Caius College on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Gonville and Caius College, often referred to simply as Caius ( ), is a
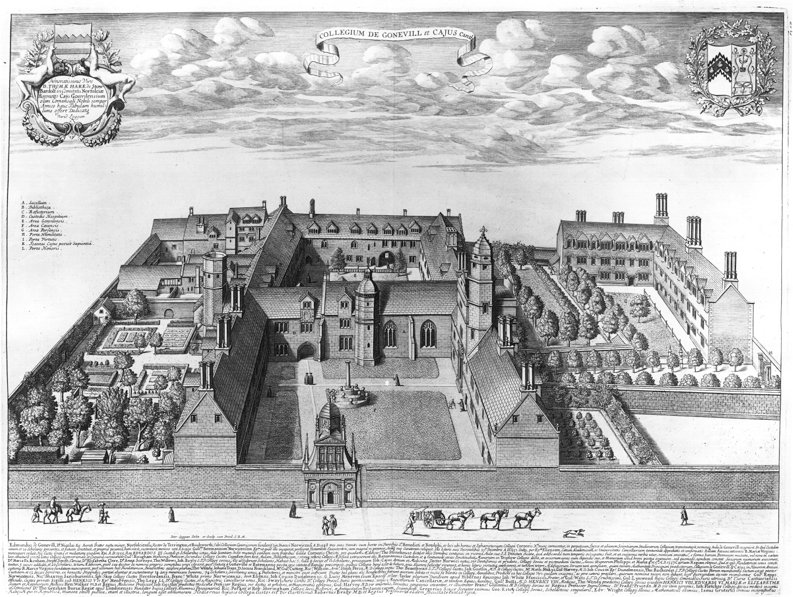 The college was founded in 1348 as Gonville Hall by
The college was founded in 1348 as Gonville Hall by

 The first buildings erected on the college's current site date from 1353 when Bateman built Gonville Court. The college chapel was added in 1393 with the Old Hall (used until recently as a library); Master's Lodge followed in the next half century. Most of the stone used to build the college came from
The first buildings erected on the college's current site date from 1353 when Bateman built Gonville Court. The college chapel was added in 1393 with the Old Hall (used until recently as a library); Master's Lodge followed in the next half century. Most of the stone used to build the college came from
 Across Trinity Street on land surrounding St Michael's Church. St. Michael's Court was completed in the 1930s; on the south side of St. Michael's Court is new campus building that overlooks Market Place. The college also owns several houses around Cambridge, on Mortimer Road and Gresham Road, where some second year undergraduates live, and on Harvey Road and St Paul's Road, which are occupied by graduate students.
Across Trinity Street on land surrounding St Michael's Church. St. Michael's Court was completed in the 1930s; on the south side of St. Michael's Court is new campus building that overlooks Market Place. The college also owns several houses around Cambridge, on Mortimer Road and Gresham Road, where some second year undergraduates live, and on Harvey Road and St Paul's Road, which are occupied by graduate students.
constituent college
A collegiate university is a university in which functions are divided between a central administration and a number of constituent colleges. Historically, the first collegiate university was the University of Paris and its first college was the C ...
of the University of Cambridge
, mottoeng = Literal: From here, light and sacred draughts.
Non literal: From this place, we gain enlightenment and precious knowledge.
, established =
, other_name = The Chancellor, Masters and Schola ...
in Cambridge
Cambridge ( ) is a university city and the county town in Cambridgeshire, England. It is located on the River Cam approximately north of London. As of the 2021 United Kingdom census, the population of Cambridge was 145,700. Cambridge bec ...
, England. Founded in 1348, it is the fourth-oldest of the University of Cambridge's 31 colleges and one of the wealthiest. The college has been attended by many students who have gone on to significant accomplishment, including fifteen Nobel Prize
The Nobel Prizes ( ; sv, Nobelpriset ; no, Nobelprisen ) are five separate prizes that, according to Alfred Nobel's will of 1895, are awarded to "those who, during the preceding year, have conferred the greatest benefit to humankind." Alfr ...
winners, the second-highest of any Oxbridge
Oxbridge is a portmanteau of Oxford and Cambridge, the two oldest, wealthiest, and most famous universities in the United Kingdom. The term is used to refer to them collectively, in contrast to other British universities, and more broadly to de ...
college after Trinity College, Cambridge
Trinity College is a constituent college of the University of Cambridge. Founded in 1546 by Henry VIII, King Henry VIII, Trinity is one of the largest Cambridge colleges, with the largest financial endowment of any college at either Cambridge ...
