Bury Line on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Bury Line is a
 The second part was opened in 1879. In order to connect the growing suburbs of Cheetham Hill, Prestwich and Whitefield, the L&YR obtained an act to construct a new line from Manchester in 1872 to the original ELR line at Radcliffe. Construction began in 1876 and was completed in 1879. Originally the line had only five intermediate stations at
The second part was opened in 1879. In order to connect the growing suburbs of Cheetham Hill, Prestwich and Whitefield, the L&YR obtained an act to construct a new line from Manchester in 1872 to the original ELR line at Radcliffe. Construction began in 1876 and was completed in 1879. Originally the line had only five intermediate stations at
 Railway operations ended on 17 August 1991, in order for the line to be converted to Metrolink operation. This mostly entailed removing the old third rail system and replacing it with a 750 volt DC overhead line system. Available funding only allowed for minimum upgrades to be made, and so most of the infrastructure such as the stations and track were changed little.
The line became the first Metrolink line to open for business on 6 April 1992, initially between Bury and Victoria. On 27 April 1992 the city centre section opened, and trams then ran from Bury to Deansgate-Castlefield, the first station on the soon to be opened Altrincham leg of the network. The rest of the line to Altrincham opened on 15 June 1992, and the branch to Piccadilly opened on 20 July 1992.
One of the original stations was closed in 2013, after two new stations, ( and ) were opened nearby.
Railway operations ended on 17 August 1991, in order for the line to be converted to Metrolink operation. This mostly entailed removing the old third rail system and replacing it with a 750 volt DC overhead line system. Available funding only allowed for minimum upgrades to be made, and so most of the infrastructure such as the stations and track were changed little.
The line became the first Metrolink line to open for business on 6 April 1992, initially between Bury and Victoria. On 27 April 1992 the city centre section opened, and trams then ran from Bury to Deansgate-Castlefield, the first station on the soon to be opened Altrincham leg of the network. The rest of the line to Altrincham opened on 15 June 1992, and the branch to Piccadilly opened on 20 July 1992.
One of the original stations was closed in 2013, after two new stations, ( and ) were opened nearby.
LRTA entry on this line
Entry on this line from thetrams.co.uk
{{Manchester Metrolink stations Manchester Metrolink lines Rail transport in Greater Manchester Bury, Greater Manchester Railway lines opened in 1992 Former railway lines converted to Manchester Metrolink lines
tram
A tram (called a streetcar or trolley in North America) is a rail vehicle that travels on tramway tracks on public urban streets; some include segments on segregated right-of-way. The tramlines or networks operated as public transport are ...
line of the Manchester Metrolink
Manchester Metrolink (branded locally simply as Metrolink) is a tram/ light rail system in Greater Manchester, England. The network has 99 stops along of standard-gauge route, making it the most extensive light rail system in the United Kin ...
running from Manchester city centre
Manchester City Centre is the central business district of Manchester in Greater Manchester, England situated within the confines of Great Ancoats Street, A6042 Trinity Way, and A57(M) Mancunian Way which collectively form an inner ring road. ...
to Bury
Bury may refer to:
*The burial of human remains
*-bury, a suffix in English placenames
Places England
* Bury, Cambridgeshire, a village
* Bury, Greater Manchester, a town, historically in Lancashire
** Bury (UK Parliament constituency) (1832–19 ...
in Greater Manchester
Greater Manchester is a metropolitan county and combined authority, combined authority area in North West England, with a population of 2.8 million; comprising ten metropolitan boroughs: City of Manchester, Manchester, City of Salford, Salford ...
. Originally a railway line, it was, along with the Altrincham Line
The Altrincham Line is a tram line of the Manchester Metrolink running from Manchester to Altrincham in Greater Manchester. Originally a railway line, it was, along with the Bury Line, converted into a tramway during 1991–92, as part of the fir ...
, converted into a tram line during 1991–92, as part of the first phase of the Metrolink system.
