Legislature consists of a 40-member Senate and 80-member Assembly. Senators serve four-year terms and Assembly members two. Members of the Assembly are subject to term limits of six terms, and members of the Senate are subject to term limits of three terms.Local government
Counties
California is divided into List of counties in California, 58 counties. Per Article 11, Section 1, of the Constitution of California, they are the legal subdivisions of the state. The county government provides countywide services such as law enforcement, jails, elections and voter registration, vital records, property assessment and records, tax collection, public health, health care, social services, libraries, flood control, fire protection, animal control, agricultural regulations, building inspections, ambulance services, and education departments in charge of maintaining statewide standards. In addition, the county serves as the local government for all unincorporated areas. Each county is governed by an elected board of supervisors.City and town governments
 Incorporated cities and towns in California are either Charter city, charter or general-law municipalities. General-law municipalities owe their existence to state law and are consequently governed by it; charter municipalities are governed by their own city or town charters. Municipalities incorporated in the 19th century tend to be charter municipalities. All ten of the state's most populous cities are charter cities. Most small cities have a Council–manager government, council–manager form of government, where the elected city council appoints a city manager to supervise the operations of the city. Some larger cities have a directly elected mayor who oversees the city government. In many council-manager cities, the city council selects one of its members as a mayor, sometimes rotating through the council membership—but this type of mayoral position is primarily ceremonial. The Government of San Francisco is the only consolidated city-county in California, where both the city and county governments have been merged into one unified jurisdiction.
Incorporated cities and towns in California are either Charter city, charter or general-law municipalities. General-law municipalities owe their existence to state law and are consequently governed by it; charter municipalities are governed by their own city or town charters. Municipalities incorporated in the 19th century tend to be charter municipalities. All ten of the state's most populous cities are charter cities. Most small cities have a Council–manager government, council–manager form of government, where the elected city council appoints a city manager to supervise the operations of the city. Some larger cities have a directly elected mayor who oversees the city government. In many council-manager cities, the city council selects one of its members as a mayor, sometimes rotating through the council membership—but this type of mayoral position is primarily ceremonial. The Government of San Francisco is the only consolidated city-county in California, where both the city and county governments have been merged into one unified jurisdiction.
School districts and special districts
 About 1,102 school districts, independent of cities and counties, handle California's public education. California school districts may be organized as elementary districts, high school districts, unified school districts combining elementary and high school grades, or community college districts.
There are about 3,400 special-purpose district, special districts in California. A Special-purpose district, special district, defined by California Government Code § 16271(d) as "any agency of the state for the local performance of governmental or proprietary functions within limited boundaries", provides a limited range of services within a defined geographic area. The geographic area of a special district can spread across multiple cities or counties, or could consist of only a portion of one. Most of California's special districts are ''single-purpose districts'', and provide one service.
About 1,102 school districts, independent of cities and counties, handle California's public education. California school districts may be organized as elementary districts, high school districts, unified school districts combining elementary and high school grades, or community college districts.
There are about 3,400 special-purpose district, special districts in California. A Special-purpose district, special district, defined by California Government Code § 16271(d) as "any agency of the state for the local performance of governmental or proprietary functions within limited boundaries", provides a limited range of services within a defined geographic area. The geographic area of a special district can spread across multiple cities or counties, or could consist of only a portion of one. Most of California's special districts are ''single-purpose districts'', and provide one service.
Federal representation
 The state of California sends California's congressional districts, 53 members to the United States House of Representatives, House of Representatives, the nation's largest congressional state delegation. Consequently, California also has the largest number of Electoral College (United States), electoral votes in national presidential elections, with 55. The current Speaker of the United States House of Representatives, speaker of the House of Representatives is the representative of California's 12th district, Nancy Pelosi; Kevin McCarthy (California politician), Kevin McCarthy, representing the state's 23rd district, is the Party leaders of the United States House of Representatives, House Minority Leader.
