History
Historically, the British Isles were a culturally grouped country and developed native traditions, however as a result of the expansion of the British Empire, the country absorbed different peoples of the world. Since the end of World War II, British culture has accented its contributions to diversity from Afro-Caribs,Language
 First spoken in
First spoken in Regional accents
Dialects and regional accents vary heavily amongst the fourArts
Literature
The United Kingdom inherited the literary traditions of England, Scotland and Wales. These include The early 18th century period of British literature is known as the Augustan Age and included the development of the novel. Daniel Defoe's ''
The early 18th century period of British literature is known as the Augustan Age and included the development of the novel. Daniel Defoe's ''
Theatre
 From its formation in 1707 the United Kingdom has had a vibrant tradition of theatre, much of it inherited from England, Scotland and Wales. The
From its formation in 1707 the United Kingdom has had a vibrant tradition of theatre, much of it inherited from England, Scotland and Wales. The ''
Music
Classical music
 British Baroque music was heavily influenced by continental fashions. This is exemplified by
British Baroque music was heavily influenced by continental fashions. This is exemplified by Popular music
Folk and sub-national music
In contrast to the comparatively homogeneous classical and pop genres, each nation of the UK has retained a distinct tradition of folk music. The traditionalCinema
 Britain has had a significant film industry for over a century. While many films focus on British culture, British cinema is also marked by its interaction and competition with Cinema of the United States, American and continental Cinema of Europe, European cinema.
The UK was the location of the oldest surviving moving picture, ''Roundhay Garden Scene'' (1888), which was shot in Roundhay, Leeds by French inventor Louis Le Prince, while the first British film, ''Incident at Clovelly Cottage'' was shot in 1895. The world's first Color motion picture film, colour motion picture was shot by Edward Raymond Turner in 1902."Martin Scorsese on world's first colour film discovery"
Britain has had a significant film industry for over a century. While many films focus on British culture, British cinema is also marked by its interaction and competition with Cinema of the United States, American and continental Cinema of Europe, European cinema.
The UK was the location of the oldest surviving moving picture, ''Roundhay Garden Scene'' (1888), which was shot in Roundhay, Leeds by French inventor Louis Le Prince, while the first British film, ''Incident at Clovelly Cottage'' was shot in 1895. The world's first Color motion picture film, colour motion picture was shot by Edward Raymond Turner in 1902."Martin Scorsese on world's first colour film discovery"BBC. Retrieved 21 August 2016 British film production suffered in the 1920s in face of competition from American imports and a legal requirement for cinemas to show a set quota of British films, which encouraged poor-quality, low-cost productions to meet this demand. This had changed by the 1940s, when the government encouraged fewer, higher-quality films to be made''.'' This era also saw the rise of Alfred Hitchcock, who soon moved to the US and become one of the twentieth century's most influential directors. During World War II the Crown Film Unit established a reputation for documentaries, while Powell and Pressburger began their influential and innovative collaboration. The post-war period was a particular high point for British filmmaking, producing ''The Third Man'' and ''Brief Encounter'', which the British Film Institute consider the best and second-best British films respectively. Laurence Olivier's 1948 ''Hamlet (1948 film), Hamlet'' was the first British film to win the Academy Award for Best Picture. The 1950s saw a focus on popular domestic topics such as comedies, including the enduring ''Carry On (franchise), Carry On'' series, and World War II epics such as The Dam Busters (film), ''The'' ''Dam Busters''. At the end of the decade Hammer Film Productions, Hammer Films took advantage of relaxed censorship laws to begin their series of successful horror films. The beginning of the 1960s saw the British New Wave style develop, influenced by its French counterpart, that sought to depict a wider strata of society in a realistic manner. The 1960s also saw renewed American financial interest in British film, which particularly manifested itself in the development of Epic film, historical epics, such as Best Picture winners ''Lawrence of Arabia (film), Lawrence of Arabia'' and ''A Man for All Seasons (1966 film), A Man for All Seasons''; Spy film, spy thrillers, including the first films in the ''James Bond'' franchise; and films based on 'Swinging Sixties, swinging London' scene. The 1970s saw a withdrawal of American support and a retrenchment in British cinema, though the decade did see culturally important productions such as the horror ''The Wicker Man'' and Monty Python's comedic films. The decade also saw the Commonwealth of Nations, Commonwealth influence British film, as ''Pressure (1976 film), Pressure'' and ''A Private Enterprise'' are considered the first Black British and British Asian films respectively. 1981's ''Chariots of Fire'' and 1982's ''Gandhi (film), Gandhi'' both won the Best Picture Oscar, the latter winning eight awards, prompting a resurgence in period films. 1982 also saw the creation of Channel 4, which had a remit to promote films for minority audiences. Films with racial and LGBT themes were produced, while Channel 4's involvement saw television stars move into feature films. American investment again increased in the 1990s, and the success of ''Four Weddings and a Funeral'' saw Romantic comedy, romantic comedies rise in popularity. Merchant Ivory Productions, boosted by the Oscars success of the previous decade's period pieces, continued to produce films in the same vein. American studios also began to base the production of Hollywood films in the UK, encouraged by tax incentives. 1996's ''Trainspotting (film), Trainspotting'' led to increased interest in regional, particularly Scottish, cinema. While American-funded films continued their influence in the 2010s, domestic European co-productions also received acclaim. ''The Queen (2006 film), The Queen'' was British-French production for which Helen Mirren won Best Actress, while the UK Film Council funded ''The King's Speech'', which won Best Picture in 2011. Asian British cinema has risen in prominence since 1999, when ''East Is East (1999 film), East is East'' was a mainstream success on a low budget.
Broadcasting
The UK has been at the forefront of developments in film, radio and television. Broadcasting in the UK has historically been dominated by the taxpayer-funded but independently run British Broadcasting Corporation (commonly known as the ''BBC''), although other independent radio and television (ITV (TV network), ITV, Channel 4, Five (channel), Five) and satellite broadcasters (especially British Sky Broadcasting, BSkyB which has over 10 million subscribers) have become more important in recent years. BBC television, and the other three main television channels are public service broadcasting, public service broadcasters who, as part of their licence allowing them to operate, broadcast a variety of minority interest programming. The BBC and Channel 4 are state-owned, though they operate independently. Launched in 1955, ITV is the oldest commercial television network in the UK. Director Ridley Scott's evocative 1973 Hovis bread television commercial captured the public imagination. Filmed on Gold Hill, Shaftesbury in Dorset, Scott's advert was voted the UK's favourite television advertisement of all time in 2006. Other notable British commercials include the 1989 British Airways face advertisement, the 2005 ''noitulovE'' advert for Guinness, the 2007 ''Gorilla (advertisement), Gorilla'' advertisement by Cadbury chocolate featuring a gorilla playing drums with Phil Collins' track "In the Air Tonight" playing in the background, and a 2013 advert for Galaxy (chocolate), Galaxy chocolate bar featuring a computer-generated image of Audrey Hepburn. Christmas commercials are screened from early November in the UK, with campaigns including the John Lewis Christmas advert for the department store chain.
International football tournaments, such as the FIFA World Cup, World Cup, are historically the most viewed sports events among the public, while ''Match of the Day'' is the most popular weekly football show. The 1966 FIFA World Cup Final and the Funeral of Diana, Princess of Wales, Funeral of Princess Diana are the two List of most-watched television broadcasts#Most watched special events, most watched television events ever in the UK. Satire has been a prominent feature in British comedy for centuries. The British satire boom of the 1960s, which consisted of writers and performers such as Peter Cook, Dudley Moore, Alan Bennett, David Frost and Jonathan Miller, has heavily influenced British television, including the sketch comedy series ''Monty Python's Flying Circus'' created in 1969 by Monty Python. Regarded as the leading figure of the satire boom, Peter Cook was ranked number one in the ''Comedians' Comedian'' poll. The puppet show ''Spitting Image'' was a satire of the British Royal Family, royal family, politics, entertainment, sport and British culture of the 1980s up to the mid-1990s.
Launched in 1955, ITV is the oldest commercial television network in the UK. Director Ridley Scott's evocative 1973 Hovis bread television commercial captured the public imagination. Filmed on Gold Hill, Shaftesbury in Dorset, Scott's advert was voted the UK's favourite television advertisement of all time in 2006. Other notable British commercials include the 1989 British Airways face advertisement, the 2005 ''noitulovE'' advert for Guinness, the 2007 ''Gorilla (advertisement), Gorilla'' advertisement by Cadbury chocolate featuring a gorilla playing drums with Phil Collins' track "In the Air Tonight" playing in the background, and a 2013 advert for Galaxy (chocolate), Galaxy chocolate bar featuring a computer-generated image of Audrey Hepburn. Christmas commercials are screened from early November in the UK, with campaigns including the John Lewis Christmas advert for the department store chain.
International football tournaments, such as the FIFA World Cup, World Cup, are historically the most viewed sports events among the public, while ''Match of the Day'' is the most popular weekly football show. The 1966 FIFA World Cup Final and the Funeral of Diana, Princess of Wales, Funeral of Princess Diana are the two List of most-watched television broadcasts#Most watched special events, most watched television events ever in the UK. Satire has been a prominent feature in British comedy for centuries. The British satire boom of the 1960s, which consisted of writers and performers such as Peter Cook, Dudley Moore, Alan Bennett, David Frost and Jonathan Miller, has heavily influenced British television, including the sketch comedy series ''Monty Python's Flying Circus'' created in 1969 by Monty Python. Regarded as the leading figure of the satire boom, Peter Cook was ranked number one in the ''Comedians' Comedian'' poll. The puppet show ''Spitting Image'' was a satire of the British Royal Family, royal family, politics, entertainment, sport and British culture of the 1980s up to the mid-1990s.
 ''Have I Got News for You'' and ''Mock the Week'' are the two longest running satirical panel shows. Satire also features heavily in the ''Grand Theft Auto'' video game series which has been ranked among Britain's most successful exports. The slapstick and double entendre of Benny Hill also achieved very high ratings on British television, as did the physical humour of ''Mr. Bean''. Popular comedy duos in television include ''The Two Ronnies'' and ''Morecambe and Wise'', with both shows featuring memorable sketches. ''Jeeves and Wooster'' starred Hugh Laurie as Bertie Wooster, an airy, nonchalant, gormless, idle young gentleman and Stephen Fry as Jeeves, his calm, well-informed, and talented valet. Created by and starring Rik Mayall as Richie and Adrian Edmondson as Eddie, ''Bottom (TV series), Bottom'' features two crude, perverted flatmates with no jobs and little money, which is noted for its chaotic, nihilistic humour and violent comedy slapstick. Steve Coogan created the character Alan Partridge, a tactless and inept television presenter who often insults his guests and whose inflated sense of celebrity drives him to shameless self-promotion. ''Da Ali G Show'' starred Sacha Baron Cohen as a faux-streetwise poseur Ali G from west London, who would conduct real interviews with unsuspecting people, many of whom are celebrities, during which they are asked absurd and ridiculous questions.
Animator Nick Park created the Wallace and Gromit characters at Aardman Animations studio in Bristol. They feature in ''A Grand Day Out'' (1989), ''The Wrong Trousers'' (1993) and ''A Close Shave'' (1995), which all have List of films with a 100% rating on Rotten Tomatoes, 100% positive ratings on the aggregation site Rotten Tomatoes, while ''A Matter of Loaf and Death'' was the most watched television programme in the UK in 2008. Aardman also produce the kid's show ''Shaun the Sheep''. Popular pre-school shows include ''Teletubbies'', ''Thomas the Tank Engine'' and ''Bob the Builder''.
First airing in 1958, ''Blue Peter'' is famous for its handicraft, arts and crafts "makes". The show has been a staple for generations of British children. Popular live action TV shows include ''The Borrowers (miniseries), The Borrowers'' (based on Mary Norton (author), Mary Norton books on little people), ''The Adventures of Black Beauty'', ''The Famous Five (1970s TV series), The Famous Five'' (based on Enid Blyton books), ''The Lion, the Witch and the Wardrobe (1988 TV serial), The Lion, the Witch and the Wardrobe'' (based on the C. S. Lewis novel), and ''Pride and Prejudice (1995 TV series), Pride and Prejudice'' (starring Colin Firth as Mr. Darcy). The actor David Jason has voiced a number of popular characters in children's animation, including ''The Wind in the Willows (1983 film), The Wind in the Willows'' (based on the children's book by Kenneth Grahame), ''Danger Mouse (1981 TV series), Danger Mouse'' and ''Count Duckula''. Other children's shows include ''Where's Wally?'' (a series based on books by author Martin Handford where readers are challenged to find Wally who is hidden in the group), ''Dennis the Menace and Gnasher'', while ''Thunderbirds (TV series), Thunderbirds'' and ''Terrahawks'' by Gerry Anderson, Gerry and Sylvia Anderson have been praised for creating Supermarionation.
Debuting in 1982, ''The Snowman'' (featuring the festive song "Walking in the Air") is annually screened at Christmas. Shown on the BBC, the UK holds two high-profile charity telethon events, Children in Need, held annually in November, and Comic Relief, which alternates with Sports Relief, every March. The 2011 edition of Comic Relief saw the first appearance of James Corden's Carpool Karaoke sketch when he drove around London singing songs with George Michael. British programmes dominate the list of TV's most watched shows in the UK, with the Kitchen sink realism, kitchen sink dramas, ITV's ''Coronation Street'' and BBC's ''EastEnders'', both often ranking high on the ratings list compiled by Broadcasters' Audience Research Board, BARB."Tracking 30 years of TV's most watched programmes"
''Have I Got News for You'' and ''Mock the Week'' are the two longest running satirical panel shows. Satire also features heavily in the ''Grand Theft Auto'' video game series which has been ranked among Britain's most successful exports. The slapstick and double entendre of Benny Hill also achieved very high ratings on British television, as did the physical humour of ''Mr. Bean''. Popular comedy duos in television include ''The Two Ronnies'' and ''Morecambe and Wise'', with both shows featuring memorable sketches. ''Jeeves and Wooster'' starred Hugh Laurie as Bertie Wooster, an airy, nonchalant, gormless, idle young gentleman and Stephen Fry as Jeeves, his calm, well-informed, and talented valet. Created by and starring Rik Mayall as Richie and Adrian Edmondson as Eddie, ''Bottom (TV series), Bottom'' features two crude, perverted flatmates with no jobs and little money, which is noted for its chaotic, nihilistic humour and violent comedy slapstick. Steve Coogan created the character Alan Partridge, a tactless and inept television presenter who often insults his guests and whose inflated sense of celebrity drives him to shameless self-promotion. ''Da Ali G Show'' starred Sacha Baron Cohen as a faux-streetwise poseur Ali G from west London, who would conduct real interviews with unsuspecting people, many of whom are celebrities, during which they are asked absurd and ridiculous questions.
Animator Nick Park created the Wallace and Gromit characters at Aardman Animations studio in Bristol. They feature in ''A Grand Day Out'' (1989), ''The Wrong Trousers'' (1993) and ''A Close Shave'' (1995), which all have List of films with a 100% rating on Rotten Tomatoes, 100% positive ratings on the aggregation site Rotten Tomatoes, while ''A Matter of Loaf and Death'' was the most watched television programme in the UK in 2008. Aardman also produce the kid's show ''Shaun the Sheep''. Popular pre-school shows include ''Teletubbies'', ''Thomas the Tank Engine'' and ''Bob the Builder''.
First airing in 1958, ''Blue Peter'' is famous for its handicraft, arts and crafts "makes". The show has been a staple for generations of British children. Popular live action TV shows include ''The Borrowers (miniseries), The Borrowers'' (based on Mary Norton (author), Mary Norton books on little people), ''The Adventures of Black Beauty'', ''The Famous Five (1970s TV series), The Famous Five'' (based on Enid Blyton books), ''The Lion, the Witch and the Wardrobe (1988 TV serial), The Lion, the Witch and the Wardrobe'' (based on the C. S. Lewis novel), and ''Pride and Prejudice (1995 TV series), Pride and Prejudice'' (starring Colin Firth as Mr. Darcy). The actor David Jason has voiced a number of popular characters in children's animation, including ''The Wind in the Willows (1983 film), The Wind in the Willows'' (based on the children's book by Kenneth Grahame), ''Danger Mouse (1981 TV series), Danger Mouse'' and ''Count Duckula''. Other children's shows include ''Where's Wally?'' (a series based on books by author Martin Handford where readers are challenged to find Wally who is hidden in the group), ''Dennis the Menace and Gnasher'', while ''Thunderbirds (TV series), Thunderbirds'' and ''Terrahawks'' by Gerry Anderson, Gerry and Sylvia Anderson have been praised for creating Supermarionation.
Debuting in 1982, ''The Snowman'' (featuring the festive song "Walking in the Air") is annually screened at Christmas. Shown on the BBC, the UK holds two high-profile charity telethon events, Children in Need, held annually in November, and Comic Relief, which alternates with Sports Relief, every March. The 2011 edition of Comic Relief saw the first appearance of James Corden's Carpool Karaoke sketch when he drove around London singing songs with George Michael. British programmes dominate the list of TV's most watched shows in the UK, with the Kitchen sink realism, kitchen sink dramas, ITV's ''Coronation Street'' and BBC's ''EastEnders'', both often ranking high on the ratings list compiled by Broadcasters' Audience Research Board, BARB."Tracking 30 years of TV's most watched programmes"BBC. Retrieved 20 January 2015 The major soap operas each feature a pub, and these pubs have become household names throughout the UK. The Rovers Return is the pub in ''Coronation Street'', the The Queen Victoria, Queen Vic (short for the Queen Victoria) is the pub in ''EastEnders'', and the Woolpack in ITV's ''Emmerdale''. The pub being a prominent setting in the three major television soap operas reflects the role pubs have as the focal point of the community in many towns and villages across the UK. Espionage and detective shows have long been a staple of British television, such as the 1960s series ''The Avengers (TV series), The Avengers'' featuring lady spy adventurer and cultural (and feminist) icon Emma Peel. The United Kingdom has a large number of national and local radio stations which cover a great variety of programming. The most listened to stations are the five main national BBC radio stations. BBC Radio 1, a new music station aimed at the 16–24 age group. BBC Radio 2, a varied popular music and chat station aimed at adults is consistently highest in the ratings. BBC Radio 4, a varied talk station, is noted for its news, current affairs (news format), current affairs, radio drama, drama and radio comedy, comedy output as well as ''The Archers'', its long running soap opera, and other unique programmes, including ''Desert Island Discs'' (1942–present), an interview programme in which a famous guest (called a "castaway") chooses eight pieces of music, a book and a luxury item that they would take with them to a desert island. Currently presented by Lauren Laverne, it is the longest running music radio programme in British history. The idea for a Royal Christmas Message, Christmas message was conceived by one of the founders of the BBC. Delivered annually by the monarch, it was first broadcast on BBC Radio in 1932. An alternative Christmas message was first broadcast on Channel 4 in 1993. Broadcast from 1951 to 1960, radio comedy ''The Goon Show'', starring Peter Sellers, Spike Milligan and Harry Secombe, mixed ludicrous plots with surreal humour, puns, catchphrases and an array of bizarre sound effects. The show has exerted considerable influence on British comedy and culture. As a film star Sellers in particular became influential to film actors by using different accents and guises and assuming multiple roles in the same film. Comedian Marty Feldman co-created the acclaimed BBC Radio comedy programme ''Round the Horne'' in 1965. The long running radio comedy ''Just a Minute'' first aired on BBC Radio 4 in 1967. Panellists must talk for sixty seconds on a given subject, "without hesitation, repetition or deviation". Guests over the years have included Stephen Fry, Eddie Izzard and Sue Perkins. First broadcast on BBC Radio 4 in 1978, the science fiction comedy radio series ''The Hitchhiker's Guide to the Galaxy (radio series), The Hitchhiker's Guide to the Galaxy'' was innovative in its use of music and sound effects. The BBC, as a public service broadcasting, public service broadcaster, also runs minority stations such as BBC Asian Network, BBC Radio 1Xtra and BBC Radio 6 Music, and local stations throughout the country. Rock music station Absolute Radio, and sports station Talksport, are among the biggest commercial radio stations in the UK. * List of radio stations in the United Kingdom * List of television stations in the United Kingdom
 Freedom of the press was established in Great Britain in 1695. Popular national newspapers include ''The Times'', ''Financial Times, The Guardian, The Daily Telegraph and The Independent.''
Founded by publisher John Walter (publisher), John Walter in 1785, ''The Times'' is the first newspaper to have borne that name, lending it to numerous other papers around the world, and is the originator of the widely used Times New Roman, Times Roman typeface, created by Victor Lardent and commissioned by Stanley Morison in 1931. Newspaper and publishing magnate Alfred Harmsworth, 1st Viscount Northcliffe, Alfred Harmsworth played a major role in "shaping the modern press" – Harmsworth introduced or harnessed "broad contents, exploitation of advertising revenue to subsidize prices, aggressive marketing, subordinate regional markets, independence from party control" – and was called "the greatest figure who ever strode down Fleet Street." ''The Economist'' was founded by James Wilson (businessman), James Wilson in 1843, and the daily ''Financial Times'' was founded in 1888. Founding ''The Gentleman's Magazine'' in 1731, Edward Cave coined the term "magazine" for a periodical, and was the first publisher to successfully fashion a wide-ranging publication. Founded by Thomas Gibson Bowles, ''Vanity Fair (UK magazine), Vanity Fair'' featured List of Vanity Fair (British magazine) caricatures, caricatures of famous people for which it is best known today.
A pioneer of children's publishing, John Newbery made children's literature a sustainable and profitable part of the literary market.Matthew O Grenby (2013). "Little Goody Two-Shoes and Other Stories: Originally Published by John Newbery". p. vii. Palgrave Macmillan ''The History of Little Goody Two-Shoes'' was published by Newbery in 1765. Founded by Sir Allen Lane in 1935, Penguin Books revolutionised publishing in the 1930s through its inexpensive paperbacks, bringing high-quality paperback fiction and non-fiction to the mass market. Formed in 1940, Puffin Books is the children's imprint of Penguin Books. Barbara Euphan Todd's scarecrow story, ''Worzel Gummidge'', was the first Puffin story book in 1941.
The ''Guinness Book of Records'' was the brainchild of Sir Hugh Beaver. On 10 November 1951 he became involved in an argument over which was the fastest Game (food), game bird in Europe, and realised that it was impossible to confirm in reference books. Beaver knew that there must be numerous other questions debated throughout the world, but there was no book with which to settle arguments about records. He realised that a book supplying the answers to this sort of question might prove successful. His idea became reality when an acquaintance of his recommended University friends Norris McWhirter, Norris and Ross McWhirter who were then commissioned to compile what became ''The Guinness Book of Records'' in August 1954. E. L. James' erotic romance Fifty Shades trilogy, trilogy ''Fifty Shades of Grey'', ''Fifty Shades Darker'', and ''Fifty Shades Freed'', have sold over 125 million copies globally, and set the record in the United Kingdom as the fastest selling paperback.
Copyright laws originated in Britain with the Statute of Anne (also known as the Copyright Act 1709), which outlined the individual rights of the artist. A right to benefit financially from the work is articulated, and court rulings and legislation have recognised a right to control the work, such as ensuring that the integrity of it is preserved. The Statute of Anne gave the publishers rights for a fixed period, after which the copyright expired.
Freedom of the press was established in Great Britain in 1695. Popular national newspapers include ''The Times'', ''Financial Times, The Guardian, The Daily Telegraph and The Independent.''
Founded by publisher John Walter (publisher), John Walter in 1785, ''The Times'' is the first newspaper to have borne that name, lending it to numerous other papers around the world, and is the originator of the widely used Times New Roman, Times Roman typeface, created by Victor Lardent and commissioned by Stanley Morison in 1931. Newspaper and publishing magnate Alfred Harmsworth, 1st Viscount Northcliffe, Alfred Harmsworth played a major role in "shaping the modern press" – Harmsworth introduced or harnessed "broad contents, exploitation of advertising revenue to subsidize prices, aggressive marketing, subordinate regional markets, independence from party control" – and was called "the greatest figure who ever strode down Fleet Street." ''The Economist'' was founded by James Wilson (businessman), James Wilson in 1843, and the daily ''Financial Times'' was founded in 1888. Founding ''The Gentleman's Magazine'' in 1731, Edward Cave coined the term "magazine" for a periodical, and was the first publisher to successfully fashion a wide-ranging publication. Founded by Thomas Gibson Bowles, ''Vanity Fair (UK magazine), Vanity Fair'' featured List of Vanity Fair (British magazine) caricatures, caricatures of famous people for which it is best known today.
