CLACL (programming language) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
CLACL, representing CLAC-Language (where CLAC stands for Logical Composition with the Assistance of Computers) is the result of ongoing theoretical research which aims to provide a formal description of the logical choices relating to the definition of organizational processes of
2009 Festival of Mathematics
held in Rome, during which th
project CLAC
was presented.
 Every design produces an organism, in which all its parts are related to create a complex and complete whole.
For a better understanding, consider the graphic planning that is the design and realization of a graphic pattern.
Those who have had a chance to prepare a composition know that every element should be in precise relation with the others, and only when all of the elements are balanced will the composition be considered complete. This process can be proven and verified.
Since the composition process is guided by logical choice, the program is centered on the information science of Artificial Intelligence. It is for this reason that the project is mentioned in the entry
Every design produces an organism, in which all its parts are related to create a complex and complete whole.
For a better understanding, consider the graphic planning that is the design and realization of a graphic pattern.
Those who have had a chance to prepare a composition know that every element should be in precise relation with the others, and only when all of the elements are balanced will the composition be considered complete. This process can be proven and verified.
Since the composition process is guided by logical choice, the program is centered on the information science of Artificial Intelligence. It is for this reason that the project is mentioned in the entry
loop(X,Y) :-
!,X < Y,
print(X),
X2 is X + 1,
loop(X2,Y).
In CLACL, a similar process is carried out using the following code:
@PRINT("$x $y",NL)
FOR ( $x, $y ) IN II[]
result:
The ''controls'' implement constructs for controlling the flow of the code with loops and expressions.
The ''commands'' require or set conditions on the domain. As with all programming languages, CLACL implements the following key concepts: * Variable * Instruction * Expression * Control structures * Subprogram * Information structures In addition CLACL will also implement specialist concepts of the domain and of the issues which address: * Statements * Tests * States * Comments The entities that can be generated via the interpretation of the script are: ;
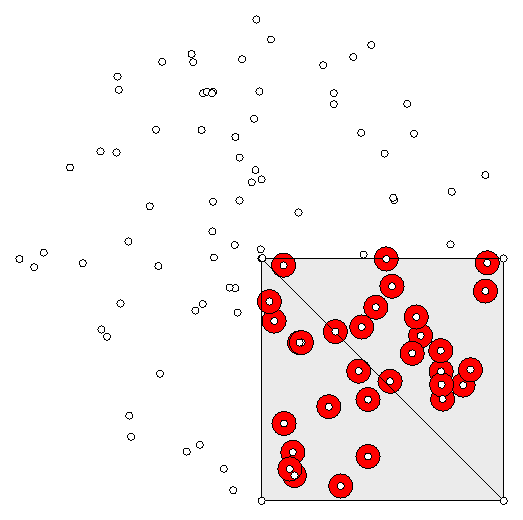 !a
!b
model:modSquare4(!a,!b,!c,!d)
#f=shape:frmSquare4(!a,!b,!c,!d)
I[]=cloud(!a,UNIFORM,100,1)
@GRFILL(Red)
FOR ($x) IN I[]
!a
!b
model:modSquare4(!a,!b,!c,!d)
#f=shape:frmSquare4(!a,!b,!c,!d)
I[]=cloud(!a,UNIFORM,100,1)
@GRFILL(Red)
FOR ($x) IN I[]
CLAC Tutorials
''CLACL design, introduzione alla Composizione Formale.''
(Italian) * M. Gazzelloni
(Italian)
Festival of Mathematics 2009 - CLAC project presentation
An example of Instances and DomainAn example of a Model
{{DEFAULTSORT:Clacl (Programming Language) Logic programming languages Composition in visual art Freeware Proprietary software Windows software
composition
Composition or Compositions may refer to:
Arts and literature
* Composition (dance), practice and teaching of choreography
*Composition (language), in literature and rhetoric, producing a work in spoken tradition and written discourse, to include ...
.