California is represented by U.S. senators Dianne Feinstein, a native and former mayor of San Francisco, and Alex Padilla, a native and former secretary of state of California. Former U.S. senator Kamala Harris, a native, former district attorney from San Francisco, former attorney general of California, resigned on January 18, 2021, to assume her role as the current Vice President of the United States. In the 1992 United States Senate election in California, 1992 U.S. Senate election, California became the first state to elect a Senate delegation entirely composed of women, due to the victories of Feinstein and Barbara Boxer. Set to follow the Vice President-Elect, Gov. Gavin Newsom, Newsom appointed Secretary of State of California, Secretary of State Alex Padilla to finish the rest of Harris's term which ends in 2022 United States Senate election in California, 2022, Padilla has vowed to run for the full term in that election cycle. Padilla was sworn in on January 20, 2021, the same day as the Inauguration of President-Elect Joe Biden as well as Harris.
The state of California sends California's congressional districts, 53 members to the United States House of Representatives, House of Representatives, the nation's largest congressional state delegation. Consequently, California also has the largest number of Electoral College (United States), electoral votes in national presidential elections, with 55. The current Speaker of the United States House of Representatives, speaker of the House of Representatives is the representative of California's 12th district, Nancy Pelosi; Kevin McCarthy (California politician), Kevin McCarthy, representing the state's 23rd district, is the Party leaders of the United States House of Representatives, House Minority Leader.
California is represented by U.S. senators Dianne Feinstein, a native and former mayor of San Francisco, and Alex Padilla, a native and former secretary of state of California. Former U.S. senator Kamala Harris, a native, former district attorney from San Francisco, former attorney general of California, resigned on January 18, 2021, to assume her role as the current Vice President of the United States. In the 1992 United States Senate election in California, 1992 U.S. Senate election, California became the first state to elect a Senate delegation entirely composed of women, due to the victories of Feinstein and Barbara Boxer. Set to follow the Vice President-Elect, Gov. Gavin Newsom, Newsom appointed Secretary of State of California, Secretary of State Alex Padilla to finish the rest of Harris's term which ends in 2022 United States Senate election in California, 2022, Padilla has vowed to run for the full term in that election cycle. Padilla was sworn in on January 20, 2021, the same day as the Inauguration of President-Elect Joe Biden as well as Harris.
Armed forces
In California, , the U.S. Department of Defense had a total of 117,806 active duty servicemembers of which 88,370 were United States Navy, Sailors or United States Marine Corps, Marines, 18,339 were United States Air Force, Airmen, and 11,097 were United States Army, Soldiers, with 61,365 Department of Defense civilian employees. Additionally, there were a total of 57,792 Reserve components of the United States Armed Forces, Reservists and Guardsman in California. In 2010, Los Angeles County was the largest origin of military recruits in the United States by county, with 1,437 individuals enlisting in the military. However, , Californians were relatively under-represented in the military as a proportion to its population. In 2000, California, had 2,569,340 veterans of United States military service: 504,010 served in World War II, 301,034 in the Korean War, 754,682 during the Vietnam War, and 278,003 during 1990–2000 (including the Persian Gulf War). , there were 1,942,775 veterans living in California, of which 1,457,875 served during a period of armed conflict, and just over four thousand served Interwar period, before World WarII (the largest population of this group of any state). California's military forces consist of the California National Guard, Army and Air National Guard, the California State Military Reserve, naval and state military reserve (militia), and the California Cadet Corps. On August 5, 1950, a Silverplate, nuclear-capable United States Air Force Boeing B-29 Superfortress bomber carrying a Mark 4 nuclear bomb, nuclear bomb crashed shortly after takeoff from Fairfield-Suisun Air Force Base. Brigadier General Robert F. Travis, command pilot of the bomber, was among the dead.Ideology