A pioneer of children's publishing, John Newbery made children's literature a sustainable and profitable part of the literary market.Matthew O Grenby (2013). "Little Goody Two-Shoes and Other Stories: Originally Published by John Newbery". p. vii. Palgrave Macmillan ''The History of Little Goody Two-Shoes'' was published by Newbery in 1765. Founded by Sir Allen Lane in 1935, Penguin Books revolutionised publishing in the 1930s through its inexpensive paperbacks, bringing high-quality paperback fiction and non-fiction to the mass market. Formed in 1940, Puffin Books is the children's imprint of Penguin Books. Barbara Euphan Todd's scarecrow story, ''Worzel Gummidge'', was the first Puffin story book in 1941.
The ''Guinness Book of Records'' was the brainchild of Sir Hugh Beaver. On 10 November 1951 he became involved in an argument over which was the fastest Game (food), game bird in Europe, and realised that it was impossible to confirm in reference books. Beaver knew that there must be numerous other questions debated throughout the world, but there was no book with which to settle arguments about records. He realised that a book supplying the answers to this sort of question might prove successful. His idea became reality when an acquaintance of his recommended University friends Norris McWhirter, Norris and Ross McWhirter who were then commissioned to compile what became ''The Guinness Book of Records'' in August 1954. E. L. James' erotic romance Fifty Shades trilogy, trilogy ''Fifty Shades of Grey'', ''Fifty Shades Darker'', and ''Fifty Shades Freed'', have sold over 125 million copies globally, and set the record in the United Kingdom as the fastest selling paperback.
Copyright laws originated in Britain with the Statute of Anne (also known as the Copyright Act 1709), which outlined the individual rights of the artist. A right to benefit financially from the work is articulated, and court rulings and legislation have recognised a right to control the work, such as ensuring that the integrity of it is preserved. The Statute of Anne gave the publishers rights for a fixed period, after which the copyright expired.
Visual arts
 From the creation of the United Kingdom, the English school of painting is mainly notable for portraits and landscapes, and indeed portraits in landscapes. Among the artists of this period are Joshua Reynolds (1723–1792), George Stubbs (1724–1806), and Thomas Gainsborough (1727–1788).
Pictorial satirist William Hogarth pioneered Western sequential art, and political illustrations in this style are often referred to as "Hogarthian". Following the work of Hogarth, political cartoons developed in England in the latter part of the 18th century under the direction of James Gillray. Regarded as being one of the two most influential cartoonists (the other being Hogarth), Gillray has been referred to as the father of the political cartoon, with his satirical work calling the king (George III), prime ministers and generals to account.
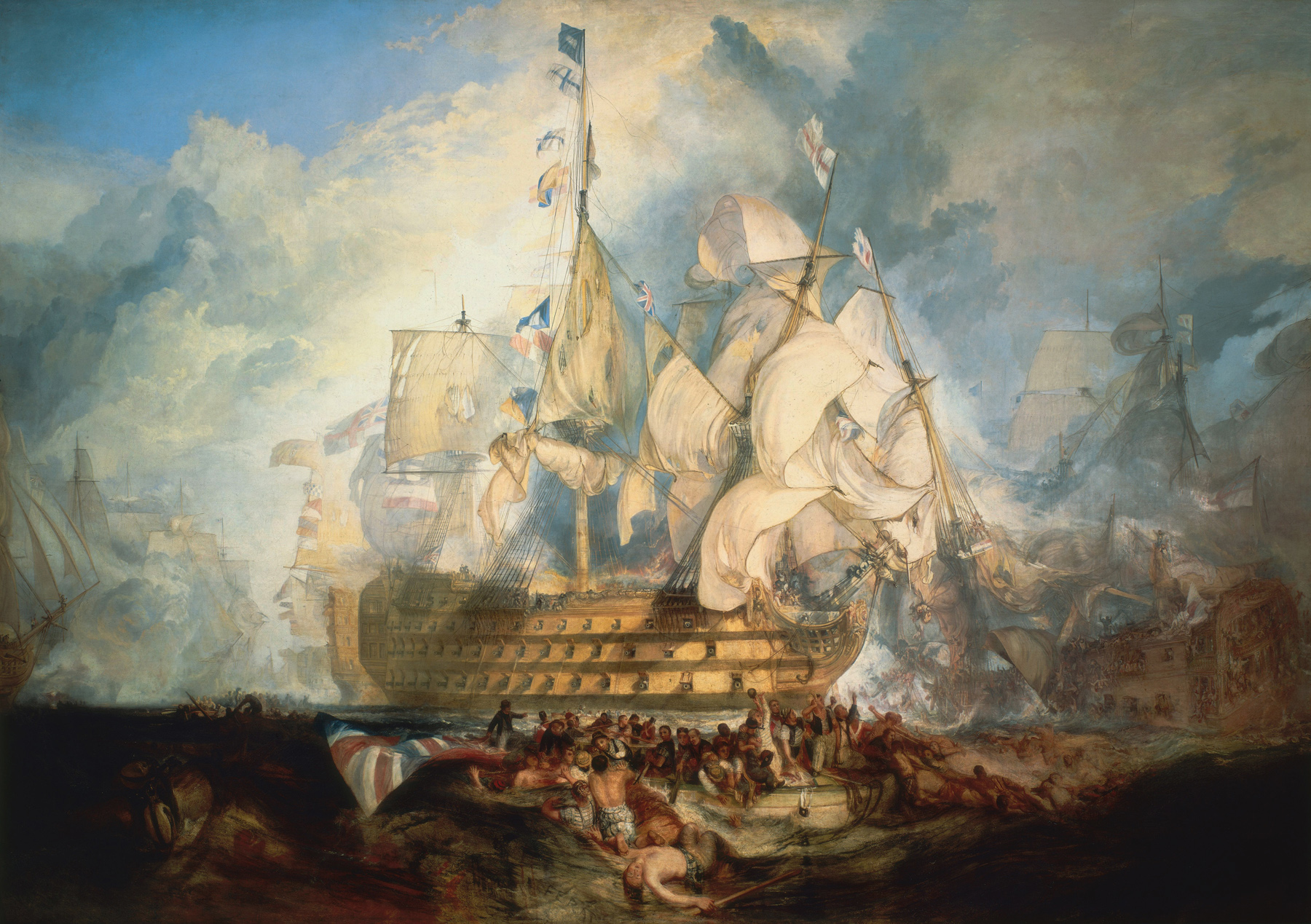
The late 18th century and the early 19th century was perhaps the most radical period in British art, producing William Blake (1757–1827), John Constable (1776–1837) and J. M. W. Turner (1775–1851), three of the most influential British artists, each of whom have dedicated spaces allocated for their work at the Tate Britain. Named after Turner, the Turner Prize (created in 1984) is an annual award presented to a British visual artist under the age of 50.
The Pre-Raphaelite Brotherhood (PRB) achieved considerable influence after its foundation in 1848 with paintings that concentrated on religious, literary, and genre subjects executed in a colourful and minutely detailed style. PRB artists included John Everett Millais, Dante Gabriel Rossetti and subsequently Edward Burne-Jones. Also associated with it was the designer William Morris, whose efforts to make beautiful objects affordable (or even free) for everyone led to his wallpaper and tile designs to some extent defining the Victorian era, Victorian aesthetic and instigating the Arts and Crafts movement.
Visual artists from the UK in the 20th century include Lucian Freud, Francis Bacon (painter), Francis Bacon, David Hockney, Bridget Riley, and the pop artists Richard Hamilton (artist), Richard Hamilton and Peter Blake (artist), Peter Blake. Also prominent amongst 20th-century artists was Henry Moore, regarded as the voice of British sculpture, and of British modernism in general. Sir Jacob Epstein was a pioneer of modern sculpture. In 1958 artist Gerald Holtom designed the protest logo for the British Campaign for Nuclear Disarmament (CND), the peace movement in the UK, which became a universal peace symbol. As a reaction to abstract expressionism, pop art emerged in England at the end of the 1950s. The 1990s saw the Young British Artists, Damien Hirst and Tracey Emin.
From the creation of the United Kingdom, the English school of painting is mainly notable for portraits and landscapes, and indeed portraits in landscapes. Among the artists of this period are Joshua Reynolds (1723–1792), George Stubbs (1724–1806), and Thomas Gainsborough (1727–1788).
Pictorial satirist William Hogarth pioneered Western sequential art, and political illustrations in this style are often referred to as "Hogarthian". Following the work of Hogarth, political cartoons developed in England in the latter part of the 18th century under the direction of James Gillray. Regarded as being one of the two most influential cartoonists (the other being Hogarth), Gillray has been referred to as the father of the political cartoon, with his satirical work calling the king (George III), prime ministers and generals to account.
The late 18th century and the early 19th century was perhaps the most radical period in British art, producing William Blake (1757–1827), John Constable (1776–1837) and J. M. W. Turner (1775–1851), three of the most influential British artists, each of whom have dedicated spaces allocated for their work at the Tate Britain. Named after Turner, the Turner Prize (created in 1984) is an annual award presented to a British visual artist under the age of 50.
The Pre-Raphaelite Brotherhood (PRB) achieved considerable influence after its foundation in 1848 with paintings that concentrated on religious, literary, and genre subjects executed in a colourful and minutely detailed style. PRB artists included John Everett Millais, Dante Gabriel Rossetti and subsequently Edward Burne-Jones. Also associated with it was the designer William Morris, whose efforts to make beautiful objects affordable (or even free) for everyone led to his wallpaper and tile designs to some extent defining the Victorian era, Victorian aesthetic and instigating the Arts and Crafts movement.
Visual artists from the UK in the 20th century include Lucian Freud, Francis Bacon (painter), Francis Bacon, David Hockney, Bridget Riley, and the pop artists Richard Hamilton (artist), Richard Hamilton and Peter Blake (artist), Peter Blake. Also prominent amongst 20th-century artists was Henry Moore, regarded as the voice of British sculpture, and of British modernism in general. Sir Jacob Epstein was a pioneer of modern sculpture. In 1958 artist Gerald Holtom designed the protest logo for the British Campaign for Nuclear Disarmament (CND), the peace movement in the UK, which became a universal peace symbol. As a reaction to abstract expressionism, pop art emerged in England at the end of the 1950s. The 1990s saw the Young British Artists, Damien Hirst and Tracey Emin.
 The auction was revived in 17th- and 18th-century England when Candle auction, auctions by candle began to be used for the sale of goods and leaseholds, some of which were recorded in Samuel Pepys's diary in 1660. Headquartered in King Street, London, Christie's, the world's largest auction house, was founded in 1766 by auctioneer James Christie (auctioneer), James Christie in London. Known for his thickly impasted portrait and figure paintings, Lucian Freud was widely considered the pre-eminent British artist of his time. Freud was depicted in Francis Bacon's 1969 oil painting, ''Three Studies of Lucian Freud'', which was sold for $142.4 million in November 2013, the List of most expensive paintings, highest price attained at auction to that point.
The auction was revived in 17th- and 18th-century England when Candle auction, auctions by candle began to be used for the sale of goods and leaseholds, some of which were recorded in Samuel Pepys's diary in 1660. Headquartered in King Street, London, Christie's, the world's largest auction house, was founded in 1766 by auctioneer James Christie (auctioneer), James Christie in London. Known for his thickly impasted portrait and figure paintings, Lucian Freud was widely considered the pre-eminent British artist of his time. Freud was depicted in Francis Bacon's 1969 oil painting, ''Three Studies of Lucian Freud'', which was sold for $142.4 million in November 2013, the List of most expensive paintings, highest price attained at auction to that point.
 Randolph Caldecott, Walter Crane, Kate Greenaway, John Tenniel, Aubrey Beardsley, Roger Hargreaves, Arthur Rackham, John Leech (caricaturist), John Leech, George Cruikshank and Beatrix Potter were notable book illustrators. Posters have played a significant role in British culture. Designed by Alfred Leete in 1914 as a recruitment poster for the British Army, "Lord Kitchener Wants You" is the most famous British recruitment poster ever produced and an iconic and enduring image of World War I. Retrieved 31 March 2011 Produced by the British government in 1939 for World War II, the ''Keep Calm and Carry On'' motivational poster is now seen as "not only as a distillation of a crucial moment in Britishness, but also as an inspiring message from the past to the present in a time of crisis".
In the late 1960s, British graphic designer Storm Thorgerson co-founded the graphic art group Hipgnosis, who have designed many iconic single and album covers for rock bands. His works were notable for their Surrealism, surreal elements, with perhaps the most famous being the cover for Pink Floyd's ''The Dark Side of the Moon''. Designed by David Bowie, the ''Aladdin Sane'' album cover features a lightning bolt across his face which is regarded as one of the most iconic images of Bowie. The subversive political artwork of Banksy (pseudonym of English graffiti artist whose identity is concealed) can be found on streets, walls and buildings in the UK and the rest of the world. Arts institutions include the Royal College of Art, Royal Society of Arts, New English Art Club, Slade School of Art, Royal Academy, and the Tate Gallery (founded as the National Gallery of British Art).
;Design
Randolph Caldecott, Walter Crane, Kate Greenaway, John Tenniel, Aubrey Beardsley, Roger Hargreaves, Arthur Rackham, John Leech (caricaturist), John Leech, George Cruikshank and Beatrix Potter were notable book illustrators. Posters have played a significant role in British culture. Designed by Alfred Leete in 1914 as a recruitment poster for the British Army, "Lord Kitchener Wants You" is the most famous British recruitment poster ever produced and an iconic and enduring image of World War I. Retrieved 31 March 2011 Produced by the British government in 1939 for World War II, the ''Keep Calm and Carry On'' motivational poster is now seen as "not only as a distillation of a crucial moment in Britishness, but also as an inspiring message from the past to the present in a time of crisis".
In the late 1960s, British graphic designer Storm Thorgerson co-founded the graphic art group Hipgnosis, who have designed many iconic single and album covers for rock bands. His works were notable for their Surrealism, surreal elements, with perhaps the most famous being the cover for Pink Floyd's ''The Dark Side of the Moon''. Designed by David Bowie, the ''Aladdin Sane'' album cover features a lightning bolt across his face which is regarded as one of the most iconic images of Bowie. The subversive political artwork of Banksy (pseudonym of English graffiti artist whose identity is concealed) can be found on streets, walls and buildings in the UK and the rest of the world. Arts institutions include the Royal College of Art, Royal Society of Arts, New English Art Club, Slade School of Art, Royal Academy, and the Tate Gallery (founded as the National Gallery of British Art).
;Design
 In 2006, 37 years after its first test flight, Concorde was named the winner of the Great British Design Quest organised by the BBC and the Design Museum. A total of 212,000 votes were cast with Concorde beating other British design icons such as the Mini, mini skirt, Jaguar E-Type, Tube map and the Supermarine Spitfire. The Spitfire featured in Christopher Nolan's 2017 action-thriller film ''Dunkirk (2017 film), Dunkirk''.
Sir Morien Morgan led research into supersonic transport in 1948 that culminated in the Concorde passenger aircraft. In November 1956 he became Chairman of the newly formed Supersonic Transport Aircraft Committee which funded research into supersonic transport at several British aviation firms though the 1950s. By the late 1950s, the committee had started the process of selecting specific designs for development, and after the forced merger of most aviation firms in 1960, selected the Bristol Type 223, designed by Archibald Russell, as the basis for a transatlantic design.
The Brit Awards statuette for the British Phonographic Industry, BPI's annual music awards, which depicts Britannia, the female personification of Britain, is regularly redesigned by some of the best known British designers, stylists and artists, including Dame Vivienne Westwood, Damien Hirst, Tracey Emin, Sir Peter Blake (artist), Peter Blake, Zaha Hadid and Sir Anish Kapoor.
In 2006, 37 years after its first test flight, Concorde was named the winner of the Great British Design Quest organised by the BBC and the Design Museum. A total of 212,000 votes were cast with Concorde beating other British design icons such as the Mini, mini skirt, Jaguar E-Type, Tube map and the Supermarine Spitfire. The Spitfire featured in Christopher Nolan's 2017 action-thriller film ''Dunkirk (2017 film), Dunkirk''.
Sir Morien Morgan led research into supersonic transport in 1948 that culminated in the Concorde passenger aircraft. In November 1956 he became Chairman of the newly formed Supersonic Transport Aircraft Committee which funded research into supersonic transport at several British aviation firms though the 1950s. By the late 1950s, the committee had started the process of selecting specific designs for development, and after the forced merger of most aviation firms in 1960, selected the Bristol Type 223, designed by Archibald Russell, as the basis for a transatlantic design.
The Brit Awards statuette for the British Phonographic Industry, BPI's annual music awards, which depicts Britannia, the female personification of Britain, is regularly redesigned by some of the best known British designers, stylists and artists, including Dame Vivienne Westwood, Damien Hirst, Tracey Emin, Sir Peter Blake (artist), Peter Blake, Zaha Hadid and Sir Anish Kapoor.
Performing arts, carnivals, parades
 Large outdoor List of music festivals in the United Kingdom, music festivals in the summer and autumn are popular, such as Glastonbury Festival, Glastonbury (the largest greenfield festival in the world), V Festival, Reading and Leeds Festivals. The UK was at the forefront of the illegal, free rave movement from the late 1980s, which led to pan-European culture of teknivals mirrored on the British free festival movement and associated travelling lifestyle. The most prominent opera house in England is the Royal Opera House at Covent Gardens.Foreman, Susan (2005). London: a musical gazetteer. Yale University Press The Proms, a season of orchestral classical music concerts held at the Royal Albert Hall, is a major cultural event held annually. The Royal Ballet is one of the world's foremost classical ballet companies, its reputation built on two prominent figures of 20th-century dance, ''prima ballerina'' Margot Fonteyn and choreographer Frederick Ashton. Irish dancing is popular in Northern Ireland and among the Irish diaspora throughout the UK; its costumes feature patterns taken from the medieval Book of Kells.
A staple of British seaside culture, the quarrelsome couple Punch and Judy made their first recorded appearance in Covent Garden, London in 1662. The various episodes of Punch and Judy are performed in the spirit of outrageous comedy – often provoking shocked laughter – and are dominated by the anarchic clowning of Mr. Punch. Regarded as British cultural icons, they appeared at a significant period in British history, with Glyn Edwards stating: "[Pulcinella] went down particularly well with Restoration British audiences, fun-starved after years of Puritanism. We soon changed Punch's name, transformed him from a marionette to a hand puppet, and he became, really, a spirit of Britain – a subversive maverick who defies authority, a kind of puppet equivalent to our political cartoons."
The circus is a traditional form of entertainment in the UK. Chipperfield's Circus dates back more than 300 years in Britain, making it one of the oldest family circus dynasties. Philip Astley is regarded as the father of the circus#Development, modern circus."The circus comes to the Circus"
Large outdoor List of music festivals in the United Kingdom, music festivals in the summer and autumn are popular, such as Glastonbury Festival, Glastonbury (the largest greenfield festival in the world), V Festival, Reading and Leeds Festivals. The UK was at the forefront of the illegal, free rave movement from the late 1980s, which led to pan-European culture of teknivals mirrored on the British free festival movement and associated travelling lifestyle. The most prominent opera house in England is the Royal Opera House at Covent Gardens.Foreman, Susan (2005). London: a musical gazetteer. Yale University Press The Proms, a season of orchestral classical music concerts held at the Royal Albert Hall, is a major cultural event held annually. The Royal Ballet is one of the world's foremost classical ballet companies, its reputation built on two prominent figures of 20th-century dance, ''prima ballerina'' Margot Fonteyn and choreographer Frederick Ashton. Irish dancing is popular in Northern Ireland and among the Irish diaspora throughout the UK; its costumes feature patterns taken from the medieval Book of Kells.
A staple of British seaside culture, the quarrelsome couple Punch and Judy made their first recorded appearance in Covent Garden, London in 1662. The various episodes of Punch and Judy are performed in the spirit of outrageous comedy – often provoking shocked laughter – and are dominated by the anarchic clowning of Mr. Punch. Regarded as British cultural icons, they appeared at a significant period in British history, with Glyn Edwards stating: "[Pulcinella] went down particularly well with Restoration British audiences, fun-starved after years of Puritanism. We soon changed Punch's name, transformed him from a marionette to a hand puppet, and he became, really, a spirit of Britain – a subversive maverick who defies authority, a kind of puppet equivalent to our political cartoons."
The circus is a traditional form of entertainment in the UK. Chipperfield's Circus dates back more than 300 years in Britain, making it one of the oldest family circus dynasties. Philip Astley is regarded as the father of the circus#Development, modern circus."The circus comes to the Circus"BBC News. Retrieved 13 December 2014 Following his invention of the circus ring in 1768, Astley's Amphitheatre opened in London in 1773. As an equestrian master Astley had a skill for trick horse-riding, and when he added tumblers, tightrope-walkers, jugglers, performing dogs, and a clown to fill time between his own demonstrations – the modern circus was born. The Hughes Royal Circus was popular in London in the 1780s. Pablo Fanque's Circus Royal, among the most popular circuses of Victorian England, showcased William Kite, which inspired John Lennon to write "Being for the Benefit of Mr. Kite!" on The Beatles' album ''Sgt. Pepper's Lonely Hearts Club Band''. Joseph Grimaldi, originator of Clown#Whiteface, whiteface clown make-up, is considered the father of modern clowning.
 The Edinburgh Festival Fringe is the world's largest arts festival. Established in 1947, it takes place in Scotland's capital during three weeks every August alongside several other arts and cultural festivals. The Fringe mostly attracts events from the performing arts, particularly theatre and comedy, although dance and music also feature. The Notting Hill Carnival is an annual event that has taken place on the streets of Notting Hill, London since 1966."About us"
The Edinburgh Festival Fringe is the world's largest arts festival. Established in 1947, it takes place in Scotland's capital during three weeks every August alongside several other arts and cultural festivals. The Fringe mostly attracts events from the performing arts, particularly theatre and comedy, although dance and music also feature. The Notting Hill Carnival is an annual event that has taken place on the streets of Notting Hill, London since 1966."About us", Notting Hill Carnival '13, London Notting Hill Enterprises Trust. Led by the British African-Caribbean people, British African-Caribbean community, the carnival has attracted around one million people, making it Britain's biggest street festival and one of the largest in the world. Also of note is the extensive impact of Irish culture for St. Patrick's Day. The largest St Patrick's Day Parade takes place in Digbeth,
 Pantomime (often referred to as "panto") is a British musical theatre, musical comedy stage production, designed for family entertainment. It is performed in theatres throughout the UK during the Christmas and New Year season. The art originated in the 18th century with John Weaver (dancer), John Weaver, a dance master and choreographer at the
Pantomime (often referred to as "panto") is a British musical theatre, musical comedy stage production, designed for family entertainment. It is performed in theatres throughout the UK during the Christmas and New Year season. The art originated in the 18th century with John Weaver (dancer), John Weaver, a dance master and choreographer at the Architecture
 The architecture of the United Kingdom includes many features that precede the creation of the United Kingdom in 1707, from as early as Skara Brae and Stonehenge to the Giant's Ring, Avebury and Roman Britain, Roman ruins. In most towns and villages the parish church is an indication of the age of the settlement. Many castles remain from the medieval period, such as Windsor Castle (longest-occupied castle in Europe), Stirling Castle (one of the largest and most important in Scotland), Bodiam Castle (a moated castle), and Warwick Castle. Over the two centuries following the Norman conquest, Norman conquest of England of 1066, and the building of the Tower of London, castles such as Caernarfon Castle in Wales and Carrickfergus Castle in Ireland were built.
