British narrow-gauge railways on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 There were more than a thousand British narrow-gauge railways ranging from large, historically significant
There were more than a thousand British narrow-gauge railways ranging from large, historically significant
 The earliest narrow-gauge railways were crude wooden trackways used in
The earliest narrow-gauge railways were crude wooden trackways used in
/ref> After the Gauges Act, most of the railway track laid in Great Britain was to standard gauge. However many minor railways, both public and industrial, were built to narrower gauges. These lines either followed local traditions or were built in locations where the smaller size of the railway proved more economical.

 The success of the Ffestiniog Railway triggered a boom in the construction of narrow-gauge railways, not just in Britain but around the world. In the
The success of the Ffestiniog Railway triggered a boom in the construction of narrow-gauge railways, not just in Britain but around the world. In the
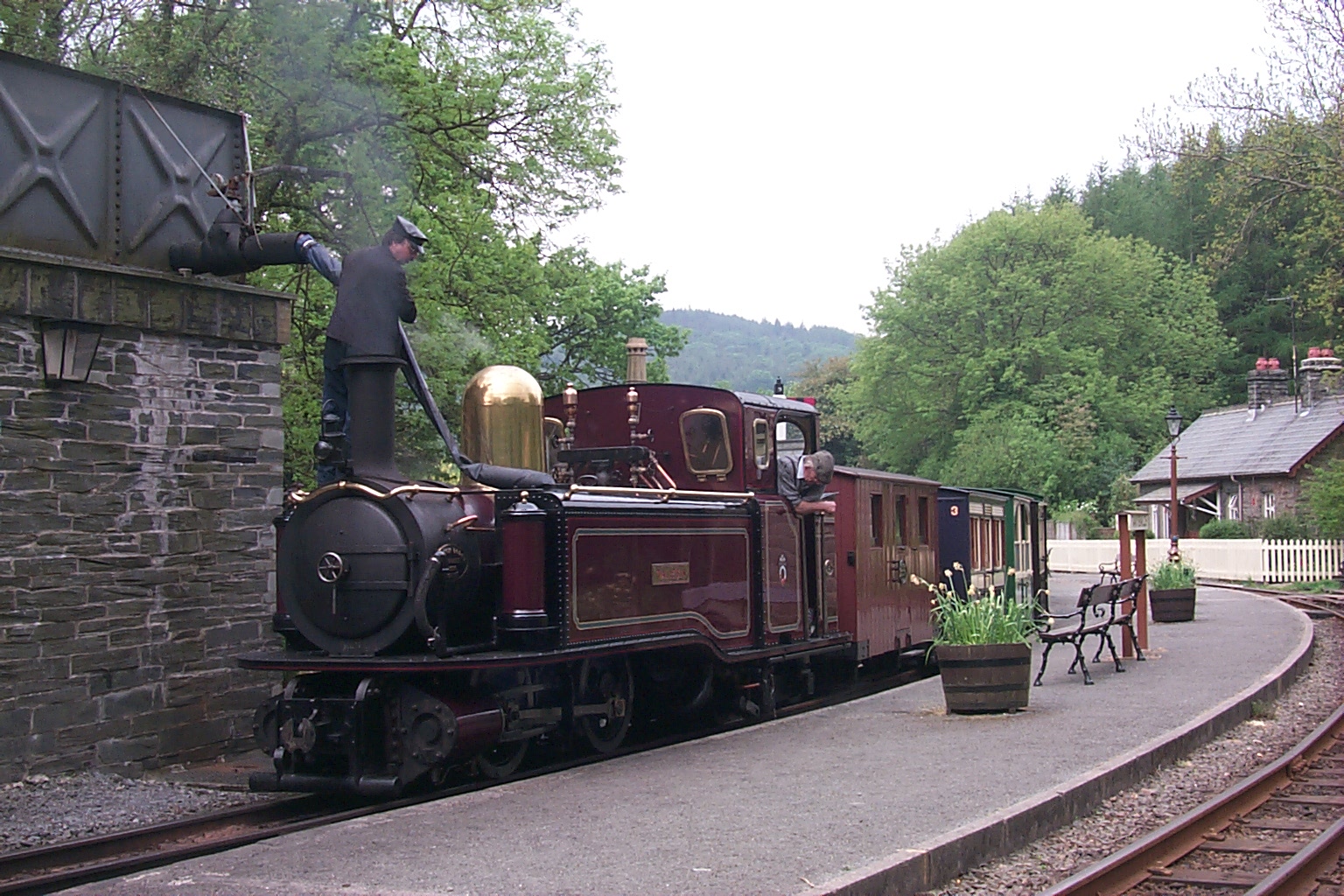 The use of narrow-gauge railways in Britain declined throughout the first half of the 20th century. This decline accelerated after the
The use of narrow-gauge railways in Britain declined throughout the first half of the 20th century. This decline accelerated after the
 Great Britain was home to many industrial narrow-gauge railways, ranging from temporary hand-powered lines a few yards long to significant locomotive-worked complexes of lines that served substantial industrial concerns.