California has an idiosyncratic political culture compared to the rest of the country, and is sometimes regarded as a trendsetter. In socio-cultural mores and national politics, Californians are perceived as more Modern liberalism in the United States, liberal than other Americans, especially those who live in the inland states. In the 2016 United States presidential election, California had the third highest percentage of Democratic votes behind Washington, D.C., the District of Columbia and Hawaii. In the 2020 United States presidential election#Results by state, 2020 United States presidential election, it had the 6th highest behind the District of Columbia, Vermont, Massachusetts, Maryland, and Hawaii. According to the Cook Political Report, California contains five of the 15 most Democratic congressional districts in the United States. Among the political idiosyncrasies, California was the second state California gubernatorial recall election, 2003, to recall their state governor (the first state being North Dakota in 1921 North Dakota gubernatorial recall election, 1921), the second state to legalize abortion, and the only state to ban marriage for gay couples twice by vote (including California Proposition 8, Proposition8 in 2008). Voters also passed California Proposition 71 (2004), Proposition 71 in 2004 to fund stem cell research, making California the Stem cell laws and policy in the United States#Legalization and funding, second state to legalize stem cell research after New Jersey, and California Proposition 14 (2010), Proposition 14 in 2010 to completely change the state's primary election process. California has also experienced California Water Wars, disputes over water rights; and a tax revolt, culminating with the passage of California Proposition 13 (1978), Proposition 13 in 1978, limiting state property taxes. California voters have rejected affirmative action on multiple occasions, most recently in November 2020. The state's trend towards the Democratic Party (United States), Democratic Party and away from the Republican Party (United States), Republican Party can be seen in state elections. From 1899 to 1939, California had Republican governors. Since 1990, California has generally elected Democratic candidates to federal, state and local offices, including current Governor Gavin Newsom; however, the state has elected Republican Governors, though many of its Republican Governors, such as Arnold Schwarzenegger, tend to be considered moderate Republicans and more Centrism, centrist than the national party. Several political movements have advocated for Partition and secession in California, Californian independence. The California National Party and the California Freedom Coalition both advocate for Californian independence along the lines of Progressivism in the United States, progressivism and civic nationalism. The Yes California movement attempted to organize an independence referendum via ballot initiative for 2019, which was then postponed.
The Democrats also now hold a supermajority in both houses of the state legislature. There are 60 Democrats and 20 Republicans in the Assembly; and 29 Democrats and 11 Republicans in the Senate.
The trend towards the Democratic Party is most obvious in presidential elections. From 1952 United States presidential election, 1952 through 1988 United States presidential election, 1988, California was a Republican leaning state, with the party carrying the state's electoral votes in nine of ten elections, with 1964 United States presidential election, 1964 as the exception. Southern California Republicans Richard Nixon and Ronald Reagan were both elected twice as the 37th and 40th U.S. Presidents, respectively. However, Democrats have won all of California's electoral votes for the last eight elections, starting in 1992 United States presidential election, 1992.
In the United States House, the Democrats held a 34–19 edge in the CA delegation of the 110th United States Congress in 2007. As the result of gerrymandering, the districts in California were usually dominated by one or the other party, and few districts were considered competitive. In 2008, Californians passed Proposition 20 to empower a 14-member independent citizen commission to redraw districts for both local politicians and Congress. After the 2012 elections, when the new system took effect, Democrats gained four seats and held a 38–15 majority in the delegation. Following the 2018 United States House of Representatives elections, 2018 midterm House elections, Democrats won 46 out of 53 congressional house seats in California, leaving Republicans with seven.
Several political movements have advocated for Partition and secession in California, Californian independence. The California National Party and the California Freedom Coalition both advocate for Californian independence along the lines of Progressivism in the United States, progressivism and civic nationalism. The Yes California movement attempted to organize an independence referendum via ballot initiative for 2019, which was then postponed.
The Democrats also now hold a supermajority in both houses of the state legislature. There are 60 Democrats and 20 Republicans in the Assembly; and 29 Democrats and 11 Republicans in the Senate.
The trend towards the Democratic Party is most obvious in presidential elections. From 1952 United States presidential election, 1952 through 1988 United States presidential election, 1988, California was a Republican leaning state, with the party carrying the state's electoral votes in nine of ten elections, with 1964 United States presidential election, 1964 as the exception. Southern California Republicans Richard Nixon and Ronald Reagan were both elected twice as the 37th and 40th U.S. Presidents, respectively. However, Democrats have won all of California's electoral votes for the last eight elections, starting in 1992 United States presidential election, 1992.