The architecture of the United Kingdom includes many features that precede the creation of the United Kingdom in 1707, from as early as Skara Brae and Stonehenge to the Giant's Ring, Avebury and Roman Britain, Roman ruins. In most towns and villages the parish church is an indication of the age of the settlement. Many castles remain from the medieval period, such as Windsor Castle (longest-occupied castle in Europe), Stirling Castle (one of the largest and most important in Scotland), Bodiam Castle (a moated castle), and Warwick Castle. Over the two centuries following the Norman conquest, Norman conquest of England of 1066, and the building of the Tower of London, castles such as Caernarfon Castle in Wales and Carrickfergus Castle in Ireland were built.
 English Gothic architecture flourished from the 12th to the early 16th century, and famous examples include Westminster Abbey, the traditional place of Coronation of the British monarch, coronation for the British monarch, which also has a long tradition as a venue for royal weddings; and was the location of the funeral of Princess Diana, Canterbury Cathedral, one of the oldest and most famous Christian structures in England; Salisbury Cathedral, which has the tallest church spire in the UK; and Winchester Cathedral, which has the longest nave and greatest overall length of any Gothic cathedral in Europe. Tudor architecture is the final development of Medieval architecture in England, during the Tudor period (1485–1603). In the United Kingdom, a listed building is a building or other structure officially designated as being of special architectural, historical or cultural significance. About half a million buildings in the UK have "listed" status.
In the 1680s, Downing Street was built by Sir George Downing, 1st Baronet, Sir George Downing, and its most famous address 10 Downing Street, became the residence of the Prime Minister of the United Kingdom, Prime Minister in 1730. One of the best-known English architects working at the time of the foundation of the United Kingdom was Sir Christopher Wren. He was employed to design and rebuild many of the ruined ancient churches of London following the Great Fire of London. His masterpiece, St Paul's Cathedral, was completed in the early years of the United Kingdom. Buckingham Palace, the London residence of the British monarch, was built in 1705. Both St Paul's Cathedral and Buckingham Palace use Portland stone, a limestone from the Jurassic period Quarry, quarried in the Jurassic Coast in Isle of Portland, Portland, Dorset, which is famous for its use in British and world architecture.
In the early 18th century Baroque architecture – popular in Europe – was introduced, and Blenheim Palace was built in this era. However, Baroque was quickly replaced by a return of the Palladian form. The Georgian architecture of the 18th century was an evolved form of Palladianism. Many existing buildings such as Woburn Abbey and Kedleston Hall are in this style. Among the many architects of this form of architecture and its successors, neoclassicism, neoclassical and Romanticism, romantic, were Robert Adam, Sir William Chambers (architect), William Chambers, and James Wyatt.
English Gothic architecture flourished from the 12th to the early 16th century, and famous examples include Westminster Abbey, the traditional place of Coronation of the British monarch, coronation for the British monarch, which also has a long tradition as a venue for royal weddings; and was the location of the funeral of Princess Diana, Canterbury Cathedral, one of the oldest and most famous Christian structures in England; Salisbury Cathedral, which has the tallest church spire in the UK; and Winchester Cathedral, which has the longest nave and greatest overall length of any Gothic cathedral in Europe. Tudor architecture is the final development of Medieval architecture in England, during the Tudor period (1485–1603). In the United Kingdom, a listed building is a building or other structure officially designated as being of special architectural, historical or cultural significance. About half a million buildings in the UK have "listed" status.
In the 1680s, Downing Street was built by Sir George Downing, 1st Baronet, Sir George Downing, and its most famous address 10 Downing Street, became the residence of the Prime Minister of the United Kingdom, Prime Minister in 1730. One of the best-known English architects working at the time of the foundation of the United Kingdom was Sir Christopher Wren. He was employed to design and rebuild many of the ruined ancient churches of London following the Great Fire of London. His masterpiece, St Paul's Cathedral, was completed in the early years of the United Kingdom. Buckingham Palace, the London residence of the British monarch, was built in 1705. Both St Paul's Cathedral and Buckingham Palace use Portland stone, a limestone from the Jurassic period Quarry, quarried in the Jurassic Coast in Isle of Portland, Portland, Dorset, which is famous for its use in British and world architecture.
In the early 18th century Baroque architecture – popular in Europe – was introduced, and Blenheim Palace was built in this era. However, Baroque was quickly replaced by a return of the Palladian form. The Georgian architecture of the 18th century was an evolved form of Palladianism. Many existing buildings such as Woburn Abbey and Kedleston Hall are in this style. Among the many architects of this form of architecture and its successors, neoclassicism, neoclassical and Romanticism, romantic, were Robert Adam, Sir William Chambers (architect), William Chambers, and James Wyatt.
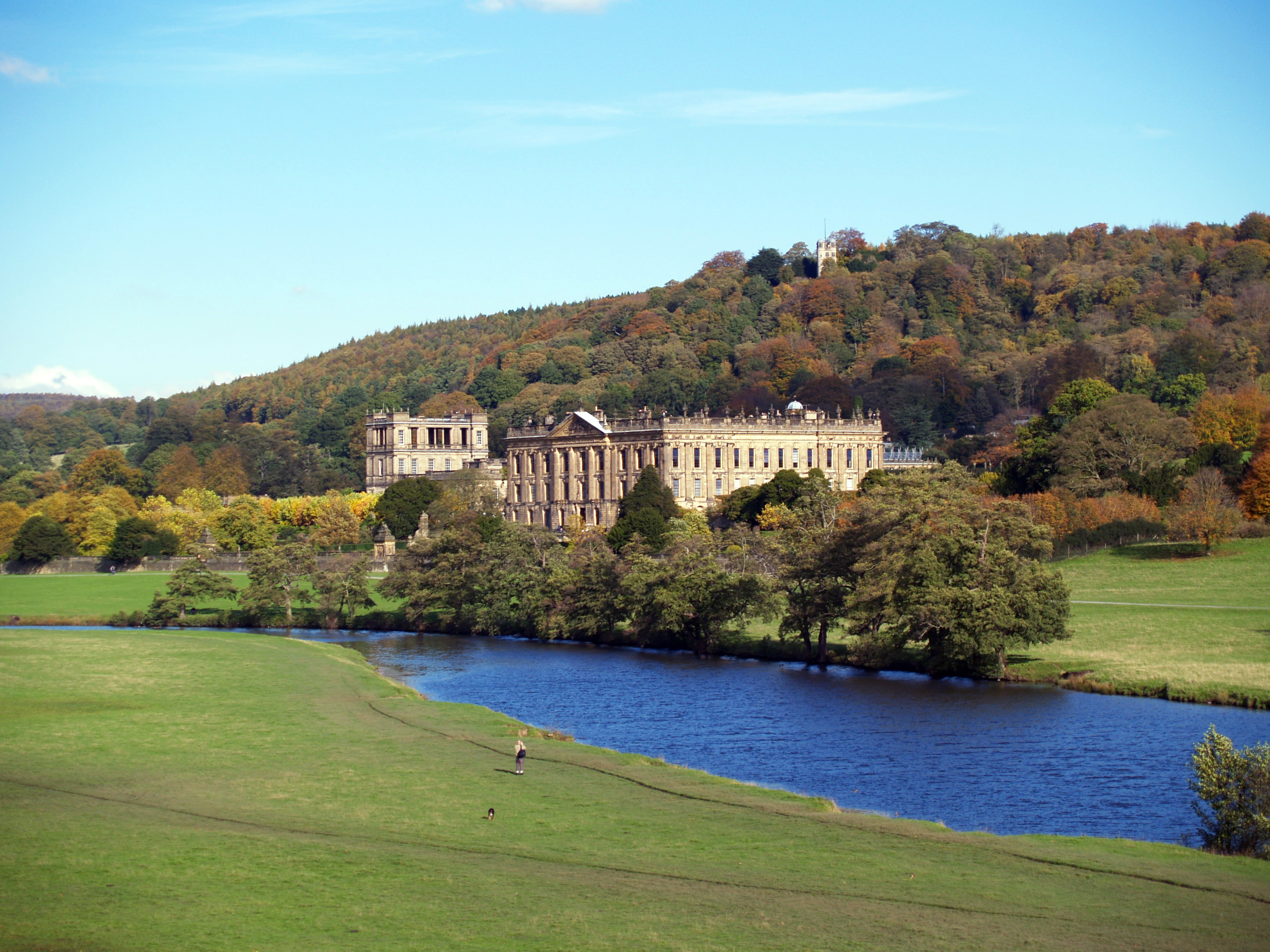 The aristocratic stately home continued the tradition of the first large gracious unfortified mansions such as the Elizabethan Montacute House and Hatfield House. Many of these houses are the setting for British period dramas, such as ''Downton Abbey''. During the 18th and 19th centuries in the highest echelons of British society, the English country house was a place for relaxing, hunting in the countryside. Many stately homes have become open to the public: Knebworth House, now a major venue for Concerts at Knebworth House, open air rock and pop concerts – Freddie Mercury's final live performance with Queen (band), Queen took place at Knebworth on 9 August 1986, Alton Towers, the most popular theme park in the UK, and Longleat, the world's first Longleat Safari Park, safari park outside Africa.
The aristocratic stately home continued the tradition of the first large gracious unfortified mansions such as the Elizabethan Montacute House and Hatfield House. Many of these houses are the setting for British period dramas, such as ''Downton Abbey''. During the 18th and 19th centuries in the highest echelons of British society, the English country house was a place for relaxing, hunting in the countryside. Many stately homes have become open to the public: Knebworth House, now a major venue for Concerts at Knebworth House, open air rock and pop concerts – Freddie Mercury's final live performance with Queen (band), Queen took place at Knebworth on 9 August 1986, Alton Towers, the most popular theme park in the UK, and Longleat, the world's first Longleat Safari Park, safari park outside Africa.
 In the early 19th century the romantic Gothic revival architecture, Gothic revival began in England as a reaction to the symmetry of Palladianism. Notable examples of Gothic revival architecture are the Palace of Westminster, Houses of Parliament and Fonthill Abbey. By the middle of the 19th century, as a result of new technology, one could incorporate steel as a building component: one of the greatest exponents of this was Joseph Paxton, architect of the Crystal Palace. Paxton also built such houses as Mentmore Towers, in the still popular retrospective English Renaissance, Renaissance styles. In this era of prosperity and development British architecture embraced many new methods of construction, but such architects as August Pugin ensured that traditional styles were retained.
Following the building of the world's first Pier#Pleasure piers, seaside pier in July 1814 in Ryde, Isle of Wight off the south coast of England, the pier became fashionable at seaside resorts in the UK during the Victorian era, peaking in the 1860s with 22 being built. Providing a walkway out to sea, the seaside pier is regarded as among the finest Victorian architecture, and is an iconic symbol of the British seaside holiday. By 1914, there were over 100 piers around the UK's coasts. Today there are 55 List of piers in the United Kingdom, seaside piers in the UK. Tower Bridge (half a mile from London Bridge) opened in 1895.
At the beginning of the 20th century a new form of design, Arts and Crafts movement, arts and crafts, became popular; the architectural form of this style, which had evolved from the 19th-century designs of such architects as George Devey, was championed by Edwin Lutyens. Arts and crafts in architecture is characterised by an informal, non-symmetrical form, often with mullioned or latticework, lattice windows, multiple gables and tall chimneys. This style continued to evolve until World War II. After that war, reconstruction went through a variety of phases, but was heavily influenced by Modernism, especially from the late 1950s to the early 1970s. Many bleak town centre redevelopments—criticised for featuring hostile, concrete-lined "windswept plazas"—were the fruit of this interest, as were many equally bleak public buildings, such as the Hayward Gallery.
In the early 19th century the romantic Gothic revival architecture, Gothic revival began in England as a reaction to the symmetry of Palladianism. Notable examples of Gothic revival architecture are the Palace of Westminster, Houses of Parliament and Fonthill Abbey. By the middle of the 19th century, as a result of new technology, one could incorporate steel as a building component: one of the greatest exponents of this was Joseph Paxton, architect of the Crystal Palace. Paxton also built such houses as Mentmore Towers, in the still popular retrospective English Renaissance, Renaissance styles. In this era of prosperity and development British architecture embraced many new methods of construction, but such architects as August Pugin ensured that traditional styles were retained.
Following the building of the world's first Pier#Pleasure piers, seaside pier in July 1814 in Ryde, Isle of Wight off the south coast of England, the pier became fashionable at seaside resorts in the UK during the Victorian era, peaking in the 1860s with 22 being built. Providing a walkway out to sea, the seaside pier is regarded as among the finest Victorian architecture, and is an iconic symbol of the British seaside holiday. By 1914, there were over 100 piers around the UK's coasts. Today there are 55 List of piers in the United Kingdom, seaside piers in the UK. Tower Bridge (half a mile from London Bridge) opened in 1895.
At the beginning of the 20th century a new form of design, Arts and Crafts movement, arts and crafts, became popular; the architectural form of this style, which had evolved from the 19th-century designs of such architects as George Devey, was championed by Edwin Lutyens. Arts and crafts in architecture is characterised by an informal, non-symmetrical form, often with mullioned or latticework, lattice windows, multiple gables and tall chimneys. This style continued to evolve until World War II. After that war, reconstruction went through a variety of phases, but was heavily influenced by Modernism, especially from the late 1950s to the early 1970s. Many bleak town centre redevelopments—criticised for featuring hostile, concrete-lined "windswept plazas"—were the fruit of this interest, as were many equally bleak public buildings, such as the Hayward Gallery.
Comics
 British comics in the early 20th century typically evolved from illustrated penny dreadfuls of the Victorian era (featuring Sweeney Todd, Dick Turpin and ''Varney the Vampire''). A growing consumer culture and an increased capacity for travel throughout the UK via the invention of railway (Stockton and Darlington Railway, in 1825) created both a market for cheap popular literature, and the ability for it to be circulated on a large scale. Created in the 1830s, ''The Guardian'' described penny dreadfuls as "Britain's first taste of mass-produced popular culture for the young". Introducing familiar features in vampire fiction, ''Varney'' is the first story to refer to sharpened teeth for a Vampire#In modern culture, vampire. After adult comics had been published – most notably ''Ally Sloper's Half Holiday'' (1880s) featuring Ally Sloper who has been called the first regular character in comics, – more juvenile British comics emerged, with the two most popular, ''The Beano'' and ''The Dandy'', released by DC Thomson (based in Dundee, Scotland) in the 1930s. By 1950 the weekly circulation of both reached two million.Armstrong, Stephen
British comics in the early 20th century typically evolved from illustrated penny dreadfuls of the Victorian era (featuring Sweeney Todd, Dick Turpin and ''Varney the Vampire''). A growing consumer culture and an increased capacity for travel throughout the UK via the invention of railway (Stockton and Darlington Railway, in 1825) created both a market for cheap popular literature, and the ability for it to be circulated on a large scale. Created in the 1830s, ''The Guardian'' described penny dreadfuls as "Britain's first taste of mass-produced popular culture for the young". Introducing familiar features in vampire fiction, ''Varney'' is the first story to refer to sharpened teeth for a Vampire#In modern culture, vampire. After adult comics had been published – most notably ''Ally Sloper's Half Holiday'' (1880s) featuring Ally Sloper who has been called the first regular character in comics, – more juvenile British comics emerged, with the two most popular, ''The Beano'' and ''The Dandy'', released by DC Thomson (based in Dundee, Scotland) in the 1930s. By 1950 the weekly circulation of both reached two million.Armstrong, Stephen"Was Pixar's Inside Out inspired by The Beano?"
''The Telegraph''. 27 July 2015 Explaining the popularity of comics during this period, Anita O'Brien, director curator at London's Cartoon Museum, states: "When comics like the ''Beano'' and ''Dandy'' were invented back in the 1930s – and through really to the 1950s and 1960s – these comics were almost the only entertainment available to children." In 1954 ''Tiger (Fleetway), Tiger'' comics introduced ''Roy of the Rovers'', the hugely popular football based strip recounting the life of Roy Race and the team he played for, Melchester Rovers. The stock media phrase "real 'Roy of the Rovers' stuff" is often used by football writers, commentators and fans when describing displays of great skill, or surprising results that go against the odds, in reference to the dramatic storylines that were the strip's trademark. Other comic books and graphic novels such as ''Eagle (comic), Eagle'', ''Valiant (comics), Valiant'', ''Warrior (comics), Warrior'', and ''2000 AD (comics), 2000 AD'' also flourished. Created by Emma Orczy in 1903, the Scarlet Pimpernel is the alter ego of Sir Percy Blakeney, a wealthy English fop who transforms into a formidable swordsman and a quick-thinking escape artist, establishing the "hero with a secret identity" into popular culture. The Scarlet Pimpernel first appeared on stage (1903) and then in novel (1905), and became very popular with the British public. He exhibits characteristics that became standard superhero conventions in comic books, including the penchant for disguise, use of a signature weapon (sword), ability to out-think and outwit his adversaries, and a calling card (he leaves behind a Anagallis arvensis, scarlet pimpernel at his interventions). Drawing attention to his alter ego Blakeney he hides behind his public face as a meek, slow thinking foppish playboy, and he establishes a network of supporters, The League of the Scarlet Pimpernel, that aid his endeavours. In the 1980s, a resurgence of British writers and artists gained prominence in mainstream comic books, which was dubbed the "British Invasion (comics), British Invasion" in comic book history. These writers and artists brought with them their own mature themes and philosophy such as anarchy, controversy and politics common in British media, but were never before seen in American comics. These elements would pave the way for mature and "darker and edgier" comic books that would jump start the Modern Age of Comics. Writers included Alan Moore, famous for his ''V for Vendetta'', ''From Hell'', ''Watchmen'', ''Marvelman'', and ''The League of Extraordinary Gentlemen''; ''Watchmen'' was described as "paving the way for a current cultural obsession" in comics; Neil Gaiman and his critically acclaimed and best-selling ''The Sandman (Vertigo), The Sandman'' mythos and ''Books of Magic''; Warren Ellis creator of ''Transmetropolitan'' and ''Planetary (comics), Planetary''; and others such as Alan Grant (writer), Alan Grant, Grant Morrison, Dave Gibbons, Alan Davis, and Mark Millar who created ''Wanted (comics), Wanted'', ''Kick-Ass (comic book), Kick-Ass'' and ''The Secret Service (comics), Kingsman: The Secret Service''. Prominent comic book artists include Steve Dillon, Simon Bisley, Dave McKean, Glen Fabry, John Ridgway (comics), John Ridgway and Sean Phillips. The comic book series ''Hellblazer'', set in Britain and starring the Liverpudlian magician John Constantine, paved the way for British writers such as Jamie Delano, Mike Carey (writer), Mike Carey and Denise Mina.
Folklore
Robin Hood and the ballad tradition
Much of the folklore of the United Kingdom pre-dates the 18th century. Though some of the characters and stories are present throughout all of the UK, most belong to specific countries or regions. Common folkloric beings include pixies, giant (mythology), giants, elves, bogeymen, trolls, goblins and dwarf (mythology), dwarves. While many legends and folk-customs are thought to be ancient, such as the tales of Offa of Angeln and Weyland Smith, others date from after the Norman invasion of England, such as Robin Hood and his Merry Men of Sherwood Forest, Sherwood and their battles with the Sheriff of Nottingham. Richard the Lionheart, Christian leader of the Third Crusade, came to be seen as a contemporary and supporter of Robin Hood. A plaque features Richard marrying Robin and Maid Marian outside Nottingham Castle. During the High Middle Ages tales originated from Brythonic traditions, notably the Arthurian legend. Deriving from Welsh source; King Arthur, Excalibur and Merlin, while the Jersey poet Wace introduced the Knights of the Round Table. These stories are most centrally brought together within Geoffrey of Monmouth's ''Historia Regum Britanniae'' (''History of the Kings of Britain''). Another early figure from Britons (historic), British tradition, King Cole, may have been based on a real figure from Sub-Roman Britain. Many of the tales make up part of the wider Matter of Britain, a collection of shared British folklore. The Loch Ness Monster is a cryptid that is reputed to inhabit Loch Ness in the Scottish Highlands. The legendary monster has been affectionately referred to by the nickname "Nessie" since the 1950s. The leprechaun figures large in Irish folklore. A mischievous fairy-type creature in emerald green clothing who when not playing tricks spends all its time busily making shoes, the leprechaun is said to have a pot of gold hidden at the end of the rainbow, and if ever captured by a human it has the magical power to grant three wishes in exchange for release. In mythology, English fairy tales such as ''Jack and the Beanstalk'' and ''Jack the Giant Killer'' helped form the modern perception of Giant (mythology), giants as stupid and violent, while the dwarf Tom Thumb is a traditional hero in English folklore. English fairy tale ''The Story of the Three Bears, Goldilocks and the Three Bears'' is one of the most popular fairy tales in the English language. Some folk figures are based on semi- or actual historical people whose story has been passed down centuries: Lady Godiva, for instance, was said to have ridden naked on horseback through Coventry; the heroic English figure Hereward the Wake resisted the Norman invasion; Herne the Hunter is an equestrian ghost associated with Windsor, Berkshire, Windsor Forest and Windsor Great Park, Great Park, and Mother Shipton is the archetypal witch. The chivalrous bandit, such as Dick Turpin, is a recurring character.Pirates
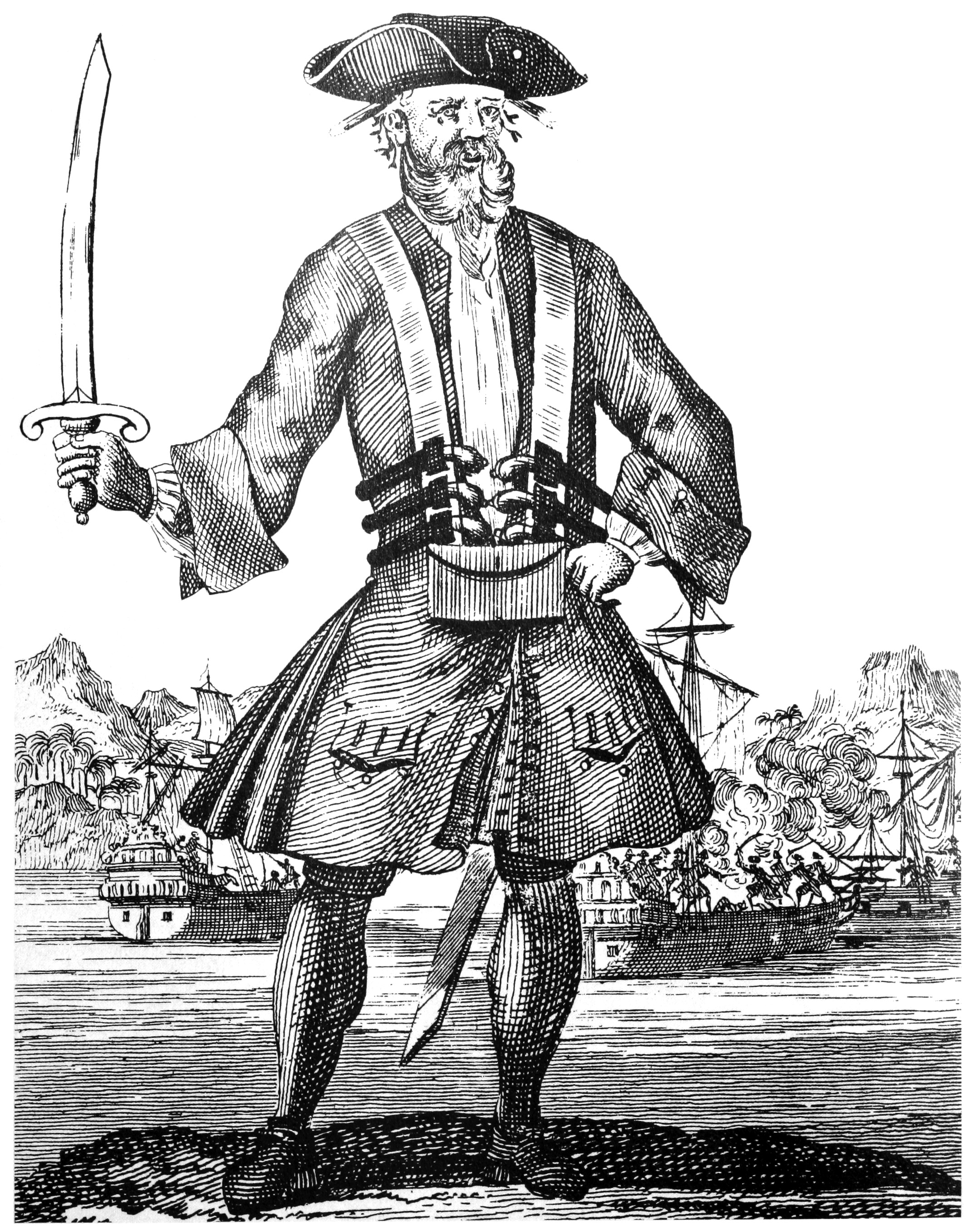 Published in 1724, ''A General History of the Pyrates'' by Charles Johnson (pirate biographer), Captain Charles Johnson provided the standard account of the lives of many pirates in the Golden Age. It influenced pirate literature of Scottish novelists Robert Louis Stevenson (''Treasure Island'') and J. M. Barrie. Many famous English pirates from the Golden Age hailed from the West Country in south west England—the stereotypical West Country English#Social stigma and future of West Country dialect, West Country "Pirates in popular culture#Appearance and mannerisms, pirate accent" was popularised by West Country native Robert Newton's portrayal of Stevenson's Long John Silver in film.Angus Konstam (2008). ''Piracy: The Complete History''. p.313. Osprey Publishing. Retrieved 11 October 2011 The concept of "walking the plank" was popularised by Barrie's ''Peter and Wendy, Peter Pan'', where Captain Hook's pirates helped define the archetype. Davy Jones' Locker, where sailors or ships' remains are consigned to the bottom of the sea, is first recorded by Daniel Defoe in 1726. Johnson's 1724 book gave a mythical status to famous English pirates such as Blackbeard and Calico Jack—Jack's Jolly Roger flag design features a skull with crossed swords.