Great Britain was home to many industrial narrow-gauge railways, ranging from temporary hand-powered lines a few yards long to significant locomotive-worked complexes of lines that served substantial industrial concerns.
 There were more than a thousand British narrow-gauge railways ranging from large, historically significant
There were more than a thousand British narrow-gauge railways ranging from large, historically significant common carriers
A common carrier in common law countries (corresponding to a public carrier in some civil law systems,Encyclopædia Britannica CD 2000 "Civil-law public carrier" from "carriage of goods" usually called simply a ''carrier'') is a person or compan ...
to small, short-lived industrial railway
An industrial railway is a type of railway (usually private) that is not available for public transportation and is used exclusively to serve a particular industrial, logistics, or military site. In regions of the world influenced by British ra ...
s. Many notable events in British railway
Rail transport (also known as train transport) is a means of transport that transfers passengers and goods on wheeled vehicles running on rails, which are incorporated in tracks. In contrast to road transport, where the vehicles run on a pre ...
history happened on narrow-gauge railways including the first use of steam locomotives, the first public railway and the first preserved railway
A heritage railway or heritage railroad (US usage) is a railway operated as living history to re-create or preserve railway scenes of the past. Heritage railways are often old railway lines preserved in a state depicting a period (or periods) i ...
.
History
Early railways: before 1865
 The earliest narrow-gauge railways were crude wooden trackways used in
The earliest narrow-gauge railways were crude wooden trackways used in coal mines
Coal mining is the process of extracting coal from the ground. Coal is valued for its energy content and since the 1880s has been widely used to generate electricity. Steel and cement industries use coal as a fuel for extraction of iron fro ...
to guide wooden tubs. Because of the restricted loading gauge of the tunnels and the need for the tubs to be small enough to be pushed by one man, these railways were almost all narrow gauge. These underground lines often had short above-ground sections as well.
After the start of the Industrial Revolution
The Industrial Revolution was the transition to new manufacturing processes in Great Britain, continental Europe, and the United States, that occurred during the period from around 1760 to about 1820–1840. This transition included going f ...
it became possible to create railways with iron tracks and wheels, which reduced the friction involved in moving wagons and made longer horse-hauled trains possible. These could move more material over longer distances, allowing the construction of railways from mines and quarries to transshipment points on rivers, canals and the coast. The earliest narrow-gauge railways that were more than internal mine or quarry systems were all horse-drawn industrial railway
An industrial railway is a type of railway (usually private) that is not available for public transportation and is used exclusively to serve a particular industrial, logistics, or military site. In regions of the world influenced by British ra ...
s. Prominent examples include: the gauge Little Eaton Gangway
The Little Eaton Gangway, officially the Derby Canal Railway, was a narrow gauge industrial wagonway serving the Derby Canal, in England, at Little Eaton in Derbyshire.
The Derby Canal
In 1792, Benjamin Outram was asked to prepare plans for ...
of 1793; the gauge Lake Lock Rail Road
The Lake Lock Rail Road was an early, approximately long, horse drawn narrow gauge railway built near Wakefield, West Yorkshire, England. The railway is recognised as the world's first public railway, though other railway schemes around the same ...
of 1796; the gauge Penrhyn Railroad of 1801; and the gauge Surrey Iron Railway
The Surrey Iron Railway (SIR) was a horse-drawn plateway that linked Wandsworth and Croydon via Mitcham, all then in Surrey but now suburbs of south London, in England. It was established by Act of Parliament in 1801, and opened partly in 1802 ...
of 1803. The Lake Lock Rail Road is recognized as the world's first public railway.