In the United States House, the Democrats held a 34–19 edge in the CA delegation of the 110th United States Congress in 2007. As the result of gerrymandering, the districts in California were usually dominated by one or the other party, and few districts were considered competitive. In 2008, Californians passed Proposition 20 to empower a 14-member independent citizen commission to redraw districts for both local politicians and Congress. After the 2012 elections, when the new system took effect, Democrats gained four seats and held a 38–15 majority in the delegation. Following the 2018 United States House of Representatives elections, 2018 midterm House elections, Democrats won 46 out of 53 congressional house seats in California, leaving Republicans with seven.
 In general, Democratic strength is centered in the populous Coastal California, coastal regions of the Los Angeles metropolitan area and the San Francisco Bay Area. Republican strength is still greatest in eastern parts of the state. Orange County, California, Orange County had remained largely Republican until the 2016 and 2018 elections, in which a majority of the county's votes were cast for Democratic candidates. One study ranked Berkeley California, Berkeley, Oakland, California, Oakland, Inglewood, California, Inglewood and San Francisco in the top 20 most liberal American cities; and Bakersfield, California, Bakersfield, Orange, California, Orange, Escondido, California, Escondido, Garden Grove, California, Garden Grove, and Simi Valley, California, Simi Valley in the top 20 most conservative cities.
In February 2021, out of the 25,166,581 people eligible to vote, 22,154,304 people were registered to vote. Of the people registered, the three largest registered groups were Democrats (10,228,144), Republicans (5,347,377), and Independent voter, No Party Preference (5,258,223). Los Angeles County had the largest number of registered Democrats (3,043,535) and Republicans (995,112) of any county in the state.
In a 2020 study, California was ranked as the 10th easiest state for citizens to vote in.
In general, Democratic strength is centered in the populous Coastal California, coastal regions of the Los Angeles metropolitan area and the San Francisco Bay Area. Republican strength is still greatest in eastern parts of the state. Orange County, California, Orange County had remained largely Republican until the 2016 and 2018 elections, in which a majority of the county's votes were cast for Democratic candidates. One study ranked Berkeley California, Berkeley, Oakland, California, Oakland, Inglewood, California, Inglewood and San Francisco in the top 20 most liberal American cities; and Bakersfield, California, Bakersfield, Orange, California, Orange, Escondido, California, Escondido, Garden Grove, California, Garden Grove, and Simi Valley, California, Simi Valley in the top 20 most conservative cities.
In February 2021, out of the 25,166,581 people eligible to vote, 22,154,304 people were registered to vote. Of the people registered, the three largest registered groups were Democrats (10,228,144), Republicans (5,347,377), and Independent voter, No Party Preference (5,258,223). Los Angeles County had the largest number of registered Democrats (3,043,535) and Republicans (995,112) of any county in the state.
In a 2020 study, California was ranked as the 10th easiest state for citizens to vote in.
Twinned regions
California has City twinning, region twinning arrangements with: * Catalonia, autonomous community of Spain * Alberta, province of CanadaSee also
* Index of California-related articles * Outline of CaliforniaNotes
References
Citations
Works cited
* * *Further reading
* * * * Matthews, Glenna. ''The Golden State in the Civil War: Thomas Starr King, the Republican Party, and the Birth of Modern California''. New York: Cambridge University Press, 2012. * *External links
State of California
*
data.ca.gov: open data portal from California state agencies
California State Facts from USDA
California Drought: Farm and Food Impacts from USDA, Economic Research Service
*
1973 documentary featuring aerial views of the California coastline from Mt. Shasta to Los Angeles
{{coord, 37, -120, dim:600000_region:US-CA_type:adm1st, name=State of California, display=title California, States and territories established in 1850 States of the United States States of the West Coast of the United States 1850 establishments in California Former Spanish colonies Western United States 1850 establishments in the United States Contiguous United States