Published in 1724, ''A General History of the Pyrates'' by Charles Johnson (pirate biographer), Captain Charles Johnson provided the standard account of the lives of many pirates in the Golden Age. It influenced pirate literature of Scottish novelists Robert Louis Stevenson (''Treasure Island'') and J. M. Barrie. Many famous English pirates from the Golden Age hailed from the West Country in south west England—the stereotypical West Country English#Social stigma and future of West Country dialect, West Country "Pirates in popular culture#Appearance and mannerisms, pirate accent" was popularised by West Country native Robert Newton's portrayal of Stevenson's Long John Silver in film.Angus Konstam (2008). ''Piracy: The Complete History''. p.313. Osprey Publishing. Retrieved 11 October 2011 The concept of "walking the plank" was popularised by Barrie's ''Peter and Wendy, Peter Pan'', where Captain Hook's pirates helped define the archetype. Davy Jones' Locker, where sailors or ships' remains are consigned to the bottom of the sea, is first recorded by Daniel Defoe in 1726. Johnson's 1724 book gave a mythical status to famous English pirates such as Blackbeard and Calico Jack—Jack's Jolly Roger flag design features a skull with crossed swords.
Superstitions
 The Gremlin is part of Royal Air Force folklore dating from the 1920s, with "gremlin" being RAF slang for a mischievous creature that sabotages aircraft, meddling in the plane's equipment. Legendary figures from 19th-century London whose tales have been romanticised include Sweeney Todd, the murderous barber of Fleet Street (accompanied with Mrs. Lovett who sells pies made from Todd's victims), and serial killer Jack the Ripper. On 5 November, people in England make bonfires, set off fireworks and eat toffee apples in Guy Fawkes Night, commemoration of the foiling of Guy Fawkes' Gunpowder Plot, which became an annual event after the Thanksgiving Act of 1606 was passed. Guy Fawkes masks are an emblem for anti-establishment protest groups.
The Gremlin is part of Royal Air Force folklore dating from the 1920s, with "gremlin" being RAF slang for a mischievous creature that sabotages aircraft, meddling in the plane's equipment. Legendary figures from 19th-century London whose tales have been romanticised include Sweeney Todd, the murderous barber of Fleet Street (accompanied with Mrs. Lovett who sells pies made from Todd's victims), and serial killer Jack the Ripper. On 5 November, people in England make bonfires, set off fireworks and eat toffee apples in Guy Fawkes Night, commemoration of the foiling of Guy Fawkes' Gunpowder Plot, which became an annual event after the Thanksgiving Act of 1606 was passed. Guy Fawkes masks are an emblem for anti-establishment protest groups.
Traditional non-religious holidays
National parks, museums, libraries, and galleries
Heritage administration
 Each country has its own body responsible for heritage matters.
English Heritage is the government body with a broad remit of managing the historic sites, artefacts and environments of England. It is currently sponsored by the Department for Culture, Media and Sport. The charity National Trust for Places of Historic Interest or Natural Beauty has a contrasting role. Seventeen of the List of World Heritage Sites of the United Kingdom, UNESCO World Heritage Sites are in England. Some of the best known of these include Hadrian's Wall, Stonehenge, Avebury and Associated Sites, Tower of London, Jurassic Coast, Palace of Westminster, Westminster, Saltaire, Ironbridge Gorge, and Studley Royal Park. The northernmost point of the Roman Empire, Hadrian's Wall, is the largest Roman artefact anywhere: it runs a total of 73 miles in northern England.
Historic Environment Scotland is the executive agency of the Scottish Government, responsible for historic monuments in Scotland, such as Stirling Castle. The Old Town, Edinburgh, Old and New Town, Edinburgh, New Town of Edinburgh is a notable Scottish World Heritage site. Balmoral Castle is the main Scottish residence of the Queen. The Wallace Monument in Stirling contains artifacts believed to have belonged to Sir William Wallace, including the Wallace Sword. The Rob Roy Way, named after Scottish folk hero and outlaw Rob Roy MacGregor, is a long-distance footpath that runs for 92 miles. A statue of Robert the Bruce and a large monument and visitor centre (operated by the National Trust for Scotland) is located in Bannockburn near the site of the Battle of Bannockburn.
Each country has its own body responsible for heritage matters.
English Heritage is the government body with a broad remit of managing the historic sites, artefacts and environments of England. It is currently sponsored by the Department for Culture, Media and Sport. The charity National Trust for Places of Historic Interest or Natural Beauty has a contrasting role. Seventeen of the List of World Heritage Sites of the United Kingdom, UNESCO World Heritage Sites are in England. Some of the best known of these include Hadrian's Wall, Stonehenge, Avebury and Associated Sites, Tower of London, Jurassic Coast, Palace of Westminster, Westminster, Saltaire, Ironbridge Gorge, and Studley Royal Park. The northernmost point of the Roman Empire, Hadrian's Wall, is the largest Roman artefact anywhere: it runs a total of 73 miles in northern England.
Historic Environment Scotland is the executive agency of the Scottish Government, responsible for historic monuments in Scotland, such as Stirling Castle. The Old Town, Edinburgh, Old and New Town, Edinburgh, New Town of Edinburgh is a notable Scottish World Heritage site. Balmoral Castle is the main Scottish residence of the Queen. The Wallace Monument in Stirling contains artifacts believed to have belonged to Sir William Wallace, including the Wallace Sword. The Rob Roy Way, named after Scottish folk hero and outlaw Rob Roy MacGregor, is a long-distance footpath that runs for 92 miles. A statue of Robert the Bruce and a large monument and visitor centre (operated by the National Trust for Scotland) is located in Bannockburn near the site of the Battle of Bannockburn.
 Many of Wales' great castles, such as the Castles and Town Walls of King Edward in Gwynedd and other monuments, are under the care of Cadw, the historic environment service of the Welsh Government. Welsh actor Sir Anthony Hopkins donated millions to the preservation of Snowdonia National Park. The five most frequently visited Welsh castles are Caernarfon Castle, Conwy Castle, Caerphilly Castle, Harlech Castle and Beaumaris Castle. The Northern Ireland Environment Agency promotes and conserves the natural and built environment in Northern Ireland, and the Giant's Causeway on the north-east coast is one of the natural World Heritage sites. Tintagel Castle is a popular tourist destination in Cornwall, with the castle associated with the legend of King Arthur since the 12th century. There are 15 National parks of the United Kingdom, National Parks, including the Lake District in England, Snowdonia in Wales, and Loch Lomond and The Trossachs National Park in Scotland
Many of Wales' great castles, such as the Castles and Town Walls of King Edward in Gwynedd and other monuments, are under the care of Cadw, the historic environment service of the Welsh Government. Welsh actor Sir Anthony Hopkins donated millions to the preservation of Snowdonia National Park. The five most frequently visited Welsh castles are Caernarfon Castle, Conwy Castle, Caerphilly Castle, Harlech Castle and Beaumaris Castle. The Northern Ireland Environment Agency promotes and conserves the natural and built environment in Northern Ireland, and the Giant's Causeway on the north-east coast is one of the natural World Heritage sites. Tintagel Castle is a popular tourist destination in Cornwall, with the castle associated with the legend of King Arthur since the 12th century. There are 15 National parks of the United Kingdom, National Parks, including the Lake District in England, Snowdonia in Wales, and Loch Lomond and The Trossachs National Park in Scotland
Museums and galleries
 The British Museum in London with its collection of more than seven million objects, is one of the largest and most comprehensive in the world, and sourced from every continent, illustrating and documenting the story of human culture from its beginning to the present. On display since 1802, the Rosetta Stone is the most viewed attraction. The Natural History Museum, London was established by Richard Owen (who coined the term "dinosaur") to display the national collection of dinosaur fossils and other biological and geological exhibits.Rupke, N. (1994). ''Richard Owen: A Victorian Naturalist''. New Haven: Yale University Press. The National Museums of Scotland bring together national collections in Scotland. National Museum Wales, Amgueddfa Cymru – National Museum Wales comprises eight museums in Wales. National Museums Northern Ireland has four museums in Northern Ireland including the Ulster Museum.
The Titanic Belfast museum, a visitor attraction in the Titanic Quarter, east Belfast, Northern Ireland on the regenerated site of the shipyard where ''RMS Titanic, Titanic'' was built, was opened to the public in 2012. The architecture is a tribute to ''Titanic'' itself, with the external facades a nod to the enormous hull of the ocean liner.
The first Madame Tussauds wax museum opened in London in 1835, and today displays waxworks of famous people from various fields, including royalty (Princess Diana), historical figures (Henry VIII), sport (David Beckham), music (Freddie Mercury), literature (
The British Museum in London with its collection of more than seven million objects, is one of the largest and most comprehensive in the world, and sourced from every continent, illustrating and documenting the story of human culture from its beginning to the present. On display since 1802, the Rosetta Stone is the most viewed attraction. The Natural History Museum, London was established by Richard Owen (who coined the term "dinosaur") to display the national collection of dinosaur fossils and other biological and geological exhibits.Rupke, N. (1994). ''Richard Owen: A Victorian Naturalist''. New Haven: Yale University Press. The National Museums of Scotland bring together national collections in Scotland. National Museum Wales, Amgueddfa Cymru – National Museum Wales comprises eight museums in Wales. National Museums Northern Ireland has four museums in Northern Ireland including the Ulster Museum.
The Titanic Belfast museum, a visitor attraction in the Titanic Quarter, east Belfast, Northern Ireland on the regenerated site of the shipyard where ''RMS Titanic, Titanic'' was built, was opened to the public in 2012. The architecture is a tribute to ''Titanic'' itself, with the external facades a nod to the enormous hull of the ocean liner.
The first Madame Tussauds wax museum opened in London in 1835, and today displays waxworks of famous people from various fields, including royalty (Princess Diana), historical figures (Henry VIII), sport (David Beckham), music (Freddie Mercury), literature (Libraries
The British Library in London is the national library and is one of the world's largest research libraries, holding over 150 million items in all known languages and formats; including around 25 million books. The library has two of the four remaining copies of the original Magna Carta (the other two copies are held in Lincoln Castle and Salisbury Cathedral) and has a room devoted solely to them. The British Library Sound Archive has over six million recordings (many from the BBC Sound Archive, including Winston Churchill's wartime speeches.) The National Library of Scotland in Edinburgh holds 7 million books, 14 million printed items (such as the last letter written by Mary, Queen of Scots) and over 2 million maps. The National Library of Wales is the national legal deposit library of Wales, and holds over 6.5 million books, portraits, maps and photographic images in Wales.Historical markers
 Blue plaques, the oldest historical marker scheme in the world, are permanent signs installed in a public places to commemorate a link between that location and a famous person or event. The scheme was the brainchild of politician William Ewart (British politician), William Ewart in 1863 and was initiated in 1866. It was formally established by the Royal Society of Arts, Society of Arts in 1867, and since 1986 has been run by English Heritage.
The first plaque was unveiled in 1867 to commemorate Lord Byron at his birthplace, 24 Holles Street, Cavendish Square, London. Events commemorated by plaques include John Logie Baird's first demonstration of television at 22 Frith Street, Westminster, W1, London, the first four-minute mile, sub 4-minute mile run by Roger Bannister on 6 May 1954 at Oxford University's Iffley Road Track, and a sweet shop in Llandaff, Cardiff that commemorates the mischief by a young Roald Dahl who put a mouse in the gobstoppers jar.
Blue plaques, the oldest historical marker scheme in the world, are permanent signs installed in a public places to commemorate a link between that location and a famous person or event. The scheme was the brainchild of politician William Ewart (British politician), William Ewart in 1863 and was initiated in 1866. It was formally established by the Royal Society of Arts, Society of Arts in 1867, and since 1986 has been run by English Heritage.
The first plaque was unveiled in 1867 to commemorate Lord Byron at his birthplace, 24 Holles Street, Cavendish Square, London. Events commemorated by plaques include John Logie Baird's first demonstration of television at 22 Frith Street, Westminster, W1, London, the first four-minute mile, sub 4-minute mile run by Roger Bannister on 6 May 1954 at Oxford University's Iffley Road Track, and a sweet shop in Llandaff, Cardiff that commemorates the mischief by a young Roald Dahl who put a mouse in the gobstoppers jar.
Science and technology
From the time of the Scientific Revolution, England and Scotland, and thereafter the United Kingdom, have been prominent in world science, scientific and technology, technological development. The Royal Society serves as the national academy for sciences, with members drawn from different institutions and disciplines. Formed in 1660, it is one of the oldest learned society, learned societies still in existence. Sir Isaac Newton's publication of the ''Philosophiae Naturalis Principia Mathematica, Principia Mathematica'' ushered in what is recognisable as modern physics. The first edition of 1687 and the second edition of 1713 framed the scientific context of the foundation of the United Kingdom. He realised that the same force is responsible for movements of celestial and terrestrial bodies, namely gravity. He is the father of classical mechanics, formulated as his Newton's laws of motion, three laws and as the co-inventor (with Gottfried Leibniz) of differential calculus. He also created the binomial theorem, worked extensively on optics, and created a Newton's law of cooling, law of cooling. Figures from the UK have contributed to the development of most major branches of science. John Napier introduced logarithms in the early 17th century as a means to simplify calculations. Michael Faraday and James Clerk Maxwell unified the electric and magnetic forces in what are now known as Maxwell's equations. Following his publication of ''A Dynamical Theory of the Electromagnetic Field'' in 1865, Maxwell predicted the existence of radio waves in 1867. James Joule worked on thermodynamics and is often credited with the discovery of the principle of conservation of energy.
Naturalist Charles Darwin wrote ''On the Origin of Species'' and discovered the principle of evolution by natural selection. James Hutton, founder of modern geology, worked on the age of the Earth (deep time) which forms a key element of Darwin's theory. Other important geologists include Charles Lyell, author of ''Principles of Geology'', who also coined the term Pleistocene, and Adam Sedgwick, who proposed (and coined) the name of the Cambrian Period. William Thomson, 1st Baron Kelvin, William Thomson (Baron Kelvin) drew important conclusions in the field of thermodynamics and invented the Kelvin scale of absolute zero. Paul Dirac was one of the pioneers of quantum mechanics. Botanist Robert Brown (Scottish botanist from Montrose), Robert Brown discovered the random movement of particles suspended in a fluid (Brownian motion). John Stewart Bell created Bell's Theorem. Harold Kroto discovered buckminsterfullerene.
Other 19th- and early 20th-century British pioneers in their field include Joseph Lister, 1st Baron Lister, Joseph Lister (Antiseptic#Usage in surgery, antiseptic surgery), Edward Jenner (vaccination), Richard Owen (palaeontology, coined the term Dinosaur), Florence Nightingale (nursing), Sir George Cayley (aerodynamics), William Fox Talbot (photography), and Howard Carter (Archaeology, modern archaeology, discovered Tutankhamun).
Scholarly descriptions of dinosaur bones first appeared in the late 17th-century England. Between 1815 and 1824, William Buckland discovered fossils of ''Megalosaurus'' and became the first person to describe a dinosaur in a scientific journal. The second dinosaur genus to be identified, ''Iguanodon'', was discovered in 1822 by Mary Ann Mantell. In 1832, Gideon Mantell discovered fossils of a third dinosaur, ''Hylaeosaurus''. Owen recognised that the remains of the three new species that had been found so far shared a number of distinctive features. He decided to present them as a distinct taxonomic group, dinosaurs.
John Harrison invented the marine chronometer, a key piece in solving the problem of accurately establishing longitude at sea, thus revolutionising and extending the possibility of safe long-distance sea travel. The most celebrated British explorers include James Cook, Walter Raleigh, Sir Francis Drake, Henry Hudson, George Vancouver, Sir John Franklin, David Livingstone, John Smith (explorer), Captain John Smith, Robert Falcon Scott, Lawrence Oates and Ernest Shackleton. The aquarium craze began in Victorian England when Philip Henry Gosse created and stocked the first public aquarium at London Zoo in 1853, and coined the term "aquarium" when he published ''The Aquarium: An Unveiling of the Wonders of the Deep Sea'' in 1854. Robert FitzRoy pioneered weather forecasting: the first daily weather forecasts were published in ''The Times'' in 1861.
A crucial advance in the development of the Flush toilet#Development of the flush toilet, flush toilet was the Trap (plumbing), S-trap invented by Alexander Cumming in 1775 – it uses the standing water to seal the outlet of the bowl, preventing the escape of foul air from the sewer. In 1824 Charles Macintosh invented the waterproof raincoat; the Mackintosh (mac) is named after him. William Sturgeon invented the electromagnet in 1824. The first commercial electrical telegraph was co-invented by Sir William Fothergill Cooke and Charles Wheatstone. They patented it in May 1837 as an alarm system, and it was first successfully demonstrated on 25 July 1837 between Euston railway station, Euston and Camden Town in London.
Postal reformer Rowland Hill (postal reformer), Sir Rowland Hill is regarded as the creator of the modern postal service and the inventor of the postage stamp (Penny Black) — with his solution of pre-payment facilitating the safe, speedy and cheap transfer of letters."Rowland Hill's Postal Reforms"
Figures from the UK have contributed to the development of most major branches of science. John Napier introduced logarithms in the early 17th century as a means to simplify calculations. Michael Faraday and James Clerk Maxwell unified the electric and magnetic forces in what are now known as Maxwell's equations. Following his publication of ''A Dynamical Theory of the Electromagnetic Field'' in 1865, Maxwell predicted the existence of radio waves in 1867. James Joule worked on thermodynamics and is often credited with the discovery of the principle of conservation of energy.
Naturalist Charles Darwin wrote ''On the Origin of Species'' and discovered the principle of evolution by natural selection. James Hutton, founder of modern geology, worked on the age of the Earth (deep time) which forms a key element of Darwin's theory. Other important geologists include Charles Lyell, author of ''Principles of Geology'', who also coined the term Pleistocene, and Adam Sedgwick, who proposed (and coined) the name of the Cambrian Period. William Thomson, 1st Baron Kelvin, William Thomson (Baron Kelvin) drew important conclusions in the field of thermodynamics and invented the Kelvin scale of absolute zero. Paul Dirac was one of the pioneers of quantum mechanics. Botanist Robert Brown (Scottish botanist from Montrose), Robert Brown discovered the random movement of particles suspended in a fluid (Brownian motion). John Stewart Bell created Bell's Theorem. Harold Kroto discovered buckminsterfullerene.
Other 19th- and early 20th-century British pioneers in their field include Joseph Lister, 1st Baron Lister, Joseph Lister (Antiseptic#Usage in surgery, antiseptic surgery), Edward Jenner (vaccination), Richard Owen (palaeontology, coined the term Dinosaur), Florence Nightingale (nursing), Sir George Cayley (aerodynamics), William Fox Talbot (photography), and Howard Carter (Archaeology, modern archaeology, discovered Tutankhamun).
Scholarly descriptions of dinosaur bones first appeared in the late 17th-century England. Between 1815 and 1824, William Buckland discovered fossils of ''Megalosaurus'' and became the first person to describe a dinosaur in a scientific journal. The second dinosaur genus to be identified, ''Iguanodon'', was discovered in 1822 by Mary Ann Mantell. In 1832, Gideon Mantell discovered fossils of a third dinosaur, ''Hylaeosaurus''. Owen recognised that the remains of the three new species that had been found so far shared a number of distinctive features. He decided to present them as a distinct taxonomic group, dinosaurs.
John Harrison invented the marine chronometer, a key piece in solving the problem of accurately establishing longitude at sea, thus revolutionising and extending the possibility of safe long-distance sea travel. The most celebrated British explorers include James Cook, Walter Raleigh, Sir Francis Drake, Henry Hudson, George Vancouver, Sir John Franklin, David Livingstone, John Smith (explorer), Captain John Smith, Robert Falcon Scott, Lawrence Oates and Ernest Shackleton. The aquarium craze began in Victorian England when Philip Henry Gosse created and stocked the first public aquarium at London Zoo in 1853, and coined the term "aquarium" when he published ''The Aquarium: An Unveiling of the Wonders of the Deep Sea'' in 1854. Robert FitzRoy pioneered weather forecasting: the first daily weather forecasts were published in ''The Times'' in 1861.
A crucial advance in the development of the Flush toilet#Development of the flush toilet, flush toilet was the Trap (plumbing), S-trap invented by Alexander Cumming in 1775 – it uses the standing water to seal the outlet of the bowl, preventing the escape of foul air from the sewer. In 1824 Charles Macintosh invented the waterproof raincoat; the Mackintosh (mac) is named after him. William Sturgeon invented the electromagnet in 1824. The first commercial electrical telegraph was co-invented by Sir William Fothergill Cooke and Charles Wheatstone. They patented it in May 1837 as an alarm system, and it was first successfully demonstrated on 25 July 1837 between Euston railway station, Euston and Camden Town in London.
Postal reformer Rowland Hill (postal reformer), Sir Rowland Hill is regarded as the creator of the modern postal service and the inventor of the postage stamp (Penny Black) — with his solution of pre-payment facilitating the safe, speedy and cheap transfer of letters."Rowland Hill's Postal Reforms"British Postal Museum. Retrieved 2 October 2017 Hill's colleague Sir Henry Cole introduced the world's first commercial Christmas card#History, Christmas card in 1843. In 1851 George Biddell Airy, Sir George Airy established the Royal Observatory, Greenwich, London, as the location of the prime meridian where longitude is defined to be 0° (one of the two lines that divide the Earth into the Eastern and Western Hemispheres). George Boole authored ''The Laws of Thought'' which contains Boolean algebra. Forming the mathematical foundations of computing, Boolean logic laid the foundations for the information age.
 Historically, many of the UK's greatest scientists have been based at either Oxford University, Oxford or Cambridge University, with laboratories such as the Cavendish Laboratory in Cambridge and the Clarendon Laboratory in Oxford becoming famous in their own right. In modern times, other institutions such as the Red Brick university, Red Brick and New Universities are catching up with Oxbridge. For instance, Lancaster University has a global reputation for work in low temperature physics.
Technologically, the UK is also amongst the world's leaders. Historically, it was at the forefront of the
Historically, many of the UK's greatest scientists have been based at either Oxford University, Oxford or Cambridge University, with laboratories such as the Cavendish Laboratory in Cambridge and the Clarendon Laboratory in Oxford becoming famous in their own right. In modern times, other institutions such as the Red Brick university, Red Brick and New Universities are catching up with Oxbridge. For instance, Lancaster University has a global reputation for work in low temperature physics.