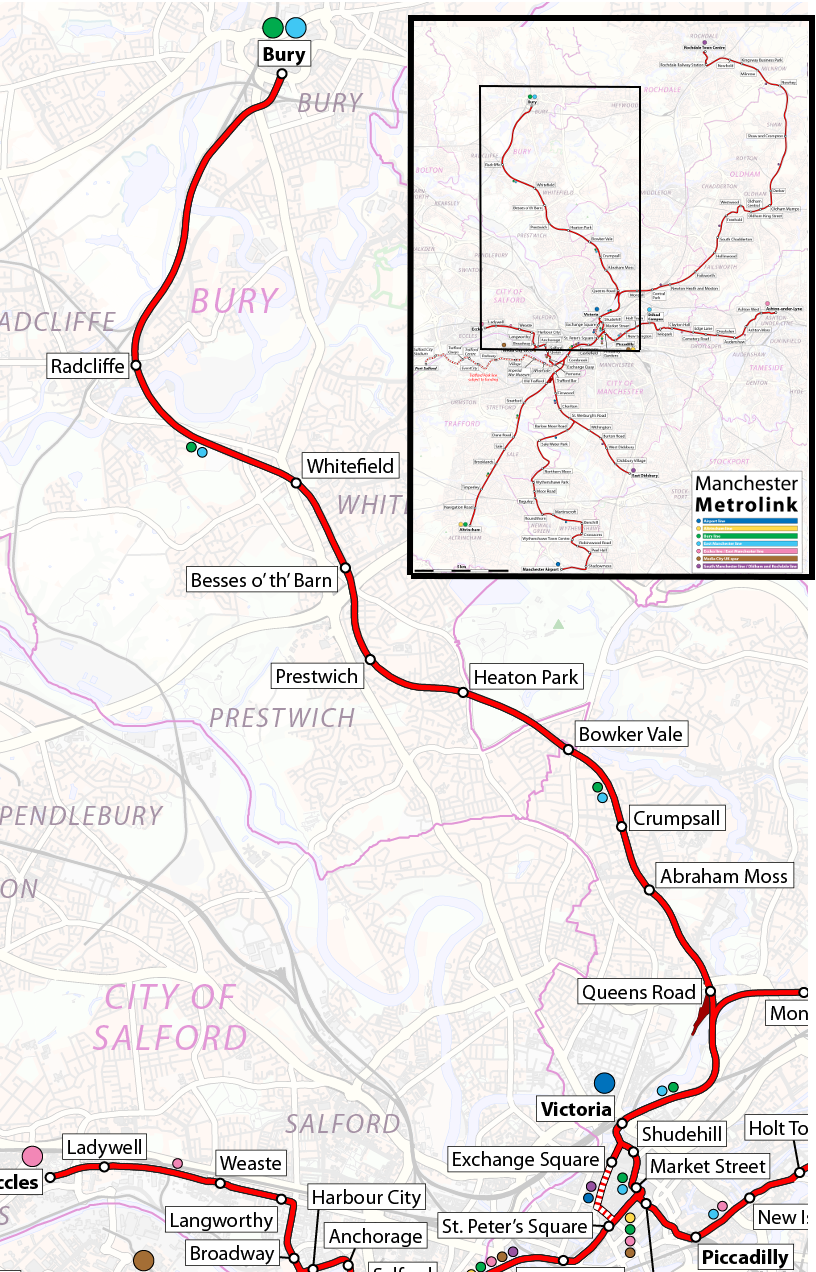
The line runs entirely on an old railway alignment without any street running. It runs north from and connects the suburbs of Cheetham Hill
Cheetham is an inner-city area and electoral ward of Manchester, England, which in 2011 had a population of 22,562. It lies on the west bank of the River Irk, north of Manchester city centre,
close to the boundary with Salford, bounded by Brou ...
, Prestwich, Whitefield and Radcliffe
Radcliffe or Radcliff may refer to:
Places
* Radcliffe Line, a border between India and Pakistan
United Kingdom
* Radcliffe, Greater Manchester
** Radcliffe Tower, the remains of a medieval manor house in the town
** Radcliffe tram stop
* ...
. The entire route from Victoria to Bury is roughly long. Two services travel along the line, both starting at Bury, and terminating at and respectively.
History
Pre-Metrolink
The line was originallyheavy rail
Various terms are used for passenger railway lines and equipment; the usage of these terms differs substantially between areas:
Rapid transit
A rapid transit system is an electric railway characterized by high speed (~) and rapid accelerati ...
. The first part of what is now the Bury Line was opened by the East Lancashire Railway
East Lancashire Railway is a heritage railway line in North West England which runs between Heywood, Greater Manchester and Rawtenstall in Lancashire. There are intermediate stations at Bury Bolton Street, , Summerseat and Ramsbottom, with ...
(ELR) in 1846, From to via Salford
Salford () is a city and the largest settlement in the City of Salford metropolitan borough in Greater Manchester, England. In 2011, Salford had a population of 103,886. It is also the second and only other city in the metropolitan county afte ...