Meanwhile, the development of the stationary steam engine was proceeding to the point where early steam locomotives
A steam locomotive is a locomotive that provides the force to move itself and other vehicles by means of the expansion of steam. It is fuelled by burning combustible material (usually coal, oil or, rarely, wood) to heat water in the locomot ...
were being proposed. In 1804, Richard Trevithick
Richard Trevithick (13 April 1771 – 22 April 1833) was a British inventor and mining engineer. The son of a mining captain, and born in the mining heartland of Cornwall, Trevithick was immersed in mining and engineering from an early age. He w ...
demonstrated the first locomotive-hauled railway in the world: the gauge Penydarren Tramway in south Wales
Wales ( cy, Cymru ) is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. It is bordered by England to the east, the Irish Sea to the north and west, the Celtic Sea to the south west and the Bristol Channel to the south. It had a population in ...
. Although this first use of locomotives was a limited and short-lived experiment, in 1812, the gauge Middleton Railway
The Middleton Railway is the world's oldest continuously working railway, situated in the English city of Leeds. It was founded in 1758 and is now a heritage railway, run by volunteers from The Middleton Railway Trust Ltd. since 1960.
The rail ...
in Leeds became the first in the world to make commercial use of steam locomotives.
Steam technology developed rapidly in the early 19th century, allowing smaller locomotives to haul more goods. The horse-drawn Ffestiniog Railway opened in 1836 to connect the slate quarries at Blaenau Ffestiniog with the coastal port of Porthmadog
Porthmadog (; ), originally Portmadoc until 1974 and locally as "Port", is a Welsh coastal town and community in the Eifionydd area of Gwynedd and the historic county of Caernarfonshire. It lies east of Criccieth, south-west of Blaenau Ff ...
. The traffic on the line quickly grew to the point where the horses could no longer haul the empty slate wagons back to the quarries quickly enough to meet demand. In 1863, steam locomotives were introduced on the gauge railway, with passenger services following in 1865. This was the first steam operated railway providing both freight and passenger services on such a small gauge and it proved the model for the introduction of narrow-gauge railways across the world.
In 1846, the British Parliament passed the Gauges Act that established as the ''standard gauge'' for Britain.Railway Regulation (Gauge) Act 1846 (PDF)/ref> After the Gauges Act, most of the railway track laid in Great Britain was to standard gauge. However many minor railways, both public and industrial, were built to narrower gauges. These lines either followed local traditions or were built in locations where the smaller size of the railway proved more economical.
The boom years: 1865–1914

 The success of the Ffestiniog Railway triggered a boom in the construction of narrow-gauge railways, not just in Britain but around the world. In the
The success of the Ffestiniog Railway triggered a boom in the construction of narrow-gauge railways, not just in Britain but around the world. In the United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Europe, off the north-western coast of the European mainland, continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotlan ...
, the centre of narrow gauge construction was North Wales
Wales ( cy, Cymru ) is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. It is bordered by England to the east, the Irish Sea to the north and west, the Celtic Sea to the south west and the Bristol Channel to the south. It had a population in ...
. The mountains of the north held large quantities of slate and their narrow valleys and steep hillsides meant that the smaller narrow-gauge railways were cost effective. The major slate mining regions at Bethesda, Llanberis
(; ) is a village, community and electoral ward in Gwynedd, northwest Wales, on the southern bank of the lake and at the foot of Snowdon, the highest mountain in Wales. It is a centre for outdoor activities in Snowdonia, including walking ...
, Blaenau Ffestiniog and Corris
Corris is a village in the county of Gwynedd, Wales, about north of the town of Machynlleth. The village lies on the west bank of the Afon Dulas (which here forms the boundary with Powys), around that river's confluence with the Afon Deri ...
all developed multiple railways to serve the quarries. Some of these lines, like the Ffestiniog Railway, the Corris Railway
The Corris Railway ( cy, Rheilffordd Corris) is a narrow gauge preserved railway based in Corris on the border between Merionethshire (now Gwynedd) and Montgomeryshire (now Powys) in Mid-Wales.
The line opened in 1859 as a horse tramway, runni ...