Technologically, the UK is also amongst the world's leaders. Historically, it was at the forefront of the  Probably the greatest driver behind the modern use of concrete was Smeaton's Tower built by John Smeaton in the 1750s. The third Eddystone Lighthouse (the world's first open ocean lighthouse), Smeaton pioneered the use of hydraulic lime in concrete. Scotsman Robert Stevenson (civil engineer), Robert Stevenson constructed the Bell Rock Lighthouse in the early 1800s. Situated 11 miles off east Scotland, it is the world's oldest surviving sea-washed lighthouse. Portland cement, the most common type of cement in general use around the world as a basic ingredient of concrete, was developed in England in the 19th century. It was coined by Joseph Aspdin in 1824 (he named it after Portland stone), and further developed by his son William Aspdin in the 1840s.
Probably the greatest driver behind the modern use of concrete was Smeaton's Tower built by John Smeaton in the 1750s. The third Eddystone Lighthouse (the world's first open ocean lighthouse), Smeaton pioneered the use of hydraulic lime in concrete. Scotsman Robert Stevenson (civil engineer), Robert Stevenson constructed the Bell Rock Lighthouse in the early 1800s. Situated 11 miles off east Scotland, it is the world's oldest surviving sea-washed lighthouse. Portland cement, the most common type of cement in general use around the world as a basic ingredient of concrete, was developed in England in the 19th century. It was coined by Joseph Aspdin in 1824 (he named it after Portland stone), and further developed by his son William Aspdin in the 1840s.
 The UK has produced some of the most famous ships in the world: Harland and Wolff in Belfast built the as well as her sister ships and HMHS Britannic, RMS ''Britannic''; in Clydebank John Brown and Company built the , and ; ships built in England include the ''Mary Rose'' (King Henry VIII of England, Henry VIII's warship), the ''Golden Hind'' (Sir Francis Drake's ship for the Francis Drake's circumnavigation, circumnavigation of the globe between 1577 and 1580), HMS Victory, HMS ''Victory'' (Horatio Nelson, 1st Viscount Nelson, Lord Nelson's flagship at the Battle of Trafalgar in 1805), and HMS Beagle, HMS ''Beagle'' (ship used in Charles Darwin's Second voyage of HMS Beagle, five-year voyage). Other important British ships include HMS Endeavour, HMS ''Endeavour'' (James Cook's ship in his First voyage of James Cook, first voyage of discovery), HMS Challenger (1858), HMS ''Challenger'' (first global marine research expedition: the Challenger expedition, ''Challenger'' expedition), and RRS Discovery, ''Discovery'' (carried Robert Falcon Scott and Ernest Shackleton in the Discovery Expedition, their first successful journey to the Antarctic). The Royal Navy troopship is known for the first appearance of the "women and children first" protocol.
Since then, the UK has continued this tradition of technical creativity. Alan Turing (leading role in the creation of the modern computer), Scottish inventor Alexander Graham Bell (the first practical telephone), John Logie Baird (world's first working television system, first electronic colour television), Frank Whittle (co-invented the jet engine) — powered by Whittle's turbojet engines, the Gloster Meteor was the first British jet aircraft, jet Fighter aircraft, fighter and the Allies of World War II, Allies' only jet aircraft to achieve combat operations during World War II, Charles Babbage (devised the idea of the computer), Alexander Fleming (discovered penicillin). The UK remains one of the leading providers of technological innovations, providing inventions as diverse as the World Wide Web by Sir Tim Berners-Lee, and Viagra by British scientists at Pfizer's Sandwich, Kent, Sandwich, Kent. Sir Alec Jeffreys pioneered DNA fingerprinting. Pioneers of fertility treatment Patrick Christopher Steptoe, Patrick Steptoe and Robert Geoffrey Edwards, Robert Edwards, achieved conception through IVF (world's first "test tube baby") in 1978.
The UK has produced some of the most famous ships in the world: Harland and Wolff in Belfast built the as well as her sister ships and HMHS Britannic, RMS ''Britannic''; in Clydebank John Brown and Company built the , and ; ships built in England include the ''Mary Rose'' (King Henry VIII of England, Henry VIII's warship), the ''Golden Hind'' (Sir Francis Drake's ship for the Francis Drake's circumnavigation, circumnavigation of the globe between 1577 and 1580), HMS Victory, HMS ''Victory'' (Horatio Nelson, 1st Viscount Nelson, Lord Nelson's flagship at the Battle of Trafalgar in 1805), and HMS Beagle, HMS ''Beagle'' (ship used in Charles Darwin's Second voyage of HMS Beagle, five-year voyage). Other important British ships include HMS Endeavour, HMS ''Endeavour'' (James Cook's ship in his First voyage of James Cook, first voyage of discovery), HMS Challenger (1858), HMS ''Challenger'' (first global marine research expedition: the Challenger expedition, ''Challenger'' expedition), and RRS Discovery, ''Discovery'' (carried Robert Falcon Scott and Ernest Shackleton in the Discovery Expedition, their first successful journey to the Antarctic). The Royal Navy troopship is known for the first appearance of the "women and children first" protocol.
Since then, the UK has continued this tradition of technical creativity. Alan Turing (leading role in the creation of the modern computer), Scottish inventor Alexander Graham Bell (the first practical telephone), John Logie Baird (world's first working television system, first electronic colour television), Frank Whittle (co-invented the jet engine) — powered by Whittle's turbojet engines, the Gloster Meteor was the first British jet aircraft, jet Fighter aircraft, fighter and the Allies of World War II, Allies' only jet aircraft to achieve combat operations during World War II, Charles Babbage (devised the idea of the computer), Alexander Fleming (discovered penicillin). The UK remains one of the leading providers of technological innovations, providing inventions as diverse as the World Wide Web by Sir Tim Berners-Lee, and Viagra by British scientists at Pfizer's Sandwich, Kent, Sandwich, Kent. Sir Alec Jeffreys pioneered DNA fingerprinting. Pioneers of fertility treatment Patrick Christopher Steptoe, Patrick Steptoe and Robert Geoffrey Edwards, Robert Edwards, achieved conception through IVF (world's first "test tube baby") in 1978.
 The prototype tank was constructed at William Foster & Co. in Lincoln, England, Lincoln in 1915, with leading roles played by Major Walter Gordon Wilson who designed the gearbox and developed practical tracks and by William Tritton whose company built it. This was a prototype of the Mark I tank, the first tank used in combat in September 1916 during WWI. The First Lord of the Admiralty, Winston Churchill, was credited by Prime Minister David Lloyd George as being the driving force behind their production. Allan Beckett designed the 'Whale' floating roadway, crucial to the success of the Mulberry harbour used in the invasion of Normandy in WWII. In 1918, became the world's first aircraft carrier capable of launching and recovering naval aircraft, and in WWII, HMS Ark Royal (91), HMS ''Ark Royal'' was involved in the first aerial and U-boat kills of the war, as well as the crippling of the German battleship the German battleship Bismarck, ''Bismarck'' in May 1941. In 1932, Cambridge engineer Francis Thomas Bacon invented the alkaline fuel cell which is used to generate power for space capsules and satellites.
Introduced in 1952, the de Havilland de Havilland Comet, Comet was the world's first commercial jet airliner."On This Day: Comet inaugurates the jet age."
The prototype tank was constructed at William Foster & Co. in Lincoln, England, Lincoln in 1915, with leading roles played by Major Walter Gordon Wilson who designed the gearbox and developed practical tracks and by William Tritton whose company built it. This was a prototype of the Mark I tank, the first tank used in combat in September 1916 during WWI. The First Lord of the Admiralty, Winston Churchill, was credited by Prime Minister David Lloyd George as being the driving force behind their production. Allan Beckett designed the 'Whale' floating roadway, crucial to the success of the Mulberry harbour used in the invasion of Normandy in WWII. In 1918, became the world's first aircraft carrier capable of launching and recovering naval aircraft, and in WWII, HMS Ark Royal (91), HMS ''Ark Royal'' was involved in the first aerial and U-boat kills of the war, as well as the crippling of the German battleship the German battleship Bismarck, ''Bismarck'' in May 1941. In 1932, Cambridge engineer Francis Thomas Bacon invented the alkaline fuel cell which is used to generate power for space capsules and satellites.
Introduced in 1952, the de Havilland de Havilland Comet, Comet was the world's first commercial jet airliner."On This Day: Comet inaugurates the jet age."''BBC News,'' 2 May 1952. Retrieved 2 September 2021. Operated by British Overseas Airways Corporation (which merged with other British operators to form today's British Airways), on 2 May 1952 the flight registered G-ALYS took off with fare-paying passengers and inaugurated scheduled service from London to Johannesburg. In 1952, ''OXO (video game), OXO'' (or ''Noughts and Crosses''), created by computer scientist Sandy Douglas, Alexander S. Douglas, is regarded as a contender for the first video game. In ''OXO'', the computer player could play perfect games of noughts and crosses against a human opponent. In the 1960s, John Shepherd-Barron invented the Automated teller machine, cash machine (ATM) and James Goodfellow invented Personal identification number (PIN) technology, and on 27 June 1967, the first cash machine was established outside a branch of Barclays Bank in Enfield Town, Enfield, north London. Dolly (sheep), Dolly the sheep, the first mammal successfully Cloning#Dolly the sheep, cloned from an adult somatic cell (by scientists at Roslin Institute in Edinburgh), became a celebrity in the 1990s.
Industrial Revolution
 The
The Cars
The UK has had a long history of car making. Some of the best known British brands are Rolls-Royce Limited, Rolls-Royce, Bentley, Aston Martin, Jaguar Cars, Jaguar, Land Rover, MG Cars, MG, and the Mini. Rolls-Royce was founded by Charles Stewart Rolls and Sir Frederick Henry Royce in 1906. In addition to the company's reputation for superior engineering quality in its cars, Rolls-Royce Limited was known for manufacturing the high-powered "R" engines, including the iconic Rolls-Royce Merlin aero engine which was used for many World War II aircraft. Bentley Motors Limited was founded by W. O. Bentley in 1919 in Cricklewood, North London, and, like Rolls-Royce, is regarded as a British luxury automobile icon. Aston Martin was founded in 1913 by Lionel Martin and Robert Bamford, and became associated with luxury grand touring cars in the 1950s and 1960s, and with the fictional British spy James Bond. Jaguar was founded in 1922. The Jaguar E-Type sports car was released in 1961; Enzo Ferrari called it "the most beautiful car ever made". Jaguar has, in recent years, manufactured cars for the Prime Minister of the United Kingdom, British Prime Minister. The company also holds Royal warrant of appointment (United Kingdom), royal warrants from Queen Elizabeth II and Charles, Prince of Wales, Prince Charles. The Land Rover launched in 1948 and specialises in four-wheel-drive. Many models have been developed for the Ministry of Defence (United Kingdom), Ministry of Defence (MoD). The Mini was released by the British Motor Corporation in 1959 and became a 1960s cultural icon. The performance versions, the Mini Cooper, was a successful rally car. The distinctive two-door Mini was designed for BMC by Sir Alec Issigonis. It has been named Britain's favourite car in a poll.Religion
Anglican Communion, Anglican churches remain the largest faith group in each country of the UK except Scotland, where Anglicanism is a small minority. The Presbyterian Church of Scotland is the national church in Scotland. Following this is Roman Catholicism and religions including Islam, Hinduism, Sikhism, Judaism, and Buddhism. Today British Jews number around 300,000; the UK has the Jewish population#By country, fifth largest Jewish community worldwide. William Tyndale's 1520s translation of the Bible was the first to be printed in English, and was a model for subsequent English translations, notably the King James Version in 1611. The Book of Common Prayer of 1549 was the first prayer book to include the complete forms of service for daily and Sunday worship in English, and the marriage and burial rites have found their way into those of other denominations and into the English language.
In 17th-century England, the Puritans condemned the celebration of Christmas.Durston, Chris, "Lords of Misrule: The Puritan War on Christmas 1642–60", ''History Today'', December 1985, 35 (12) pp. 7 – 14. In contrast, the Anglican Church "pressed for a more elaborate observance of feasts, penitential seasons, and saints' days. The calendar reform became a major point of tension between the Anglicans and Puritans." The Catholic Church also responded, promoting the festival in a more religiously orientated form. King Charles I of England directed his noblemen and gentry to return to their landed estates in midwinter to keep up their old-style Christmas generosity. Following the Roundhead, Parliamentarian victory over Charles I in the English Civil War, Puritan rulers banned Christmas in 1647.
William Tyndale's 1520s translation of the Bible was the first to be printed in English, and was a model for subsequent English translations, notably the King James Version in 1611. The Book of Common Prayer of 1549 was the first prayer book to include the complete forms of service for daily and Sunday worship in English, and the marriage and burial rites have found their way into those of other denominations and into the English language.
In 17th-century England, the Puritans condemned the celebration of Christmas.Durston, Chris, "Lords of Misrule: The Puritan War on Christmas 1642–60", ''History Today'', December 1985, 35 (12) pp. 7 – 14. In contrast, the Anglican Church "pressed for a more elaborate observance of feasts, penitential seasons, and saints' days. The calendar reform became a major point of tension between the Anglicans and Puritans." The Catholic Church also responded, promoting the festival in a more religiously orientated form. King Charles I of England directed his noblemen and gentry to return to their landed estates in midwinter to keep up their old-style Christmas generosity. Following the Roundhead, Parliamentarian victory over Charles I in the English Civil War, Puritan rulers banned Christmas in 1647.
 Protests followed as pro-Christmas rioting broke out in several cities; and for weeks Canterbury was controlled by the rioters, who decorated doorways with holly and shouted Royalism, royalist slogans. The book, ''The Vindication of Christmas'' (London, 1652), argued against the Puritans, and notes old English Christmas traditions: dinner, roast apples on the fire, card playing, dances with "plow-boys" and "maidservants", old Father Christmas and carol singing. The English Restoration, Restoration of Charles II of England, King Charles II in 1660 ended the ban.
Following the Restoration, ''Poor Robins Almanack'' contained the lines:
:Now thanks to God for Charles return
:Whose absence made old Christmas mourn
:For then we scarcely did it know
:Whether it Christmas were or no.
The diary of James Woodforde, from the latter half of the 18th century, details Christmas observance and celebrations associated with the season over a number of years.
In the early 19th century, writers imagined Tudor period, Tudor Christmas as a time of heartfelt celebration. In 1843,
Protests followed as pro-Christmas rioting broke out in several cities; and for weeks Canterbury was controlled by the rioters, who decorated doorways with holly and shouted Royalism, royalist slogans. The book, ''The Vindication of Christmas'' (London, 1652), argued against the Puritans, and notes old English Christmas traditions: dinner, roast apples on the fire, card playing, dances with "plow-boys" and "maidservants", old Father Christmas and carol singing. The English Restoration, Restoration of Charles II of England, King Charles II in 1660 ended the ban.
Following the Restoration, ''Poor Robins Almanack'' contained the lines:
:Now thanks to God for Charles return
:Whose absence made old Christmas mourn
:For then we scarcely did it know
:Whether it Christmas were or no.
The diary of James Woodforde, from the latter half of the 18th century, details Christmas observance and celebrations associated with the season over a number of years.
In the early 19th century, writers imagined Tudor period, Tudor Christmas as a time of heartfelt celebration. In 1843, Politics and government
The Crown and parliament
The UK has a parliamentary system, parliamentary government based on the Westminster system that has been emulated around the world – a legacy of the A prominent part of British political culture, Prime Minister's Questions – often referred to as "PMQs" – is held every Wednesday at noon when the House of Commons is sitting. The Prime Minister of the United Kingdom, Prime Minister spends around half an hour responding to questions from Member of Parliament (United Kingdom), Members of Parliament (MPs). In questioning the policies of government ministers, MP Amber Rudd states "PMQs is central to our democracy". Due to the drama of the sessions, PMQs is among the best-known parliamentary business in the country. It is broadcast live on BBC News, Sky News and BBC Parliament television channels, as well as streamed online by many news outlets via numerous services, such as Twitch (service), Twitch or YouTube.
The United Kingdom has an uncodified constitution, the Constitution of the United Kingdom, consisting mostly of a collection of disparate written sources, including statutes, judge-made case law, and international treaties. As there is no technical difference between ordinary statutes and "constitutional law," the Parliament of the United Kingdom, British Parliament can perform "constitutional reform" simply by passing Act of Parliament, Acts of Parliament and thus has the political power to change or abolish almost any written or unwritten element of the constitution. However, no Parliament can pass laws that future Parliaments cannot change.
A prominent part of British political culture, Prime Minister's Questions – often referred to as "PMQs" – is held every Wednesday at noon when the House of Commons is sitting. The Prime Minister of the United Kingdom, Prime Minister spends around half an hour responding to questions from Member of Parliament (United Kingdom), Members of Parliament (MPs). In questioning the policies of government ministers, MP Amber Rudd states "PMQs is central to our democracy". Due to the drama of the sessions, PMQs is among the best-known parliamentary business in the country. It is broadcast live on BBC News, Sky News and BBC Parliament television channels, as well as streamed online by many news outlets via numerous services, such as Twitch (service), Twitch or YouTube.
The United Kingdom has an uncodified constitution, the Constitution of the United Kingdom, consisting mostly of a collection of disparate written sources, including statutes, judge-made case law, and international treaties. As there is no technical difference between ordinary statutes and "constitutional law," the Parliament of the United Kingdom, British Parliament can perform "constitutional reform" simply by passing Act of Parliament, Acts of Parliament and thus has the political power to change or abolish almost any written or unwritten element of the constitution. However, no Parliament can pass laws that future Parliaments cannot change.
The law
British constitutional documents include Magna Carta (foundation of the "great writ" ''Habeas corpus'' — safeguarding individual freedom against arbitrary state action), the Bill of Rights 1689 (one provision granting freedom of speech in Parliament), Petition of Right, Habeas Corpus Act 1679 and Parliament Acts 1911 and 1949. A separate but similar document, the Claim of Right Act 1689, Claim of Right Act, applies in Scotland. Jurist Albert Venn Dicey wrote that the British Habeas Corpus Acts "declare no principle and define no rights, but they are for practical purposes worth a hundred constitutional articles guaranteeing individual liberty". An advocate of the "unwritten constitution", Dicey stated English rights were embedded in the general English common law of personal liberty, and "the institutions and manners of the nation". According to 2016 figures from the Ministry of Justice (United Kingdom), Ministry of Justice, there is a 35% chance of people in England and Wales being summoned for jury duty over the course of their lifetime. In Scotland the percentage is higher due to Scotland having a lower population as well having juries made up of fifteen people as opposed to twelve in England and Wales. The 17th-century English patriot John Hampden was a leading parliamentarian involved in challenging the authority of Charles I of England, Charles I when he refused to be taxed for ship money in 1637, and was one of the Five Members whose attempted unconstitutional arrest by the King in the House of Commons of England, House of Commons in 1642 sparked the English Civil War. The wars established the constitutional rights of parliament, a concept legally established as part of the Glorious Revolution in 1688 and the subsequent Bill of Rights 1689. Since that time, no British monarch has entered the House of Commons when it is sitting."Democracy Live: Black Rod"
The 17th-century English patriot John Hampden was a leading parliamentarian involved in challenging the authority of Charles I of England, Charles I when he refused to be taxed for ship money in 1637, and was one of the Five Members whose attempted unconstitutional arrest by the King in the House of Commons of England, House of Commons in 1642 sparked the English Civil War. The wars established the constitutional rights of parliament, a concept legally established as part of the Glorious Revolution in 1688 and the subsequent Bill of Rights 1689. Since that time, no British monarch has entered the House of Commons when it is sitting."Democracy Live: Black Rod"BBC. Retrieved 6 August 2008 Hampden is annually commemorated at the State Opening of Parliament by the British monarch when the doors of the House of Commons of the United Kingdom, House of Commons are slammed in the face of the Black Rod, monarch's messenger, symbolising the rights of Parliament and its independence from the monarch. Other important British political figures include Sir Edward Coke, 17th-century jurist; the legal directive that nobody may enter a home, which in the 17th-century would typically have been male owned, unless by the owners invitation or consent, was established as common law in Coke's ''Institutes of the Lawes of England''. "For a man's house is his castle, et domus sua cuique est tutissimum refugium [and each man's home is his safest refuge]." It is the origin of the famous dictum, “Property#Whether and to what extent the state may interfere with property, an Englishman's home is his castle”. Sir William Blackstone, 18th-century jurist, judge and politician best known for his ''Commentaries on the Laws of England'', containing his formulation: "It is better that ten guilty persons escape than that one innocent suffer", a principle that government and the courts must err on the side of innocence, Emmeline Pankhurst, leading suffragette which helped win women the women's suffrage, right to vote, William Wilberforce, leading parliamentary abolitionist. An influential thinker in the history of Classical liberalism, liberalism, 19th century philosopher, political economist and politician John Stuart Mill justified the freedom of the individual in opposition to unlimited state and social control. A member of the Liberal Party (UK), Liberal Party, he was also the first Member of Parliament to call for women's suffrage.
 Robert Walpole is generally regarded as the first British Prime Minister (1721–1742). Twice Prime Minister, Sir Robert Peel, founded the Conservative party (which was expanded by Benjamin Disraeli), and created the modern police force. Margaret Thatcher was the first female British Prime Minister (1979–1990). She became known as the "Iron Lady", a term coined by a Soviet journalist for her uncompromising politics and leadership style. In 1938, Neville Chamberlain believed he had secured "Peace for our time" with Germany, a year before WWII broke out.
English poet William Cowper wrote in 1785, "We have no slaves at home – Then why abroad? Slaves cannot breathe in England; if their lungs receive our air, that moment they are free, They touch our country, and their shackles fall. That's noble, and bespeaks a nation proud. And jealous of the blessing. Spread it then, And let it circulate through every vein." Thomas Clarkson described fellow British abolitionist Josiah Wedgwood's 1787 anti-slavery medallion, "Am I Not A Man And A Brother?", as "promoting the cause of justice, humanity and freedom". Following the Slave Trade Act 1807, Britain pressed other nations to end their trade with a series of treaties, and in 1839 the world's oldest international human rights organisation, Anti-Slavery International, was formed in London, which worked to outlaw slavery abroad; Wilberforce's abolitionist colleague Thomas Clarkson was the organisation's first key speaker. The Murder (Abolition of Death Penalty) Act 1965, 1965 suspension of the death penalty for murder had been introduced to Parliament as a private member's bill by Sydney Silverman MP. The world's largest human rights organisation, Amnesty International, was founded by Peter Benenson in London in 1961.
Robert Walpole is generally regarded as the first British Prime Minister (1721–1742). Twice Prime Minister, Sir Robert Peel, founded the Conservative party (which was expanded by Benjamin Disraeli), and created the modern police force. Margaret Thatcher was the first female British Prime Minister (1979–1990). She became known as the "Iron Lady", a term coined by a Soviet journalist for her uncompromising politics and leadership style. In 1938, Neville Chamberlain believed he had secured "Peace for our time" with Germany, a year before WWII broke out.
English poet William Cowper wrote in 1785, "We have no slaves at home – Then why abroad? Slaves cannot breathe in England; if their lungs receive our air, that moment they are free, They touch our country, and their shackles fall. That's noble, and bespeaks a nation proud. And jealous of the blessing. Spread it then, And let it circulate through every vein." Thomas Clarkson described fellow British abolitionist Josiah Wedgwood's 1787 anti-slavery medallion, "Am I Not A Man And A Brother?", as "promoting the cause of justice, humanity and freedom". Following the Slave Trade Act 1807, Britain pressed other nations to end their trade with a series of treaties, and in 1839 the world's oldest international human rights organisation, Anti-Slavery International, was formed in London, which worked to outlaw slavery abroad; Wilberforce's abolitionist colleague Thomas Clarkson was the organisation's first key speaker. The Murder (Abolition of Death Penalty) Act 1965, 1965 suspension of the death penalty for murder had been introduced to Parliament as a private member's bill by Sydney Silverman MP. The world's largest human rights organisation, Amnesty International, was founded by Peter Benenson in London in 1961.