, Clifton Junction and Radcliffe, continuing north from Bury to Rawtenstall
Rawtenstall () is a town in the borough of Rossendale, Lancashire, England. The town lies 15 miles/24 km north of Manchester, 22 miles/35 km east of Preston and 45 miles/70 km south east of the county town of Lancaster. The town is at the ...
. The ELR was absorbed into the Lancashire and Yorkshire Railway
The Lancashire and Yorkshire Railway (L&YR) was a major British railway company before the 1923 Grouping. It was incorporated in 1847 from an amalgamation of several existing railways. It was the third-largest railway system based in northern ...
(L&YR) in 1859.
 The second part was opened in 1879. In order to connect the growing suburbs of Cheetham Hill, Prestwich and Whitefield, the L&YR obtained an act to construct a new line from Manchester in 1872 to the original ELR line at Radcliffe. Construction began in 1876 and was completed in 1879. Originally the line had only five intermediate stations at
The second part was opened in 1879. In order to connect the growing suburbs of Cheetham Hill, Prestwich and Whitefield, the L&YR obtained an act to construct a new line from Manchester in 1872 to the original ELR line at Radcliffe. Construction began in 1876 and was completed in 1879. Originally the line had only five intermediate stations at Crumpsall
Crumpsall is an outer suburb and Wards of the United Kingdom, electoral ward of Manchester, England, north of Manchester city centre, bordered by Cheetham Hill, Blackley, Harpurhey, Broughton, Greater Manchester, Broughton, and Prestwich. The po ...
, Heaton Park
Heaton Park is a public park in Manchester, England, covering an area of over . The park includes the grounds of a Grade I listed, neoclassical 18th century country house, Heaton Hall. The hall, remodelled by James Wyatt in 1772, is now only ...
, Prestwich, Whitefield and Radcliffe
Radcliffe or Radcliff may refer to:
Places
* Radcliffe Line, a border between India and Pakistan
United Kingdom
* Radcliffe, Greater Manchester
** Radcliffe Tower, the remains of a medieval manor house in the town
** Radcliffe tram stop
* ...
. Three more stations were added later: Woodlands Road, Bowker Vale and Besses o' th' Barn.
In response to competition from tram
A tram (called a streetcar or trolley in North America) is a rail vehicle that travels on tramway tracks on public urban streets; some include segments on segregated right-of-way. The tramlines or networks operated as public transport are ...
s, the line was electrified
Electrification is the process of powering by electricity and, in many contexts, the introduction of such power by changing over from an earlier power source.
The broad meaning of the term, such as in the history of technology, economic history ...
in 1916 using a unique 1200 V DC side-contact third rail
A third rail, also known as a live rail, electric rail or conductor rail, is a method of providing electric power to a railway locomotive or train, through a semi-continuous rigid conductor placed alongside or between the rails of a railway t ...
system, which remained in operation until the line was converted to Metrolink operation in 1991. From 1959 until 1991, the line was operated by EMU
The emu () (''Dromaius novaehollandiae'') is the second-tallest living bird after its ratite relative the ostrich. It is endemic to Australia where it is the largest native bird and the only extant member of the genus '' Dromaius''. The emu ...
s. In 1961 they were scheduled to cover the 9Âľ miles from Bolton Street to Victoria in 23 minutes and take 24 minutes in the other direction, running at 20 minute intervals for most of the day, but half-hourly on Sundays. With an extra stop, the trams take 23 minutes uphill and 24 minutes downhill.
In August 1953, the Irk Valley Junction rail crash
The Irk Valley Junction rail crash occurred on 15 August 1953 at Collyhurst, just over a mile from Manchester Victoria station. At that point, the electrified line to Bury passes through Irk Valley Junction, so called because it lies on a via ...
occurred on the line near Manchester Victoria, resulting in ten deaths and 58 injuries. It was caused by an electric train overrunning a danger signal which collided with a steam train, resulting in the front carriage of the electric train crashing into the River Irk
The River Irk is a river in the historic county of Lancashire in the North West England that flows through the northern most Lancastrian towns of the ceremonial county of Greater Manchester.
It rises to the east of Royton and runs west past ...
.
The original station was closed in 1980 and replaced by the new, more conveniently located Bury Interchange
Bury Interchange is a transport hub in the town of Bury, Greater Manchester, England. Opened in 1980, it is the northern terminus of the Manchester Metrolink's Bury Line, which prior to 1992 was a heavy-rail line. It also incorporates a bus s ...