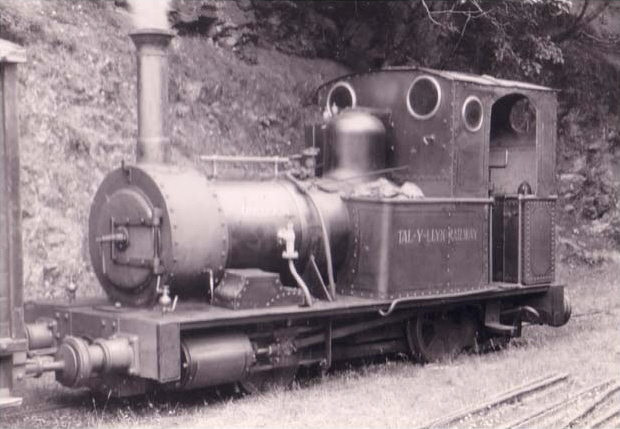
and the Talyllyn Railway
The Talyllyn Railway ( cy, Rheilffordd Talyllyn) is a narrow gauge preserved railway in Wales running for from Tywyn on the Mid-Wales coast to Nant Gwernol near the village of Abergynolwyn. The line was opened in 1865Drummond 2015, page 17 ...
were common carriers
A common carrier in common law countries (corresponding to a public carrier in some civil law systems,Encyclopædia Britannica CD 2000 "Civil-law public carrier" from "carriage of goods" usually called simply a ''carrier'') is a person or compan ...
, while others like the Penrhyn Quarry Railway
The Penrhyn Quarry Railway was a narrow gauge railway in Caernarfonshire (now Gwynedd), Wales. It served the Penrhyn quarry near Bethesda, taking their slate produce to Port Penrhyn, near Bangor. The railway was around long and used a gauge ...
and the Padarn Railway
The Padarn Railway was a narrow gauge railway in North Wales, built to the unusual gauge of . It carried slate from Dinorwic Quarry to Port Dinorwic. The line opened on 3 March 1843, replacing the Dinorwic Railway. It initially used horses, ...
were industrial lines.
Outside Wales, other industries started to use narrow-gauge railways to move freight, notably ironstone, limestone, china clay, brick clay and metals. Many common carrier lines were built: most of the railways on the Isle of Man were narrow gauge – mostly gauge. A number of railways were built to connect standard gauge railways with smaller towns, including the Southwold Railway, the Wolverton and Stony Stratford Tramway and the famous Lynton and Barnstaple Railway
The Lynton and Barnstaple Railway (L&B) opened as an independent railway in May 1898. It was a single track, narrow gauge railway and was slightly over long running through the rugged and picturesque area bordering Exmoor in North Devon, ...
in Devon
Devon ( , historically known as Devonshire , ) is a ceremonial and non-metropolitan county in South West England. The most populous settlement in Devon is the city of Plymouth, followed by Devon's county town, the city of Exeter. Devo ...
. These lines allowed communities that did not merit a full railway service to connect to the mainline network at low cost.
The 1880s were the high point of British narrow-gauge railways as traffic on many of these lines reached its peak volume and new lines were built across the country.
In 1896, the Light Railways Act was passed which allowed the construction of railways to less stringent standards than had previously been allowed. This led to a short resurgence in the building of narrow-gauge railways, especially in rural locations. In Wales, the Welshpool and Llanfair Light Railway
The Welshpool and Llanfair Light Railway (W&LLR) ( cy, Rheilffordd y Trallwng a Llanfair Caereinion) is a narrow gauge heritage railway in Powys, Wales. The line is around long and runs westwards from the town of Welshpool ( cy, Y Trallwng) ...
was built to serve farming communities and the Vale of Rheidol Light Railway was a tourist line that also served lead mines; in England the Leek and Manifold Valley Light Railway
The Leek and Manifold Valley Light Railway (L&MVLR) was a narrow gauge railway in Staffordshire, England that operated between 1904 and 1934. The line mainly carried milk from dairies in the region, acting as a feeder to the system. It also ...
served similar purposes in the Staffordshire Moorlands.
The 1904 Railway Clearing House Railway Atlas showed the major narrow gauge railways:
Decline of the narrow gauge: 1914–1950
After the First World War, rail traffic declined with the widespread adoption of motor vehicles and public narrow gauge lines in Britain began to struggle financially. Most of these railways were built to serve marginal traffic that would not support a larger line. As road competition increased, many existing lines fell into decline and fewer new railways were built. The 1920s saw a brief resurgence of the narrow gauge as surplus equipment from theWar Department Light Railways
The War Department Light Railways were a system of narrow gauge trench railways run by the British War Department in World War I. Light railways made an important contribution to the Allied war effort in the First World War, and were used for th ...