.
The college has long historical associations with the teaching of medicine, especially due to its prominent alumni in the medical profession. It also has globally-recognized and prestigious academic programmes in law, economics, English literature, and history. Famous Gonville and Caius alumni include physicians John Caius
John Caius (born John Kays ; 6 October 1510 – 29 July 1573), also known as Johannes Caius and Ioannes Caius, was an English physician, and second founder of the present Gonville and Caius College, Cambridge.
Biography
Early years
Caius was ...
(who gave the college the caduceus
The caduceus (☤; ; la, cādūceus, from grc-gre, κηρύκειον "herald's wand, or staff") is the staff carried by Hermes in Greek mythology and consequently by Hermes Trismegistus in Greco-Egyptian mythology. The same staff was also ...
in its insignia) and William Harvey
William Harvey (1 April 1578 – 3 June 1657) was an English physician who made influential contributions in anatomy and physiology. He was the first known physician to describe completely, and in detail, the systemic circulation and proper ...
. Other alumni in the sciences include Francis Crick
Francis Harry Compton Crick (8 June 1916 – 28 July 2004) was an English molecular biologist, biophysicist, and neuroscientist. He, James Watson, Rosalind Franklin, and Maurice Wilkins played crucial roles in deciphering the helical struc ...
(joint discoverer of the structure of DNA with James Watson
James Dewey Watson (born April 6, 1928) is an American molecular biologist, geneticist, and zoologist. In 1953, he co-authored with Francis Crick the academic paper proposing the double helix structure of the DNA molecule. Watson, Crick and ...
), James Chadwick
Sir James Chadwick, (20 October 1891 – 24 July 1974) was an English physicist who was awarded the 1935 Nobel Prize in Physics for his discovery of the neutron in 1932. In 1941, he wrote the final draft of the MAUD Report, which inspi ...
(discoverer of the neutron
The neutron is a subatomic particle, symbol or , which has a neutral (not positive or negative) charge, and a mass slightly greater than that of a proton. Protons and neutrons constitute the nuclei of atoms. Since protons and neutrons beh ...
), and Howard Florey
Howard Walter Florey, Baron Florey (24 September 189821 February 1968) was an Australian pharmacologist and pathologist who shared the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in 1945 with Sir Ernst Chain and Sir Alexander Fleming for his role in ...
(developer of penicillin
Penicillins (P, PCN or PEN) are a group of β-lactam antibiotics originally obtained from ''Penicillium'' moulds, principally '' P. chrysogenum'' and '' P. rubens''. Most penicillins in clinical use are synthesised by P. chrysogenum using ...
). Stephen Hawking, previously Cambridge's Lucasian Chair of Mathematics
The Lucasian Chair of Mathematics () is a mathematics professorship in the University of Cambridge, England; its holder is known as the Lucasian Professor. The post was founded in 1663 by Henry Lucas, who was Cambridge University's Member of Pa ...
Emeritus
''Emeritus'' (; female: ''emerita'') is an adjective used to designate a retired chair, professor, pastor, bishop, pope, director, president, prime minister, rabbi, emperor, or other person who has been "permitted to retain as an honorary title ...
, was a fellow of the college from 1965 until his death in 2018. Other notable alumni include John Venn
John Venn, Fellow of the Royal Society, FRS, Fellow of the Society of Antiquaries of London, FSA (4 August 1834 – 4 April 1923) was an English mathematician, logician and philosopher noted for introducing Venn diagrams, which are used in l ...
(inventor of the Venn diagram
A Venn diagram is a widely used diagram style that shows the logical relation between set (mathematics), sets, popularized by John Venn (1834–1923) in the 1880s. The diagrams are used to teach elementary set theory, and to illustrate simple ...
), former Chancellor of the Exchequer and Father of the House of Commons Kenneth Clarke
Kenneth Harry Clarke, Baron Clarke of Nottingham, (born 2 July 1940), often known as Ken Clarke, is a British politician who served as Home Secretary from 1992 to 1993 and Chancellor of the Exchequer from 1993 to 1997 as well as serving as de ...
, comedian and Channel 4
Channel 4 is a British free-to-air public broadcast television network operated by the state-owned enterprise, state-owned Channel Four Television Corporation. It began its transmission on 2 November 1982 and was established to provide a four ...
television presenter Jimmy Carr
James Anthony Patrick Carr (born 15 September 1972) is a British-Irish comedian, presenter, writer, and actor. He is known for his deadpan delivery of controversial one-liners and distinctive laugh, for which he has been both praised and criti ...