. The original Bolton Street station is now part of the East Lancashire Railway
East Lancashire Railway is a heritage railway line in North West England which runs between Heywood, Greater Manchester and Rawtenstall in Lancashire. There are intermediate stations at Bury Bolton Street, , Summerseat and Ramsbottom, with ...
heritage railway.
Conversion to Metrolink
The Bury line was identified by transport planners in the 1980s as one of the local railway lines in the Greater Manchester area which was used mostly for local traffic, and could therefore be split off from the main line network and converted to light-rail operation. It was chosen for conversion as part of the first phase of the Metrolink, along with the Manchester Piccadilly to Altrincham Line to the south of Manchester: The two previously unconnected lines were to be linked together by a new street-running line across Manchester city-centre, which included a branch toManchester Piccadilly railway station
Manchester Piccadilly is the principal railway station in Manchester, England. Opened as Store Street in 1842, it was renamed Manchester London Road in 1847 and became Manchester Piccadilly in 1960. Located to the south-east of Manchester city ...
. Trams on the Bury Line would thus continue from Victoria station into the city-centre, to either Altrincham or Piccadilly via a new exit into the streets to the south.
 Railway operations ended on 17 August 1991, in order for the line to be converted to Metrolink operation. This mostly entailed removing the old third rail system and replacing it with a 750 volt DC overhead line system. Available funding only allowed for minimum upgrades to be made, and so most of the infrastructure such as the stations and track were changed little.
The line became the first Metrolink line to open for business on 6 April 1992, initially between Bury and Victoria. On 27 April 1992 the city centre section opened, and trams then ran from Bury to Deansgate-Castlefield, the first station on the soon to be opened Altrincham leg of the network. The rest of the line to Altrincham opened on 15 June 1992, and the branch to Piccadilly opened on 20 July 1992.
One of the original stations was closed in 2013, after two new stations, ( and ) were opened nearby.
Railway operations ended on 17 August 1991, in order for the line to be converted to Metrolink operation. This mostly entailed removing the old third rail system and replacing it with a 750 volt DC overhead line system. Available funding only allowed for minimum upgrades to be made, and so most of the infrastructure such as the stations and track were changed little.
The line became the first Metrolink line to open for business on 6 April 1992, initially between Bury and Victoria. On 27 April 1992 the city centre section opened, and trams then ran from Bury to Deansgate-Castlefield, the first station on the soon to be opened Altrincham leg of the network. The rest of the line to Altrincham opened on 15 June 1992, and the branch to Piccadilly opened on 20 July 1992.
One of the original stations was closed in 2013, after two new stations, ( and ) were opened nearby.
Services
As of February 2017, trams between Bury and Manchester run as follows: *A 12-minute interval service from Bury to . Running during Monday to Saturday daytimes and early evenings only. *A 12-minute interval service From Bury to . Running during all operating hours. These two services combined mean that trams between Bury and Manchester operate every six minutes during Monday to Saturday daytimes, and every 12 minutes during evenings and Sundays. During evenings, trams run to Piccadilly only, so journeys to Altrincham require a change of tram at .Rolling stock
All services are operated byM5000
The Bombardier M5000, is a model of light rail passenger vehicle. It is part of the Flexity Swift range of vehicles, built specifically as a high-floor, articulated bi-directional tram to operate solely on the Manchester Metrolink system in Engl ...
trams. Between 1992 and 2009, the line was operated by the original fleet of 26 T-68
The Firema T-68 was a model of light rail passenger vehicle first operated on the Manchester Metrolink network in England in 1992. Constructed by Firema specifically as a high-floor, articulated bi-directional tram to operate solely on the Ma ...
trams. From 2009 the new fleet of M5000 trams was introduced, and these replaced the original T-68 trams. which were withdrawn from service during 2012–14.
Route map

See also
*Bury to Holcombe Brook Line
Bury may refer to:
*The burial of human remains
*-bury, a suffix in English placenames
Places England
* Bury, Cambridgeshire, a village
* Bury, Greater Manchester, a town, historically in Lancashire
** Bury (UK Parliament constituency) (1832†...
References
External links
LRTA entry on this line
Entry on this line from thetrams.co.uk
{{Manchester Metrolink stations Manchester Metrolink lines Rail transport in Greater Manchester Bury, Greater Manchester Railway lines opened in 1992 Former railway lines converted to Manchester Metrolink lines