Honours system
The British honours system is a means of rewarding individuals' personal bravery, achievement or service to the United Kingdom. Candidates are identified by public or private bodies or by government departments or are nominated by members of the public. Nominations are reviewed by honours committees, made up of government officials and private citizens from different fields, who meet twice a year to discuss the candidates and make recommendations for appropriate honours to be awarded by the Queen. Historically a knighthood was conferred upon mounted warriors. By the Late Middle Ages, the rank had become associated with the ideals of chivalry, a code of conduct for the perfect Court (royal), courtly Christian warrior. An example of warrior chivalry in medieval literature is Sir Gawain (King Arthur's nephew and a Round Table, Knight of the Round Table) in ''Sir Gawain and the Green Knight'' (late 14th century). Since the early modern period, the title of knight is purely honorific, usually bestowed by a monarch, often for non-military service to the country. The modern female equivalent in the UK is damehood. The ceremony often takes place at Buckingham Palace, and family members are invited to attend. A few examples of knights are Nicholas Winton, Sir Nicholas Winton: for "services to humanity, in saving Jewish children from Nazi occupied Czechoslovakia", Elton John, Sir Elton John: for "services to music and charitable services", Ridley Scott, Sir Ridley Scott: for "services to the British film industry", and Richard Branson, Sir Richard Branson: for "services to entrepreneurship". Examples of dames are: actress Julie Andrews, Dame Julie Andrews and singer Shirley Bassey, Dame Shirley Bassey: both for "services to the performing arts", actress Joan Collins, Dame Joan Collins: for "services to charity", and Agatha Christie, Dame Agatha Christie: for "contribution to literature."Counties
The suffix "shire" is attached to most of the names of English, Scottish and Welsh counties. Shire is a term for a division of land first used in England during the Anglo-Saxon period. Examples in England are Cheshire, Hampshire, Nottinghamshire, Oxfordshire, Staffordshire, Worcestershire and Yorkshire; in Scotland, Aberdeenshire (traditional), Aberdeenshire, Perthshire, Inverness-shire and Stirlingshire; and in Wales, Carmarthenshire, Flintshire (historic), Flintshire and Pembrokeshire. This suffix tends not to be found in the names of counties that were pre-existing divisions. Essex, Kent, and Sussex, for example, have never borne a ''-shire'', as each represents a former Heptarchy, Anglo-Saxon kingdom. SimilarlyUnits of measurement
 Use of the British Imperial units, imperial system of measure, particularly among the public, is widespread in the United Kingdom and is in many cases permitted by the law. Human height and weight, long distances and speed are measured in imperial units by the vast majority of Brits. A Brit would normally give their weight as "12 and a half stone" rather than 80 kilograms, though younger people increasingly use kilograms rather than stone. Body height is usually given in Foot (unit), feet and inches. Younger generations tend to use more metric units of measurement, creating a generational gap, for example in short distances and item weight. Although the majority of Brits now use Celsius, degrees Celsius to measure temperature, the use of Fahrenheit persists in older generations. Distances shown on road signs must be in miles and yards, while miles per hour appear on speed limit signs and car speedometers.
Britain has been transitioning to metric since 1965, when the UK Government announced financial support for metrication with a target of 10 years.A chronological history of the modern metric system (to 2008)
Use of the British Imperial units, imperial system of measure, particularly among the public, is widespread in the United Kingdom and is in many cases permitted by the law. Human height and weight, long distances and speed are measured in imperial units by the vast majority of Brits. A Brit would normally give their weight as "12 and a half stone" rather than 80 kilograms, though younger people increasingly use kilograms rather than stone. Body height is usually given in Foot (unit), feet and inches. Younger generations tend to use more metric units of measurement, creating a generational gap, for example in short distances and item weight. Although the majority of Brits now use Celsius, degrees Celsius to measure temperature, the use of Fahrenheit persists in older generations. Distances shown on road signs must be in miles and yards, while miles per hour appear on speed limit signs and car speedometers.
Britain has been transitioning to metric since 1965, when the UK Government announced financial support for metrication with a target of 10 years.A chronological history of the modern metric system (to 2008)''metricationmatters.com''. Retrieved 20 November 2022. When the UK joined the European Economic Community in 1973, the UK re-affirmed its commitment to metrication, but in 2007, the European Commission abandoned completely the deadline for full metrication in the UK. In 2022, the Boris Johnson-led Government announced it was planning to revive imperial measurements. The move received criticism from industry and was branded as "nonsense" by ''The Guardian'' and the chairman of supermarket Asda.
Driving
By custom and law, traffic in Britain drives on the left. Research shows that countries driving on the left have a lower collision rate than those that drive on the right, and it has been suggested that this is partly because the predominantly better-performing right eye is used to monitor oncoming traffic and the driver's wing mirror. The name of the zebra crossing is attributed to British Member of Parliament (United Kingdom), MP and subsequent Prime Minister, James Callaghan, who in 1948 visited the Transport Research Laboratory which was working on a new idea for safe pedestrian crossings. On being shown a design he is said to have remarked that it resembled a zebra. Located inCuisine


 Fish and chips are also regarded as a national institution: Winston Churchill called them "the good companions", John Lennon smothered them in tomato ketchup, while George Orwell referred to them as a "chief comfort" of the working class. The meal was created in 1860 in the East End of London by a Jewish immigrant, Joseph Malin, who came up with the idea of combining fried fish with chips. A blue plaque at Oldham's Tommyfield Market marks the 1860s origin of the fish and chip shop and fast food industries. Various meat pies are consumed such as steak and kidney pie, shepherd's pie, cottage pie, Cornish pasty and pork pie.
A quintessential British custom, afternoon tea, is a small meal typically eaten between 4 pm and 6 pm. The most popular drink in Britain, tea became more widely drunk due to Catherine of Braganza. It is traditionally accompanied with biscuits, sandwiches, scones, cakes or pastries (such as Battenberg cake, fruit cake or Victoria sponge). In his 1946 essay "A Nice Cup of Tea", author George Orwell wrote: "Tea is one of the mainstays of civilisation in this country." McVitie's are the best selling biscuit brand in the UK, and the most popular biscuits to Dunking (biscuit), "dunk" in tea, with McVitie's chocolate digestives, rich tea and hobnob biscuit, hobnobs ranked the nation's top three favourite biscuits."Chocolate digestive is nation's favourite dunking biscuit"
Fish and chips are also regarded as a national institution: Winston Churchill called them "the good companions", John Lennon smothered them in tomato ketchup, while George Orwell referred to them as a "chief comfort" of the working class. The meal was created in 1860 in the East End of London by a Jewish immigrant, Joseph Malin, who came up with the idea of combining fried fish with chips. A blue plaque at Oldham's Tommyfield Market marks the 1860s origin of the fish and chip shop and fast food industries. Various meat pies are consumed such as steak and kidney pie, shepherd's pie, cottage pie, Cornish pasty and pork pie.
A quintessential British custom, afternoon tea, is a small meal typically eaten between 4 pm and 6 pm. The most popular drink in Britain, tea became more widely drunk due to Catherine of Braganza. It is traditionally accompanied with biscuits, sandwiches, scones, cakes or pastries (such as Battenberg cake, fruit cake or Victoria sponge). In his 1946 essay "A Nice Cup of Tea", author George Orwell wrote: "Tea is one of the mainstays of civilisation in this country." McVitie's are the best selling biscuit brand in the UK, and the most popular biscuits to Dunking (biscuit), "dunk" in tea, with McVitie's chocolate digestives, rich tea and hobnob biscuit, hobnobs ranked the nation's top three favourite biscuits."Chocolate digestive is nation's favourite dunking biscuit"''The Daily Telegraph''. 2 May 2009 Other popular British biscuits include Bourbon biscuit, bourbons, custard creams, Jammie Dodgers, ginger nuts and shortbread. The first documented figure-shaped biscuits (gingerbread man) was at the court of Elizabeth I in the 16th century.
 The first English recipe for Ice cream#True ice cream, ice cream was published in ''Mrs. Mary Eales's Receipts'' in London in 1718, and arguably the earliest reference to an edible ice cream cone, appears in Charles Elmé Francatelli's 1846 ''The Modern Cook''.
The 18th-century English aristocrat John Montagu, 4th Earl of Sandwich is best known for his links to the modern concept of the sandwich which was named after him. When he ordered his valet to bring him meat tucked between two pieces of bread, others began to order "the same as Sandwich!". In the city of Leeds in 1767, Joseph Priestley made his "happiest" discovery when he invented carbonated water (also known as soda water), the major and defining component of most soft drinks. Carbonated lemonade was available in British refreshment stalls in 1833, with R. White's Lemonade sold in 1845. By 1887 they sold a wide variety of soft drink flavours. Irn-Bru is the best-selling soft drink in Scotland. Invented by a Newcastle pharmacist in 1927, Lucozade is the No. 1 sports drink in the UK.
Sausages are commonly eaten as bangers and mash, in sausage rolls or as toad in the hole. Lancashire hotpot is a well-known stew. Popular cheeses include Cheddar cheese, Cheddar and Wensleydale (cheese), Wensleydale. Sweet British dishes include scones, apple pie, mince pies, spotted dick, Eccles cakes, pancakes, sponge cake, trifle, Gelatin dessert, jelly, custard, sticky toffee pudding, Tunnock's teacake, and Jaffa cakes; the best-selling cake in the UK. Marmalade is a popular British spread for toast or sandwich: a spread famous for its association with Paddington Bear, a beloved bear in British culture that featured in the critically acclaimed films ''Paddington (film), Paddington'' (2014) and ''Paddington 2'' (2017).
The first English recipe for Ice cream#True ice cream, ice cream was published in ''Mrs. Mary Eales's Receipts'' in London in 1718, and arguably the earliest reference to an edible ice cream cone, appears in Charles Elmé Francatelli's 1846 ''The Modern Cook''.
The 18th-century English aristocrat John Montagu, 4th Earl of Sandwich is best known for his links to the modern concept of the sandwich which was named after him. When he ordered his valet to bring him meat tucked between two pieces of bread, others began to order "the same as Sandwich!". In the city of Leeds in 1767, Joseph Priestley made his "happiest" discovery when he invented carbonated water (also known as soda water), the major and defining component of most soft drinks. Carbonated lemonade was available in British refreshment stalls in 1833, with R. White's Lemonade sold in 1845. By 1887 they sold a wide variety of soft drink flavours. Irn-Bru is the best-selling soft drink in Scotland. Invented by a Newcastle pharmacist in 1927, Lucozade is the No. 1 sports drink in the UK.
Sausages are commonly eaten as bangers and mash, in sausage rolls or as toad in the hole. Lancashire hotpot is a well-known stew. Popular cheeses include Cheddar cheese, Cheddar and Wensleydale (cheese), Wensleydale. Sweet British dishes include scones, apple pie, mince pies, spotted dick, Eccles cakes, pancakes, sponge cake, trifle, Gelatin dessert, jelly, custard, sticky toffee pudding, Tunnock's teacake, and Jaffa cakes; the best-selling cake in the UK. Marmalade is a popular British spread for toast or sandwich: a spread famous for its association with Paddington Bear, a beloved bear in British culture that featured in the critically acclaimed films ''Paddington (film), Paddington'' (2014) and ''Paddington 2'' (2017).
 Home baking has always been a significant part of British home cooking. Influential cookbooks include ''The Experienced English Housekeeper'' (1769), ''Modern Cookery for Private Families'' (1845) by food author Eliza Acton that introduced the now-universal practice of listing ingredients and giving suggested cooking times for each recipe, and Isabella Beeton's ''Mrs Beeton's Book of Household Management, Book of Household Management'' (1861). Home-made cakes and jams are part of the traditional English village fête. Filmed in bunting-draped marquees in scenic gardens, the success of the 2010s television show ''The Great British Bake Off'' (which was inspired by the village fête) is credited with spurring a renewed interest in home baking, with supermarkets and department stores in the UK reporting sharp rises in sales of baking ingredients and accessories. A popular cake to bake, Victoria sponge (named after Queen Victoria who enjoyed a slice with her tea), was created following the discovery of baking powder by English food manufacturer Alfred Bird in 1843, which enabled the sponge to rise higher in cakes.
The hot cross bun is a popular British sweet bun traditionally eaten on Good Friday, but are now eaten all year round. Treacle tart was created after the invention of golden syrup by chemists working for Abram Lyle in 1885. With its logo and green-and-gold packaging having remained almost unchanged since then, Golden syrup#History, Lyle's Golden Syrup was listed by ''Guinness World Records'' as having the world's oldest branding and packaging. Scottish cuisine includes Arbroath smokie and haggis; Northern Irish cuisine features the Ulster fry and the pastie and Welsh cuisine is noted for Welsh rarebit (often using Worcestershire sauce) and cawl. Brown sauce is a traditional British condiment, with its best known variety HP Sauce (named after and featuring an image of the Houses of Parliament on the label) a popular spread on chicken and bacon sandwiches. The Scottish Aberdeen Angus is a popular native Beef cattle, beef breed, accounting for almost 20% of the UK beef industry. Cavendish bananas were cultivated by Sir Joseph Paxton in the greenhouses of Chatsworth House, Derbyshire in 1836. Named after William Cavendish, 6th Duke of Devonshire, William Cavendish, they make up the vast majority of bananas consumed in the western world.
Home baking has always been a significant part of British home cooking. Influential cookbooks include ''The Experienced English Housekeeper'' (1769), ''Modern Cookery for Private Families'' (1845) by food author Eliza Acton that introduced the now-universal practice of listing ingredients and giving suggested cooking times for each recipe, and Isabella Beeton's ''Mrs Beeton's Book of Household Management, Book of Household Management'' (1861). Home-made cakes and jams are part of the traditional English village fête. Filmed in bunting-draped marquees in scenic gardens, the success of the 2010s television show ''The Great British Bake Off'' (which was inspired by the village fête) is credited with spurring a renewed interest in home baking, with supermarkets and department stores in the UK reporting sharp rises in sales of baking ingredients and accessories. A popular cake to bake, Victoria sponge (named after Queen Victoria who enjoyed a slice with her tea), was created following the discovery of baking powder by English food manufacturer Alfred Bird in 1843, which enabled the sponge to rise higher in cakes.
The hot cross bun is a popular British sweet bun traditionally eaten on Good Friday, but are now eaten all year round. Treacle tart was created after the invention of golden syrup by chemists working for Abram Lyle in 1885. With its logo and green-and-gold packaging having remained almost unchanged since then, Golden syrup#History, Lyle's Golden Syrup was listed by ''Guinness World Records'' as having the world's oldest branding and packaging. Scottish cuisine includes Arbroath smokie and haggis; Northern Irish cuisine features the Ulster fry and the pastie and Welsh cuisine is noted for Welsh rarebit (often using Worcestershire sauce) and cawl. Brown sauce is a traditional British condiment, with its best known variety HP Sauce (named after and featuring an image of the Houses of Parliament on the label) a popular spread on chicken and bacon sandwiches. The Scottish Aberdeen Angus is a popular native Beef cattle, beef breed, accounting for almost 20% of the UK beef industry. Cavendish bananas were cultivated by Sir Joseph Paxton in the greenhouses of Chatsworth House, Derbyshire in 1836. Named after William Cavendish, 6th Duke of Devonshire, William Cavendish, they make up the vast majority of bananas consumed in the western world.
 The pub is an important aspect of British culture, and is often the focal point of local communities. Referred to as their "local" by regulars, pubs are typically chosen for their proximity to home or work, the availability of a particular beer or ale or a good selection, good food, a social atmosphere, the presence of friends and acquaintances, and the availability of pub games such as darts or snooker. Pubs will often screen sports events, such as English Premier League and Scottish Premier League games (or for international tournaments, the FIFA World Cup). The pub quiz was established in the UK in the 1970s.
In 1393, Richard II of England, Richard II introduced a law that pubs had to display a sign outdoors to make them easily visible for passing ale tasters who would assess the quality of ale sold. Most pubs still have decorated signs hanging over their doors. The owner or tenant (licensee) is known as the pub landlord or publican, while barmaids are a common feature in pubs. Alcoholic drinks served in pubs include wines and English beers such as bitter (beer), bitter, mild ale, mild, stout and brown ale. Whisky originated in Ireland and Scotland in the Middle Ages: Irish whiskey and Scotch whisky.
On Christmas Day, goose was previously served at Christmas dinner, dinner; however since appearing on Christmas tables in England in the late 16th century, the turkey (bird), turkey has become more popular, with Christmas pudding served for dessert.Broomfield, Andrea (2007). ''Food and cooking in Victorian England: a history''. pp. 149–150. Greenwood Publishing Group, 2007 The 16th-century English navigator William Strickland (navigator), William Strickland is credited with introducing the turkey into England, and 16th-century farmer Thomas Tusser noted that by 1573 turkeys were common in the Christmas dinner#United Kingdom, English Christmas dinner. This custom gave rise to the humorous English idiom, "like turkeys voting for Christmas". The turkey is sometimes accompanied with roast beef or ham, and is served with stuffing, gravy, potatoes, roast potatoes, mashed potatoes and vegetables. Invented in London in the 1840s, Christmas crackers are an integral part of Christmas celebrations, often pulled before or after dinner, or at parties.
The pub is an important aspect of British culture, and is often the focal point of local communities. Referred to as their "local" by regulars, pubs are typically chosen for their proximity to home or work, the availability of a particular beer or ale or a good selection, good food, a social atmosphere, the presence of friends and acquaintances, and the availability of pub games such as darts or snooker. Pubs will often screen sports events, such as English Premier League and Scottish Premier League games (or for international tournaments, the FIFA World Cup). The pub quiz was established in the UK in the 1970s.
In 1393, Richard II of England, Richard II introduced a law that pubs had to display a sign outdoors to make them easily visible for passing ale tasters who would assess the quality of ale sold. Most pubs still have decorated signs hanging over their doors. The owner or tenant (licensee) is known as the pub landlord or publican, while barmaids are a common feature in pubs. Alcoholic drinks served in pubs include wines and English beers such as bitter (beer), bitter, mild ale, mild, stout and brown ale. Whisky originated in Ireland and Scotland in the Middle Ages: Irish whiskey and Scotch whisky.
On Christmas Day, goose was previously served at Christmas dinner, dinner; however since appearing on Christmas tables in England in the late 16th century, the turkey (bird), turkey has become more popular, with Christmas pudding served for dessert.Broomfield, Andrea (2007). ''Food and cooking in Victorian England: a history''. pp. 149–150. Greenwood Publishing Group, 2007 The 16th-century English navigator William Strickland (navigator), William Strickland is credited with introducing the turkey into England, and 16th-century farmer Thomas Tusser noted that by 1573 turkeys were common in the Christmas dinner#United Kingdom, English Christmas dinner. This custom gave rise to the humorous English idiom, "like turkeys voting for Christmas". The turkey is sometimes accompanied with roast beef or ham, and is served with stuffing, gravy, potatoes, roast potatoes, mashed potatoes and vegetables. Invented in London in the 1840s, Christmas crackers are an integral part of Christmas celebrations, often pulled before or after dinner, or at parties.
Sport
 Most of the major sports have separate administrative structures and national teams for each of the
Most of the major sports have separate administrative structures and national teams for each of the Football
Both in participation and viewing, the Sport in the United Kingdom#Popularity, most popular sport in the UK is association football. The sport's origin can be traced to English public school football games. The Laws of the Game (association football), rules were first drafted in England in 1863 by Ebenezer Cobb Morley, and the UK has the oldest football clubs in the world. England is recognised as the birthplace of club football by FIFA, with Sheffield F.C., founded in 1857, the world's oldest football club. The home nations all have separate national teams and domestic competitions, most notably England's Premier League and FA Cup, and the Scottish Premiership and Scottish Cup. The top three Welsh football clubs feature in the English league system. The first international football match was between Scotland national football team, Scotland and England national football team, England in 1872. Referred to as the "home of football" by FIFA, England hosted the 1966 FIFA World Cup, and won the tournament. The British television audience for the 1966 World Cup 1966 FIFA World Cup Final, final peaked at 32.30 million viewers, making it the List of most-watched television broadcasts#Most watched special events, most watched television event ever in the UK. The four home nations have produced some of the greatest players in the game's history, including, from England, Bobby Moore and Gordon Banks; from Northern Ireland, George Best and Pat Jennings; from Scotland, Kenny Dalglish and Jimmy Johnstone; and from Wales, Ian Rush and Ryan Giggs. The first recipient of the Ballon d'Or, Stanley Matthews was knighted while still a player. The English Premier League (formed in 1992 by member clubs of the old Football League First Division) is the most-watched football league in the world, and its biggest clubs include Manchester United F.C., Manchester United, Liverpool F.C., Liverpool, Arsenal F.C., Arsenal, Chelsea F.C., Chelsea, Tottenham Hotspur and Manchester City F.C., Manchester City. Scotland's Celtic F.C., Celtic and Rangers F.C., Rangers also have a global fanbase. Leicester City F.C., Leicester City's 2016 Premier League title win is regarded among the greatest sporting upsets ever. The best-placed teams in the domestic leagues of England and Scotland qualify for Europe's premier competition, the UEFA Champions League (European Cup). Previous winners from the UK are Liverpool, Manchester United, Nottingham Forest F.C., Nottingham Forest, Celtic, Chelsea and Aston Villa F.C., Aston Villa. The UEFA Champions League Anthem, written by Tony Britten and based on Handel's ''Zadok the Priest'', is played before each game. Henry Francis Lyte, Henry Lyte's Christian hymn "Abide with Me" is sung prior to kick-off at every FA Cup Final, a tradition since 1927 FA Cup Final, 1927.
The practice of "jumpers for goalposts" alludes to street football, street/park football in the UK where Sweater, jumpers would be placed on the ground and used as goalposts. This practice was referenced by singer Ed Sheeran in his DVD ''Jumpers for Goalposts: Live at Wembley Stadium'' as a nod to playing concerts at Wembley Stadium, the home of English football. Early references to Dribbling#Association football, dribbling come from accounts of medieval football games in England.
The best-placed teams in the domestic leagues of England and Scotland qualify for Europe's premier competition, the UEFA Champions League (European Cup). Previous winners from the UK are Liverpool, Manchester United, Nottingham Forest F.C., Nottingham Forest, Celtic, Chelsea and Aston Villa F.C., Aston Villa. The UEFA Champions League Anthem, written by Tony Britten and based on Handel's ''Zadok the Priest'', is played before each game. Henry Francis Lyte, Henry Lyte's Christian hymn "Abide with Me" is sung prior to kick-off at every FA Cup Final, a tradition since 1927 FA Cup Final, 1927.