, and former Downing Street director of communications
The Downing Street director of communications is the post of director of communications for the prime minister of the United Kingdom. The position is held by an appointed special adviser.
In September 2022, as part of the incoming Truss mini ...
Alastair Campbell
Alastair John Campbell (born 25 May 1957) is a British journalist, author, strategist, broadcaster and activist known for his roles during Tony Blair's leadership of the Labour Party. Campbell worked as Blair's spokesman and campaign director ...
.
Several streets in the city, including Harvey Road, Glisson Road, and Gresham Road, are named after Gonville and Caius alumni. The college and its masters have been influential in the development of the university, including in the founding of other colleges, including Trinity Hall and Darwin College and providing land on Sidgwick Site
The Sidgwick Site is one of the largest sites within the University of Cambridge, England.
Overview and history
The Sidgwick Site is located on the western side of Cambridge city centre, near the Backs. The site is north of Sidgwick Avenue an ...
on which Faculty of Law
A faculty is a division within a university or college comprising one subject area or a group of related subject areas, possibly also delimited by level (e.g. undergraduate). In American usage such divisions are generally referred to as colleges ...
was built.
History
 The college was founded in 1348 as Gonville Hall by
The college was founded in 1348 as Gonville Hall by Edmund Gonville Edmund Gonville (died 1351) founded Gonville Hall in 1348, which later was re-founded by John Caius to become Gonville and Caius College. Gonville Hall was his third foundation. Before this he had founded two religious houses, a College at Rushford, ...
, a clergyman who hailed from a gentry family of French origin. Gonville held various positions in the English Church, serving as Rector of three parishes, Thelnetham
Thelnetham is a village and civil parish in the West Suffolk district of Suffolk in eastern England. Located on the southern bank of the River Little Ouse (the Norfolk-Suffolk border), six miles west of Diss, in 2005 its population was 230. The ...
(1320–26), Rushford, Norfolk
Rushford is a small village in the English county of Norfolk. It is situated on the north bank of the River Little Ouse, east of the town of Thetford and south of the main A1066 road. The river forms the boundary between Norfolk and Suffolk and ...
(1326-1342), and Terrington St Clement
Terrington St Clement is a village and civil parish in King's Lynn and West Norfolk borough and district in Norfolk, England. It is in the drained marshlands to the south of the Wash, west of King's Lynn, Norfolk, and east of Sutton Bridge, L ...
(1343-1351). Such occupations afforded him sufficient wealth that he was able to lend money to Edward III
Edward III (13 November 1312 – 21 June 1377), also known as Edward of Windsor before his accession, was King of England and Lord of Ireland from January 1327 until his death in 1377. He is noted for his military success and for restoring r ...
, an act that saw him appointed a King's Clerk.
With the support of Sir Walter Manny, Gonville petitioned the king for permission to found a college at Cambridge consisting of 20 scholars. In January 1348, Edward III granted this request and issued Letters patent
Letters patent ( la, litterae patentes) ( always in the plural) are a type of legal instrument in the form of a published written order issued by a monarch, president or other head of state, generally granting an office, right, monopoly, titl ...
. Its 1348 founding makes Gonville and Caius the fourth-oldest surviving college at Cambridge.
Gonville died three years later, in 1351, and left behind an institution that begun to struggle financially. William Bateman, Bishop of Norwich
The Bishop of Norwich is the ordinary of the Church of England Diocese of Norwich in the Province of Canterbury. The diocese covers most of the county of Norfolk and part of Suffolk. The bishop of Norwich is Graham Usher.
The see is in the ...
, intervened and moved the college to its current location off Trinity Street in central Cambridge. He also leased himself land close to River Cam
The River Cam () is the main river flowing through Cambridge in eastern England. After leaving Cambridge, it flows north and east before joining the River Great Ouse to the south of Ely, at Pope's Corner. The total distance from Cambridge to ...
to set up his own college, Trinity Hall. Gonville Hall was renamed The Hall of the Annunciation of the Blessed Virgin Mary and Bateman appointed his former chaplain John Colton, who was later made Archbishop of Armagh
In Christian denominations, an archbishop is a bishop of higher rank or office. In most cases, such as the Catholic Church, there are many archbishops who either have jurisdiction over an ecclesiastical province in addition to their own archdio ...