The logic of CLACL is based on 'spatial-relational' information rather than on the processing of numerical information. It generates a logical configuration and, with a tool called Plasma, shapes the created domain in a physical form such as music
Music is generally defined as the The arts, art of arranging sound to create some combination of Musical form, form, harmony, melody, rhythm or otherwise Musical expression, expressive content. Exact definition of music, definitions of mu ...
or graphics
Graphics () are visual images or designs on some surface, such as a wall, canvas, screen, paper, or stone, to inform, illustrate, or entertain. In contemporary usage, it includes a pictorial representation of data, as in design and manufacture, ...
.
CLACL is a computing language that integrates into a production environment to provide several tools to facilitate writing code and representing it graphically.
The first version (00.02.00) of the language was made available to the Internet in 2000 at the project site. The version 00.06.00 was distributed at th2009 Festival of Mathematics
held in Rome, during which th
project CLAC
was presented.
Characteristics of the Language
The target users of the language are those who work within creative fields, including design and music. Every design produces an organism, in which all its parts are related to create a complex and complete whole.
For a better understanding, consider the graphic planning that is the design and realization of a graphic pattern.
Those who have had a chance to prepare a composition know that every element should be in precise relation with the others, and only when all of the elements are balanced will the composition be considered complete. This process can be proven and verified.
Since the composition process is guided by logical choice, the program is centered on the information science of Artificial Intelligence. It is for this reason that the project is mentioned in the entry
Every design produces an organism, in which all its parts are related to create a complex and complete whole.
For a better understanding, consider the graphic planning that is the design and realization of a graphic pattern.
Those who have had a chance to prepare a composition know that every element should be in precise relation with the others, and only when all of the elements are balanced will the composition be considered complete. This process can be proven and verified.
Since the composition process is guided by logical choice, the program is centered on the information science of Artificial Intelligence. It is for this reason that the project is mentioned in the entry Computational creativity
Computational creativity (also known as artificial creativity, mechanical creativity, creative computing or creative computation) is a multidisciplinary endeavour that is located at the intersection of the fields of artificial intelligence, cogn ...
External_links
An internal link is a type of hyperlink on a web page to another page or resource, such as an image or document, on the same website or domain name, domain.
Hyperlinks are considered either "external" or "internal" depending on their target or ...
in Wikipedia, as one of the few examples of the application of Information Science to Creativity.
The closely logic-driven syntax, somewhat challenging for anyone not accustomed to working in the field of Artificial Intelligence ( AI), was supplemented by constructs more readily usable in practice.
As an example, see the description of a cycle (loop) implemented in Prolog
Prolog is a logic programming language associated with artificial intelligence and computational linguistics.
Prolog has its roots in first-order logic, a formal logic, and unlike many other programming languages, Prolog is intended primarily a ...
and CLACL.
With the following example in prolog
Prolog is a logic programming language associated with artificial intelligence and computational linguistics.
Prolog has its roots in first-order logic, a formal logic, and unlike many other programming languages, Prolog is intended primarily a ...
, a loop is a run that prints the loop index:
$x $y !a !a !a !b !a !c !b !a !b !b !b !c !c !a !c !b !c !cThe formation of the cycle in CLACL is carried out in a very similar way to the C (programming language), C-Language. The language adopts a combination of the declarative and procedural paradigms. The two languages are Prolog and C (programming language), C-Language. The declarative aspect comes from Prolog, and is used in statements and in scanning the tree of alternatives (
backtracking
Backtracking is a class of algorithms for finding solutions to some computational problems, notably constraint satisfaction problems, that incrementally builds candidates to the solutions, and abandons a candidate ("backtracks") as soon as it de ...
).
The procedural aspect is derived from C (programming language), C-Language, and is highlighted in particular in the control structures of the procedural flow.
Structure of the language
The commands are listed in a script, that is subjected to an interpreter that generates the result. The purpose of carrying out command controls is to produce a logical configuration of entities, and represent them in graphic form and, as a product of processing, it will generate a graph. The set of entities that form part of the graph are called a domain. CLACL has three groups of statements: * Declarations * Controls * Commands The ''declarations'' reflect the situations of the domain and are the most similar to Prolog.The ''controls'' implement constructs for controlling the flow of the code with loops and expressions.