The practice of "jumpers for goalposts" alludes to street football, street/park football in the UK where Sweater, jumpers would be placed on the ground and used as goalposts. This practice was referenced by singer Ed Sheeran in his DVD ''Jumpers for Goalposts: Live at Wembley Stadium'' as a nod to playing concerts at Wembley Stadium, the home of English football. Early references to Dribbling#Association football, dribbling come from accounts of medieval football games in England. Golf
The modern game of golf originated in Scotland, with the Fife town of St Andrews known internationally as the "Golf in Scotland, home of golf".Keay (1994) ''op cit'' page 839. "In 1834 the The Royal and Ancient Golf Club of St Andrews, Royal and Ancient Golf Club declared St. Andrews 'the Alma Mater of golf'". and to many golfers the Old Course at St Andrews, Old Course, an ancient links (golf), links course dating to before 1574, is considered to be a site of pilgrimage. In 1764, the standard 18 hole golf course was created at St Andrews when members modified the course from 22 to 18 holes. Golf is documented as being played on Musselburgh Links, East Lothian, Scotland as early as 2 March 1672, which is certified as the oldest golf course in the world by Guinness World Records. The oldest known Rules of golf#Origin, ''rules of golf'' were compiled in March 1744 in Leith Links, Leith. The oldest golf tournament in the world, and the first major championship in golf, The Open Championship, first took place in Ayrshire, Scotland in 1860, and today it is played on the weekend of the third Friday in July. Golf's first superstar Harry Vardon, a member of the fabled Great Triumvirate (golf), Great Triumvirate who were pioneers of the modern game, won the Open a record six times. Since the 2010s, three Northern Irish golfers have had major success; Graeme McDowell, Darren Clarke and four time major winner Rory McIlroy. The biennial golf competition, the Ryder Cup, is named after English businessman Samuel Ryder who sponsored the event and donated the trophy. Sir Nick Faldo is the most successful British Ryder Cup player.Rugby
 In 1845, rugby union was created when the first rules were written by pupils at Rugby School, Warwickshire. A former pupil of the school William Webb Ellis, is often fabled with the invention of running with the ball in hand in 1823. The 1871 England versus Scotland rugby union match, first rugby international took place on 27 March 1871, played between England national rugby union team, England and Scotland national rugby union team, Scotland. By 1881 both Ireland national rugby union team, Ireland and Wales national rugby union team, Wales had teams, and in 1883 the first international competition the annual Six Nations Championship, Home Nations Championship took place. In 1888, the Home Nations combined to form what is today called the British and Irish Lions, who now tour every four years to face a Southern Hemisphere team. The Wales team of the 1970s, which included a backline consisting of Gareth Edwards, J. P. R. Williams and Phil Bennett who were known for their feints, sidesteps and attacking running rugby, are regarded as one of the greatest teams in the game – all three players were involved in ''The greatest try ever scored'' in 1973. Jonny Wilkinson scored the winning drop kick, drop goal for England in the last minute of extra time in the 2003 Rugby World Cup Final. The major domestic club competitions are the English Premiership (rugby union), Premiership in England and the Pro14, Celtic League in Ireland, Scotland, Wales and (since 2010–11 Celtic League, 2010) Italy. Of Cornish origin, the chant “Oggy Oggy Oggy, Oggy Oggy Oggy, Oi Oi Oi!” is associated with rugby union (and its personalised variant with football); it inspired the “Maggie Out, Maggie Maggie Maggie, Out Out Out!" chant by opponents of Prime Minister Margaret Thatcher in the 1980s. In 1895, rugby league was created in Huddersfield, West Riding of Yorkshire, as the result of a split with the other Rugby code. The Super League is the sports top-level club competition in Britain, and the sport is especially popular in towns in the northern English counties of Yorkshire, Lancashire and Cumbria. The Challenge Cup is the major rugby league cup competition.
In 1845, rugby union was created when the first rules were written by pupils at Rugby School, Warwickshire. A former pupil of the school William Webb Ellis, is often fabled with the invention of running with the ball in hand in 1823. The 1871 England versus Scotland rugby union match, first rugby international took place on 27 March 1871, played between England national rugby union team, England and Scotland national rugby union team, Scotland. By 1881 both Ireland national rugby union team, Ireland and Wales national rugby union team, Wales had teams, and in 1883 the first international competition the annual Six Nations Championship, Home Nations Championship took place. In 1888, the Home Nations combined to form what is today called the British and Irish Lions, who now tour every four years to face a Southern Hemisphere team. The Wales team of the 1970s, which included a backline consisting of Gareth Edwards, J. P. R. Williams and Phil Bennett who were known for their feints, sidesteps and attacking running rugby, are regarded as one of the greatest teams in the game – all three players were involved in ''The greatest try ever scored'' in 1973. Jonny Wilkinson scored the winning drop kick, drop goal for England in the last minute of extra time in the 2003 Rugby World Cup Final. The major domestic club competitions are the English Premiership (rugby union), Premiership in England and the Pro14, Celtic League in Ireland, Scotland, Wales and (since 2010–11 Celtic League, 2010) Italy. Of Cornish origin, the chant “Oggy Oggy Oggy, Oggy Oggy Oggy, Oi Oi Oi!” is associated with rugby union (and its personalised variant with football); it inspired the “Maggie Out, Maggie Maggie Maggie, Out Out Out!" chant by opponents of Prime Minister Margaret Thatcher in the 1980s. In 1895, rugby league was created in Huddersfield, West Riding of Yorkshire, as the result of a split with the other Rugby code. The Super League is the sports top-level club competition in Britain, and the sport is especially popular in towns in the northern English counties of Yorkshire, Lancashire and Cumbria. The Challenge Cup is the major rugby league cup competition.
Tennis
 The modern game of tennis originated in Birmingham, England in the 1860s, and after its creation, tennis spread throughout the upper-class English-speaking population, before spreading around the world. Major Walter Clopton Wingfield is credited as being a pioneer of the game. The world's oldest tennis tournament, the Wimbledon championships, first occurred in 1877, and today the event takes place over two weeks in late June and early July.“125 years of Wimbledon: From birth of lawn tennis to modern marvels”
The modern game of tennis originated in Birmingham, England in the 1860s, and after its creation, tennis spread throughout the upper-class English-speaking population, before spreading around the world. Major Walter Clopton Wingfield is credited as being a pioneer of the game. The world's oldest tennis tournament, the Wimbledon championships, first occurred in 1877, and today the event takes place over two weeks in late June and early July.“125 years of Wimbledon: From birth of lawn tennis to modern marvels”CNN. Retrieved 28 September 2011 Created in the Tudor period in the court of Henry VIII, the English dessert Strawberry#Uses, Strawberries and cream is synonymous with the British summer, and is famously consumed at Wimbledon. The tournament itself has a major place in the British cultural calendar. The eight-time Slam winner and Britain's most successful player Fred Perry is one of only seven men in history to have won all four Grand Slam events, which included three Wimbledons. Virginia Wade won three Grand Slams, the most famous of which was Wimbledon in 1977, the year of the Silver Jubilee of Queen Elizabeth II (the Queen attended Wimbledon for the first time since 1962 to watch the final). The 2013 and 2016 Wimbledon champion, Scotland's Andy Murray, is Britain's most recent male Grand Slam winner. In 2021, Emma Raducanu became the most recent British female Grand Slam winner.
Boxing
 The Marquess of Queensberry rules, 'Queensberry rules', the code of general rules in boxing, was named after John Douglas, 9th Marquess of Queensberry in 1867, that formed the basis of modern boxing. Britain's first heavyweight world champion Bob Fitzsimmons made boxing history as the sport's first three-division world champion. The 1980s saw the emergence of heavyweight Frank Bruno who would become hugely popular with the British public. In the 1990s, Chris Eubank, Nigel Benn, Steve Collins and Michael Watson had a series of fights against each other in the super-middleweight division, drawing audiences of up to 20 million in the UK. Eubank's eccentric personality made him one of the most recognisable celebrities in the UK along with the cocky Naseem Hamed, ”Prince" Naseem Hamed. The Nigel Benn vs. Gerald McClellan fight in 1995 drew 13 million. Other big draw fighters in the UK included Lennox Lewis, Joe Calzaghe and Ricky Hatton.
The Marquess of Queensberry rules, 'Queensberry rules', the code of general rules in boxing, was named after John Douglas, 9th Marquess of Queensberry in 1867, that formed the basis of modern boxing. Britain's first heavyweight world champion Bob Fitzsimmons made boxing history as the sport's first three-division world champion. The 1980s saw the emergence of heavyweight Frank Bruno who would become hugely popular with the British public. In the 1990s, Chris Eubank, Nigel Benn, Steve Collins and Michael Watson had a series of fights against each other in the super-middleweight division, drawing audiences of up to 20 million in the UK. Eubank's eccentric personality made him one of the most recognisable celebrities in the UK along with the cocky Naseem Hamed, ”Prince" Naseem Hamed. The Nigel Benn vs. Gerald McClellan fight in 1995 drew 13 million. Other big draw fighters in the UK included Lennox Lewis, Joe Calzaghe and Ricky Hatton.
Cricket
 The modern game of
The modern game of Horse racing
Originating in 17th and 18th-century England, the Thoroughbred is a horse breed best known for its use in horse racing. Horse racing was popular with the aristocrats and royalty of British society, earning it the title "Sport of Kings." Named after Edward Smith-Stanley, 12th Earl of Derby, Epsom Derby, The Derby was first run in 1780. The race serves as the middle leg of the Triple Crown of Thoroughbred Racing#English Triple Crowns, Triple Crown, preceded by the 2000 Guineas Stakes, 2000 Guineas and followed by the St Leger Stakes, St Leger. The name "Derby (horse race), Derby" has since become synonymous with great races all over the world, and as such has been borrowed many times in races abroad. The National Hunt horse race the Grand National, is held annually at Aintree Racecourse in early April. It is the most watched horse race in the UK, attracting casual observers, and three-time winner Red Rum is the most successful racehorse in the event's history. Red Rum is the best-known racehorse in the UK, named by 45% of Britons, with Black Beauty (from Anna Sewell's novel) in second with 33%. Bolton company J.W. Foster and Sons's pioneering running spikes appear in the book, ''Golden Kicks: The Shoes that changed Sport''. They were made famous by 1924 100 m Olympic champion Harold Abrahams who would be immortalised in ''Chariots of Fire'', the British Oscar winning film. Foster's grandsons formed the sportswear company Reebok in Bolton.Motor sports
The 1950 British Grand Prix was the first Formula One World Championship race. Britain has produced some of the greatest drivers in Formula One, including Stirling Moss, Jim Clark (twice F1 champion), Graham Hill (only driver to have won the Triple Crown of Motorsport, Triple Crown), John Surtees (only world champion in two and four wheels), Jackie Stewart (three-time F1 champion), James Hunt, Nigel Mansell (only man to hold F1 and IndyCar titles at the same time), Jenson Button and Lewis Hamilton (seven-time champion). The British Grand Prix is held at Silverstone Circuit, Silverstone every July. Also, the United Kingdom is home to some of the most prestigious teams in Formula One, including McLaren and Williams Grand Prix Engineering, Williams. It is also home to the headquarters of six of the ten List of Formula One constructors, current F1 teams, including current champions Mercedes-Benz in Formula One, Mercedes, four-time champions Red Bull Racing, Alpine F1 Team, Alpine and Aston Martin F1 Team, Aston Martin.National sporting events
Other major sporting events in the UK include the London Marathon, and The Boat Race on the River Thames. The most successful male Rowing (sport), rower in Olympic history, Steve Redgrave won gold medals at five consecutive Olympic Games. Cycling is a popular physical activity in the UK. In 1888, inventor Sir Frank Bowden, 1st Baronet, Frank Bowden founded the Raleigh Bicycle Company, and by 1913, Raleigh was the biggest bicycle manufacturing company in the world. The Raleigh Chopper was named in the list of British design icons. In 1965 Tom Simpson became the first British world road race champion, and in 2012 Bradley Wiggins became the first British Tour de France winner. Chris Froome has subsequently won the Tour de France four times (2013, 2015, 2016 and 2017). Welsh cyclist Geraint Thomas won in 2018. Sprint specialist Mark Cavendish has won thirty Tour de France stages, putting him second on the Tour de France records and statistics#Stage wins per rider, all-time list. In Ice Dance, many of the compulsory moves were developed by dancers from the UK in the 1930s. At the 1984 Winter Olympics, Jayne Torvill and Christopher Dean won ice dancing gold with the highest-ever score for a single programme. The pair received perfect 6.0 scores from every judge for artistic impression, and twelve 6.0s and six 5.9s overall.
At the 1988 Winter Olympics, ski jumper Eddie "The Eagle" Edwards gained fame as an underdog. Eddie was portrayed by Taron Egerton in the 2016 biographical sports comedy-drama film ''Eddie the Eagle (film), Eddie the Eagle''.
In Ice Dance, many of the compulsory moves were developed by dancers from the UK in the 1930s. At the 1984 Winter Olympics, Jayne Torvill and Christopher Dean won ice dancing gold with the highest-ever score for a single programme. The pair received perfect 6.0 scores from every judge for artistic impression, and twelve 6.0s and six 5.9s overall.
At the 1988 Winter Olympics, ski jumper Eddie "The Eagle" Edwards gained fame as an underdog. Eddie was portrayed by Taron Egerton in the 2016 biographical sports comedy-drama film ''Eddie the Eagle (film), Eddie the Eagle''.
 A great number of major sports originated in the United Kingdom, including association football, golf, tennis, boxing, rugby league, rugby union,
A great number of major sports originated in the United Kingdom, including association football, golf, tennis, boxing, rugby league, rugby union, Sub-national sports
The Highland games are held throughout the year in Scotland as a way of celebrating Scottish and Celtic culture and heritage, especially that of the Scottish Highlands, with more than 60 games taking place across the country every year. Each December, the BBC Sports Personality of the Year Award, BBC Sports Personality of the Year is announced, an award given to the best British sportsperson of the year, as voted for by the British public. The public also votes for the BBC Overseas Sports Personality of the Year, presented to a non-British sportsperson considered to have made the most substantial contribution to a sport each year which has also captured the imagination of the British public. Recipients have included Pelé (after winning his third World Cup in 1970), Muhammad Ali (after regaining the heavyweight title in 1974), Jonah Lomu (for his performances at the 1995 Rugby World Cup), Ronaldo (Brazilian footballer), Ronaldo (for his comeback in winning the 2002 World Cup), and Roger Federer (for his record eighth Wimbledon in 2017).Healthcare
 Each of the four countries of the UK has a publicly funded health care system referred to as the National Health Service (NHS). The terms "National Health Service" or "NHS" are also used to refer to the four systems collectively. All of the services were founded in 1948, based on legislation passed by the Labour Party (UK), Labour Government that had been elected in 1945 with a manifesto commitment to implement the Beveridge Report recommendation to create "comprehensive health and rehabilitation services for prevention and cure of disease".
Each of the four countries of the UK has a publicly funded health care system referred to as the National Health Service (NHS). The terms "National Health Service" or "NHS" are also used to refer to the four systems collectively. All of the services were founded in 1948, based on legislation passed by the Labour Party (UK), Labour Government that had been elected in 1945 with a manifesto commitment to implement the Beveridge Report recommendation to create "comprehensive health and rehabilitation services for prevention and cure of disease".
 The NHS was born out of a long-held ideal that good healthcare should be available to all, regardless of wealth. At its launch by the then minister of health, Aneurin Bevan, on 5 July 1948, it had at its heart three core principles: That it meet the needs of everyone, that it be free at the point of delivery, and that it be based on clinical need, not ability to pay. The NHS had a prominent slot during the 2012 Summer Olympics opening ceremony#Second to the right, and straight on till morning (21:35–21:47), 2012 London Summer Olympics opening ceremony directed by Danny Boyle, being described as "the institution which more than any other unites our nation", according to the programme. Cancer Research UK, Alzheimer's Research UK and Together for Short Lives are among hundreds of health charities in the UK.
Florence Nightingale laid the foundation of modern nursing with the establishment of her nursing school at St Thomas' Hospital in London. It was the Florence Nightingale Faculty of Nursing and Midwifery, first secular nursing school in the world, now part of King's College London. Nightingale wrote ''Notes on Nursing'' in 1859. The book served as the cornerstone of the curriculum at the Nightingale School and other nursing schools. The Nightingale Pledge is taken by many new nurses in the US (but not the UK), and the annual International Nurses Day (12 May) is celebrated around the world on her birthday. Her social reforms improved healthcare for all sections of society in the UK and around the world.
The NHS was born out of a long-held ideal that good healthcare should be available to all, regardless of wealth. At its launch by the then minister of health, Aneurin Bevan, on 5 July 1948, it had at its heart three core principles: That it meet the needs of everyone, that it be free at the point of delivery, and that it be based on clinical need, not ability to pay. The NHS had a prominent slot during the 2012 Summer Olympics opening ceremony#Second to the right, and straight on till morning (21:35–21:47), 2012 London Summer Olympics opening ceremony directed by Danny Boyle, being described as "the institution which more than any other unites our nation", according to the programme. Cancer Research UK, Alzheimer's Research UK and Together for Short Lives are among hundreds of health charities in the UK.
Florence Nightingale laid the foundation of modern nursing with the establishment of her nursing school at St Thomas' Hospital in London. It was the Florence Nightingale Faculty of Nursing and Midwifery, first secular nursing school in the world, now part of King's College London. Nightingale wrote ''Notes on Nursing'' in 1859. The book served as the cornerstone of the curriculum at the Nightingale School and other nursing schools. The Nightingale Pledge is taken by many new nurses in the US (but not the UK), and the annual International Nurses Day (12 May) is celebrated around the world on her birthday. Her social reforms improved healthcare for all sections of society in the UK and around the world.
Pets
Statistics
 In the UK, about 40% of the population own a pet. The top pets in the UK for 2018 and 2019 are:
* Dogs: 25%
* Cats: 17%
* Rabbits, indoor birds, guinea pigs, hamsters: ≈1%
* Tortoises and Turtles: 0.7%
* Lizards: 0.6%
However, the population of pets in the UK declined from 71 million in 2013 (a significant peak) to 51 million in 2018. This decline has seen some reversal as a result of the COVID-19 pandemic; an article published in May 2021 stated that a total of 3.2 million households in the UK had acquired a pet since the start of the pandemic, according to the Pet Food Manufacturers' Association.
In the UK, about 40% of the population own a pet. The top pets in the UK for 2018 and 2019 are:
* Dogs: 25%
* Cats: 17%
* Rabbits, indoor birds, guinea pigs, hamsters: ≈1%
* Tortoises and Turtles: 0.7%
* Lizards: 0.6%
However, the population of pets in the UK declined from 71 million in 2013 (a significant peak) to 51 million in 2018. This decline has seen some reversal as a result of the COVID-19 pandemic; an article published in May 2021 stated that a total of 3.2 million households in the UK had acquired a pet since the start of the pandemic, according to the Pet Food Manufacturers' Association.
History
Founded in 1824, the Royal Society for the Prevention of Cruelty to Animals (RSPCA) is the oldest and largest animal welfare organisation in the world. The British Shorthair cat is the most popular pedigreed breed in its native country, as registered by the UK's Governing Council of the Cat Fancy (GCCF). The breed's broad cheeks and relatively calm temperament make it a frequent media star. The cat's profile reads: "When gracelessness is observed, the British Shorthair is duly embarrassed, quickly recovering with a 'Cheshire cat smile'”. There are almost one million horses and ponies in the UK, with popular native breeds including Clydesdale horse (used as drum horses by the British Household Cavalry), Thoroughbred (used in horse racing), Cleveland Bay (pull carriages in royal processions), Highland pony and Shetland pony. The UK's indigenous dog breeds include Bulldog, Jack Russell Terrier, Golden Retriever, Yorkshire Terrier, Airedale Terrier, Beagle, Border Collie, Staffordshire Bull Terrier, English Cocker Spaniel, Scottish Terrier, Welsh Corgi, Bullmastiff, Greyhound, English Springer Spaniel and Old English Sheepdog. The Kennel Club, with its headquarters in London, is the oldest kennel club in the world, and acts as a lobby group on issues involving dogs in the UK. Its main objectives are to promote the general improvement of dogs and responsible dog ownership. Held since 1891, Crufts is an annual dog show in the UK. The event takes place over four days in early March. In 1928, the very first winner of List of Best in Show winners of Crufts, Best in Show at Crufts was Primley Sceptre, a greyhound.National costume and dress
 As a multi-national state, the UK has no single national costume. However, different countries within the United Kingdom have national costumes or at least are associated with styles of dress. Scotland has the kilt and Tam o'shanter (hat), Tam o'shanter, and tartan clothing – its pattern consisting of criss-crossed horizontal and vertical bands in multiple colours – is a notable aspect of Gaelic culture. A traditional Welsh costume with Welsh hat is worn by some women during Eisteddfodau. In England, the topic of a national costume has been in debate, since no officially recognized clothing is anointed "national". However, the closest to an English national costume can be the smock or smock-frock in the Midlands and Southern England and the Maud (plaid), maud in Northern England. English Country Clothing is also very popular among rural folk, flat caps and brogue shoes also forming part of the country clothing.Katie Wales (2006). ''Northern English: a cultural and social history''. p. 26. Cambridge University Press
As a multi-national state, the UK has no single national costume. However, different countries within the United Kingdom have national costumes or at least are associated with styles of dress. Scotland has the kilt and Tam o'shanter (hat), Tam o'shanter, and tartan clothing – its pattern consisting of criss-crossed horizontal and vertical bands in multiple colours – is a notable aspect of Gaelic culture. A traditional Welsh costume with Welsh hat is worn by some women during Eisteddfodau. In England, the topic of a national costume has been in debate, since no officially recognized clothing is anointed "national". However, the closest to an English national costume can be the smock or smock-frock in the Midlands and Southern England and the Maud (plaid), maud in Northern England. English Country Clothing is also very popular among rural folk, flat caps and brogue shoes also forming part of the country clothing.Katie Wales (2006). ''Northern English: a cultural and social history''. p. 26. Cambridge University Press
 Certain military uniforms such as the Yeomen Warders, Beefeater or the Queen's Guard are considered to be symbolic of Englishness. Morris dancers or the costumes for the traditional English May dance are sometimes cited as examples of traditional English costume, but are only worn by participants in those events. Designed in 1849 by the London hat-makers Thomas and William Bowler, the Bowler hat is arguably the most iconic stereotyped view of an Englishman (complete with Bowler and rolled umbrella), and was commonly associated with City of London businessmen. Traced back to the north of England in the 14th century, the flat cap is associated with the working classes in the UK. The flat cap has seen a 21st-century resurgence in popularity, possibly influenced by various British public figures wearing them, including David Beckham, Harry Styles and Guy Ritchie, with clothing sellers Marks & Spencer reporting that flat cap sales significantly increased in the 2010s. In 1856 William Henry Perkin discovered the first synthetic dye (Mauveine – a purple colour), which was suitable as a dye of silk and other textiles, helping to revolutionise the world of fashion.
Burberry is most famous for creating the trench coat: they were worn by British soldiers in the trenches in World War I. Among various British youth subcultures, Dr. Martens boots (often referred to as DMs) have been the choice of footwear: in the 1960s skinheads started to wear them, and they later became popular among Scooter (motorcycle), scooter riders, punk subculture, punks, and some new wave musicians. Male Mod (subculture), mods adopted a sophisticated look that included tailor-made suits, thin ties, button-down collar shirts, Chelsea boots and C. & J. Clark, Clarks desert boots.
Certain military uniforms such as the Yeomen Warders, Beefeater or the Queen's Guard are considered to be symbolic of Englishness. Morris dancers or the costumes for the traditional English May dance are sometimes cited as examples of traditional English costume, but are only worn by participants in those events. Designed in 1849 by the London hat-makers Thomas and William Bowler, the Bowler hat is arguably the most iconic stereotyped view of an Englishman (complete with Bowler and rolled umbrella), and was commonly associated with City of London businessmen. Traced back to the north of England in the 14th century, the flat cap is associated with the working classes in the UK. The flat cap has seen a 21st-century resurgence in popularity, possibly influenced by various British public figures wearing them, including David Beckham, Harry Styles and Guy Ritchie, with clothing sellers Marks & Spencer reporting that flat cap sales significantly increased in the 2010s. In 1856 William Henry Perkin discovered the first synthetic dye (Mauveine – a purple colour), which was suitable as a dye of silk and other textiles, helping to revolutionise the world of fashion.
Burberry is most famous for creating the trench coat: they were worn by British soldiers in the trenches in World War I. Among various British youth subcultures, Dr. Martens boots (often referred to as DMs) have been the choice of footwear: in the 1960s skinheads started to wear them, and they later became popular among Scooter (motorcycle), scooter riders, punk subculture, punks, and some new wave musicians. Male Mod (subculture), mods adopted a sophisticated look that included tailor-made suits, thin ties, button-down collar shirts, Chelsea boots and C. & J. Clark, Clarks desert boots.
 British sensibilities have played an influential role in world clothing since the 18th century. Particularly during the Victorian era, British fashions defined acceptable dress for men of business. Key figures such as the future Edward VII, Edward VIII, and Beau Brummell, created the modern Suit (clothing), suit and cemented its dominance. Brummell is credited with introducing and establishing as fashion the modern man's suit, worn with a Necktie, tie. The use of a coloured and patterned tie (a common feature in School uniforms in the United Kingdom, British school uniforms) indicating the wearer's membership in a club, regiment, school, professional association etc. stems from the 1880 Sport rowing, oarsmen of Exeter College Boat Club, Exeter College, Oxford, who tied the bands of their straw hats around their necks. The Wellington boot (first worn by Arthur Wellesley, 1st Duke of Wellington) became a staple for outdoor wear.