, as the college's master.
By the sixteenth century, the college had fallen into disrepair. In 1557, it was refounded by Royal Charter
A royal charter is a formal grant issued by a monarch under royal prerogative as letters patent. Historically, they have been used to promulgate public laws, the most famous example being the English Magna Carta (great charter) of 1215, bu ...
as Gonville and Caius College by alumnus John Caius
John Caius (born John Kays ; 6 October 1510 – 29 July 1573), also known as Johannes Caius and Ioannes Caius, was an English physician, and second founder of the present Gonville and Caius College, Cambridge.
Biography
Early years
Caius was ...
. Caius had read divinity at the college between 1529 and 1533 and later travelled to Renaissance
The Renaissance ( , ) , from , with the same meanings. is a period in European history marking the transition from the Middle Ages to modernity and covering the 15th and 16th centuries, characterized by an effort to revive and surpass ideas ...
Italy, where he studied medicine at the University of Padua
The University of Padua ( it, Università degli Studi di Padova, UNIPD) is an Italian university located in the city of Padua, region of Veneto, northern Italy. The University of Padua was founded in 1222 by a group of students and teachers from B ...
under Montanus
Montanus was the second century founder of Montanism and a self proclaimed prophet. Montanus emphasized the work of the Holy Spirit, in a manner which set him apart from the Great church.
Life
Only very little is known about the life of Montanu ...
and Vesalius
Andreas Vesalius (Latinized from Andries van Wezel) () was a 16th-century anatomist, physician, and author of one of the most influential books on human anatomy, ''De Humani Corporis Fabrica Libri Septem'' (''On the fabric of the human body'' '' ...
. Following his return to England, Caius had become a renowned physician and served many terms as president of the Royal College of Physicians
The Royal College of Physicians (RCP) is a British professional membership body dedicated to improving the practice of medicine, chiefly through the accreditation of physicians by examination. Founded by royal charter from King Henry VIII in 1 ...
. At the time of the college's re-founding, he had worked as physician to two English monarchs, Edward VI
Edward VI (12 October 1537 – 6 July 1553) was King of England and Ireland from 28 January 1547 until his death in 1553. He was crowned on 20 February 1547 at the age of nine. Edward was the son of Henry VIII and Jane Seymour and the first E ...
and Mary I
Mary I (18 February 1516 – 17 November 1558), also known as Mary Tudor, and as "Bloody Mary" by her Protestant opponents, was Queen of England and Ireland from July 1553 and Queen of Spain from January 1556 until her death in 1558. She ...
, and later served in the same capacity for Elizabeth I
Elizabeth I (7 September 153324 March 1603) was Queen of England and Ireland from 17 November 1558 until her death in 1603. Elizabeth was the last of the five House of Tudor monarchs and is sometimes referred to as the "Virgin Queen".
El ...
.
Following the death of Thomas Bacon, Caius was appointed master of the college on 24 January 1559, a position he held until shortly before his death in 1573. He provided the college with significant funds and greatly expanded the college's buildings. Caius accepted no payment for his services but insisted on several rules, including that the college admit no scholar who "is deformed, dumb, blind, lame, maimed, mutilated, a Welshman, or suffering from any grave or contagious illness, or an invalid, that is sick in a serious measure". Caius also built a three-sided court, Caius Court, "lest the air from being confined within a narrow space should become foul". Caius was responsible for developing the college's strong global reputation in medicine, which continues to this day.
By 1630, the college had expanded greatly with roughly 25 fellows and 150 students. But the number of fellows and strudents fell in the following century, returning to the 1630 level only in the early nineteenth century. Since then, Gonville and Caius has grown considerably, and it has now one of the University of Cambridge's largest undergraduate populations. In 1979, the college first admitted women as fellows and students. It now has over 110 Fellows, over 700 students and about 200 staff.
Gonville and Caius is one of the wealthiest of all Cambridge colleges with an endowment of £221 million in 2018.
The college's present 43rd Master
Master or masters may refer to:
Ranks or titles
* Ascended master, a term used in the Theosophical religious tradition to refer to spiritually enlightened beings who in past incarnations were ordinary humans
*Grandmaster (chess), National Master ...
, appointed in 2018, is Pippa Rogerson.