(WDLR) became available. Several industrial railways were built using second-hand WDLR equipment, notably the Leighton Buzzard Light Railway. Other lines such as the Glyn Valley Tramway
Glyn means "Valley" in Welsh and may refer to:
*Glyn (name), including a list of people with the name
*Baron Glyn, a title in the Peerage of the United Kingdom
*Glyn baronets, created for members of the Glyn family
*Glyn Ceiriog, a former slate ...
and the Snailbeach District Railways
Snailbeach District Railways was a British narrow gauge railway in Shropshire. It was built to carry lead ore from mines in the Stiperstones to Pontesbury where the ore was transshipped to the Great Western Railway's Minsterley branch line. Co ...
were able to replace ageing locomotives relatively cheaply and continue to operate on shoestring budgets. Even the famed Ffestiniog Railway acquired a Baldwin locomotive to shore up the fleet working the Welsh Highland Railway
The Welsh Highland Railway (WHR) or Rheilffordd Eryri is a long, restored narrow gauge heritage railway in the Welsh county of Gwynedd, operating from Caernarfon to Porthmadog, and passing through a number of popular tourist destinations ...
which it now owned.
The last narrow-gauge commercial carrier in Britain was the Ashover Light Railway
The Ashover Light Railway was a narrow gauge railway in Derbyshire, England that connected Clay Cross and Ashover. It was built by the Clay Cross Company to transport minerals such as limestone, fluorite, barytes and gritstone to its wor ...
, opened in 1925 using surplus war equipment. This was the epitome of cheaply constructed light railways and was one of several minor railways owned by Colonel Stephens.
Meanwhile, the use of narrow-gauge railways in industry continued to flourish. Many small railways were built to serve sand and gravel pits, cement works and the peat and timber extraction industries, often using ex-WDLR equipment.
The continued development of road transport and the economic crises of the 1930s saw a slow decline in the use of narrow-gauge railways across the country. The Second World War
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposi ...
pushed many struggling enterprises into bankruptcy as labour and materials were diverted to the war effort. During and immediately after the war, the majority of the remaining lines closed: between 1946 and 1950 the Ffestiniog, Corris, Ashover Light, Rye and Camber and Eaton Hall railways all closed. Many industrial lines did not survive the war years.
The narrow gauge after 1950
Second World War
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposi ...
as improved road transport displaced railways in industry and for passenger service.
In 1951 however, a group of railway enthusiasts, alarmed at the loss of this part of British industrial heritage, stepped in to save the failing Talyllyn Railway
The Talyllyn Railway ( cy, Rheilffordd Talyllyn) is a narrow gauge preserved railway in Wales running for from Tywyn on the Mid-Wales coast to Nant Gwernol near the village of Abergynolwyn. The line was opened in 1865Drummond 2015, page 17 ...
. This became the first railway to be run entirely by volunteers and sparked a movement to preserve many railways, both narrow and standard gauge as tourist attractions. Since then many lines have been preserved as working museums, and new narrow-gauge railways are being constructed for the tourist industry.
In the 21st century a very few industrial and common carrier
A common carrier in common law countries (corresponding to a public carrier in some civil law systems,Encyclopædia Britannica CD 2000 "Civil-law public carrier" from "carriage of goods" usually called simply a ''carrier'') is a person or compan ...
lines survive. Notable among the latter are the Glasgow Subway, an underground metro line that operates on a gauge, and the Manx Electric Railway
The Manx Electric Railway ( Manx: ''Raad Yiarn Lectragh Vannin'') is an electric interurban tramway connecting Douglas, Laxey and Ramsey in the Isle of Man. It connects with the Douglas Bay Horse Tramway at its southern terminus at Derby Castle ...
on the Isle of Man
)
, anthem = "O Land of Our Birth"
, image = Isle of Man by Sentinel-2.jpg
, image_map = Europe-Isle_of_Man.svg
, mapsize =
, map_alt = Location of the Isle of Man in Europe
, map_caption = Location of the Isle of Man (green)
in Europe ...
.
Significant lines
Amongst the most well-known narrow-gauge lines in Britain are the Ffestiniog, the oldest independent railway company in the world, the Talyllyn, the world's first preserved railway of any gauge, and the Welshpool & Llanfair in Wales; and the Lynton & Barnstaple in England. Unique among British railways is the rack-and-pinionSnowdon Mountain Railway
The Snowdon Mountain Railway (SMR; cy, Rheilffordd yr Wyddfa) is a Narrow-gauge railway, narrow gauge Rack railway, rack and pinion mountain railway in Gwynedd, north-west Wales. It is a tourist railway that travels for from Llanberis to the ...
which climbs to just below the summit of Wales' highest peak.