The tradition of a white wedding is commonly credited to Queen Victoria's choice to wear a white wedding dress at her wedding to Albert, Prince Consort, Prince Albert in 1840, at a time when white was associated with purity and conspicuous consumption (because it was difficult to keep clean, and thus could not be worn by servants or labourers), and when it was the colour required of girls being presented to the royal court. The 1981 wedding dress of Lady Diana Spencer became one of the most famous dresses in the world, and was considered one of the most closely guarded secrets in fashion history.
British sensibilities have played an influential role in world clothing since the 18th century. Particularly during the Victorian era, British fashions defined acceptable dress for men of business. Key figures such as the future Edward VII, Edward VIII, and Beau Brummell, created the modern Suit (clothing), suit and cemented its dominance. Brummell is credited with introducing and establishing as fashion the modern man's suit, worn with a Necktie, tie. The use of a coloured and patterned tie (a common feature in School uniforms in the United Kingdom, British school uniforms) indicating the wearer's membership in a club, regiment, school, professional association etc. stems from the 1880 Sport rowing, oarsmen of Exeter College Boat Club, Exeter College, Oxford, who tied the bands of their straw hats around their necks. The Wellington boot (first worn by Arthur Wellesley, 1st Duke of Wellington) became a staple for outdoor wear.
The tradition of a white wedding is commonly credited to Queen Victoria's choice to wear a white wedding dress at her wedding to Albert, Prince Consort, Prince Albert in 1840, at a time when white was associated with purity and conspicuous consumption (because it was difficult to keep clean, and thus could not be worn by servants or labourers), and when it was the colour required of girls being presented to the royal court. The 1981 wedding dress of Lady Diana Spencer became one of the most famous dresses in the world, and was considered one of the most closely guarded secrets in fashion history.
Fashion
 London, as one of the world's four fashion capitals, is host to the London Fashion Week – one of the 'Big Four' fashion weeks. Organised by the British Fashion Council, the event takes place twice each year, in February and September. The current venue for most of the "on-schedule" events is Somerset House in central London, where a large marquee in the central courtyard hosts a series of catwalk shows by top designers and fashion houses, while an exhibition, housed within Somerset House itself, showcases over 150 designers. However, many "off-schedule" events, such as On, Off and Vauxhall Fashion Scout, are organised independently and take place at other venues in central London.
British designers whose collections have been showcased at the fashion week include Vivienne Westwood, Alexander McQueen, John Galliano and Stella McCartney. British models who have featured at the event include Kate Moss, Naomi Campbell, Jade Jagger, David Gandy, Cara Delevingne and Rosie Huntington-Whiteley. For almost two decades, Princess Diana was a fashion icon whose style was emulated by women around the world.
Fashion designer Mary Quant was at the heart of the "Swinging London" scene of the 1960s, and her work culminated in the creation of the miniskirt and hot pants. Quant named the miniskirt after her favourite make of car, the Mini. The Swinging London fashion scene has featured in films, and was spoofed in the ''Austin Powers (film series), Austin Powers'' comedy series. The English fashion designer Charles Frederick Worth is widely considered the father of Haute couture.
London, as one of the world's four fashion capitals, is host to the London Fashion Week – one of the 'Big Four' fashion weeks. Organised by the British Fashion Council, the event takes place twice each year, in February and September. The current venue for most of the "on-schedule" events is Somerset House in central London, where a large marquee in the central courtyard hosts a series of catwalk shows by top designers and fashion houses, while an exhibition, housed within Somerset House itself, showcases over 150 designers. However, many "off-schedule" events, such as On, Off and Vauxhall Fashion Scout, are organised independently and take place at other venues in central London.
British designers whose collections have been showcased at the fashion week include Vivienne Westwood, Alexander McQueen, John Galliano and Stella McCartney. British models who have featured at the event include Kate Moss, Naomi Campbell, Jade Jagger, David Gandy, Cara Delevingne and Rosie Huntington-Whiteley. For almost two decades, Princess Diana was a fashion icon whose style was emulated by women around the world.
Fashion designer Mary Quant was at the heart of the "Swinging London" scene of the 1960s, and her work culminated in the creation of the miniskirt and hot pants. Quant named the miniskirt after her favourite make of car, the Mini. The Swinging London fashion scene has featured in films, and was spoofed in the ''Austin Powers (film series), Austin Powers'' comedy series. The English fashion designer Charles Frederick Worth is widely considered the father of Haute couture.
Symbols, flags, and emblems
 The United Kingdom as a whole has a number of national symbols, as do its constituent nations. The Union Flag is the Flag of the United Kingdom, national flag of the United Kingdom. The first flag combined the Saint George's Cross, cross of St George with the Flag of Scotland, saltire of Saint Andrew to represent the
The United Kingdom as a whole has a number of national symbols, as do its constituent nations. The Union Flag is the Flag of the United Kingdom, national flag of the United Kingdom. The first flag combined the Saint George's Cross, cross of St George with the Flag of Scotland, saltire of Saint Andrew to represent the Traditional communication and greeting cards
 A familiar sight throughout the UK, the red telephone box and Royal Mail red pillar box, post box are considered British cultural icons. Designed by Giles Gilbert Scott, Sir Giles Gilbert in 1924, the red telephone box features a prominent Crown (headgear), crown representing the British government. The post pillar box was introduced in the 1850s during the reign of Queen Victoria following Rowland Hill (postal reformer), Sir Rowland Hill's postal reforms in the 1830s where the Penny Post#United Kingdom, reduction in postal rates with the invention of the postage stamp (Penny Black) made sending post an affordable means of personal communication.
The red telephone box has appeared in British pop culture, such as in
A familiar sight throughout the UK, the red telephone box and Royal Mail red pillar box, post box are considered British cultural icons. Designed by Giles Gilbert Scott, Sir Giles Gilbert in 1924, the red telephone box features a prominent Crown (headgear), crown representing the British government. The post pillar box was introduced in the 1850s during the reign of Queen Victoria following Rowland Hill (postal reformer), Sir Rowland Hill's postal reforms in the 1830s where the Penny Post#United Kingdom, reduction in postal rates with the invention of the postage stamp (Penny Black) made sending post an affordable means of personal communication.
The red telephone box has appeared in British pop culture, such as in . Retrieved 12 June 2011. Sir Henry Cole devised the concept of sending greetings cards at Christmas time. Designed by John Callcott Horsley for Cole in 1843, the Christmas card accounts for almost half of the volume of greeting card sales in the UK, with over 600 million cards sold annually. The European robin, robin is a common sight in gardens throughout the UK. It is relatively tame and drawn to human activities, and is frequently voted Britain's national bird in polls. The robin began featuring on many Christmas cards in the mid-19th century. The association with Christmas arises from postmen in Victorian Britain who wore red jackets and were nicknamed "Robins"; the robin featured on the Christmas card is an emblem of the postman delivering the card. Sending Valentine's Day#Modern times, Valentine's Day cards became hugely popular in Britain in the late 18th century, a practice which has since spread to other nations. The day first became associated with Romance (love), romantic love within the circle of
St. Valentine, Chaucer, and Spring in February
. ''Speculum'', 56 (1981): 534–65. In Chaucer's ''Parlement of Foules'' (1382) he wrote; ''For this was on seynt Volantynys day. When euery bryd comets there to chese his make''. The modern cliché Valentine's Day poem can be found in the 1784 English nursery rhyme ''Roses Are Red''; "The rose is red, the violet's blue. 'The honey's sweet, and so are you. Thou art my love and I am thine. I drew thee to my Valentine." In 1797, a British publisher issued ''The Young Man's Valentine Writer'' which contained scores of suggested sentimental Verse (poetry), verses for the young lover unable to compose his own. In 1835, 60,000 Valentine cards were sent by post in the UK, despite postage being expensive. A reduction in postal rates (with the 1840 invention of the postage stamp, the Penny Black) increased the practice of mailing Valentines, with 400,000 sent in 1841. In the UK just under half the population spend money on gifts. Other popular occasions for sending greeting cards in the UK are birthdays, Mother's Day, Easter and Father's Day.
Education
Each country of the United Kingdom has a separate education system. Power over education matters in Scotland, Wales and Northern Ireland is devolution, devolved but education in England is dealt with by the British government since there is no Devolved English parliament, devolved administration for England.England
 Most schools came under state control in the Victorian era; a formal state school system was instituted after the Second World War. Initially, schools were categorised as infant schools, primary schools and secondary schools (split into more academic grammar schools and more vocational secondary modern schools). Under the Labour governments of the 1960s and 1970s most secondary modern and grammar schools were combined to become comprehensive schools. England has many independent (fee-paying) schools, some founded hundreds of years ago; independent secondary schools are known as public school (England), public schools. Eton College, Eton, Harrow School, Harrow, Shrewsbury School, Shrewsbury and Rugby School, Rugby are four of the best-known. The nature and peculiarities of these Public schools have frequently featured in British literature. Prior to 1999, School corporal punishment, corporal punishment was allowed in such schools, whilst the use of corporal punishment was outlawed in state schools in 1987. Most primary and secondary schools in both the private and state sectors have compulsory School uniforms in England, school uniforms. Allowances are almost invariably made, however, to accommodate religious dress, including the Islamic hijab and Sikh bangle (kara).
Most schools came under state control in the Victorian era; a formal state school system was instituted after the Second World War. Initially, schools were categorised as infant schools, primary schools and secondary schools (split into more academic grammar schools and more vocational secondary modern schools). Under the Labour governments of the 1960s and 1970s most secondary modern and grammar schools were combined to become comprehensive schools. England has many independent (fee-paying) schools, some founded hundreds of years ago; independent secondary schools are known as public school (England), public schools. Eton College, Eton, Harrow School, Harrow, Shrewsbury School, Shrewsbury and Rugby School, Rugby are four of the best-known. The nature and peculiarities of these Public schools have frequently featured in British literature. Prior to 1999, School corporal punishment, corporal punishment was allowed in such schools, whilst the use of corporal punishment was outlawed in state schools in 1987. Most primary and secondary schools in both the private and state sectors have compulsory School uniforms in England, school uniforms. Allowances are almost invariably made, however, to accommodate religious dress, including the Islamic hijab and Sikh bangle (kara).
 Although the Minister of Education is responsible to Parliament for education, the day-to-day administration and funding of state schools is the responsibility of local education authority, local education authorities.
List of universities in England, England's universities include some of the highest-ranked universities in the world: the University of Cambridge, Imperial College London, the University of Oxford and University College London are all ranked in the global top 10 in the 2010 ''QS World University Rankings''. The London School of Economics has been described as the world's leading social science institution for both teaching and research."The Sunday Times Good University Guide 2007 – Profile for London School of Economics"
Although the Minister of Education is responsible to Parliament for education, the day-to-day administration and funding of state schools is the responsibility of local education authority, local education authorities.
List of universities in England, England's universities include some of the highest-ranked universities in the world: the University of Cambridge, Imperial College London, the University of Oxford and University College London are all ranked in the global top 10 in the 2010 ''QS World University Rankings''. The London School of Economics has been described as the world's leading social science institution for both teaching and research."The Sunday Times Good University Guide 2007 – Profile for London School of Economics"The Times. The London Business School is considered one of the world's leading business schools and in 2010 its MBA programme was ranked best in the world by the ''Financial Times''."FT Global MBA Rankings"
Financial Times Academic degrees in England are usually split into classes: first class (I), upper second class (II:1), lower second class (II:2) and third (III), and unclassified (below third class).
Northern Ireland
The Northern Ireland Assembly is responsible for education in Northern Ireland. Schools are administered by five Education and Library Boards covering different geographical areas.Scotland
 Scotland has a long history of universal provision of public education which, traditionally, has emphasised breadth across a range of subjects rather than depth of education in a smaller range of subjects. The majority of schools are non-denominational, but by law separate Roman Catholic schools, with an element of control by the Roman Catholic Church, are provided by the state school, state system. Qualifications at the secondary school and post-secondary education, post-secondary (further education) levels are provided by the Scottish Qualifications Authority and delivered through various schools, colleges and other centres. Political responsibility for education at all levels is vested in the
Scotland has a long history of universal provision of public education which, traditionally, has emphasised breadth across a range of subjects rather than depth of education in a smaller range of subjects. The majority of schools are non-denominational, but by law separate Roman Catholic schools, with an element of control by the Roman Catholic Church, are provided by the state school, state system. Qualifications at the secondary school and post-secondary education, post-secondary (further education) levels are provided by the Scottish Qualifications Authority and delivered through various schools, colleges and other centres. Political responsibility for education at all levels is vested in the Wales
 The National Assembly for Wales has responsibility for education in Wales. A significant number of students in Wales are educated either wholly or largely through the medium of the Welsh language, and lessons in the language are compulsory for all until the age of 16. There are plans to increase the provision of Welsh medium education as part of the policy of promoting a fully bilingual Wales.
The National Assembly for Wales has responsibility for education in Wales. A significant number of students in Wales are educated either wholly or largely through the medium of the Welsh language, and lessons in the language are compulsory for all until the age of 16. There are plans to increase the provision of Welsh medium education as part of the policy of promoting a fully bilingual Wales.
Outdoor education
Scouting is the largest co-educational youth movement in the UK. Scouting began in 1907 when Robert Baden-Powell, Lieutenant General in the British Army, held the Brownsea Island Scout camp, first Scout camp at Brownsea Island in Dorset, England. Baden-Powell wrote the principles of Scouting in ''Scouting for Boys'' in 1908. In July 2009, adventurer Bear Grylls became the youngest Chief Scout (The Scout Association), Chief Scout ever, aged 35. In 2010, scouting in the UK experienced its biggest growth since 1972, taking total membership to almost 500,000.Scouting sees biggest membership surge in 40 yearsRetrieved 3 March 2011.
Sociological issues
Housing
 The UK (England in particular) has a relatively high Demography of the United Kingdom, population density so housing tends to be more closely packed than in other countries. Thus terrace (architecture), terraced houses are widespread, dating back to the aftermath of the Great Fire of London.
As the first industrialised country in the world, the UK has long been urbanised. In the 20th century, suburbanisation led to a spread of semi-detached and detached housing. After the Second World War, public housing was dramatically expanded to create a large number of council estates. There are many historic country houses and stately homes in rural areas, though only a minority of these are still used as private living accommodation.
In recent times, more detached housing has started to be built. Also, city living has boomed, with city centre populations rising rapidly. Most of this population growth has been accommodated in new apartment blocks in residential schemes in many towns and cities. Demographic changes (see below) are putting great pressure on the housing market, especially in London and the South East England, South East.
The UK (England in particular) has a relatively high Demography of the United Kingdom, population density so housing tends to be more closely packed than in other countries. Thus terrace (architecture), terraced houses are widespread, dating back to the aftermath of the Great Fire of London.
As the first industrialised country in the world, the UK has long been urbanised. In the 20th century, suburbanisation led to a spread of semi-detached and detached housing. After the Second World War, public housing was dramatically expanded to create a large number of council estates. There are many historic country houses and stately homes in rural areas, though only a minority of these are still used as private living accommodation.
In recent times, more detached housing has started to be built. Also, city living has boomed, with city centre populations rising rapidly. Most of this population growth has been accommodated in new apartment blocks in residential schemes in many towns and cities. Demographic changes (see below) are putting great pressure on the housing market, especially in London and the South East England, South East.
Living arrangements
 Historically most people in the United Kingdom lived either in Marriage, conjugal extended family, extended families or nuclear family, nuclear families. This reflected an Economic system, economic landscape where the general populace tended to have less spending power, meaning that it was more practical to stick together rather than go their individual ways. This pattern also reflected gender roles. Men were expected to go out to work and women were expected to stay at home and look after the families.
Historically most people in the United Kingdom lived either in Marriage, conjugal extended family, extended families or nuclear family, nuclear families. This reflected an Economic system, economic landscape where the general populace tended to have less spending power, meaning that it was more practical to stick together rather than go their individual ways. This pattern also reflected gender roles. Men were expected to go out to work and women were expected to stay at home and look after the families.
 In the 20th century the feminism, emancipation of women, the greater freedoms enjoyed by both men and women in the years following the Second World War, greater affluent, affluence and easier divorce have changed gender roles and living arrangements significantly. The general trend is a rise in single people living alone, the virtual extinction of the extended family (outside certain ethnic minority communities), and the nuclear family arguably reducing in prominence.
From the 1990s, the break-up of the traditional family unit, when combined with low interest rates and other demographic changes, has created great pressure on the housing market, in particular on accommodation for "key workers" such as nurses, other emergency service workers and teachers, who are priced out of most housing, especially in the South East England, South East. Some research indicates that in the 21st century young people are tending to continue to live in the parental home for much longer than their predecessors.
In the 20th century the feminism, emancipation of women, the greater freedoms enjoyed by both men and women in the years following the Second World War, greater affluent, affluence and easier divorce have changed gender roles and living arrangements significantly. The general trend is a rise in single people living alone, the virtual extinction of the extended family (outside certain ethnic minority communities), and the nuclear family arguably reducing in prominence.
From the 1990s, the break-up of the traditional family unit, when combined with low interest rates and other demographic changes, has created great pressure on the housing market, in particular on accommodation for "key workers" such as nurses, other emergency service workers and teachers, who are priced out of most housing, especially in the South East England, South East. Some research indicates that in the 21st century young people are tending to continue to live in the parental home for much longer than their predecessors.
Happiness
When Brits were asked to rate their happiness yesterday on a scale of 1 to 10 in 2018, respondent's mean answer was 7.54 (ranked 'High') in 2018. Northern Irish respondents were ranked the happiest of the United Kingdom (with a mean of 7.74), followed by the English (with 7.54), then the Scots (with 7.52) and finally the Welsh (with 7.51). However, only 25% of women and girls between the ages of 7 and 21 claim to be very happy, which has fallen from 41% in 2009. They claimed that it was due to the pressure from exams and social media, which exerted undue amounts of stress on them. In that category, the oldest were the least happy: 27% of young women aged 17 to 21 claimed they were not happy, compared to 11% in 2009. This negatively influenced their confidence by 61%, health by 50%, relationships by 49% and studying by 39%. 69% of respondents in that age group claimed school exams were the chief stressor, 59% felt pressure from social media was making them less happy, and compared to 5 years ago, more claimed they had experienced unkind, threatening or negative reactions on social media. The proportion of the population who knew someone with Mental health in the United Kingdom, mental health issues rose from 62% in 2015 to 71% in 2018. Many young women and girls feel unsafe walking alone: over half aged from 13 to 21 have experienced harassment or know someone who has, and almost half feel unsafe using public transport.UK survey finds sharp decline in happiness of young women and girls''The Guardian''
Feminism
The proportion of young girls considering themselves feminists has risen from 35% in 2013 to 47% in 2018. 36% of young women and girls aged 11 to 21 had spoken up about an issue that mattered to them, this rose from 28% in 2011 but only 60% felt they had been listened to. Girls have also become more interested in science, maths and technology. Girls are more likely to want to become leaders in their careers, 53% compared to 42% in 2016. Maria Miller said, “#MeToo may have left its mark in Hollywood but for women and girls around the country their ambitions to succeed are still too often met with sexism. It's important more women and girls are now speaking out about how this behaviour undermines their confidence and mental health; but this harmful, negative behaviour has to be stopped".Naming conventions
The common naming convention throughout the United Kingdom is for everyone to have one or more given names (a forename, still often referred to as a "Christian name") usually (but not always) indicating the child's sex, and a surname ("family name"). A four-year study by the University of the West of England, which concluded in 2016, analysed sources dating from the 11th to the 19th centuries to explain the origins of the surnames in the British Isles. The study found that over 90% of the 45,602 surnames in the dictionary are native to the British Isles; the most common in the UK are Smith (surname), Smith, Jones (surname), Jones, Williams (surname), Williams, Brown (surname), Brown, Taylor (surname), Taylor, Johnson, and Lee (English name), Lee. Since the 19th century middle names (additional forenames) have become very common and are sometimes taken from the name of a family member. Most surnames of British origin fall into seven categories: * Occupations e.g. ''Smith (surname), Smith'', ''Sawyer'', ''Fuller (surname), Fuller'', ''Brewer'', ''Clark'', ''Cooper (surname), Cooper'', ''Cook (surname), Cook'', ''Carpenter (surname), Carpenter'', ''Bailey (surname), Bailey'', ''Parker (surname), Parker'', ''Forrester'', ''Head'', ''Palmer (surname), Palmer'', ''Archer'', ''Hunt (surname), Hunt'', ''Baker'', ''Miller (name), Miller'', ''Dyer'', ''Walker (surname), Walker'', ''Woodman'', ''Taylor (surname), Taylor'', ''Turner (surname), Turner'', ''Knight (surname), Knight'', ''Slater (disambiguation), Slater'', ''Mason (surname), Mason'', ''Weaver'', ''Carter (disambiguation), Carter'', ''Wright'' * Personal characteristics e.g. ''Short'', ''Brown (surname), Brown'', ''Black'', ''Whitehead'', ''Young (surname), Young'', ''Stout'', ''Long'', ''White (surname), White'' * Geographical features e.g. ''Pond'', ''Bridge'', ''Camp (surname), Camp'', ''Hill (surname), Hill'', ''Bush (surname), Bush'', ''Lake'', ''Lee (English name), Lee'', ''Wood (surname), Wood'', ''Holmes (surname), Holmes'', ''Forest'', ''Underwood (surname), Underwood'', ''Hall (surname), Hall'', ''Brooks (surname), Brooks'', ''Fields'', ''Stone (surname), Stone'', ''Morley'', ''Moore (surname), Moore'', ''Perry (surname), Perry'' * Place names e.g. ''Murray (surname), Murray'', ''Everingham'', ''Burton (name), Burton'', ''Leighton'', ''Hamilton (surname and title), Hamilton'', ''Sutton'', ''Flint'', ''Laughton'' * Estate For those descended from landowners, the name of their holdings, manor or estate * Patronymics, matronymics or ancestral, often from a person's given name. e.g. from male name: ''Richardson (surname), Richardson'', ''Jones (surname), Jones'' (Welsh for John), ''Williams (surname), Williams'', ''Thomas (surname), Thomas'', ''Jackson (name), Jackson'', ''Wilson (surname), Wilson'', ''Thompson (surname), Thompson'', ''Johnson'', ''Harris (surname), Harris'', ''Evans (surname), Evans'', ''Simpson (surname), Simpson'', ''Willis (surname), Willis'', ''Davies'', ''Reynolds (surname), Reynolds'', ''Adams (surname), Adams'', ''Dawson (surname), Dawson'', ''Lewis (surname), Lewis'', ''Rogers (surname), Rogers'', ''Murphy'', ''Nicholson (surname), Nicholson'', ''Robinson (name), Robinson'', ''Powell (surname), Powell'', ''Ferguson (name), Ferguson'', ''Davis (surname), Davis'', ''Edwards (surname), Edwards'', ''Hudson (surname), Hudson'', ''Roberts (surname), Roberts'', ''Harrison (name), Harrison'', ''Watson (surname), Watson'', or female names ''Molson'' (from Moll for Mary), ''Gilson'' (from Gill), ''Emmott'' (from Emma), ''Marriott'' (from Mary) or from a clan name (for those of Scottish origin, e.g. ''Macdonald (name), MacDonald'', ''Clan Forbes, Forbes'', ''Henderson (surname), Henderson'', ''Armstrong (surname), Armstrong'', ''Grant (surname), Grant'', ''Cameron (surname), Cameron'', ''Stewart (name), Stewart'', ''Douglas (surname), Douglas'', ''Crawford (name), Crawford'', ''Campbell (surname), Campbell'', ''Houston (surname), Houston'', ''Hunter (name), Hunter'') with "Mac"See also
* British humour * Department for Culture, Media and Sport (deals with Culture for England) * Minister for Culture and External Affairs (deals with Culture for Scotland) * Shrove Tuesday (Pancake Day) * April Fools' Day * Lord Kitchener Wants You * List of venues in the United KingdomNotes
References
External links
* Culture *Department for Culture, Media and Sport
*
United Kingdom/Ireland for Visitors
* Television *
BBC television
*
ITV
*
Sky television
* Radio *
BBC radio
{{DEFAULTSORT:Culture of the United Kingdom British culture,