Buildings and grounds
Old Courts

 The first buildings erected on the college's current site date from 1353 when Bateman built Gonville Court. The college chapel was added in 1393 with the Old Hall (used until recently as a library); Master's Lodge followed in the next half century. Most of the stone used to build the college came from
The first buildings erected on the college's current site date from 1353 when Bateman built Gonville Court. The college chapel was added in 1393 with the Old Hall (used until recently as a library); Master's Lodge followed in the next half century. Most of the stone used to build the college came from Ramsey Abbey
Ramsey Abbey was a Benedictine abbey in Ramsey, Huntingdonshire (now part of Cambridgeshire), England. It was founded about AD 969 and dissolved in 1539.
The site of the abbey in Ramsey is now a Scheduled Ancient Monument. Most of the abbey's ...
near Ramsey, Cambridgeshire
Ramsey is a market town and civil parish in the Huntingdonshire district of Cambridgeshire, England. The town is about north of Huntingdon. Ramsey parish includes the settlements of Ramsey Forty Foot, Ramsey Heights, Ramsey Mereside, Ramsey ...
. Gonville and Caius has the oldest purpose-built college chapel in continuous use in either Oxford
Oxford () is a city in England. It is the county town and only city of Oxfordshire. In 2020, its population was estimated at 151,584. It is north-west of London, south-east of Birmingham and north-east of Bristol. The city is home to the ...
or Cambridge
Cambridge ( ) is a university city and the county town in Cambridgeshire, England. It is located on the River Cam approximately north of London. As of the 2021 United Kingdom census, the population of Cambridge was 145,700. Cambridge bec ...
. The chapel is situated centrally within the college, reflecting the college's religious foundation.
On the re-foundation by Caius, the college was expanded and updated. In 1565, the building of Caius Court began, and Caius planted an avenue of trees in what is now known as Tree Court. He was also responsible for building the college's three gates, symbolising the path of academic life. On matriculation, graduates arrive at the Gate of Humility, near the Porters' Lodge in the centre of the campus, and then pass through the Gate of Honour to the neighbouring Senate House, where they receive their degrees. The Gate of Honour is only used for special occasions, including graduation. Students of Gonville and Caius commonly refer to the fourth gate in the college, between Tree Court and Gonville Court, which also gives access to some lavatories, as the Gate of Necessity.
The buildings of Gonville Court were given classical facades in the 1750s. The Old Library and Hall were designed by Anthony Salvin
Anthony Salvin (17 October 1799 – 17 December 1881) was an English architect. He gained a reputation as an expert on medieval buildings and applied this expertise to his new buildings and his restorations. He restored castles and country ho ...
in 1854. On the wall of the Hall hangs a college flag, which in 1912 was flown at the South Pole
The South Pole, also known as the Geographic South Pole, Terrestrial South Pole or 90th Parallel South, is one of the two points where Earth's axis of rotation intersects its surface. It is the southernmost point on Earth and lies antipod ...
by Cambridge's Edward Wilson during the Terra Nova Expedition
The ''Terra Nova'' Expedition, officially the British Antarctic Expedition, was an expedition to Antarctica which took place between 1910 and 1913. Led by Captain Robert Falcon Scott, the expedition had various scientific and geographical objec ...
of 1910–1913. Gonville Court, though remodelled in the 18th and 19th centuries, is the oldest part of the college. Newrt lecture rooms were designed by Alfred Waterhouse
Alfred Waterhouse (19 July 1830 – 22 August 1905) was an English architect, particularly associated with the Victorian Gothic Revival architecture, although he designed using other architectural styles as well. He is perhaps best known f ...
and completed by Rattee and Kett
Rattee and Kett was a building contractor based in Cambridge
History
The business was founded by James Rattee in 1843. After George Kett joined the business in 1848, the partners worked together on the wood carvings for the Palace of Westminster. ...
in 1884.
West Road site
Caius owns a substantial amount of land between West Road andSidgwick Avenue
Sidgwick Avenue is a road located in western Cambridge, England. The avenue runs east-west and links Grange Road to the west with Queen's Road to the east. The line of the road continues northeast into central Cambridge as Silver Street. Sidg ...
. Set in landscaped gardens, the modern Harvey Court (named after William Harvey
William Harvey (1 April 1578 – 3 June 1657) was an English physician who made influential contributions in anatomy and physiology. He was the first known physician to describe completely, and in detail, the systemic circulation and proper ...
and designed by Leslie Martin
Sir John Leslie Martin (17 August 1908, in Manchester – 28 July 2000) was an English architect, and a leading advocate of the International Style. Martin's most famous building is the Royal Festival Hall. His work was especially influenced ...