Several significant lines operate on the Isle of Man
)
, anthem = "O Land of Our Birth"
, image = Isle of Man by Sentinel-2.jpg
, image_map = Europe-Isle_of_Man.svg
, mapsize =
, map_alt = Location of the Isle of Man in Europe
, map_caption = Location of the Isle of Man (green)
in Europe ...
. The gauge Isle of Man Steam Railway operates as a tourist attraction. The Manx Electric Railway
The Manx Electric Railway ( Manx: ''Raad Yiarn Lectragh Vannin'') is an electric interurban tramway connecting Douglas, Laxey and Ramsey in the Isle of Man. It connects with the Douglas Bay Horse Tramway at its southern terminus at Derby Castle ...
has the two oldest operating electric trams in the world. The gauge Snaefell Mountain Railway
The Snaefell Mountain Railway ( gv, Raad Yiarn Sniaull) is an electric mountain railway on the Isle of Man in Europe. It joins the village of Laxey with the summit of Snaefell, at above sea level the highest point on the island. It connects w ...
climbs the island's main peak and is the sole operating Fell system railway in the world.
The narrow-gauge railways of Britain and the Isle of Man
Public railways
These are narrow-gauge railways that ran public passenger trains for a significant portion of their existence. In 1951 theTalyllyn Railway
The Talyllyn Railway ( cy, Rheilffordd Talyllyn) is a narrow gauge preserved railway in Wales running for from Tywyn on the Mid-Wales coast to Nant Gwernol near the village of Abergynolwyn. The line was opened in 1865Drummond 2015, page 17 ...
was the first railway in the world to be taken over and preserved by volunteers. This was the birth of the heritage railway movement, which has flourished in Britain and around the world in the years since. As a result, many of these lines passed from being common carriers
A common carrier in common law countries (corresponding to a public carrier in some civil law systems,Encyclopædia Britannica CD 2000 "Civil-law public carrier" from "carriage of goods" usually called simply a ''carrier'') is a person or compan ...
and were preserved as heritage railways
A heritage railway or heritage railroad (US usage) is a railway operated as living history to re-create or preserve railway scenes of the past. Heritage railways are often old railway lines preserved in a state depicting a period (or periods) i ...
after their demise. Where this has happened their heritage existence is included as a second row.
Estate railways
Narrow-gauge railways serving private estates. These were often minimum-gauge railways.Museums
Museums devoted to narrow-gauge railwaysVisitor attractions
Narrow-gauge railways that operate as part of a larger tourist attraction, such as an estate or theme park.Private railways
These are private lines or collections owned by individuals or small groups and generally not open to the public.Industrial railways
 Great Britain was home to many industrial narrow-gauge railways, ranging from temporary hand-powered lines a few yards long to significant locomotive-worked complexes of lines that served substantial industrial concerns.
Great Britain was home to many industrial narrow-gauge railways, ranging from temporary hand-powered lines a few yards long to significant locomotive-worked complexes of lines that served substantial industrial concerns.
Military railways
Many British military establishments and former UK Government-owned explosives sites used narrow-gauge railways. These locations were often subject to the Official Secrets Act and other government restrictions, so many of them are less well documented.See also
*British quarrying and mining narrow-gauge railways
Some industrial narrow-gauge railways in the United Kingdom and the Isle of Man were primarily built to serve quarrying, mining, and similar industries. Some of these narrow-gauge railways offered passenger services for employees or workme ...
* British narrow-gauge slate railways
Narrow-gauge railways were used extensively in the slate industry of Great Britain, especially in Wales. Many quarries had internal tramways, some using many dozens of miles of track. Others had private lines that stretched from the quarry to tran ...
* Decauville
Decauville () was a manufacturing company which was founded by Paul Decauville (1846–1922), a French pioneer in industrial railways. Decauville's major innovation was the use of ready-made sections of light, narrow gauge track fastened to stee ...
* Industrial railway
An industrial railway is a type of railway (usually private) that is not available for public transportation and is used exclusively to serve a particular industrial, logistics, or military site. In regions of the world influenced by British ra ...
s
* List of British heritage and private railways
This is a list of heritage, private and preserved railways throughout the United Kingdom, the Crown dependencies, and British Overseas Territories whether operational or closed, that are operated for charitable purposes or shareholder profit ...
Notes
References
* * * * * * * {{DEFAULTSORT:British narrow-gauge railways British, narrow