The ''commands'' require or set conditions on the domain. As with all programming languages, CLACL implements the following key concepts: * Variable * Instruction * Expression * Control structures * Subprogram * Information structures In addition CLACL will also implement specialist concepts of the domain and of the issues which address: * Statements * Tests * States * Comments The entities that can be generated via the interpretation of the script are: ;
Instance
Instantiation or instance may refer to:
Philosophy
* A modern concept similar to ''participation'' in classical Platonism; see the Theory of Forms
* The instantiation principle, the idea that in order for a property to exist, it must be had by ...
:An instance can be seen as a geometric point in the plane, but we are not interested in its position; our interest is its existence within the domain and its relationship with other entities.
; Relation
:A relation describes the relationship between different instances.
;Model
A model is an informative representation of an object, person or system. The term originally denoted the plans of a building in late 16th-century English, and derived via French and Italian ultimately from Latin ''modulus'', a measure.
Models c ...
:A model allows the description of complex relations.
;Shape
A shape or figure is a graphical representation of an object or its external boundary, outline, or external surface, as opposed to other properties such as color, texture, or material type.
A plane shape or plane figure is constrained to lie on ...
:The shape describes the characteristics of a ''logical figure."
;Figure
:A ''logical figure'' can be seen as a geometrical figure.
Examples
Generation of an instance: instance:a or !a Generation of a relation: relation:rl1(instance:a, instance:b) or: &rl1(!a, !b) Definition of a model that represents a triangular configuration: define model: tris(!a,!b,!c) Implementation of a cycle: FOR ($a$,b) in SET[] Implementation of a condition: CASE ($x 0) Definition of a function: define function: switch($a$,b$,c) Some operations on the set: def INSI1[4] // definition of the set of 4 items ST1[] = [ ST1[] + ST2[] ] // add ST1[] = [ ST1[] - ST2[] ] // subtract ( ST1[] ST2[] ) // equals Example of a logic expression: (( ST1[] ST2[] ) AND (( ST3[] ST2[] ) OR ( ST4[] ST1[] )) AND pos(!a !b))Spatial Expression Example
 !a
!b
model:modSquare4(!a,!b,!c,!d)
#f=shape:frmSquare4(!a,!b,!c,!d)
I[]=cloud(!a,UNIFORM,100,1)
@GRFILL(Red)
FOR ($x) IN I[]
!a
!b
model:modSquare4(!a,!b,!c,!d)
#f=shape:frmSquare4(!a,!b,!c,!d)
I[]=cloud(!a,UNIFORM,100,1)
@GRFILL(Red)
FOR ($x) IN I[]
CLAC tutorials
CLAC Tutorials
See also
* Artificial architecture * C (programming language) *Composition (visual arts)
The term composition means "putting together". It can be thought of as the organization of the elements of art according to the principles of art. Composition can apply to any work of art, from music through writing and into photography, that is ...
* Computational creativity
Computational creativity (also known as artificial creativity, mechanical creativity, creative computing or creative computation) is a multidisciplinary endeavour that is located at the intersection of the fields of artificial intelligence, cogn ...
* Logic programming
Logic programming is a programming paradigm which is largely based on formal logic
Logic is the study of correct reasoning. It includes both formal and informal logic. Formal logic is the science of deductively valid inferences or of log ...
* Prolog
Prolog is a logic programming language associated with artificial intelligence and computational linguistics.
Prolog has its roots in first-order logic, a formal logic, and unlike many other programming languages, Prolog is intended primarily a ...
Further reading
* M. Gazzelloni''CLACL design, introduzione alla Composizione Formale.''
(Italian) * M. Gazzelloni
(Italian)
External links
*Festival of Mathematics 2009 - CLAC project presentation
Example images
An example of Instances and Domain
{{DEFAULTSORT:Clacl (Programming Language) Logic programming languages Composition in visual art Freeware Proprietary software Windows software