) was built on West Road in 1961. Adjacent to Harvey Court is the Stephen Hawking Building, which opened its doors to first-year undergraduates in October 2006. The Stephen Hawking Building provides suite accommodations for 75 students and eight fellows and conference facilities. It boasts some of the highest-standard student accommodation in Cambridge
Cambridge ( ) is a university city and the county town in Cambridgeshire, England. It is located on the River Cam approximately north of London. As of the 2021 United Kingdom census, the population of Cambridge was 145,700. Cambridge bec ...
.
Additional buildings provide housing for older students, a day care, and various study and music rooms. The college also owns extensive gardens and the land on which the adjacent Squire Law Library
The Faculty of Law, Cambridge is the law school of the University of Cambridge.
The study of law at the University of Cambridge began in the thirteenth century. The faculty sits the oldest law professorship in the English-speaking world, the R ...
has stood since 1995.
Libraries
Caius has one of the largest libraries inOxbridge
Oxbridge is a portmanteau of Oxford and Cambridge, the two oldest, wealthiest, and most famous universities in the United Kingdom. The term is used to refer to them collectively, in contrast to other British universities, and more broadly to de ...
, housed in the Cockerell Building. Caius acquired the lease on the building, which previously housed the Seeley History Library and the Squire Law Library
The Faculty of Law, Cambridge is the law school of the University of Cambridge.
The study of law at the University of Cambridge began in the thirteenth century. The faculty sits the oldest law professorship in the English-speaking world, the R ...
, in the 1990s. The college library was relocated there from Gonville Court in the summer of 1996, following an extensive renovation.
Other courts and college accommodations
 Across Trinity Street on land surrounding St Michael's Church. St. Michael's Court was completed in the 1930s; on the south side of St. Michael's Court is new campus building that overlooks Market Place. The college also owns several houses around Cambridge, on Mortimer Road and Gresham Road, where some second year undergraduates live, and on Harvey Road and St Paul's Road, which are occupied by graduate students.
Across Trinity Street on land surrounding St Michael's Church. St. Michael's Court was completed in the 1930s; on the south side of St. Michael's Court is new campus building that overlooks Market Place. The college also owns several houses around Cambridge, on Mortimer Road and Gresham Road, where some second year undergraduates live, and on Harvey Road and St Paul's Road, which are occupied by graduate students.
Grounds
The Fellows' garden lies just beyond Harvey Court, onSidgwick Avenue
Sidgwick Avenue is a road located in western Cambridge, England. The avenue runs east-west and links Grange Road to the west with Queen's Road to the east. The line of the road continues northeast into central Cambridge as Silver Street. Sidg ...
. The extensive sports fields are located on Barton Road, a short walk from Harvey Court.
Traditions
Gonville and Caius College maintains many traditions. It offers two seatings in Hall three nights a week. Typically attended by between 150–200 students, Hall consists of a three-course meal served after 18:00 (First Hall) or 19:15 (Formal Hall); Formal Hall requires a gown be worn, and seats Fellows at its high table. It is preceded by the benediction, which is said inLatin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power of the ...
:
''Benedic, Domine, nobis et donis tuis quae ex largitate tua sumus sumpturi; et concede ut, ab iis salubriter enutriti, tibi debitum obsequium praestare valeamus, per Jesum Christum dominum nostrum; mensae caelestis nos participes facias, Rex aeternae gloriae.''
As at most Oxbridge colleges, it is tradition that only the Fellows may walk on the grass.
The college also enforces the system of exeat
The Latin word ''exeat'' ("he/she may leave") is most commonly used to describe a period of absence from a centre of learning.Caius Boat Club is the college's boat club, with the men's 1st VIII remaining unbeaten in the seasons of 2010/11 and of 2011/2012, and (as of 2019) is currently in possession of both the Lent and May
Gonville and Caius Updates
File:Gate of Honour, Gonville & Caius College.jpg, The Gate of Honour
File:Cambridge - Gonville and Caius College - 0951.jpg, Dining Hall
File:Cambridge - Gonville and Caius College - 0903.jpg, Fellow Dining Room
File:Fisher-stainedglass-gonville-caius.jpg, Stained glass window in dining hall
File:Sherrington-stainedglass-gonville-caius.jpg, Stained glass window in dining hall
File:Venn-stainedglass-gonville-caius.jpg, Stained glass window in dining hall
File:Crick-stainedglass-gonville-caius.jpg, Stained glass window in dining hall
File:View from Great St Mary's Cambridge - 04.jpg, View from Great St Mary's Church
File:Cambridge - Gonville and Caius College - 1048.jpg, The library
File:Cambridge boathouses - Caius (2).jpg, The old boathouse (demolished in 2015)
File:Gonville and Caius College shield of arms on Rose Crescent, Cambridge.jpg, College crest
Gonville and Caius College Choir
{{DEFAULTSORT:Gonville And Caius College, Cambridge 1348 establishments in England 1557 establishments in England Alfred Waterhouse buildings Colleges of the University of Cambridge Grade I listed buildings in Cambridge Grade I listed educational buildings Organisations based in Cambridge with royal patronage
Bumps
A bumps race is a form of rowing race in which a number of boats chase each other in single file, each crew attempting to catch and ‘bump’ the boat in front without being caught by the boat behind.
The form is mainly used in intercollegia ...
headships.
Caius Jazz takes place most terms in the college bar, inviting 'some of the most illustrious names in the contemporary scene' and a house band of students studying at London conservatoires to play in the college bar. In recent years Steve Fishwick, Sam Mayne, Ian Shaw, Barry Green, Gareth Lockrane, and Paul Jarvis have all been featured.
The Caius May Ball
A May Ball is a ball at the end of the academic year that takes place at any of the colleges of the University of Cambridge. They are elaborate and lavish formal affairs, requiring black tie or sometimes white tie, with ticket prices ranging f ...
is an all-night party in June, held every two years.
Squires is an all-male drinking society; although it is not officially affiliated with the college, all of its members are Caians. They hold an annual garden party to kick off May Week. The female equivalent is called Cupids.
Choir
The Gonville and Caius Choir was founded by composer Charles Wood in the late 19th century. It was most recently directed by the college's scholar of South American choral musicGeoffrey Webber
Geoffrey Webber is a musician and academic, and the former Director of Music at Gonville and Caius College, Cambridge.
Webber was a chorister at Salisbury Cathedral, and was educated at the King's School Worcester and New College, Oxford, where ...
until his 2019 resignation. The choir tours abroad and records eclectically. The choir is made up from scholars and exhibitioners from the college, and a few volunteers from other Cambridge colleges.
JCR
The college's union is Gonville and Caius Student Union (GCSU). George Skeen is the current president.Gonville and Caius Updates
Notable alumni
Since its founding, Gonville and Caius has graduated List of alumni of Gonville and Caius College, Cambridge, accomplished and famed individuals across most fields, including 15Nobel Prize
The Nobel Prizes ( ; sv, Nobelpriset ; no, Nobelprisen ) are five separate prizes that, according to Alfred Nobel's will of 1895, are awarded to "those who, during the preceding year, have conferred the greatest benefit to humankind." Alfr ...
laureates:
Nobel Prize laureates
* 1932Charles Scott Sherrington
Sir Charles Scott Sherrington (27 November 1857 – 4 March 1952) was an eminent English neurophysiologist. His experimental research established many aspects of contemporary neuroscience, including the concept of the spinal reflex as a system ...
– neurophysiologist (student and fellow)
* 1935 James Chadwick
Sir James Chadwick, (20 October 1891 – 24 July 1974) was an English physicist who was awarded the 1935 Nobel Prize in Physics for his discovery of the neutron in 1932. In 1941, he wrote the final draft of the MAUD Report, which inspi ...
– physicist, discoverer of the neutron
The neutron is a subatomic particle, symbol or , which has a neutral (not positive or negative) charge, and a mass slightly greater than that of a proton. Protons and neutrons constitute the nuclei of atoms. Since protons and neutrons beh ...
(student, fellow and master)
* 1945 Howard Florey
Howard Walter Florey, Baron Florey (24 September 189821 February 1968) was an Australian pharmacologist and pathologist who shared the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in 1945 with Sir Ernst Chain and Sir Alexander Fleming for his role in ...
– co-developer of penicillin
Penicillins (P, PCN or PEN) are a group of β-lactam antibiotics originally obtained from ''Penicillium'' moulds, principally '' P. chrysogenum'' and '' P. rubens''. Most penicillins in clinical use are synthesised by P. chrysogenum using ...
(fellow).
* 1954 Max Born
Max Born (; 11 December 1882 – 5 January 1970) was a German physicist and mathematician who was instrumental in the development of quantum mechanics. He also made contributions to solid-state physics and optics and supervised the work of a n ...
– physicist
* 1962 Francis Crick
Francis Harry Compton Crick (8 June 1916 – 28 July 2004) was an English molecular biologist, biophysicist, and neuroscientist. He, James Watson, Rosalind Franklin, and Maurice Wilkins played crucial roles in deciphering the helical struc ...
– discovered DNA's structure (PhD student and honorary fellow)
* 1972 John Hicks
Sir John Richards Hicks (8 April 1904 – 20 May 1989) was a British economist. He is considered one of the most important and influential economists of the twentieth century. The most familiar of his many contributions in the field of economic ...
– economist (fellow)
* 1974 Antony Hewish
Antony Hewish (11 May 1924 – 13 September 2021) was a British radio astronomer who won the Nobel Prize for Physics in 1974 (together with fellow radio-astronomer Martin Ryle) for his role in the discovery of pulsars. He was also awarded the ...
– astronomer (student and fellow)
* 1976 Milton Friedman
Milton Friedman (; July 31, 1912 – November 16, 2006) was an American economist and statistician who received the 1976 Nobel Memorial Prize in Economic Sciences for his research on consumption analysis, monetary history and theory and the ...
– economist (visiting fellow)
* 1977 Nevill Francis Mott
Sir Nevill Francis Mott (30 September 1905 – 8 August 1996) was a British physicist who won the Nobel Prize for Physics in 1977 for his work on the electronic structure of magnetic and disordered systems, especially amorphous semiconductors. ...
– theoretical physicist (fellow and master)
* 1984 Richard Stone
Sir John Richard Nicholas Stone (30 August 1913 – 6 December 1991) was an eminent British economist, educated at Westminster School and Gonville and Caius College and King's College at the University of Cambridge. In 1984, he was awarded t ...
– economist
* 2001 Joseph Stiglitz
Joseph Eugene Stiglitz (; born February 9, 1943) is an American New Keynesian economist, a public policy analyst, and a full professor at Columbia University. He is a recipient of the Nobel Memorial Prize in Economic Sciences (2001) and the Joh ...
– economist (fellow)
* 2008 Roger Tsien
Roger Yonchien Tsien (pronounced , "'' CHEN''"'';'' February 1, 1952 – August 24, 2016) was an American biochemist. He was a professor of chemistry and biochemistry at the University of California, San Diego and was awarded the Nobel Prize in ...
– chemist (fellow)
* 2013 Michael Levitt
Michael Levitt, ( he, מיכאל לויט; born 9 May 1947) is a South African-born biophysicist and a professor of structural biology at Stanford University, a position he has held since 1987. Levitt received the 2013 Nobel Prize in Chemistr ...
– chemist (PhD student and research fellow)
* 2016 Michael Kosterlitz – physicist
* 2019 Peter J. Ratcliffe – physician-scientist (student)
Notable fellows and masters
Notable organ scholars
*Heathcote Dicken Statham
Heathcote Dicken Statham CBE (7 December 1889 - 29 October 1973) was a conductor, composer and organist of international repute.
Early life
He was the eldest son of Henry Heathcote Statham (1839-1924) and Florence Elizabeth Dicken (1856-1938). Hi ...
(1908–1911)
Burials
*John Caius
John Caius (born John Kays ; 6 October 1510 – 29 July 1573), also known as Johannes Caius and Ioannes Caius, was an English physician, and second founder of the present Gonville and Caius College, Cambridge.
Biography
Early years
Caius was ...
* Thomas Legge
Thomas Legge (; 1535 – 12 July 1607) was an English playwright, prominently known for his play ''Richardus Tertius'', which is considered to be the first history play written in England.
Biography
Legge was the second of three sons born to S ...
* Stephen Perse
Gallery
See also
* Caius Boat Club * Gonville & Caius Association Football Club * John of Padua * List of organ scholarsReferences
Bibliography
* Brooke, C. ''A history of Gonville and Caius College''. Woodbridge, Suffolk: Boydell, 1985 (corrected reprint, 1996). .External links
*Gonville and Caius College Choir
{{DEFAULTSORT:Gonville And Caius College, Cambridge 1348 establishments in England 1557 establishments in England Alfred Waterhouse buildings Colleges of the University of Cambridge Grade I listed buildings in Cambridge Grade I listed educational buildings Organisations based in Cambridge with royal patronage